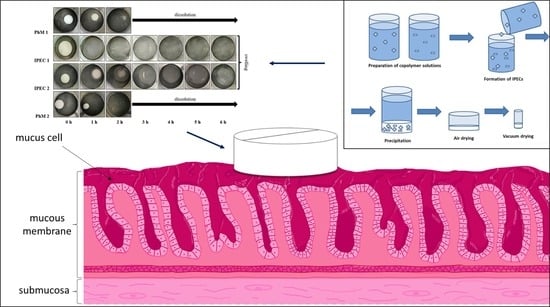
New Carriers for Bioadhesive Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Based on Eudragit® EPO/Eudragit® L100 Interpolyelectrolyte Complexes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Solid Interpolyelectrolyte Complexes (IPEC) and Physical Mixtures (PhM)
2.3. Preparation of Tablets
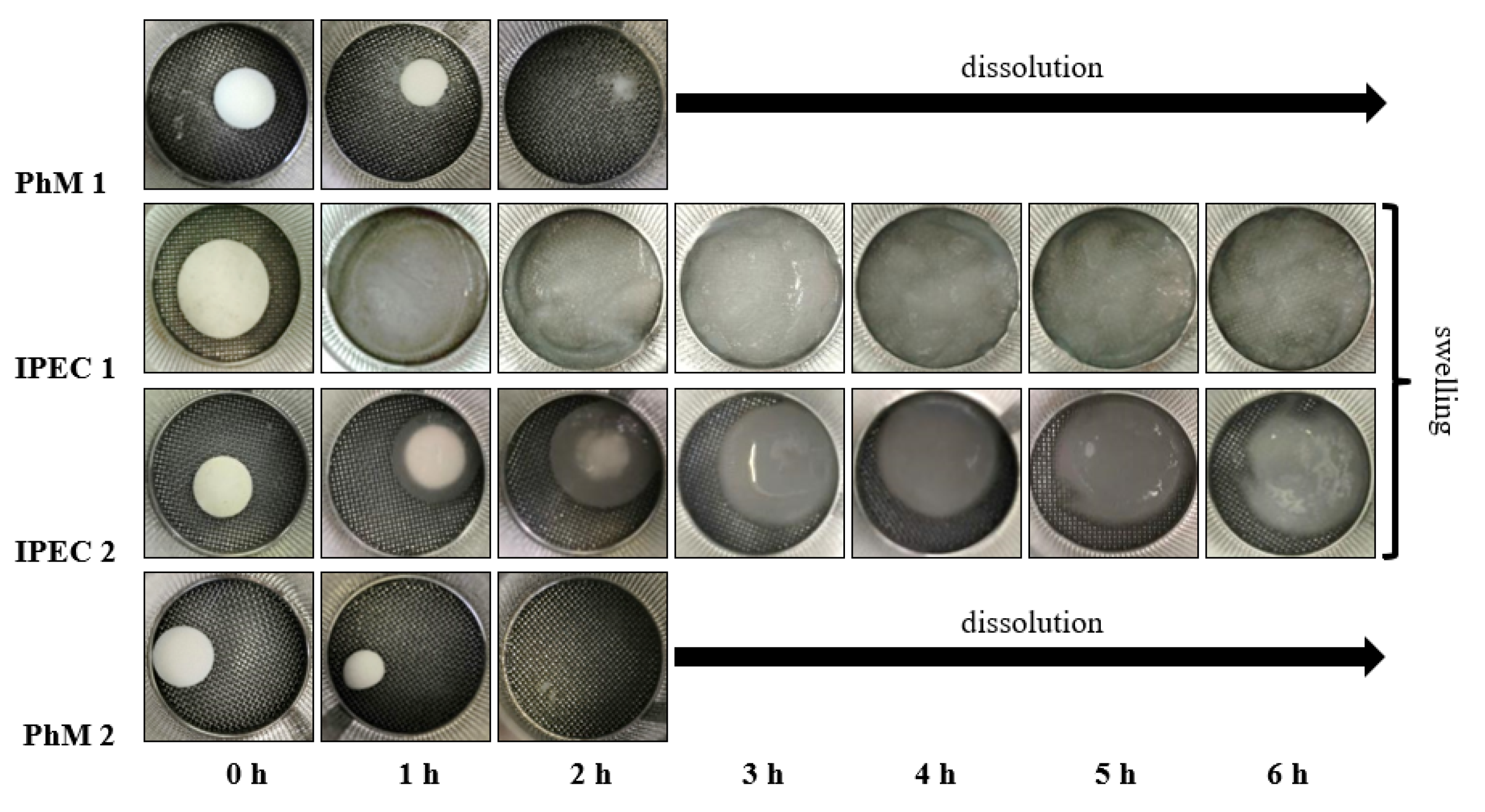
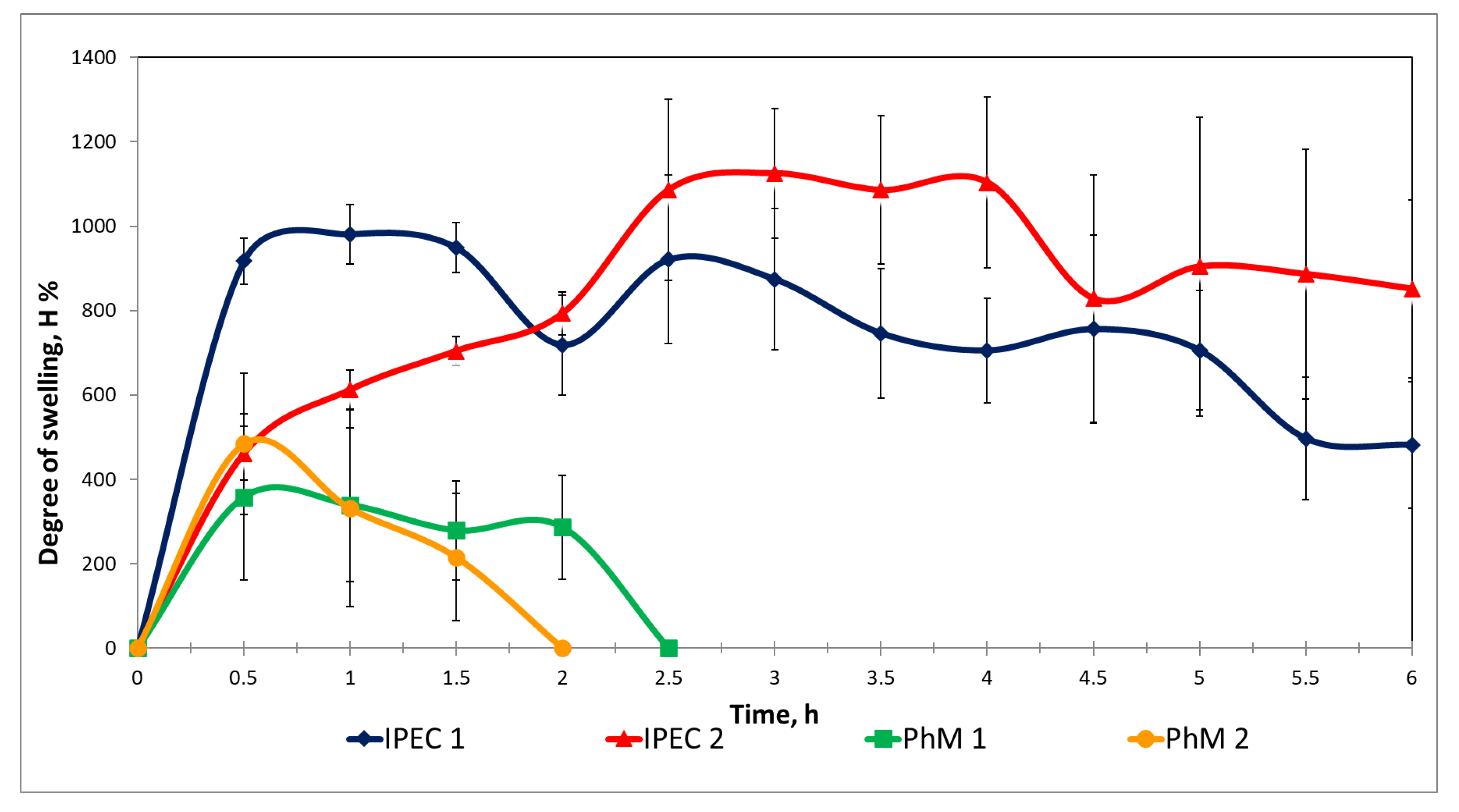
2.4. Determination of the Degree of Swelling of Matrices
2.5. Elemental Analysis
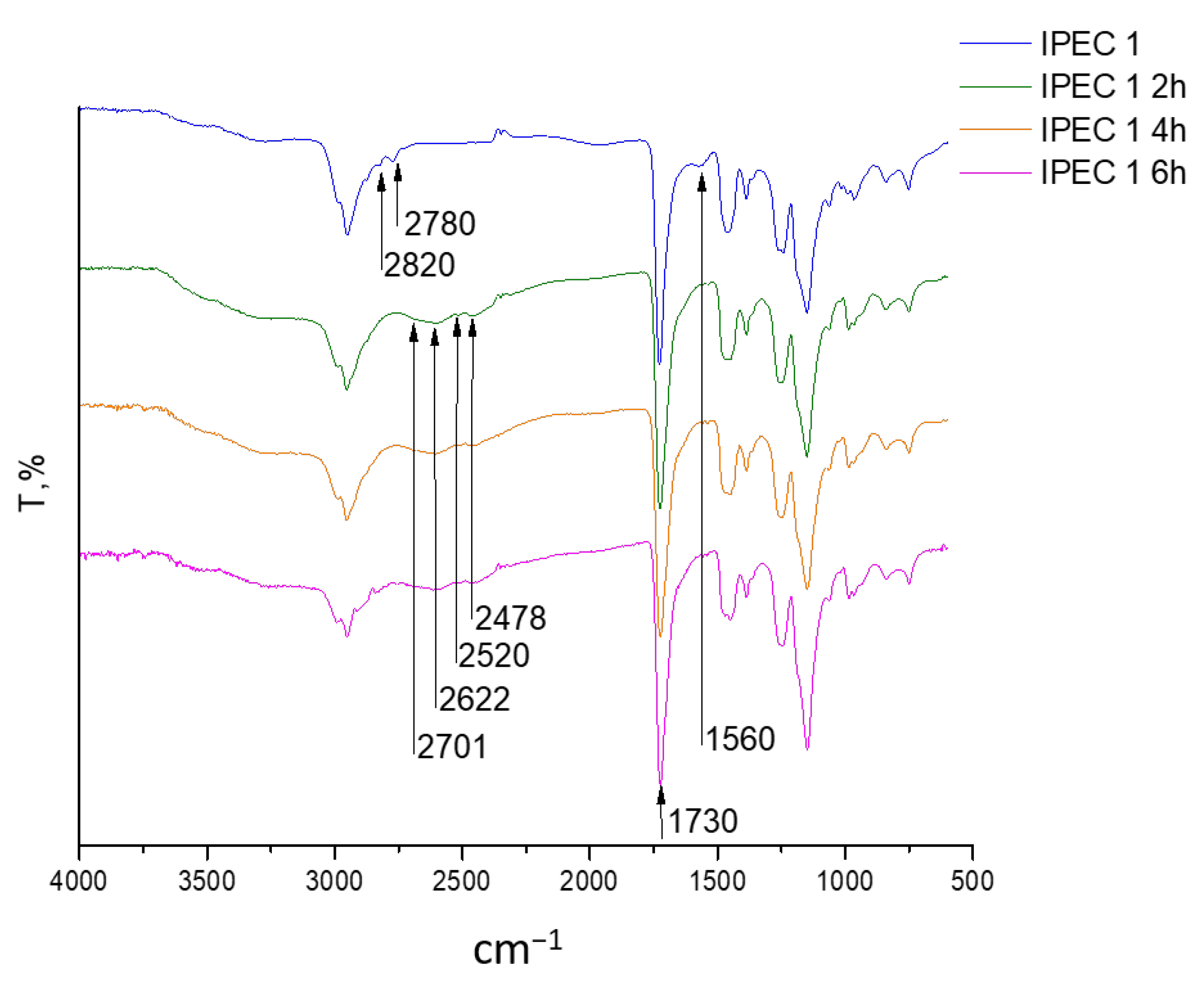
2.6. Fourier-Transformed Infrared (ATR-FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.7. Thermal Analysis
2.8. Study of Model Drug Release
2.9. Analysis of Bioadhesive Properties
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Composition Study
3.2. Assessment of the IPEC Behavior in Acidic Medium
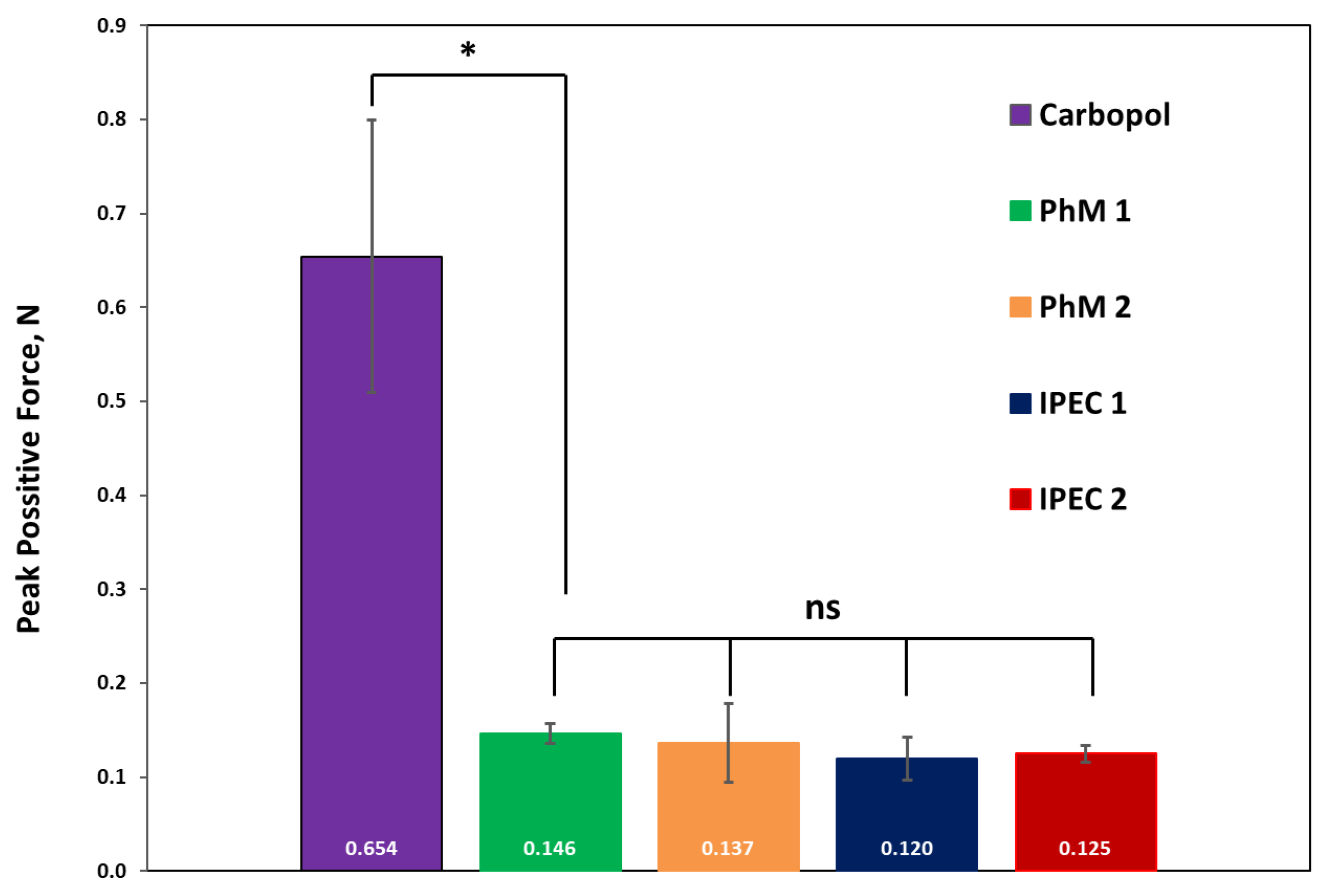
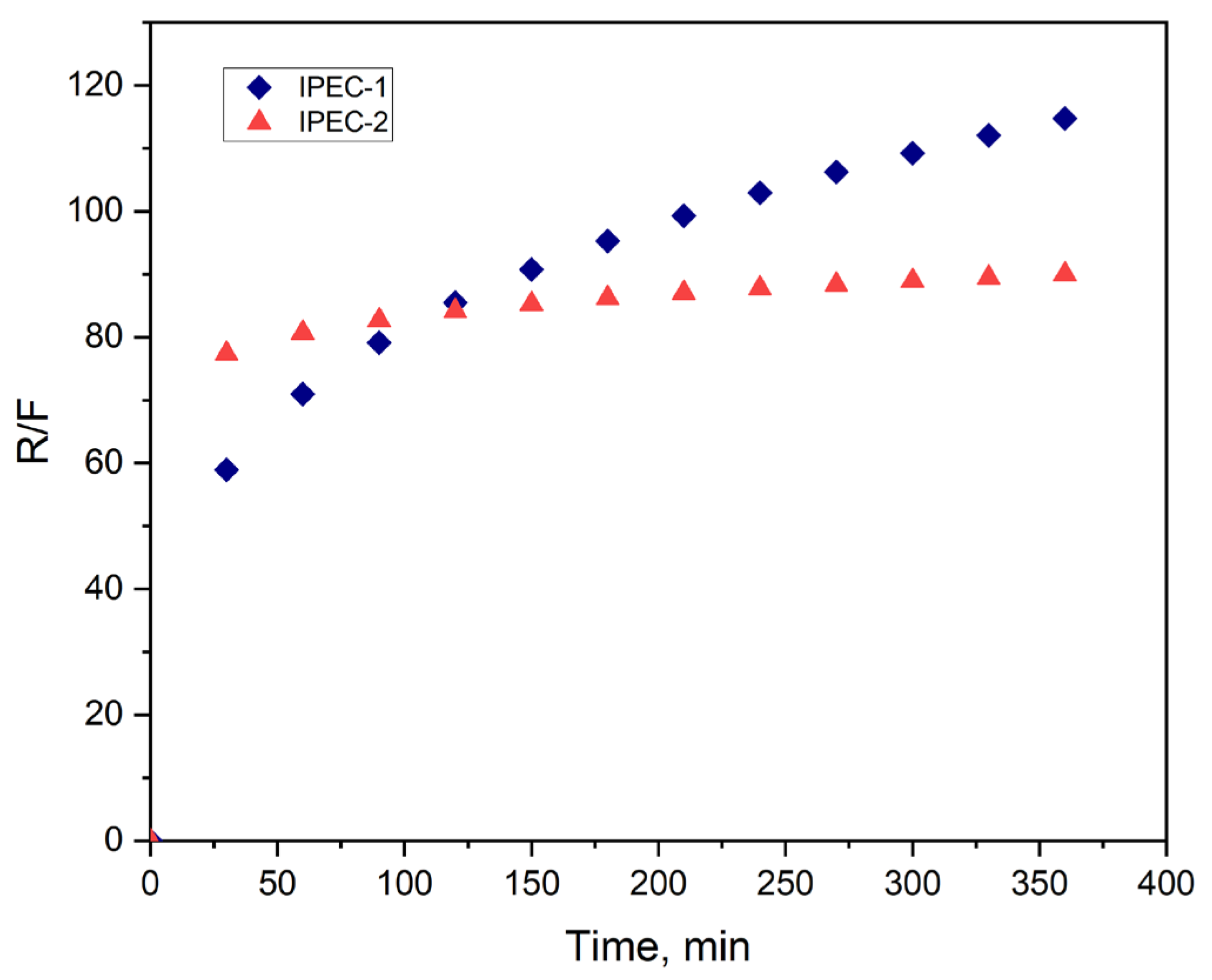
3.3. Analysis of Bioadhesive Properties
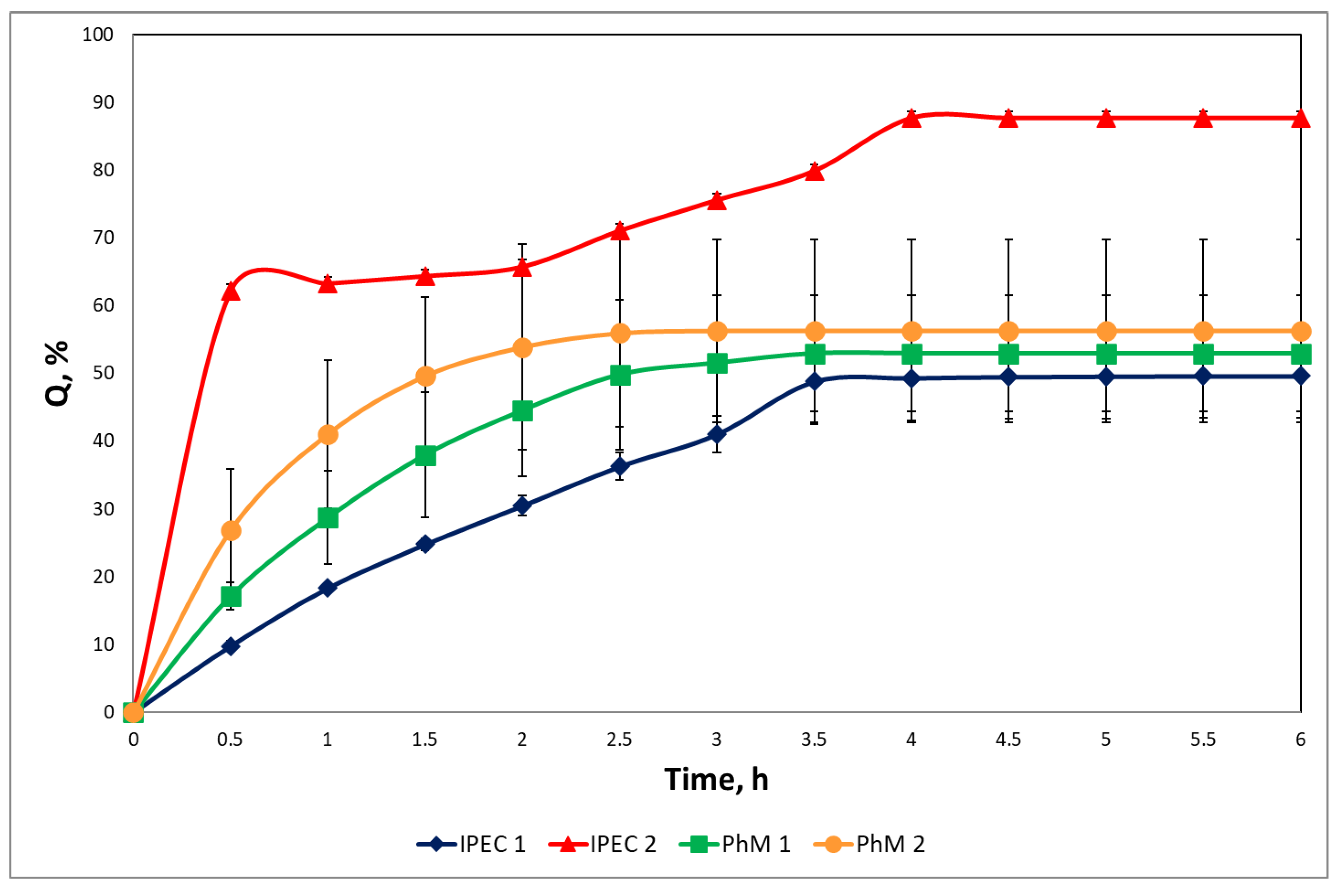
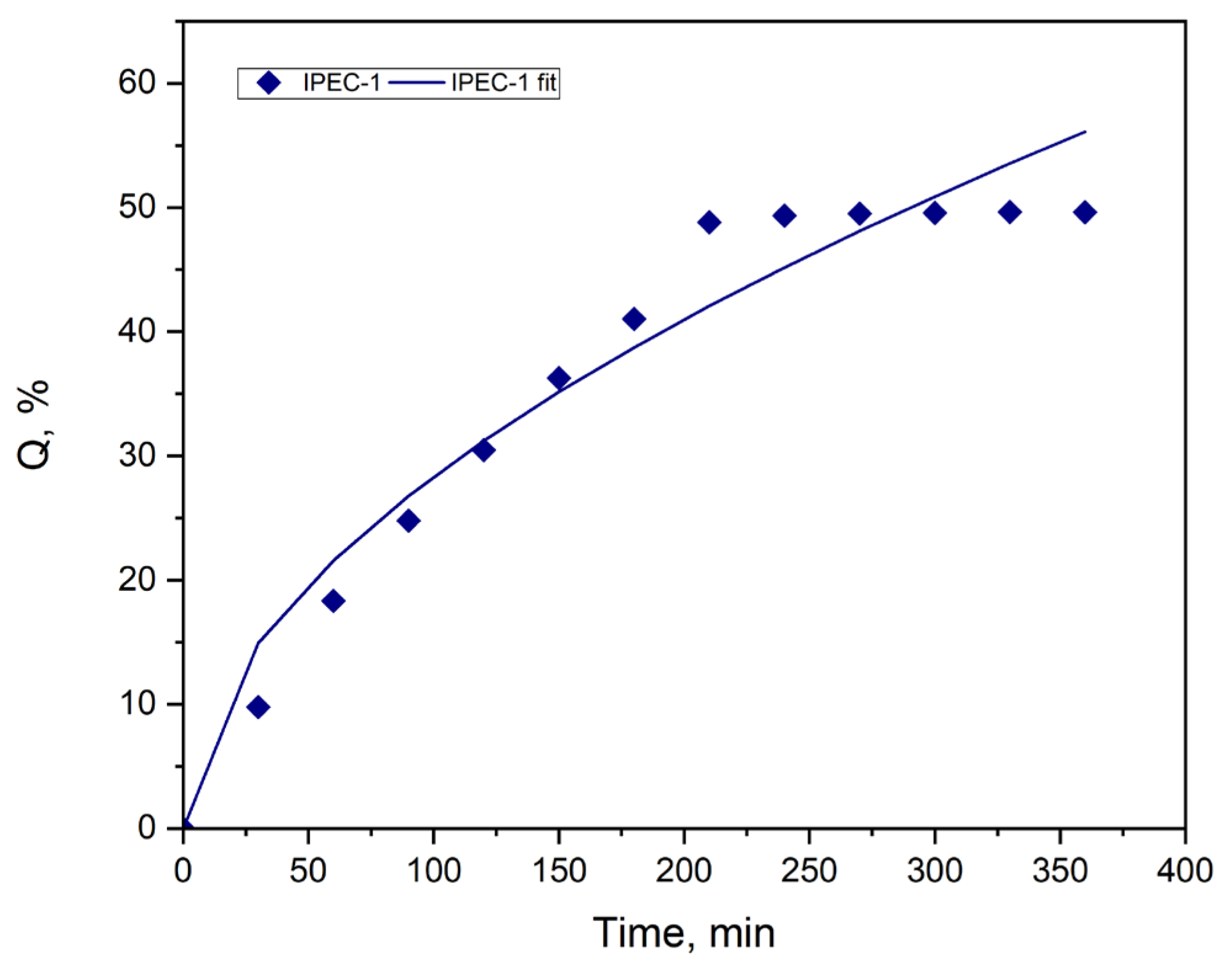
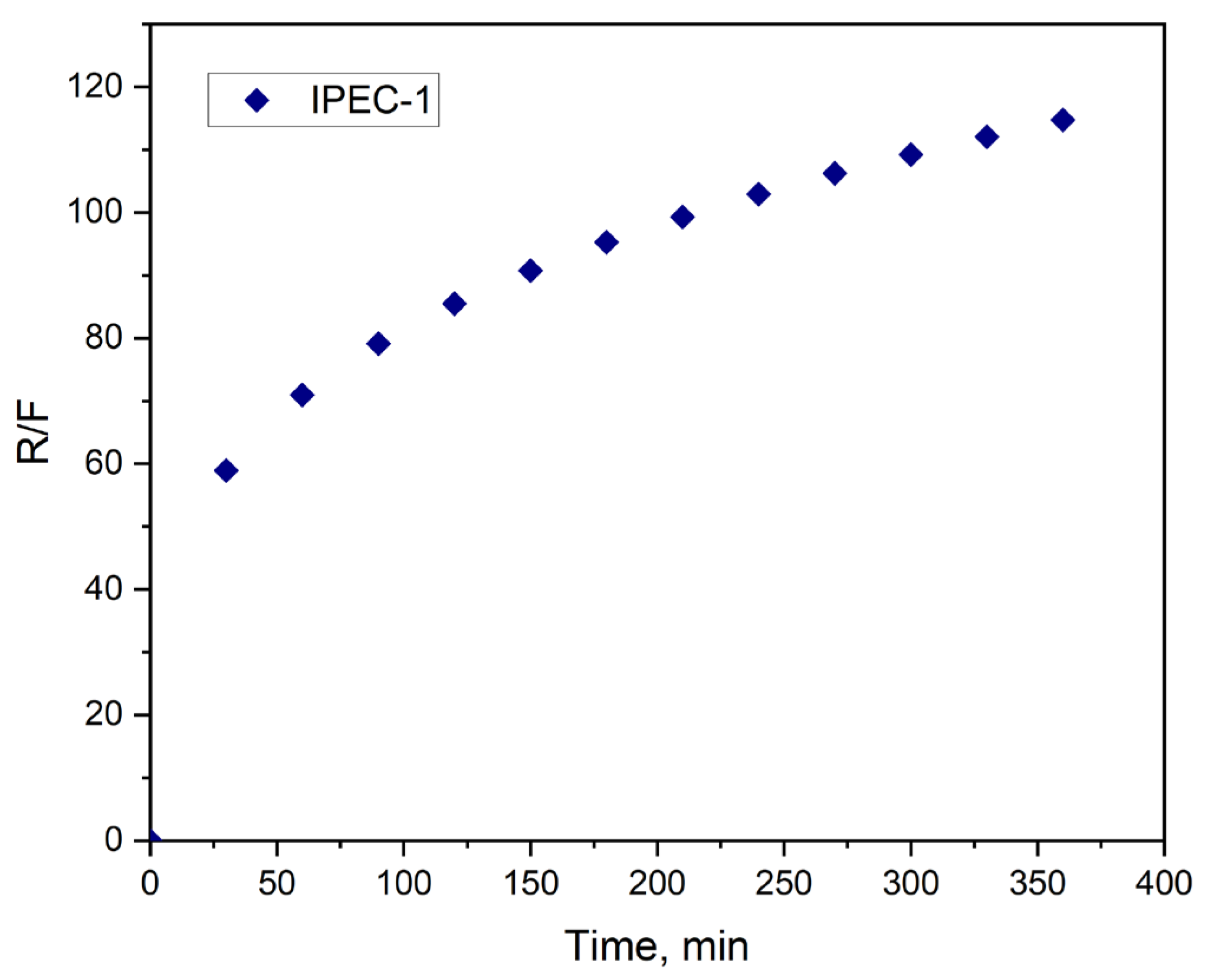
3.4. Study of Drug Release
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alqahtani, A.A.; Mohammed, A.A.; Fatima, F.; Ahmed, M.M. Fused Deposition Modelling 3D-Printed Gastro-Retentive Floating Device for Propranolol HCl Tablets. Polymers 2023, 15, 3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Shelke, S.; Shaikh, F.; Surti, N.; Panzade, P.; Panjwani, D. Gastroretentive Floating Microsponges of Mitiglinide: Design, Preparation, and Pharmacokinetic Evaluation. J. Pharm. Innov. 2023, 14, 1500–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malladia, M.; Jukanti, R. Formulation development and evaluation of a novel bi-dependent clarithromycin gastroretentive drug delivery system using Box-Behnken design. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 35, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uboldi, M.; Melocchi, A.; Moutaharrik, S.; Palugan, L.; Cerea, M.; Foppoli, A.; Maroni, A.; Gazzaniga, A.; Zema, L. Administration strategies and smart devices for drug release in specific sites of the upper GI tract. J. Control. Release 2022, 348, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awasthi, R.; Kulkarni, G.T. Decades of research in drug targeting to the upper gastrointestinal tract using gastroretention technologies: Where do we stand? Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 378–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseem, F.; Shah, S.U.; Rashid, S.A.; Farid, A.; Almehmadi, M.; Alghamdi, S. Metronidazole Based Floating Bioadhesive Drug Delivery System for Potential Eradication of H. pylori: Preparation and In Vitro Characterization. Polym. J. 2022, 14, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sravya, V.; Suresh, K.P.; Jagannath, P.V.; Sunitha, C. Formulate gastroretentive floating bioadhesive drug delivery system of nizatidine by direct compression technique. World J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 10, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altreuter, D.H.; Kirtane, A.R.; Grant, T.; Kruger, C.; Traverso, G.; Bellinger, A.M. Changing the pill: Developments toward the promise of an ultra-long-acting gastroretentive dosage form. Exp. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Tang, J.; Liu, D.; Li, X.; Cheng, L.; Tang, X. Design and evaluation of an innovative floating and bioadhesive and multiparticulate drug delivery system based on hollow structure. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 503, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Chouksey, R. A Recent Advantage on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System: An Overview. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2023, 15, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, V.K.; Kansal, S.; Asthana, S.; Chourasia, M.K. Industrial perspective of gastroretentive drug delivery systems: Physicochemical, biopharmaceutical, technological and regulatory consideration. Exp. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2012, 9, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, J.; Thapa, P.; Maharjan, R.; Jeong, S.H. Current State and Future Perspectives on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Sharma, V.; Mohan, M.; Rohit; Sharma, P.; Ram, K. Design of ciprofloxacin impregnated dietary fiber psyllium-moringa gum-alginate network hydrogels via green approach for use in gastro-retentive drug delivery system. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fiber 2023, 29, 100345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhaj, S.; Conway, B.R.; Ghori, M.U. Nanofibres in Drug Delivery Applications. Fibers 2023, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Kaur, S.; Rai, V.K. Gastro-retentive drug delivery systems: A recent update on clinical pertinence and drug delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 1849–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, R.; Pandey, P.; Nogai, L.; Arushi; Anand, A.; Suthar, P.; Keskar, M.S.; Kumar, V. The Future Perspectives and Novel Approach on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) with Current State. Can. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 30, 594–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Qi, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xing, J.; Li, X. Preparation of multiple-unit floating-bioadhesive cooperative minitablets for improving the oral bioavailability of famotidine in rats. Drug Deliv. 2014, 21, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Darbasizadeha, B.; Motasadizadehb, H.; Foroughi-Niac, B.; Farhadnejad, H. Tripolyphosphate-crosslinked chitosan/poly (ethylene oxide) electrospun nanofibrous mats as a floating gastro-retentive delivery system for ranitidine hydrochloride. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 153, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Wang, S.; Piao, M.G. Prescription Optimization of Gastroretentive Furosemide Hollow-Bioadhesive Microspheres via Box-Behnken Design: In Vitro Characterization and in Vivo Evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 70, 103235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwuluka, N.C.; Choonara, Y.E.; Modi, G.; du Toit, L.C.; Kumar, P.; Ndesendo, V.M.K.; Pillay, V.A. Design of an Interpolyelectrolyte Gastroretentive Matrix for the Site-Specific Zero-Order Delivery of Levodopa in Parkinson’s Disease. AAPS PharmSciTech 2013, 14, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, D.; Skalsky, B.; Kleinebudde, P. Controlled release solid dosage forms using combinations of (meth)acrylate copolymer. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2008, 13, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, F.; Siepmann, J.; Walther, M.; MacRae, R.J.; Bodmeier, R. Polymer blends for controlled release coatings. J. Control. Release 2008, 125, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafin, R.I. Interpolymer combinations of chemically complementary grades of Eudragit copolymers: A new direction in the design of peroral solid dosage forms of drug delivery systems with controlled release (review). Pharm. Chem. J. 2011, 45, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafine, R.I. Role of macromolecular interactions of pharmaceutically acceptable polymers in functioning oral drug delivery systems. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2014, 84, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafine, R.I.; Kabanova, T.V.; Kemenova, V.A.; Van den Mooter, G. Characteristics of interpolyelectrolyte complexes of Eudragit E100 with Eudragit L100. J. Control. Release 2005, 103, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafine, R.I.; Bukhovets, A.V.; Sitenkov, A.Y.; Kemenova, V.A.; Rombaut, P.; Van den Mooter, G. Eudragit® E PO as a complementary material for designing oral drug delivery systems with controlled release properties: Comparative evaluation of new interpolyelectrolyte complexes with countercharged Eudragit® L100 copolymers. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 2630–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, D.; McGinity, J.W. Properties of theophylline tablets dry powder coated with Eudragit E PO and Eudragit L 100–55. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2009, 16, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeidat, W.M.; Abu Znait, A.H.; Sallam, A.A. Novel combination of anionic and cationic polymethacrylate polymers for sustained release tablet preparation. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2008, 34, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeidat, W.M.; Abu Znait, A.H.; Sallam, A.A. Sustained release tablets containing soluble polymethacrylates: Comparison with tableted polymethacrylate IPEC polymers. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bani-Jaber, A.H.; Alkawareek, M.J.; Al-Gousous, J.J.; Abu Helwa, A.Y. Floating and sustained-release characteristics of efferverscent tablets prepared with a mixed matrix of Eudragit L100-55 and Eudragit E PO. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 59, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bani-Jaber, A.H.; Al-Aani, L.; Alkhatib, H.; Al-Khalidi, B. Prolonged intragastric drug delivery mediated by Eudragit E carrageenan polyelectrolyte matrix tablets. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinteros, D.A.; Manzo, R.H.; Allemandi, D.A. Interaction between Eudragit E100 and anionic drugs: Addition of anionic polyelectrolytes and their influence on drug release performance. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 4664–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulff, R.; Leopold, C.S. Coatings from blends of Eudragit® RL and L55: A novel approach in pH-controlled drug release. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 476, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulff, R.; Leopold, C.S. Coatings of Eudragit® RL and L55 blends: Investigations on the drug release mechanism. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcíaa, M.C.; Martinellic, M.; Ponced, N.E.; Sanmarcoe, L.M.; Aokie, M.P.; Manzo, R.H.; Jimenez-Kairuz, A.F. Multi-kinetic release of benznidazole-loaded multiparticulate drug delivery systems based on polymethacrylate interpolyelectrolyte complexes. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 120, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sester, C.; Ofridam, F.; Lebaz, N.; Gagnière, E.; Mangin, D.; Elaissari, A. pH-Sensitive methacrylic acid–methyl methacrylate copolymer Eudragit L100 and dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate, butyl methacrylate, and methyl methacrylate tri-copolymer Eudragit E100. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 31, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhovets, A.V.; Fotaki, N.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V.; Moustafine, R.I. Interpolymer complexes of Eudragit® copolymers as novel carriers for colon-specific drug delivery. Polymers 2020, 12, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordeeva, D.S.; Sitenkova, A.V.; Moustafine, R.I. Interpolyelectrolyte complexes based on Eudragit® copolymers as carriers for bioadhesive gastroretentive metronidazole delivery system. Drug Dev. Reg. 2020, 9, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankalapalli, S.; Kolapalli, V.R.M. Polyelectrolyte complexes: A review of their applicability in drug delivery technology. Ind. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 71, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Robertis, S.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Elviri, L.; Sandri, G.; Caramella, C.; Bettini, R. Advances in oral controlled drug delivery: The role of drug—Polymer and interpolymer non-covalent interactions. Exp. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porfiryeva, N.N.; Nasibullin, S.F.; Abdullina, S.G.; Tukhbatullina, I.K.; Moustafine, R.I.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Acrylated Eudragit® E PO as a novel polymeric excipient with enhanced mucoadhesive properties for application in nasal drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 562, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porfiryeva, N.N.; Semina, I.I.; Salakhov, I.A.; Moustafine, R.I.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Mucoadhesive and mucus-penetrating interpolyelectrolyte complexes for nose-to-brain drug delivery. Nanomed. NBM 2021, 37, 102432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.; Kim, T.H.; Jeong, S.W.; Chung, S.E.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Shin, B.S. Development of a gastroretentive delivery system for acyclovir by 3D printing technology and its in vivo pharmacokinetic evaluation in Beagle dogs. PLoS ONE 2017, 14, e0216875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farshforoush, P.; Ghanbarzadeh, S.; Gpganian, A.M.; Hamishehkar, H. Novel metronidazole-loaded hydrogel as a gastroretentive drug delivery system. Iran. Polym. J. 2017, 26, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.; Sahlin, J. A simple equation for the description of solute release. III. Coupling of diffusion and relaxation. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 57, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, A.; Li, W.; Yao, C.; Xie, S. DDSolver: An Add-In Program for Modeling and Comparison of Drug Dissolution Profiles. AAPS J. 2010, 3, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boddupalli, B.M.; Mohammed, Z.N.; Nath, R.A.; Banji, D. Mucoadhesive drug delivery system: An overview. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2010, 1, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Fang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, T. Evaluating the bioequivalence of metronidazole tablets and analyzing the effect of in vitro dissolution on in vivo absorption based on PBPK modeling. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 1646–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulistiawati; Dwipayanti, K.S.; Azhar, M.; Rahman, L.; Pakki, E.; Himawan, A.; Permana, A.D. Enhanced skin localization of metronidazole using solid lipid microparticles incorporated into polymeric hydrogels for potential improved of rosacea treatment: An ex vivo proof of concept investigation. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 628, 122327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Cristofoletti, R.; Zhao, L.; Rostami-Hodjegan, A. Scientific considerations to move towards biowaiver for biopharmaceutical classification system classIII drugs: How modeling and simulation can help. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2021, 42, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mady, O.I.; Osman, M.A.; Sarhan, N.I.; Shatla, A.A.; Haggag, Y.A. Bioavailability enhancement of acyclovir by honey: Analytical and histological evidence. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 80, 104155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippova, N.I.; Teslev, A.A. Application of mathematical modeling in the evaluation of in vitro drug release. Drug Dev. Reg. 2017, 4, 218–226. [Google Scholar]
- Unagollaa, J.M.; Jayasuriya, A.C. Drug transport mechanisms and in vitro release kinetics of vancomycin encapsulated chitosan-alginate polyelectrolyte microparticles as a controlled drug delivery system. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 114, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Sample Symbol | pH at Which IPEC Was Obtained | IPEC Composition | Tg Value, °C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z = [EPO]/[L100] | EPO:L100 (mol/mol) | |||
| IPEC 1 | 6.0 | 1.02 | 1:0.98 | 146.6 ± 0.3 |
| IPEC 2 | 6.5 | 1.49 | 1:0.67 | 117.4 ± 0.2 |
| Glass Transition, °C | Elemental Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tg | Composition Z = EPO:L100 (mol/mol) | N, % | |
| IPEC 1–2 h | 165.8 ± 0.1 | 1:1.17 | 2.84 ± 0.16 |
| IPEC 1–4 h | 170.7 ± 0.1 | 1:1.11 | 2.91 ± 0.26 |
| IPEC 1–6 h | 170.6 ± 0.1 | 1:1.08 | 3.11 ± 0.10 |
| IPEC 2–2 h | 169.5 ± 0.1 | 1:1.22 | 2.78 ± 0.11 |
| IPEC 2–4 h | 172.3 ± 0.5 | 1:1.47 | 2.54 ± 0.12 |
| IPEC 2–6 h | 173.9 ± 0.3 | 1:1.27 | 2.75 ± 0.31 |
| Sample | Model | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| IPEC 1 | Zero-order | 0.5952 |
| First-order | 0.8459 | |
| Peppas–Sahlin | 0.9762 |
| Sample | Model | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| IPEC 1 | Zero-order | −17.3238 |
| First-order | 0.9935 | |
| Peppas–Sahlin | 0.9813 | |
| IPEC 2 | Zero-order | −17.3238 |
| First-order | −15.0387 | |
| Peppas–Sahlin | 0.9892 |
| Parameters | IPEC 1 |
|---|---|
| m | 0.2681 |
| K1 | 0.1000 |
| K2 | 2.3675 |
| R2 | 0.9762 |
| Parameters | IPEC 1 | IPEC 2 |
|---|---|---|
| m | 0.2681 | 0.0605 |
| K1 | 0.1000 | 0.1675 |
| K2 | 2.3676 | 10.5505 |
| R2 | 0.9813 | 0.9892 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gordeeva, D.S.; Sitenkova, A.V.; Moustafine, R.I. New Carriers for Bioadhesive Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Based on Eudragit® EPO/Eudragit® L100 Interpolyelectrolyte Complexes. Sci. Pharm. 2024, 92, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm92010014
Gordeeva DS, Sitenkova AV, Moustafine RI. New Carriers for Bioadhesive Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Based on Eudragit® EPO/Eudragit® L100 Interpolyelectrolyte Complexes. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2024; 92(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm92010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleGordeeva, Daria S., Aleksandra V. Sitenkova (Bukhovets), and Rouslan I. Moustafine. 2024. "New Carriers for Bioadhesive Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Based on Eudragit® EPO/Eudragit® L100 Interpolyelectrolyte Complexes" Scientia Pharmaceutica 92, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm92010014
APA StyleGordeeva, D. S., Sitenkova, A. V., & Moustafine, R. I. (2024). New Carriers for Bioadhesive Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Based on Eudragit® EPO/Eudragit® L100 Interpolyelectrolyte Complexes. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 92(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm92010014