A Control Strategy for a Three-Phase Grid Connected PV System under Grid Faults
Abstract
1. Introduction
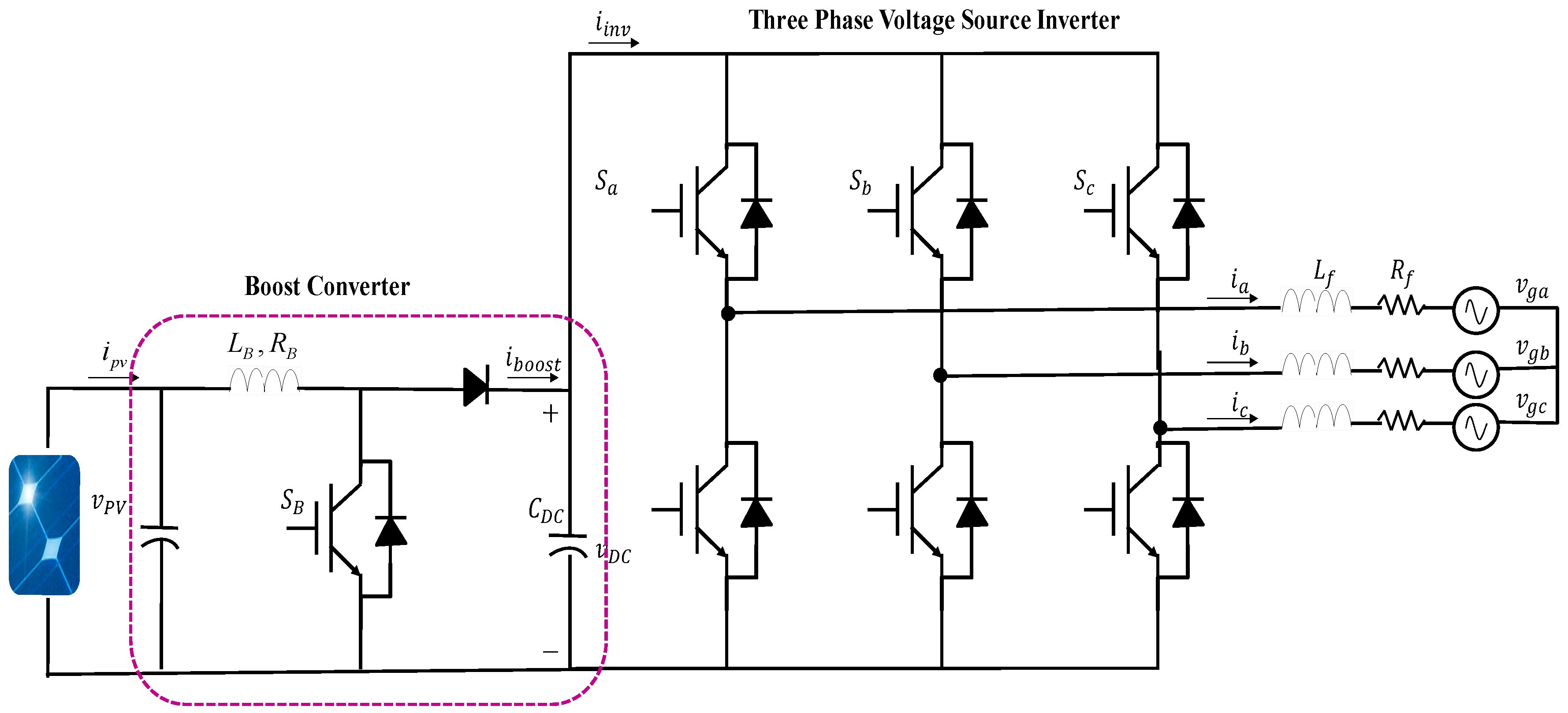
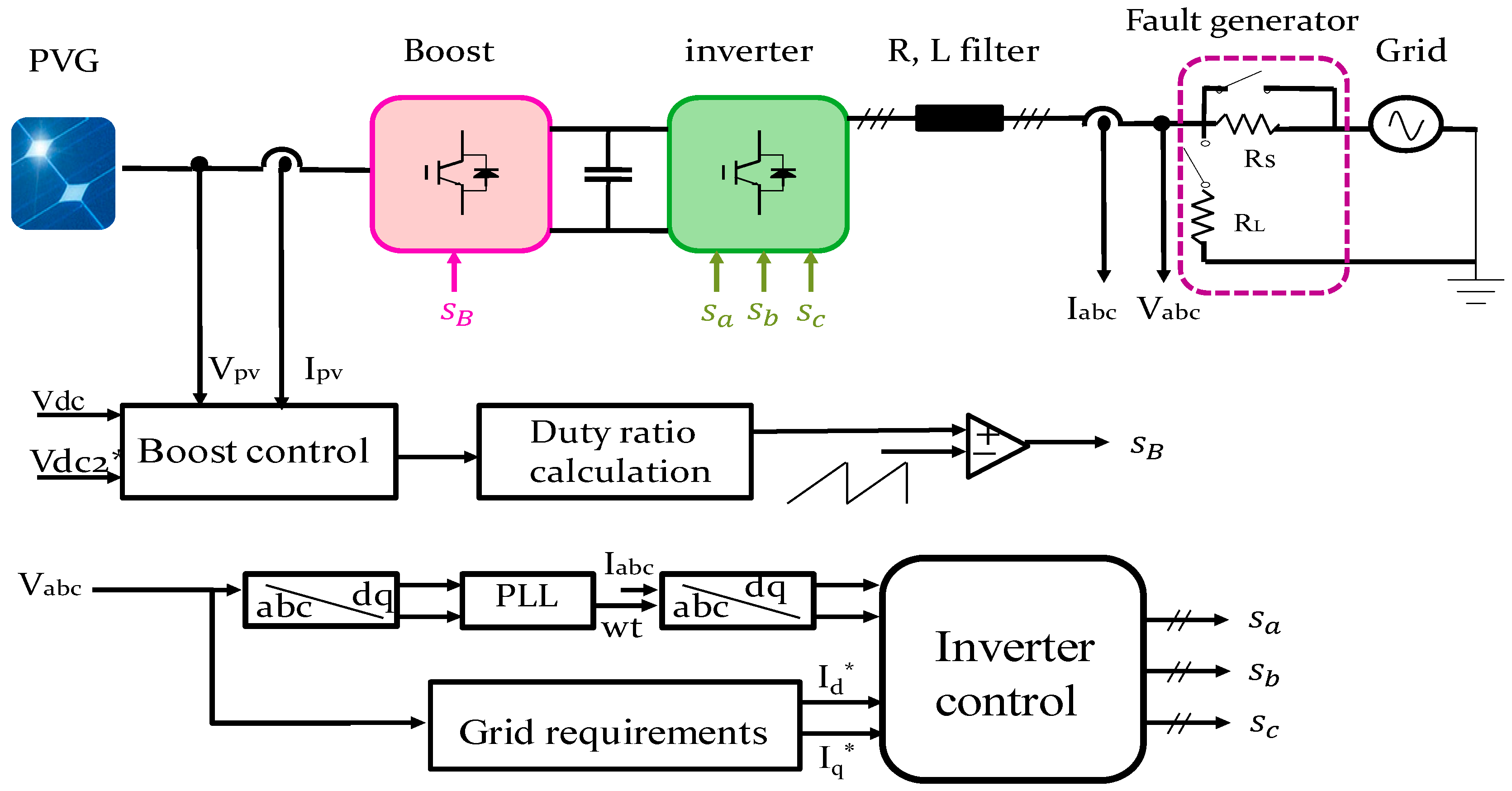
2. System Configuration
3. Control Approach
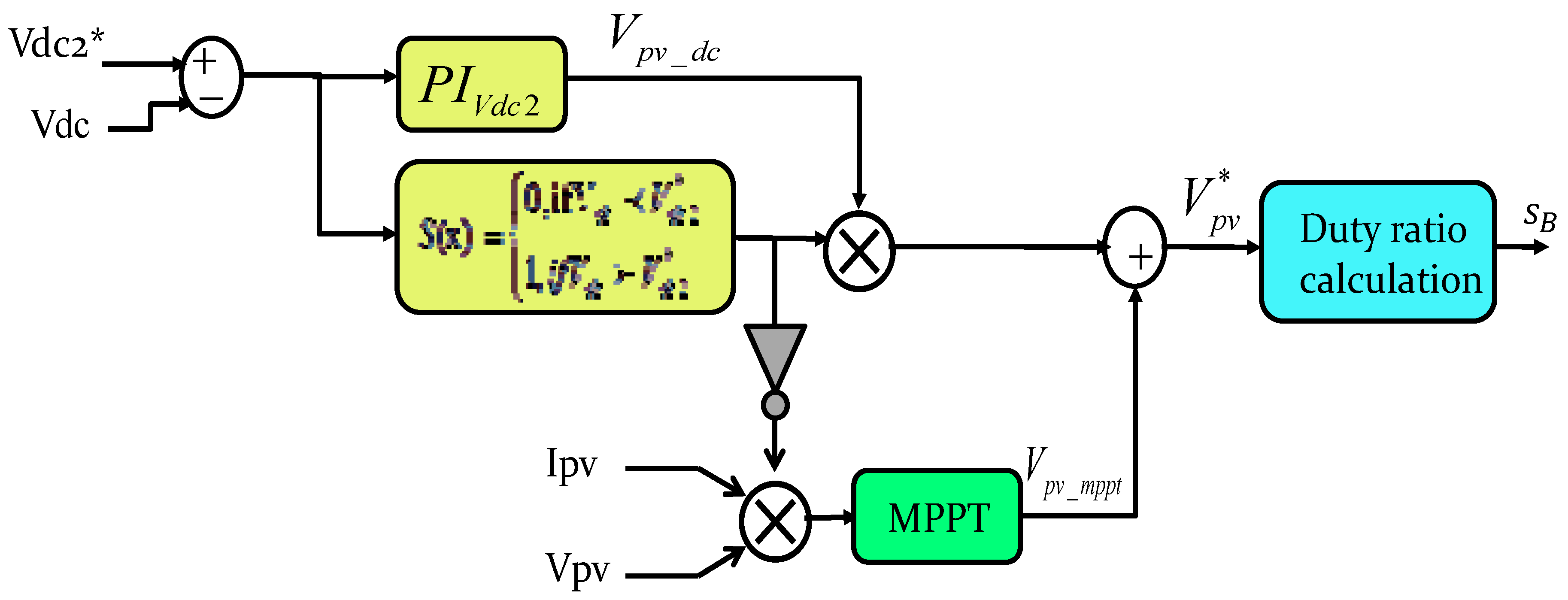
3.1. MPPT Mode
3.2. LVRT Control System and VSC Control
3.2.1. Generation of PV Voltage Reference (Mode: Non-MPPT)
3.2.2. Control of the Voltage Source Inverter (VSI)
4. Simulation Results
- Symetrial voltage sag
- Asymmetrical voltage sag: type B (phase a)
- Asymmetrical voltage sag: type B (phase b)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, T.; Soon, T.K.; Mekhilef, S.A. Single Phase Doubly Grounded Semi-Z-Source Inverter for Photovoltaic (PV) Systems with Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT). Energies 2014, 7, 3618–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brando, G.; Dannier, A.; Del Pizzo, A.; Spina, I. Control and Modulation Techniques for a Centralized PV Generation System Grid Connected via an Interleaved Inverter. App. Sci. 2016, 6, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, S.; Xi, X. An Improved Coordinated Control Strategy for PV System Grid Integration with VSC-MVDC Technology. Energies 2017, 10, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Yang, K.; Quan, X.; Hu, Q.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, B.; Li, P.; Zhang, S.; Jiao, Y. An Optimal PR Control Strategy with Load Current Observer for a Three-Phase Voltage Source Inverter. Energies 2015, 8, 7542–7562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, N.; Guo, L.; Yao, G. Model Preddictive Direct Power Control for Nonredundant Fault Tolerant Grid-Connected Bidirectional Voltage Source Converter. Energies 2017, 10, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wu, Y.-C.; Huang, Y. Dynamic behavior of a grid-connected microgrid with power conditioning system. Int. J. Numer. Model. 2014, 27, 318–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Martinez, S.; Gomez-Lazaro, E.; Molina-Garcia, A.; Vigueras-Rodriguez, A.; Milligan, M.; Muljadi, E. Participation of wind power plants in the Spanish power system during events. In Proceedings of the Power Energy Society, General Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 22–26 July 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Altin, M.; Goksu, O.; Teodorescu, R.; Rodriguez, P.; Jensen, B.B.; Helle, L. Overview of recent grid codes for wind power integration. In Proceedings of the 2010 12th International Conference on Optimization of Electrical and Electronic Equipment, Basov, Romania, 20–22 May 2010; pp. 1152–1160. [Google Scholar]
- Offprint of the Operation Procedure O.P. 12.2: Technical Requirements for Wind Power and Photovoltaic Installations and Any Generating Facilities Whose Technology Does Not Consist on a Synchronous Generator Directly Connected to the Grid, Asociaci´onEmpresarialE´olica. 2004. Available online: www.aeeolica.org (accessed on 30 December 2018).
- Characteristics of the Utility Interface for Photovoltaic Systems; IEC Standard 61727; IEC–International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- Alepuz, S.; Busquets-Monge, S.; Bordonau, J.; Martinez-Velasco, J.A. Control strategies based on symmetrical components for grid-connected converters under voltage dips. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 6, 2162–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Duarte, J.L.; Hendrix, M.A.M. Pliant active and reactive power control for grid-interactive converters under unbalanced voltage dips. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 5, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, A.; Castilla, M.; Miret, J.; Vasquez, J.C.; Alarcon-Gallo, E. Flexible voltage support control for three phase distributed generation inverters under grid fault. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 4, 1429–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miret, J.; Camacho, A.; Castilla, M.; de Vicuña, L.G.; Matas, J. Control scheme with voltage support capability for distributed generation inverters under-voltage sags. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 11, 5252–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, A.; Castilla, M.; Miret, J.; Guzman, R.; Borrell, A. Reactive power control for distributed generation power plants to comply with voltage limits during grid faults. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 2624–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miret, J.; Castilla, M.; Camacho, A.; de Vicuña, L.G.; Matas, J. Control scheme for photovoltaic three-phase inverters to minimize peak currents during unbalanced grid-voltage sags. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 10, 4262–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, P.; Luna, A.; Hermoso, J.; Etxeberria-Otadui, I. Current control method for distributed generation power generation plants under grid fault conditions. In Proceedings of the IECON 2011–37th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics, Melbourne, Australia, 7–10 November 2011; pp. 1262–1269. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, P.; Medeiros, G.; Luna, A.; Cavalcanti, M.C. Safe current injection strategies for a STATCOM under asymmetrical grid faults. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Atlanta, GA, USA, 12–16 September 2010; pp. 3929–3935. [Google Scholar]
- Suul, J.; Luna, A.; Rodriguez, P.; Undeland, T. Virtual-flux-based voltage-sensor-less power control for unbalanced grid conditions. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 9, 4071–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-T.; Hsu, C.-W.; Cheng, P.-T. A low-voltage ride-through technique for grid-connected converters of distributed energy resources. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 4, 1821–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, A.; Castilla, M.; Miret, J. Active and reactive power strategies with peak current limitation for distributed generation inverters during unbalanced grid faults. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 3, 1515–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, P.; Luna, A.; Munoz-Aguilar, R.; Teodorescu, R. Control of power converters in distributed generation applications under grid fault conditions. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 17–22 September 2011; pp. 2649–2656. [Google Scholar]
- Azevedo, M.G.S.; Rodriguez, P.; Cavalcanti, M.C. New control strategy to allow the photovoltaic systems operation under grid faults. In Proceedings of the 2009 Brazilian Power Electronics Conference, Bonito-Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil, 27 September–1 October 2009; pp. 196–201. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Baabjerg, F. Low voltage ride through capability of a single phase photovoltaic system connected to the low voltage grid. Int. J. Photo Energy 2013, 2013, 257487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, D.; Cheng, K.W.E.; Xue, X.D. A novel detection method for voltage sags. In Proceedings of the 2006 2nd International Conference on Power Electronics Systems and Applications, Hong Kong, China, 12–14 November 2006; pp. 250–255. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.M.; Habetler, T.G.; Harley, R.G.; Rostron, J. A voltage sag supporter utilizing a PWM-switched auto transformer. IEEE Trans Power Electron. 2007, 2, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, B.; Lee, J.; Jeong, J.; Han, B. Line-interactive single phase dynamic voltage restorer with novel sag detection algorithm. IEEE Trans. Power 2010, 4, 2702–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzer, C.; Barnes, M.; Green, P. Voltage sag detection technique for a dynamic voltage restorer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2004, 1, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, G.M.S.; Cavalcanti, M.C.; Neves, F.A.S. Implementation of a grid connected photovoltaic system controlled by digital signal processor. In Proceedings of the COBEP, Blumenau, Santa Catarina, Brazil, 30 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kjaer, S.B.; Pedersen, J.K.; Blaabjerg, F. Power inverter topologies for photovoltaic modules—A review. In Proceedings of the 37th IAS Annual Meeting Conference, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 13–18 October 2002; Volume 2, pp. 782–788. [Google Scholar]
- Casaro, M.; Martins, D.C. Grid-connected PV system: Introduction to behavior matching. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Rhodes, Greece, 15–19 June 2008; pp. 951–956. [Google Scholar]
- Kerekes, T.; Teodorescu, R.; Klumpner, C. Evaluation of three phase transformerless photovoltaic inverter topologies. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 2202–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

























| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Maximum power point (MPP) voltage of PV generator | 274 V |
| Open circuit voltage of the PV generator | 321 V |
| Grid voltage | 230 V |
| Grid angular frequency (w) | 314 rd/s |
| Switching frequency | 5 kHz |
| Sample time | 1 × 10−6 s |
| Inductance of the boost | 5 × 10−3 H |
| DC-link capacitance | 1.2 × 10−2 F |
| Inductance of the boost | 5 × 10−3 H |
| Reference voltage of the DC-link Vdc1* | 660 V |
| Reference voltage of the DC-link Vdc2* | 680 V |
| PIVdc2 (Kp2, Ki2) | (200, 5) |
| PI_Vdc (Kp1, Ki1) | (22.9, 762.4) |
| Current regulator PI (Kp, Ki) | (0.0511, 1.2) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khawla, E.M.; Chariag, D.E.; Sbita, L. A Control Strategy for a Three-Phase Grid Connected PV System under Grid Faults. Electronics 2019, 8, 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8080906
Khawla EM, Chariag DE, Sbita L. A Control Strategy for a Three-Phase Grid Connected PV System under Grid Faults. Electronics. 2019; 8(8):906. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8080906
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhawla, El Malleh, Dhia Elhak Chariag, and Lassaad Sbita. 2019. "A Control Strategy for a Three-Phase Grid Connected PV System under Grid Faults" Electronics 8, no. 8: 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8080906
APA StyleKhawla, E. M., Chariag, D. E., & Sbita, L. (2019). A Control Strategy for a Three-Phase Grid Connected PV System under Grid Faults. Electronics, 8(8), 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8080906





