Modified Technique of Parameter Identification of a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with PWM Inverter in the Presence of Dead-Time Effect and Measurement Noise
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Model of a SPMSM with a PWM Inverter
2.1. Mathematical Model of a SPMSM with an Ideal PWM Inverter
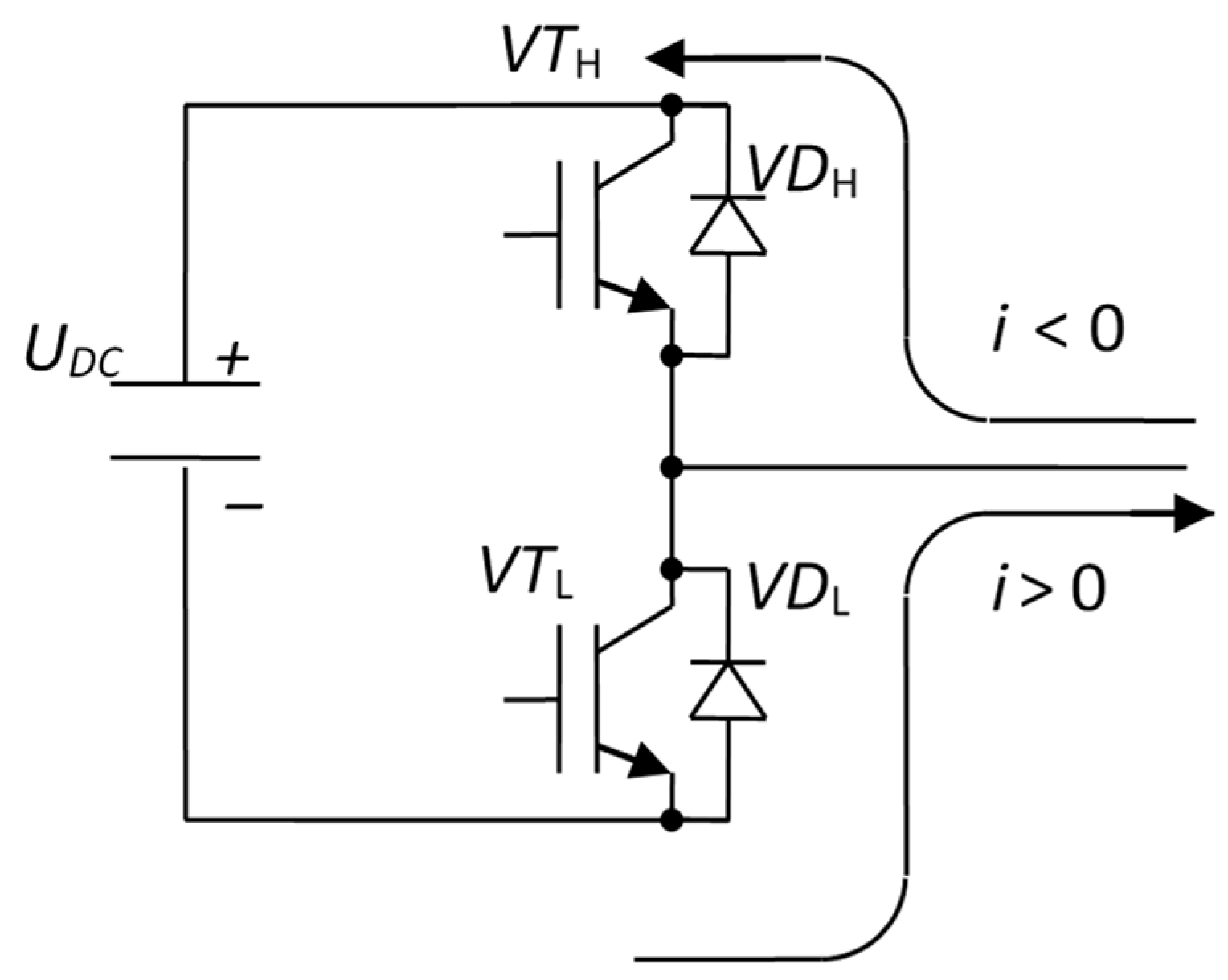
2.2. Mathematical Model of a SPMSM with PWM Inverter in the Presence of the Dead-Time Effect.
3. The Problem of Parameter Identification of SPMSM with a PWM Inverter
4. Modified Technique of Parameter Identification of a SPMSM
4.1. Design of Identification Experiment
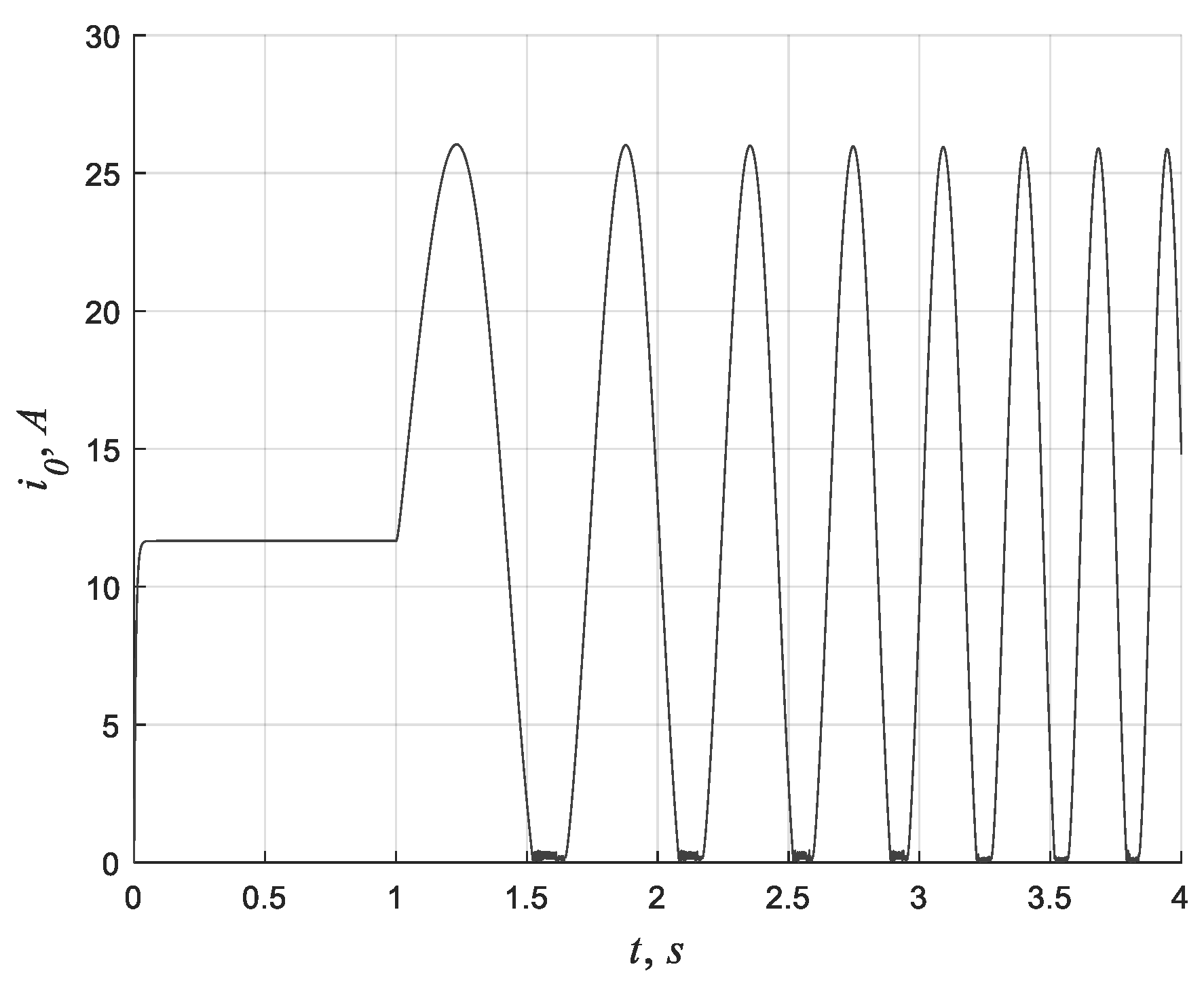
4.2. Excitation Input Signal
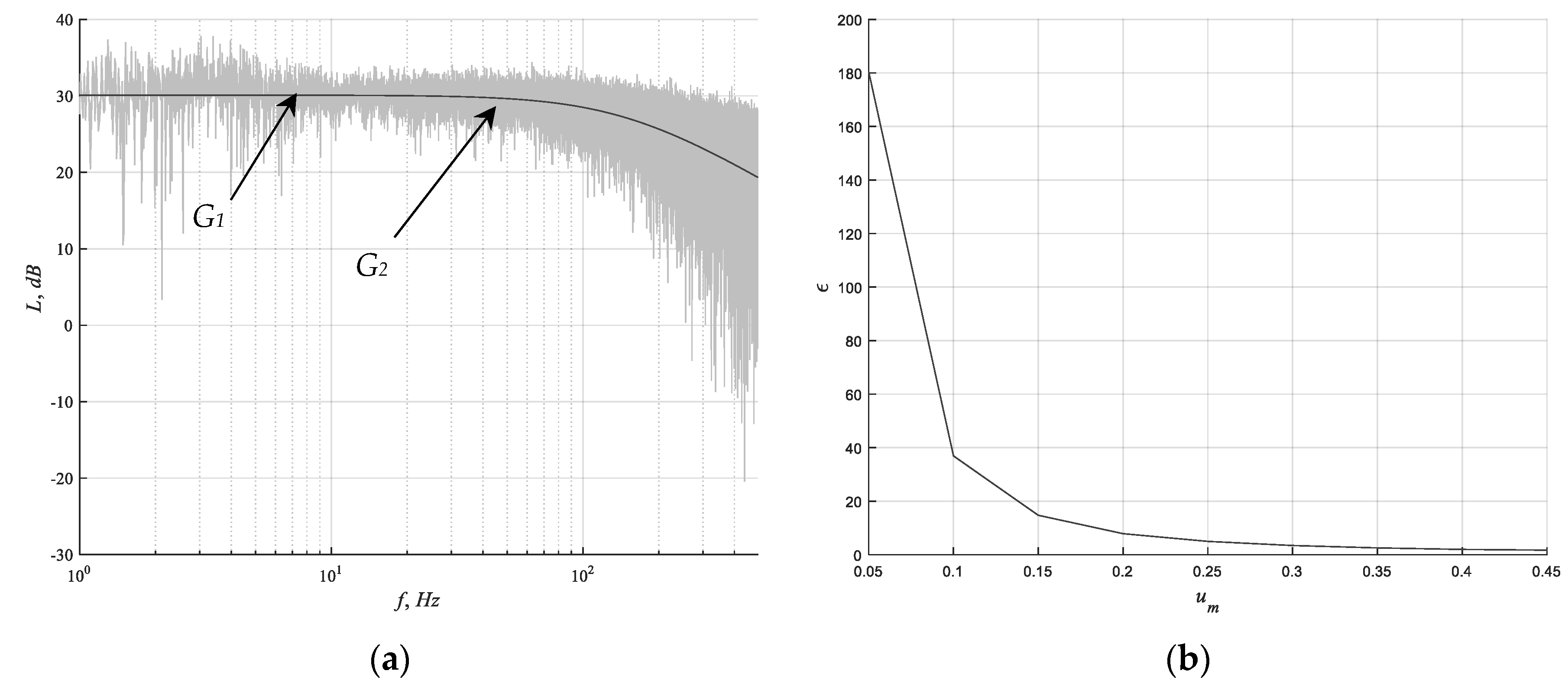
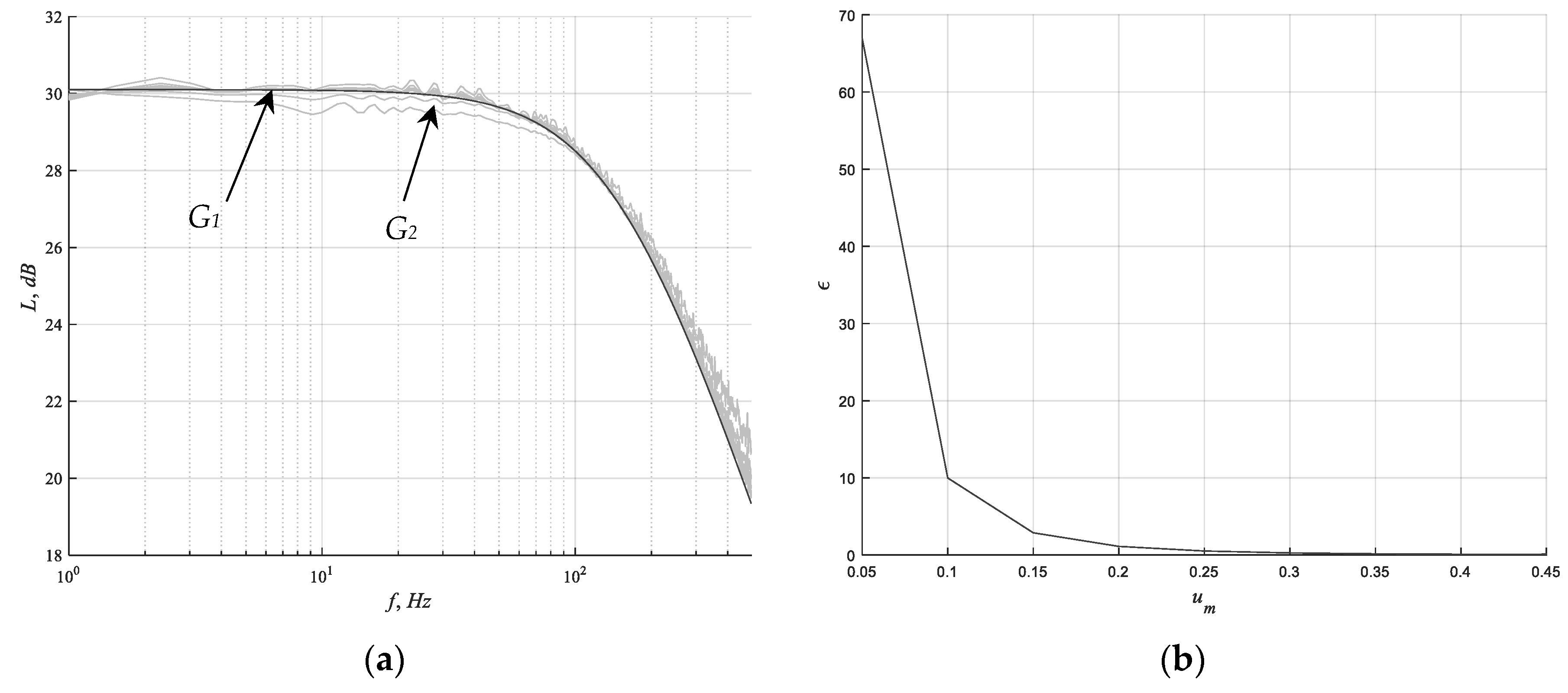
4.3. Data Processing
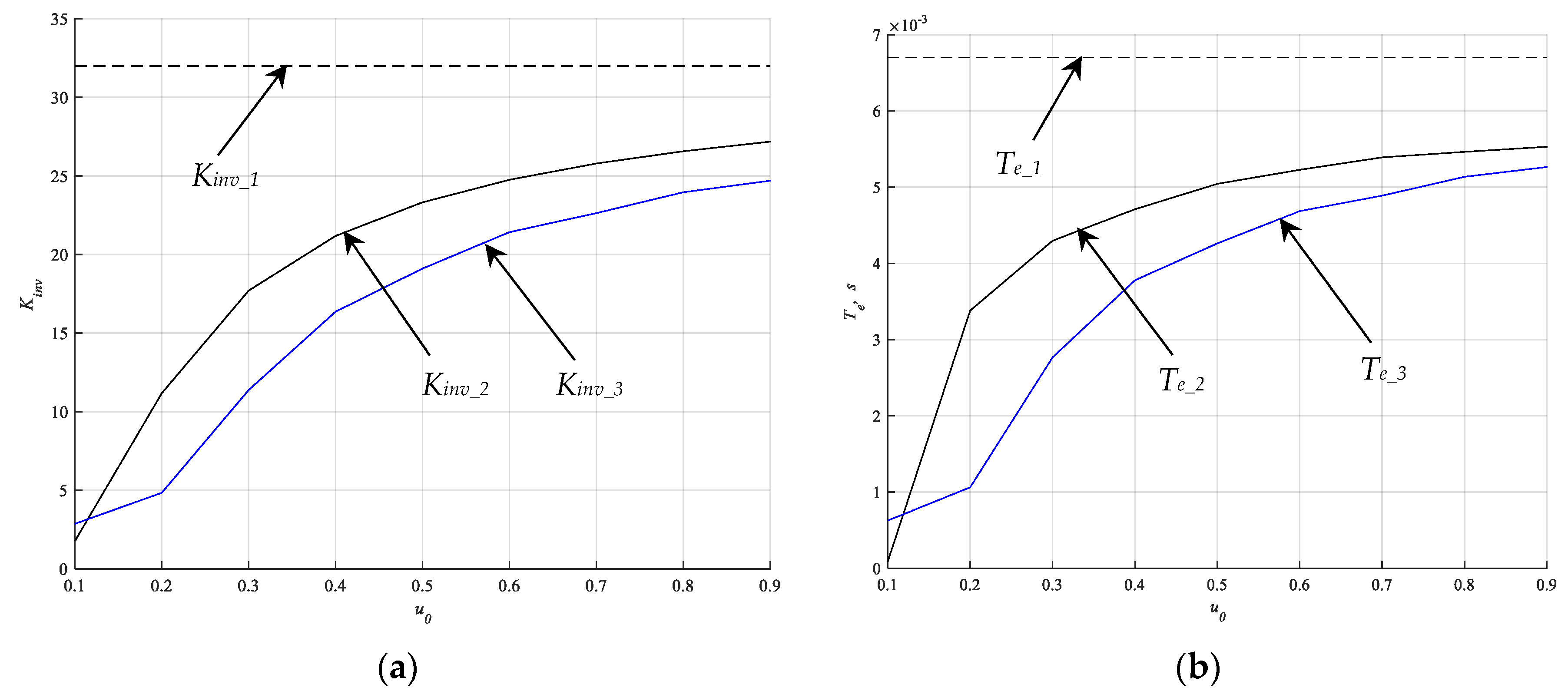
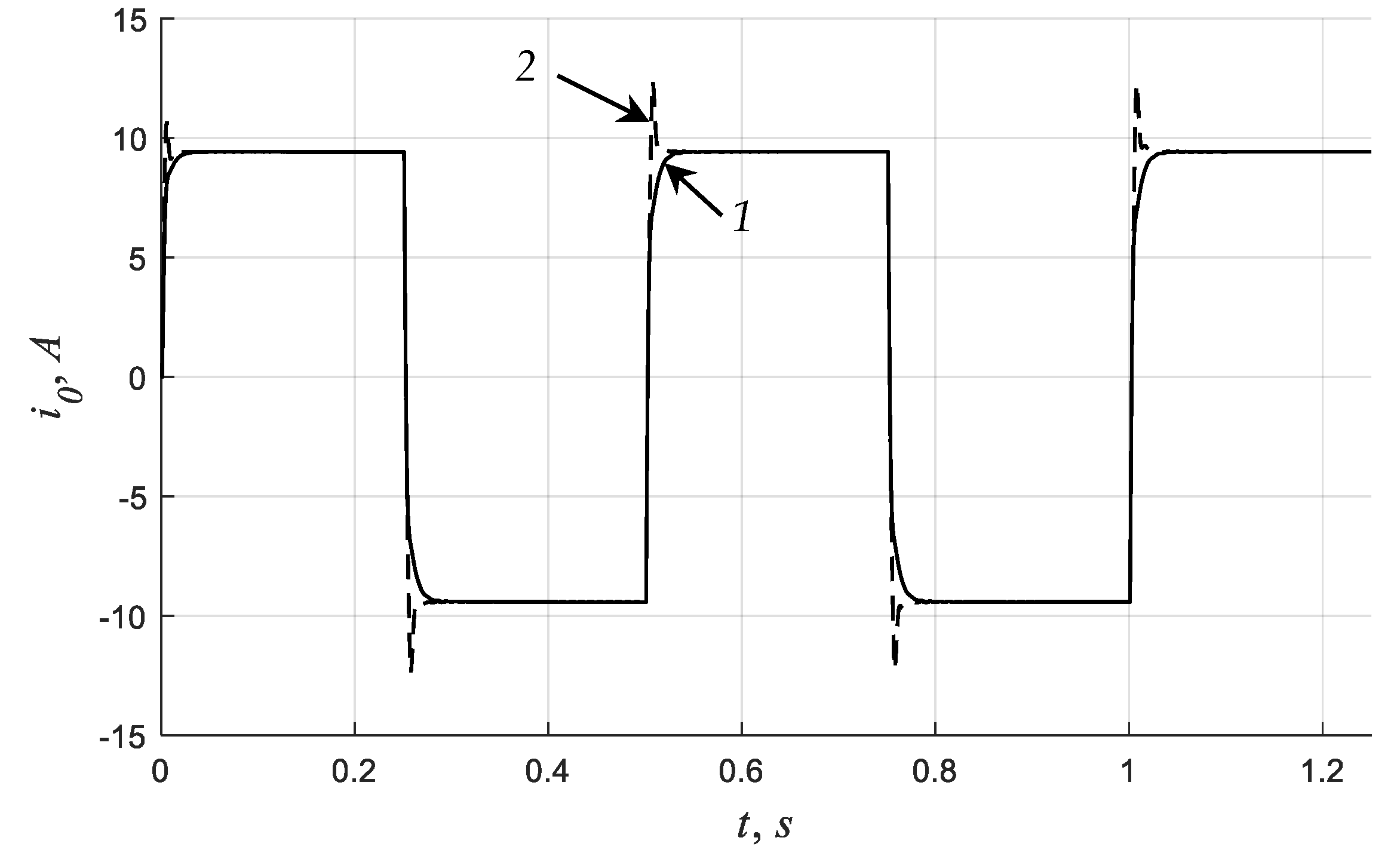
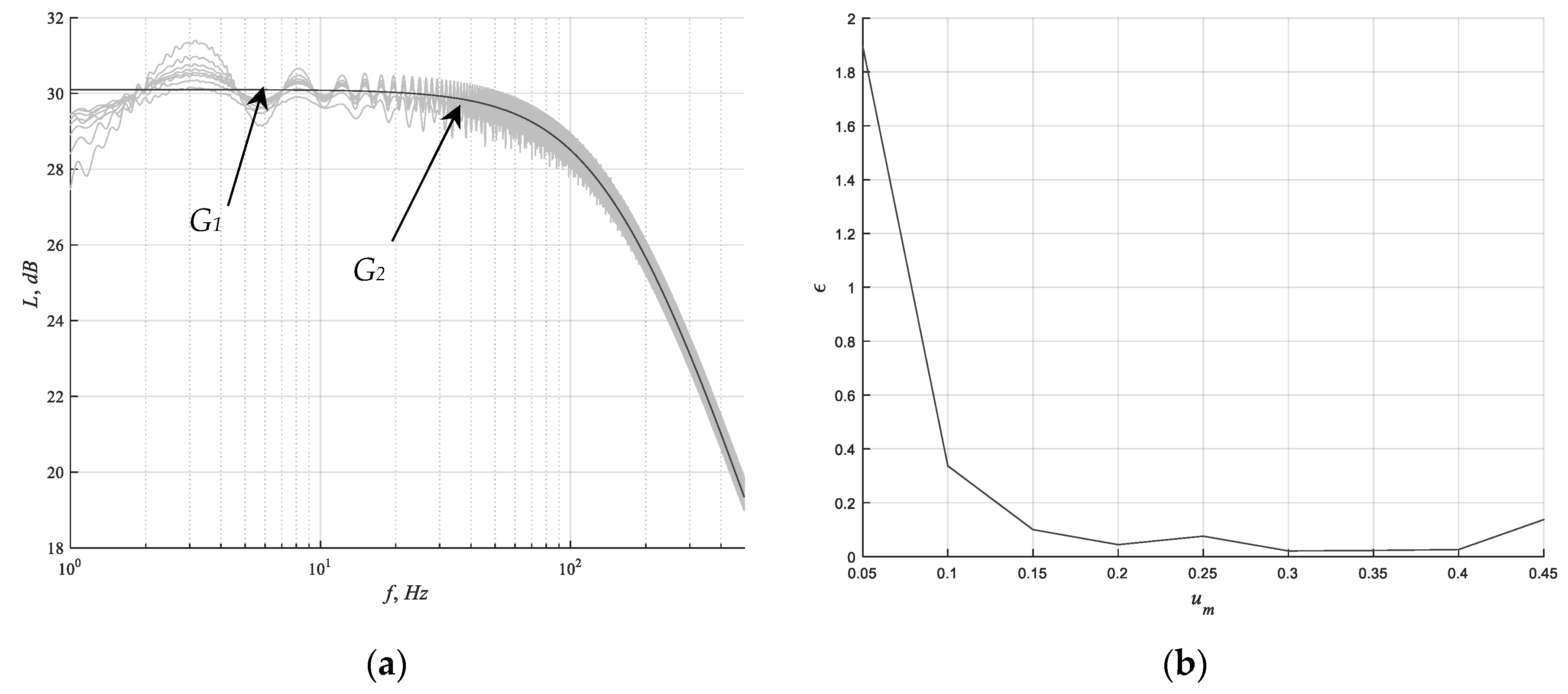
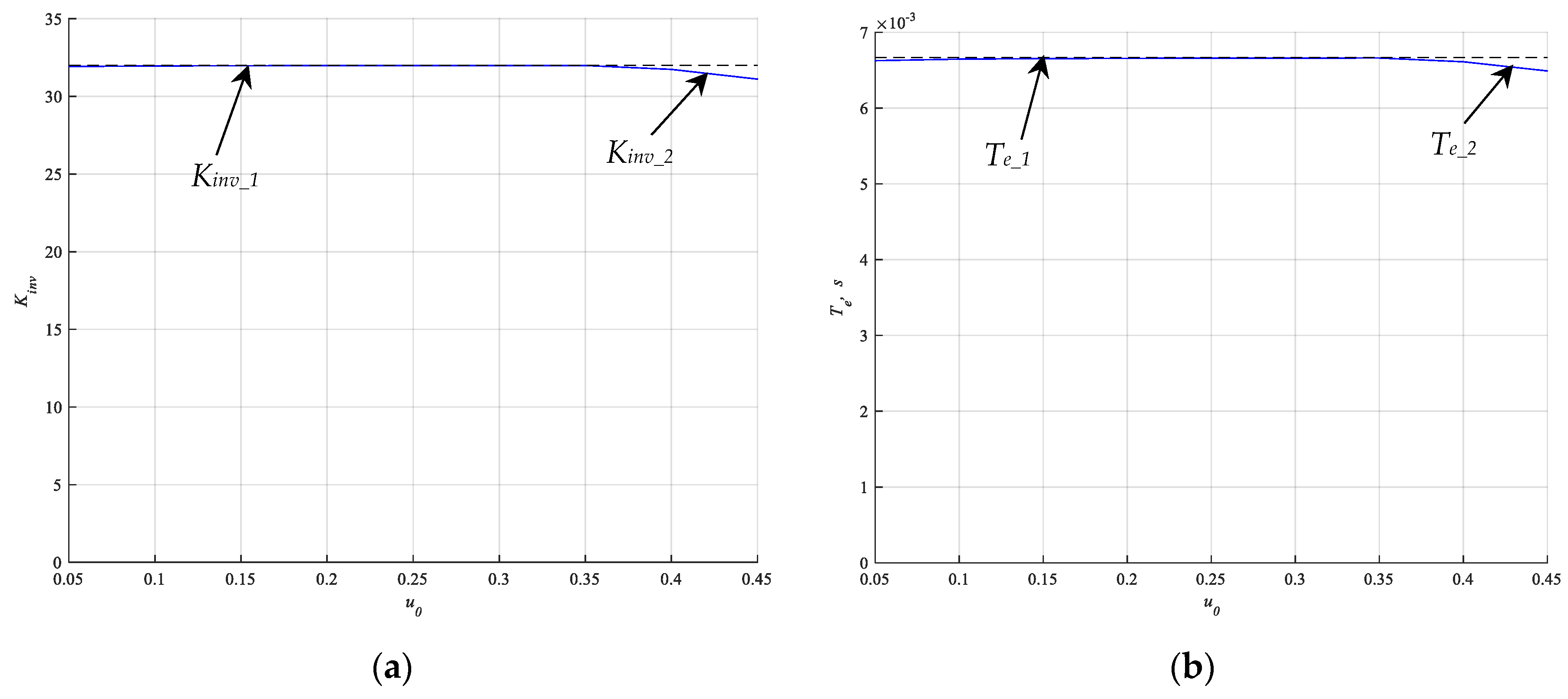
4.4. Simulation Results
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krause, P.C.; Wasynczuk, O.; Sudhoff, S.D. Analysis of Electric Machinery; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1986; Volume 564. [Google Scholar]
- Bose, B.K. Modern Power Electronics and AC Drives; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2002; Volume 123. [Google Scholar]
- Pillay, P.; Krishnan, R. Modeling, simulation, and analysis of permanent-magnet motor drives. I. The permanent-magnet synchronous motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1989, 25, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovlin, S.; Abdullin, A. Adaptive system for compensation of periodic disturbances in servo drive. In Proceedings of the 2016 IX International Conference on Power Drives Systems (ICPDS), Perm, Russia, 3–7 October 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Holtz, J.; Springob, L. Identification and compensation of torque ripple in high-precision permanent magnet motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1996, 43, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, A.; Orellana, Á.; Juliet, J.; Cardenas, R. Model Predictive Torque Control for Torque Ripple Compensation in Variable Speed PMSMs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 4584–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Deng, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Fei, Q. Sliding Mode Observer-Based Parameter Identification and Disturbance Compensation for Optimizing the Mode Predictive Control of PMSM. Energies 2019, 12, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Wang, S.; Zou, M.; Liu, M. Predictive Current Control for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on MRAS Parameter Identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Power Electronics and Application Conference and Exposition (PEAC), Shenzhen, China, 4–7 November 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Urbanski, K.; Janiszewski, D. Sensorless Control of the Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. Sensors 2019, 19, 3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, R.; Monshizadeh, N.; Monshizadeh, P.; Bazylev, D.; Pyrkin, A. Permanent magnet synchronous motors are globally asymptotically stabilizable with PI current control. Automatica 2018, 98, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran-Carbajal, F.; Tapia-Olvera, R.; Lopez-Garcia, I.; Valderrabano-Gonzalez, A.; Rosas-Caro, J.C.; Hernandez-Avila, J.L. Extended PI Feedback Tracking Control for Synchronous Motors. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2019, 17, 1346–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Tang, X.; Zheng, S.; Xie, Y.; Song, B. Adaptive two-degree-of-freedom PI for speed control of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on fractional order GPC. ISA Trans. 2016, 64, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orłowska-Kowalska, T.; Lovlin, S.Y.; Tsvetkova, M.H.; Abdullin, A.A.; Mamatov, A.G. Parametric identification of a servo drive model with deadtime-type nonlinearities. J. Instrum. Eng. 2019, 62, 576–584. [Google Scholar]
- Urasaki, N.; Senjyu, T.; Uezato, K.; Funabashi, T. Adaptive Dead-Time Compensation Strategy for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drive. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2007, 22, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuchin, A.; Gulyaeva, M.; Briz, F.; Gulyaev, I. Modeling of AC voltage source inverter with dead-time and voltage drop compensation for DPWM with switching losses minimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Modern Power Systems (MPS), Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 6–9 June 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Kou, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H. Analysis and Compensation of Dead-Time Effect of a ZVT PWM Inverter Considering the Rise- and Fall-Times. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ding, H.; Guo, X.; Padmanaban, S. Control Strategies of Mitigating Dead-time Effect on Power Converters: An Overview. Electronics 2019, 8, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Wen, X.; Zhao, F. Adaptive-Linear-Neuron-Based Dead-Time Effects Compensation Scheme for PMSM Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 2530–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diallo, D.; Arias, A.; Cathelin, J. An inverter dead-time feedforward compensation scheme for PMSM sensorless drive operation. In Proceedings of the 2014 First International Conference on Green Energy (ICGE), Sfax, Tunisia, 25–27 March 2014; pp. 296–301. [Google Scholar]
- Munoz, A.R.; Lipo, T.A. On-line dead-time compensation technique for open-loop PWM-VSI drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1999, 14, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haifeng, X.; Yuyao, H. Compensation of dead-time effects based on adaptive voltage disturbance estimator in PMSM drives. In Proceedings of the 26th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Changsha, China, 31 May–2 June 2014; pp. 3439–3444. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, F.; Liu, X. Online adaptive parameter identification of PMSM based on the dead-time compensation. Int. J. Electron. 2014, 102, 1132–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsky, T.; Stichweh, H.; Theßeling, M.; Wettlaufer, J.; Quattrone, F. Modeling and parameter identification of multiphase permanent magnet synchronous motors including saturation effects. In Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’15 ECCE-Europe), Geneva, Switzerland, 8–10 September 2015; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, F.; Pan, J.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T. Gradient-Based Iterative Parameter Estimation Algorithms for Dynamical Systems from Observation Data. Mathematics 2019, 7, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liling, S.; Heming, L.; Boqiang, X. Precise determination of permanent magnet synchronous motor parameters based on parameter identification technique. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Beijing, China, 9–11 November 2003; Volume 1, pp. 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, J.; Hu, J.; Qin, X. Online identification for permanent magnet synchronous motor based on recursive fixed memory least square method under steady state. In Proceedings of the 36th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Dalian, China, 26–28 July 2017; pp. 4824–4829. [Google Scholar]
- Vaseghi, B.; Takorabet, N.; Meibody-Tabar, F. Fault Analysis and Parameter Identification of Permanent-Magnet Motors by the Finite-Element Method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 3290–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulvirenti, M.; Scarcella, G.; Scelba, G.; Testa, A.; Harbaugh, M.M. On-Line Stator Resistance and Permanent Magnet Flux Linkage Identification on Open-End Winding PMSM Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folgheraiter, M. A combined B-spline-neural-network and ARX model for online identification of nonlinear dynamic actuation systems. Neurocomputing 2016, 175, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoukens, J.; Pintelon, R.; Dobrowiecki, T.; Rolain, Y. Identification of linear systems with nonlinear distortions. Automatica 2005, 41, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljung, L. System Identification. In Encyclopedia of Electrical and Electronics Engineering; American Cancer Society, Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999; ISBN 978-0-471-34608-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hägg, P.; Hjalmarsson, H.; Wahlberg, B. A least squares approach to direct frequency response estimation. In Proceedings of the 50th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 12–15 December 2011; pp. 2160–2165. [Google Scholar]
- Ilvedson, C.R. Transfer Function Estimation Using Time-Frequency Analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Samygina, E.; Tiapkin, M.; Rassudov, L.; Balkovoi, A. Extended Algorithm of Electrical Parameters Identification via Frequency Response Analysis. In Proceedings of the 26th International Workshop on Electric Drives: Improvement in Efficiency of Electric Drives (IWED), Moscow, Russia, 30 January–2 February 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Feron, E.; Brenner, M.; Paduano, J.; Turevskiy, A. Time-Frequency Analysis for Transfer Function Estimation and Application to Flutter Clearance. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 1998, 21, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saupe, F.; Knoblach, A. Experimental determination of frequency response function estimates for flexible joint industrial manipulators with serial kinematics. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 52, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljung, L.; Glover, K. Frequency domain versus time domain methods in system identification. Automatica 1981, 17, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villwock, S.; Pacas, M. Application of the Welch-Method for the Identification of Two- and Three-Mass-Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifeachor, E.C.; Jervis, B.W. Digital Signal Processing: A Practical Approach; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2002; ISBN 978-0-201-59619-9. [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaumer, T.; Heldwein, M.L.; Gong, G.; Round, S.D.; Kolar, J.W. Comparison of Prediction Techniques to Compensate Time Delays Caused by Digital Control of a Three-Phase Buck-Type PWM Rectifier System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Blaabjerg, F.; Harnefors, L.; Song, W. Accuracy Analysis of the Zero-Order Hold Model for Digital Pulse Width Modulation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 10826–10834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, R.; Takeshita, T.; Matsui, N. Current model-based sensorless drives of salient-pole PMSM at low speed and standstill. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1998, 34, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Kuang, J.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, G.; Xu, D. Rotor Position Estimation of PMSM in Low-Speed Region and Standstill Using Zero-Voltage Vector Injection. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 7948–7958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Unit of Measurement | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Phase inductance, L | mH | 10 |
| Phase resistance, R | Ohm | 1.5 |
| Back emf constant, ce | V/(rad/s) | 14.4 |
| DC link voltage, UDC | V | 96 |
| Number of pole pairs, p | 48 | |
| Dead time, tdead | μs | 3 |
| PWM switching time, Tsw | μs | 100 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mamatov, A.; Lovlin, S.; Vaimann, T.; Rassõlkin, A.; Vakulenko, S.; Abramian, A. Modified Technique of Parameter Identification of a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with PWM Inverter in the Presence of Dead-Time Effect and Measurement Noise. Electronics 2019, 8, 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8101200
Mamatov A, Lovlin S, Vaimann T, Rassõlkin A, Vakulenko S, Abramian A. Modified Technique of Parameter Identification of a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with PWM Inverter in the Presence of Dead-Time Effect and Measurement Noise. Electronics. 2019; 8(10):1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8101200
Chicago/Turabian StyleMamatov, Aleksandr, Sergey Lovlin, Toomas Vaimann, Anton Rassõlkin, Sergei Vakulenko, and Andrei Abramian. 2019. "Modified Technique of Parameter Identification of a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with PWM Inverter in the Presence of Dead-Time Effect and Measurement Noise" Electronics 8, no. 10: 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8101200
APA StyleMamatov, A., Lovlin, S., Vaimann, T., Rassõlkin, A., Vakulenko, S., & Abramian, A. (2019). Modified Technique of Parameter Identification of a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with PWM Inverter in the Presence of Dead-Time Effect and Measurement Noise. Electronics, 8(10), 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8101200







