ParaLarPD: Parallel FPGA Router Using Primal-Dual Sub-Gradient Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Formulation of the Optimization Problem
- Number of nets: N in ParaLaR and in ParaLarPD.
- Cost/time delay associated to edge e: in ParaLaR and in ParaLarPD.
- Node–arch incidence matrix: in ParaLaR and in ParaLarPD.
2.1. The Channel Width Constraints
2.2. The Choice of Decision Variable
3. Proposed Approach
Our Algorithm
- If at an iteration k, the constraints violation (2a) (i.e., ) is satisfied and , then we obtain the optimal point. Therefore, we stop here because there is no constraint violation (a necessary condition of Lagrange relaxation) [11]. However, this stopping criterion is achieved only if strong duality holds but, in case of our problem, there is weak duality. Details of strong and weak duality can be found in [9,22].
- Let at iteration k, and be the optimal function value and the available function value at the kth iteration, respectively, then the sub-gradient iterations can be stopped when (where is a very small positive number). In this criterion, the optimal value of the objective function is required in advance, which we do not have.
- Another approach is to stop when the step size becomes too small. This is, because the sub-gradient method would get stuck at the current iteration.
| Algorithm 1 ParaLarPD |
| Input: Architecture description file and benchmark file. Output: Route edges.
|
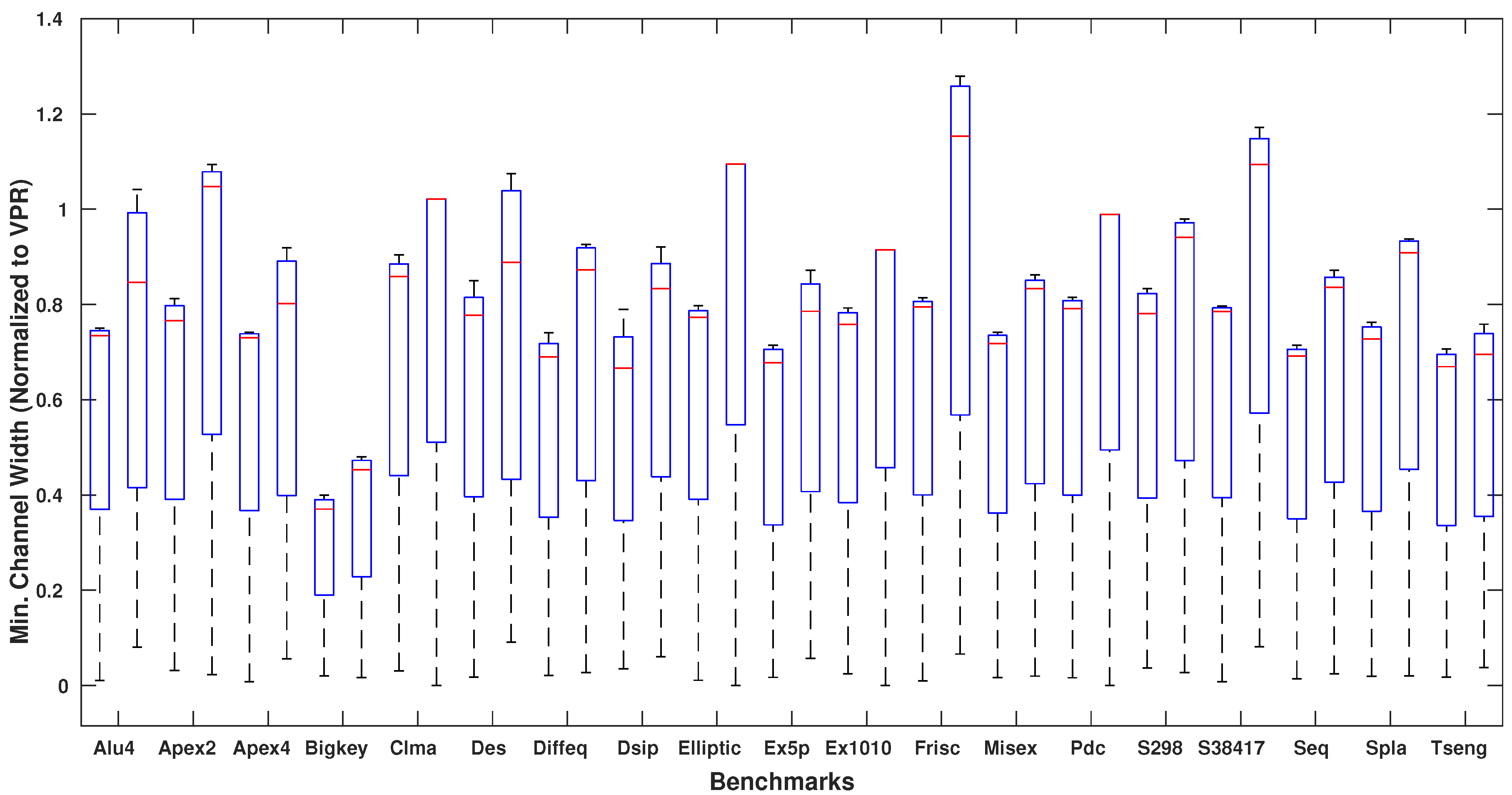
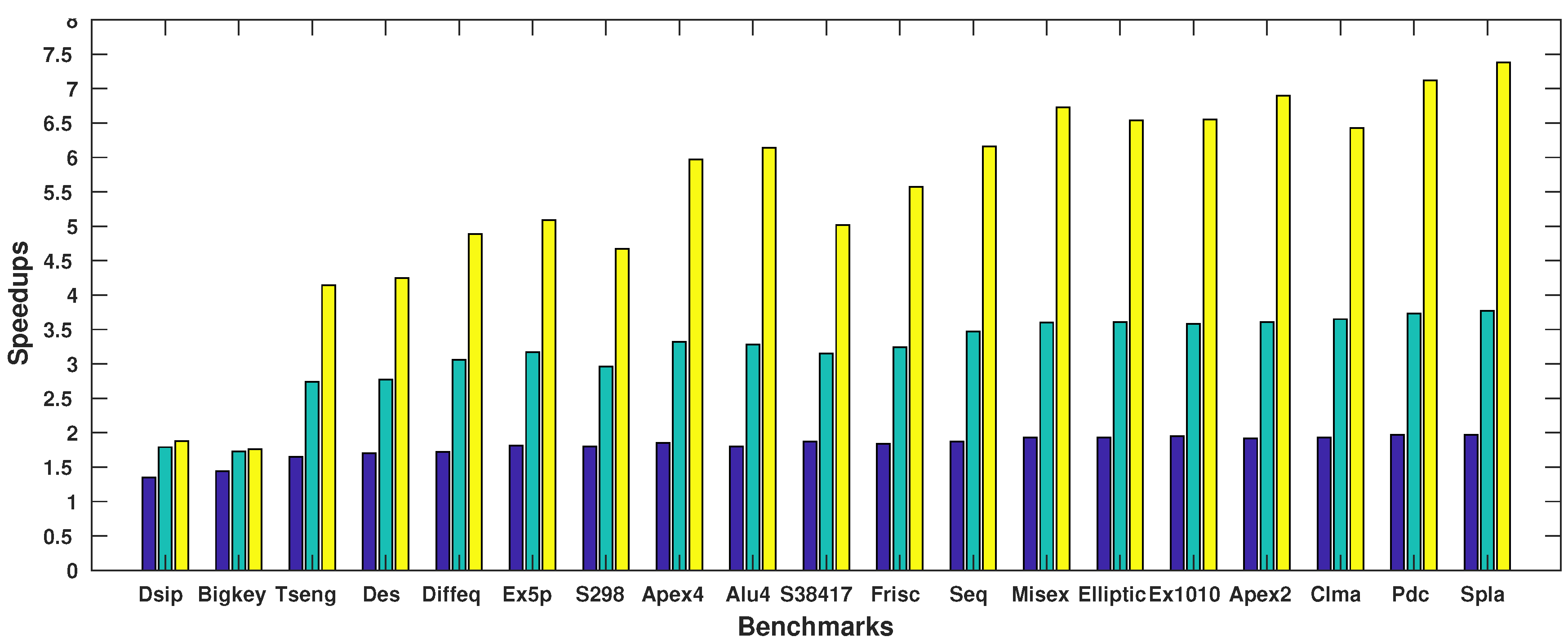
4. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Code Snippet of ParaLarPD
# include " pch . hpp"
# include " router . hpp"
# include " netlist . hpp"
# include " mst . hpp"
# include " timing . hpp"
# include <cmath>
GridGraph create_grid_graph ( int nx , int ny )
{
// Create a grid graph .
}
extern int MAX_ITER;
void Router : : parallel_route_tbb_new_netlist ( Netlist &netlist , int num_threads )
{
Mst<GridGraph> mst ;
int max_iter = MAX_ITER;
boost : : timer : : nanosecond_type total _ routing_ time = 0 ;
for ( const auto &e : grid . edges ( ) ) {
// Initialization of varialbes .
}
vector <Net> nets ;
nets . reserve ( netlist . nets . size ( ) ) ;
int temp = 0 ;
for ( const auto &net : netlist . nets ) {
Net temp_net ;
temp_net . index = temp++;
temp_net . name = net . second−>name ;
temp_net . points . emplace_back ( net . second−>source−>port−>block−>position ) ;
for (const auto &sink : net . second−>s inks ) {
temp_net . points . emplace_back ( sink−>port−>block−>pos i t ion ) ;
}
nets . emplace_back ( std : :move( temp_net ) ) ;
}
vector < list <Point >> previous _ steiners ( nets . size ( ) ) ;
for ( int iter = 0 ; iter < max_iter ; ++ iter ) {
for ( const auto &e : grid . edges ( ) ) {
GridGraphEdgeObject &obj = get ( edge_object , grid , e ) ;
obj . util = 0 ;
assert ( obj . delay == 1 ) ;
put ( edge_weight , grid , e , obj . delay + obj . mult ) ;
}
mst . init ( grid ) ;
vector < list <GridGraph : : edge_descriptor >> route_edges ( nets . size ( ) ) ;
boost : : timer : : cpu_timer timer ;
clock_ t iter _ begin = clock ( ) ;
timer . start ( ) ;
int total _wirelength = 0 ;
const bool nested_zel = true ;
i f ( iter == 0) {
if ( ! nested_zel ) {
int net_num = 0 ;
for ( const auto &net : nets ) {
mst . parallel_zel_new_reduce ( grid , net . points , previous _ steiners [ net_num ] ) ;
net_num++;
}
} else {
tbb : : parallel _ for ( tbb : : blocked_range <int >(0 , nets . size ( ) ) ,
[&mst , &nets , &previous _ steiners , this ]
( const tbb : : blocked_range <int > &range ) −> void
{
for ( int i = range . begin ( ) ; i != range . end ( ) ; ++i ) {
if ( nets [ i ] . point s . size ( ) <= 70) {
mst . parallel_zel_new_reduce ( grid , nets [ i ] . points , previous _ steiners [ i ] ) ;
}
}
} ) ;
}
}
tbb : : spin_mutex mutex ;
tbb : : parallel _ for ( tbb : : blocked_range <int >(0 , nets . size ( ) ) ,
[&mutex , &route_edges , &total _wirelength , &mst , &nets , &previous _ steiners , this ]
( const tbb : : blocked_range <int > &range ) −> void
{
for ( int i = range . begin ( ) ; i != range . end ( ) ; ++i ) {
{
tbb : : spin_mutex : : scoped_lock lock (mutex ) ;
total _wirelength += route_edges [ i ] . size ( ) ;
}
for ( const auto &e : route_edges [ i ] ) {
GridGraphEdgeObject &obj = get ( edge_object , grid , e ) ;
{
tbb : : spin_mutex : : scoped_lock lock (mutex ) ;
obj . util += 1 ; / / channel width
}
}
}
}
) ;
// Calculate 2−norm of the KKT operator of the objective function .
// Update the step size .
for ( const auto &e : grid . edges ( ) ) {
// Update Lagrangian relaxation multipliers , channel width and wire length .
}
// Do timing analysis ( calculate the critical path delay and the execution time ) .
// Print results of each iteration .
// Update the best results .
}
// Print the best results at the end of all iterations
}
References
- Yu, H.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.; Lee, H.M. Recent advances in FPGA reverse engineering. Electronics 2018, 7, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Sun, Z.; Quan, W. Design and Implementation of CPU & FPGA Co-Design Tester for SDN Switches. Electronics 2019, 8, 950. [Google Scholar]
- McMurchie, L.; Ebeling, C. PathFinder: A negotiation-based performance-driven router for FPGAs. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Field-Programmable Gate Arrays, Napa, VA, USA, 12–14 February 1995; pp. 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Cabral, L.A.F.; Aude, J.S.; Maculan, N. TDR: A distributed-memory parallel routing algorithm for FPGAs. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Field-Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL), Montpellier, France, 2–4 September 2002; pp. 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Gort, M.; Anderson, J.H. Accelerating FPGA routing through parallelization and engineering enhancements special section on PAR-CAD 2010. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2012, 31, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoo, C.H.; Kumar, A.; Ha, Y. ParaLaR: A parallel FPGA router based on Lagrangian relaxation. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Field-Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL), London, UK, 2–4 September 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Kim, K. Real-Time Monte Carlo Optimization on FPGA for the Efficient and Reliable Message Chain Structure. Electronics 2019, 8, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, R.H.; Golub, G.H. The Simplex method of linear programming using LU decomposition. Commun. ACM 1969, 12, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.M.; Modarres, M.; Nasrabadi, E.; Nasrabadi, M.M. Fully fuzzified linear programming, solution and duality. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2006, 17, 253–261. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, H.; Ali, Y.M.; Mashaalah, M. Linear programming with rough interval coefficients. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2014, 26, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, M.L. The Lagrangian relaxation method for solving integer programming problems. Manag. Sci. 1981, 27, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, V.; Rose, J. VPR: A new packing, placement and routing tool for FPGA research. In Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on Field-Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL), London, UK, 1–3 September 1997; pp. 213–222. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Circuit Clustering for Cluster-Based FPGAs Using Novel Multiobjective Genetic Algorithms. Ph.D. Thesis, University of York, York, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Czibula, O.G.; Gu, H.; Zinder, Y. A Lagrangian relaxation-based heuristic to solve large extended graph partitioning problems. In WALCOM: Algorithms and Computation; Kaykobad, M., Petreschi, R., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science 9627; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 327–338. [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg, K.; Joborn, M.; Melin, K. Lagrangian based heuristics for the multicommodity network flow problem with fixed costs on paths. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2008, 188, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleplanque, S.; Sidhoum, S.K.; Quilliot, A. Lagrangean heuristic for a multi-plant lot-sizing problem with transfer and storage capacities. RAIRO-Oper. Res. 2013, 47, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Polo-López, L.; Córcoles, J.; Ruiz-Cruz, J. Antenna Design by Means of the Fruit Fly Optimization Algorithm. Electronics 2018, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustig, I.J.; Marsten, R.E.; Shanno, D.F. Interior point methods for linear programming: Computational state of the art. ORSA J. Comput. 1994, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.; Xiao, L.; Mutapcic, A. Subgradient methods. Notes for EE392o Stanford University. Available online: https://web.stanford.edu/class/ee392o/ (accessed on 24 January 2019).
- Bertsekas, D.P. Nondifferentiable optimization via approximation. In Nondifferentiable Optimization; Balinski, M.L., Wolfe, P., Eds.; Mathematical Programming Studies 3; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1975; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, S. Primal-Dual Subgradient Method. Notes for EE364b Stanford University. Available online: https://stanford.edu/class/ee364b/lectures/ (accessed on 24 January 2019).
- Guta, B. Subgradient Optimization Methods in Integer Programming with an Application to a Radiation Therapy Problem. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Kaiserslautern, Kaiserlautern, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Moctar, Y.; Stojilović, M.; Brisk, P. Deterministic parallel routing for FPGAs based on Galois parallel execution model. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Field-Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL), Dublin, Ireland, 27–31 August 2018; pp. 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S. Logic Synthesis and Optimization Benchmarks User Guide: Version 3.0; Microelectronics Center of North Carolina (MCNC): Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
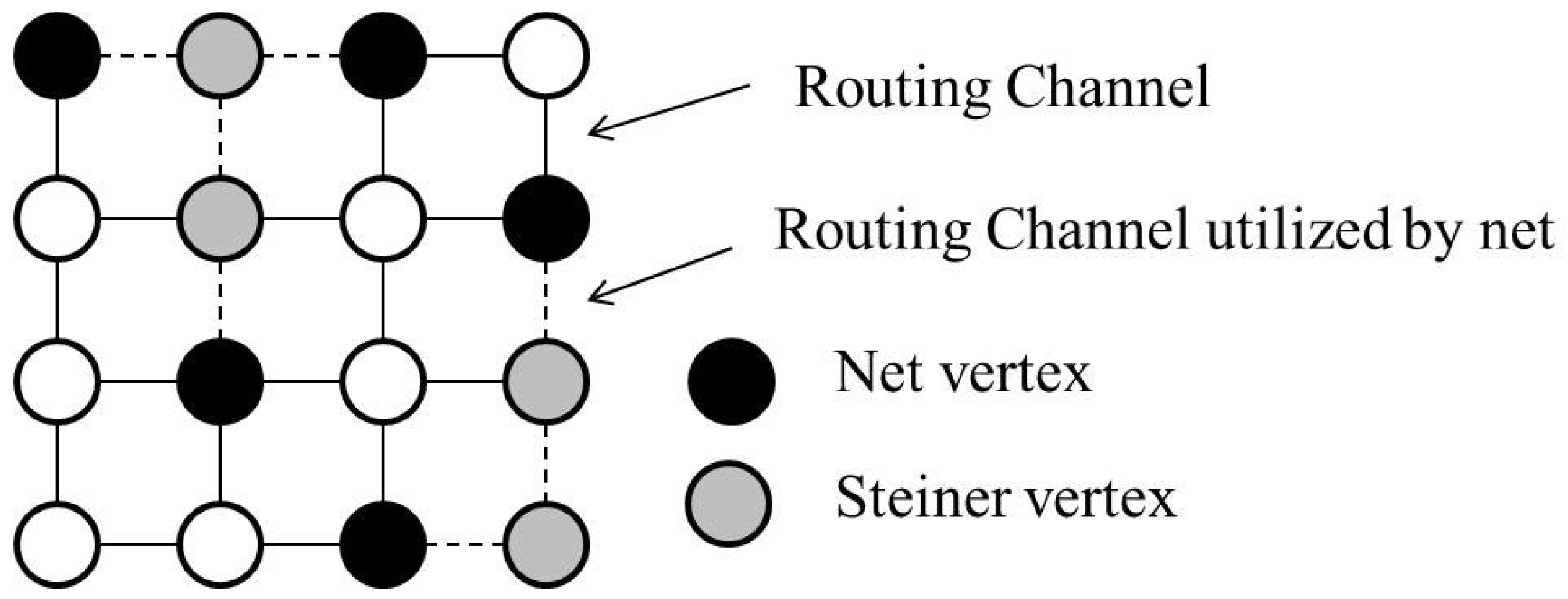
| N | K | Length | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 6 | 0.15 | 0.10 | {3, 6} | 4 |
| Benchmark | Channel Width | Total Wire Length | Critical Path Delay (ns) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| circuits [24] | ParaLarPD | ParaLaR | VPR | ParaLarPD | ParaLaR | VPR | ParaLarPD | ParaLaR | VPR |
| Alu4 | 35.54 | 45.27 | 48 | 5030 | 5029 | 10,480 | 7.30 | 7.01 | 7.50 |
| Apex2 | 50.07 | 68.06 | 64 | 7935 | 7934 | 15,881 | 7.41 | 7.16 | 7.26 |
| Apex4 | 45.57 | 53.48 | 62 | 5630 | 5632 | 10,746 | 7.08 | 6.73 | 6.92 |
| Bigkey | 19.03 | 23.27 | 50 | 3896 | 3896 | 7052 | 4.01 | 4.44 | 3.53 |
| Clma | 81.44 | 96.00 | 94 | 49,278 | 49,284 | 87,398 | 15.46 | 16.31 | 15.08 |
| Des | 31.17 | 40.10 | 40 | 6952 | 6952 | 14,739 | 5.54 | 5.54 | 5.83 |
| Diffeq | 37.52 | 49.23 | 54 | 4349 | 4350 | 9140 | 5.65 | 5.72 | 7.09 |
| Dsip | 25.63 | 32.33 | 38 | 4778 | 4778 | 9742 | 3.62 | 3.45 | 4.20 |
| Elliptic | 57.42 | 81.00 | 74 | 15,124 | 15,124 | 28,271 | 10.83 | 10.91 | 13.98 |
| Ex5p | 48.82 | 57.00 | 70 | 4889 | 4881 | 10,169 | 6.94 | 6.28 | 7.69 |
| Ex1010 | 63.31 | 75.00 | 82 | 23,596 | 23,950 | 43,919 | 14.57 | 12.71 | 10.05 |
| Frisc | 68.71 | 106.38 | 86 | 19,484 | 19,484 | 35,664 | 13.13 | 12.84 | 15.38 |
| Misex | 42.27 | 48.67 | 58 | 5194 | 5192 | 10,061 | 6.49 | 6.68 | 6.08 |
| Pdc | 73.67 | 91.00 | 92 | 30,423 | 30,425 | 53,661 | 12.63 | 12.49 | 11.75 |
| S298 | 39.00 | 46.29 | 48 | 5250 | 5250 | 10,291 | 12.71 | 12.08 | 16.62 |
| S38417 | 50.48 | 72.00 | 64 | 21,907 | 21,906 | 42,597 | 10.43 | 10.03 | 8.82 |
| Seq | 48.85 | 59.00 | 70 | 7654 | 7653 | 14,203 | 6.14 | 6.18 | 6.09 |
| Spla | 59.41 | 74.33 | 80 | 20,117 | 20,117 | 37,384 | 10.43 | 10.69 | 10.11 |
| Tseng | 39.65 | 41.67 | 58 | 2484 | 2484 | 6148 | 5.78 | 5.78 | 6.75 |
| Geo. Mean | 45.55 | 57.05 | 62.75 | 9041 | 9047 | 17,679 | 8.03 | 7.91 | 8.24 |
| Benchmark | Channel Width | Total Wire Length | Critical Path Delay (ns) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| circuits [24] | ParaLarPD | ParaLaR | VPR | ParaLarPD | ParaLaR | VPR | ParaLarPD | ParaLaR | VPR |
| Alu4 | 35.71 | 46.11 | 44 | 5118 | 5118 | 9545 | 8.05 | 7.59 | 6.82 |
| Apex2 | 50.80 | 59.62 | 60 | 7933 | 7933 | 15,629 | 7.40 | 7.79 | 7.29 |
| Apex4 | 45.50 | 64.21 | 58 | 5609 | 5607 | 10,620 | 7.01 | 7.05 | 6.94 |
| Bigkey | 18.50 | 24.75 | 52 | 3919 | 3919 | 6680 | 4.58 | 3.92 | 3.40 |
| Clma | 77.02 | 96.00 | 88 | 49,606 | 49,592 | 84,684 | 16.48 | 15.05 | 13.50 |
| Des | 34.38 | 37.54 | 50 | 7010 | 7011 | 12,977 | 6.30 | 6.30 | 6.08 |
| Diffeq | 38.30 | 52.73 | 50 | 4424 | 4426 | 9109 | 6.44 | 6.27 | 6.63 |
| Dsip | 24.41 | 29.65 | 34 | 4733 | 4733 | 9086 | 4.47 | 3.95 | 4.25 |
| Elliptic | 57.69 | 78.00 | 70 | 15,072 | 15,069 | 27,483 | 10.26 | 10.20 | 11.78 |
| Ex5p | 46.25 | 57.75 | 62 | 4817 | 4815 | 9003 | 6.81 | 6.32 | 6.36 |
| Ex1010 | 64.52 | 80.00 | 74 | 23,014 | 23,012 | 40,995 | 12.89 | 12.46 | 10.75 |
| Frisc | 67.50 | 82.84 | 78 | 19,483 | 19,487 | 34,065 | 12.97 | 13.18 | 14.91 |
| Misex | 45.42 | 50.56 | 52 | 5223 | 5223 | 9513 | 6.06 | 6.27 | 5.75 |
| Pdc | 74.27 | 85.13 | 84 | 30,401 | 30,396 | 53,924 | 13.27 | 13.27 | 11.75 |
| S298 | 39.81 | 45.00 | 44 | 5330 | 5330 | 9237 | 12.70 | 10.99 | 10.99 |
| S38417 | 51.38 | 75.87 | 60 | 21,949 | 21,952 | 39,836 | 10.99 | 9.44 | 9.71 |
| Seq | 55.23 | 58.00 | 64 | 7651 | 7650 | 13,620 | 7.31 | 6.74 | 6.75 |
| Spla | 60.38 | 71.75 | 74 | 20,471 | 20,471 | 36,146 | 11.40 | 11.09 | 9.24 |
| Tseng | 35.70 | 38.73 | 50 | 2472 | 2472 | 5226 | 5.25 | 5.25 | 6.04 |
| Geo. Mean | 45.81 | 56.19 | 58.74 | 9057 | 9058 | 16,653 | 8.36 | 7.98 | 7.86 |
| Value of | Channel Width | Total Wire Length | Critical Path Delay | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max. | Min. | Ave. | STD | Max. | Min. | Ave. | STD | Max. | Min. | Ave. | STD | |
| 3 | 19.98 | 16.7 | 20.16 | 52.63 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 20.69 | 86.9 | |||
| 6 | 18.2 | 16.49 | 18.47 | 39.73 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.011 | |||||
| Benchmark | Execution Time of ParaLarPD (s) | ParaLarPD’s Speed-Ups | Comparison with VPR | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Circuits [24] | 1X | 2X | 4X | 8X | 2X vs. 1X | 4X vs. 1X | 8X vs. 1X | VPR(s) | 1X vs. VPR |
| Alu4 | 8.47 | 4.7 | 2.58 | 1.38 | 1.8 | 3.28 | 6.14 | 12.8 | 1.51 |
| Apex2 | 32.9 | 17.18 | 9.12 | 4.77 | 1.92 | 3.61 | 6.90 | 15.88 | 0.48 |
| Apex4 | 6.93 | 3.74 | 2.09 | 1.16 | 1.85 | 3.32 | 5.97 | 11.69 | 1.69 |
| Bigkey | 1.02 | 0.71 | 0.59 | 0.58 | 1.44 | 1.73 | 1.76 | 18.9 | 18.53 |
| Clma | 84.78 | 43.87 | 23.2 | 13.18 | 1.93 | 3.65 | 6.43 | 496.53 | 5.86 |
| Des | 2.55 | 1.5 | 0.92 | 0.60 | 1.70 | 2.77 | 4.25 | 25.87 | 10.15 |
| Diffeq | 3.18 | 1.85 | 1.04 | 0.65 | 1.72 | 3.06 | 4.89 | 8.57 | 2.69 |
| Dsip | 0.77 | 0.57 | 0.43 | 0.41 | 1.35 | 1.79 | 1.88 | 17.31 | 22.48 |
| Elliptic | 25.06 | 12.98 | 6.95 | 3.83 | 1.93 | 3.61 | 6.54 | 57.31 | 2.29 |
| Ex1010 | 27.95 | 14.36 | 7.8 | 4.27 | 1.95 | 3.58 | 6.55 | 91.38 | 3.27 |
| Ex5p | 4.12 | 2.28 | 1.3 | 0.81 | 1.81 | 3.17 | 5.09 | 9.54 | 2.32 |
| Frisc | 11.65 | 6.34 | 3.6 | 2.09 | 1.84 | 3.24 | 5.57 | 10.52 | 0.90 |
| Misex | 19.71 | 10.2 | 5.47 | 2.93 | 1.93 | 3.60 | 6.73 | 9.77 | 0.50 |
| Pdc | 94.9 | 48.06 | 25.44 | 13.33 | 1.97 | 3.73 | 7.12 | 202.43 | 2.13 |
| S298 | 4.95 | 2.75 | 1.67 | 1.06 | 1.80 | 2.96 | 4.67 | 16.61 | 3.36 |
| S38417 | 10.1 | 5.4 | 3.21 | 2.01 | 1.87 | 3.15 | 5.02 | 115.95 | 11.48 |
| Seq | 14.66 | 7.82 | 4.22 | 2.38 | 1.87 | 3.47 | 6.16 | 15.41 | 1.05 |
| Spla | 109.22 | 55.58 | 28.96 | 14.79 | 1.97 | 3.77 | 7.38 | 78.47 | 0.72 |
| Tseng | 1.45 | 0.88 | 0.53 | 0.35 | 1.65 | 2.74 | 4.14 | 5.78 | 3.99 |
| Geo. Mean | 9.86 | 5.49 | 3.17 | 1.93 | 1.80 | 3.11 | 5.11 | 26.62 | 2.70 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agrawal, R.; Ahuja, K.; Hau Hoo, C.; Duy Anh Nguyen, T.; Kumar, A. ParaLarPD: Parallel FPGA Router Using Primal-Dual Sub-Gradient Method. Electronics 2019, 8, 1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8121439
Agrawal R, Ahuja K, Hau Hoo C, Duy Anh Nguyen T, Kumar A. ParaLarPD: Parallel FPGA Router Using Primal-Dual Sub-Gradient Method. Electronics. 2019; 8(12):1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8121439
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgrawal, Rohit, Kapil Ahuja, Chin Hau Hoo, Tuan Duy Anh Nguyen, and Akash Kumar. 2019. "ParaLarPD: Parallel FPGA Router Using Primal-Dual Sub-Gradient Method" Electronics 8, no. 12: 1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8121439
APA StyleAgrawal, R., Ahuja, K., Hau Hoo, C., Duy Anh Nguyen, T., & Kumar, A. (2019). ParaLarPD: Parallel FPGA Router Using Primal-Dual Sub-Gradient Method. Electronics, 8(12), 1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8121439






