Virtual Pheromone Based Network Flow Control For Modular Robotic Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
Related Work
2. Problem Formulation
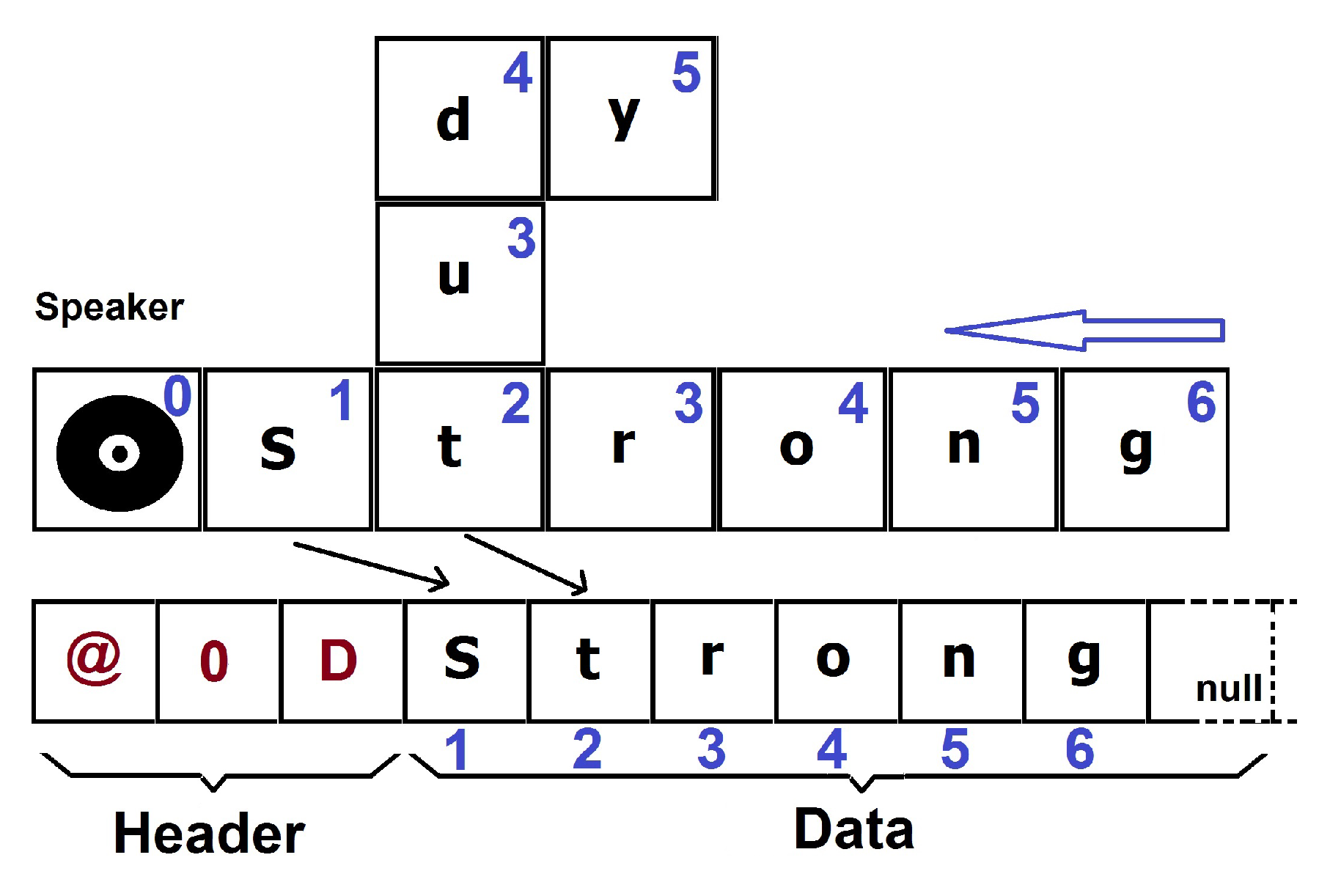
3. Virtual Pheromone Based Network Flow Control
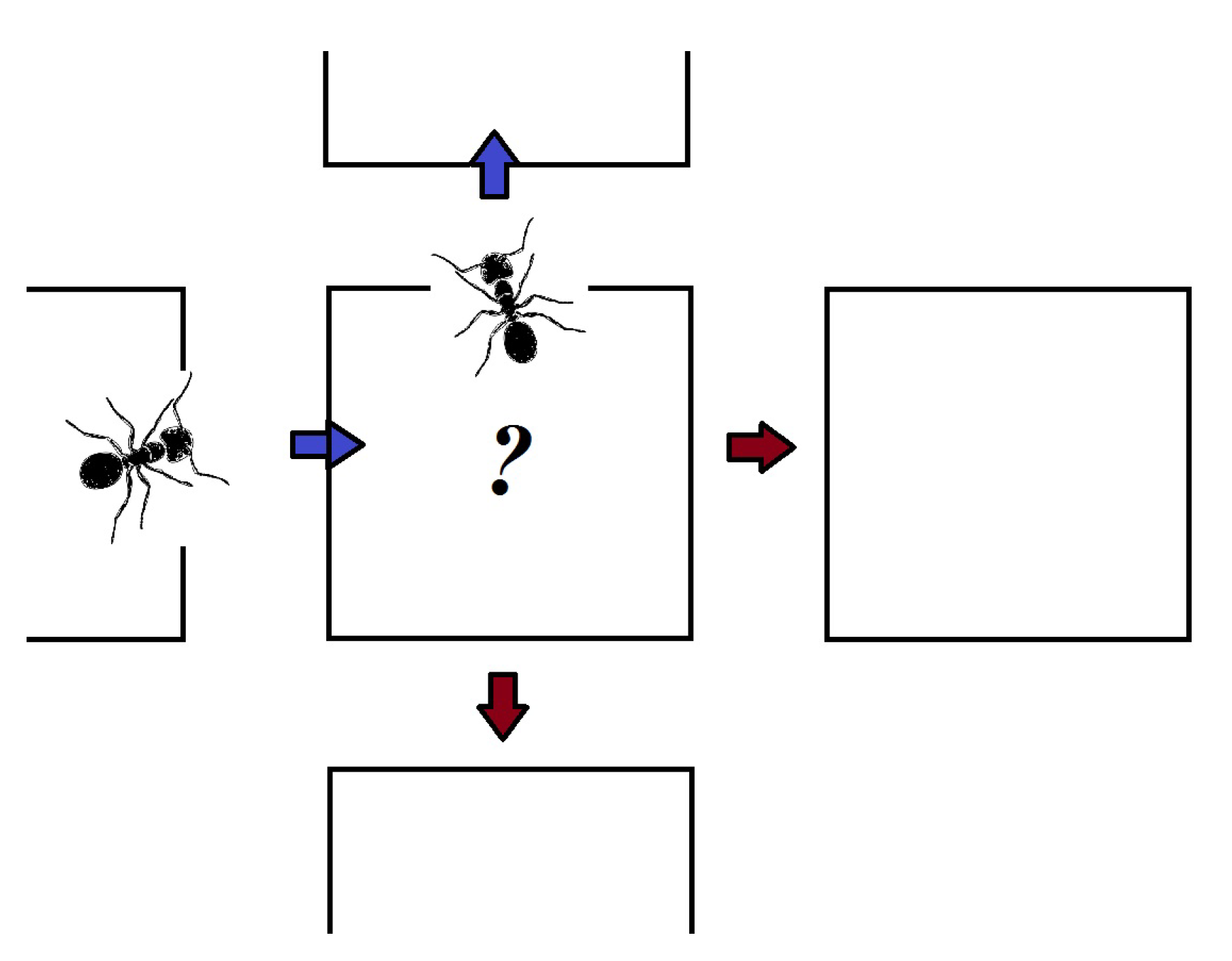
3.1. Neighbourhood Discovery & Awareness and Link Maintenance
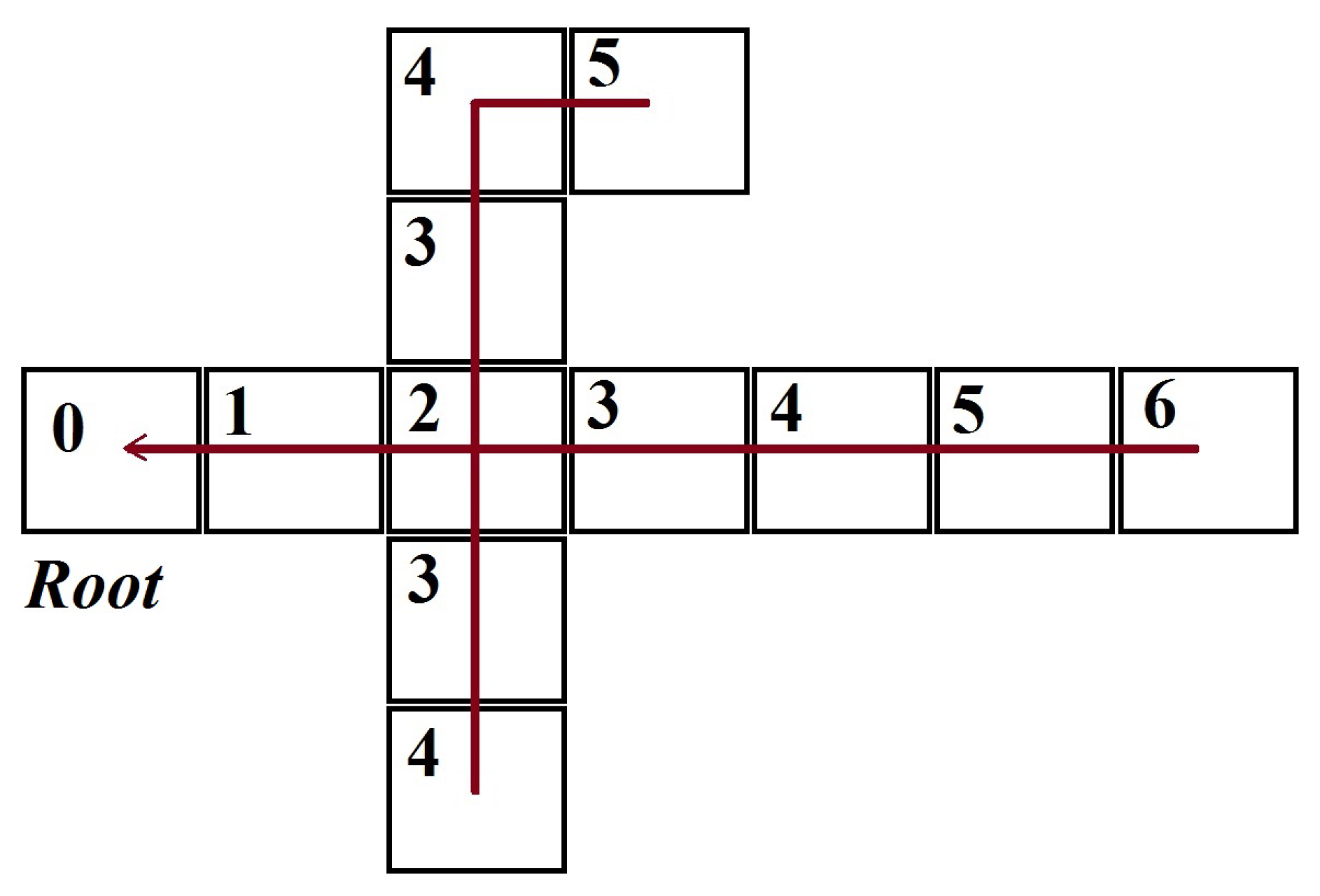
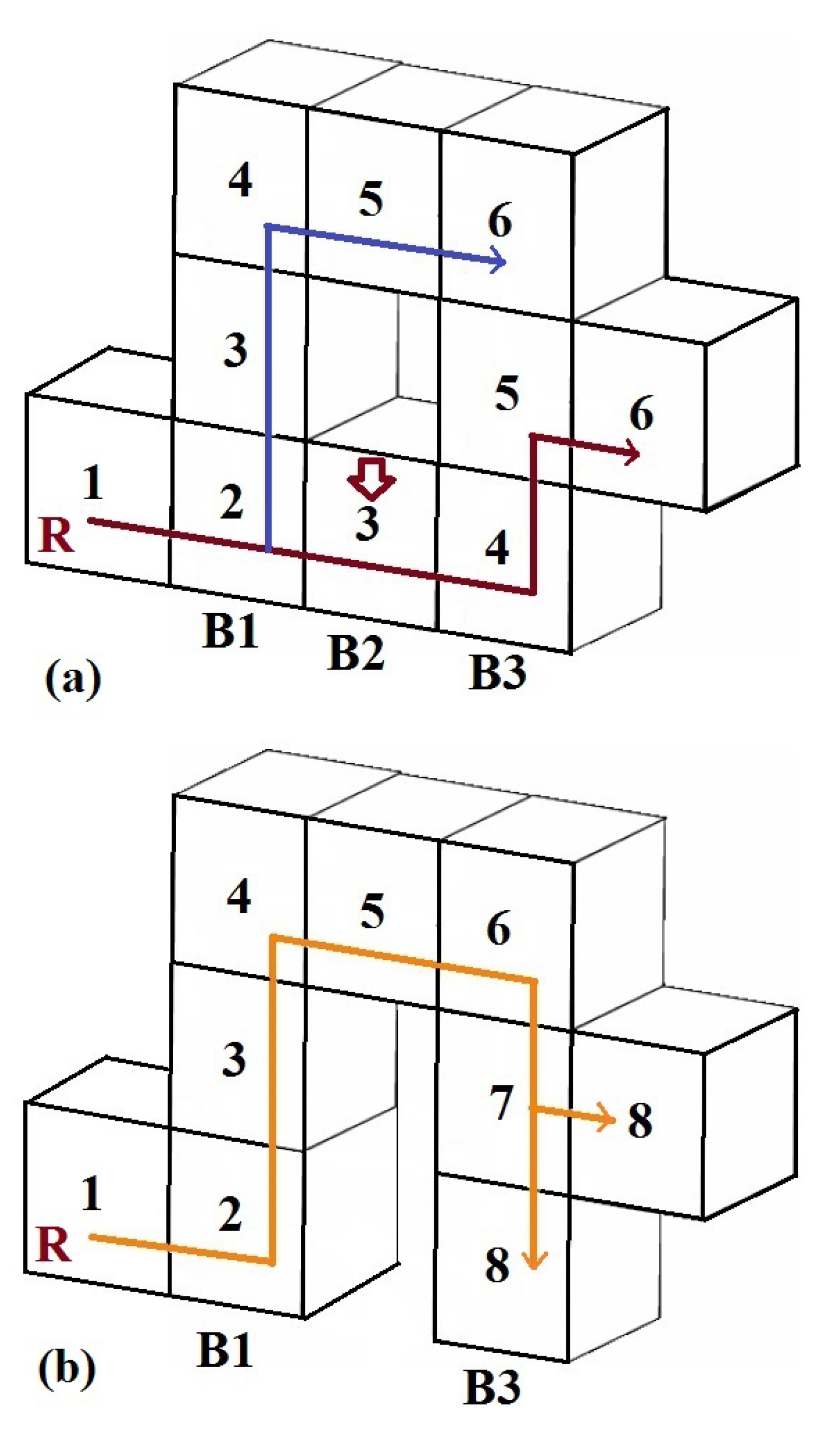
3.2. Gradient-Based Routing Algorithm
| Algorithm 1 Network gradient generation |
|
| Algorithm 2 Communication path recovery mechanism |
|
3.3. Virtual Pheromone-Based Routing Algorithm
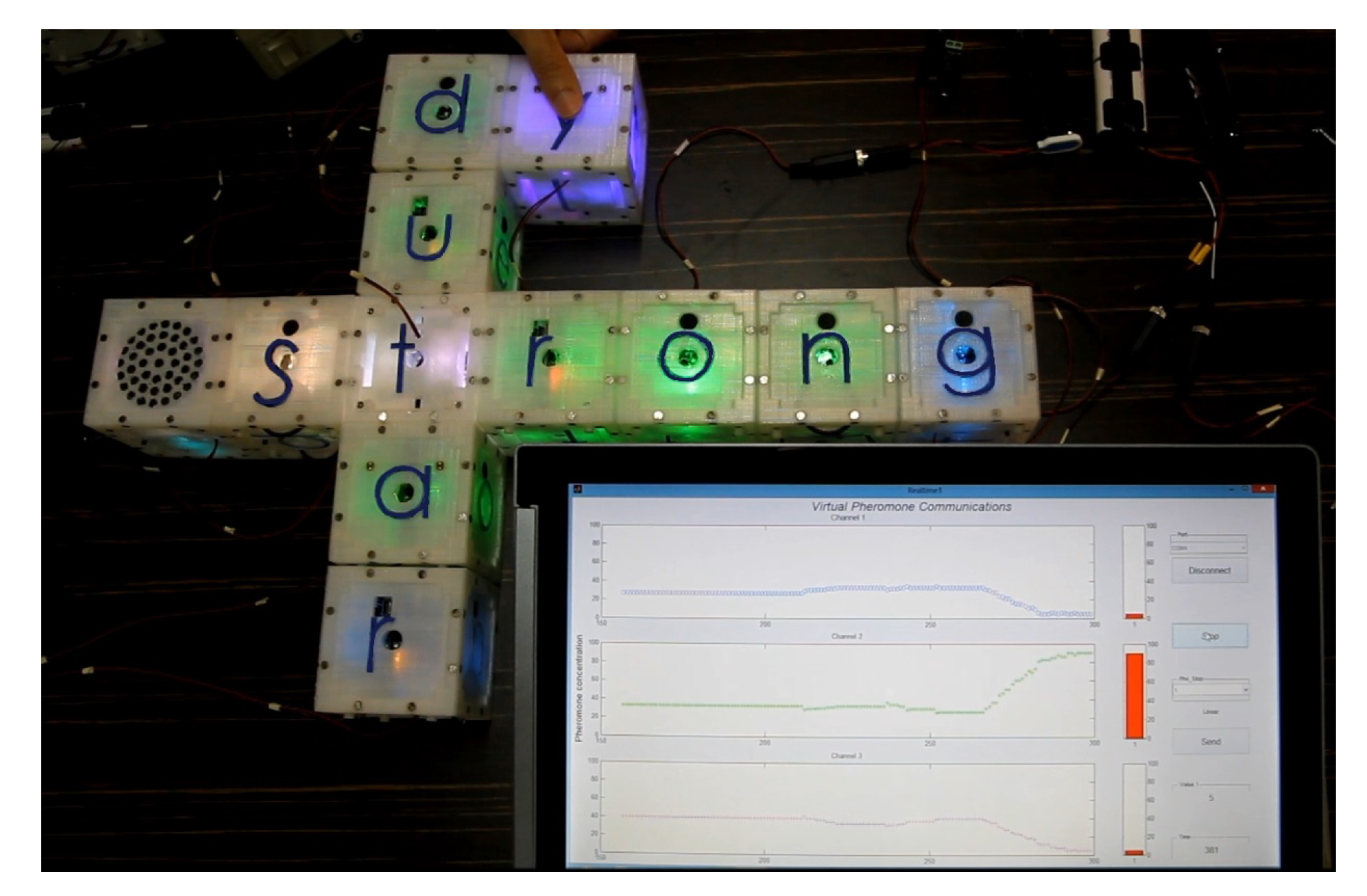
3.4. Virtual Pheromone-Based Network Flow Control
4. Experiments and Results
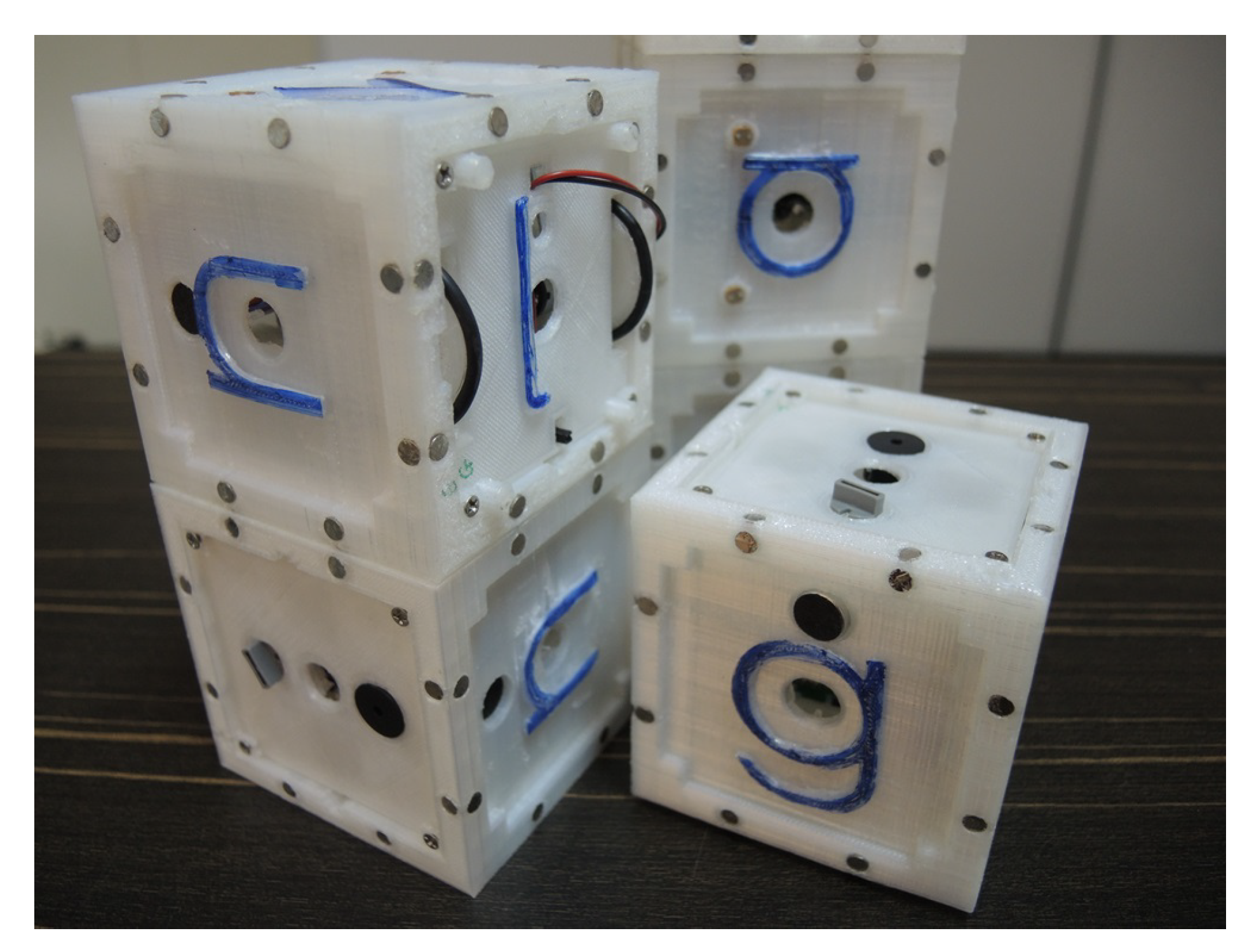
4.1. Hardware Platform
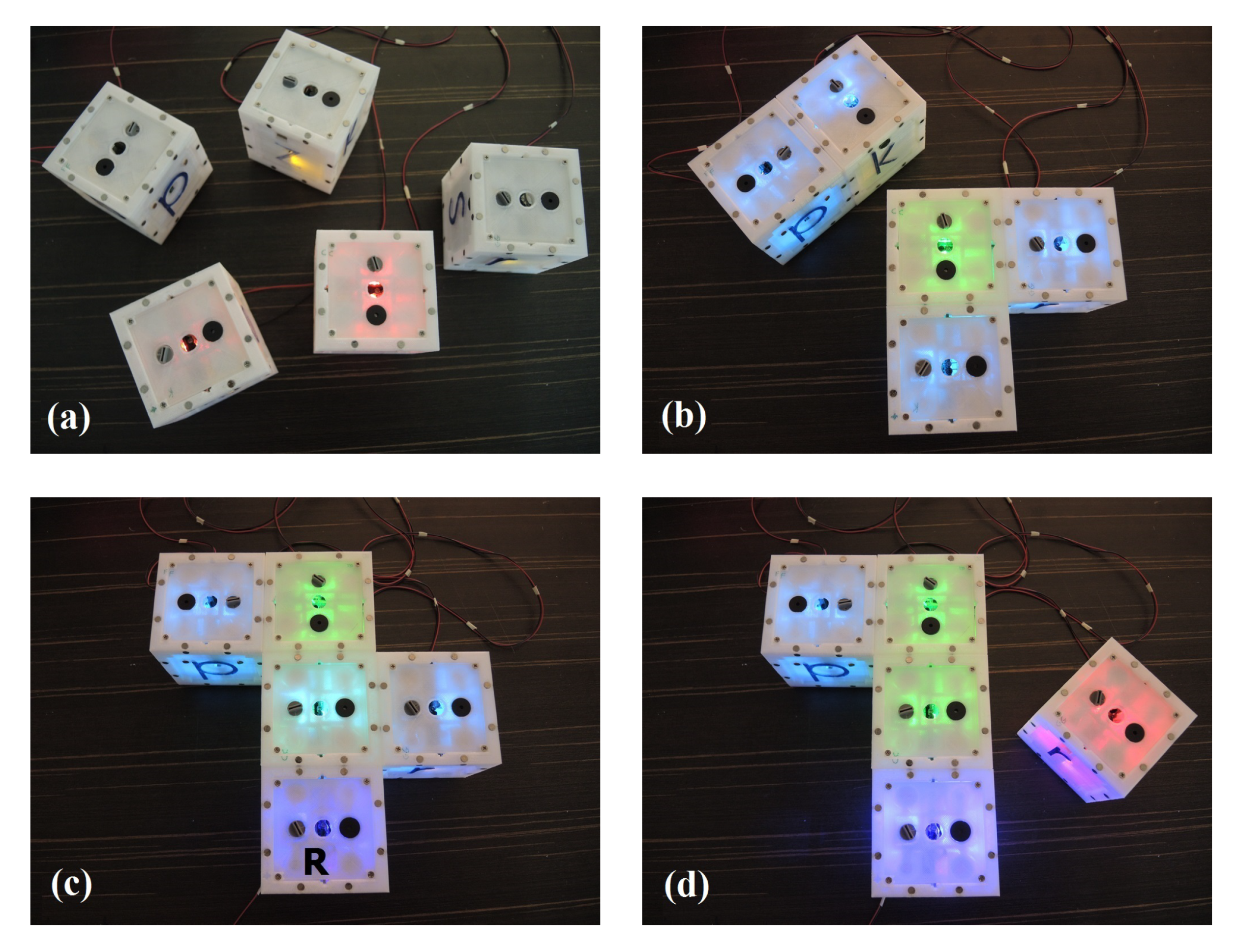
4.2. Preliminary Results
4.3. Virtual Pheromone-Based Routing Algorithm
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goss, S.; Aron, S.; Deneubourg, J.L.; Pasteels, J.M. Self-organized shortcuts in the Argentine ant. Naturwissenschaften 1989, 76, 579–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alers, S.; Tuyls, K.; Ranjbar-Sahraei, B.; Claes, D.; Weiss, G. Insect-inspired robot coordination: Foraging and coverage. Artif. Life 2014, 14, 761–768. [Google Scholar]
- Hrolenok, B.; Luke, S.; Sullivan, K.; Vo, C. Collaborative foraging using beacons. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems: Volume 3-Volume 3. International Foundation for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, Toronto, ON, Canada, 10–14 May 2010; pp. 1197–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, K.; Schader, M.; Andrea, K.; Luke, S. Swarm robot foraging with wireless sensor motes. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems. International Foundation for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, Istanbul, Turkey, 4–8 May 2015; pp. 287–295. [Google Scholar]
- Purnamadjaja, A.H.; Russell, R.A. Guiding robots’ behaviors using pheromone communication. Auton. Robot. 2007, 23, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, R.; Imamura, H.; Hashimoto, T.; Matsuno, F. Communication using pheromone field for multiple robots. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Nice, France, 22–26 September 2008; pp. 1391–1396. [Google Scholar]
- Payton, D.; Estkowski, R.; Howard, M. Pheromone robotics and the logic of virtual pheromones. In International Workshop on Swarm Robotics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2004; pp. 45–57. [Google Scholar]
- Garnier, S.; Tache, F.; Combe, M.; Grimal, A.; Theraulaz, G. Alice in pheromone land: An experimental setup for the study of ant-like robots. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Swarm Intelligence Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 1–5 April 2007; pp. 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Mayet, R.; Roberz, J.; Schmickl, T.; Crailsheim, K. Antbots: A feasible visual emulation of pheromone trails for swarm robots. In International Conference on Swarm Intelligence; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 84–94. [Google Scholar]
- Arvin, F.; Krajník, T.; Turgut, A.E.; Yue, S. COSΦ: Artificial pheromone system for robotic swarms research. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 407–412. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadzadeh, H.; Masehian, E.; Asadpour, M. Modular Robotic Systems: Characteristics and Applications. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2016, 81, 317–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunes, M.; Sorges, U.; Bouazizi, I. ARA-the ant-colony based routing algorithm for MANETs. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Parallel Processing Workshops, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 21 August 2002; pp. 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Baras, J.S.; Mehta, H. A probabilistic emergent routing algorithm for mobile ad hoc networks. In Proceedings of theWiOpt’03: Modeling and Optimization in Mobile, Ad Hoc and Wireless Networks, Sophia-Antipolis, France, 3–5 March 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Agüero, C.; Cañas, J.M.; Ortuno, M.; Matellán, V. Design and implementation of an ad-hoc routing protocol for mobile robots. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2007, 15, 307–320. [Google Scholar]
- Di Caro, G.A.; Ducatelle, F.; Gambardella, L.M. Wireless communications for distributed navigation in robot swarms. In Workshops on Applications of Evolutionary Computation; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kambayashi, Y. A review of routing protocols based on ant-like mobile agents. Algorithms 2013, 6, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.T.; Ngo, T.D. A Distributed Communication Protocol for Modular Robotic Systems. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Banff, AB, Canada, 12–15 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, J.; Paik, J.; Yim, M. Modular Reconfigurable Robotics. Annu. Rev. Control. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2019, 2, 63–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, A.; Gutiérrez, Á.; Nouyan, S.; Pinciroli, C.; Longchamp, V.; Garnier, S.; Dorigo, M. Artificial pheromone for path selection by a foraging swarm of robots. Biol. Cybern. 2010, 103, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, V.T.; Ngo, T.D. Virtual pheromone based information foraging in modular robotics. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots and Ambient Intelligence (URAI), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 12–15 November 2014; pp. 379–384. [Google Scholar]
- Klassner, F.; Anderson, S.D. Lego MindStorms: Not just for K-12 anymore. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2003, 10, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbet, M.G.; Orth, M.; Ishii, H. Triangles: Tangible interface for manipulation and exploration of digital information topography. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 18–23 April 1998; pp. 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Wyeth, P.; Wyeth, G.F. Electronic blocks: Tangible programming elements for preschoolers. In IFIP TC. 13 International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction; IOC Press: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2001; Volume 1, pp. 496–503. [Google Scholar]
- Ngo, T.D.; Lund, H.H. Modular artefacts. In Proceedings of the Component-Oriented Approaches to Context-aware Computing (ECOOP 2004), Oslo, Norway, 14–18 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, R.; Itoh, Y.; Asai, M.; Kitamura, Y.; Kishino, F.; Kikuchi, H. The soul of ActiveCube: Implementing a flexible, multimodal, three-dimensional spatial tangible interface. Comput. Entertain. (CIE) 2004, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffle, H.S.; Parkes, A.J.; Ishii, H. Topobo: A constructive assembly system with kinetic memory. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Vienna, Austria, 24–29 April 2004; pp. 647–654. [Google Scholar]
- Parkes, A.; LeClerc, V.; Ishii, H. Glume: Exploring materiality in a soft augmented modular modeling system. In Proceedings of the CHI’06 Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 22–27 April 2006; pp. 1211–1216. [Google Scholar]
- Möckel, R.; Jaquier, C.; Drapel, K.; Dittrich, E.; Upegui, A.; Ijspeert, A. YaMoR and Bluemove—An autonomous modular robot with bluetooth interface for exploring adaptive locomotion. In Climbing and Walking Robots; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 685–692. [Google Scholar]
- Schweikardt, E.; Gross, M.D. roBlocks: A robotic construction kit for mathematics and science education. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Multimodal Interfaces, Banff, AB, Canada, 2–4 November 2006; pp. 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Dekel, A.; Yavne, G.; Ben-Tov, E.; Roschak, Y. The spelling bee: An augmented physical block system that knows how to spell. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Computer Entertainment Technology, Salzburg, Austria, 13–15 June 2007; pp. 212–215. [Google Scholar]
- LeClerc, V.; Parkes, A.; Ishii, H. Senspectra: A computationally augmented physical modeling toolkit for sensing and visualization of structural strain. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, San Jose, CA, USA, 28 April–3 May 2007; pp. 801–804. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, J.; Lund, H.H. Modular robotics as a tool for education and entertainment. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2008, 24, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiettecatte, B.; Vanderdonckt, J. AudioCubes: A distributed cube tangible interface based on interaction range for sound design. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Tangible and Embedded Interaction, Bonn, Germany, 18–20 February 2008; pp. 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Weller, M.P.; Do, E.Y.L.; Gross, M.D. Posey: Instrumenting a poseable hub and strut construction toy. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Tangible and Embedded Interaction, Bonn, Germany, 18–20 February 2008; pp. 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Zykov, V.; William, P.; Lassabe, N.; Lipson, H. Molecubes extended: Diversifying capabilities of open-source modular robotics. In Proceedings of the IROS-2008 Self-Reconfigurable Robotics Workshop, Nice, France, 22–26 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lund, H.H.; Marti, P. Designing modular robotic playware. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, Toyama, Japan, 27 September–2 October 2009; pp. 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Goh, W.B.; Kasun, L.; Fitriani; Tan, J.; Shou, W. The i-Cube: Design considerations for block-based digital manipulatives and their applications. In Proceedings of the Designing Interactive Systems Conference, Newcastle, UK, 12–15 June 2012; pp. 398–407. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco, M.; Moghadam, M.; Magnússon, A.; Silverman, B.; Lund, H.H.; Christensen, D.J. Fable: Design of a modular robotic playware platform. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on IEEE Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 544–550. [Google Scholar]
- Le, V.T.; Ngo, T.D. Gradient-Based Routing Protocol for Modular Robotic Systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration, Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–15 January 2020. [Google Scholar]


| System Name | Controller | Communication | Routing Protocol | Structure | Transmission Medium | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LEGO Mindstorm [21] | Centralized | Global | N/A | 3D | Physical | 1998 |
| Triangle [22] | Centralized | Local | Gradient | 2D | Physical | 1998 |
| Electronic block [23] | Distributed | Local | N/A | 2D | Physical | 2001 |
| Modular Artefact [24] | Distributed | Local | N/A | 2D | Physical | 2004 |
| Active Cube [25] | Centralized | Global | Serial RS485 | 3D | Physical | 2004 |
| Topobo [26] | Centralized | Global | N/A | 3D | Physical | 2004 |
| Glume [27] | Distributed | Local | N/A | 3D | Capacitive | 2006 |
| YaMoR [28] | Centralized | Global | N/A | 2D | Wireless | 2006 |
| roBlocks [29] | Distributed | Global | N/A | 3D | Physical | 2006 |
| Spelling bee [30] | Centralized | Global | N/A | 2D | Physical | 2007 |
| Senspectra [31] | Centralized | Global | Gradient | 3D | Physical | 2007 |
| IBlocks [32] | Distributed | Local | N/A | 3D | Infrared | 2008 |
| Audiocubes [33] | Centralized | Local | N/A | 3D | Infrared | 2008 |
| Posey [34] | Centralized | Local | N/A | 2D | Infrared | 2008 |
| Molecubes [35] | Hybrid | Hybrid | Serial RS232 | 3D | Physical | 2008 |
| Playware [36] | Distributed | Hybrid | N/A | 2D | Infrared | 2009 |
| iCube [37] | Centralized | Global | N/A | 3D | Capacitive | 2012 |
| Fable [38] | Centralized | Hybrid | N/A | 3D | Wireless | 2013 |
| moreBot [17] | Distributed | Local | Gradient | 3D | Infrared | 2016 |
| Communication Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| USART Baud-rate | 19,200 |
| Closing time | 1.8 ms |
| Processing time (free state) | 300 ms |
| Processing time (busy state) | 700 ms |
| Processing time (link maintenance) | 1100 ms |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Maximum ant rate | 1 ants/second |
| Deposition rate d | 2 unit/ant |
| Evaporation rate e | 0.5 unit/second |
| Delay | 25 / module |
| Concentration upper limit | 95% |
| Concentration lower limit | 5% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le, V.T.; Ngo, T.D. Virtual Pheromone Based Network Flow Control For Modular Robotic Systems. Electronics 2020, 9, 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9030481
Le VT, Ngo TD. Virtual Pheromone Based Network Flow Control For Modular Robotic Systems. Electronics. 2020; 9(3):481. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9030481
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe, Van Tung, and Trung Dung Ngo. 2020. "Virtual Pheromone Based Network Flow Control For Modular Robotic Systems" Electronics 9, no. 3: 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9030481
APA StyleLe, V. T., & Ngo, T. D. (2020). Virtual Pheromone Based Network Flow Control For Modular Robotic Systems. Electronics, 9(3), 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9030481





