Multi-Port Current Source Inverter for Smart Microgrid Applications: A Cyber Physical Paradigm
Abstract
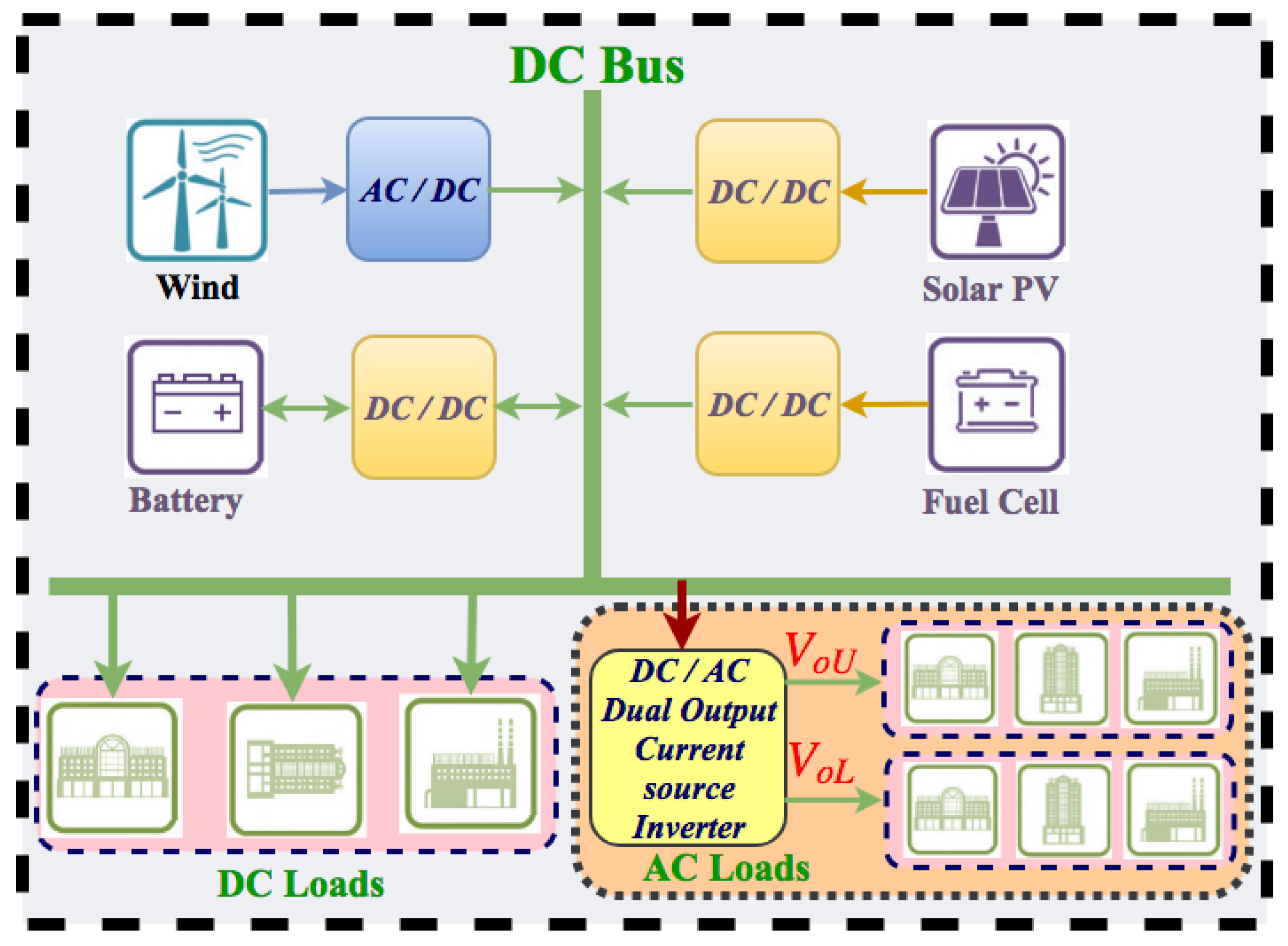
1. Introduction
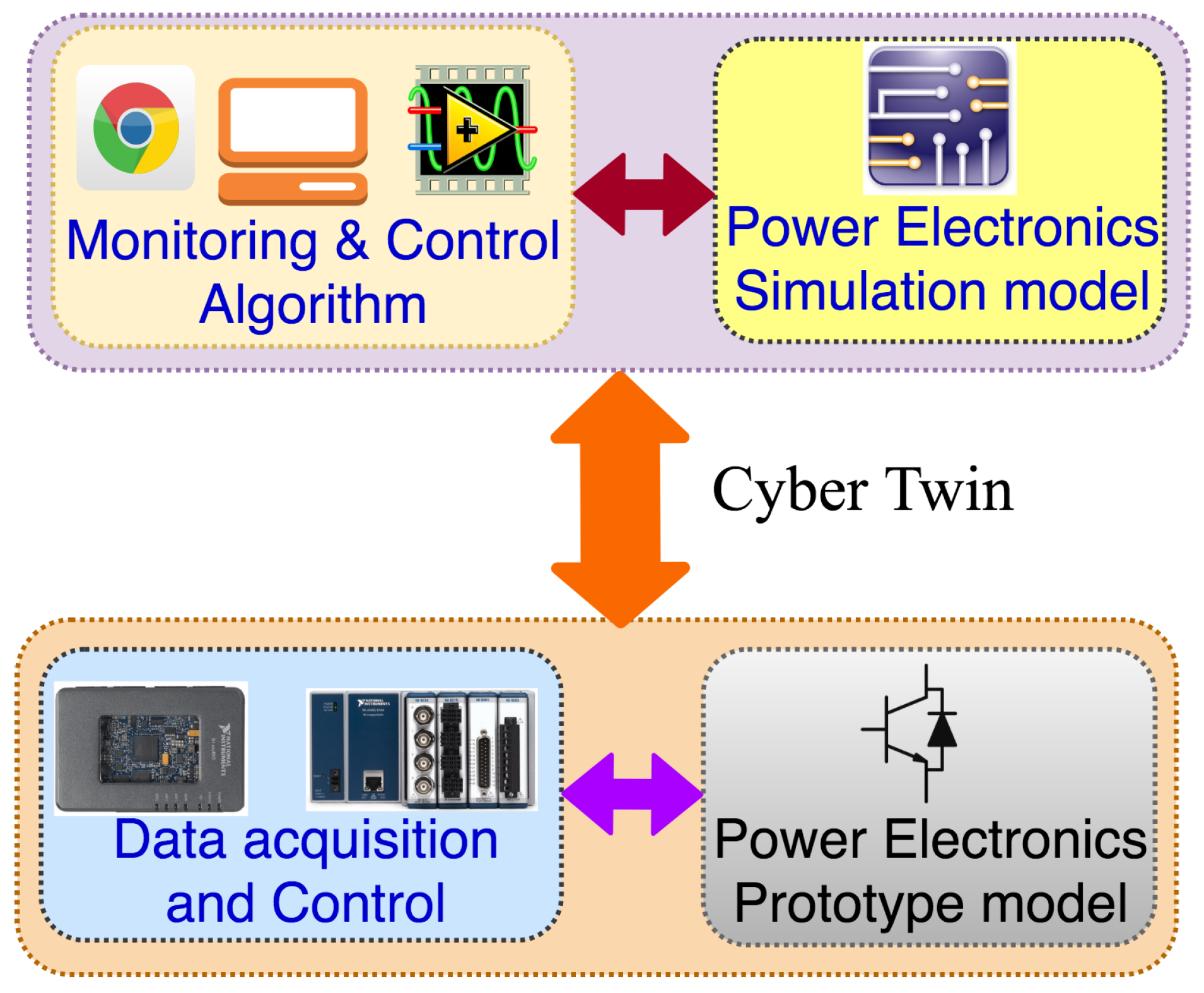
2. A Cyber Perspective Model
Generalised CPS Model
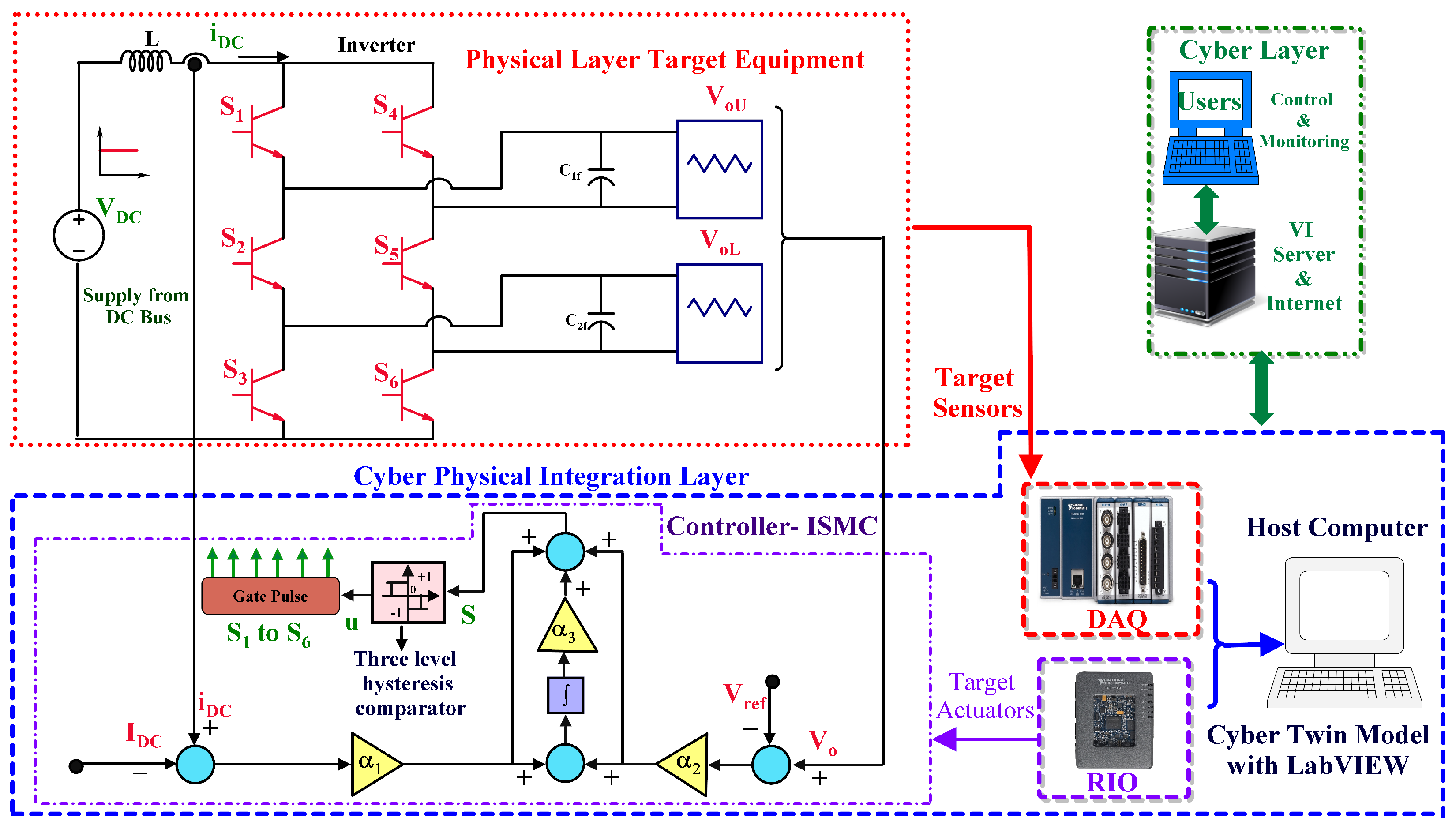
3. Physical Layer: Dual Output Current Source Inverter
3.1. Equal Voltage (EV) Mode of Operation
3.2. Different Voltage (DV) Mode of Operation
3.3. System Modelling
4. Cyber–Physical Integration Layer: Cyber Twin Model, C-DAQ, RIO with Sliding Mode Controllers
4.1. Sliding Mode Control (SMC)
4.2. Integral Sliding Mode Control (ISMC)
4.3. Cyber Physical Test Bench
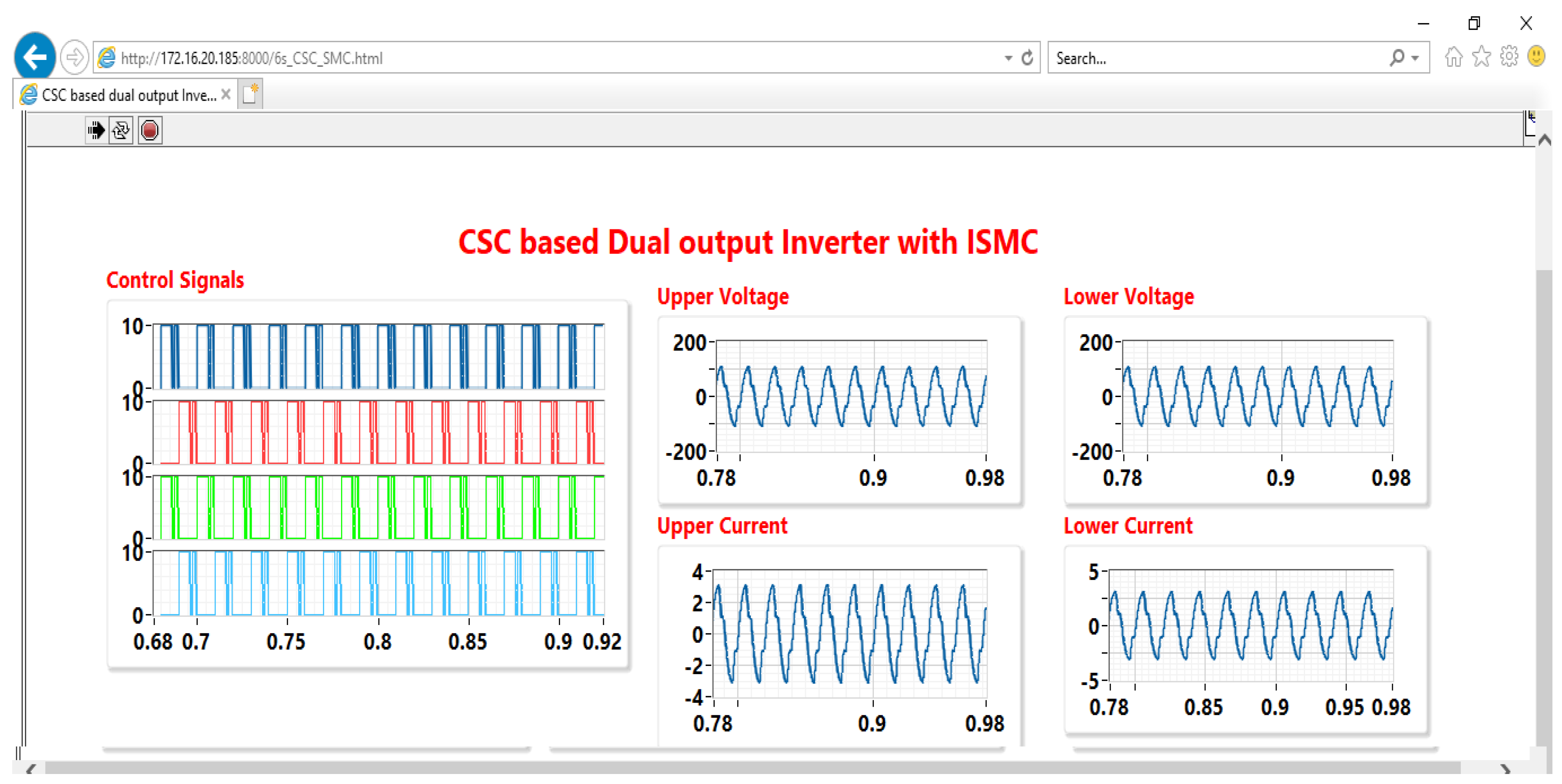
5. Cyber Layer—LabVIEW Based CPS
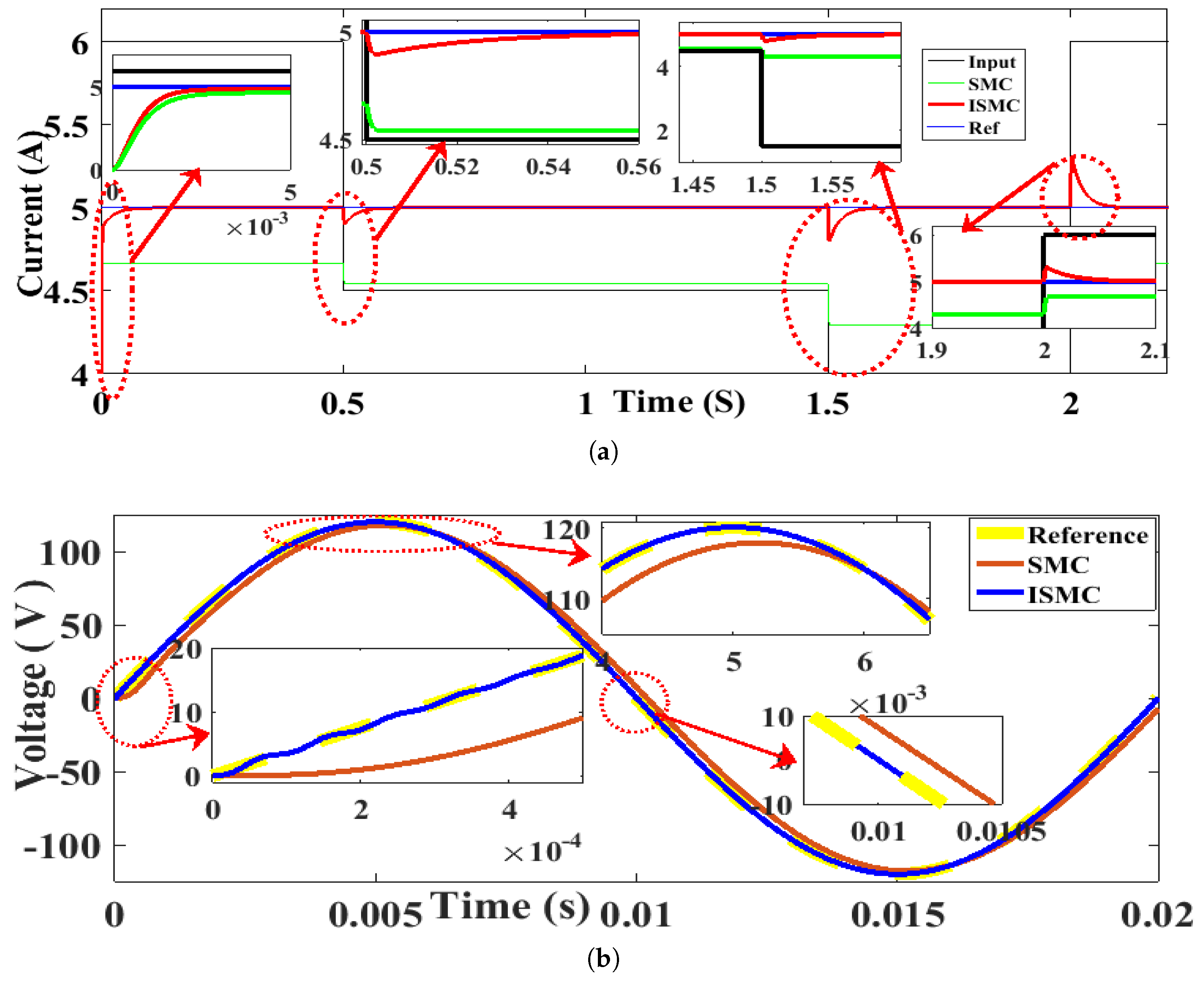
6. Results and Discussions
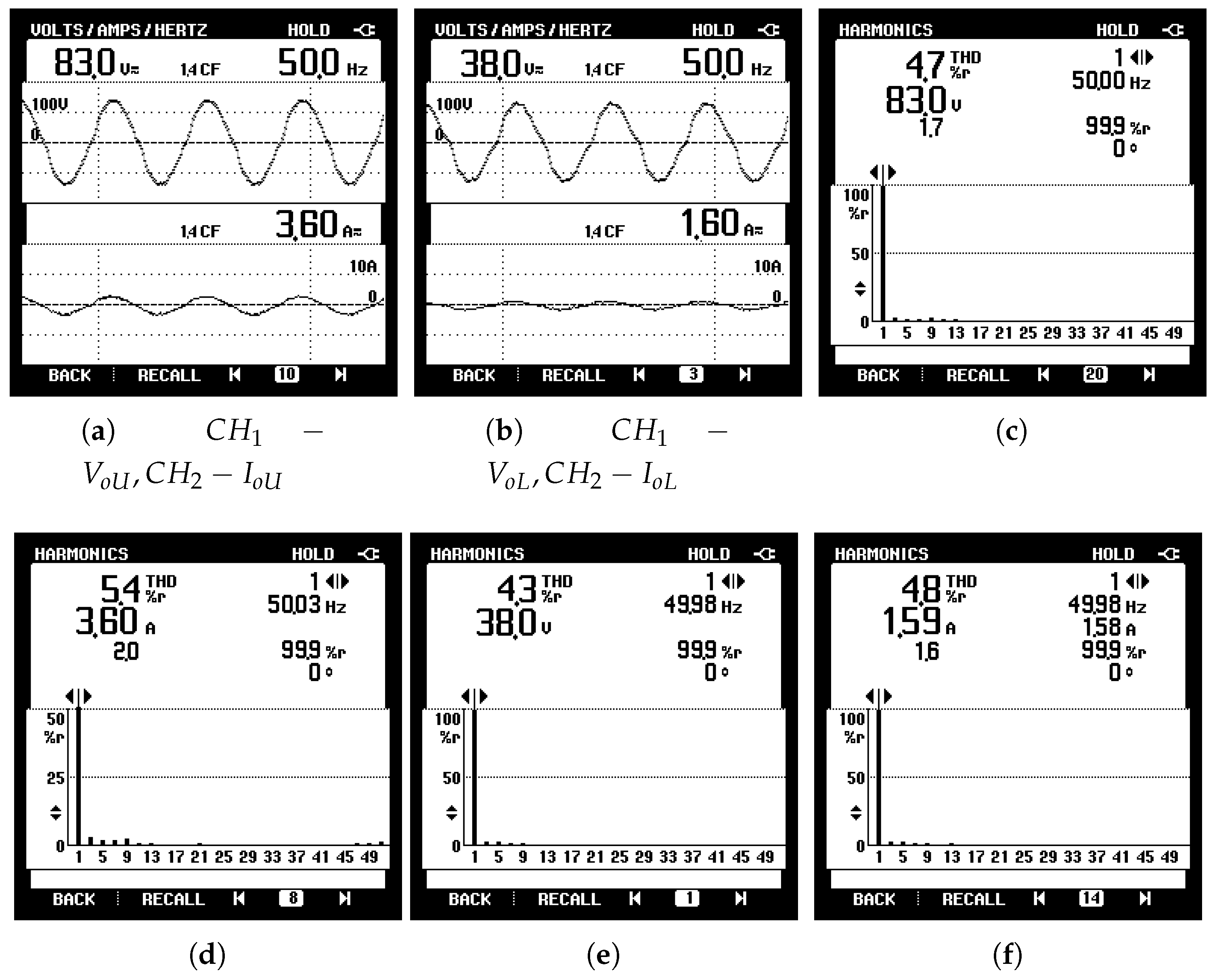
6.1. Steady State Performance
6.2. Response to Load Variations
6.3. Harmonic Analysis
6.4. Voltage Stress
6.5. Loss Analysis
6.5.1. IGBT Conduction Loss
6.5.2. IGBT Switching Loss
6.6. Online Monitoring
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pichan, M.; Karimi, M.; Simorgh, H. Improved low-cost sliding mode control of 4-leg inverter for isolated microgrid applications. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Cheng, Q. Structure analysis and sliding mode control of new dual quasi-Z-source inverter in microgrid. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobina, C.; de Freitas, I.; Lima, A. DC-Link Three-Phase-to-Three-Phase Four-Leg Converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 1953–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Starke, M.; Tolbert, L.; Ozpineci, B. Fuel cell power conditioning for electric power applications: A summary. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2007, 1, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, A.; Azizi, M.; Mohamadian, M.; Varjani, A.Y.; Shahparasti, M. Single-Phase Dual-Output Inverters With Three-Switch Legs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 1769–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.L.H.; Cha, H.; Kim, H.G. Single-Phase Six-Switch Dual-Output Inverter Using Dual-Buck Structure. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilnathan, K.; Annapoorani, I. Implementation of unified power quality conditioner (UPQC) based on current source converters for distribution grid and performance monitoring through LabVIEW Simulation Interface Toolkit server: A cyber physical model. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2016, 10, 2622–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komurcugil, H. Integral sliding-mode-based current-control strategy for single-phase current-source inverters. Electr. Eng. 2011, 93, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.T.H.; Chung, H.S.; Chan, T.K.M. An Active Modulation Technique for Single-Phase Grid-Connected CSI. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2007, 22, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komurcugil, H. Steady-State Analysis and Passivity-Based Control of Single-Phase PWM Current-Source Inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 1026–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukrer, O.; Komurcugil, H.; Doganalp, A. A Three-Level Hysteresis Function Approach to the Sliding-Mode Control of Single-Phase UPS Inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 3477–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afghoul, H.; Krim, F.; Babes, B.; Beddar, A.; Kihel, A. Design and real time implementation of sliding mode supervised fractional controller for wind energy conversion system under sever working conditions. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 167, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komurcugil, H.; Biricik, S. Time-Varying and Constant Switching Frequency-Based Sliding-Mode Control Methods for Transformerless DVR Employing Half-Bridge VSI. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 2570–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.; de Vicuna, L.G.; Guzman, R.; Castilla, M.; Miret, J. Modeling and Sliding Mode Control for Three-Phase Active Power Filters Using the Vector Operation Technique. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 6828–6838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadzadeh, S.; Markadeh, G.A.; Blaabjerg, F. Voltage regulation of the Y-source boost DC–DC converter considering effects of leakage inductances based on cascaded sliding-mode control. IET Power Electron. 2017, 10, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, A.; Sabug, L.R.; Monti, A. Robust Predictive Sliding Mode Control for Multiterminal HVDC Grids. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2018, 33, 1545–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ge, X.; Liu, Y.C. Second-Order Sliding-Mode MRAS Observer Based Sensorless Vector Control of Linear Induction Motor Drives for Medium-Low Speed Maglev Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Zhuang, S.; Ren, H.; Chen, Y.; He, K. Discrete modelling and state-mutation analysis for sliding mode controlled non-isolated grid-connected inverter with H6-type. IET Power Electron. 2017, 10, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Saeedifard, M.; Perez, M.A. Sliding Mode Control of the Modular Multilevel Converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, K.; Jana, A.K. Nonlinear multivariable sliding mode control of a reversible PEM fuel cell integrated system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 171, 541–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instruments, N. NI Single-Board RIO General-Purpose Inverter Controller Features; Technical Report; National Instruments: Austin, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Balda, J.C.; Mantooth, A.; Blum, R.; Tenti, P. Cybersecurity and Power Electronics: Addressing the Security Vulnerabilities of the Internet of Things. IEEE Power Electron. Mag. 2017, 4, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meer, A.A.; Palensky, P.; Heussen, K.; Bondy, D.M.; Gehrke, O.; Steinbrinki, C.; Blanki, M.; Lehnhoff, S.; Widl, E.; Moyo, C.; et al. cyber–physical energy systems modeling, test specification, and co-simulation based testing. In Proceedings of the 2017 Workshop on Modeling and Simulation of Cyber–Physical Energy Systems (MSCPES), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 18–21 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, H.; Shon, T. Challenges and research directions for heterogeneous cyber–physical system based on IEC 61850: Vulnerabilities, security requirements, and security architecture. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2016, 61, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffei, A.; Srinivasan, S. A cyber–physical Systems Approach for Implementing the Receding Horizon Optimal Power Flow in Smart Grids. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Comput. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntalampiras, S.; Soupionis, Y. Gaussian Mixture Modeling for Detecting Integrity Attacks in Smart Grids. Electronics 2016, 5, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.C.; Liu, C.C.; Xie, J. cyber–physical System Security of a Power Grid: State-of-the-Art. Electronics 2016, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.A. Computing Foundations and Practice for CPS: A Preliminary Report; Technical Report; University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, B.; Yao, S.; Liu, Z. Review on cyber–physical systems. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2017, 4, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andalam, S.; Ng, D.J.X.; Easwaran, A.; Thangamariappan, K. Contract-based Methodology for Developing Resilient Cyber-Infrastructure in the Industry 4.0 Era. IEEE Embed. Syst. Lett. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.; Besanger, Y.; Tran, Q.; Nguyen, T. On Conceptual Structuration and Coupling Methods of Co-Simulation Frameworks in cyber–physical Energy System Validation. Energies 2017, 10, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, I.; Calderon, A.; Andujar, J. Novel remote monitoring platform for RES-hydrogen based smart microgrid. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 148, 489–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, M.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, W. An IoT-Based Online Monitoring System for Continuous Steel Casting. IEEE Internet Things J. 2016, 3, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moness, M.; Moustafa, A.M. A Survey of cyber–physical Advances and Challenges of Wind Energy Conversion Systems: Prospects for Internet of Energy. IEEE Internet Things J. 2016, 3, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonizzi, P.; Ferrari, G.; Gay, V.; Leguay, J. Data dissemination scheme for distributed storage for IoT observation systems at large scale. Inf. Fusion 2015, 22, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Huang, G.; Zhang, L.; Tsang, K.F. Wireless sensor network based monitoring system for a large-scale indoor space: Data process and supply air allocation optimization. Energy Build. 2015, 103, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, Y.E.; Korpeoglu, I.; Ulusoy, O. A framework for use of wireless sensor networks in forest fire detection and monitoring. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2012, 36, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, S.; Anderl, R. Digital twin—Proof of concept. Manuf. Lett. 2018, 15, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.M.; Saddik, A.E. C2PS: A Digital Twin Architecture Reference Model for the Cloud-Based cyber–physical Systems. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 2050–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhang, D.; Leng, J. A Digital Twin-Based Approach for Designing and Multi-Objective Optimization of Hollow Glass Production Line. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 26901–26911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Tao, F. Digital Twin and Big Data Towards Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0: 360 Degree Comparison. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 3585–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
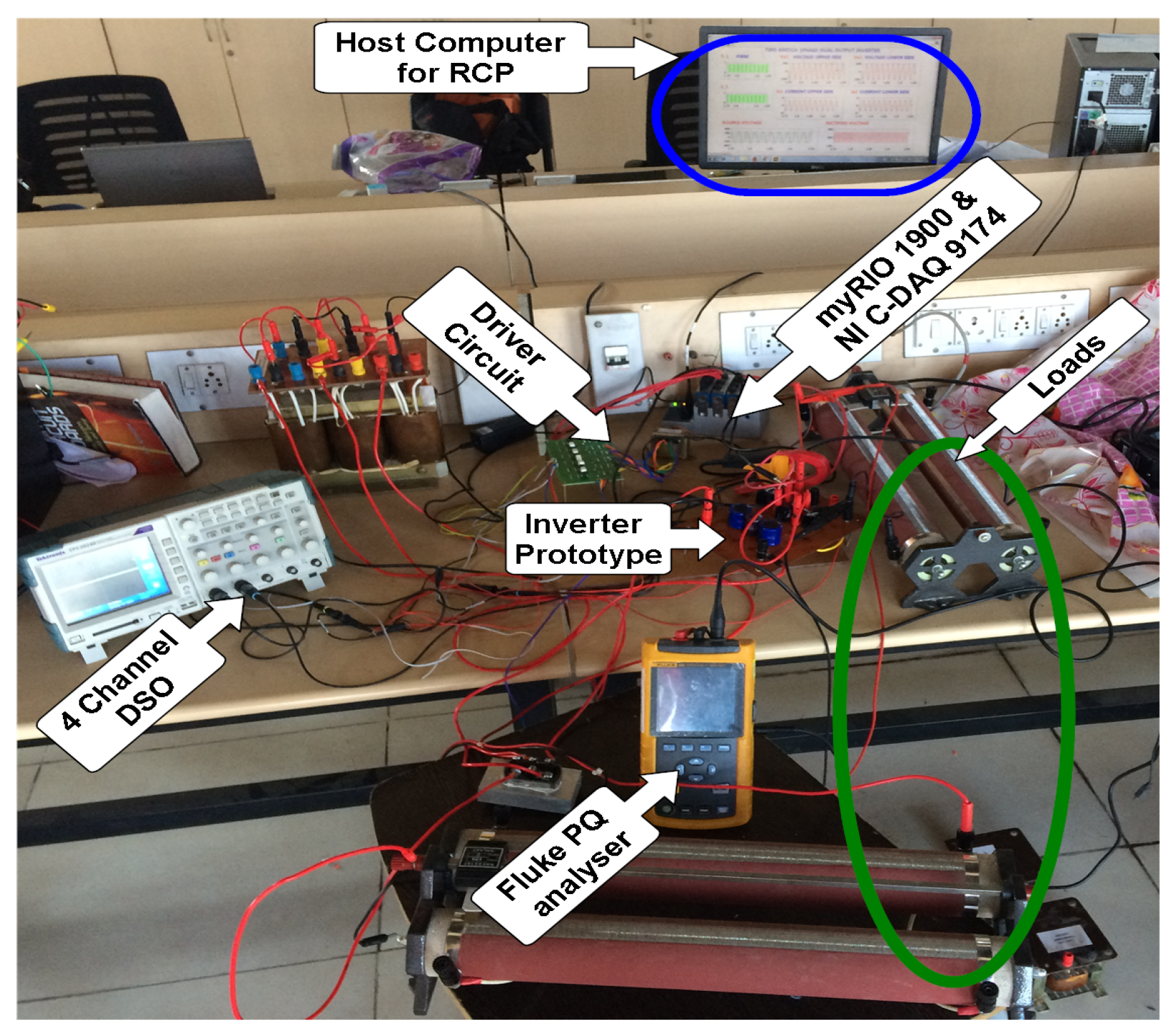
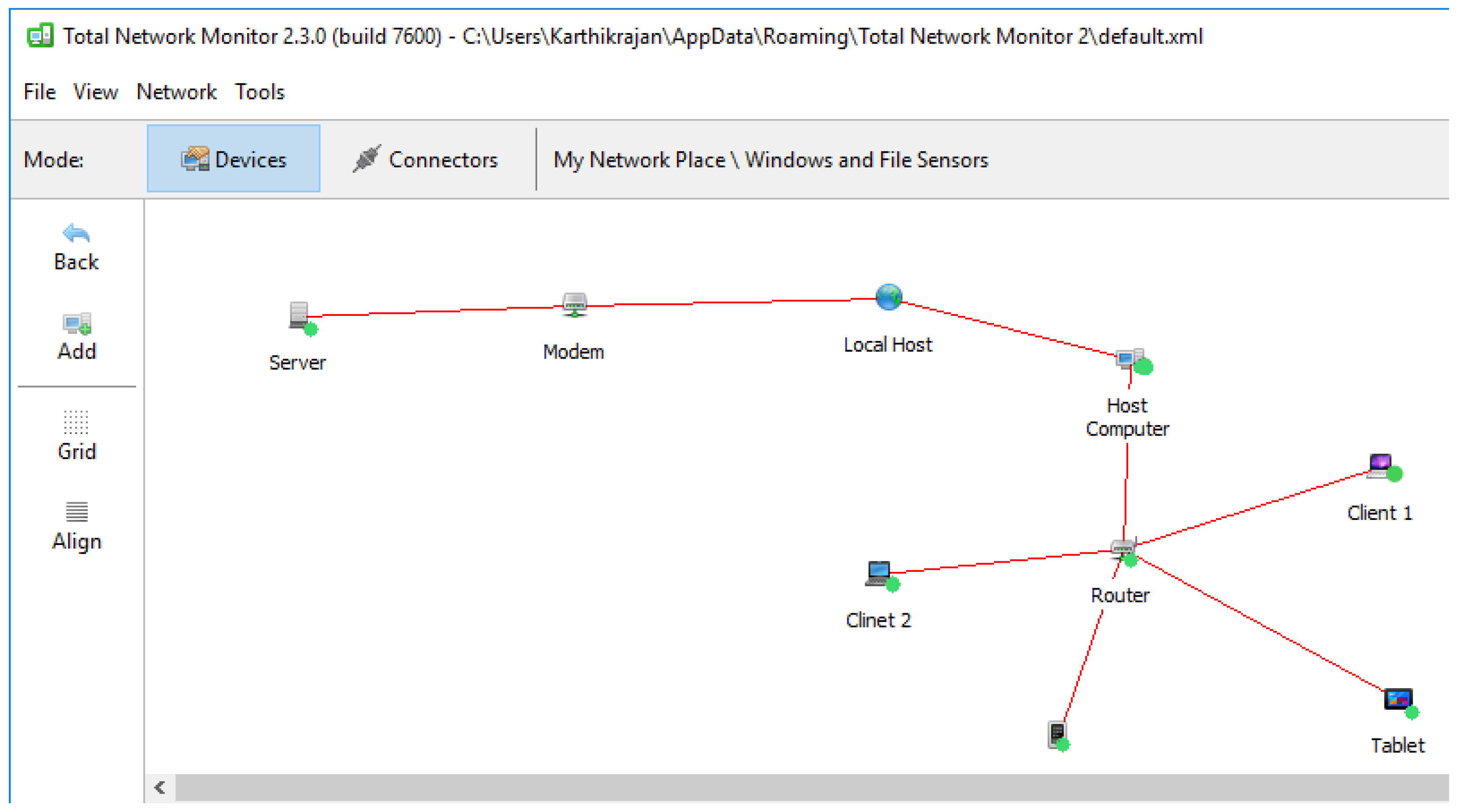
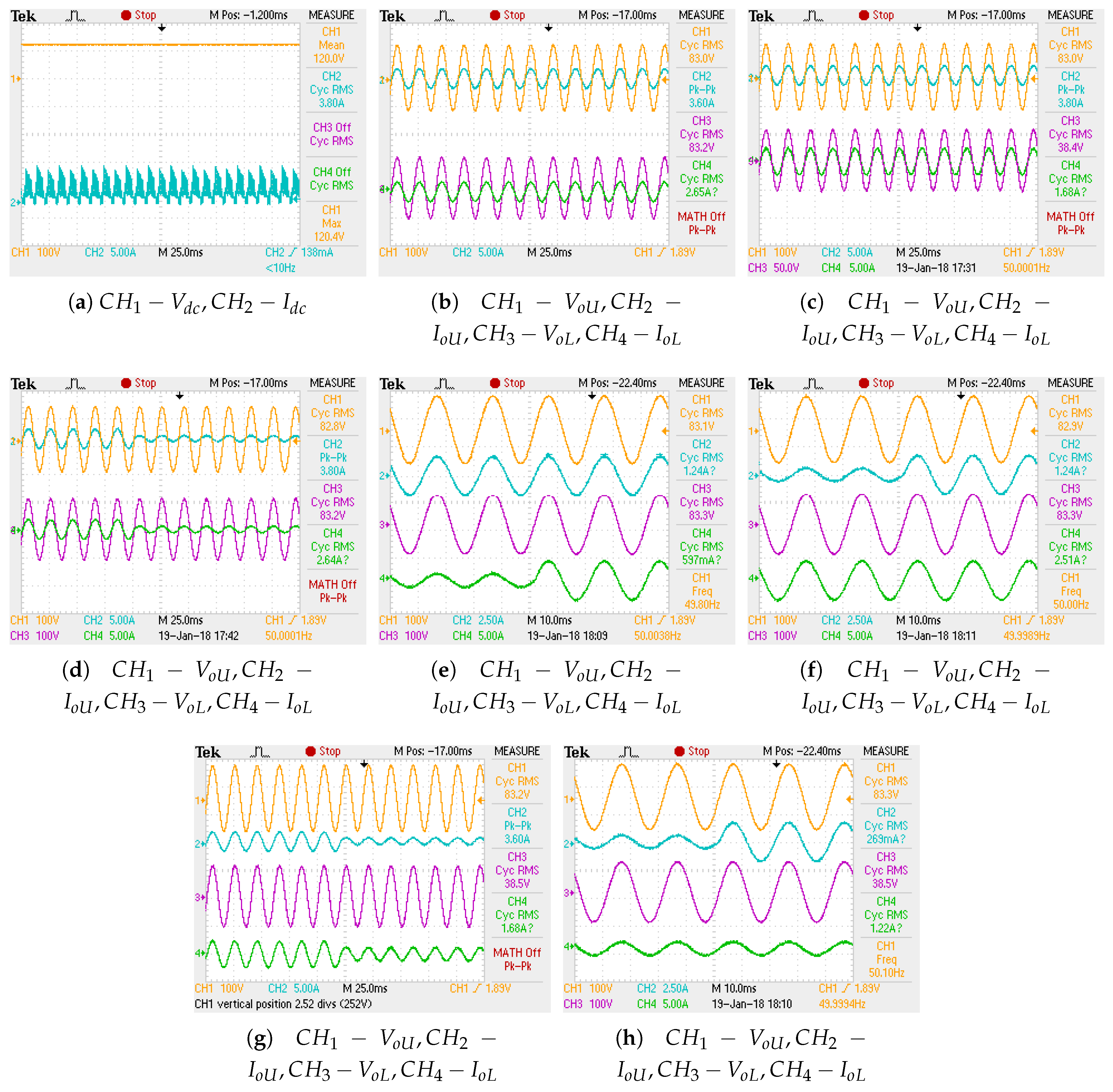
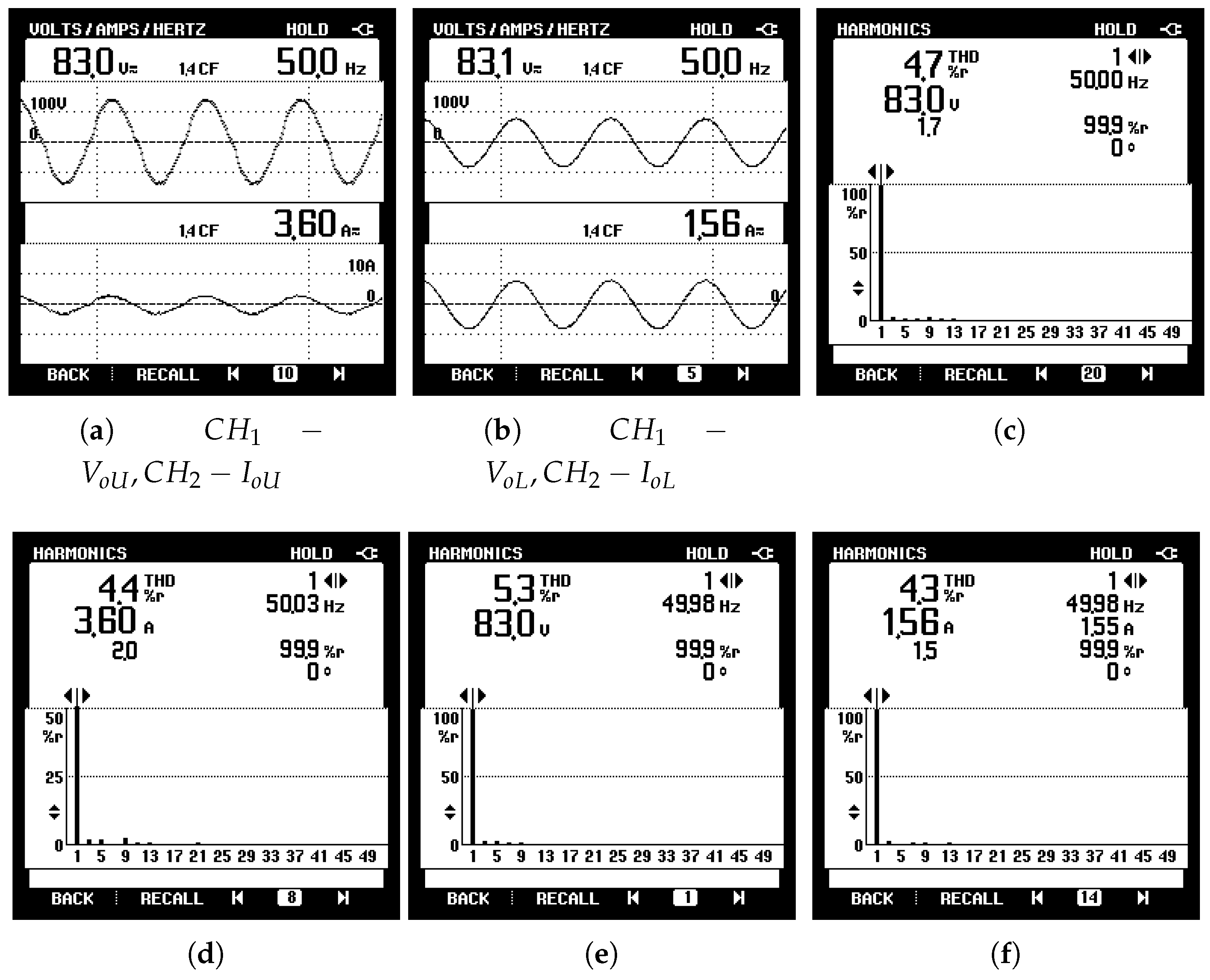
| Ref. | Sensors Type | Mode | Network/ Monitoring | Programming Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [33] | RFID Tag | Zigbee, CAN, RFID | XML | Multi domain |
| [34] | RTU | WSN | CC studio, SCADA/HMI | Multi domain |
| [35] | SenseLab Sensor | WSN | Cooja network simulator | Multi domain |
| [36] | Sensor nodes Green orbs | WSN, Zigbee | Green orbs host computer | Multi domain |
| [32] | Sensors PLC | WIFI | LabVIEW JIL server | Multi domain |
| Proposed | NI Sensors MyRIO | WIFI | LabVIEW VI Server | Single domain |
| Inverter Type | Switches | Source Type | EV | DV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dual phase with single DC bus with split Capacitor | 4 | Voltage | Yes | No |
| Dual phase with three wire | 6 | Voltage | Yes | No |
| Dual phase dual DC bus | 4 | Voltage | Yes | No |
| Dual phase with transformer | 4 | Voltage | Yes | No |
| Dual output VSI | 6 | Voltage | Yes | No |
| Single port conventional CSI | 4 | Current | Yes | No |
| Proposed | 6 | Current | Yes | Yes |
| Parameters | Values (Units) |
|---|---|
| Maximum Rated Power | 1 kW |
| DC Voltage | 120 V |
| Inductor | 10 mH |
| IGBT | IRG4BC30S |
| Controller | NI myRIO 1900 |
| Data Acquisition Systems | NI C-DAQ 9174 |
| Driver Circuit | Texas Instruments SM72295 |
| Server | NI web server |
| Network Monitoring | Total Network Manager (TNM) |
| Oscilloscope | Textronix TPS 2024B four channel |
| THD | Upper Side THD % | Lower Side THD % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EV | DV | EV | DV | |
| Voltage THD | 4.7 | 4.7 | 5.3 | 4.3 |
| Current THD | 4.4 | 5.4 | 4.3 | 4.8 |
| Inverter Type | No of Outputs | No of Switches | Total Loss (w) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional CSI | 1 | 4 | 11.032 |
| Two conventional CSI | 2 | 8 | 22.064 |
| Proposed dual output CSI | 2 | 6 | 16.548 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Senthilnathan, K.; Annapoorani, I. Multi-Port Current Source Inverter for Smart Microgrid Applications: A Cyber Physical Paradigm. Electronics 2019, 8, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8010001
Senthilnathan K, Annapoorani I. Multi-Port Current Source Inverter for Smart Microgrid Applications: A Cyber Physical Paradigm. Electronics. 2019; 8(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleSenthilnathan, Karthikrajan, and Iyswarya Annapoorani. 2019. "Multi-Port Current Source Inverter for Smart Microgrid Applications: A Cyber Physical Paradigm" Electronics 8, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8010001
APA StyleSenthilnathan, K., & Annapoorani, I. (2019). Multi-Port Current Source Inverter for Smart Microgrid Applications: A Cyber Physical Paradigm. Electronics, 8(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8010001





