A Novel Moisture Diffusion Modeling Approach Using Finite Element Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Classical Wetness Formulation
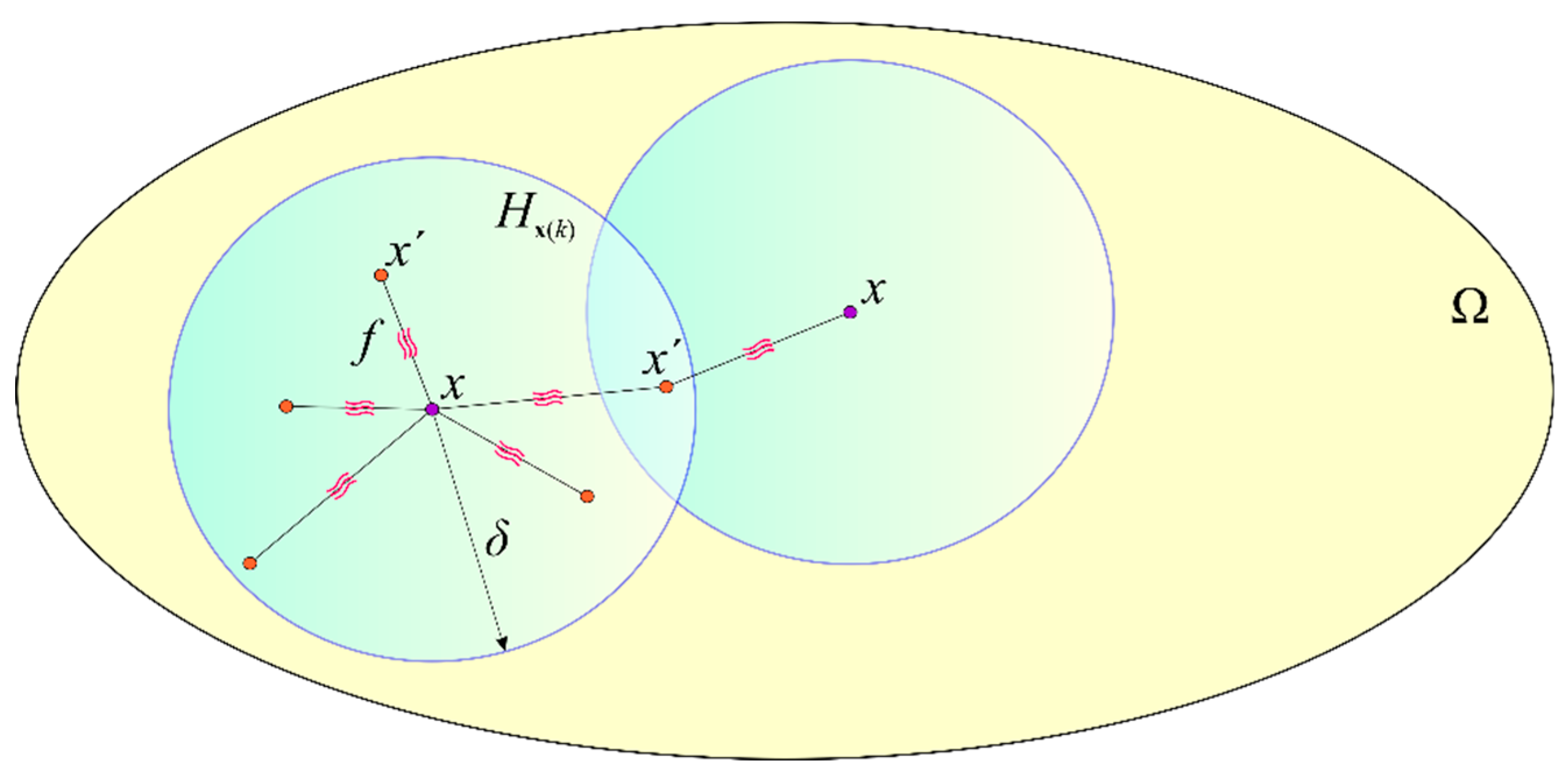
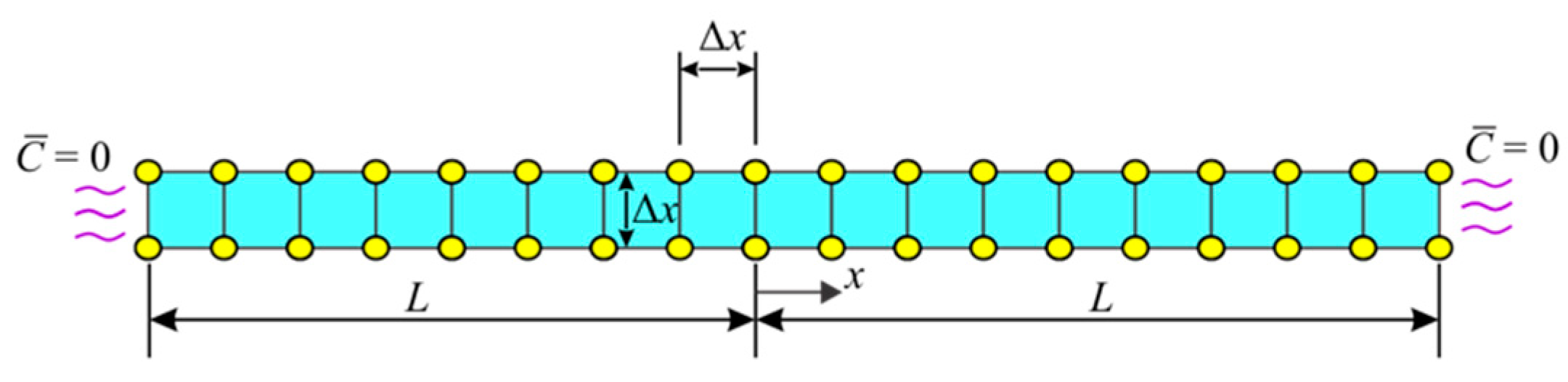
3. Peridynamic Wetness Formulation
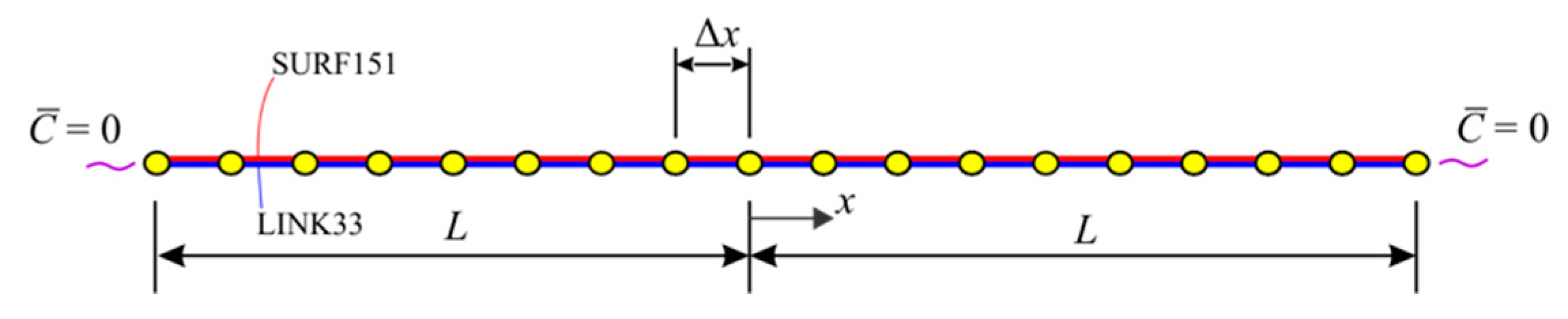
4. ANSYS Coupled Field and Diffusion Element Formulations
5. ANSYS Thermal and Surface Effect Element Formulations
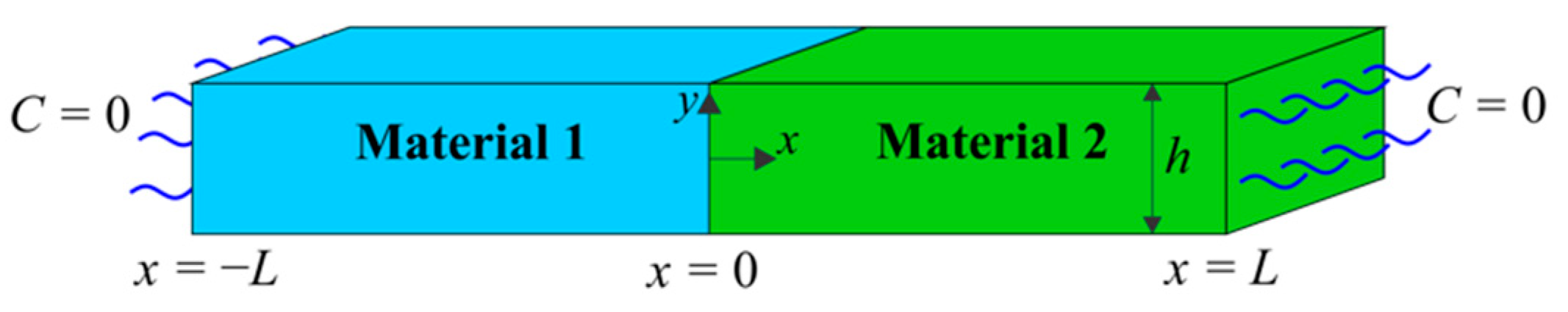
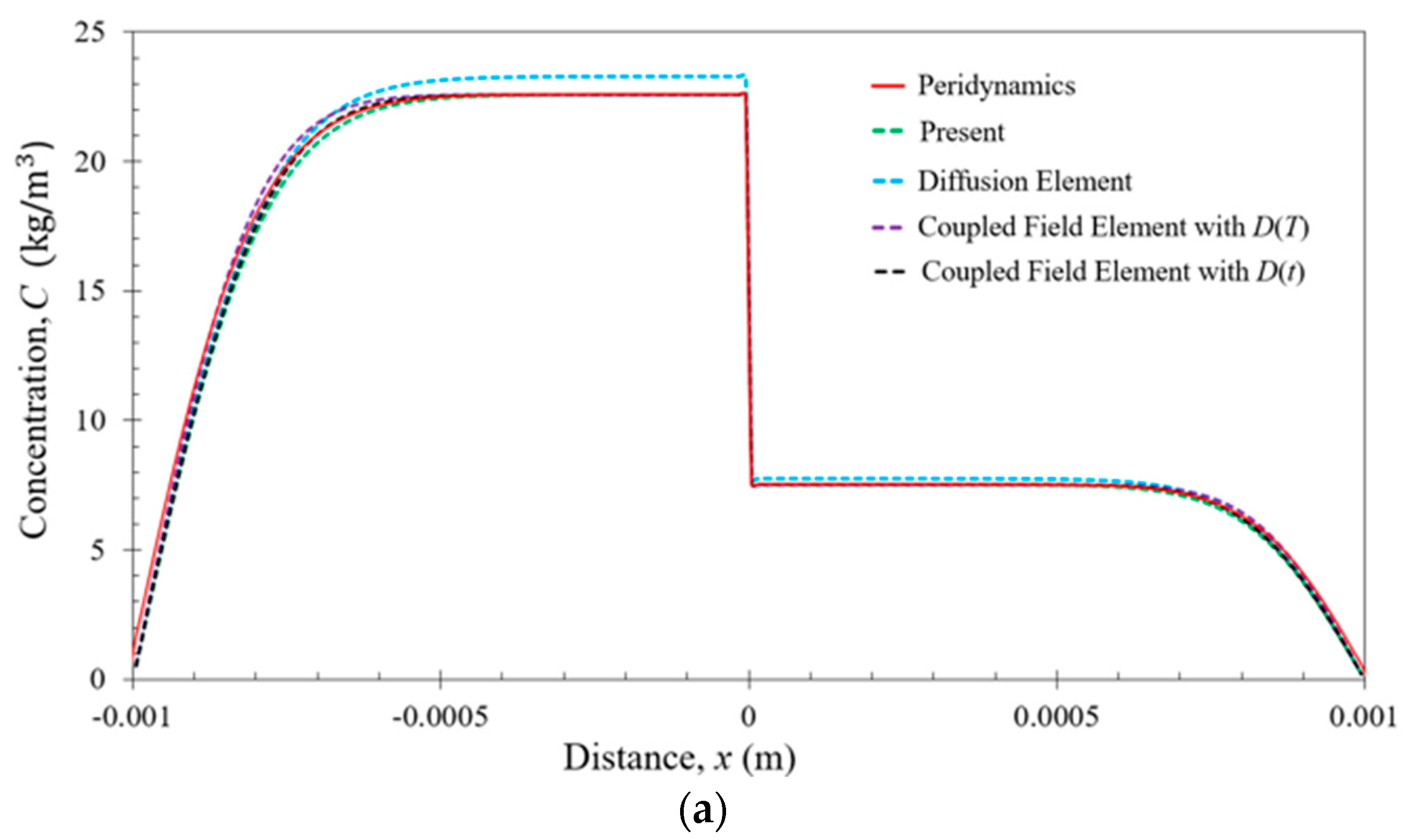
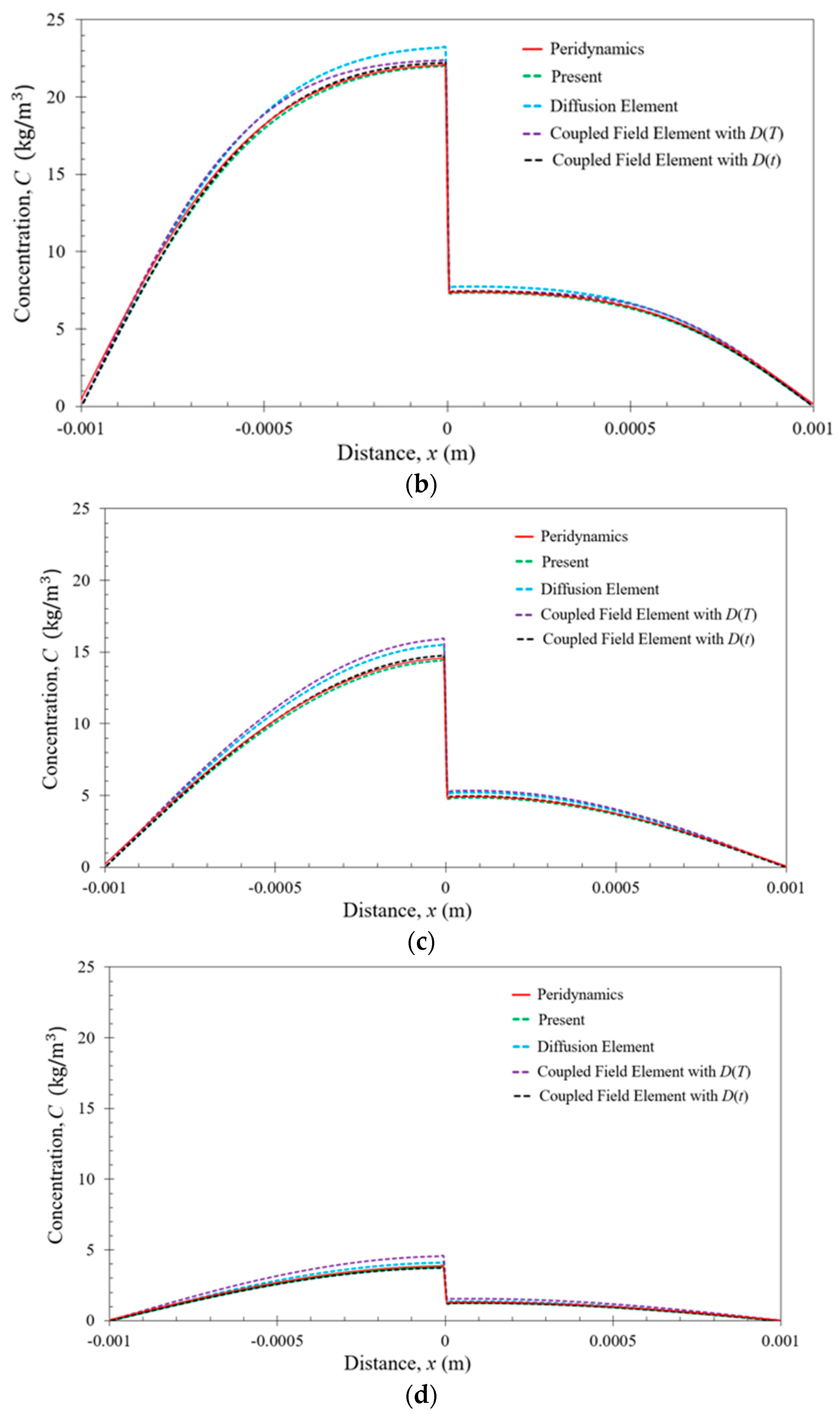
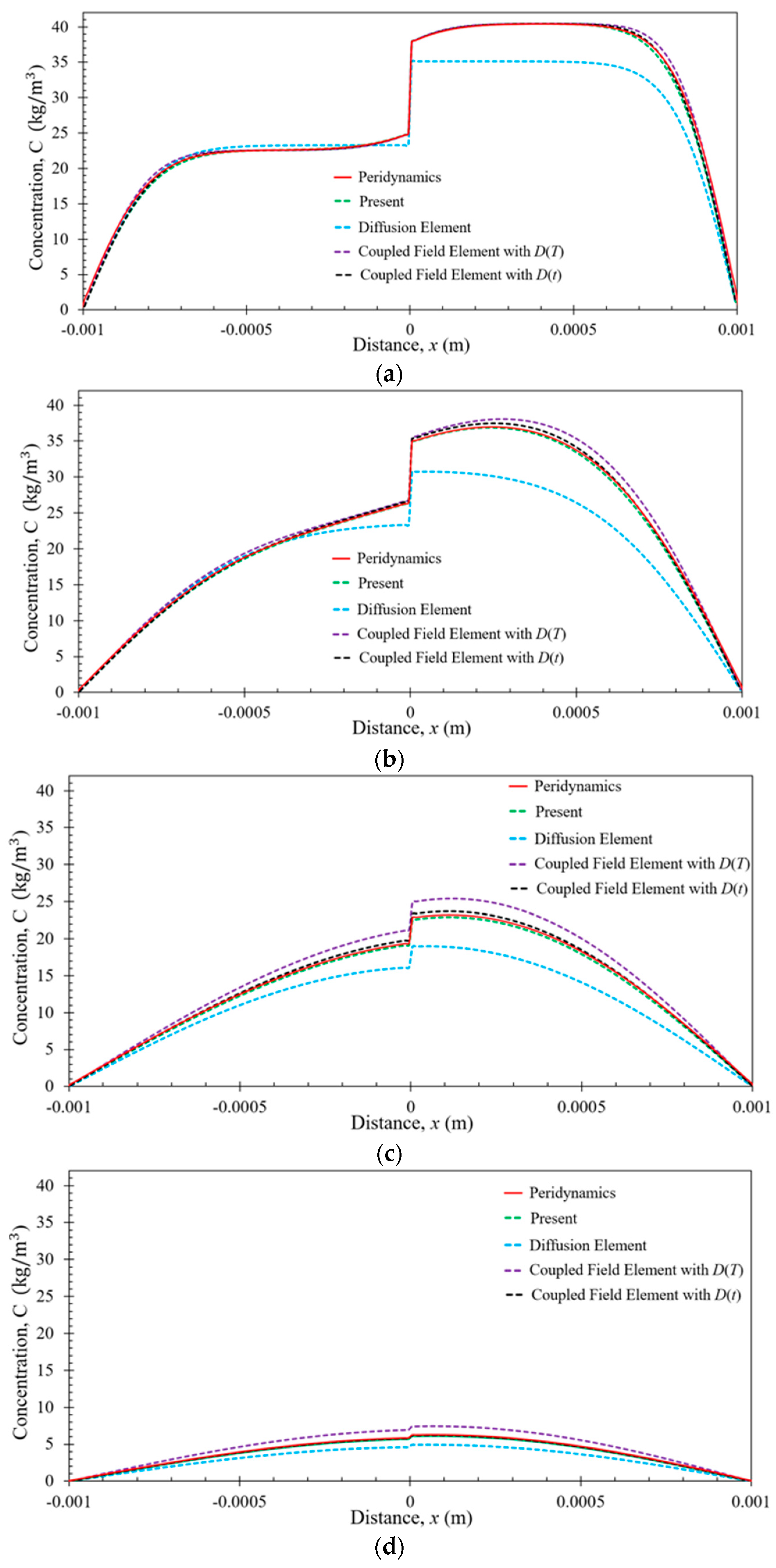
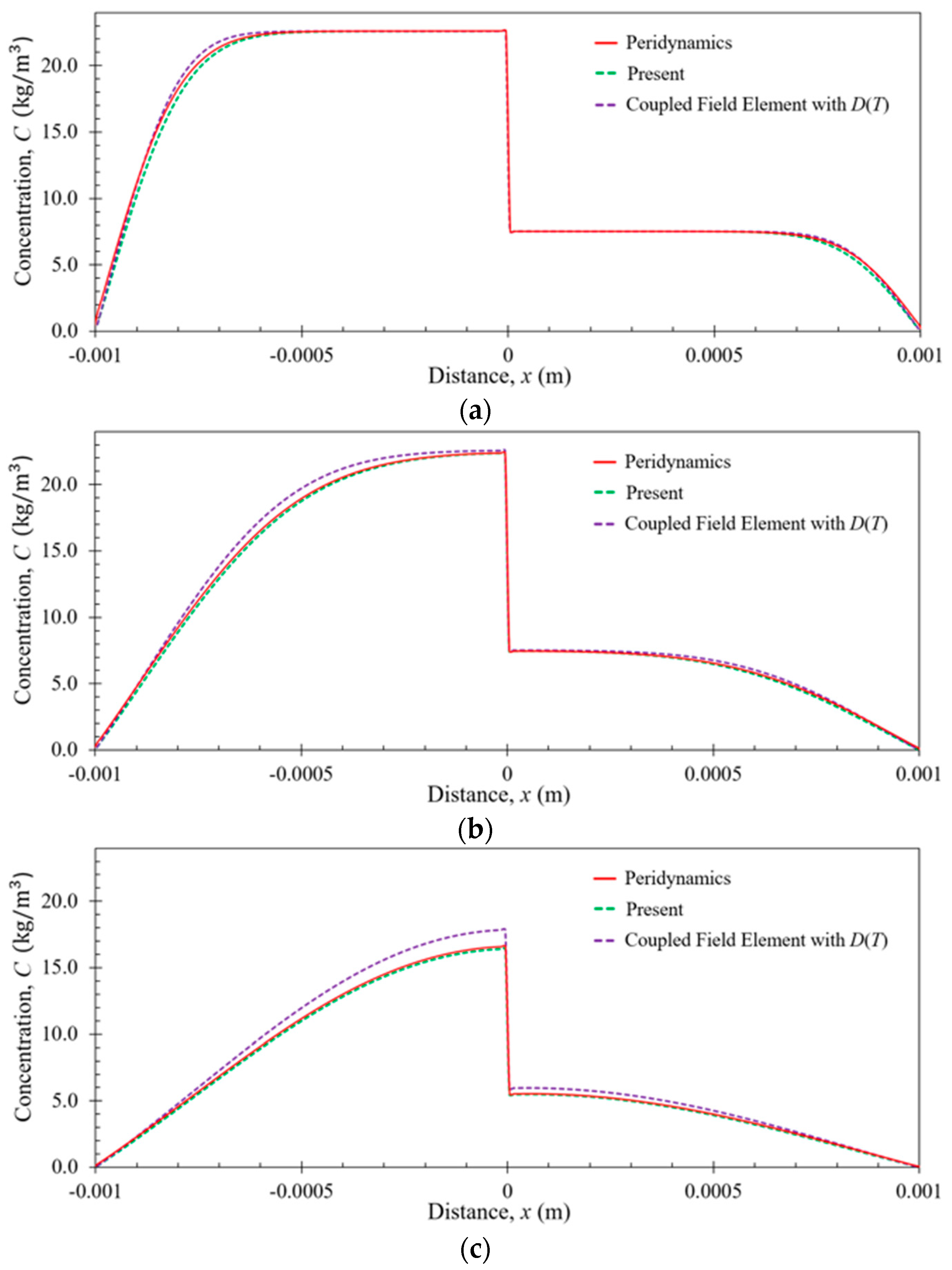
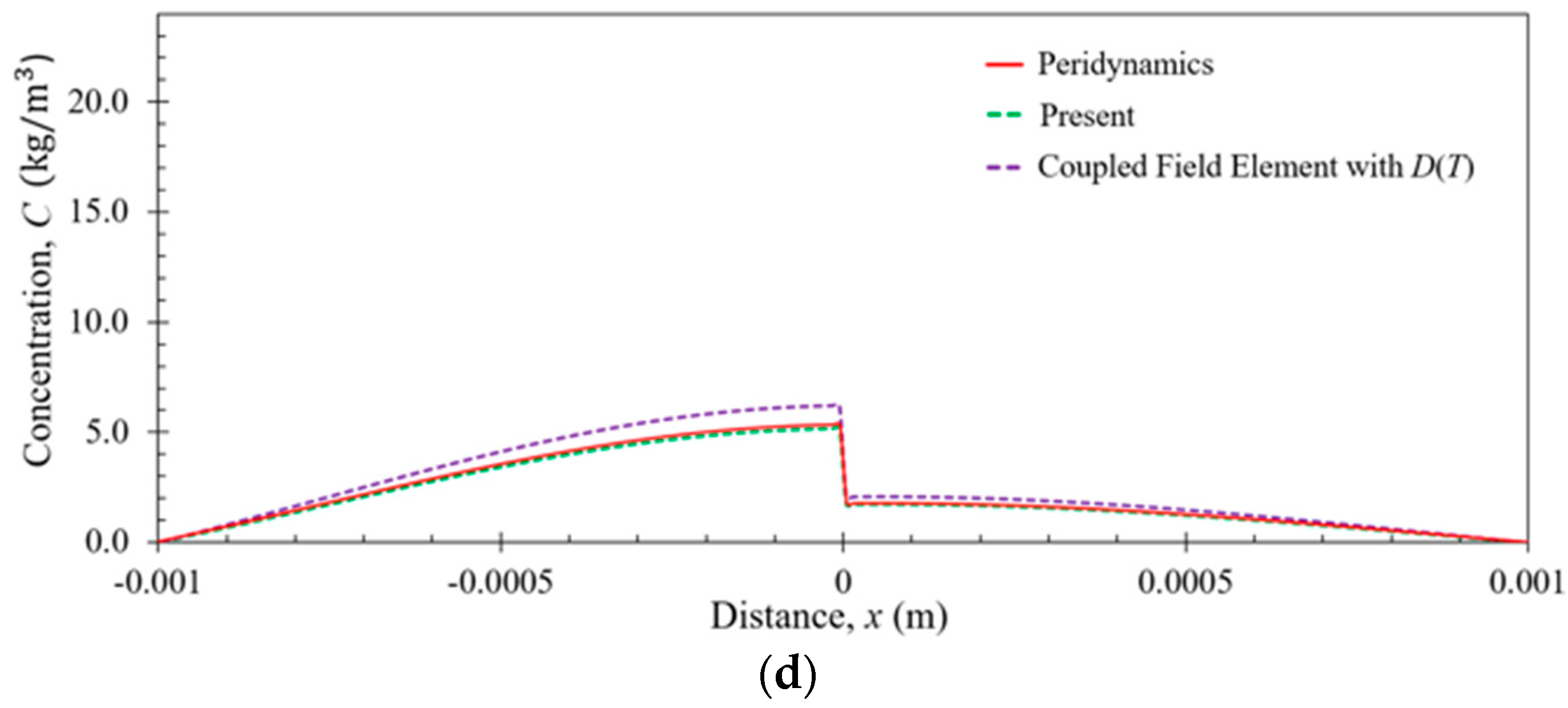
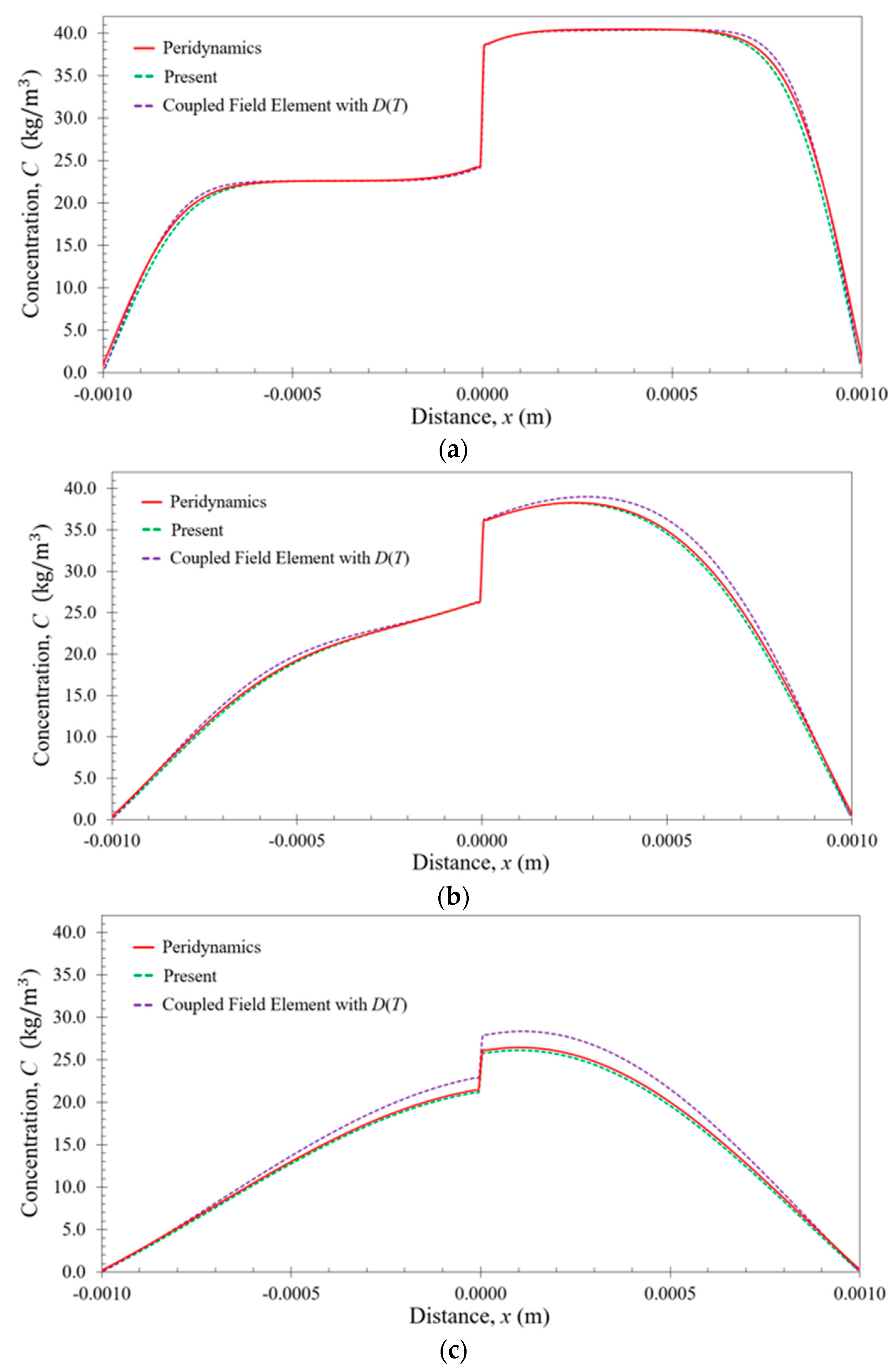
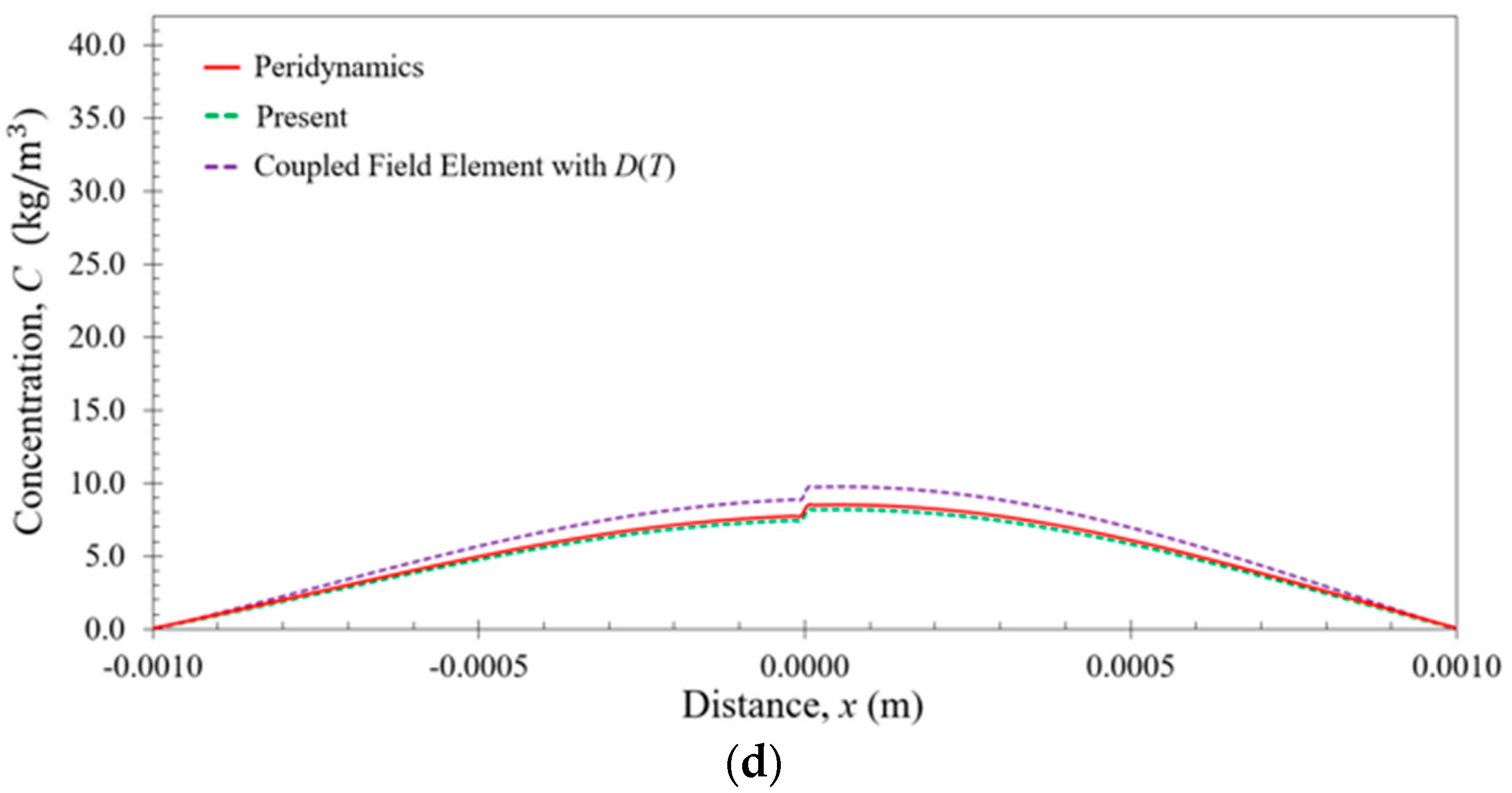
6. Numerical Results
6.1. Bar Subjected to Uniform Temperature
6.2. Bar Subjected to Nonuniform Temperature
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, E.H.; Park, B. Moisture diffusion modeling—A critical review. Microelectron. Reliab. 2016, 65, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.H.; Teo, Y.C.; Lim, T.B. Moisture diffusion and vapor pressure modeling of IC packaging. In Proceedings of the 48th Electronic Components and Technology Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 25–28 May 1998; pp. 1372–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.; Han, B.; Wang, Z. On moisture diffusion modeling using thermal-moisture analogy. ASME J. Electron. Packag. 2007, 129, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, C.; Park, S.; Han, B.; Yoon, S. Advanced thermal-moisture analogy scheme for anisothermal moisture diffusion problem. ASME J. Electron. Packag. 2008, 130, 011004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.H.; Koh, S.W.; Lee, K.H.; Rajoo, R. Advanced moisture diffusion modeling & characterization for electronic packaging. In Proceedings of the 52nd Electronic Components and Technology Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 28–31 May 2002; pp. 1297–1303. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, E.H. The fundamentals of thermal-mass diffusion analogy. Microelectron. Reliab. 2015, 55, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diyaroglu, C.; Oterkus, S.; Oterkus, E.; Madenci, E.; Han, S.; Hwang, Y. Peridynamic wetness approach for moisture concentration analysis in electronic packages. Microelectron. Relia. 2017, 70, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diyaroglu, C.; Oterkus, S.; Oterkus, E.; Madenci, E. Peridynamic modeling of diffusion by using finite element analysis. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 7, 1823–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Fan, X. Application of water activity-based theory for moisture diffusion in electronic packages using ANSYS. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Thermal, Mechanical and Multi-Physics Simulation and Experiments in Microelectronics and Microsystems, Toulouse, France, 15–18 April 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, J.; Chu, H.W.; Zhang, G.; Fan, X. Modeling nonlinear moisture diffusion in inhomogeneous media. Microelectron. Reliab. 2017, 75, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Park, S. A note on the normalized approach to simulating moisture diffusion in a multimaterial system under transient thermal conditions using ANSYS 14 and 14.5. ASME J. Electron. Packag. 2014, 136, 034501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M. Moisture Diffusion Modeling with ANSYS at R14 and Beyond. Available online: http://www.padtinc.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/oldblog/PADT-Webinar-Moisture-Diffusion-2012_05_24.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2018).
- Diyaroglu, C.; Madenci, E.; Oterkus, S.; Oterkus, E. A novel finite element technique for moisture diffusion modeling using ANSYS. In Proceedings of the 68th Electronic Components and Technology Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 29 May–1 June 2018; pp. 227–235. [Google Scholar]
- ANSYS 19.0 Mechanical User’s Guide; ANSYS: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2018.
- Wang, J.; Liu, R.; Liu, D.; Park, S. Advancement in simulating moisture diffusion in electronic packages under dynamic thermal loading conditions. Microelectron. Reliab. 2017, 73, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| LINK33 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material Properties | Original | Modified | ANSYS Command | |
| Thermal Conductivity | MP, KXX, MAT 1, | |||
| Density | 1.0 | MP, DENS, MAT 1, 1.0 | ||
| Specific Heat | c | MP, C, MAT 1, | ||
| Real Constants | Cross Sectional Area | A | A | R, NSET 2, A |
| SURF151 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Applying Surface loads on elements (SFE) | Convection (CONV) | Original | Modified | ANSYS Command |
| Film Coefficient | SFE, Elem 1, CONV, 1, | |||
| Bulk Temperature | 0.0 | SFE, Elem 1, CONV, 2, 0.0 | ||
| Material 1 | Material 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Diffusivity factor, () | ||
| Solubility factor, | ||
| Pressure factor, () | ||
| Diffusion activation energy, () | ||
| Solubility activation energy, () | ||
| Vapor pressure activation energy, () |
| Material 1 | Material 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Density, () | ||
| Specific Heat, () | ||
| Thermal Conductivity, () |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diyaroglu, C.; Madenci, E.; Oterkus, S.; Oterkus, E. A Novel Moisture Diffusion Modeling Approach Using Finite Element Analysis. Electronics 2018, 7, 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7120438
Diyaroglu C, Madenci E, Oterkus S, Oterkus E. A Novel Moisture Diffusion Modeling Approach Using Finite Element Analysis. Electronics. 2018; 7(12):438. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7120438
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiyaroglu, Cagan, Erdogan Madenci, Selda Oterkus, and Erkan Oterkus. 2018. "A Novel Moisture Diffusion Modeling Approach Using Finite Element Analysis" Electronics 7, no. 12: 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7120438
APA StyleDiyaroglu, C., Madenci, E., Oterkus, S., & Oterkus, E. (2018). A Novel Moisture Diffusion Modeling Approach Using Finite Element Analysis. Electronics, 7(12), 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7120438







