Abstract
This review aims to present the Quality by Design (QbD) model as a suitable methodology to perform research in the academic Costa Rican institutions that teach Pharmacy. Pubmed, Science Direct, and Google Scholar databases were screened for original research papers and review papers published not more than ten years ago. Institutional repositories from the different universities were reviewed as well. The QbD model stands out as a great methodology for carrying out research projects regarding Pharmaceutical Sciences, but especially for Industrial Pharmacy, where it has contributed in terms of formulation development, manufacturing, and quality control. Academic research based on this model enables the training and development of practical, scientific, and leadership skills in Industrial Pharmacy students. The generated knowledge can be shared in classrooms, which represents an ideal environment to communicate research results and to foster collaborative work between researchers, professors, and students. Moreover, research performed through a QbD approach increases the confidence shown by the industrial sector and health regulatory authorities in the quality of the research, products, and knowledge that are developed and created in an Academy. As a result, the implementation of the model has allowed the creation, transfer, and materialization of knowledge from the Costa Rican Academy to different local pharmaceutical industries.
1. Introduction
Historically, public universities in Costa Rica have taken the lead in research activities; however, only one of them teaches Pharmacy, which is the University of Costa Rica (UCR). On the other hand, the private educational system has played a role in the knowledge economy; i.e., it is a university corporate system that focuses on instrumentalism and marketability. As a result, the private university model in Costa Rica is characterized by academic institutions with little research and personnel dedicated to it [1,2,3,4]. Specifically, these private institutions that offer Pharmacy majors lack a research system properly focused on Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences.
Every university, either public or private, with a Pharmacy major as part of its academic offer has policies created by the International Federation of Pharmacy (FIP) that can be used as tools for the evaluation, review, and improvement of its educational and scientific standards [5]. Currently, the FIP has focused its efforts on supporting research for Drug Discovery, Drug Development, Pharmaceutical Technology, Natural Products, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics, Pharmacology, Personalized Medicine, Biotechnology, Analytical Science and Quality Control, Regulatory Affairs, Drug Metabolism, Pharmacoeconomics, and Pharmacovigilance, among others [6].
A methodology that allows research in some of the mentioned areas, especially the ones related to Industrial Pharmacy, is Quality by Design (QbD). The model is based on an adequate understanding of the sources of variability and the processes involved. All the knowledge about the impact caused by materials and process parameters on the quality profile of the finished product is of great importance [7,8]. The concept of QbD was initially introduced by a quality expert, Joseph Juran, who, in his book Juran on Quality by Design, described it through a dynamic triad, consisting of Quality Planning, Quality Control, and Quality Improvement [9]. Since then, there have been advances in the model, and its benefits in Academies have been demonstrated by high-quality works carried out by Yu et al. [10], Sangshetti et al. [11], and Grangeia et al. [12].
Costa Rican universities that teach the Pharmacy major must follow a strategy that systematically guides the development of scientific research in the industrial field. Therefore, this comprehensive review aims to present the QbD model as an opportunity and suitable methodology for research in Industrial Pharmacy in academic Costa Rican institutions. Pubmed, Science Direct, and Google Scholar databases were screened for original research papers and review papers not older than ten years. Publications were screened by title and abstract. In addition, institutional repositories from different universities were reviewed, and valid guidelines from the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) and the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) related to QbD were considered suitable references due to their relevance to the topic.
To the best of our knowledge, there are no other papers that describe a research system for Industrial Pharmacy in Costa Rican universities or that present a suitable methodology for the promotion of feasible and high-quality research in the field.
2. University’s Research Model in Costa Rica
Bentley et al. stated that universities along with industry and government research entities are the main actors in national research, development, and innovation systems [13]. Nonetheless, the public academic environment possesses the greatest research freedom within society. According to the philosopher Immanuel Kant, generated knowledge has a social impact with a bidirectional behavior, that is, from the world to science, and from science to the world [14].
Research projects from an Academy can influence the theory of a certain phenomenon. The term “Academy” is used to describe a community composed of students and academics, committed to higher education and research as a fundamental activity in the creation of knowledge [15]. A large majority of high-impact publications are the product of the thesis work of master’s students and doctoral candidates affiliated with a specific research group from public universities to become trained scientists [16,17,18].
In this sense, the creation of knowledge must be ethical, always emphasizing the quality of research over quantity and avoiding any practice that encourages the opposite. Unfortunately, the latter has not always been put into practice, and it directly affects first-year Pharmacy students who do not yet know how to validate a scientific reference from the literature [19]. According to the famous library scientist Jeffrey Beall, this student population tends to consult papers from predatory journals for their assignments and evaluations [20].
In addition, Costa Rican private universities where Pharmacy majors are taught have not paid special attention to research activities for the discipline as such; thus, they cannot be considered an Academy yet. This private system, however, is being replaced by a university model with more complex thinking, which seeks to participate in the national social agenda, as well as taking a leading role in the generation of knowledge as the central axis of the research process. Authors such as Egri et al. [21] and Salau et al. [22] have recognized this new model as a means by which research priorities can be organized around strategic areas to bring “non-academia” universities closer to becoming Academies in various countries.
The new vision adopted by the Costa Rican private educational system, besides focusing on the search and design of research methodologies, allows the dissemination of scientific knowledge. The participation of their personnel and students in national and international events (e.g., conferences and symposia) and the production of scientific manuscripts are of great relevance when evaluating the quality of a certain institution [23,24]. According to Pineda et al., these activities give great support to the research program established by the majors and, at the same time, provide prestige to it, its researchers, and the universities [25].
Likewise, some Costa Rican universities have created open-access journals, which facilitate the publication of research without the financial issue that submitting the manuscripts to a large majority of international journals would represent. This open-access model is also a transparent and affordable means of knowledge that also allows the development of collaborative inter-institutional networks, expanding the ideals of the universities [26,27,28].
Nonetheless, despite the consolidated system from the UCR and the great progress experienced by private universities, the establishment of scientific work in both cases is based on the institutional development plan. This promotes the well-defined figure by Berg et al. [2] of the “slow professor”, i.e., an individual with few research tasks, either due to little affinity with the research topics or due to poor suitability to participate in them [29]. Similarly, it is important to highlight that not every university is capable of conducting research, or at least, not at the same level. Moreover, not all teaching personnel can be included in the category of academics. In many cases, their research possibilities are reduced due to a lack of resources, economic and political pressures, or unavailability due to overload in teaching [30,31].
Based on the presented overview, the adoption of methodological guidelines or research models for Industrial Pharmacy in Costa Rican universities that teach Pharmacy may improve professor and student integration into research activities. This will not only provide great academic training tools for both, but it will also represent an integral indicator of credibility, compliance, efficiency, and competitiveness of the major and the research system [32,33,34]. The relevance of such parameters also lies in their use as an internal mechanism of evaluation in budgetary control and the prioritization of research [35].
3. Quality by Design Approach for Industrial Pharmacy in Costa Rican Academy
3.1. Model’s Basic Characteristics
The ICH guideline Q8 (R2) defines the QbD model as a systematic approach to Pharmaceutical Development, which begins with predefined objectives and places special emphasis on understanding the product, the process, and its controls [36]. Moreover, the FDA considers that quality in a Drug Quality System cannot be evaluated or determined in a product but must be introduced and promoted from its design [37].
Despite the aforementioned, the quality of the products has been historically determined through “Quality by Test”, i.e., to evaluate the quality of the finished product without prior controls [38]. Nevertheless, the demand to produce medicines of the highest quality and to improve competitiveness within the pharmaceutical, industrial, and health fields forced many institutions to take on new measures to guarantee the quality of their products. Therefore, the adoption of the QbD is of great relevance, as the predictions made by the model are useful in the design of experimental investigations, time management, and the use of resources throughout the process [39].
The QbD model’s lifecycle (Figure 1) [40] is directly related to the different constituent elements, such as the Target Product Profile (TPP), Quality Target Product Profile (QTPP), Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs), Critical Material Attributes (CMAs), Critical Process Parameters (CPPs), and Design Space [41,42]. In addition, Quality Risk Management (QRM), Design of Experiments (DoE), and Process Analytical Technologies (PATs) are used as tools to guarantee the quality of the products being developed [43]. These tools also make the QbD model an approach that meets the current demand for research processes, as it is considered cost effective in project development [44,45,46].
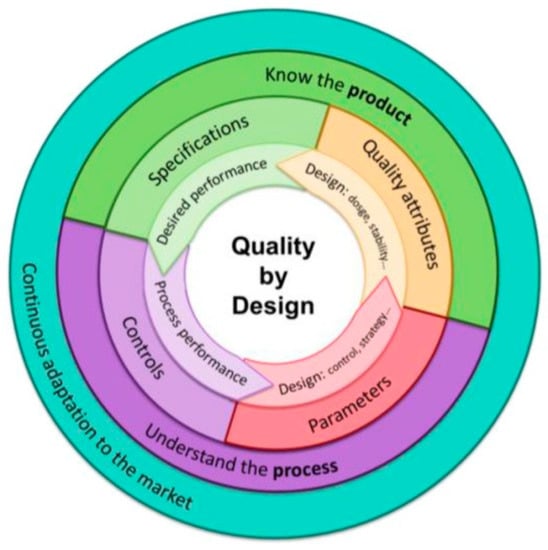
Figure 1.
QbD lifecycle. Reprinted with permission from Fornaguera. et al. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 7(4). Copyright (2017) MDPI [40].
According to the ICH Q9 guideline on Quality Risk Management [47], CQAs, CMAs, and CPPs can be identified through adequate risk management, as it detects those problems in the development of the product and their associated risks [48,49]. In general, nine tools are recommended for risk management. However, among the most widely used tools are Ishikawa’s fishbone diagram (Figure 2) [44] and the Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) [48,50,51]. These two tools are thoroughly explained to the Pharmacy students in Drug Analysis courses.
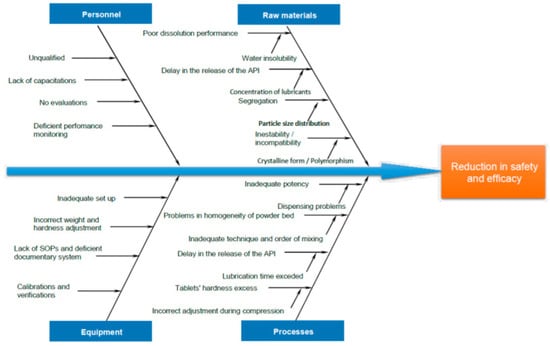
Figure 2.
Example of an Ishikawa diagram for risk management in Formulation Development carried out in the Academy. Reprinted with permission from Castillo, L. et al. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 45(10). Copyright (2019) Taylor & Francis [44].
In addition, DoE allows researchers to use their knowledge regarding the product and/or process instead of merely applying the commonly known “trial and error” [52,53]. This tool is used to organize, conduct, and interpret the results of experiments efficiently, guaranteeing the collection of the greatest possible amount of useful information through the execution of a small number of tests. The main objective of an experimental study is to find the relationship between independent variables (i.e., factors) and dependent variables (i.e., responses) that affects a certain process and its final product (Figure 3) [54]. An adequate DoE can help identify optimal conditions, CMAs, CPPs, and their impact on CQAs [55].
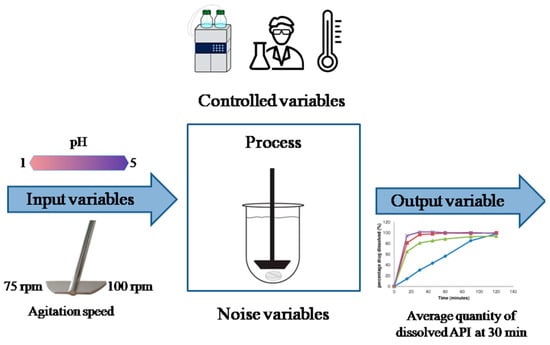
Figure 3.
Example of a Design of Experiments carried out in the Academy to assess the performance of solid formulations in the dissolution test. Adapted with permission from Castillo, L. et al. Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics, 9(1-s). Copyright (2019) JDDT [54].
3.2. Implementation in Academic Research
QbD can be used in any section of the Pharmaceutical Development process, from the drug substance development stages to clinical trials (Figure 4) [39].
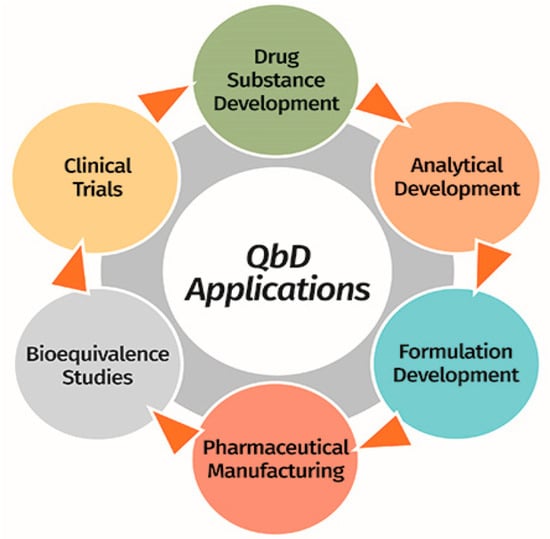
Figure 4.
Potential applications of the QbD approach in diverse stages of the Drug development lifecycle. Reprinted with permission from Rahman, M. et al. European Pharmaceutical Review, 22(1). Copyright (2017) Rusell Publishing Limited [39].
Table 1 presents a scientific summarization of the QbD methodology in different areas of the pharmaceutical discipline, such as excipients development [56], analytical methods [57,58,59], dissolution tests [60,61], stability studies [61], bioequivalence development/validation [62], clinical trials [63], and others [64,65]. These examples have allowed advances in the Academy, Pharmaceutical Development, and the regulatory environment, moving from empirical processes to research based on science and risk control [66,67]. Therefore, the application of the model allows tangible results (e.g., pharmaceutical products and analytical methods) of the highest and most reproducible quality to be obtained, which can be easily predicted or anticipated [68].

Table 1.
Quality by Design applications in Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences developed by the Academy.
Moreover, Orozco et al. previously described the Costa Rican innovation system as weak, mainly due to a poorly effective linkage of the universities with the industrial sector [69]. However, a direct benefit of the increase in students and the research groups’ practical and scientific skills due to the implementation of the QbD approach is the confidence shown by customers, the industrial sector, and health authorities on the quality of the research, products, and knowledge that are developed and created in the Academy. The empowerment demonstrated by the students during the execution of their graduation projects, and the increase in learning engagement owing to the application of this methodology have also developed leadership and team-work skills, necessary to conduct research [10,11,70].
As a result, the QbD model has allowed the creation, transfer, and materialization of knowledge from Costa Rican universities to different local pharmaceutical industries, as discussed in the following sections. Different QbD approaches carried out regarding formulation, the manufacturing process design, and the quality control of drugs and natural products are addressed. An emphasis is placed on the different QbD elements and tools employed throughout the research.
3.2.1. Formulation Development
The QbD model satisfactorily deals with the challenges posed by the design and development of pharmaceutical formulations, being also able to accelerate them [82]. The thorough comprehension of CMAs, the assessment of physicochemical compatibility, the application of QRM, the performance of DoE, and the use of PAT to assess and predict stability are responsible for the great success experienced [83].
Castillo et al. employed QbD for the development of different pharmaceutical formulations. In 2017, a collaboration between UCR and the National Laboratory of Nanotechnology (LANOTEC) worked on developing an immediate-release formulation of rupatadine fumarate 10 mg tablets by direct compression. The research involved identifying the TPP in terms of the target population, administration route, posology, potency, composition, and desired performance regarding drug release and physicochemical stability compared to a commercialized reference product, Rupax® [44]. Later on, knowledge and technological transference to a local pharmaceutical industry resulted in the commercialization of the drug product.
Moreover, an adequate QRM during formulation can provide products of the highest quality and safety, thus becoming an excellent resource for the identification and control of possible quality problems during research [84]. This tool allows for better decision making when quality-related issues arise, making their justification easier and generating greater confidence in the research group [85]. In the rupatadine research, QRM was employed to identify the CMAs and CPPs, and it led to the definition of the CQAs, a safe process, and formulations with no physicochemical incompatibilities. Additionally, spectroscopic and thermal analysis techniques were used to assess the physicochemical compatibility and the suitability of the manufacturing process [44].
Following that, in 2021, another investigation involving students at UCR applied a QbD approach for pharmaceutical formulation development. Hanley et al. developed an oral suspension with anti-ulcer and gastroprotective effects. Remarkably, they reported the thickening agents’ concentration as a CMA and the pretreatment of the drug using a wetting agent as a CPP. Once the previous aspects were identified, a DoE was designed and executed to determine the effect of these on the suspension’s viscosity, which was defined as a CQA [86]. In general, DoE is conceived as an excellent tool that allows forsystematic manipulation of factors according to a design prior to the establishment of specifications [87,88]. The independent variables are usually formulation factors or manufacturing/test conditions, while the dependent variables are product properties or parameters that indicate the performance of the process [89]. Using this tool, Hanley’s research results revealed that only one of the prototype formulations was suitable for development. In this case, the technology was transferred to another local pharmaceutical industry, which is currently in the process of registering the product and commercializing it in the country [86].
At a private university, Universidad Internacional de Las Américas (UIA), Ramírez, et al. developed a sustained-release tablet formulation of a non-steroidal and anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) to treat chronic pain. In this approach, the research group sought to fulfill the CQAs established by the United States Pharmacopoeia (USP) and the British Pharmacopoeia (BP) for the product. The performed QRM was based on Ishikawa’s diagram, FMEA, and the creation of an adequate strategy for risk control and mitigation [90]. Furthermore, other research projects are currently applying this methodology at UIA, such as in the development of a self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS) to improve itraconazole oral bioavailability and chlorpheniramine/guaifenesin chewing tablets for cold treatment in children.
More recently, collaborative work between the Faculty of Pharmacy of UCR, LANOTEC, the Laboratory of Biopharmacy and Pharmacokinetics (LABIOFAR) of UCR, and the Laboratory of Polymers of the National University (POLIUNA) allowed the development of a topical chitosan-based thermo-responsive scaffold loaded with dexketoprofen trometamol (DKT). In this case, the TPP was defined as a function of the intended application for chronic and non-healing wounds caused by different diseases (e.g., diabetes), as well as for local pain and inflammation management. The scaffold was required to provide controlled release of DKT for 24 h use, having a small release rate at or below the normothermia and taking advantage of the local hyperthermia presented in wounds. The latter induces a sol–gel transition in the polymer’s structure, which increases the drug’s release rate. This QbD approach contributed to the avoidance of excessive DKT loading in the polymer matrix as most conventional drug systems do to achieve a concentration gradient for Fickian diffusion as the main release mechanism [91].
3.2.2. Manufacturing Process Design
In many cases, the definition of scalable and consistent methods of drug preparation or manufacturing is hard to achieve. Nevertheless, a QbD approach can bring solutions to many of the related issues by making use of three key steps: (a) QRM, (b) DoE, and (c) the execution and analysis of studies to determine their impact on the process quality, as well as on the Design Space [92]. In addition, the ICH Q8 (R2) [36], Q9 [47], Q11 Development and Manufacture of Drug Substances [93], Q13 Continuous Manufacturing of Drug Substances and Drug Products [94], and the FDA Guidance for Industry on PAT [95] represent a magnificent framework for the manufacturing of pharmaceutical products [12,96]. In fact, the use of PAT and Continuous Manufacturing has been increasing in QbD-based developments. Both have enabled real-time measurements for process monitoring, higher operational flexibility, reducing batch rejection, faster manufacture, and fewer resources and efforts for regulatory compliance [97]. The reduction in R&D costs and time has also been associated with the implementation of QbD [98].
At UCR, Cantillo et al. designed a film coating process of tablets at a pilot scale for a local pharmaceutical industry. In this case, the group employed a full factorial design to evaluate the impact of the CMAs (friability, density, and tablet dimensions) and CPPs (drum’s rotational speed, core bed temperature, and feed rate of the coating solution) on the weight increase and appearance of defects. In conclusion, they reported the drum’s rotational speed, the core bed temperature, and the feed rate of the coating solution as the main effects, and created a control strategy for these process parameters [99].
3.2.3. Quality Control
QbD can also be expanded to analytical methods for the quality control of pharmaceutical formulations, also known as Analytical Quality by Design (AQbD), which is different from the classical approach for Analytical Method Development (Figure 5) [100]. AQbD demands that the goal to be achieved is initially defined, i.e., the analytical target profile, as well as properly selecting the analytical method from the different alternatives that are systematically evaluated. This allows a well-understood method to be obtained that not only exhibits the best performance but also has the possibility to be improved, if necessary. As the next step, a control strategy is designed and established to manage risks and guarantee robustness. Then, the validation of the method is developed, and finally, continuous monitoring is mandatory throughout the lifecycle [101].
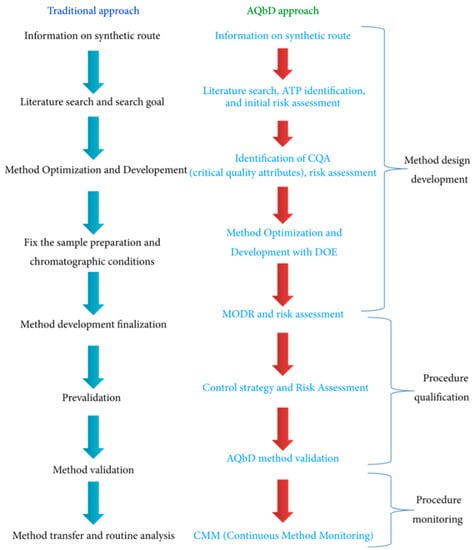
Figure 5.
Traditional and AQbD approaches for Analytical Method Development. Reprinted with permission from Raman, N. et al. Journal of Chemistry, 2015. Copyright (2015) Hindawi [100].
Furthermore, AQbD facilitates regulatory flexibility in analytical methods. Given the fact that health regulatory agencies only allow minor modifications, the ease of changing parameters within a method operable design region (MODR) in the AQbD approach provides a multidimensional space based on the factors and settings that provide a suitable method performance [67].
Recently, at UCR, Murillo et al. developed and validated a bioanalytical HPLC method with a diode array for the simultaneous quantification in human plasma of carbamazepine and its active 10,11-epoxide metabolite. The risk assessment focused on the separation and recovery of the analytes from properly preserved human plasma, using a solid-phase component extraction strategy. For this critical parameter, three types of extraction cartridges were evaluated to optimize the process, which allowed more than 95% recovery of the analytes to be obtained. However, validating a bioanalytical method presents some issues posed by the biological matrix. Thus, applying the AQbD approach allowed them to optimize and save reagents and consumables in the execution of the validation process, as well as fulfilling validation criteria in terms of linearity, specificity, precision, and accuracy, among others, to ensure reproducible and reliable results. This was achieved by implementing the use of a 50 mm column with a particle size of 3.5 μm, obtaining good integration and a resolution higher than 2.0 for the chromatographic peaks [102].
QbD has also gained importance in natural product development and quality control due to the current high demand [103]. On top of that, the use of DoE in an AQbD approach for these products implies a higher contribution due to the intrinsic variability that occurs when working with natural raw materials. However, it is important to note that, according to QbD, risk management has priority over DoE [50,51,104].
For instance, Castillo et al. evaluated a sample’s mass and temperature impact on the moisture content in Camellia sinensis, Cassia fistula, Chamaemelum nobile, Lippia alba, and Tilia platyphyllos using a gravimetric method developed through a 32 full factorial design. A response optimizer was used to define the test conditions that allow results to be obtained according to a target value from a certified method (Figure 6) [105]. The designed model was able to explain the response variability for all samples based on the R2 (adj), which led to the definition of the range of mass and temperature for the analyses based on each materials’ properties, as well as considering the capacity, precision, moisture range, heating technology, and operational temperature range of the dryer and the available moisture balances.
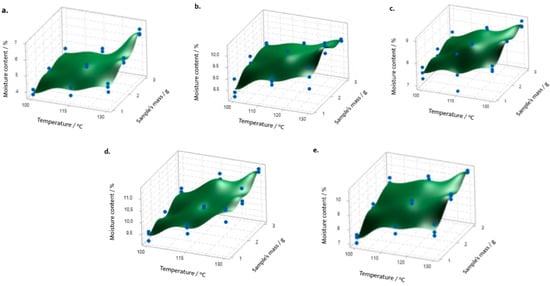
Figure 6.
Example of a 32 full factorial design carried out in the Academy to evaluate the moisture content (%) in natural raw materials as a function of the balance’s temperature (°C) and sample’s mass (g): (a) Camelia sinensis, (b) Cassia fistula, (c) Chamaemelum nobile, (d) Lippia alba, and (e) Tilia platyphyllos. Reprinted with permission from Castillo, L. et al. Borneo Journal of Pharmacy, 3(1). Copyright (2020) Institute for Research and Community Services Universitas Muhammadiyah Palangkaraya [105].
4. Conclusions
The change in the educational paradigm and the organizational structure of Costa Rican universities has allowed some Pharmacy Schools from these institutions to stand out in terms of scientific research and to seek the consolidation of groups of experts in the industrial field of the discipline. The implementation of research methodologies such as QbD explains the progress achieved in recent years. The QbD model has been exceptional in carrying out research projects in Costa Rican universities regarding Pharmaceutical Sciences since 2017, especially for the formulation, manufacturing process design, and quality control of drugs and natural products. The model has also allowed the creation, transfer, and materialization of knowledge from academic institutions to different local pharmaceutical industries, resulting in a closer linkage between the two sectors. Furthermore, academic research based on this model enables the training and development of practical, scientific, and leadership skills in Pharmacy students. The generated knowledge can be shared in the classroom, which represents an ideal environment for the professors to communicate their results and foster collaborative work between researchers, professors, and students. The participation of all of these sectors allows a high level of commitment to research work, which benefits the scientific advancement of universities and society.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.C.-H. and É.H.-M.; methodology, L.C.-H. and L.C.-S.; writing—original draft preparation, L.C.-H. and B.M.-C.; writing—review and editing, L.C.-H., L.C.-S., J.J.M.-R., N.R.-A. and J.V.-B.; visualization, L.C.-H.; supervision, É.H.-M. and J.V.-B.; project administration, É.H.-M. and J.V.-B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
First author L.C.-H. is a funded student by the Education, Audiovisual and Culture Executive Agency (EACEA) of the European Commission in the field of the Erasmus Mundus Joint Master Degree (EMJMD) of Nanomedicine for Drug Delivery (NANOMED).
Acknowledgments
This work represents a collaborative work between different Costa Rican institutions involved in the academic and scientific training of Pharmacy students. The authors would like to thank the contribution of the students who had previously worked with the QbD model during their graduation projects and Georgia Hanley for designing the graphical abstract. The icons used were taken from www.flaticon.com (accessed on 1 March 2022).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Aithal, P.S.; Kumar, P.M. Opportunities and Challenges for Private Universities in India; Social Science Research Network: Rochester, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, M.; Seeber, B.K. The Slow Professor: Challenging the Culture of Speed in the Academy; University of Toronto Press: Toronto, TO, Canada, 2016; ISBN 978-1-4426-6310-7. [Google Scholar]
- Morales-López, Y. Costa Rica: The Preparation of Mathematics Teachers. In Mathematics Teacher Preparation in Central America and the Caribbean: The Cases of Colombia, Costa Rica, the Dominican Republic and Venezuela; Ruiz, A., Ed.; SpringerBriefs in Education; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 39–56. ISBN 978-3-319-44177-1. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, R.A. Location of the University Regionalization in Costa Rica. Congreso Universidad. 2016, 5. Available online: http://www.congresouniversidad.cu/revista/index.php/congresouniversidad/index (accessed on 6 December 2021).
- Law, M.; Bader, L.; Uzman, N.; Williams, A.; Bates, I. The FIP Nanjing Statements: Shaping Global Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences Education. Res. Soc. Adm. Pharm. 2019, 15, 1472–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, G.; DeSilva, B.; Dressman, J.; Ito, M.; Kumamoto, T.; Mager, D.; Mahler, H.-C.; Maitland-van der Zee, A.H.; Pauletti, G.M.; Sasaki, H.; et al. Current Challenges and Potential Opportunities for the Pharmaceutical Sciences to Make Global Impact: An FIP Perspective. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2489–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Aponte, O.F.; Vallejo Díaz, B.M.; Mora Huertas, C.E. La calidad desde el diseño: Principios y oportunidades para la industria farmacéutica. Estud. Gerenc. 2015, 31, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramod, K.; Tahir, M.A.; Charoo, N.A.; Ansari, S.H.; Ali, J. Pharmaceutical Product Development: A Quality by Design Approach. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2016, 6, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juran, J. Juran on Quality by Design; The Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.X.; Amidon, G.; Khan, M.A.; Hoag, S.W.; Polli, J.; Raju, G.K.; Woodcock, J. Understanding Pharmaceutical Quality by Design. AAPS J. 2014, 16, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangshetti, J.N.; Deshpande, M.; Zaheer, Z.; Shinde, D.B.; Arote, R. Quality by Design Approach: Regulatory Need. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3412–S3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grangeia, H.B.; Silva, C.; Simões, S.P.; Reis, M.S. Quality by Design in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: A Systematic Review of Current Status, Challenges and Future Perspectives. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 147, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, P.J.; Gulbrandsen, M.; Kyvik, S. The Relationship between Basic and Applied Research in Universities. High Educ. 2015, 70, 689–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, A.; Javaid, M.; Vaishya, R.; Deshmukh, S.G. Areas of Academic Research with the Impact of COVID-19. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 38, 1524–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, P.; Derani, N.E.S. A Comparative Study on Quality of Education Received by Students of Private Universities versus Public Universities. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2016, 35, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M. Principles of Scientific Methods; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-0-429-17190-1. [Google Scholar]
- Pagliaro, M. Enhancing the Use of E-Mail in Scientific Research and in the Academy. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, S.; Neri, S.; Lean, J. The Role of Theory in the Business/Management PhD: How Students May Use Theory to Make an Original Contribution to Knowledge. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 2019, 17, 100316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubowitz, J.H.; Brand, J.C.; Rossi, M.J. Medical Device and Pharmaceutical Industry Employees as Medical Research Publication Authors. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2018, 34, 2745–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beall, J. Pharmacy Research and Predatory Journals: Authors Beware. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2016, 73, 1548–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egri, N.; Ortiz de Landazuri, I.; San Bartolomé, C.; Ortega, J.R.; Español-Rego, M.; Juan, M. CART Manufacturing Process and Reasons for Academy-Pharma Collaboration. Immunol. Lett. 2020, 217, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salau, O.; Osibanjo, A.; Adeniji, A.; Oludayo, O.; Falola, H.; Igbinoba, E.; Ogueyungbo, O. Data Regarding Talent Management Practices and Innovation Performance of Academic Staff in a Technology-Driven Private University. Data Brief 2018, 19, 1040–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, D.; Klein, S. The Use of Theory in Research. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2016, 38, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, M.; Mabe, M. The STM Report: An Overview of Scientific and Scholarly Journal Publishing. In Copyright, Fair Use, ScholarlyCommunication, etc.; University of Nebraska: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pineda, M.A. Cómo comunicar la investigación desde la academia. Rev. Cienc. Tecnol. 2019, 24, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Peñalvo, F.J. Publishing in Open Access. J. Inf. Technol. Res. 2017, 10, vi–viii. [Google Scholar]
- Tapasco, O.A.; Giraldo, J.A. Estudio Comparativo Sobre Percepción y Uso de Las TIC Entre Profesores de Universidades Públicas y Privadas. Form. Univ. 2017, 10, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vicente-Saez, R.; Gustafsson, R.; Van den Brande, L. The Dawn of an Open Exploration Era: Emergent Principles and Practices of Open Science and Innovation of University Research Teams in a Digital World. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2020, 156, 120037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, A.K.; Preet, K. The Influence of Organizational Commitment on Work Motivation: A Comparative Study of State and Private University Teachers. IUP J. Organ. Behav. 2017, 16, 55–69. [Google Scholar]
- Asaduzzaman, M.; Hossain, M.; Rahman, M. Service Quality and Student Satisfaction: A Case Study on Private Universities in Bangladesh. Int. J. Econ. Financ. Manag. Sci. 2014, 1, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Yang, G.; Guan, Z. Estimating the Multi-Period Efficiency of High-Tech Research Institutes of the Chinese Academy of Sciences: A Dynamic Slacks-Based Measure. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2020, 71, 100855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayá, P.; Brydon-Miller, M. Carpe the Academy: Dismantling Higher Education and Prefiguring Critical Utopias through Action Research. Futures 2017, 94, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez Vargas, M.; Galeano Higuita, C.; Jaramillo Muñoz, D.A. El estado del arte: Una metodología de investigación. Rev. Colomb. Cienc. Soc. 2015, 6, 423–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, K. Propelling the Profession with Outcomes and Evidence: Building a Robust Research Agenda at the Academy. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 1014–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshkina, I.; Sharamko, M. Economic Security and Internal Control of the Academic Research Projects. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 214, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- International Conference on Harmonisation(ICH) of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline: Q8(R2) Pharmaceutical Development; International Conference on Harmonisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Drug Administration Guidance for Industry; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Guidance for Industry: Quality Systems Approach to Pharmaceutical CGMP Regulations. 2006. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/71023/download (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Pallagi, E.; Ambrus, R.; Szabó-Révész, P.; Csóka, I. Adaptation of the Quality by Design Concept in Early Pharmaceutical Development of an Intranasal Nanosized Formulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 491, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Beg, S.; Panda, S.S. Pharmaceutical QbD: Omnipresence in the Product Development Lifecycle. Eur. Pharm. Rev. 2017, 22, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Fornaguera, C.; García-Celma, M.J. Personalized Nanomedicine: A Revolution at the Nanoscale. J. Pers. Med. 2017, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faulhammer, E.; Fink, M.; Llusa, M.; Lawrence, S.M.; Biserni, S.; Calzolari, V.; Khinast, J.G. Low-Dose Capsule Filling of Inhalation Products: Critical Material Attributes and Process Parameters. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzon, D.; Claeys-Bruno, M.; Declomesnil, S.; Carité, C.; Sergent, M. Quality by Design: Comparison of Design Space Construction Methods in the Case of Design of Experiments. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2020, 200, 104002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepika, P.; Manisha, S.; Parijat, P.; Swagat, T.; Harish, D. Implementation of Quality by Design: A Review. Appl. Clin. Res. Clin. Trials Regul. Aff. Discontin. 2019, 6, 99–111. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo, L.; Zúñiga, V.; Carazo, G.; Calvo, B.; Baltodano, E. Development of Immediate Release Rupatadine Fumarate 10 Mg Tablets: A Quality by Design (QbD) Approach. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 1674–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Thakur, S.; Patil, A.; Shukla, A. Quality by Design (QbD) Approaches in Current Pharmaceutical Set-Up. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 737–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G. Chapter 5—Target Product Profile and Clinical Development Plan. In Pharmaceutical Medicine and Translational Clinical Research; Vohora, D., Singh, G., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 65–80. ISBN 978-0-12-802103-3. [Google Scholar]
- International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline: Q9 Quality Risk Management; International Conference on Harmonisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Nichols, B.L.B.; Norris, A.M.; Frazier, C.E.; Edgar, K.J. All-Polysaccharide, Self-Healing Injectable Hydrogels Based on Chitosan and Oxidized Hydroxypropyl Polysaccharides. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 4261–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, E.; Becker, K.; Hate, S.; Hohl, R.; Schiemenz, W.; Sacher, S.; Zimmer, A.; Salar-Behzadi, S. Application of ICH Q9 Quality Risk Management Tools for Advanced Development of Hot Melt Coated Multiparticulate Systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Coccia, M. The Fishbone Diagram to Identify, Systematize and Analyze the Sources of General Purpose Technologies; Social Science Research Network: Rochester, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Paciarotti, C.; Mazzuto, G.; D’Ettorre, D. A Revised FMEA Application to the Quality Control Management. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2014, 31, 788–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, M.; Goh, T.N. A Review of Analysis of Dynamic Response in Design of Experiments. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2015, 31, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politis, S.; Colombo, P.; Colombo, G.; Rekkas, D.M. Design of Experiments (DoE) in Pharmaceutical Development. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, L. Design of Experiments for the Establishment of the Dissolution Test Conditions of Rupatadine Fumarate 10 mg Tablets. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2019, 9, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulo, F.; Santos, L. Design of Experiments for Microencapsulation Applications: A Review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 77, 1327–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoorens, G.; Krier, F.; Leclercq, B.; Carlin, B.; Evrard, B. Microcrystalline Cellulose, a Direct Compression Binder in a Quality by Design Environment—A Review. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, J.; Zauner, F.B.; Pell, A.; Hausjell, J.; Humer, D.; Ebner, J.; Herwig, C.; Spadiut, O.; Slouka, C.; Pell, R. Development of a Generic Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography Method for Protein Quantification Using Analytical Quality-by-Design Principles. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 188, 113412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabré, M.; Ferey, L.; Somé, T.I.; Sivadier, G.; Gaudin, K. Development of a Green HPLC Method for the Analysis of Artesunate and Amodiaquine Impurities Using Quality by Design. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 190, 113507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deidda, R.; Avohou, H.T.; Baronti, R.; Davolio, P.L.; Pasquini, B.; Del Bubba, M.; Hubert, C.; Hubert, P.; Orlandini, S.; Furlanetto, S. Analytical Quality by Design: Development and Control Strategy for a LC Method to Evaluate the Cannabinoids Content in Cannabis Olive Oil Extracts. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 166, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yekpe, K.; Abatzoglou, N.; Bataille, B.; Gosselin, R.; Sharkawi, T.; Simard, J.-S.; Cournoyer, A. Developing a Quality by Design Approach to Model Tablet Dissolution Testing: An Industrial Case Study. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2018, 23, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadella, N.P.; Ratnakaram, V.N.; Srinivasu, N. Quality-by-Design-Based Development and Validation of a Stability-Indicating UPLC Method for Quantification of Teriflunomide in the Presence of Degradation Products and Its Application to in-Vitro Dissolution. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2017, 40, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnain, M.S.; Siddiqui, S.; Rao, S.; Mohanty, P.; Ara, T.J.; Beg, S. QbD-Driven Development and Validation of a Bioanalytical LC-MS Method for Quantification of Fluoxetine in Human Plasma. J Chromatogr. Sci. 2016, 54, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, M.F.; Silva, G.; Pinto, A.C.; Fonseca, M.; Silva, N.E.; Pinto, R.M.A.; Simões, S. Artificial Neural Networks Applied to Quality-by-Design: From Formulation Development to Clinical Outcome. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 152, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butreddy, A.; Bandari, S.; Repka, M.A. Quality-by-Design in Hot Melt Extrusion Based Amorphous Solid Dispersions: An Industrial Perspective on Product Development. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 158, 105655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurumukhi, V.C.; Bari, S.B. Fabrication of Efavirenz Loaded Nano-Formulation Using Quality by Design (QbD) Based Approach: Exploring Characterizations and in Vivo Safety. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 101545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patwardhan, D.; Amrutkar, S.; Kotwal, T.; Wagh, P. Application of Quality by Design to Different Aspects of Pharmaceutical Technologies. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2017, 5, 3649–3662. [Google Scholar]
- Peraman, R.; Bhadraya, K.; Padmanabha Reddy, Y. Analytical Quality by Design: A Tool for Regulatory Flexibility and Robust Analytics. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 2015, e868727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Chen, Z.; Raines, K.; Chen, H.; Dave, K.; Lin, H.-P.; Zolnik, B.S. Assessment of Applications of Design of Experiments in Pharmaceutical Development for Oral Solid Dosage Forms. J. Pharm. Innov. 2020, 15, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco, J.; Ruiz, K. Contributions of Universities and Public Research Centers to Innovation Processes in the Industry: The Costa Rican Case; Georgia Institute of Technology: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jagan, B.G.V.S.; Mahapatra, A.K.; Murthy, N.P.; Patra, R.K. Quality by Design (QbD): Principles, Underlying Concepts and Regulatory Prospects. Thai J. Pharm. Sci. (TJPS) 2021, 45, 54–69. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, Z.; Xu, X.; Katragadda, U.; Krishnaiah, Y.S.R.; Yu, L.; Khan, M.A. Quality by Design Approach for Understanding the Critical Quality Attributes of Cyclosporine Ophthalmic Emulsion. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, G.-H.; Park, J.-H.; Shin, H.-W.; Kim, J.-E.; Park, Y.-J. Quality-by-Design Approach for the Development of Telmisartan Potassium Tablets. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SimonoskaCrcarevska, M.; Dimitrovska, A.; Sibinovska, N.; Mladenovska, K.; SlavevskaRaicki, R.; GlavasDodov, M. Implementation of Quality by Design Principles in the Development of Microsponges as Drug Delivery Carriers: Identification and Optimization of Critical Factors Using Multivariate Statistical Analyses and Design of Experiments Studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 489, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, L.; Wan, F.; Bera, H.; Cun, D.; Rantanen, J.; Yang, M. Quality by Design Thinking in the Development of Long-Acting Injectable PLGA/PLA-Based Microspheres for Peptide and Protein Drug Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 585, 119441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alt, N.; Zhang, T.Y.; Motchnik, P.; Taticek, R.; Quarmby, V.; Schlothauer, T.; Beck, H.; Emrich, T.; Harris, R.J. Determination of Critical Quality Attributes for Monoclonal Antibodies Using Quality by Design Principles. Biologicals 2016, 44, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.R.; Kwon, S.Y.; Choi, D.H.; Park, E.S. Quality by Design (QbD) Approach to Optimize the Formulation of a Bilayer Combination Tablet (Telmiduo®) Manufactured via High Shear Wet Granulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 534, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, G.; Liu, X.; Liu, C.; Deng, Y.; Bai, Z. Quality by Design-Driven Process Development of Severe Fever With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Vaccine. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 3785–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, D.; Nanda, S. Quality by Design Driven Development of Resveratrol Loaded Ethosomal Hydrogel for Improved Dermatological Benefits via Enhanced Skin Permeation and Retention. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 567, 118448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alalaiwe, A.; Fayed, M.H.; Alshahrani, S.M.; Alsulays, B.B.; Alshetaili, A.S.; Tawfeek, H.M.; Khafagy, E.-S. Application of Design of Experiment Approach for Investigating the Effect of Partially Pre-Gelatinized Starch on Critical Quality Attributes of Rapid Orally Disintegrating Tablets. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, R.; An, F.; Nie, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ahamada, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, C.; Deng, Y.; et al. Quality by Design-Driven Process Development of Cell Culture in Bioreactor for the Production of Foot-And-Mouth Veterinary Vaccine. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 2288–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Mehta, P.; KyriakiMonou, P.; Arshad, M.S.; Panteris, E.; Rasekh, M.; Singh, N.; Qutachi, O.; Wilson, P.; Tzetzis, D.; et al. Electrospinning/Electrospraying Coatings for Metal Microneedles: A Design of Experiments (DOE) and Quality by Design (QbD) Approach. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 156, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan Hafiz, M.; Abbas, N.; Bukhari, N.I. Quality by Design Approach for Formulation Development and Evaluation of Carboplatin Loaded EthylcelluloseNanosponges. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoo, N.A.; Shamsher, A.A.A.; Zidan, A.S.; Rahman, Z. Quality by Design Approach for Formulation Development: A Case Study of Dispersible Tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 423, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Jha, A. Quality Risk Management during Pharmaceutical ‘Good Distribution Practices’—A Plausible Solution. Bull. Fac. Pharm. Cairo Univ. 2018, 56, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westgard, J.O.; Westgard, S.A. Six Sigma Quality Management System and Design of Risk-Based Statistical Quality Control. Clin. Lab. Med. 2017, 37, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, G. Desarrollo de una Suspensión Oral con Efecto Anti-Ulceroso y Protector Gástrico Mediante el Modelo de Calidad por Diseño en Laboratorios Raven S.A. Bachelor’s Thesis, Facultad de Farmacia, Universidad de Costa Rica, San Pedro, Costa Rica, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda, I.M.; Pinto, C.F.F.; dos Santos Moreira, C.; Saviano, A.M.; Lourenço, F.R. DesignofExperiments (DoE) AppliedtoPharmaceutical and AnalyticalQualitybyDesign (QbD). Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnain, M.S.; Ahmed, S.A.; Khatoon, A.; Afzal, M.; Ansari, M.T.; Khatoon, S.; Tabish, M.; Al-Marshad, F.M.; Nayak, A.K. Chapter 4—Pharmaceutical Product Development: A Quality by Design (QbD) Approach. In Advances and Challenges in Pharmaceutical Technology; Nayak, A.K., Pal, K., Banerjee, I., Maji, S., Nanda, U., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 131–146. ISBN 978-0-12-820043-8. [Google Scholar]
- Dhoot, A.S.; Fernandes, G.J.; Naha, A.; Rathnanand, M.; Kumar, L. Design of Experiments in Pharmaceutical Development. Pharm. Chem. J. 2019, 53, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, J. Preformulación de un Medicamento de Liberación Prolongada Mediante el Enfoque de Calidad por Diseño en Laboratorios Medigray Durante el Segundo y Tercer Cuatrimestre 2021. Bachelor’s Thesis, Facultad de Farmacia, Universidad Internacional de Las Américas, San José, Costa Rica, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo-Henríquez, L.; Sanabria-Espinoza, P.; Murillo-Castillo, B.; Montes de Oca-Vásquez, G.; Batista-Menezes, D.; Calvo-Guzmán, B.; Ramírez-Arguedas, N.; Vega-Baudrit, J. Topical Chitosan-Based Thermo-Responsive Scaffold Provides Dexketoprofen Trometamol Controlled Release for 24 h Use. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, A.S.; Winkle, H. Quality by Design for Biopharmaceuticals. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline: Q11 Development and Manufacture of Drug Substances (Chemical Entities and Biotechnological/Biological Entities); International Conference on Harmonisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline: Q13 Continuous Manufacturing of Drug Substances and Drug Products; International Conference on Harmonisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Health and Human Service—FDA. Guidance for Industry PAT—A Framework for Innovative Pharmaceutical Development, Manufacuring, and Quality Assurance; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Reklaitis, G.V.; Khinast, J.; Muzzio, F. Pharmaceutical Engineering Science—New Approaches to Pharmaceutical Development and Manufacturing. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, iv–vii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Ganesh, S.; Moreno, M.; Bommireddy, Y.; Gonzalez, M.; Reklaitis, G.V.; Nagy, Z.K. A Perspective on Quality-by-Control (QbC) in Pharmaceutical Continuous Manufacturing. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2019, 125, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.X.; Kopcha, M. The Future of Pharmaceutical Quality and the Path to Get There. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 528, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantillo, G. Diseño del Proceso de Recubrimiento Pelicular de Tabletas a Escala Piloto Mediante la Aplicación del Modelo de Calidad por Diseño en el Departamento de Investigación y Desarrollo en Laboratorios Infarma LTDA. Bachelor’s Thesis, Facultad de Farmacia, Universidad de Costa Rica, San Pedro, Costa Rica, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Raman, N.V.V.S.S.; Mallu, U.R.; Bapatu, H.R. Analytical Quality by Design Approach to Test Method Development and Validation in Drug Substance Manufacturing. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, e435129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, F.G.; Kord, A.S. Development of Quality-By-Design Analytical Methods. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 797–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo, B. Desarrollo y Validación de un Método Bioanalítico por Cromatografía Líquida de Alta Resolución con Detector de Arreglo de Diodos para la Cuantificación Simultánea de Carbamazepina y su Metabolito Activo Carbamazepina 10,11 Epóxido en Plasma Humano. Bachelor’s Thesis, Facultad de Farmacia, Universidad de Costa Rica, San Pedro, Costa Rica, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rodino, S.; Butu, M. 3—Herbal Extracts—New Trends in Functional and Medicinal Beverages. In Functional and Medicinal Beverages; Grumezescu, A.M., Holban, A.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 73–108. ISBN 978-0-12-816397-9. [Google Scholar]
- Prajapati, P.; Patel, H.; Shah, S. Quality risk assessment and DoE-based analytical quality by design approach to stability-indicating assay method for acidic degradation kinetic study of apremilast. J. Planar Chromatogr. 2020, 33, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, L.; Baltodano, E.; Ramírez, N.; Vargas, R.; Hanley, G. Design of Experiments Assessment for the Determination of Moisture Content in Five Herbal Raw Materials Contained in Tea Products. Borneo J. Pharm. 2020, 3, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).