Visual Closed-Loop Dynamic Model Identification of Parallel Robots Based on Optical CMM Sensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
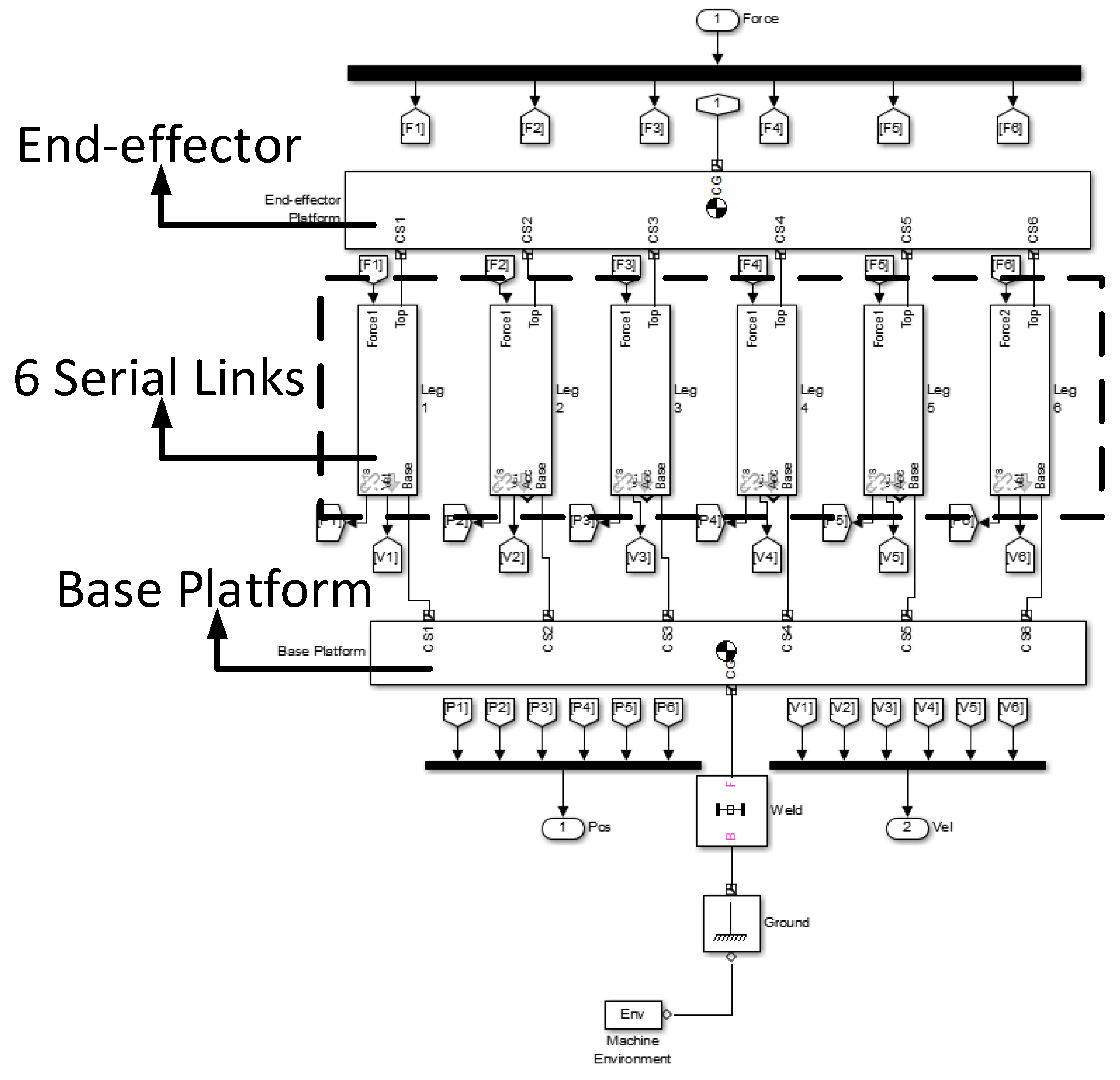
2. Dynamic Modeling
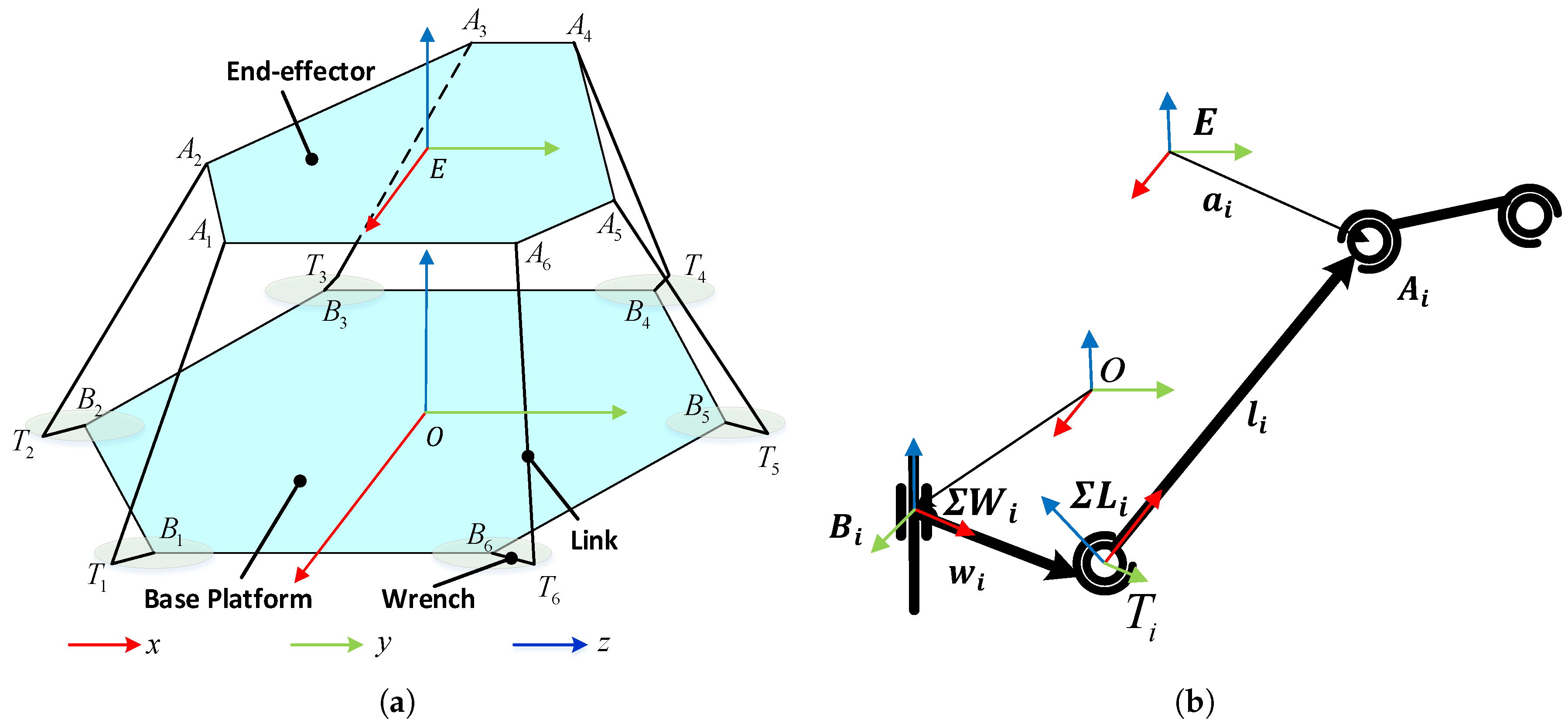
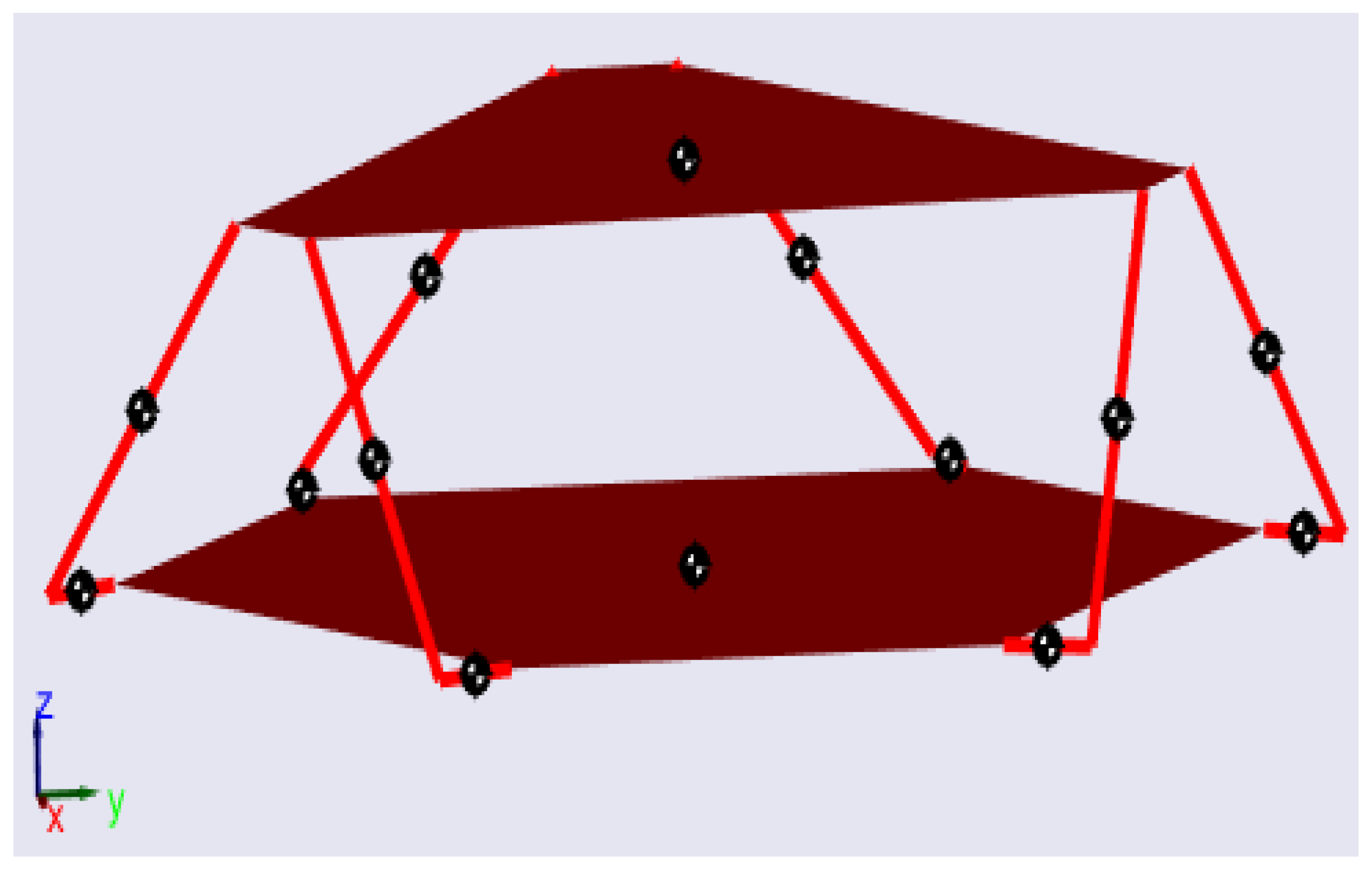
2.1. Kinematic Analysis
- The end-effector platform, wrenches and links are symmetric with respect to their axes.
- The links do not rotate about its symmetric axes.
2.2. Dynamic Modeling
2.3. Dynamic Model Simplification
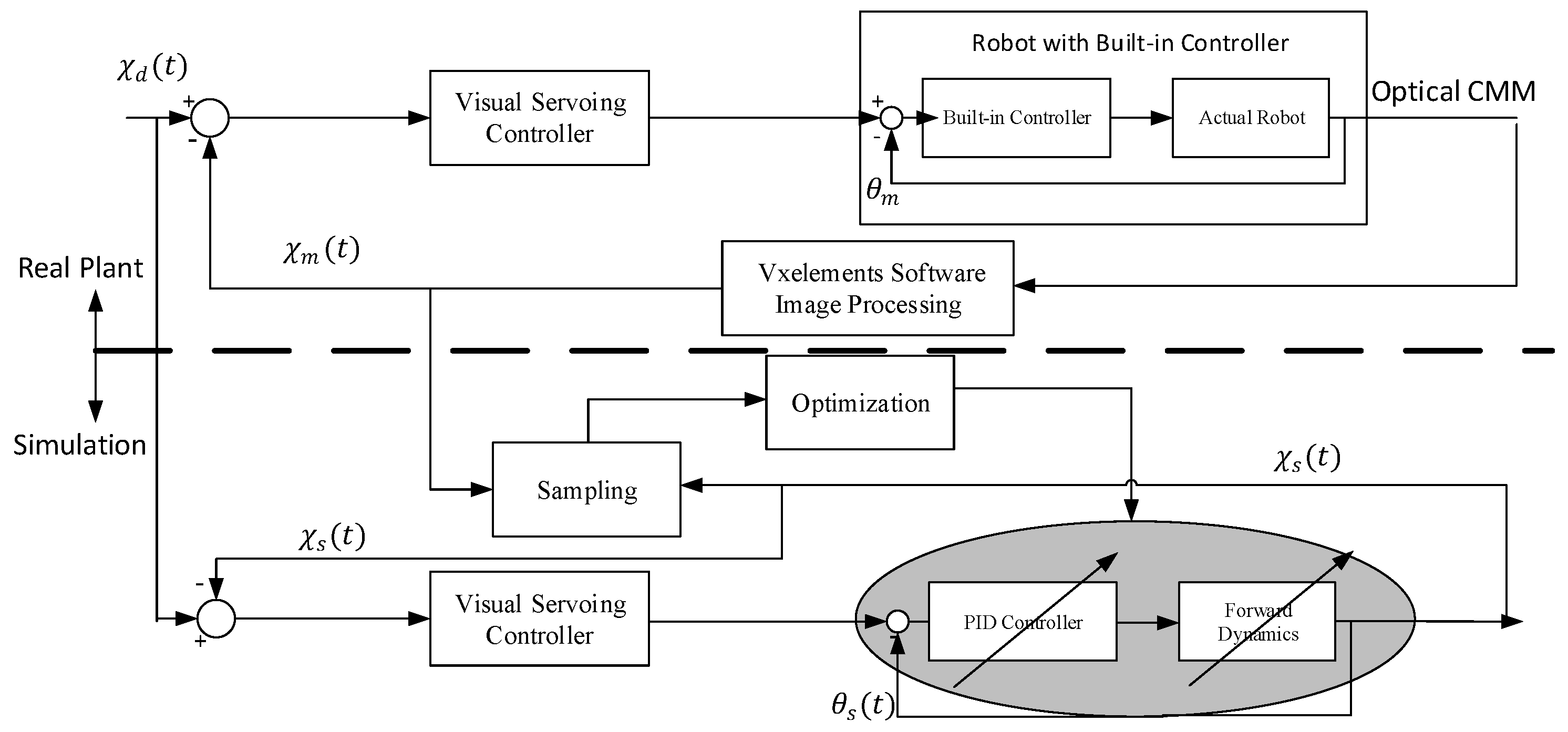
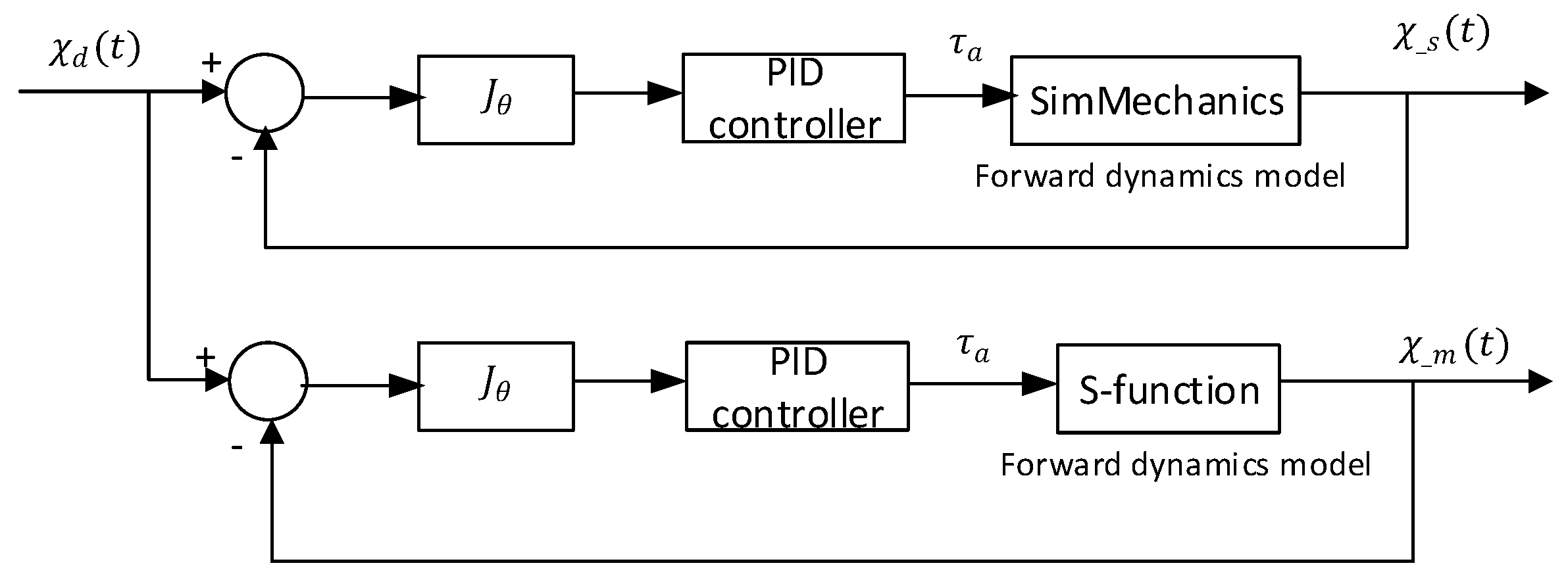
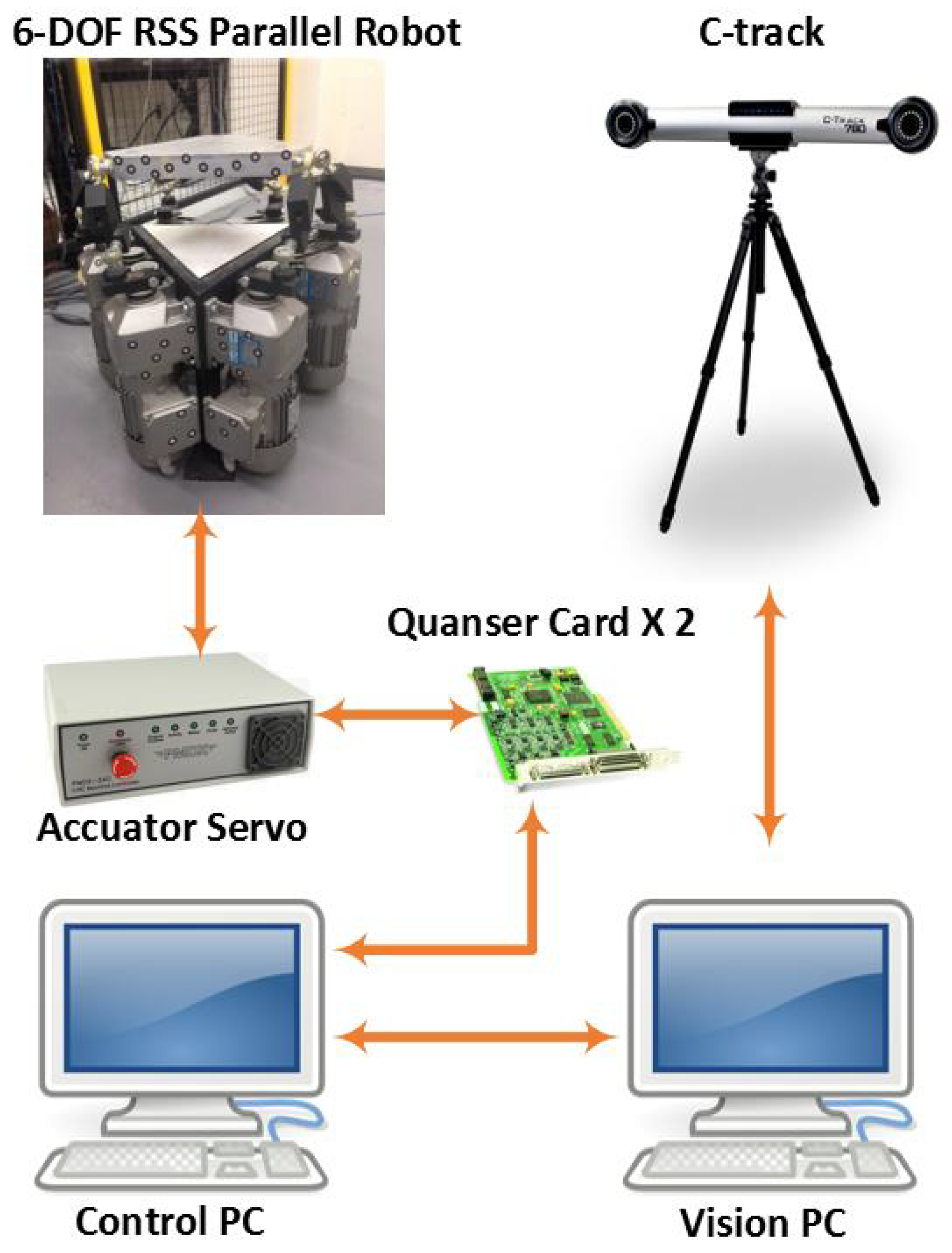
3. Closed-Loop Output-Error Identification Based on Vision Feedback
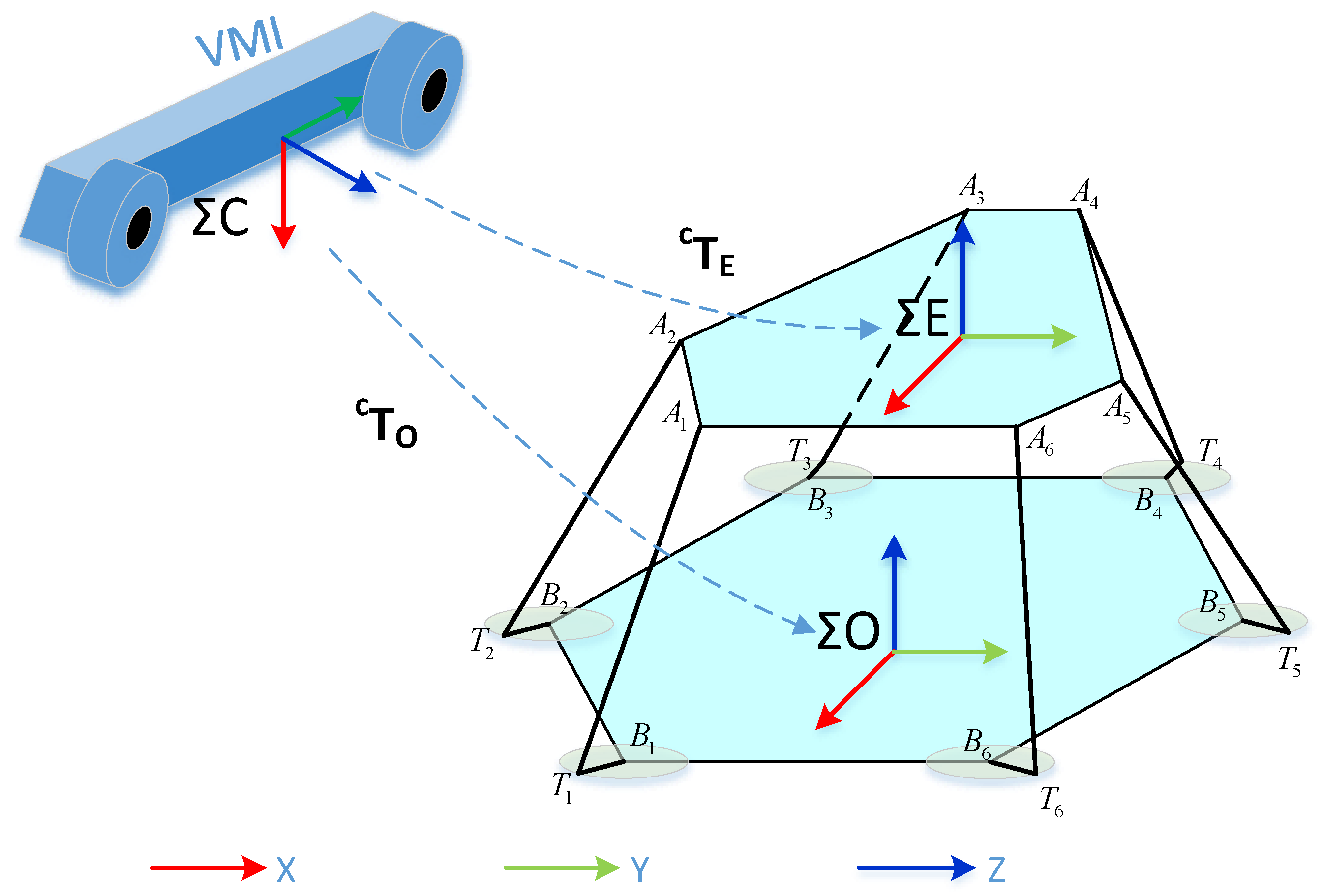
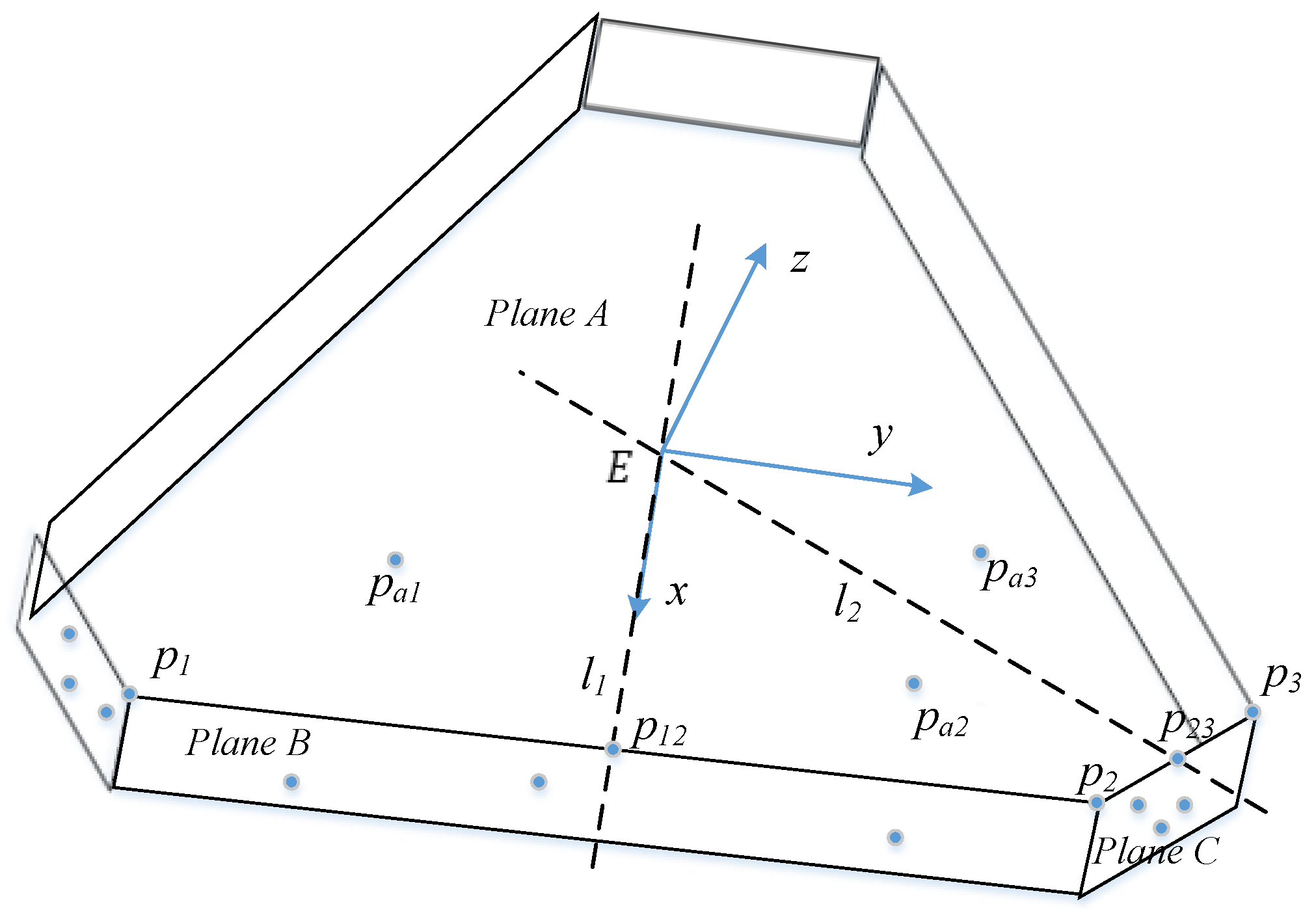
3.1. Pose Estimation Using Optical CMM
3.2. Closed-Loop Output-Error Identification Method
3.3. Modified Exciting Trajectory
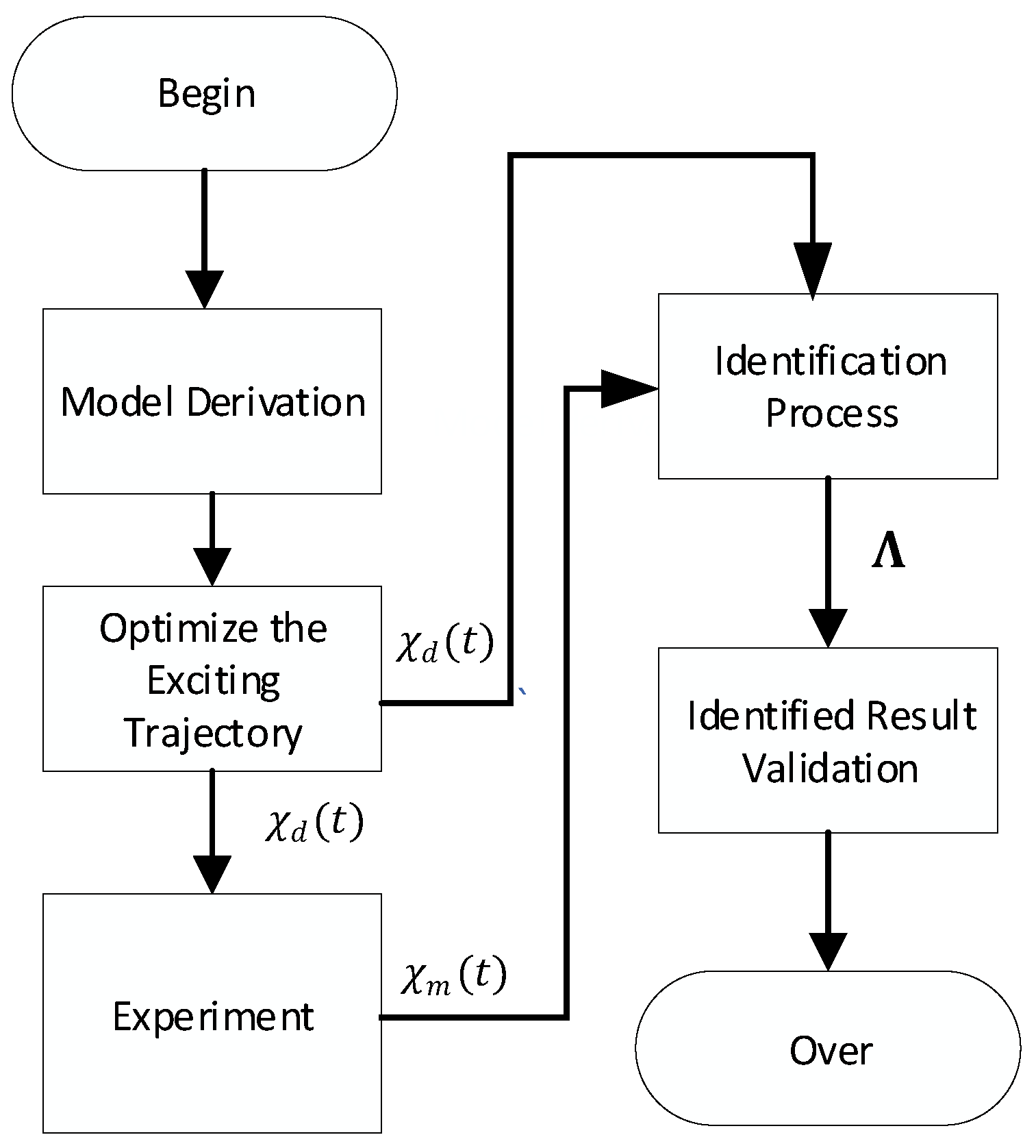
3.4. The Procedure of Identification
4. Simulation and Experiment Results
4.1. Model Validation
4.2. Identification Experiment
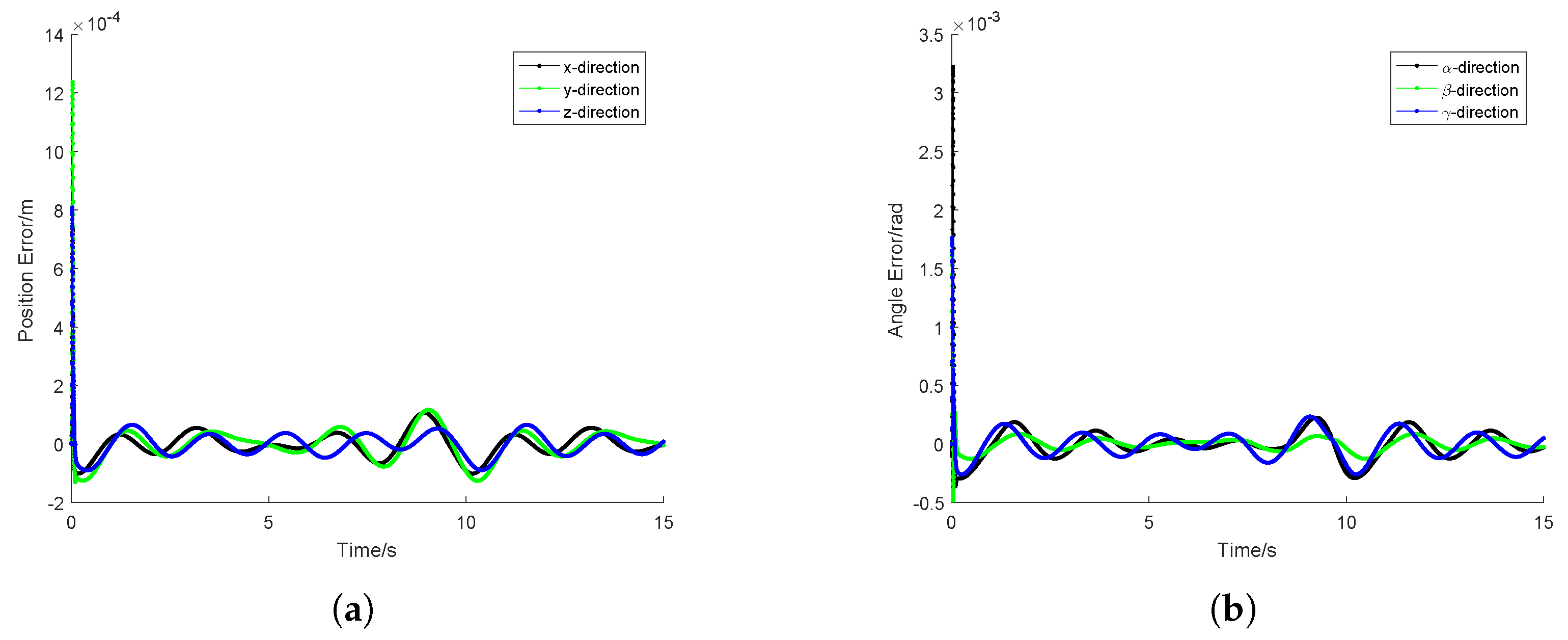
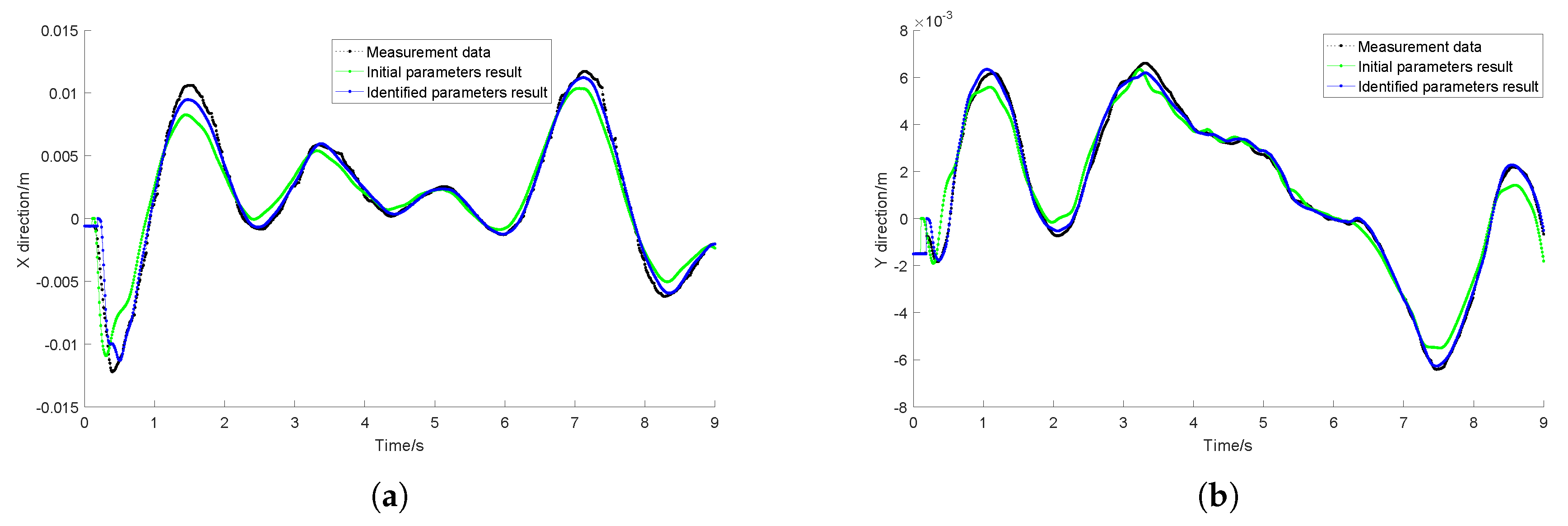
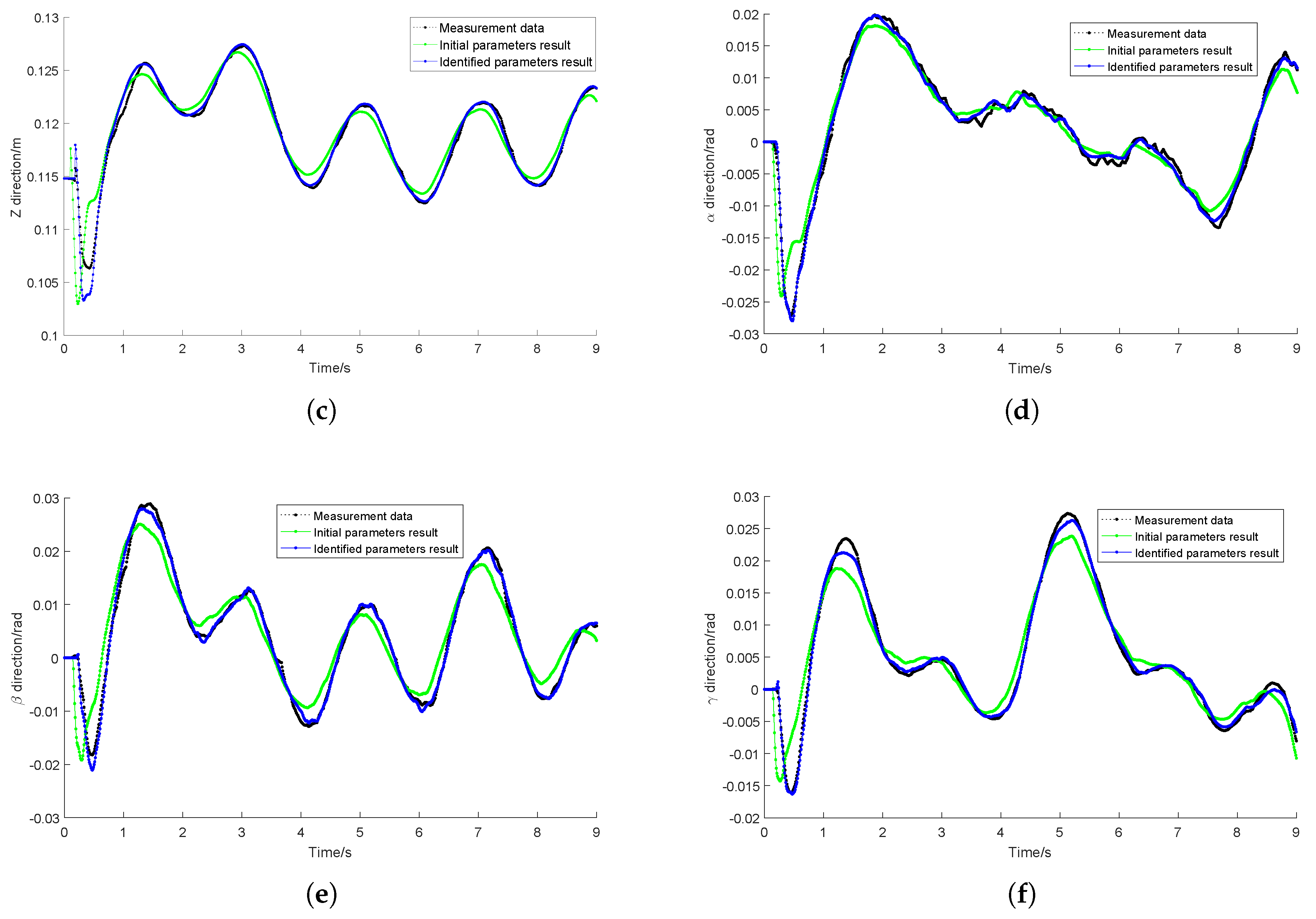
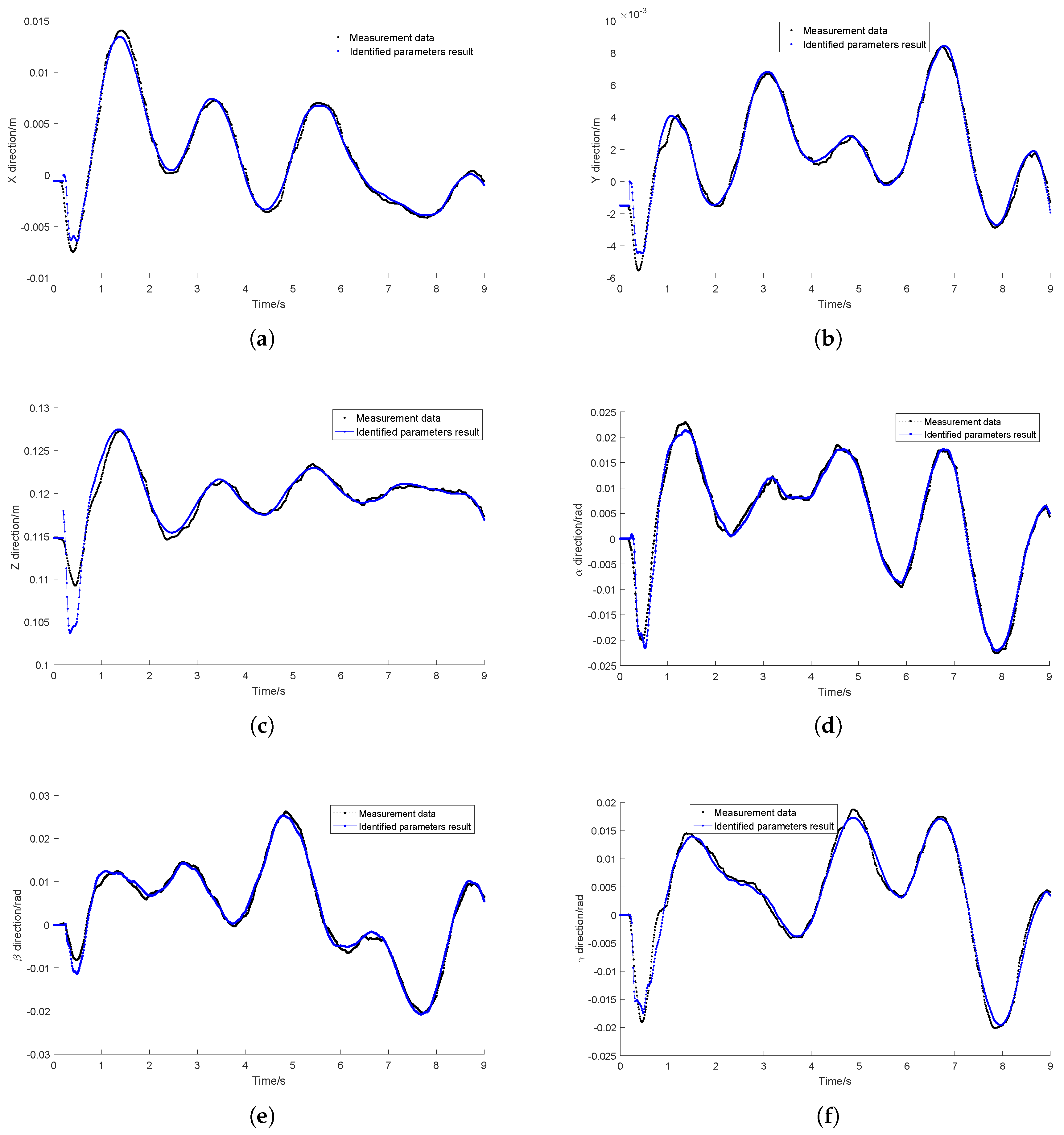
4.3. Identified Results Validation
5. Conclusions and Further Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Miletović, I.; Pool, D.; Stroosma, O.; van Paassen, M.; Chu, Q. Improved Stewart platform state estimation using inertial and actuator position measurements. Control Eng. Pract. 2017, 62, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdellatif, H.; Heimann, B. Model-Based Control for Industrial Robots: Uniform Approaches for Serial and Parallel Structures. In Industrial Robotics; Cubero, S., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2006; Chapter 19; pp. 523–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Teo, M.Y. Kinematic calibration and pose measurement of a medical parallel manipulator by optical position sensors. J. Robot. Syst. 2003, 20, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Absolute Accuracy Industrial Robot Option. 2011. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=2&ved=2ahUKEwiK6L_fndLjAhUQTY8KHYTaBjcQFjABegQIChAE&url=https%3A%2F%2Flibrary.e.abb.com%2Fpublic%2F0f879113235a0e1dc1257b130056d133%2FAbsolute%2520Accuracy%2520EN_R4%2520US%252002_05.pdf&usg=AOvVaw2YHKD4M3X8PjRHuBDV8y_F (accessed on 7 November 2018).
- Taghirad, H.D. Parallel Robots: Mechanics and Control; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Merlet, J.P. Parallel Robots; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta, B.; Mruthyunjaya, T. A Newton-Euler formulation for the inverse dynamics of the Stewart platform manipulator. Mech. Mach. Theory 1998, 33, 1135–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.C.; Pooran, F.J. Dynamic analysis of a 6 DOF CKCM robot end-effector for dual-arm telerobot systems. Robot. Auton. Syst. 1989, 5, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gosselin, C.M. A new approach for the dynamic analysis of parallel manipulators. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 1998, 2, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanganeh, K.E.; Sinatra, R.; Angeles, J. Kinematics and dynamics of a six-degree-of-freedom parallel manipulator with revolute legs. Robotica 1997, 15, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumlu, A.; Erenturk, K. Modeling and trajectory tracking control of 6-DOF RSS type parallel manipulator. Robotica 2014, 32, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljung, L. (Ed.) System Identification (2nd ed.): Theory for the User; Prentice Hall PTR: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hollerbach, J.; Khalil, W.; Gautier, M. Model identification. In Springer Handbook of Robotics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 113–138. [Google Scholar]
- Swevers, J.; Verdonck, W.; De Schutter, J. Dynamic model identification for industrial robots. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 2007, 27, 58–71. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Wang, J.; You, Z. An overview of dynamic parameter identification of robots. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2010, 26, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calanca, A.; Capisani, L.M.; Ferrara, A.; Magnani, L. MIMO closed loop identification of an industrial robot. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2010, 19, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, M.M.; Swevers, J.; Verdonck, W. Maximum likelihood identification of a dynamic robot model: Implementation issues. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2002, 21, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janot, A.; Vandanjon, P.O.; Gautier, M. An instrumental variable approach for rigid industrial robots identification. Control Eng. Pract. 2014, 25, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, M.; Janot, A.; Vandanjon, P.O. A new closed-loop output error method for parameter identification of robot dynamics. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2013, 21, 428–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, E.; Pronzato, L. Identification of Parametric Models from Experimental Data; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Del Prete, A.; Mansard, N.; Ramos, O.E.; Stasse, O.; Nori, F. Implementing torque control with high-ratio gear boxes and without joint-torque sensors. Int. J. Humanoid Robot. 2016, 13, 1550044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunot, M.; Janot, A.; Young, P.C.; Carrillo, F. An improved instrumental variable method for industrial robot model identification. Control Eng. Pract. 2018, 74, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Briot, S.; Gautier, M. Global identification of joint drive gains and dynamic parameters of parallel robots. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 2015, 33, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotjahn, M.; Heimann, B.; Abdellatif, H. Identification of friction and rigid-body dynamics of parallel kinematic structures for model-based control. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 2004, 11, 273–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatif, H.; Heimann, B. Advanced model-based control of a 6-DOF hexapod robot: A case study. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2010, 15, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivas, A.; Poignet, P.; Marquet, F.; Pierrot, F.; Gautier, M. Experimental dynamic identification of a fully parallel robot. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No. 03CH37422), Taipei, Taiwan, 14–19 September 2003; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2003; Volume 3, pp. 3278–3283. [Google Scholar]
- Guegan, S.; Khalil, W.; Lemoine, P. Identification of the dynamic parameters of the orthoglide. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No. 03CH37422), Taipei, Taiwan, 14–19 September 2003; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2003; Volume 3, pp. 3272–3277. [Google Scholar]
- Renaud, P.; Vivas, A.; Andreff, N.; Poignet, P.; Martinet, P.; Pierrot, F.; Company, O. Kinematic and dynamic identification of parallel mechanisms. Control Eng. Pract. 2006, 14, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightcap, C.; Banks, S. Dynamic identification of a mitsubishi pa10-6ce robot using motion capture. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, San Diego, CA, USA, 29 October–2 November 2007; pp. 3860–3865. [Google Scholar]
- Chellal, R.; Cuvillon, L.; Laroche, E. Model identification and vision-based H∞ position control of 6-DoF cable-driven parallel robots. Int. J. Control 2017, 90, 684–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zeng, R.; Xie, W.; Zhang, X. Relative posture-based kinematic calibration of a 6-RSS parallel robot by optical coordinate measurement machine. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2018, 15, 1729881418765861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, T.; Gharaaty, S.; Xie, W.; Joubair, A.; Bonev, I.A. Dynamic Path Tracking of Industrial Robots With High Accuracy Using Photogrammetry Sensor. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 23, 1159–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Krzeminski, M.; El-Tahan, H.; El-Tahan, M. Intelligent friction compensation (IFC) in a harmonic drive. In Proceedings of the IEEE NECEC, St. John’s, NL, Canada, 13 November 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hartley, R.I.; Sturm, P. Triangulation. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 1997, 68, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.J.; Hulls, C.C.W.; Bell, G.S. Relative end-effector control using cartesian position based visual servoing. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1996, 12, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.S. A general photogrammetric method for determining object position and orientation. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1989, 5, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosilow, C.; Joseph, B. Techniques of Model-Based Control; Prentice Hall Professional: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Marlin, T.E. Process Control, Designing Processes and Control Systems for Dynamic Performance. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/c068/dedc943743ce3ee416ba9202a7172b715e3a.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2019).
- Park, K.J. Fourier-based optimal excitation trajectories for the dynamic identification of robots. Robotica 2006, 24, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bona, B.; Curatella, A. Identification of industrial robot parameters for advanced model-based controllers design. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Barcelona, Spain, 18–22 April 2005; pp. 1681–1686. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, R.; Dai, S.; Xie, W.; Zhang, X. Determination of the proper motion range of the rotary actuators of 6-RSS parallel robot. In Proceedings of the 2015 CCToMM Symposium on Mechanisms, Machines, and Mechatronics, Carleton University, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 28–29 May 2015; pp. 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Van Boekel, J. SimMechanics, MapleSim and Dymola: A First Look on Three Multibody Packages. 2009. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/SimMechanics-%2C-MapleSim-and-Dymola- %3A-a-first-look-Boekel/c51909107f1ddb67faf8bda1b387b0659ec04a7f (accessed on 7 November 2018).
- Gautier, M. Numerical calculation of the base inertial parameters of robots. J. Robot. Syst. 1991, 8, 485–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghirad, H.; Belanger, P. Modeling and parameter identification of harmonic drive systems. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 1998, 120, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Dynamic Model Parameters | Initial Value |
|---|---|
| 24.0 | |
| 17.8 | |
| 17.8 | |
| 35.0 | |
| 68.5 | |
| 22.9 | |
| 22.9 | |
| 60.5 | |
| 1.31 | |
| 52.3 | |
| 52.3 | |
| 21.3 |
| Parameters | Initial Value | Identified Value | Parameters | Initial Value | Identified Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24.0 | 23.5 | 1.31 | 1.24 | ||
| 17.8 | 16.1 | 52.3 | 12.9 | ||
| 17.8 | 14.4 | 52.3 | 39.2 | ||
| 35.0 | 33.7 | 1.31 | 1.33 | ||
| 68.5 | 67.1 | 52.3 | 30.7 | ||
| 60.5 | 69.4 | 52.3 | 49.7 | ||
| 68.5 | 68.7 | 1.31 | 1.34 | ||
| 60.5 | 10.0 | 52.3 | 47.0 | ||
| 68.5 | 68.0 | 52.3 | 50.9 | ||
| 60.5 | 22.6 | 0 | 0.104 | ||
| 68.5 | 67.7 | 0 | 0.148 | ||
| 60.5 | 76.0 | 0 | 0.111 | ||
| 68.5 | 68.3 | 0 | 0.187 | ||
| 60.5 | 44.1 | 0 | 0.0336 | ||
| 68.5 | 68.4 | 0 | 0.0993 | ||
| 60.5 | 69.6 | 0 | 0.147 | ||
| 1.31 | 1.33 | 0 | 0.854 | ||
| 52.3 | 63.0 | 0 | 0.104 | ||
| 52.3 | 68.4 | 0 | 0.0803 | ||
| 1.31 | 1.32 | 0 | 0.0828 | ||
| 52.3 | 60.7 | 0 | 0.0349 | ||
| 52.3 | 71.8 | 10 | 10.5 | ||
| 1.31 | 1.25 | 12 | 11.4 | ||
| 52.3 | 22.4 | 0.1 | 0.164 | ||
| 52.3 | 35.5 |
| Before Identification | After Identification | |
|---|---|---|
| x direction (mm) | 1.26 | 0.408 |
| y direction (mm) | 1.16 | 0.235 |
| z direction (mm) | 1.55 | 0.494 |
| direction (rad) | 2.52 | 0.956 |
| direction (rad) | 3.58 | 0.797 |
| direction (rad) | 2.80 | 0.725 |
| x (mm) | y (mm) | z (mm) | (rad) | (rad) | (rad) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 0.517 | 0.384 | 0.709 | 1.091 | 0.963 | 0.966 |
| 2nd | 0.273 | 0.410 | 0.522 | 1.157 | 1.071 | 0.932 |
| 3rd | 0.381 | 0.403 | 0.600 | 1.242 | 0.830 | 1.143 |
| 4th | 0.341 | 0.511 | 0.617 | 1.136 | 0.814 | 1.161 |
| 5th | 0.322 | 0.394 | 0.464 | 1.219 | 0.877 | 0.835 |
| 6th | 0.310 | 0.301 | 0.441 | 1.195 | 1.111 | 1.040 |
| 7th | 0.360 | 0.402 | 0.455 | 1.263 | 1.176 | 1.024 |
| 8th | 0.418 | 0.483 | 0.460 | 1.251 | 1.211 | 1.015 |
| 9th | 0.342 | 0.510 | 0.557 | 1.411 | 1.156 | 0.711 |
| 10th | 0.318 | 0.379 | 0.473 | 1.219 | 1.023 | 0.905 |
| Parameters | Variation Measure | Parameters | Variation Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Ghasemi, A.; Xie, W.; Tian, W. Visual Closed-Loop Dynamic Model Identification of Parallel Robots Based on Optical CMM Sensor. Electronics 2019, 8, 836. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8080836
Li P, Ghasemi A, Xie W, Tian W. Visual Closed-Loop Dynamic Model Identification of Parallel Robots Based on Optical CMM Sensor. Electronics. 2019; 8(8):836. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8080836
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Pengcheng, Ahmad Ghasemi, Wenfang Xie, and Wei Tian. 2019. "Visual Closed-Loop Dynamic Model Identification of Parallel Robots Based on Optical CMM Sensor" Electronics 8, no. 8: 836. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8080836
APA StyleLi, P., Ghasemi, A., Xie, W., & Tian, W. (2019). Visual Closed-Loop Dynamic Model Identification of Parallel Robots Based on Optical CMM Sensor. Electronics, 8(8), 836. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8080836





