Satellite IoT Edge Intelligent Computing: A Research on Architecture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Related Research on Satellite Internet of Things
2.2. Related Research on Distributed Deep Learning
2.3. Related Research on Edge Intelligent Computing
3. Satellite IoT Edge Intelligent Computing Architecture
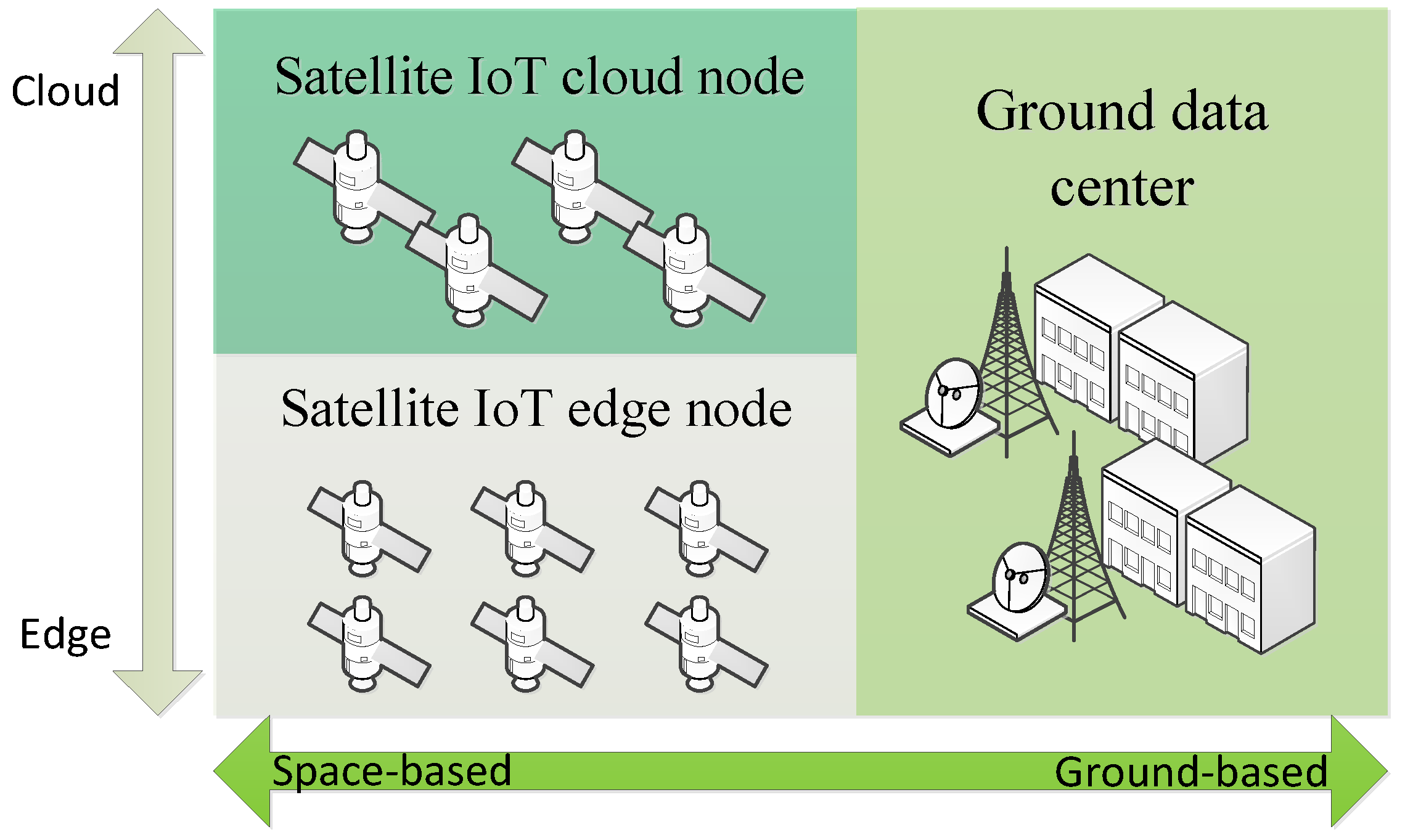
3.1. Satellite IoT Edge Computing
3.2. Distributed Intelligent Computing Architecture in Satellite IoT Edge Computing
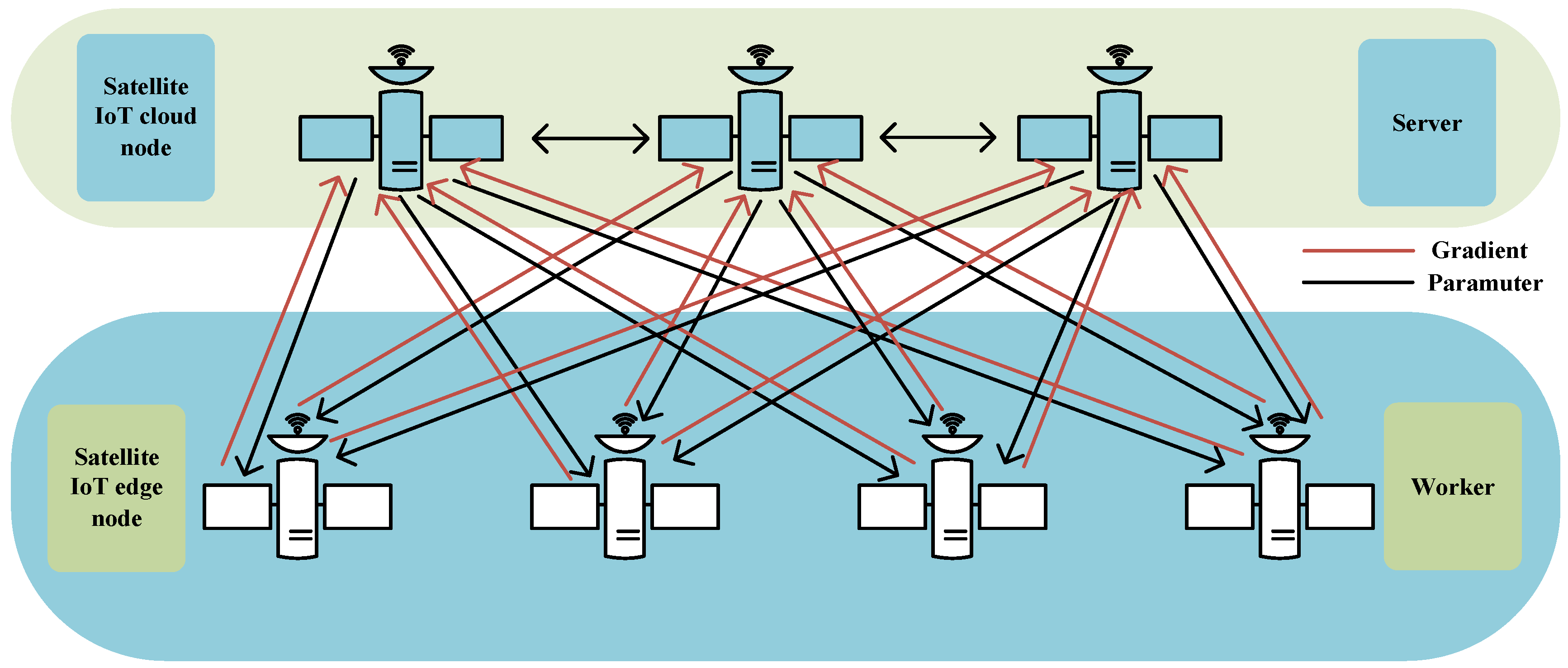
3.2.1. Cross-Layer Satellite IoT Edge Intelligent Computing Architecture
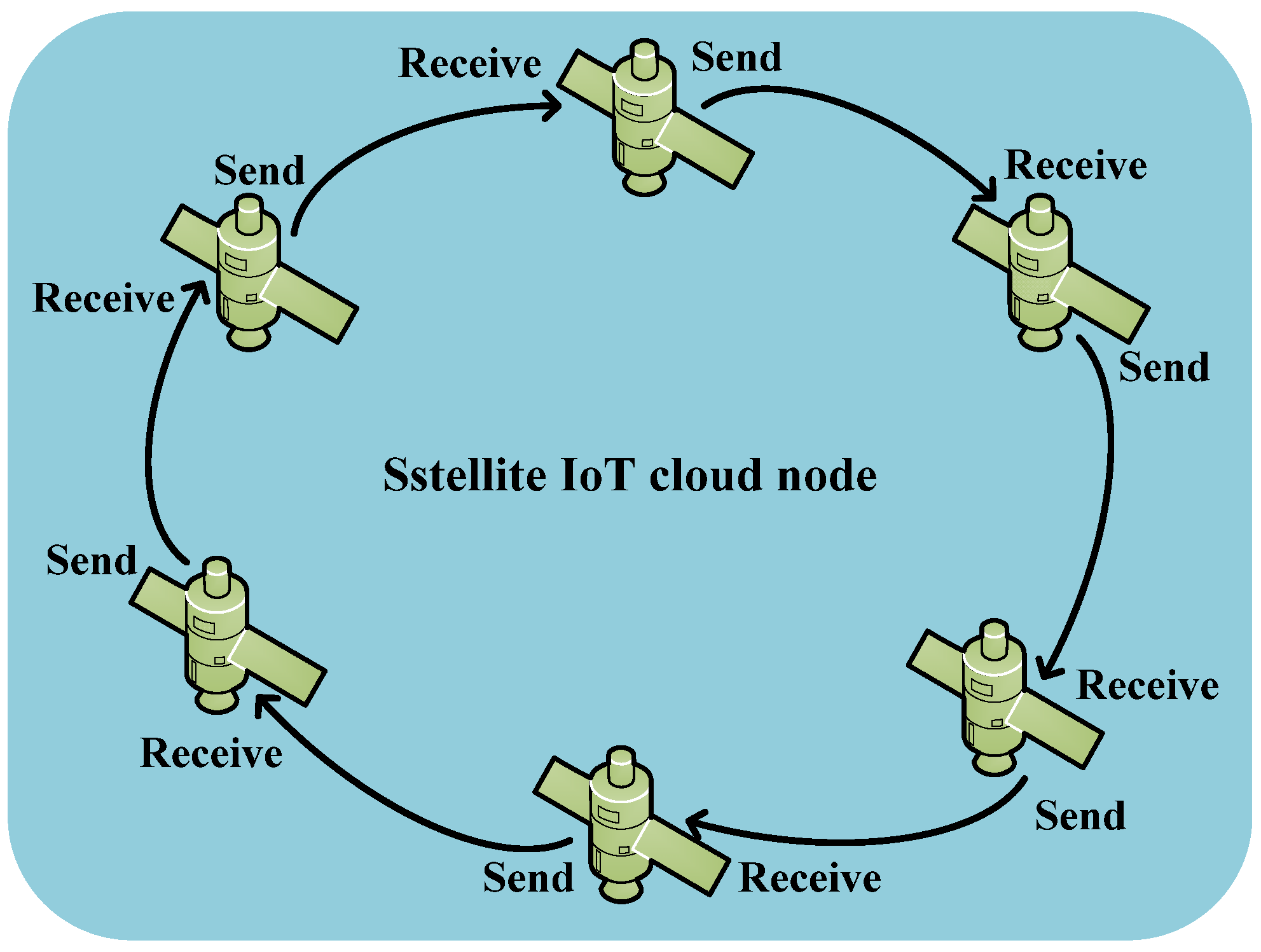
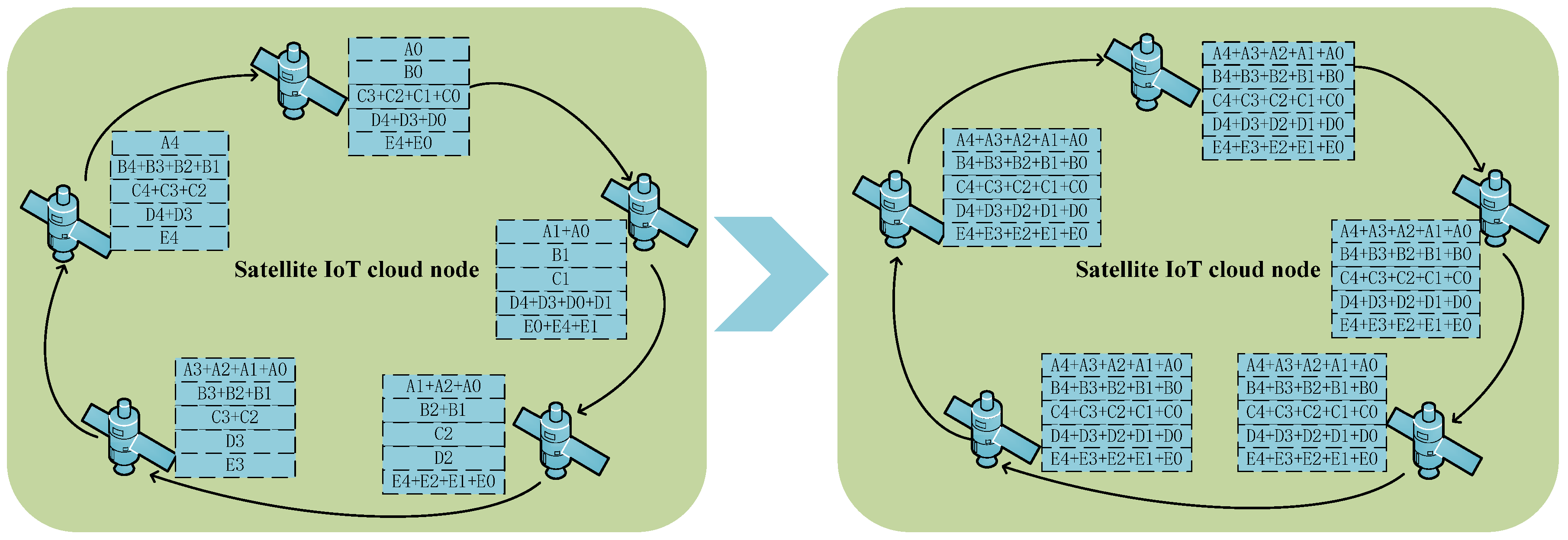
3.2.2. Training-Inference-Isolated Satellite IoT Edge Intelligent Computing Architecture
3.3. Summary of Satellite IoT Edge Intelligent Computing Architecture
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Satellite IoT Connectivity and Coverage Performance
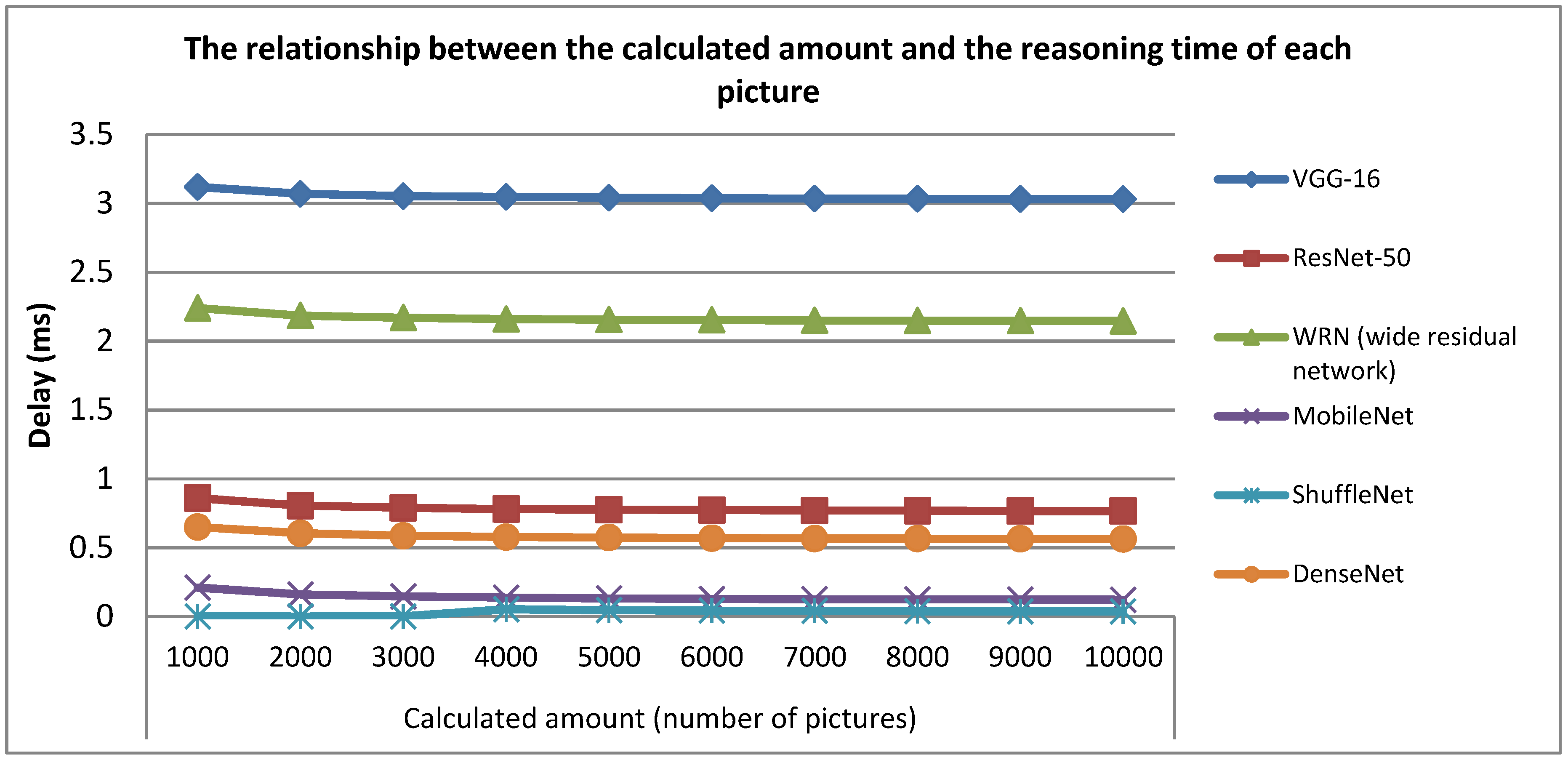
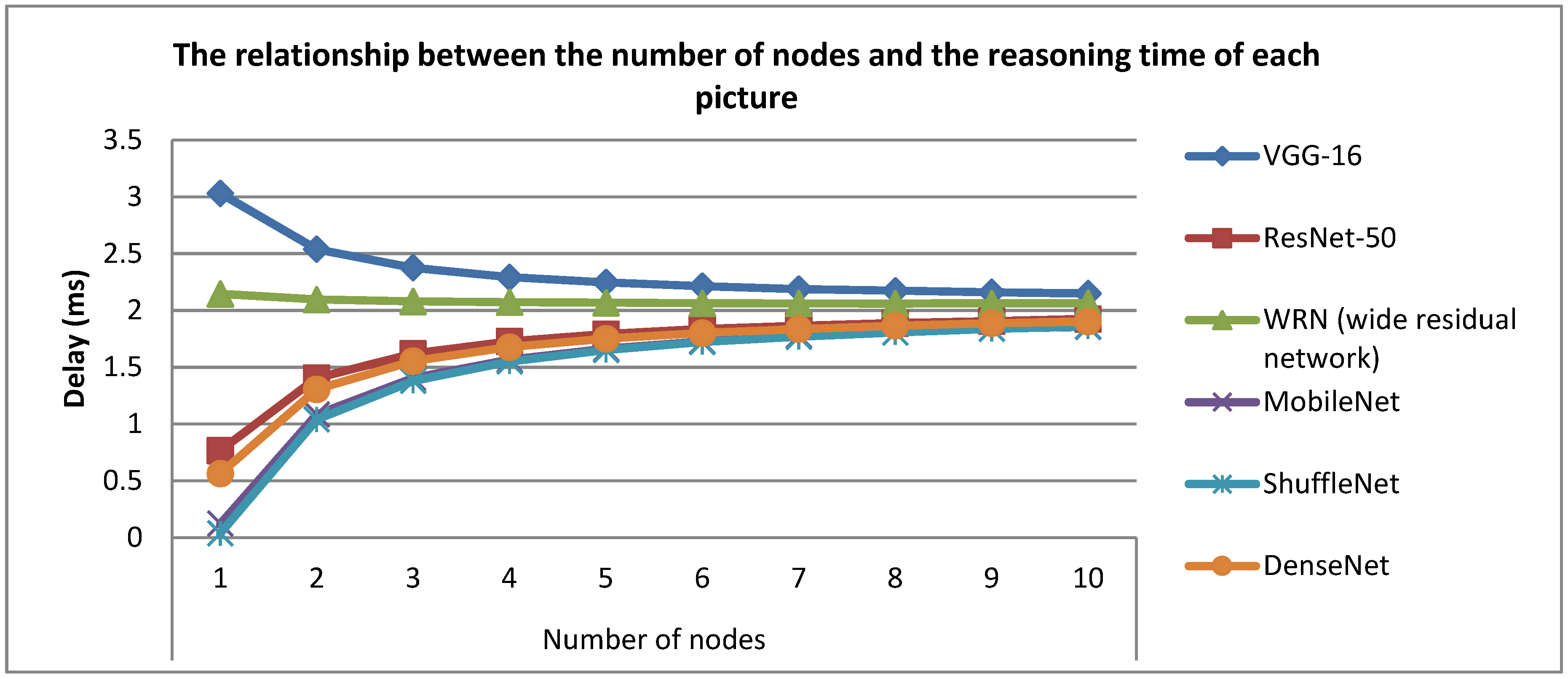
4.2. Satellite IoT Edge Intelligent Computing Architecture Performance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atzori, L.; Iera, A.; Morabito, G. The Internet of Things: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2010, 54, 2787–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, L.D.; Zhao, S. The internet of things: A survey. Inf. Syst. Front. 2015, 17, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coverage Maps. 2019. Available online: https://opensignal.com/networks (accessed on 20 September 2019).
- Qu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Cao, H.; Xie, J. LEO Satellite Constellation for Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 18391–18401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanctis, M.D.; Cianca, E.; Araniti, G.; Bisio, I.; Prasad, R. Satellite communications supporting internet of remote things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2016, 3, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueck, M.; Strinati, E.C.; Kim, I.; Clemente, A.; Dore, J.; Domenico, A.D.; Kim, T.; Choi, T.; Chung, H.K.; Destino, G.; et al. 5G CHAMPION-Rolling out 5G in 2018. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Washington, DC, USA, 4–8 December 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kodheli, O.; Guidotti, A.; Vanelli-Coralli, A. Integration of Satellites in 5G through LEO Constellations. In Proceedings of the GLOBECOM 2017-2017 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Singapore, 4–8 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Boero, L.; Bruschi, R.; Davoli, F.; Marchese, M.; Patrone, F. Satellite networking integration in the 5g ecosystem: Research trends and open challenges. IEEE Netw. 2018, 32, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaceflight Now/Pole Star Publications Ltd. The Completed Space Launch Log. 2019. Available online: https://spaceflightnow.com/launch-log/ (accessed on 28 September 2019).
- Krebs, G.D. Chronology of Space Launches. 2019. Available online: https://space.skyrocket.de/directories/chronology.htm (accessed on 28 September 2019).
- Lovelly, T.M.; Bryan, D.; Cheng, K.; Kreynin, R.; George, A.D.; Gordon-Ross, A.; Mounce, G. A framework to analyze processor architectures for next-generation on-board space computing. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 1–8 March 2014; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, L.; Lou, Y.; Olusola, O. Revisiting elliptical satellite orbits to enhance the O3b constellation. arXiv 2014, arXiv:14072521. [Google Scholar]
- Foreman, V.; Siddiqi, A.; de Weck, O. Large satellite constellation orbital debris impacts: Case studies of oneweb and spacex proposals. In Proceedings of the AIAA SPACE and Astronautics Forum and Exposition, Orlando, FL, USA, 12–14 September 2017; p. 5200. [Google Scholar]
- Yousefpour, A.; Fung, C.; Nguyen, T.; Kadiyala, K.P.; Jalali, F.; Niakanlahiji, A.; Kong, J.; Jue, J.P. All One Needs to Know about Fog Computing and Related Edge Computing Paradigms: A Complete Survey. CoRR 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, P.; Becvar, Z. Mobile edge computing: A survey on architecture and computation offloading. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 1628–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.C.; Patel, M.; Sabella, D.; Sprecher, N.; Young, V. Mobile edge computing—A key technology towards 5G. ETSI White Paper 2015, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Bonomi, F.; Milito, R.; Zhu, J.; Addepalli, S. Fog computing and its role in the internet of things. In Proceedings of the First Edition of the MCC Workshop on Mobile Cloud Computing, Helsinki, Finland, 17 August 2012; pp. 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Puliafito, C.; Mingozzi, E.; Anastasi, G. Fog computing for the internet of mobile things: Issues and challenges. In Proceedings of the Smart Computing (SMARTCOMP), Hong Kong, China, 29–31 May 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kak, A.; Guven, E.; Ergin, U.E.; Akyildiz, I.F. Performance Evaluation of SDN-Based Internet of Space Things. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Globecom Workshops, Abu Dhabi, UAE, 9–13 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Niu, D.; Li, B. Distributed Machine Learning with a Serverless Architecture. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2019—IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Paris, France, 29 April–2 May 2019; pp. 1288–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M. Scaling distributed machine learning with the parameter server. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Big Data Science and Computing, Beijing, China, 6–8 October 2014; pp. 583–598. [Google Scholar]
- Technical, B.R. Bringing HPC Techniques to Deep Learning. 2017. Available online: http://andrew.gibiansky.com/blog/machine-learning/baidu-allreduce/ (accessed on 21 February 2017).
- Sergeev, A.; Balso, M.D. Horovod: Fast and easy distributed deep learning in TensorFlow. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.05799. [Google Scholar]
- Developers, P. PaddlePaddle. 2019. Available online: https://github.com/PaddlePaddle (accessed on 20 September 2019).
- Alibaba. Mobile Neural Network. 2019. Available online: https://github.com/alibaba/MNN (accessed on 20 September 2019).
- Yerabolu, S.; Kim, S.; Gomena, S.; Li, X.; Patel, R.; Bhise, S.; Aryafar, E. DeepMarket: An Edge Computing Marketplace with Distributed TensorFlow Execution Capability. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2019—IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), Paris, France, 29 April–2 May 2019; pp. 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Starkman, J.; Lee, Y.; Chen, H.; Qian, X.; Huang, M. Distributed Deep Learning Optimized System over the Cloud and Smart Phone Devices. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, X. Edge intelligence: On-demand deep learning model co-inference with device-edge synergy. In Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Mobile Edge Communications, MECOMM 2018, Budapest, Hungary, 20 August 2018; pp. 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Ota, K.; Dong, M. Learning IoT in Edge: Deep Learning for the Internet of Things with Edge Computing. IEEE Netw. 2018, 32, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Seo, J.; Baek, Y. CamThings: IoT Camera with Energy-Efficient Communication by Edge Computing based on Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 28th International Telecommunication Networks and Applications Conference (ITNAC 2018), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 21–23 November 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Plastiras, G.; Terzi, M.; Kyrkou, C.; Theocharidcs, T. Edge Intelligence: Challenges and Opportunities of Near-Sensor Machine Learning Applications. In Proceedings of the 29th IEEE International Conference on Application-Specific Systems, Architectures and Processors (ASAP 2018), Milan, Italy, 10–12 July 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Keshavarzi, A.; Van Den Hoek, W. Edge Intelligence—On the Challenging Road to a Trillion Smart Connected IoT Devices. IEEE Des. Test 2019, 36, 41–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Cao, S.; Gong, Y.; Han, H.; Wei, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, S. SatEC: A 5G Satellite Edge Computing Framework Based on Microservice Architecture. Sensors 2019, 19, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Tseng, F. Satellite mobile edge computing: improving QoS of high-speed satellite-terrestrial networks using edge computing techniques. IEEE Netw. 2019, 33, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Cao, S. Application of Edge Intelligent Computing in Satellite Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Smart Internet of Things (SmartIoT), Tianjin, China, 9–11 August 2019; pp. 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Calheiros, R.N.; Ranjan, R.; Beloglazov, A.; De Rose, C.A.F.; Buyya, R. CloudSim: A toolkit for modeling and simulation of cloud computing environments and evaluation of resource provisioning algorithms. Softw. Pract. Exp. 2011, 41, 23–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonmez, C.; Ozgovde, A.; Ersoy, C. EdgeCloudSim: An environment for performance evaluation of Edge Computing systems. In Proceedings of the 2017 Second International Conference on Fog and Mobile Edge Computing (FMEC), Valencia, Spain, 8–11 May 2017; pp. 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:14091556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Zagoruyko, S.; Komodakis, N. Wide Residual Networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:160507146. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Bo, C.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:170404861. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet: An Extremely Efficient Convolutional Neural Network for Mobile Devices. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6848–6856. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2261–2269. [Google Scholar]
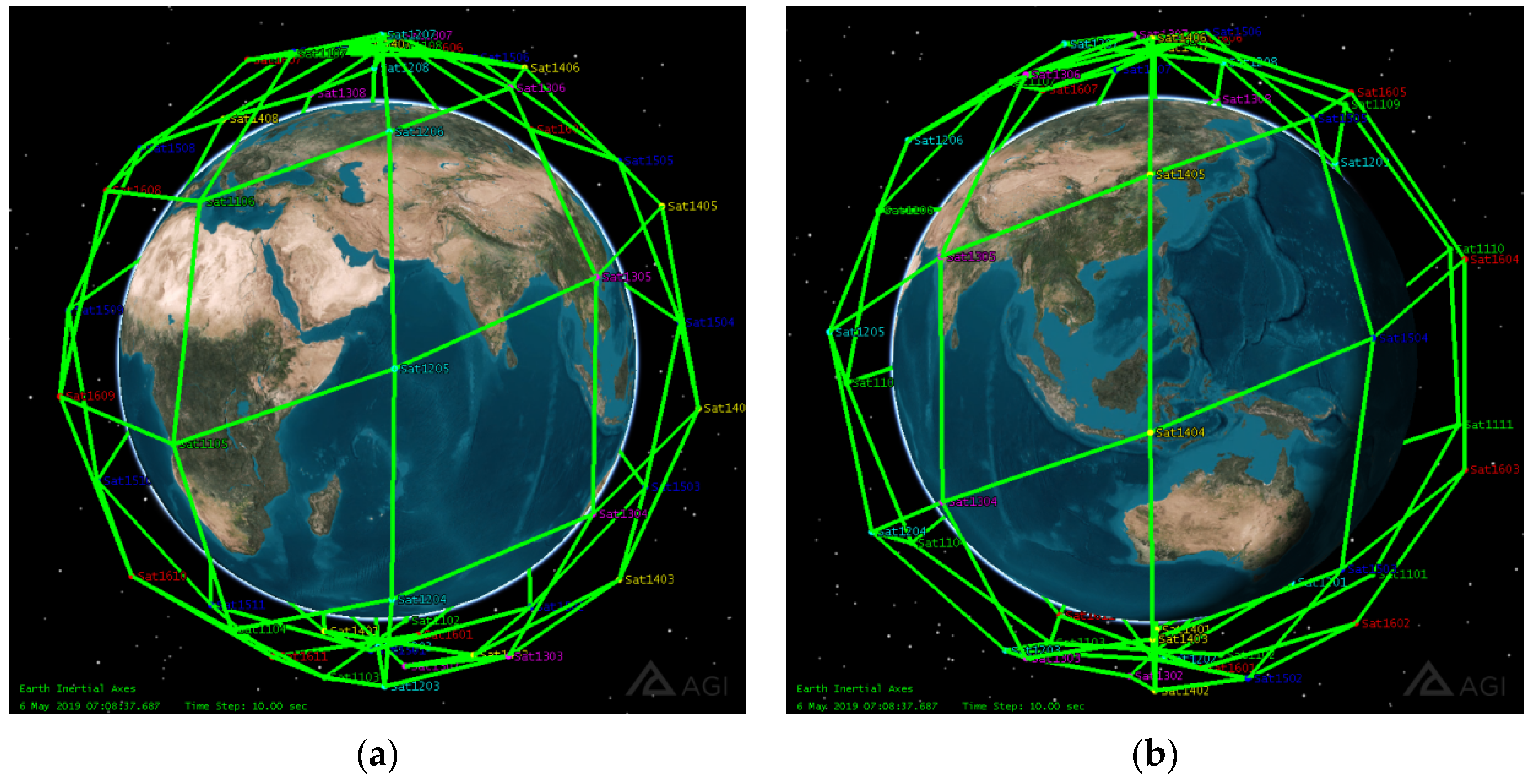
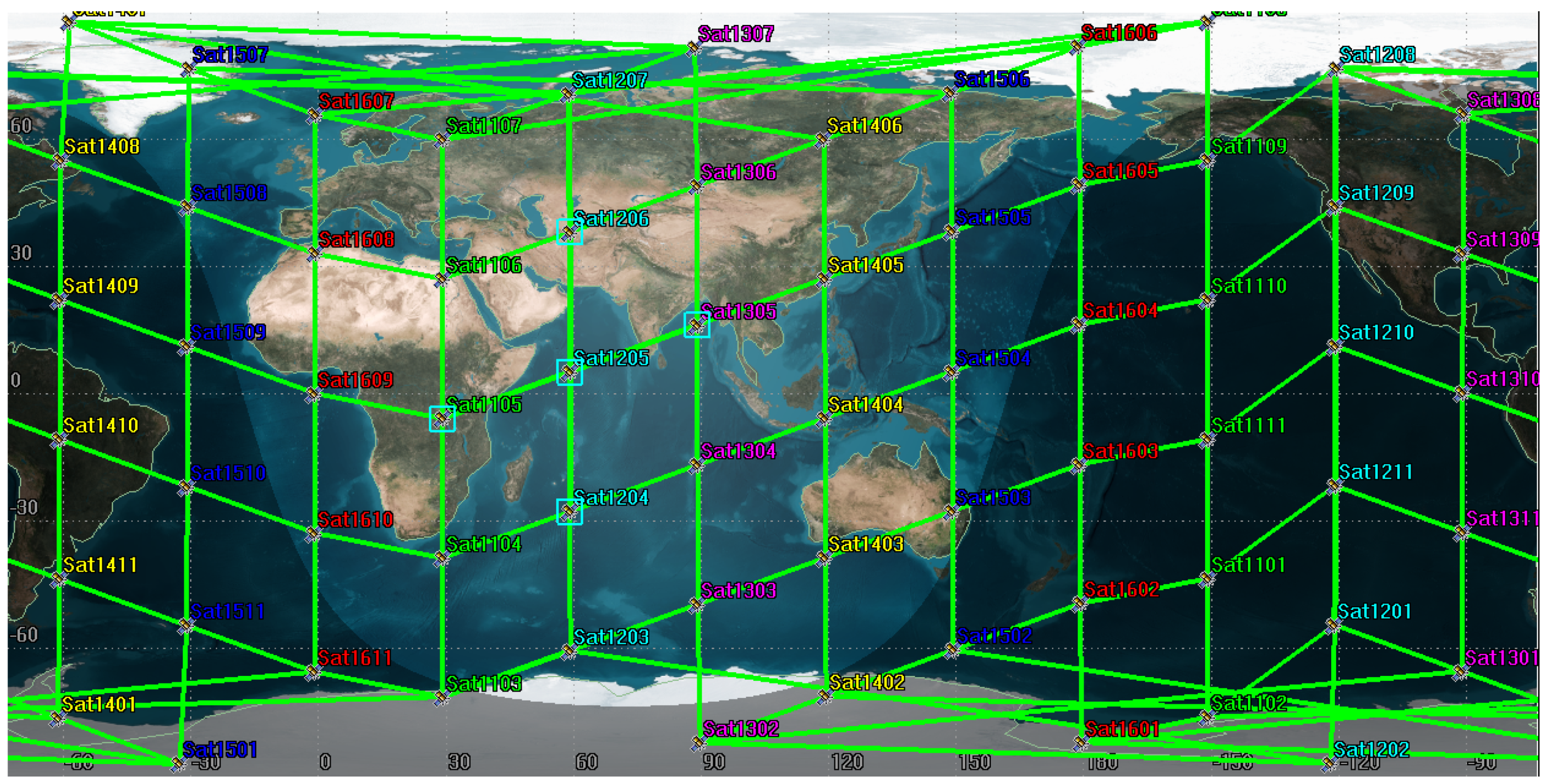
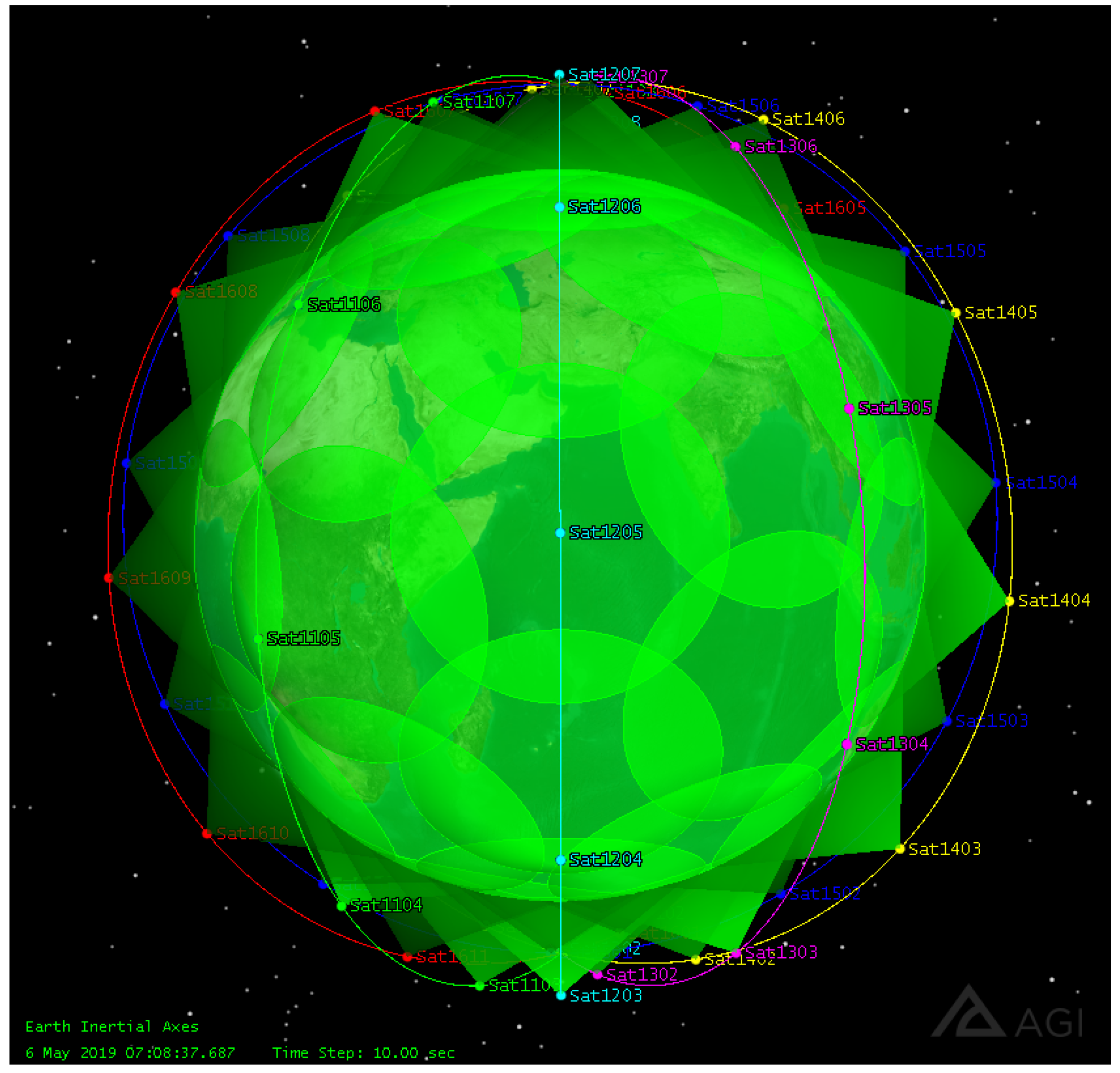
| Connection Pair | Connection Duration/Day | Connection Distance/km |
|---|---|---|
| Sat1205-to-Sat1105 | 24 h | 1446.81–4327.11 1 |
| Sat1205-to-Sat1204 | 24 h | 4439.16 |
| Sat1205-to-Sat1206 | 24 h | 4439.16 |
| Sat1205-to-Sat1305 | 24 h | 1446.81–4327.11 1 |
| Percent Coverage (Global) | Covering Latitude | Coverage Time of Different Latitudes |
|---|---|---|
| 100% | −90° to 90° | 100% |
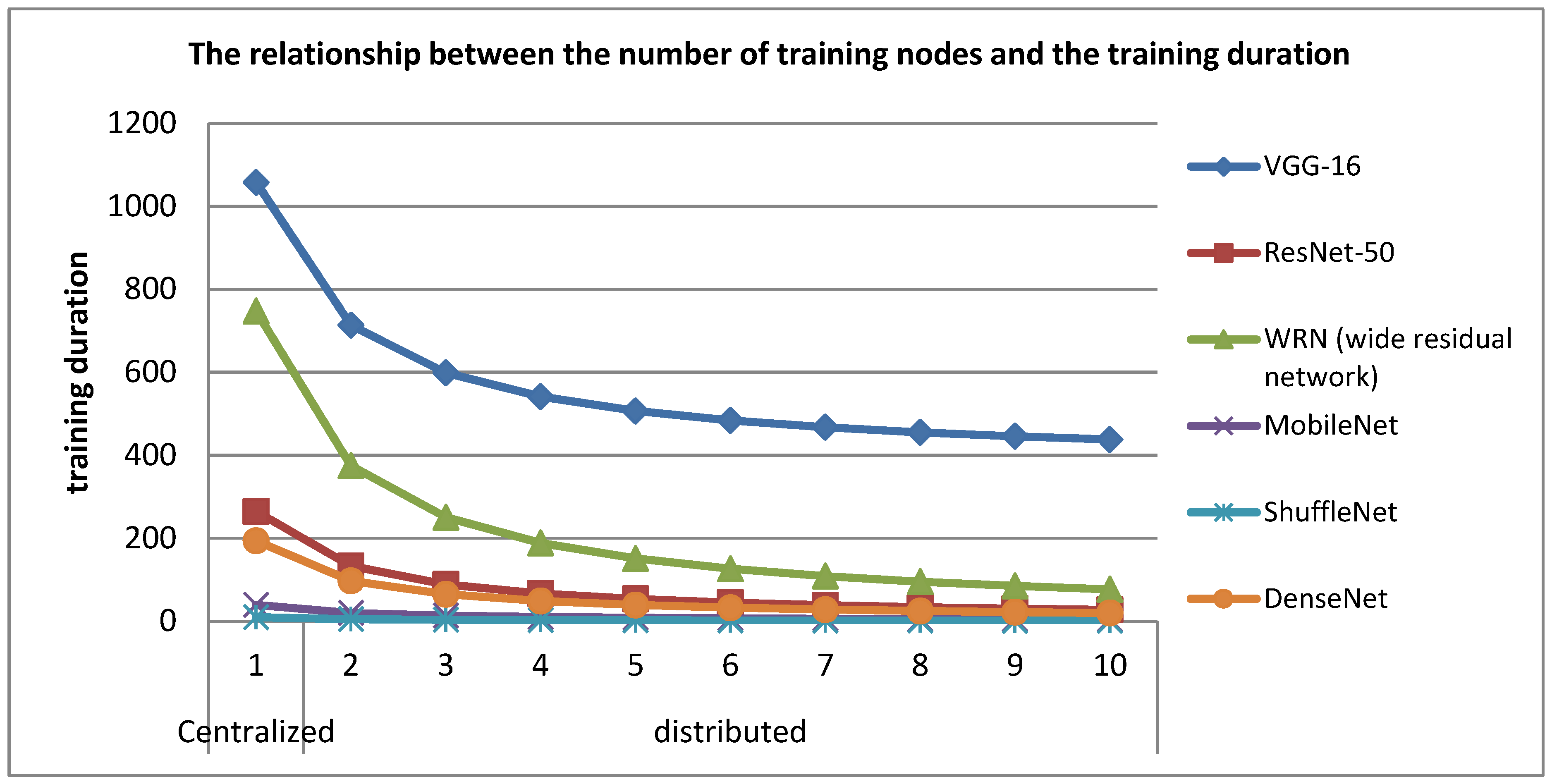
| Model | Input Size | Training Set Size | Epochs | Flops (One Pass) | Number of Parameters | Total Calculation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VGG-16 [38] | 224*224*3 | 7000 pcs | 50 | 15.470GFLOPS | 138.38M | 5.164PFLOPS |
| ResNet-50 [39] | 224*224*3 | 7000 pcs | 50 | 3.870GFLOPS | 25.609M | 1.292PFLOPS |
| WRN (wide residual network) [40] | 224*224*3 | 7000 pcs | 50 | 10.935GFLOPS | 68.950M | 3.650PFLOPS |
| MobileNet [41] | 224*224*3 | 7000 pcs | 50 | 0.573GFLOPS | 4.253M | 0.191PFLOPS |
| ShuffleNet [42] | 224*224*3 | 7000 pcs | 50 | 0.136GFLOPS | 1.74M | 0.045PFLOPS |
| DenseNet [43] | 224*224*3 | 7000 pcs | 50 | 2.834GFLOPS | 7.894M | 0.946PFLOPS |
| Floating point computation | 5 TFLOPS (FP16) |
| Operating system / Architecture | Linux/X64 |
| Virtual machine monitor | XEN |
| RAM | 16GB 256 bit LPDDR4x |
| RAM Bandwidth | 2133MHz - 137GB/s |
| Disk | 10T |
| Power | 30W |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, J.; Han, J.; Cao, S. Satellite IoT Edge Intelligent Computing: A Research on Architecture. Electronics 2019, 8, 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8111247
Wei J, Han J, Cao S. Satellite IoT Edge Intelligent Computing: A Research on Architecture. Electronics. 2019; 8(11):1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8111247
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Junyong, Jiarong Han, and Suzhi Cao. 2019. "Satellite IoT Edge Intelligent Computing: A Research on Architecture" Electronics 8, no. 11: 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8111247
APA StyleWei, J., Han, J., & Cao, S. (2019). Satellite IoT Edge Intelligent Computing: A Research on Architecture. Electronics, 8(11), 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8111247





