A Long-Range 2.4G Network System and Scheduling Scheme for Aquatic Environmental Monitoring
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
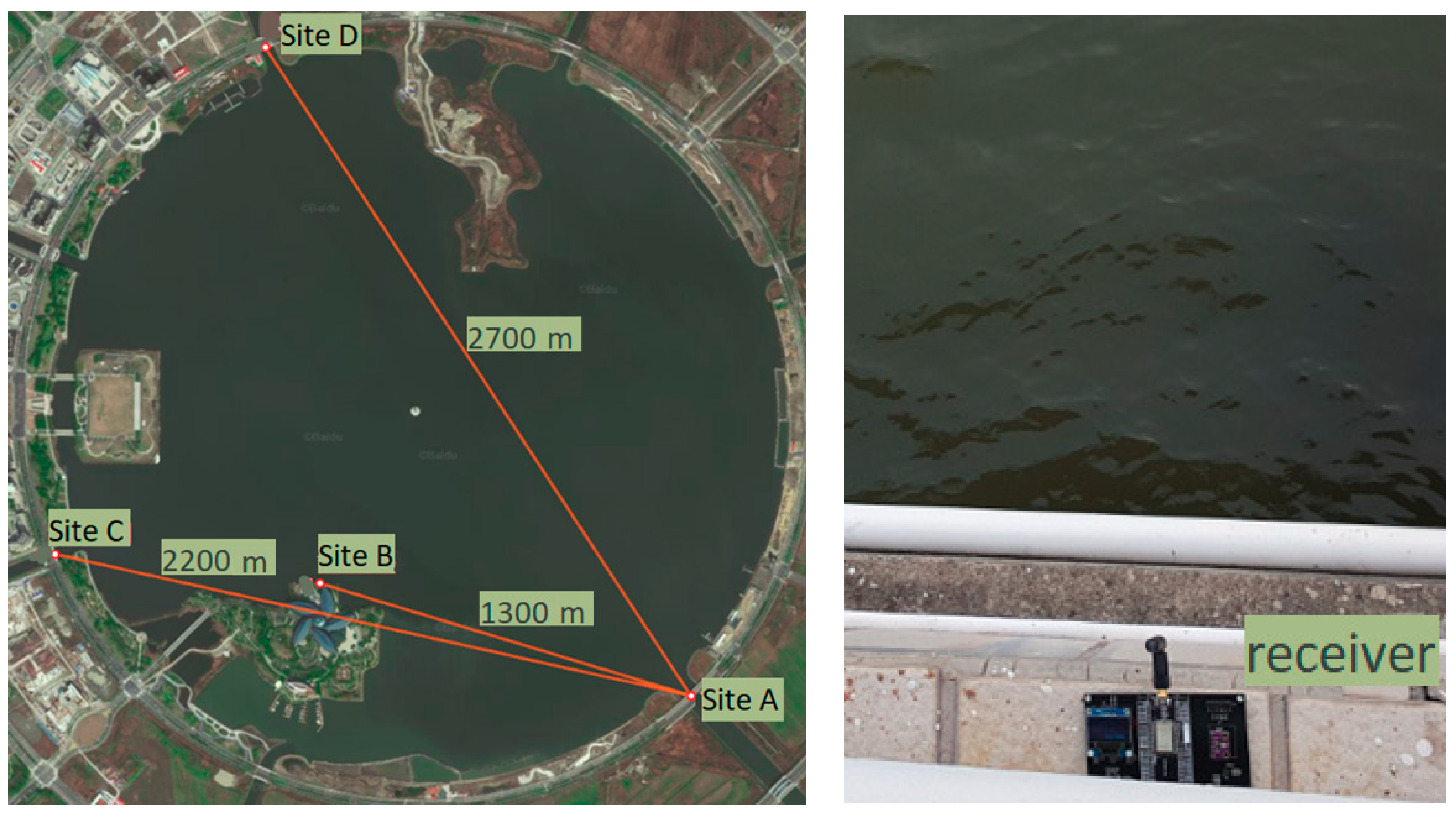
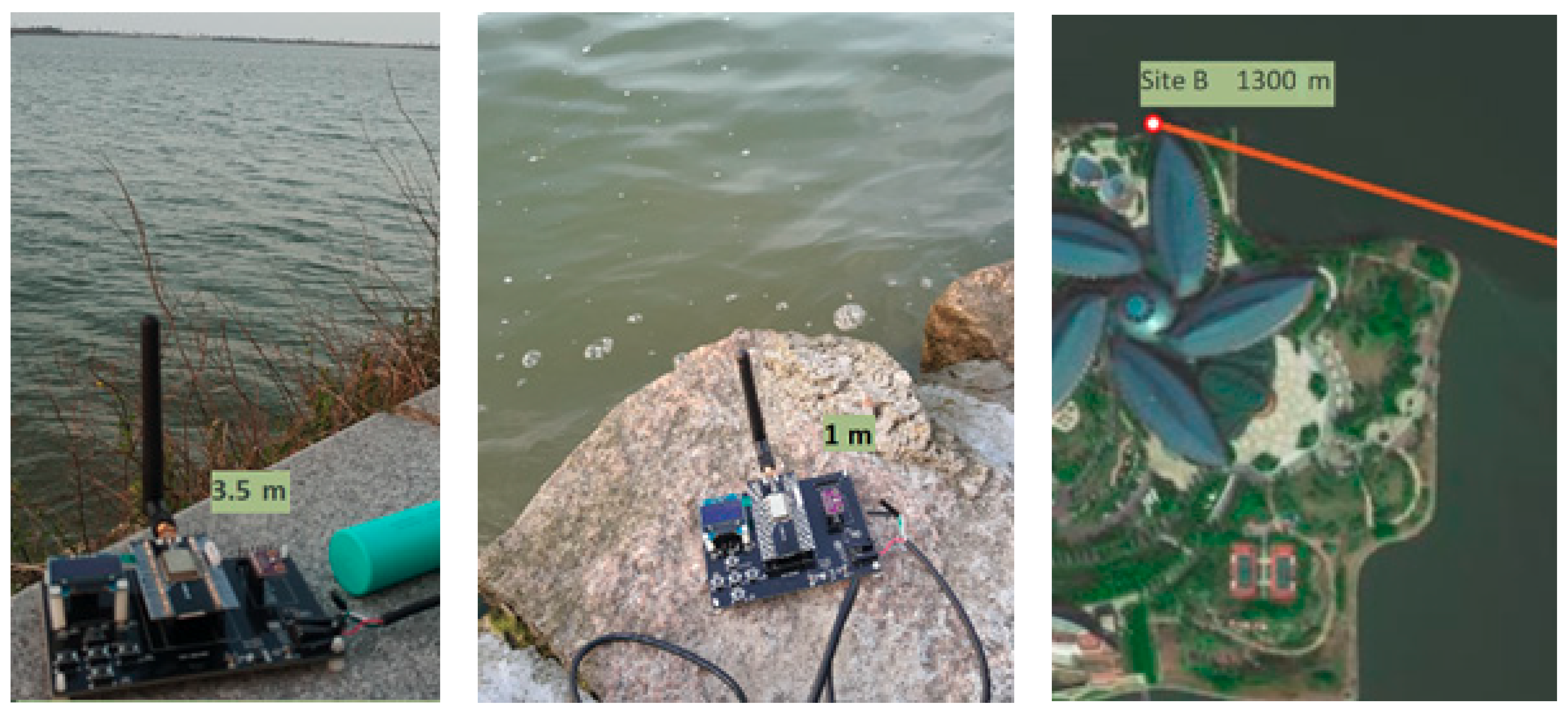
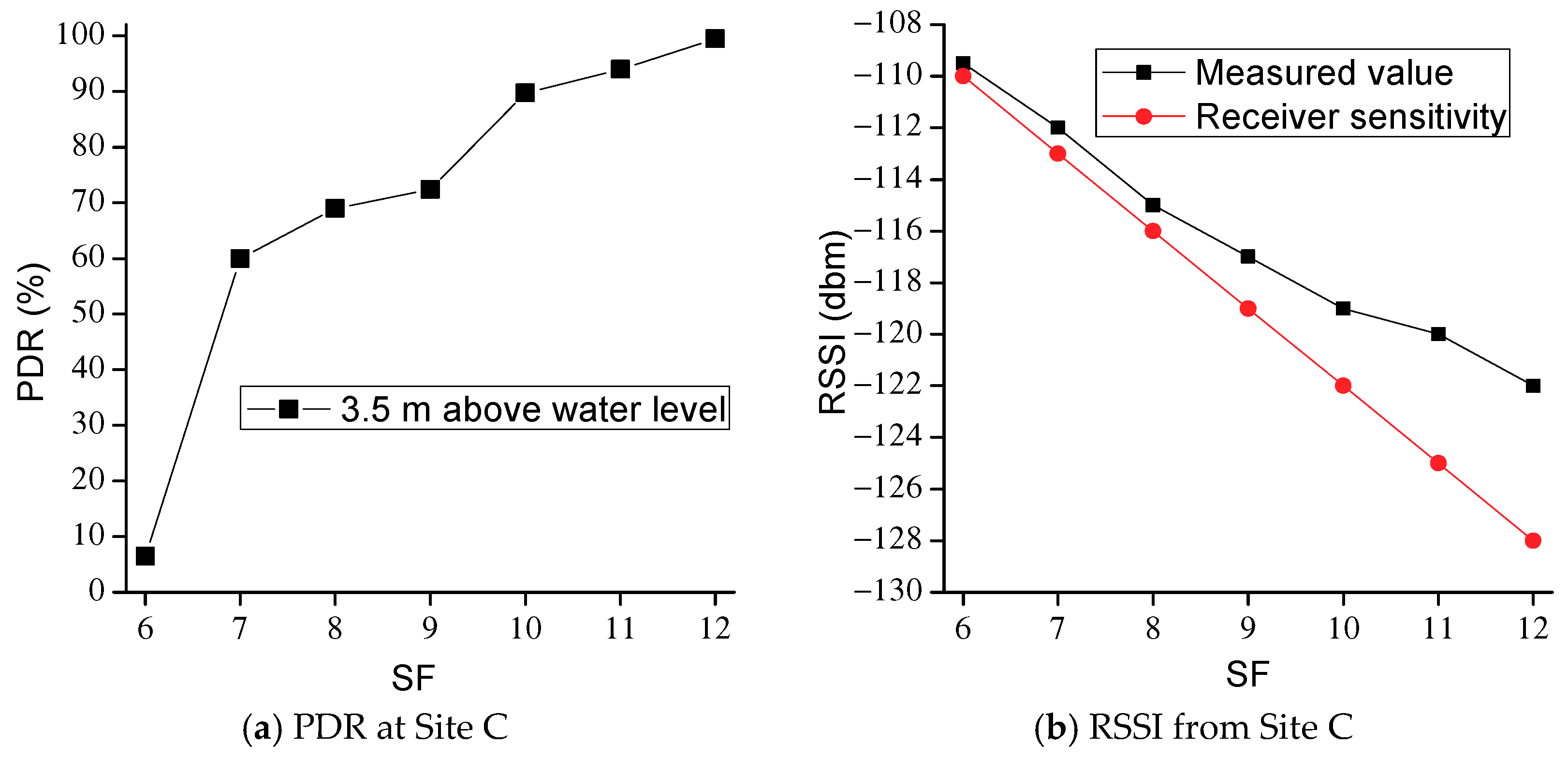
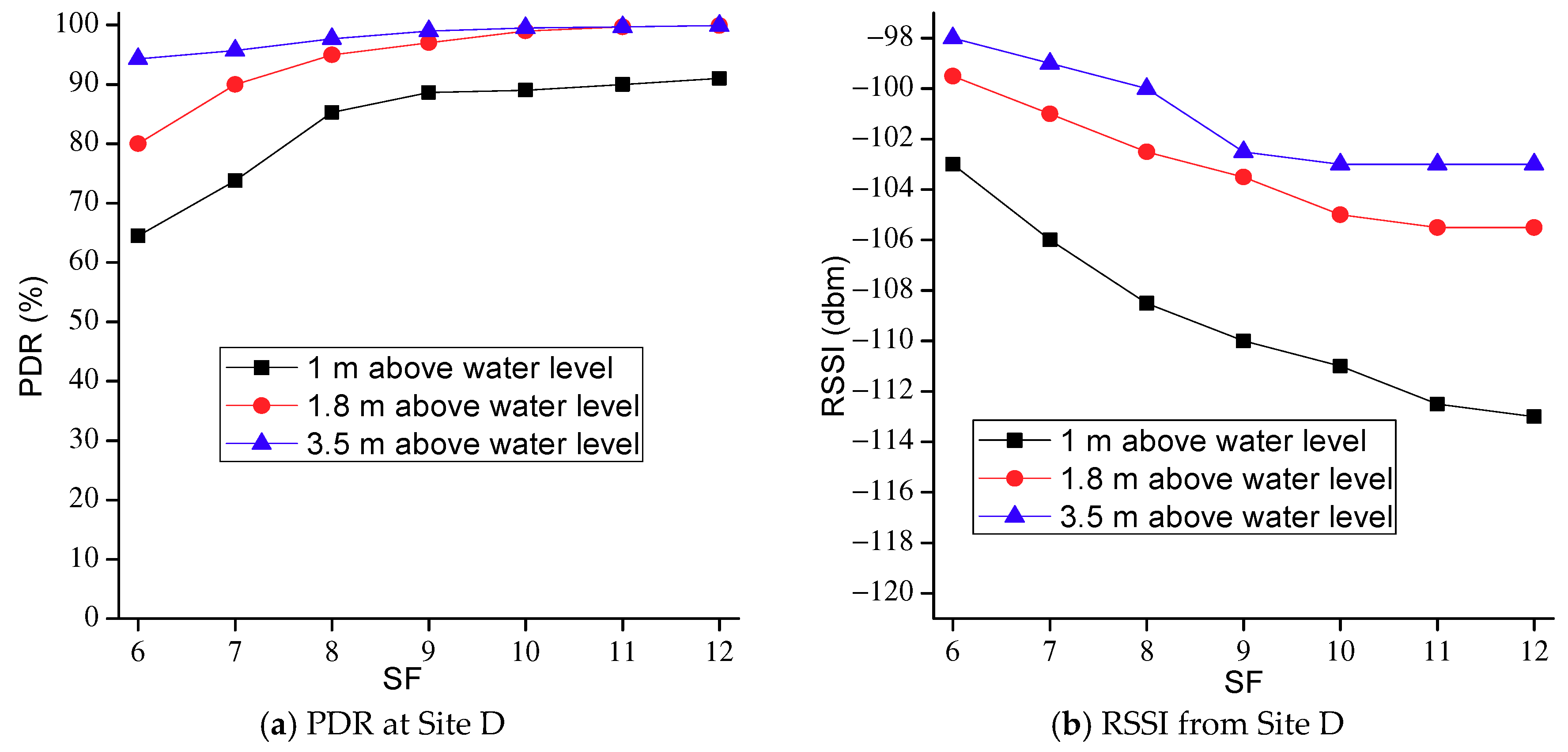
3. Experiments of LoRa 2.4G
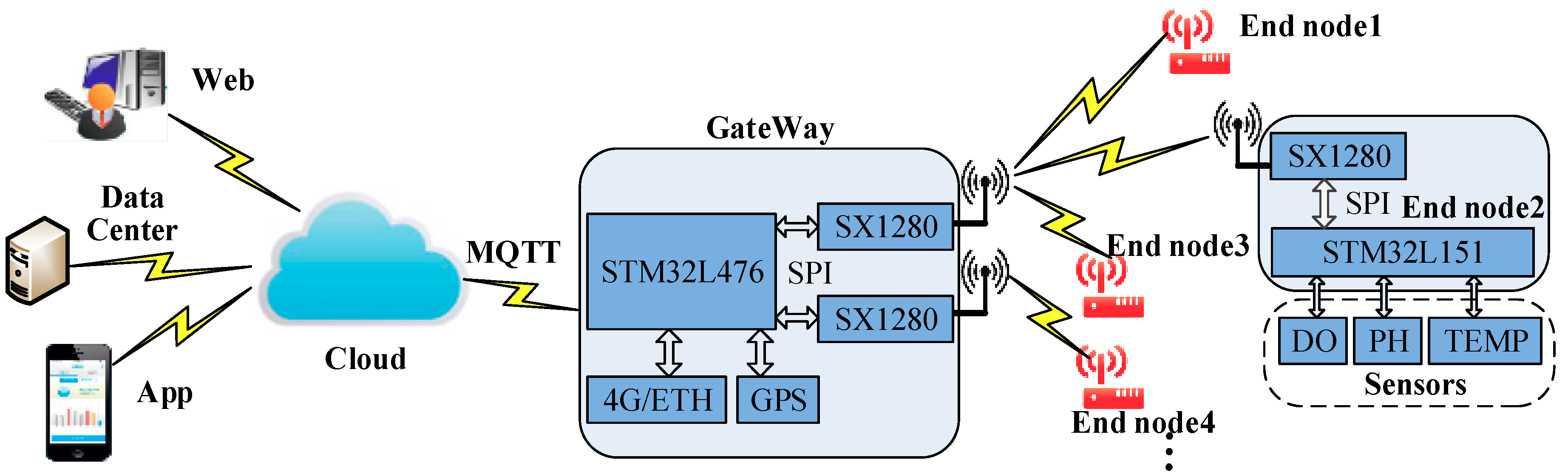
4. Network Architecture and the DMSF–TDMA Scheme
4.1. Network Architecture
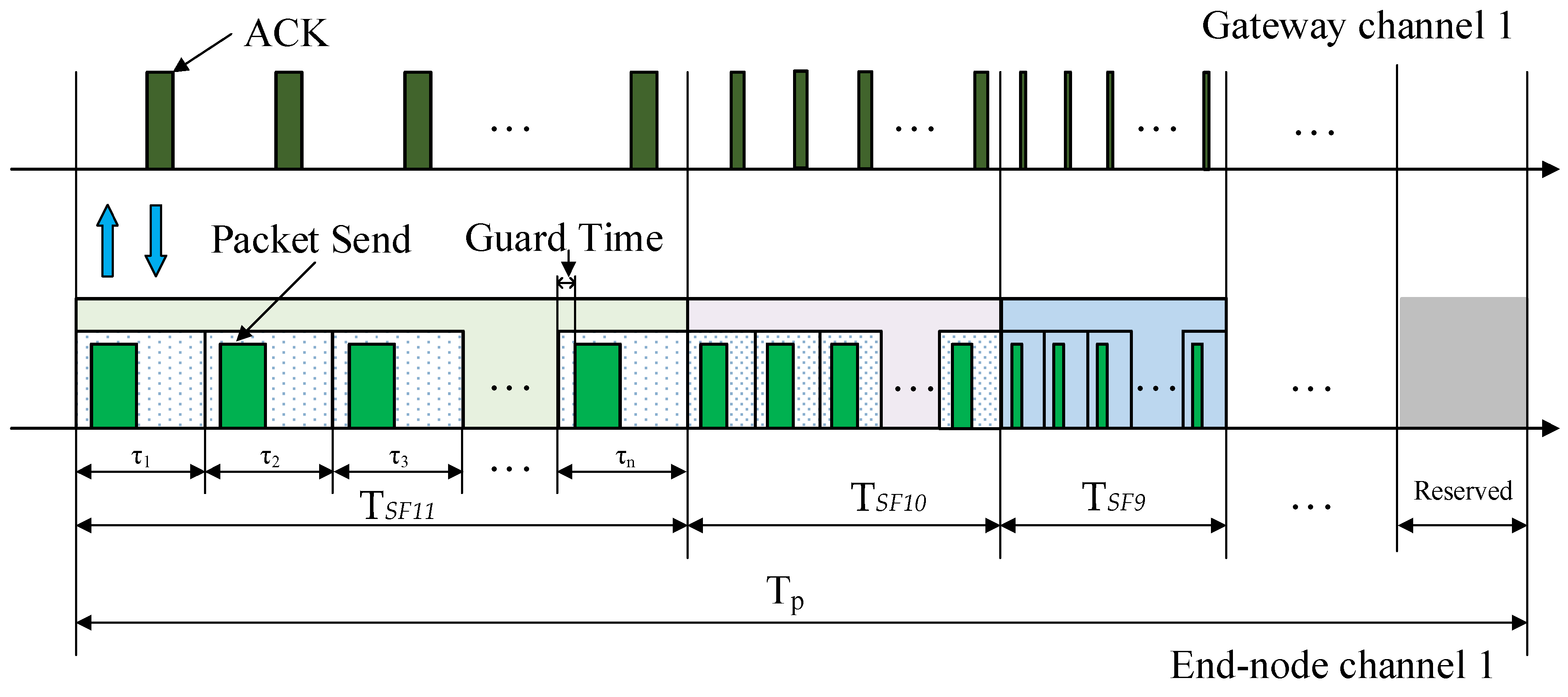
4.2. The DMSF–TDMA Scheme
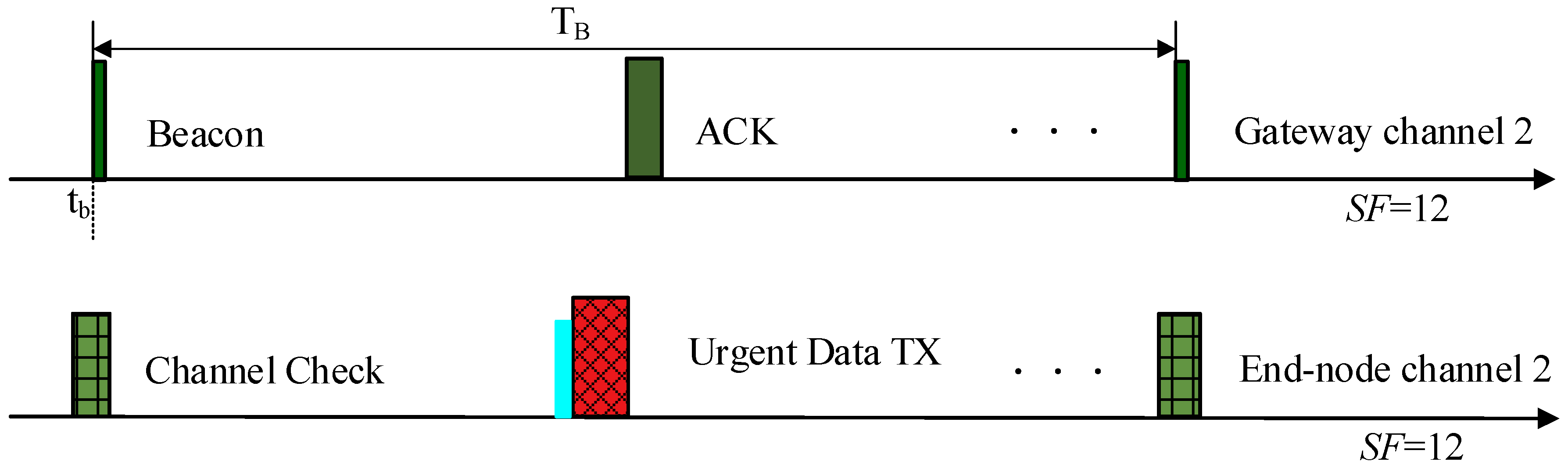
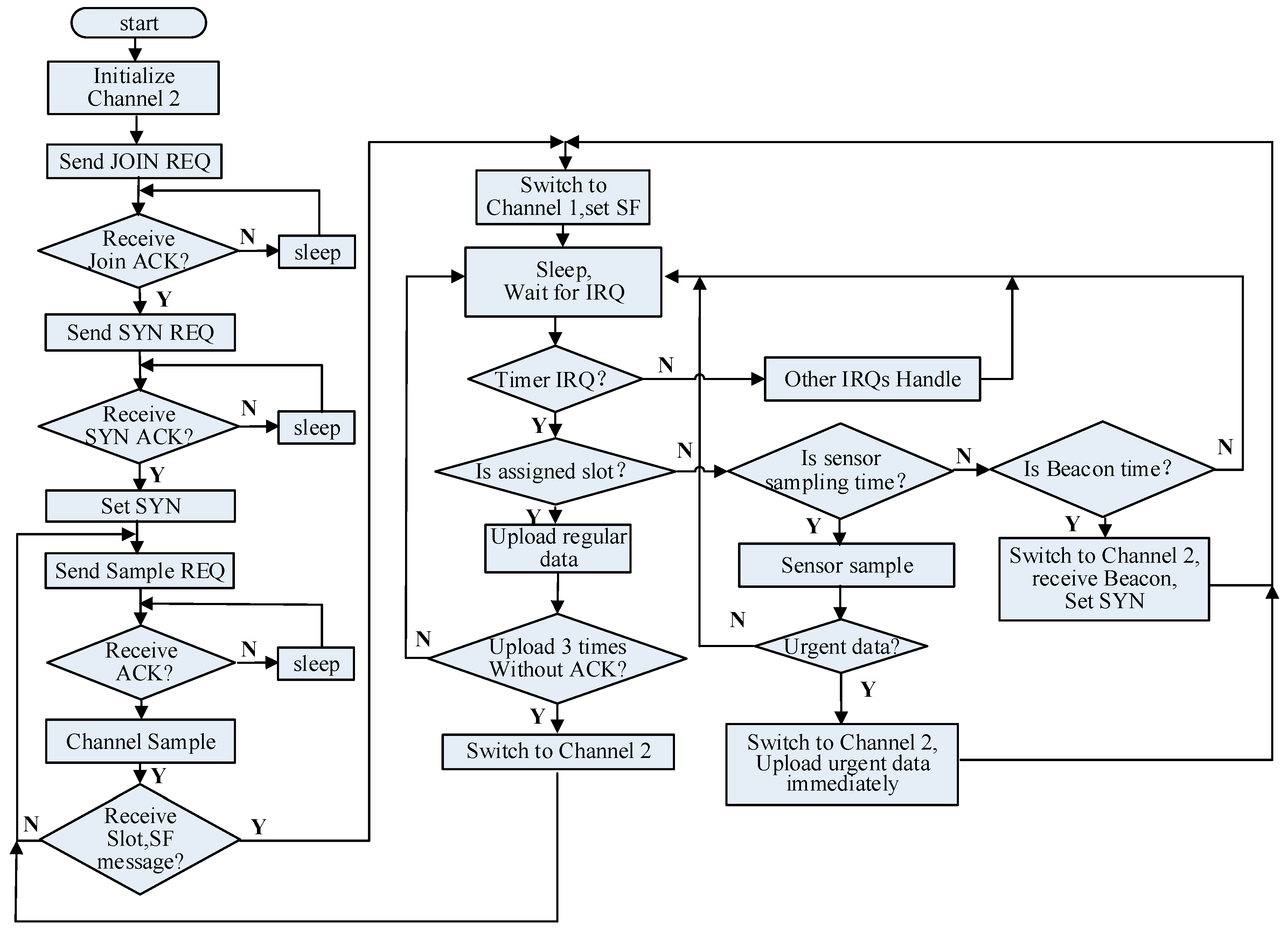
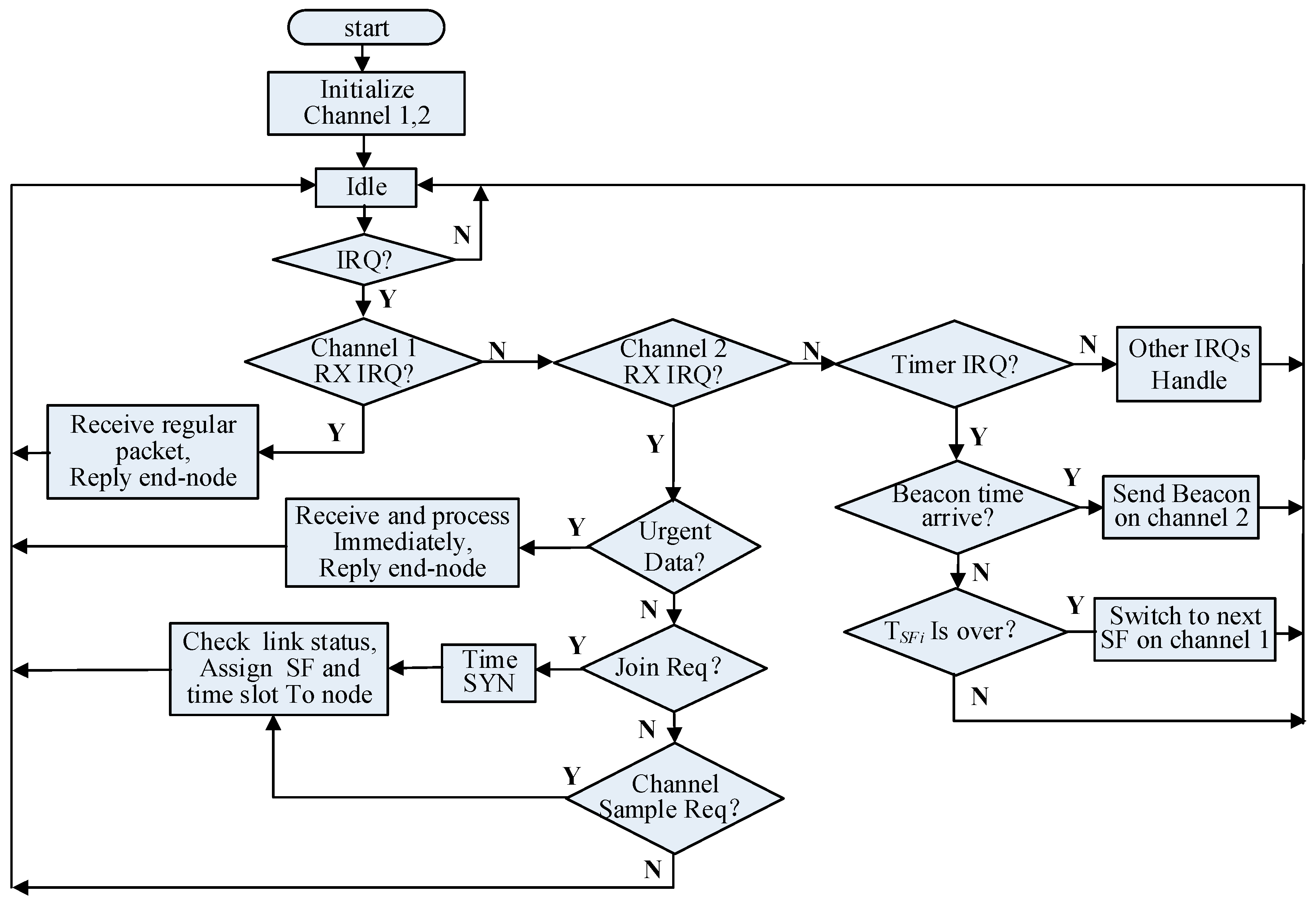
4.2.1. Schedule of Channel 1
4.2.2. Schedule of Channel 2
5. Performance Evaluation
5.1. Simulation Model
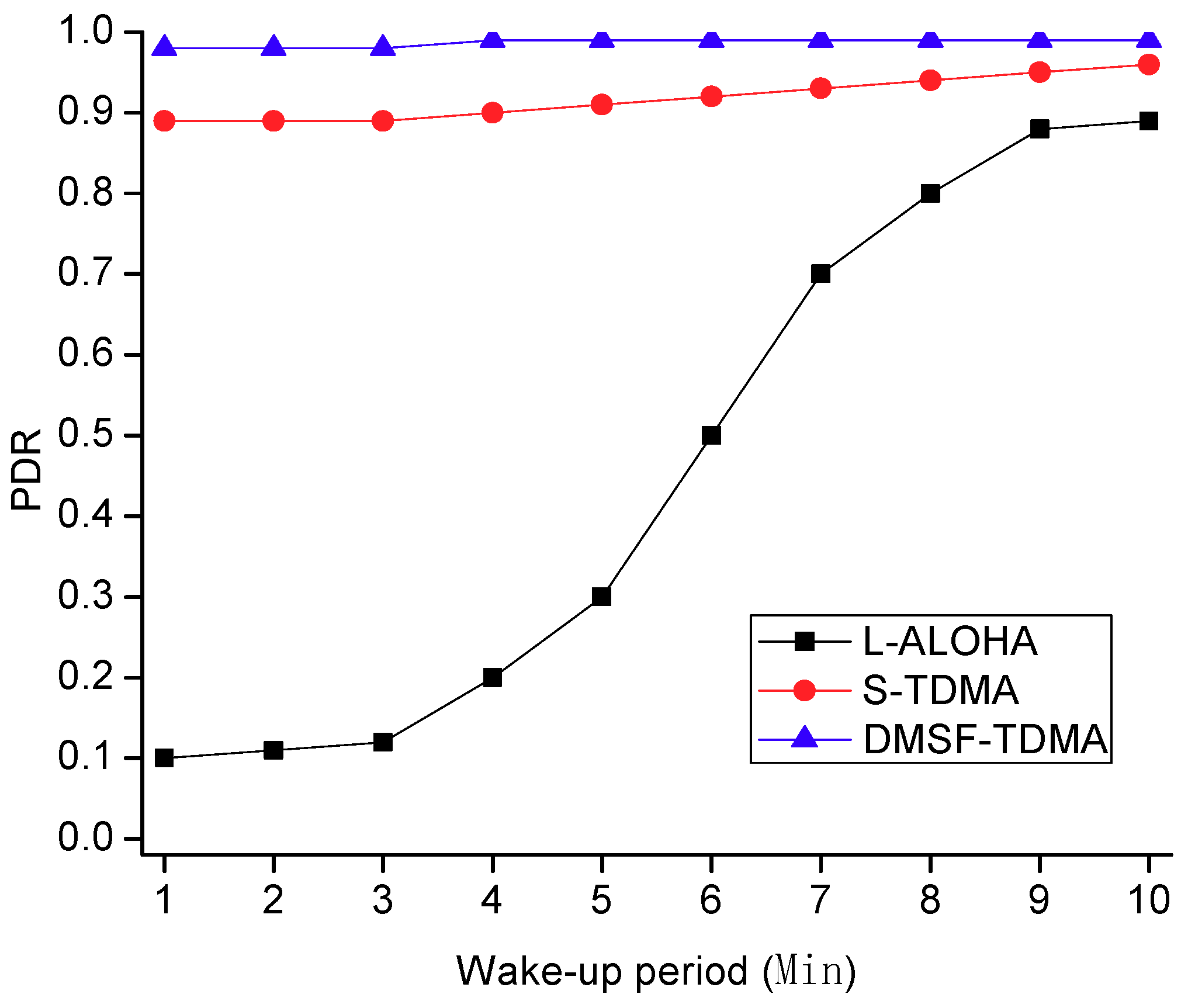
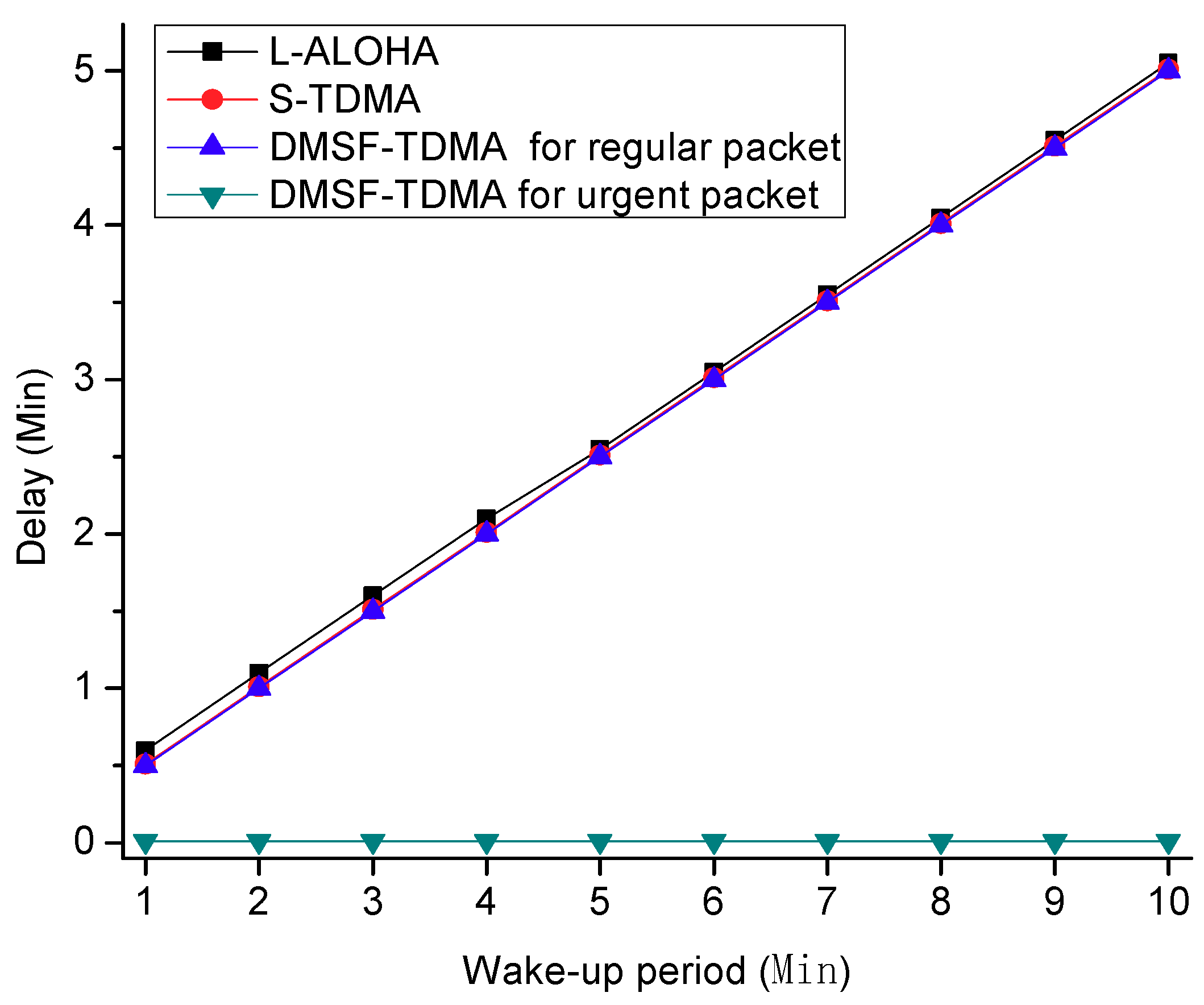
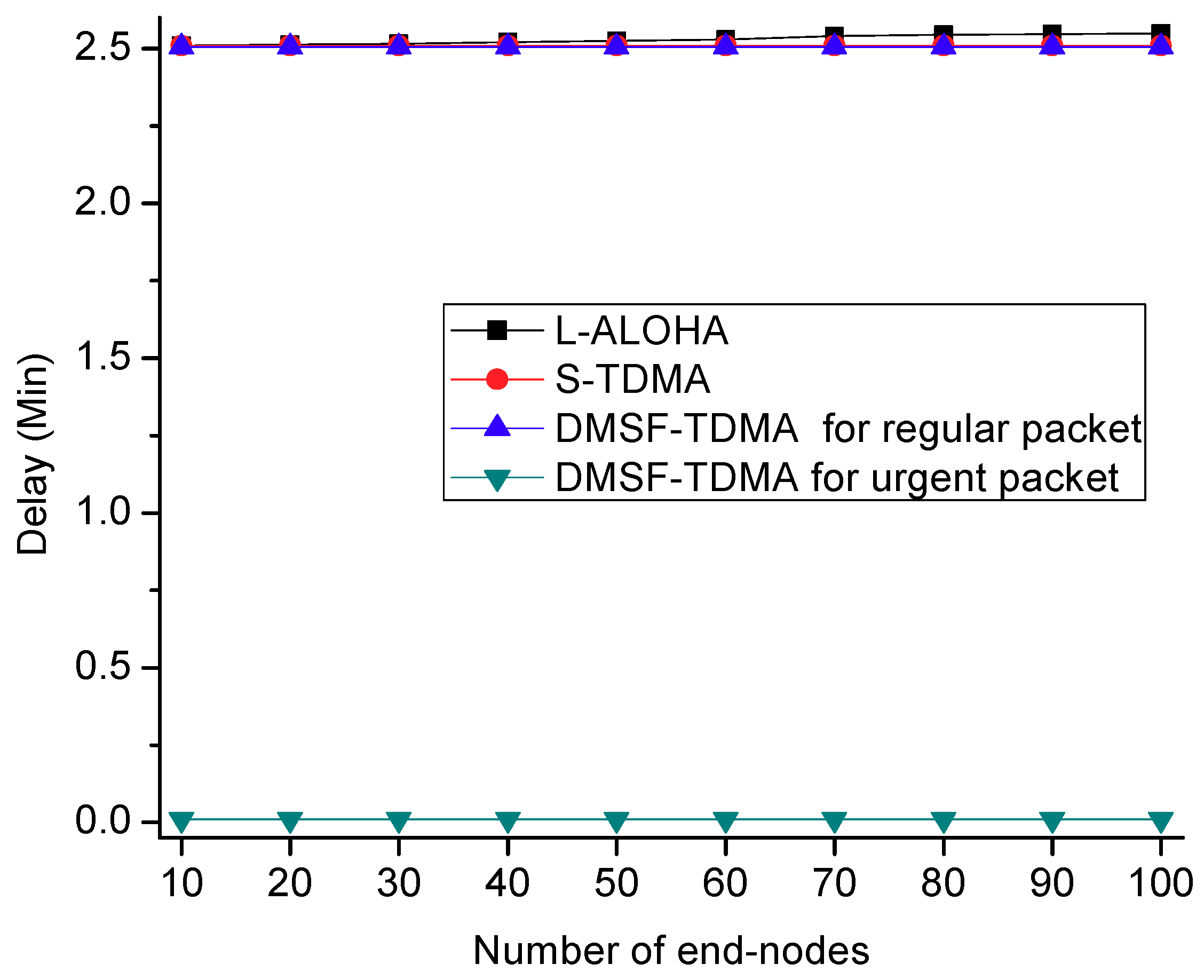
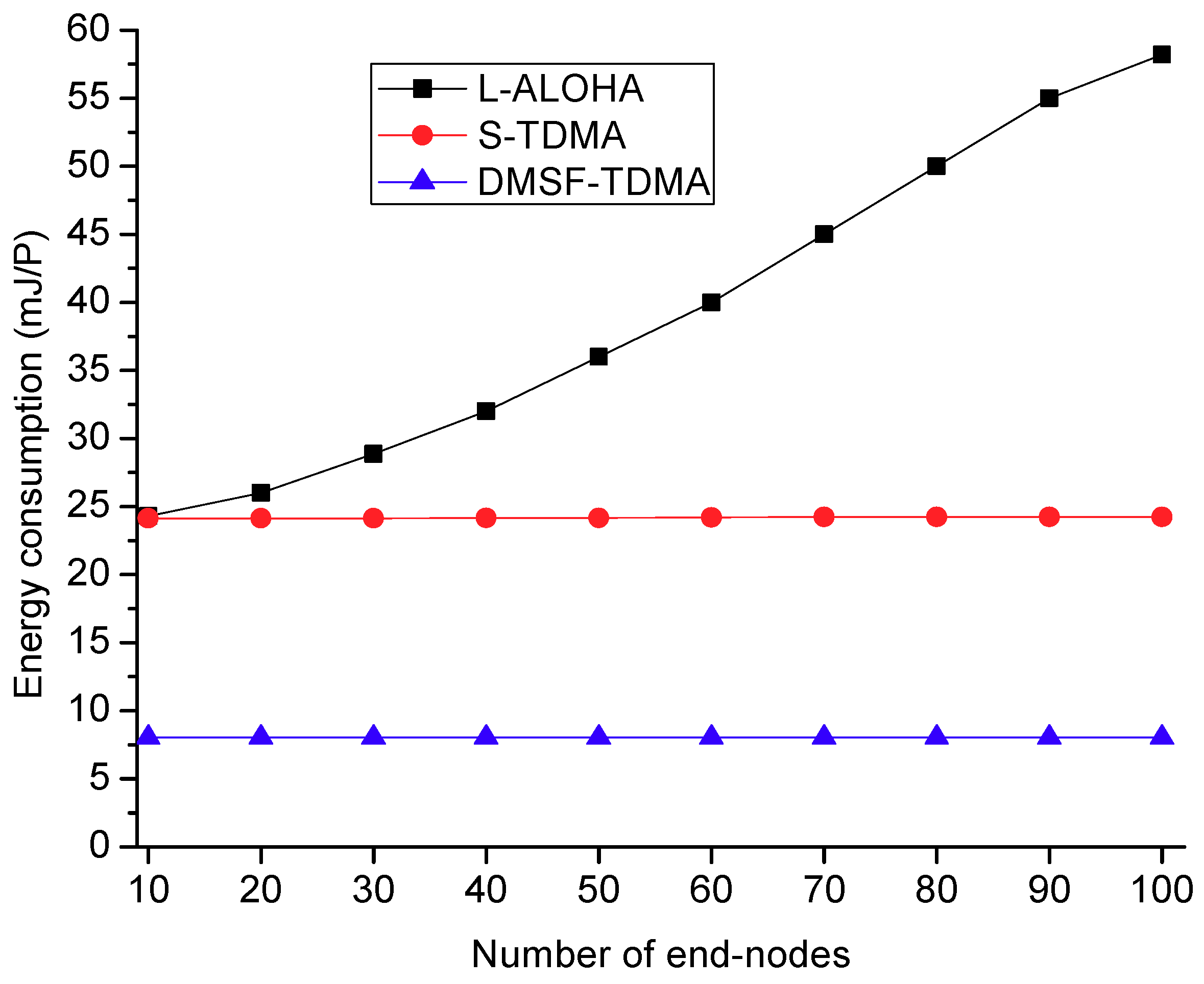
5.2. Simulation Analysis and Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gubbi, J.; Buyya, R.; Marusic, S.; Palaniswami, M. Internet of Things (IoT): A vision, architectural elements, and future directions. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2013, 29, 1645–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bandyopadhyay, D.; Sen, J. Internet of Things: Applications and challenges in technology and standardization. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2011, 55, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, L.; Iera, A.; Morabito, G. The Internet of Things: A Survey. Comput. Netw. 2010, 54, 2787–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Guo, Q.; Shi, Z. Design of WSN node for water pollution remote monitoring. Telecommun. Syst. 2013, 53, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosma, R.H.; Verdegem, M.C.J. Sustainable aquaculture in ponds: Principles, practices and limits. Livest. Sci. 2011, 139, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marziani, C.; Alcoleas, R.; Colombo, F.; Costa, N.; Pujana, F.; Colombo, A.; Aparicio, J.; Álvarez, F.J.; Jimenez, A.; Ureña, J.; et al. A low cost reconfigurable sensor network for coastal monitoring. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on OCEANS, Santander, Spain, 6–9 June 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Albaladejo, C.; Soto, F.; Torres, R.; Sánchez, P.; López, J.A. A low-cost sensor buoy system for monitoring shallow marine environments. Sensors 2012, 12, 9613–9634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Yang, Z.; Li, M.; Guo, Z.; Guo, Y.; Hong, F.; Yang, X.; He, Y.; Feng, Y.; Liu, Y. Oceansense: Monitoring the sea with wireless sensor networks. Mob. Comput. Commun. Rev. 2010, 14, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Shen, W.; Wang, X. Applications of Wireless Sensor Networks in Marine Environment Monitoring: A Survey. Sensors 2014, 14, 16932–16954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simbeye, D.S.; Zhao, J.; Yang, S. Design and deployment of wireless sensor networks for aquaculture monitoring and control based on virtual instruments. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2014, 102, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, C.; Bellalta, B.; Sfairopoulou, A.; Oliver, M. Low energy operation in WSNs: A survey of preamble sampling MAC protocols. Comput. Netw. 2011, 55, 3351–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasi, G.; Conti, M.; Francesco, M.D.; Passarella, A. Energy conservationin wireless sensor networks: A survey. Ad Hoc Netw. 2009, 7, 537–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alippi, C.; Camplani, R.; Galperti, C.; Roveri, M. A Robust, Adaptive, Solar-Powered WSN Framework for Aquatic Environmental Monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 11, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albaladejo Pérez, C.; Soto Valles, F.; Torres Sánchez, R.; Jiménez Buendía, M.; López-Castejón, F.; Gilabert Cervera, J. Design and Deployment of a Wireless Sensor Network for the Mar Menor Coastal Observation System. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2017, 42, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustine, A.; Mvuma, A.N.; Mongi, H.J.; Gabriel, M.C.; Tenge, A.J.; Kucel, S.B. Wireless Sensor Networks for Water Quality Monitoring and Control within Lake Victoria Basin: Prototype Development. Wirel. Sens. Netw. 2014, 6, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yi, J.; Chen, S.; Zhu, X. A Wireless Sensor Network-Based Approach with Decision Support for Monitoring Lake Water Quality. Sensors 2015, 15, 29273–29296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hongpin, L.; Guanglin, L.; Weifeng, P.; Jie, S.; Qiuwei, B. Real-time remote monitoring system for aquaculture water quality. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2015, 8, 136–143. [Google Scholar]
- Adamo, F.; Attivissimo, F.; Carducci, C.G.C.; Lanzolla, A.M.L. A Smart Sensor Network for Sea Water Quality Monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 2514–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandanapalli, S.B.; Reddy, E.S.; Davuluri, D.R.L. Efficient Design and Deployment of Aqua Monitoring Systems Using WSNs and Correlation Analysis. Int. J. Comput. Commun. Control 2015, 10, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Shah, G.A.; Farooq, M.O.; Ghani, U. Technologies and challenges in developing Machine-to-Machine applications: A survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2017, 83, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekki, K.; Bajic, E.; Chaxel, F.; Meyer, F. A comparative study of LPWAN technologies for large-scale IoT deployment. ICT Express 2019, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, A.; Yi, J.; Clausen, T.; Townsley, W.M. A Study of LoRa: Long Range & Low Power Networks for the Internet of Things. Sensors 2016, 16, 1466. [Google Scholar]
- Petajajarvi, J.; Mikhaylov, K.; Pettissalo, M.; Janhunen, J.; Iinatti, J. Performance of a low-power wide-area network based on lora technology: Doppler robustness, scalability, and coverage. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2017, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LoRa-Alliance. LoRaWAN Specification; Technical Report; LoRa Alliance: Beaverton, OR, USA, July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Feltrin, L.; Buratti, C.; Vinciarelli, E.; De Bonis, R.; Verdone, R. LoRaWAN: Evaluation of Link- and System-Level Performance. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 2249–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynders, B.; Wang, Q.; Tuset-Peiro, P.; Vilajosana, X.; Pollin, S. Improving reliability and scalability of lorawans through lightweight scheduling. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 1830–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ren, J.; Zhu, Q. On the application of LoRa LPWAN technology in Sailing Monitoring System. In Proceedings of the 13th Annual Conference on Wireless On-demand Network Systems and Services (WONS), Jackson, WY, USA, 21–24 February 2017; pp. 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Petajajarvi, J.; Mikhaylov, K.; Roivainen, A.; Hanninen, T.; Pettissalo, M. On the coverage of LPWANs: Range evaluation and channel attenuation model for lora technology. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on ITS Telecommunications (ITST), Copenhagen, Denmark, 2–4 December 2015; pp. 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Iborra, R.G.; Liaño, I.; Simoes, C.; Couñago, E.; Skarmeta, A. Tracking and Monitoring System Based on LoRa Technology for Lightweight Boats. Electronics 2019, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovalekic, N.; Drndarevic, V.; Pietrosemoli, E.; Zennaro, I. Experimental Study of LoRa Transmission over Seawater. Sensors 2018, 18, 2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, O.; Raza, U. Low power wide area network analysis: Can LoRa scale? IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2017, 6, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylov, K.; Petäjäjärvi, J.; Haenninen, T. Analysis of capacity and scalability of the LoRa low power wide area network technology. In Proceedings of the European Wireless 2016, 22th European Wireless Conference, Oulu, Finland, 18–20 May 2016; pp. 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Piyare, R.; Murphy, A.; Magno, M.; Benini, L. On-demand lora: Asynchronous tdma for energy efficient and low latency communication in iot. Sensors 2018, 18, 3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, C. Enabling and deploying long-range IoT image sensors with LoRa technology. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Middle East and North Africa Communications Conference (MENACOMM), Jounieh, Lebanon, 18–20 April 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Dinh, N.T.; Kim, Y. Information-centric dissemination protocol for safety information in vehicular ad-hoc networks. Wirel. Netw. 2017, 23, 1359–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, T.; Kim, Y.; Gu, T.; Vasilakos, A.V. L-mac: A wake-up time self-learning mac protocol for wireless sensor networks. Comput. Netw. 2016, 105, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SX1280 Transceivers. July 2019. Available online: https://www.semtech.com/uploads/documents/ DS_SX1280-1_V2.2.pdf (accessed on 19 July 2019).








| Bandwidth (kHz) | Raw Data Rates (kb/s) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SF5 | SF6 | SF7 | SF8 | SF9 | SF10 | SF11 | SF12 | |
| 203 | 31.72 | 19.03 | 11.1 | 6.34 | 3.57 | 1.98 | 1.09 | 0.595 |
| 406 | 63.44 | 38.06 | 22.2 | 12.69 | 7.14 | 3.96 | 2.18 | 1.19 |
| 812 | 126.88 | 76.13 | 44.41 | 25.38 | 14.27 | 7.93 | 4.36 | 2.38 |
| 1625 | 253.91 | 152.34 | 88.87 | 50.78 | 28.56 | 15.87 | 8.73 | 4.76 |
| Transceiver | SX1278 | SX1280 | CC2520 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modulation | LoRa | LoRa | IEEE 802.15.4 |
| Band | 470 MHz | 2.4 GHz | 2.4 GHz |
| Data rate (Max) | 37.5 kb/s | 202 kb/s | 250 kb/s |
| Receiver sensitivity | −148 dBm | −132 dBm | −98 dBm |
| Tx current | 29 mA @ + 13 dBm | 24 mA @ + 12.5 dBm | TX 33.6 mA @ + 5 dBm |
| RX current | 9.9 mA | 8.2 mA | 18.5 mA |
| SF | SNR | RSSI |
|---|---|---|
| 6 | 0 | −85 |
| 7 | 0 | −90 |
| 8 | −5 | −95 |
| 9 | −10 | −108 |
| 10 | −15 | −115 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| LoRa Setting | BW = 406 kHz, CR = 4/5, SF ∈ (6, 12), Preamble length = 8 symbol |
| Rx current | 6.7 mA |
| Tx current | 24 mA@ + 12.5 dBm |
| Sleep current | 0.4 μA |
| Payload | 16 Bytes |
| Beacon period | 20 min |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Cao, S.; Wang, Y. A Long-Range 2.4G Network System and Scheduling Scheme for Aquatic Environmental Monitoring. Electronics 2019, 8, 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8080909
Zhang Z, Cao S, Wang Y. A Long-Range 2.4G Network System and Scheduling Scheme for Aquatic Environmental Monitoring. Electronics. 2019; 8(8):909. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8080909
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zheng, Shouqi Cao, and Yuntengyao Wang. 2019. "A Long-Range 2.4G Network System and Scheduling Scheme for Aquatic Environmental Monitoring" Electronics 8, no. 8: 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8080909
APA StyleZhang, Z., Cao, S., & Wang, Y. (2019). A Long-Range 2.4G Network System and Scheduling Scheme for Aquatic Environmental Monitoring. Electronics, 8(8), 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8080909




