JUMPm: A Tool for Large-Scale Identification of Metabolites in Untargeted Metabolomics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Design and Implementation of JUMPm Program
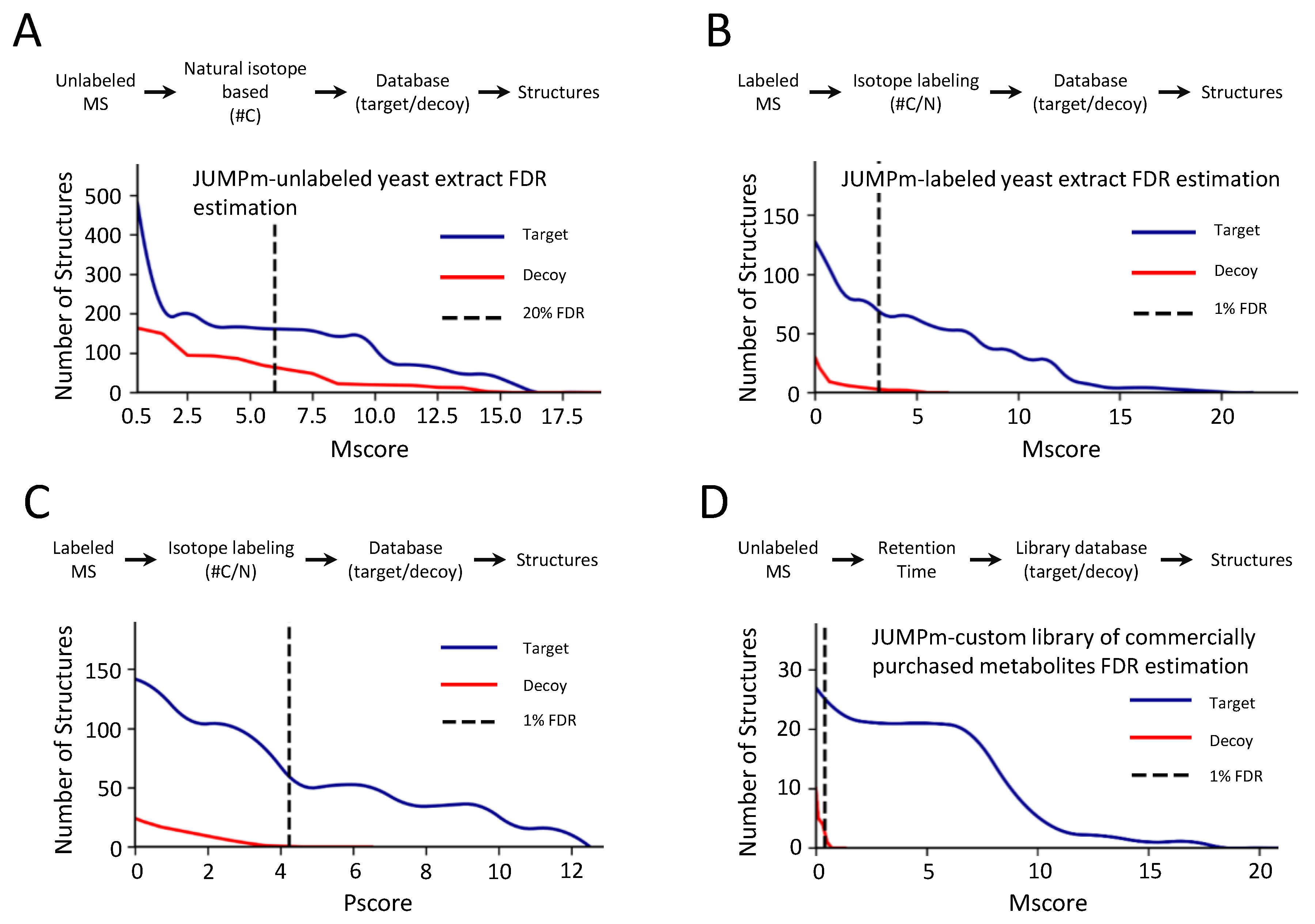
2.2. Evaluation of False Discovery Rate Based on the Target-Decoy Strategy by JUMPm
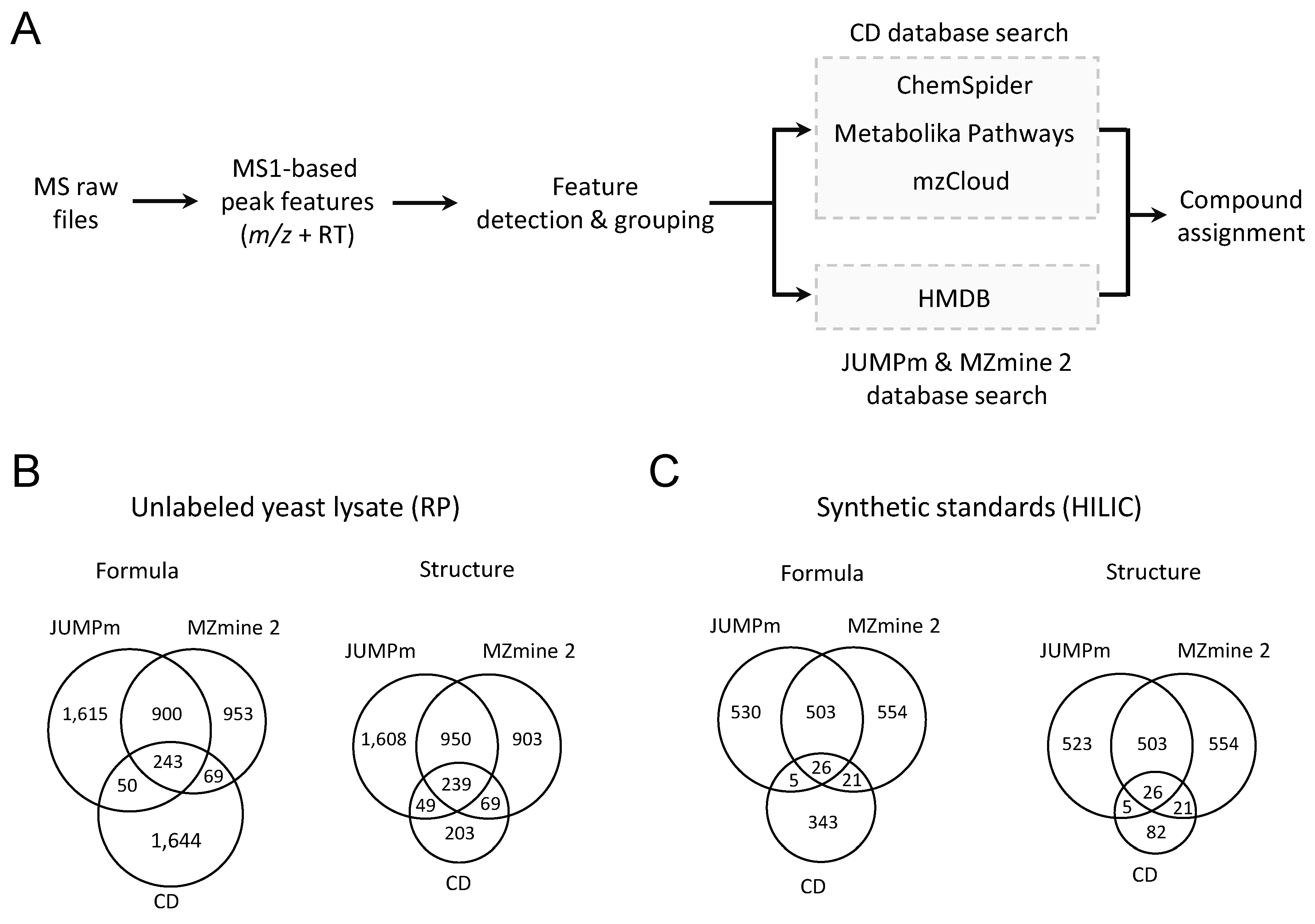
2.3. Performance Comparison with the Other Metabolite Identification Tools
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Isotope Labeling Protocol
4.3. Sample Preparation
4.4. LC-MS Analysis and Parameters
4.5. Construction of the Theoretical Mass-Formula Database
4.6. Feature Detection and Signal-to-Noise Definition
4.7. Mass Calibration
4.8. Detection and Scoring of Candidate Peak Pairs
4.8.1. Calculating p Value for Mass Defect
4.8.2. Calculating p Value for Relative Intensity
4.8.3. Calculating p Value for Pearson Correlation (Co-Elution)
4.8.4. Generating the Combined Pair Score
4.9. Formula Identification
4.10. Structure Database and Identification
4.11. Structure Scoring (Mscore)
4.12. Structure Clustering
4.13. Input and Output
4.14. Parallel Computing and High-Performance Computation
4.15. Parameters Used in CD and MZmine 2
4.16. Software
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rinschen, M.M.; Ivanisevic, J.; Giera, M.; Siuzdak, G. Identification of bioactive metabolites using activity metabolomics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Boil. 2019, 20, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: Beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Boil. 2016, 17, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S. Emerging applications of metabolomics in drug discovery and precision medicine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellogg, R.A.; Dunn, J.; Snyder, M.P. Personal Omics for Precision Health. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 1169–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karczewski, J.; Snyder, M.P. Integrative omics for health and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.R.; Wu, Z.; Chauhan, D.; Anderson, K.C.; Peng, J. A Nano Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography–High Resolution Mass Spectrometry Approach for Global Metabolomic Profiling and Case Study on Drug-Resistant Multiple Myeloma. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 3667–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, G.J.; Yanes, O.; Siuzdak, G. Innovation: Metabolomics: The apogee of the omics trilogy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A.; Want, E.J.; O’Maille, G.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS: Processing Mass Spectrometry Data for Metabolite Profiling Using Nonlinear Peak Alignment, Matching, and Identification. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Nakabayashi, R.; Mori, T.; Yamada, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Rai, A.; Sugiyama, R.; Yamamoto, H.; Nakaya, T.; Yamazaki, M.; et al. A cheminformatics approach to characterize metabolomes in stable-isotope-labeled organisms. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluskal, T.; Castillo, S.; Villar-Briones, A.; Orešič, M. MZmine 2: Modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry-based molecular profile data. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dührkop, K.; Fleischauer, M.; Ludwig, M.; Aksenov, A.A.; Melnik, A.V.; Meusel, M.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Rousu, J.; Böcker, S. SIRIUS 4: A rapid tool for turning tandem mass spectra into metabolite structure information. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, W.B.; Erban, A.; Weber, R.J.M.; Creek, D.J.; Brown, M.; Breitling, R.; Hankemeier, T.; Goodacre, R.; Neumann, S.; Kopka, J.; et al. Mass appeal: Metabolite identification in mass spectrometry-focused untargeted metabolomics. Metabolomics 2012, 9, 44–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.A.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.-M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis Chemical Analysis Working Group (CAWG) Metabolomics Standards Initiative (MSI). Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kind, T.; Tsugawa, H.; Cajka, T.; Ma, Y.; Lai, Z.; Mehta, S.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Barupal, D.K.; Showalter, M.R.; Arita, M.; et al. Identification of small molecules using accurate mass MS/MS search. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2017, 37, 513–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaženović, I.; Kind, T.; Ji, J.; Fiehn, O. Software Tools and Approaches for Compound Identification of LC-MS/MS Data in Metabolomics. Metabolites 2018, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horai, H.; Arita, M.; Kanaya, S.; Nihei, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Suwa, K.; Ojima, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Tanaka, S.; Aoshima, K.; et al. MassBank: A public repository for sharing mass spectral data for life sciences. J. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 45, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milmana, B.L.; Zhurkovich, I.K. The chemical space for non-target analysis. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2017, 97, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Kind, T.; Nakabayashi, R.; Yukihira, D.; Tanaka, W.; Cajka, T.; Saito, K.; Fiehn, O.; Arita, M. Hydrogen Rearrangement Rules: Computational MS/MS Fragmentation and Structure Elucidation Using MS-FINDER Software. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 7946–7958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feunang, Y.D.; Pon, A.; Karu, N.; Zheng, J.; Li, C.; Arndt, D.; Gautam, M.D.; Allen, F.; Wishart, D.S. CFM-ID 3.0: Significantly Improved ESI-MS/MS Prediction and Compound Identification. Metabolites 2019, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruttkies, C.; Schymanski, E.L.; Wolf, S.; Hollender, J.; Neumann, S. MetFrag relaunched: Incorporating strategies beyond in silico fragmentation. J. Cheminform. 2016, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laponogov, I.; Sadawi, N.; Galea, D.; Mirnezami, R.; Veselkov, K. ChemDistiller: An engine for metabolite annotation in mass spectrometry. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2096–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dührkop, K.; Shen, H.; Meusel, M.; Rousu, J.; Böcker, S. Searching molecular structure databases with tandem mass spectra using CSI: FingerID. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12580–12585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taraji, M.; Haddad, P.R.; Amos, R.I.J.; Talebi, M.; Szucs, R.; Dolan, J.W.; Pohl, C.A. Prediction of retention in hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography using solute molecular descriptors based on chemical structures. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1486, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giavalisco, P.; Köhl, K.; Hummel, J.; Seiwert, B.; Willmitzer, L. 13C Isotope-Labeled Metabolomes Allowing for Improved Compound Annotation and Relative Quantification in Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry-based Metabolomic Research. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 6546–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giavalisco, P.; Li, Y.; Matthes, A.; Eckhardt, A.; Hubberten, H.-M.; Hesse, H.; Segu, S.; Hummel, J.; Köhl, K.; Willmitzer, L. Elemental formula annotation of polar and lipophilic metabolites using13C,15N and34S isotope labelling, in combination with high-resolution mass spectrometry. Plant J. 2011, 68, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llufrio, E.M.; Cho, K.; Patti, G.J. Systems-level analysis of isotopic labeling in untargeted metabolomic data by X13CMS. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 1970–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokkathukalam, A.; Kim, D.-H.; Barrett, M.; Breitling, R.; Creek, D.J. Stable isotope-labeling studies in metabolomics: New insights into structure and dynamics of metabolic networks. Bioanalysis 2014, 6, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Chen, Y.-J.; Cho, K.; Nikolskiy, I.; Crawford, P.; Patti, G.J. X13CMS: Global Tracking of Isotopic Labels in Untargeted Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Feldberg, L.; Aharoni, A. Miso: An R package for multiple isotope labeling assisted metabolomics data analysis. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 3524–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueschl, C.; Kluger, B.; Berthiller, F.; Lirk, G.; Winkler, S.; Krska, R.; Schuhmacher, R. MetExtract: A new software tool for the automated comprehensive extraction of metabolite-derived LC/MS signals in metabolomics research. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 736–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokkathukalam, A.; Jankevics, A.; Creek, D.J.; Achcar, F.; Barrett, M.; Breitling, R. mzMatch-ISO: An R tool for the annotation and relative quantification of isotope-labelled mass spectrometry data. Bioinformatics 2012, 29, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Jones, D.R.; Shaw, T.; Cho, J.-H.; Wang, Y.; Tan, H.; Xie, B.; Zhou, S.; Li, Y.; Peng, J. Target-Decoy-Based False Discovery Rate Estimation for Large-Scale Metabolite Identification. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 2328–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- E Elias, J.; Haas, W.; Faherty, B.K.; Gygi, S.P. Comparative evaluation of mass spectrometry platforms used in large-scale proteomics investigations. Nat. Methods 2005, 2, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Elias, J.E.; Thoreen, C.C.; Licklider, L.J.; Gygi, S.P. Evaluation of multidimensional chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (LC/LC-MS/MS) for large-scale protein analysis: The yeast proteome. J. Proteome Res. 2003, 2, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, H.; Tan, H.; Peng, J. JUMP: A tag-based database search tool for peptide identification with high sensitivity and accuracy. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 3663–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Wang, Y.; Jones, D.R.; Dey, K.K.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Cho, J.-H.; Shaw, T.; Tan, H.; Peng, J. Isotope Labeling-Assisted Evaluation of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Liquid Chromatograph–Mass Spectrometry for Metabolomics Profiling. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8538–8545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.; Mann, M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosser, A.; Volkmer-Engert, R. Volatile polydimethylcyclosiloxanes in the ambient laboratory air identified as source of extreme background signals in nanoelectrospray mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 38, 523–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.; Schmidt, S.; Müller-Hannemann, M.; Neumann, S. In silico fragmentation for computer assisted identification of metabolite mass spectra. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, F.; Pon, A.; Wilson, M.; Greiner, R.; Wishart, D.S. CFM-ID: A web server for annotation, spectrum prediction and metabolite identification from tandem mass spectra. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W94–W99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.H., Jr. Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1963, 58, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample Name | Sample Introduction | LC | MS Ionization Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unlabeled yeast lysate | Unlabeled yeast sample | RP | Positive |
| Labeled yeast lysate | 4-plex mixture of one unlabeled sample and three stable-isotope-labeled yeast samples (C13, N15, and double labeling) | RP | Positive |
| Synthetic standards (HILIC) | A mixture of purchased synthetic metabolites | HILIC | Negative |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Cho, J.-H.; Poudel, S.; Li, Y.; Jones, D.R.; Shaw, T.I.; Tan, H.; Xie, B.; Peng, J. JUMPm: A Tool for Large-Scale Identification of Metabolites in Untargeted Metabolomics. Metabolites 2020, 10, 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10050190
Wang X, Cho J-H, Poudel S, Li Y, Jones DR, Shaw TI, Tan H, Xie B, Peng J. JUMPm: A Tool for Large-Scale Identification of Metabolites in Untargeted Metabolomics. Metabolites. 2020; 10(5):190. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10050190
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xusheng, Ji-Hoon Cho, Suresh Poudel, Yuxin Li, Drew R. Jones, Timothy I. Shaw, Haiyan Tan, Boer Xie, and Junmin Peng. 2020. "JUMPm: A Tool for Large-Scale Identification of Metabolites in Untargeted Metabolomics" Metabolites 10, no. 5: 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10050190
APA StyleWang, X., Cho, J.-H., Poudel, S., Li, Y., Jones, D. R., Shaw, T. I., Tan, H., Xie, B., & Peng, J. (2020). JUMPm: A Tool for Large-Scale Identification of Metabolites in Untargeted Metabolomics. Metabolites, 10(5), 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10050190





