Polarization-Shift Backscatter Identification for SWIPT-Based Battery-Free Sensor Nodes
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Non-intrusive integration:
- 2.
- Improved robustness through polarization shifting:
- 3.
- Cost-effective deployment:
- 4.
- High energy efficiency:
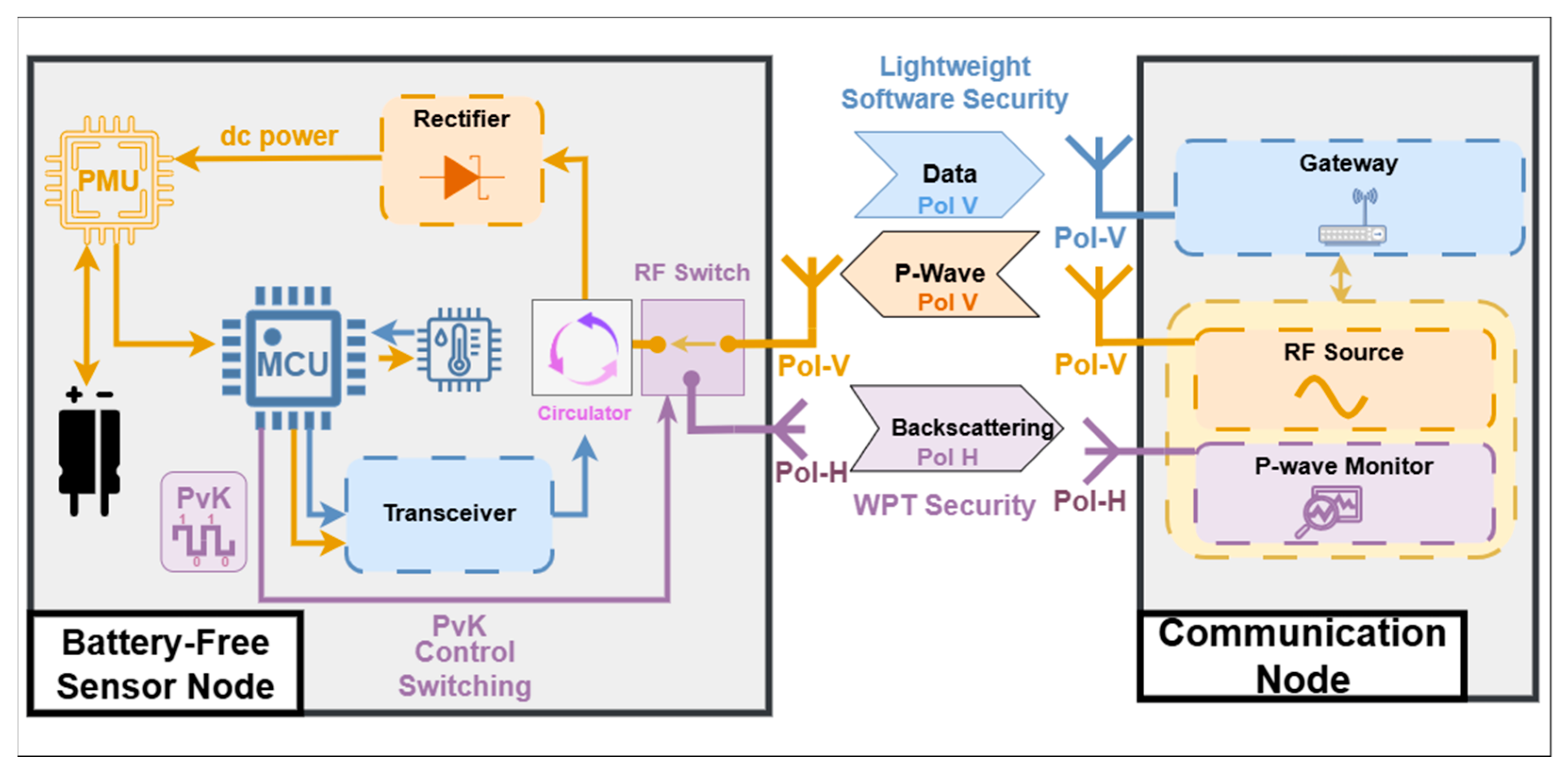
2. The Polarization-Shift Backscattering Security
3. Experiments and Results
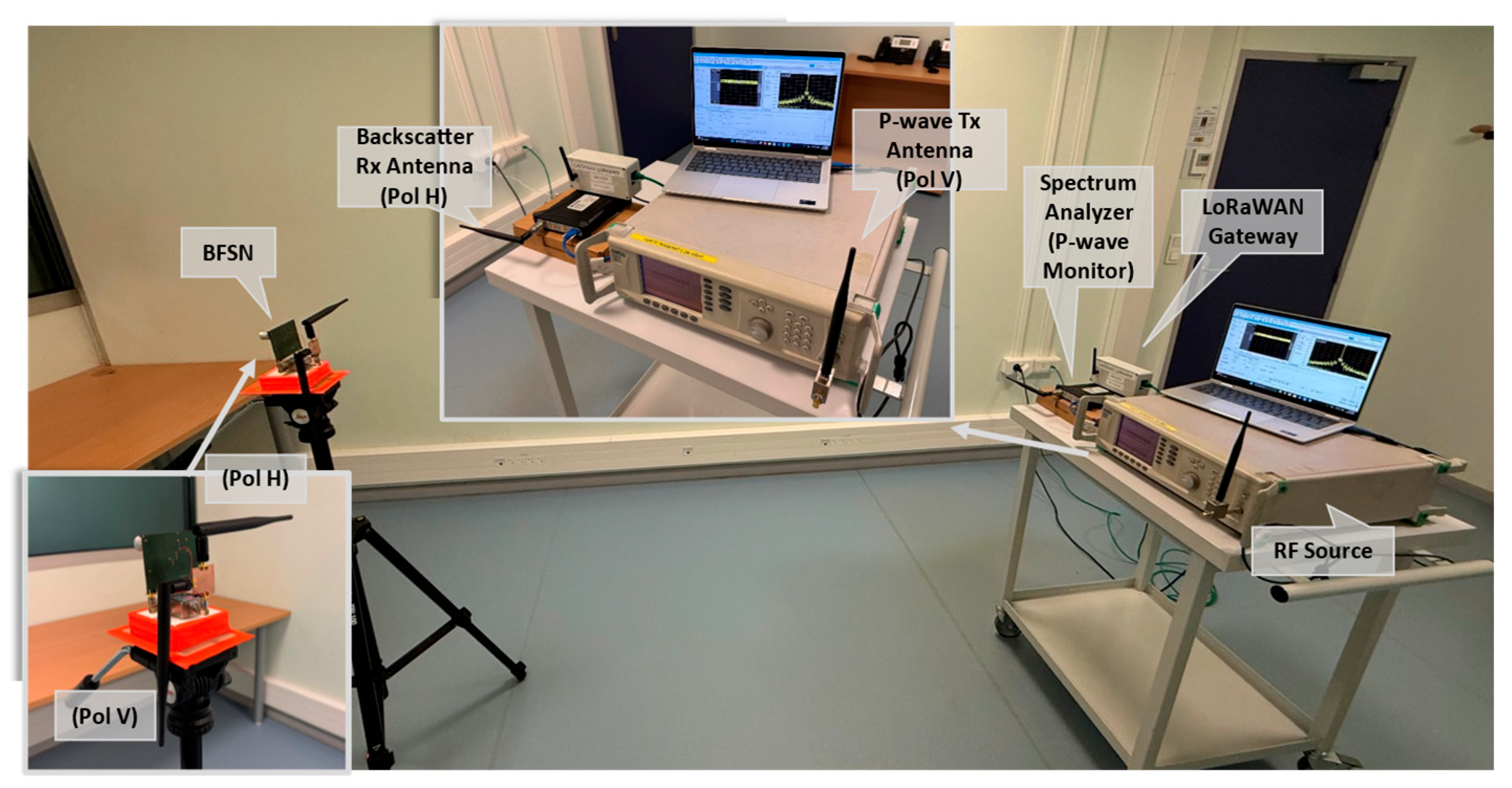
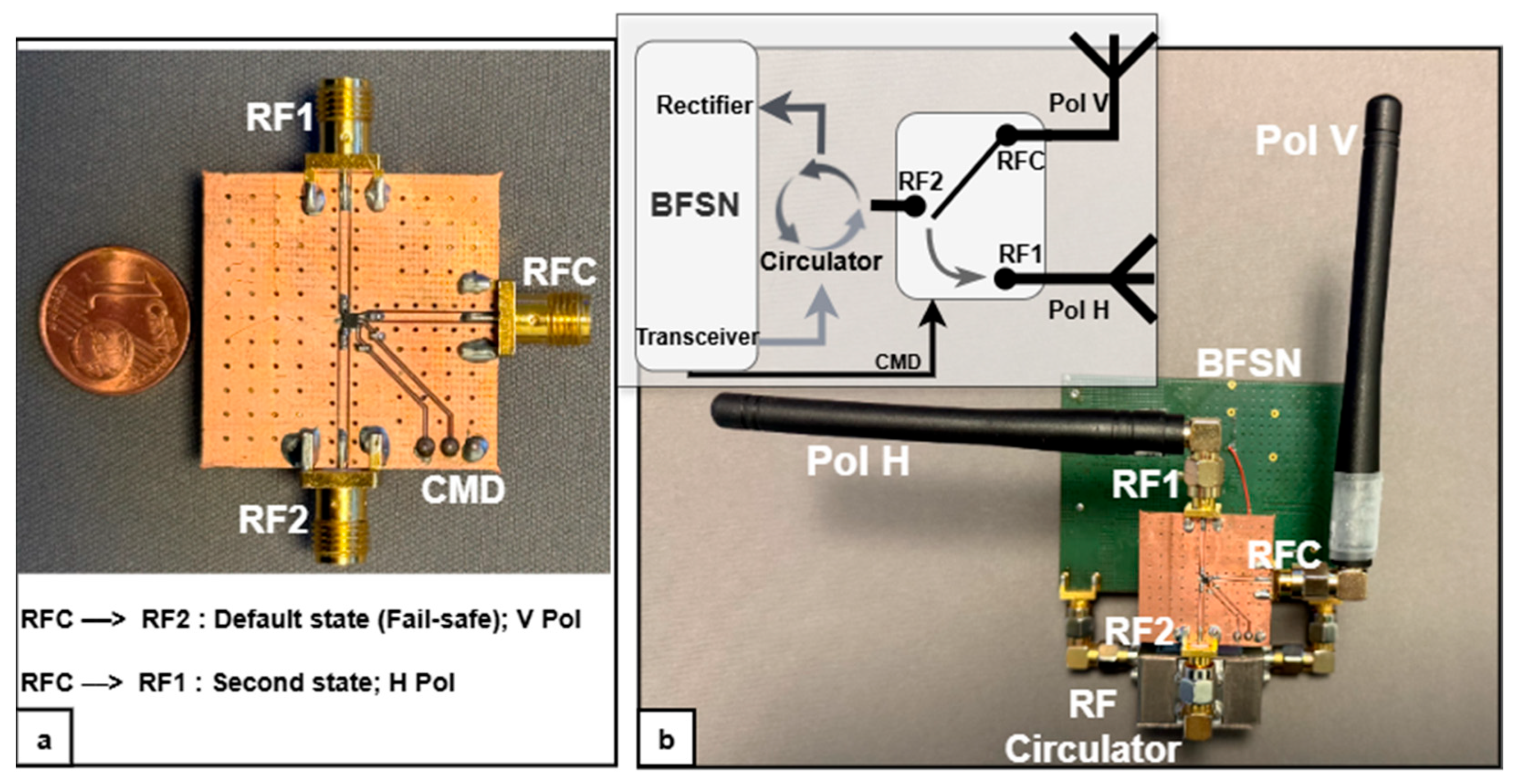
3.1. Antenna and Polarization Configuration
3.2. Operating Conditions
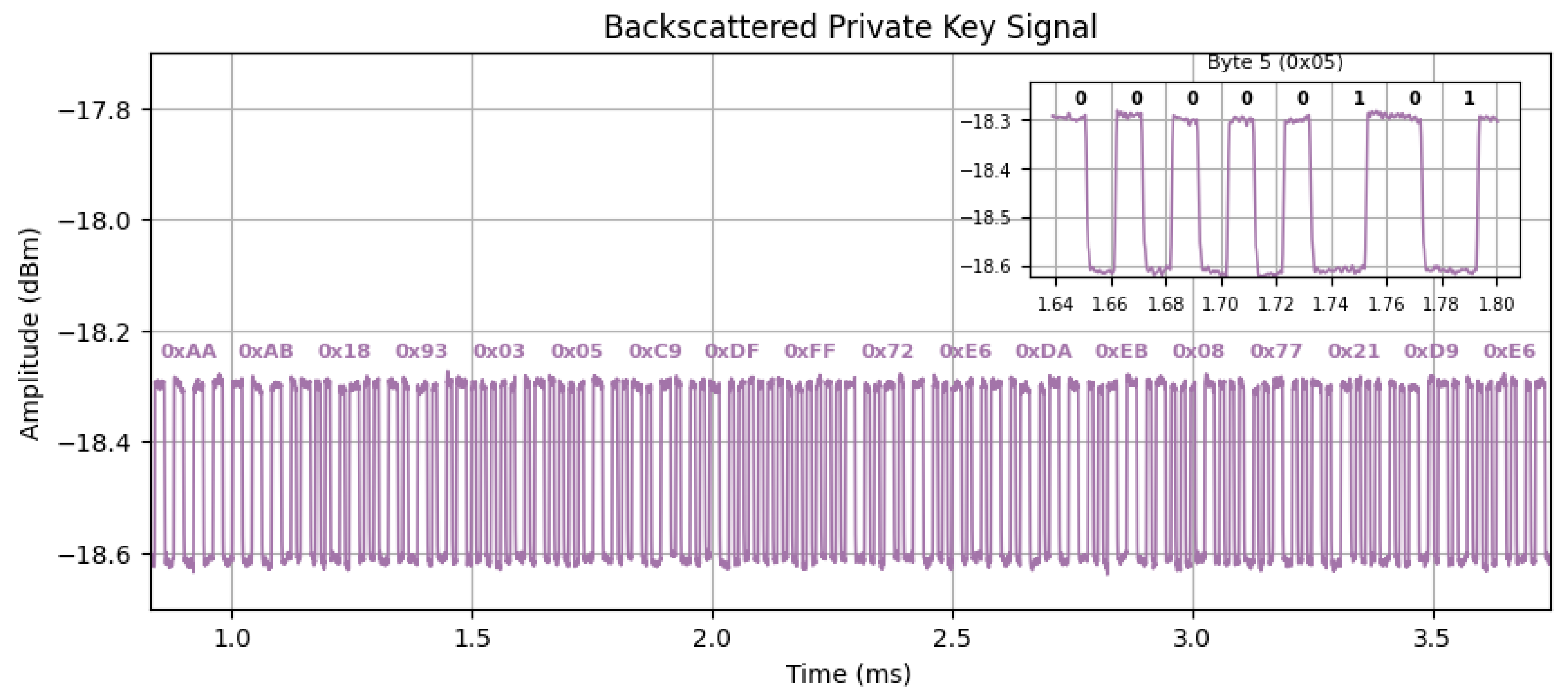
3.3. Backscattering Identification
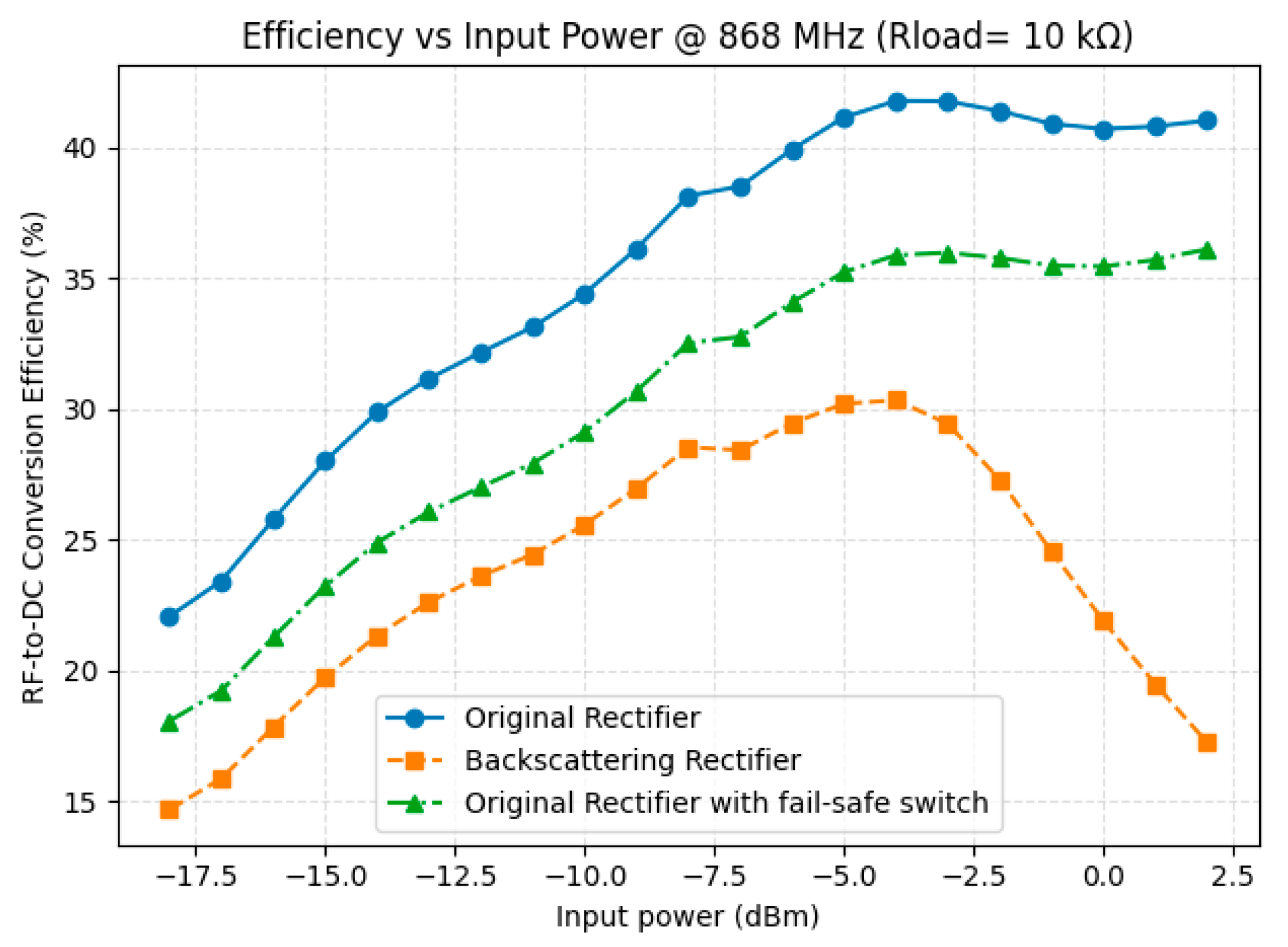
3.4. RF-to-DC Conversion Efficiency Comparison
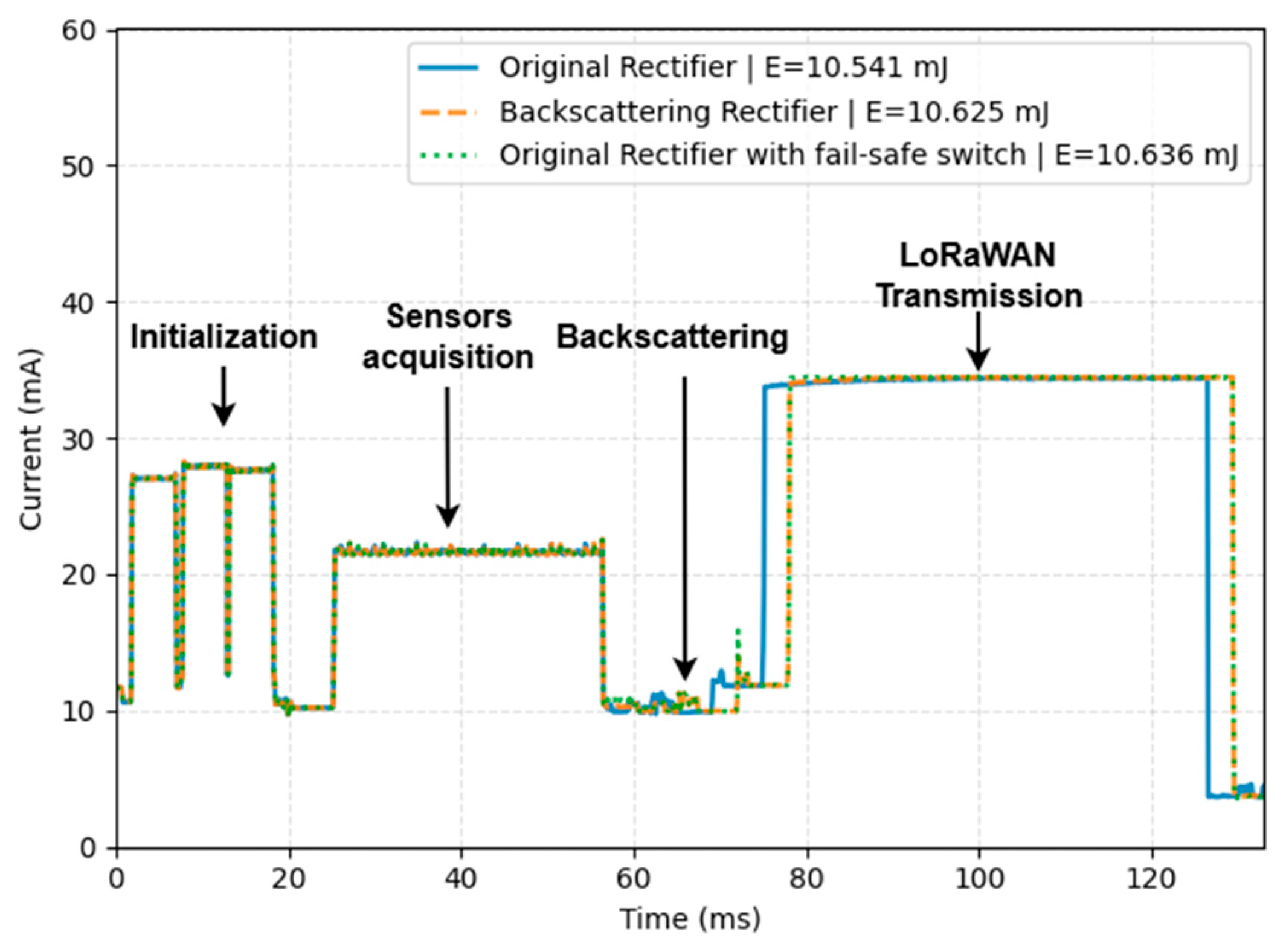
3.5. Energy Consumption Comparison
3.6. Experimental Outcomes Summary
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ni, T.; Sun, Z.; Han, M.; Xie, Y.; Lan, G.; Li, Z.; Gu, T.; Xu, W. REHSense: Towards Battery-Free Wireless Sensing via Radio Frequency Energy Harvesting. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Fifth International Symposium on Theory, Algorithmic Foundations, and Protocol Design for Mobile Networks and Mobile Computing, Athens, Greece, 1 October 2024; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 211–220. [Google Scholar]
- Palazzi, V.; Correia, R.; Gu, X.; Hemour, S.; Wu, K.; Costanzo, A.; Masotti, D.; Fazzini, E.; Georgiadis, A.; Kazemi, H.; et al. Radiative Wireless Power Transfer: Where We Are and Where We Want to Go. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2023, 24, 57–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, J.V.; Gu, X.; Wu, K. SWIPT Base Stations for Battery-Free, Wirelessly Powered IoT Networks: A Review on Architectures, Circuits and Technologies. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2024, 25, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Sun, P.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D. Simultaneous Wireless Power and Data Transfer: A Comprehensive Review. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 3650–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xing, C.-C.; Wang, C. Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer: Technologies, Applications, and Research Challenges. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 55, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, W.; Peng, M.; Peng, Y.; Feng, M.; Liu, G. Backscatter Communication Meets Practical Battery-Free Internet of Things: A Survey and Outlook. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2023, 25, 2021–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepecik, A.; Ağrak, A.F. Analysis of Lorawan Protocol and Attacks Against Lorawan-Based IoT Devices. Int. J. Appl. Methods Electron. Comput. 2024, 12, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milarokostas, C.; Tsolkas, D.; Passas, N.; Merakos, L. A Comprehensive Study on LPWANs with a Focus on the Potential of LoRa/LoRaWAN Systems. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2023, 25, 825–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, D.H. Bluetooth 5/6 Overview. In 5G/5G-Advanced, Wi-Fi 6/7, and Bluetooth 5/6: A Primer on Smartphone Wireless Technologies; Morais, D.H., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 181–204. ISBN 978-3-031-82830-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, R.; Wu, H.; Ou, J.; Yang, S.; Gao, Y. Power Splitting-Based SWIPT Systems with Full-Duplex Jamming. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 9822–9836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Chen, T.M.; Xu, P.; Chen, Q. DS-SWIPT: Secure Communication with Wireless Power Transfer for Internet of Things. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2022, 2022, 2650474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thien, H.T.; Tuan, P.-V.; Koo, I. A Secure-Transmission Maximization Scheme for SWIPT Systems Assisted by an Intelligent Reflecting Surface and Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 31851–31867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xie, H.; Liang, C.; Yu, F.R. Robust Secure Energy-Efficiency Optimization in SWIPT-Aided Heterogeneous Networks with a Nonlinear Energy-Harvesting Model. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 14908–14919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapathy, V.; Ramachandran, R.; Ohtsuki, T. Deep Learning Methods for Secure IoT SWIPT Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 19657–19677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, J.; Hsiung, K.-L.; Chen, H.-Y. GRNN-Based Detection of Eavesdropping Attacks in SWIPT-Enabled Smart Grid Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 37381–37393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djidjekh, T.E.; Loubet, G.; Sanogo, L.; Sidibé, A.; Delai, G.; Dragomirescu, D.; Takacs, A. Backscattering Rectifier for Security and Identification in the Context of Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer. In Proceedings of the 2024 54th European Microwave Conference (EuMC), Paris, France, 24–26 September 2024; IEEE: Paris, France, 2024; pp. 300–303. [Google Scholar]
- Djidjekh, T.E.; Loubet, G.; Takacs, A. Backscattering-Based Security in Wireless Power Transfer Applied to Battery-Free BLE Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE Wireless Power Technology Conference and Expo (WPTCE), Rome, Italy, 3–6 June 2025; IEEE: Rome, Italy, 2025; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Loubet, G.; Sidibe, A.; Herail, P.; Takacs, A.; Dragomirescu, D. Autonomous Industrial IoT for Civil Engineering Structural Health Monitoring. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 8921–8944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.-G.; Kim, J.-H.; Ahn, S.-H.; Lee, W.-S. A 915 MHz Dual Polarized Meandered Dipole Antenna with Dual Resonance. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP), Busan, Republic of Korea, 23–26 October 2018; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.; Chu, Q.-X. A Wideband Dual-Polarized Antenna for LTE700/GSM850/GSM900 Applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 2098–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Zhou, S.-G.; Gong, S.-X.; Liu, Y. A compact dual-polarized antenna for base station application. PIER Lett. 2016, 59, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miran, E.A.; Çiydem, M. A Low-Profile High Isolation Wideband Dual-Polarized Antenna for Sub-1 GHz Base Stations. Gazi Univ. J. Sci. 2024, 37, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Wu, C.; Qiu, J.; Denisov, O.; Molebny, V. A Dual-Polarized Crisscross-Shaped Antenna with Enhanced Front-to-Back Ratio for Base Stations. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Workshop Series on Advanced Materials and Processes for RF and THz Applications (IMWS-AMP), Guangzhou, China, 13–15 November 2022; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]

| Approach | Extra Hardware | Invasive to Circuitry | Protocol-Independent | Energy Efficiency Impact | Validation | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jamming-based PHY security | High (full-duplex + self-interference cancellation) | Yes | Limited (only for power-splitting schemes) | High, due to full-duplex and self-interference cancellation (energy cost typically non-negligible) | Mostly simulation | [10] |
| DSSS/spread-spectrum PHY security | Medium (spreading/coding support) | Yes | Limited (only DSSS-based schemes) | Medium (time switching between energy harvesting and decoding) | Mostly simulation | [11] |
| Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces (IRS) | High (additional infrastructure: IRS panels and control) | No | Limited (only for IRS-assisted SWIPT with power splitting) | Low at node, but requires external infrastructure | Mostly simulation | [12] |
| Secure energy optimization | Low extra hardware but high processing complexity | No | Limited (only for SWIPT-aided Het-Nets with beamforming and power splitting) | Low, but with high signal-processing burden and dependence on CSI | Mostly simulation | [13] |
| Deep-learning-based security | Low extra hardware, high computation requirements | No | Often limited (training and CSI dependence) | Low, but requires training, CSI, and is environment-sensitive | Mostly simulation | [14,15] |
| Backscattering rectifier (BR) identification | Low (dedicated backscattering rectifier) | Yes | Yes (protocol-independent) | Low, ~84 µJ overhead for a ~10 mJ cycle, with harvesting efficiency loss >10% | Experimental proof of concept | [16,17] |
| Polarization-Shift Backscatter Identification | Low, dedicated polarization backscattering add-on module | No | Yes (protocol-independent) | Very low, ~96 µJ overhead for a ~10 mJ cycle, with low harvesting efficiency loss (~5%) | Experimental proof of concept | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Djidjekh, T.E.; Takacs, A. Polarization-Shift Backscatter Identification for SWIPT-Based Battery-Free Sensor Nodes. Electronics 2026, 15, 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15010186
Djidjekh TE, Takacs A. Polarization-Shift Backscatter Identification for SWIPT-Based Battery-Free Sensor Nodes. Electronics. 2026; 15(1):186. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15010186
Chicago/Turabian StyleDjidjekh, Taki E., and Alexandru Takacs. 2026. "Polarization-Shift Backscatter Identification for SWIPT-Based Battery-Free Sensor Nodes" Electronics 15, no. 1: 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15010186
APA StyleDjidjekh, T. E., & Takacs, A. (2026). Polarization-Shift Backscatter Identification for SWIPT-Based Battery-Free Sensor Nodes. Electronics, 15(1), 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15010186






