Effectiveness and Safety of Fenofibrate in Routine Treatment of Patients with Hypertriglyceridemia and Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Setting
2.2. Participants
2.3. Study Design
2.4. Ethical Approval
2.5. Study Procedures
2.6. Endpoints
- -
- T2DM;
- -
- Impaired glucose tolerance at inclusion;
- -
- Concomitant cardiovascular (CV) disease;
- -
- Perimenopausal women;
- -
- Postmenopausal women.
2.7. Statistical Methods
3. Results
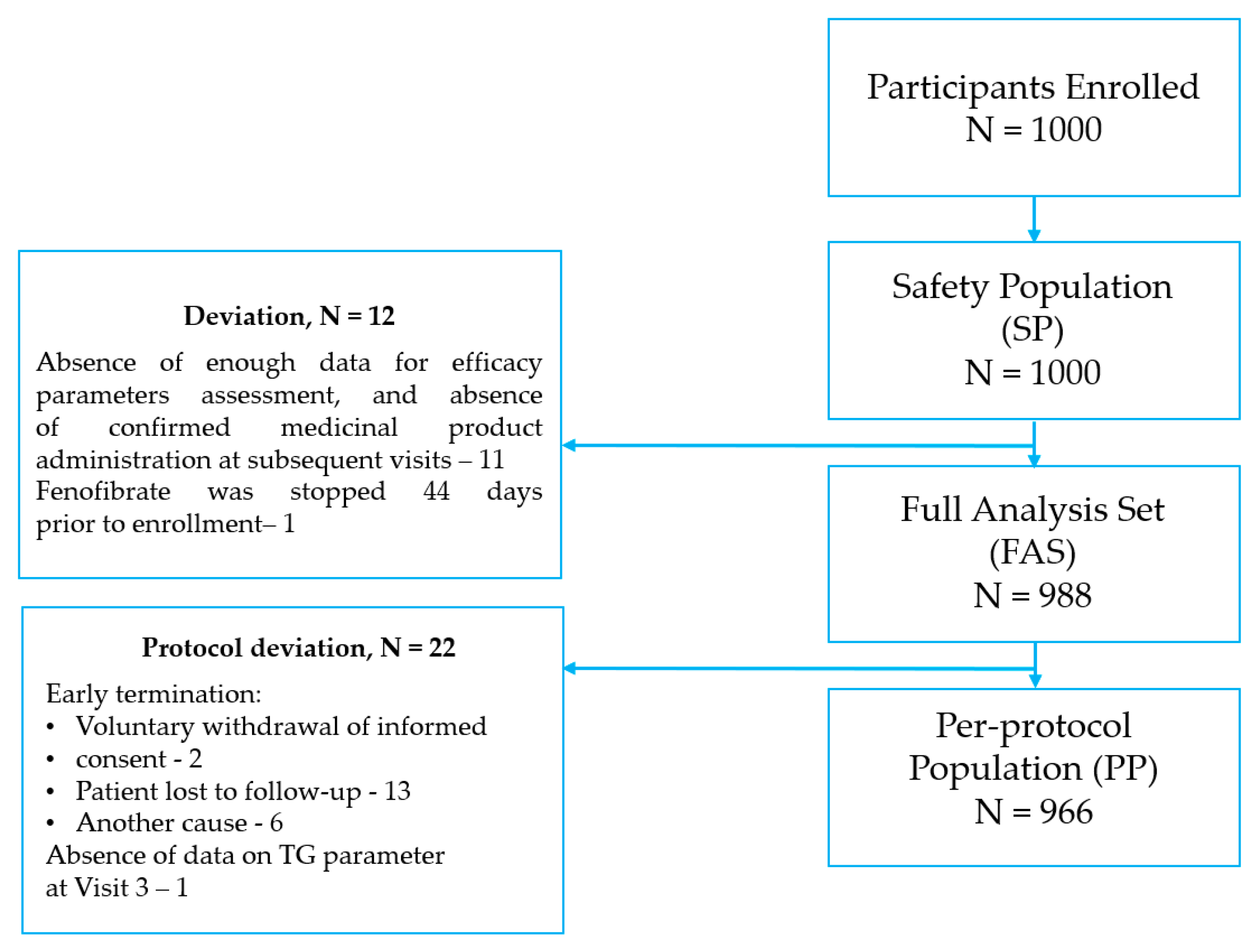
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Fenofibrate Treatment Compliance
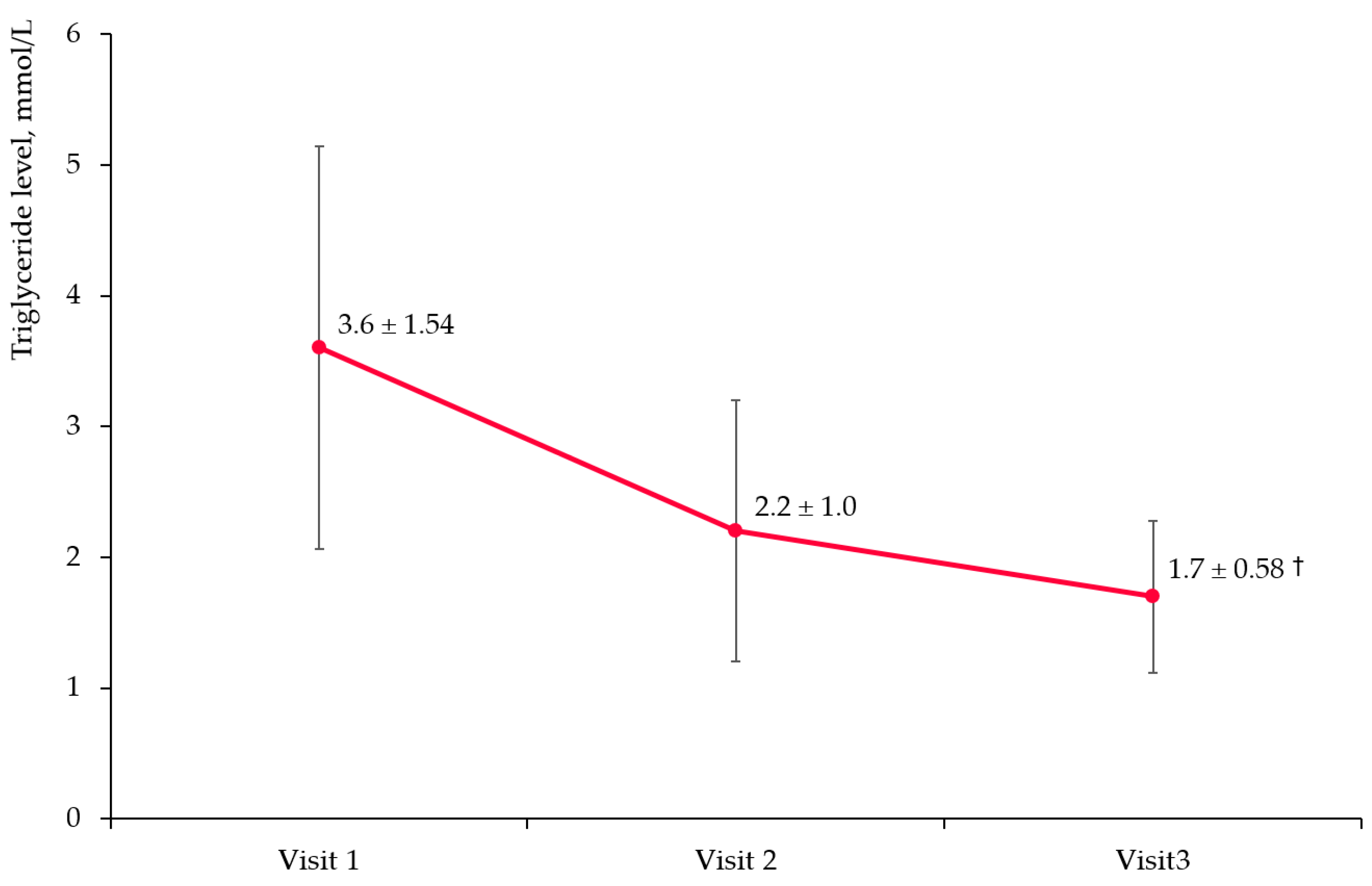
3.3. Triglyceride Level Change
3.3.1. Overall Cohort
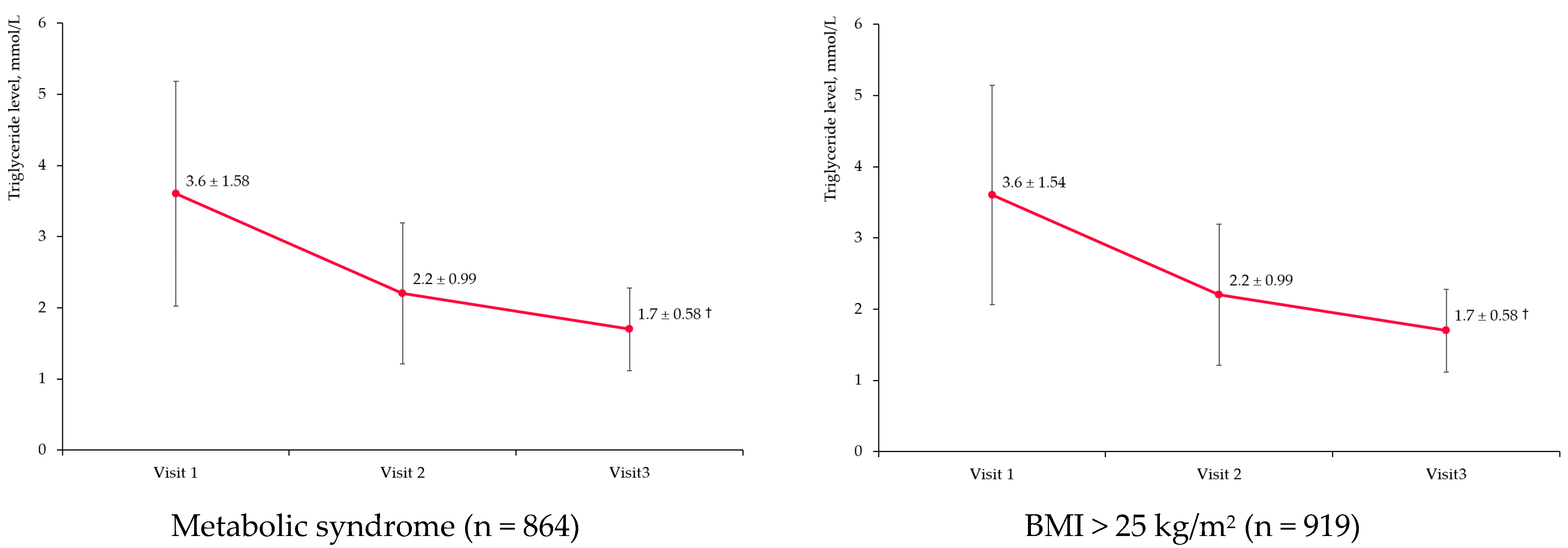
3.3.2. Target Subgroups
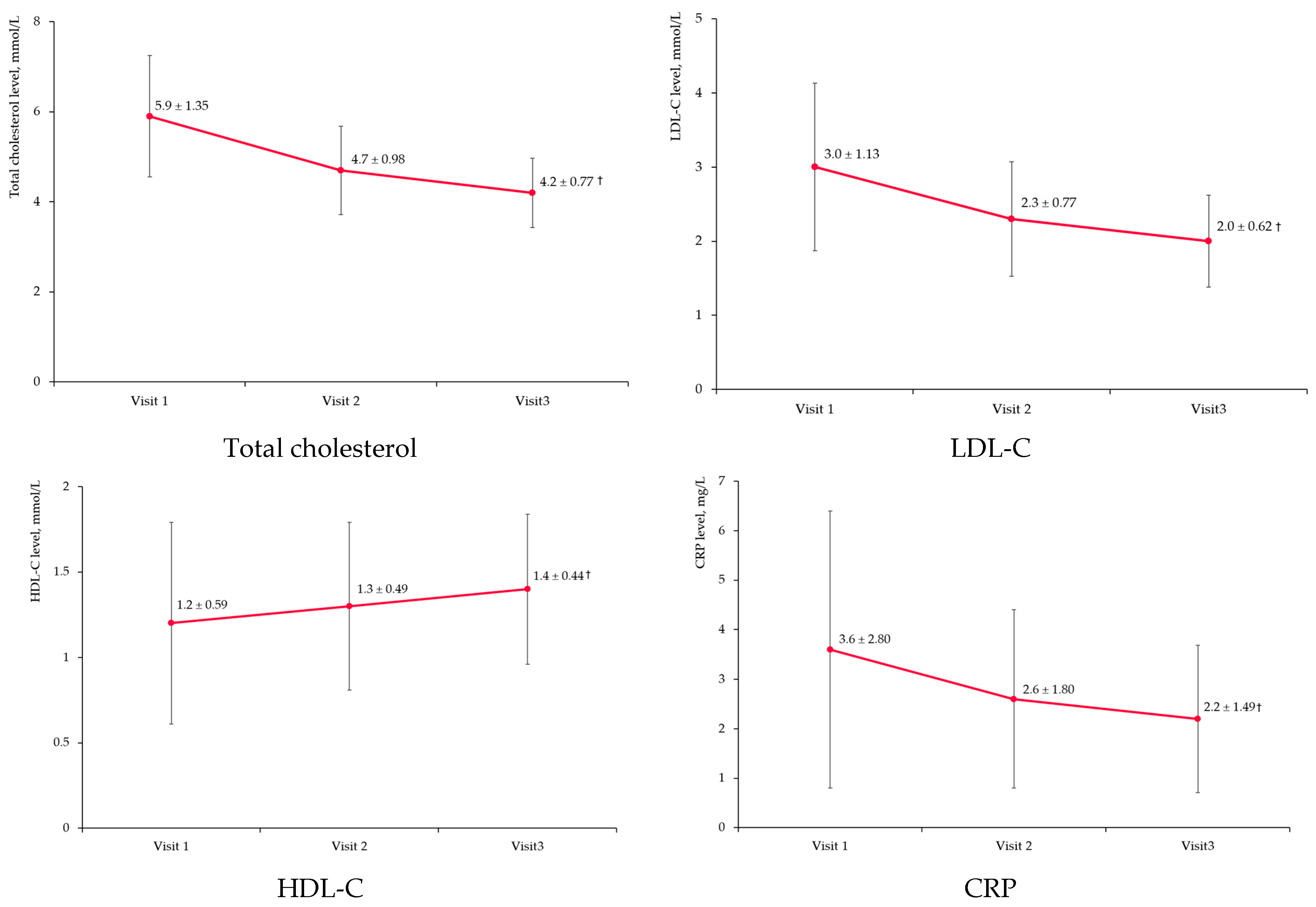
3.4. Non-High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol
3.5. Other Laboratory Markers
3.6. Safety
4. Discussion
4.1. Effectiveness Results
4.1.1. Fenofibrate Studies
Impact on Triglycerides
Non-High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Change
Impact on Inflammatory Status
4.1.2. Other Fibrates
4.2. Safety
4.3. Study Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Lipid Parameter | Visit 1 | Visit 2 | Visit 3 | % Change Visit 1/3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total cholesterol, mmol/L | 5.9 ± 1.35 | 4.7 ± 0.98 | 4.2 ± 0.77 † | −24.7 |
| LDL-C, mmol/L | 3.0 ± 1.13 | 2.3 ± 0.77 | 2.0 ± 0.62 † | −25.5 |
| HDL-C, mmol/L | 1.2 ± 0.59 | 1.3 ± 0.49 | 1.4 ± 0.44 † | +23.0 |
| CRP, mg/L | 3.6 ± 2.80 | 2.6 ± 1.80 | 2.2 ± 1.49 † | −38.9 |
References
- Grundy, S.M. Metabolic Syndrome Update. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2016, 26, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, S.; O’Driscoll, L. Metabolic Syndrome: A Closer Look at the Growing Epidemic and Its Associated Pathologies. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, K.G.; Zimmet, P.Z. Definition, Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications. Part 1: Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus Provisional Report of a WHO Consultation. Diabet. Med. 1998, 15, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saklayen, M.G. The Global Epidemic of the Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassi, E.; Pervanidou, P.; Kaltsas, G.; Chrousos, G. Metabolic Syndrome: Definitions and Controversies. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metelskaya, V.A.; Shalnova, S.A.; Deev, A.D.; Perova, N.V.; Gomyranova, N.V.; Litinskaya, O.A.; Evstifeeva, S.E.; Artamonova, G.V.; Gatagonova, T.M.; Grinshtein, Y.I.; et al. Analysis of Atherogenic Dyslipidemias Prevalence among Population of Russian Federation (Results of the ESSE-RF Study). Profil. Med. 2016, 19, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, M.; Foote, C.; Lv, J.; Neal, B.; Patel, A.; Nicholls, S.J.; Grobbee, D.E.; Cass, A.; Chalmers, J.; Perkovic, V. Effects of Fibrates on Cardiovascular Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staels, B.; Dallongeville, J.; Auwerx, J.; Schoonjans, K.; Leitersdorf, E.; Fruchart, J.-C. Mechanism of Action of Fibrates on Lipid and Lipoprotein Metabolism. Circulation 1998, 98, 2088–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.H.; Kim, S.G. Fibrates Revisited: Potential Role in Cardiovascular Risk Reduction. Diabetes Metab. J. 2020, 44, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.N.; Park, J.-S. Exploring Fenofibrate Formulations for the Treatment of Lipid Disorders: Past, Present, and Future. Cardio Metab. Syndr. J. 2022, 2, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Correa, R. Fibrate Medications. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu, G.; Tripp, J. Fenofibrate. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.; Stone, N.J.; Ballantyne, C.; Bittner, V.; Criqui, M.H.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Goldberg, A.C.; Howard, W.J.; Jacobson, M.S.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; et al. Triglycerides and Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation 2011, 123, 2292–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, M.J.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Amarenco, P.; Andreotti, F.; Borén, J.; Catapano, A.L.; Descamps, O.S.; Fisher, E.; Kovanen, P.T.; Kuivenhoven, J.A.; et al. Triglyceride-Rich Lipoproteins and High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Patients at High Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: Evidence and Guidance for Management. Eur. Heart J. 2011, 32, 1345–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varbo, A.; Benn, M.; Tybjærg-Hansen, A.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Elevated Remnant Cholesterol Causes Both Low-Grade Inflammation and Ischemic Heart Disease, Whereas Elevated Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Causes Ischemic Heart Disease Without Inflammation. Circulation 2013, 128, 1298–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visseren, F.L.J.; Mach, F.; Smulders, Y.M.; Carballo, D.; Koskinas, K.C.; Bäck, M.; Benetos, A.; Biffi, A.; Boavida, J.-M.; Capodanno, D.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3227–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FIELD Study Investigators. Effects of Long-Term Fenofibrate Therapy on Cardiovascular Events in 9795 People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (the FIELD Study): Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2005, 366, 1849–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACCORD Study Group. Effects of Combination Lipid Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1563–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambon, A. The Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Fibrates in Patients with Hypertriglyceridemia: Real Life Data from a Lipid Clinic Cohort. Arch. Turk. Soc. Cardiol. 2020, 48, 357–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalnova, S.A.; Drapkina, O.M. Contribution of the ESSE-RF study to preventive healthcare in Russia. Cardiovasc. Ther. Prev. 2020, 19, 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metelskaya, V.; Shalnova, S.; Yarovaya, E.; Kutsenko, V.; Boytsov, V.; Shlyakhto, E.; Drapkina, O. Lipoprotein Profile in Populations from Regions of the Russian Federation: ESSE-RF Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Hayen, A.; Bell, K.J.L. Legacy Effect of Fibrate Add-on Therapy in Diabetic Patients with Dyslipidemia: A Secondary Analysis of the ACCORDION Study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.S.; Youn, J.-C.; Kim, E.J.; Han, K.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, B.J.; Kwon, S.U.; Ryu, K.-H. Efficacy and Safety of Fenofibrate-Statin Combination Therapy in Patients with Inadequately Controlled Triglyceride Levels Despite Previous Statin Monotherapy: A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase IV Study. Clin. Ther. 2021, 43, 1735–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.H.; Han, K.H.; Choi, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.G. Use of Fenofibrate on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Statin Users with Metabolic Syndrome: Propensity Matched Cohort Study. BMJ 2019, 366, l5125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayikcioglu, M. Cumulative Non-HDL-Cholesterol Burden in Patients with Hypertriglyceridemia Receiving Long-Term Fibrate Therapy: Real Life Data from a Lipid Clinic Cohort. Arch. Turk. Soc. Cardiol. 2020, 48, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.D.; Shin, W.G.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kang, B.C. Safety and Efficacy of Fibrate-Statin Combination Therapy Compared to Fibrate Monotherapy in Patients with Dyslipidemia: A Meta-Analysis. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 65–66, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Gutierrez, R.; Garcia-Leal, M.; Raygoza-Cortez, K.; Flores-Rodríguez, A.; Moreno-Alvarado, M.; Heredia-Martínez, E.M.; Vazquez-Baquerizo, B.; Guerra-Espiricueta, R.; Muñoz-Silva, V.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, J.G. Benefits and Harms of Fibrate Therapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Endocrine 2023, 81, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipman, K.E.; Strange, R.C.; Ramachandran, S. Use of Fibrates in the Metabolic Syndrome: A Review. World J. Diabetes 2016, 7, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Son, M.K.; Park, H.-Y. Substantial Lipid Increases During Menopausal Transition in Korean Middle-Aged Women. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2023, 38, e238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostis, P.; Bitzer, J.; Cano, A.; Ceausu, I.; Chedraui, P.; Durmusoglu, F.; Erkkola, R.; Goulis, D.G.; Hirschberg, A.L.; Kiesel, L.; et al. Menopause Symptom Management in Women with Dyslipidemias: An EMAS Clinical Guide. Maturitas 2020, 135, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiortsis, D.N.; Elisaf, M.S. Serum Uric Acid Levels: A Useful but Not Absolute Marker of Compliance with Fenofibrate Treatment. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2001, 15, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arutyunov, G.P.; Arutyunov, A.G.; Ageev, F.T.; Fofanova, T.V. Use of Digital Technology Tools to Characterize Adherence to Prescription-Grade Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Therapy in Postmyocardial or Hypertriglyceridemic Patients in the DIAPAsOn Study: Prospective Observational Study. JMIR Cardio 2022, 6, e37490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.G.; Wang, S.; Smith, B.J.; Jacobson, T.A. Meta-Analysis of the Relationship Between Non–High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Reduction and Coronary Heart Disease Risk. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Emden, M.C.; Jenkins, A.J.; Li, L.; Zannino, D.; Mann, K.P.; Best, J.D.; Stuckey, B.G.A.; Park, K.; Saltevo, J.; Keech, A.C.; et al. Favourable Effects of Fenofibrate on Lipids and Cardiovascular Disease in Women with Type 2 Diabetes: Results from the Fenofibrate Intervention and Event Lowering in Diabetes (FIELD) Study. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 2296–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S.M.; Vega, G.L.; Yuan, Z.; Battisti, W.P.; Brady, W.E.; Palmisano, J. Effectiveness and Tolerability of Simvastatin plus Fenofibrate for Combined Hyperlipidemia (the SAFARI Trial). Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 95, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihm, S.-H.; Chung, W.-B.; Lee, J.-M.; Hwang, B.-H.; Yoo, K.-D.; Her, S.-H.; Song, W.-H.; Chae, I.-H.; Park, T.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; et al. Efficacy and Tolerability of Pitavastatin Versus Pitavastatin/Fenofibrate in High-Risk Korean Patients with Mixed Dyslipidemia: A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blinded, Parallel, Therapeutic Confirmatory Clinical Trial. Clin. Ther. 2020, 42, 2021–2035.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, J. Critical Roles of Inflammation in Atherosclerosis. J. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration; Kaptoge, S.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Lowe, G.; Pepys, M.B.; Thompson, S.G.; Collins, R.; Danesh, J. C-Reactive Protein Concentration and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease, Stroke, and Mortality: An Individual Participant Meta-Analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado-Duque, M.E.; Gaviria-Mendoza, A.; Machado-Alba, J.E. Real-World Effectiveness of Therapy With Rosuvastatin Combined With Fenofibric Acid in a Sample of Colombian Patients With Mixed Dyslipidemia. J. Prim. Care Community Health 2020, 11, 2150132720977733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Kagaya, Y.; Saito, H.; Kanazawa, M.; Sato, K.; Miura, M.; Kondo, M.; Endo, H. Efficacy and Safety of Pemafibrate Versus Bezafibrate to Treat Patients with Hypertriglyceridemia: A Randomized Crossover Study. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2023, 30, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das Pradhan, A.; Glynn, R.J.; Fruchart, J.-C.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Zaharris, E.S.; Everett, B.M.; Campbell, S.E.; Oshima, R.; Amarenco, P.; Blom, D.J.; et al. Triglyceride Lowering with Pemafibrate to Reduce Cardiovascular Risk. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1923–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Ghumman, G.M.; Baqi, A.; Shah, J.; Aziz, M.; Mir, T.; Tahir, A.; Katragadda, S.; Singh, H.; Taleb, M.; et al. Efficacy of Pemafibrate Versus Fenofibrate Administration on Serum Lipid Levels in Patients with Dyslipidemia: Network Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2023, 23, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godycki-Ćwirko, M.; Koziarska-Rościszewska, M.; Kosiek, K. Medical Errors–an Attempt to Evaluate the Semantics and Taxonomy of the Concept and Statistical Data. Orzecz. Lek. 2009, 6, 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Chodankar, D. Introduction to Real-World Evidence Studies. Perspect. Clin. Res. 2021, 12, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camm, A.J.; Fox, K.A.A. Strengths and Weaknesses of ‘Real-World’ Studies Involving Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants. Open Heart 2018, 5, e000788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Age, years, mean (SD) | 58.3 (10.11) |
| Female sex, n (%) | 458 (46.4) |
| BMI, kg/m2, mean (SD) | 31.2 (4.67) |
| Race, n (%) | |
| Caucasian | 972 (98.4) |
| Asian | 16 (1.6) |
| Smoking status, n (%) | |
| Smoker | 797 (80.7) |
| Non-smoker | 191 (19.3) |
| Menopausal status, n (%) | |
| Perimenopause | 45 (9.8) |
| Menopause | 361 (78.8) |
| Not applicable | 52 (11.4) |
| Concomitant disease | |
| Hypertension | 784 (79.36) |
| Type 2 diabetes | 265 (26.82) |
| Coronary heart disease | 307 (31.07) |
| Myocardial infarction | 100 (10.12) |
| Group of concomitant medications | |
| Statins | 963 (97.47) |
| Renin-angiotensin blockers | 799 (80.87) |
| Beta blockers | 565 (57.19) |
| Antithrombotics | 467 (47.27) |
| Diuretics | 275 (27.83) |
| Calcium channel blockers | 263 (26.62) |
| Antidiabetics | 210 (21.26) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ezhov, M.V.; Arutyunov, G.P. Effectiveness and Safety of Fenofibrate in Routine Treatment of Patients with Hypertriglyceridemia and Metabolic Syndrome. Diseases 2023, 11, 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11040140
Ezhov MV, Arutyunov GP. Effectiveness and Safety of Fenofibrate in Routine Treatment of Patients with Hypertriglyceridemia and Metabolic Syndrome. Diseases. 2023; 11(4):140. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11040140
Chicago/Turabian StyleEzhov, Marat V., and Gregory P. Arutyunov. 2023. "Effectiveness and Safety of Fenofibrate in Routine Treatment of Patients with Hypertriglyceridemia and Metabolic Syndrome" Diseases 11, no. 4: 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11040140
APA StyleEzhov, M. V., & Arutyunov, G. P. (2023). Effectiveness and Safety of Fenofibrate in Routine Treatment of Patients with Hypertriglyceridemia and Metabolic Syndrome. Diseases, 11(4), 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11040140






