Enhancing Retrieval-Oriented Twin-Tower Models with Advanced Interaction and Ranking-Optimized Loss Functions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional Retrieval Methods
2.2. Sparse Feature Methods
2.3. Dense Retrieval Methods
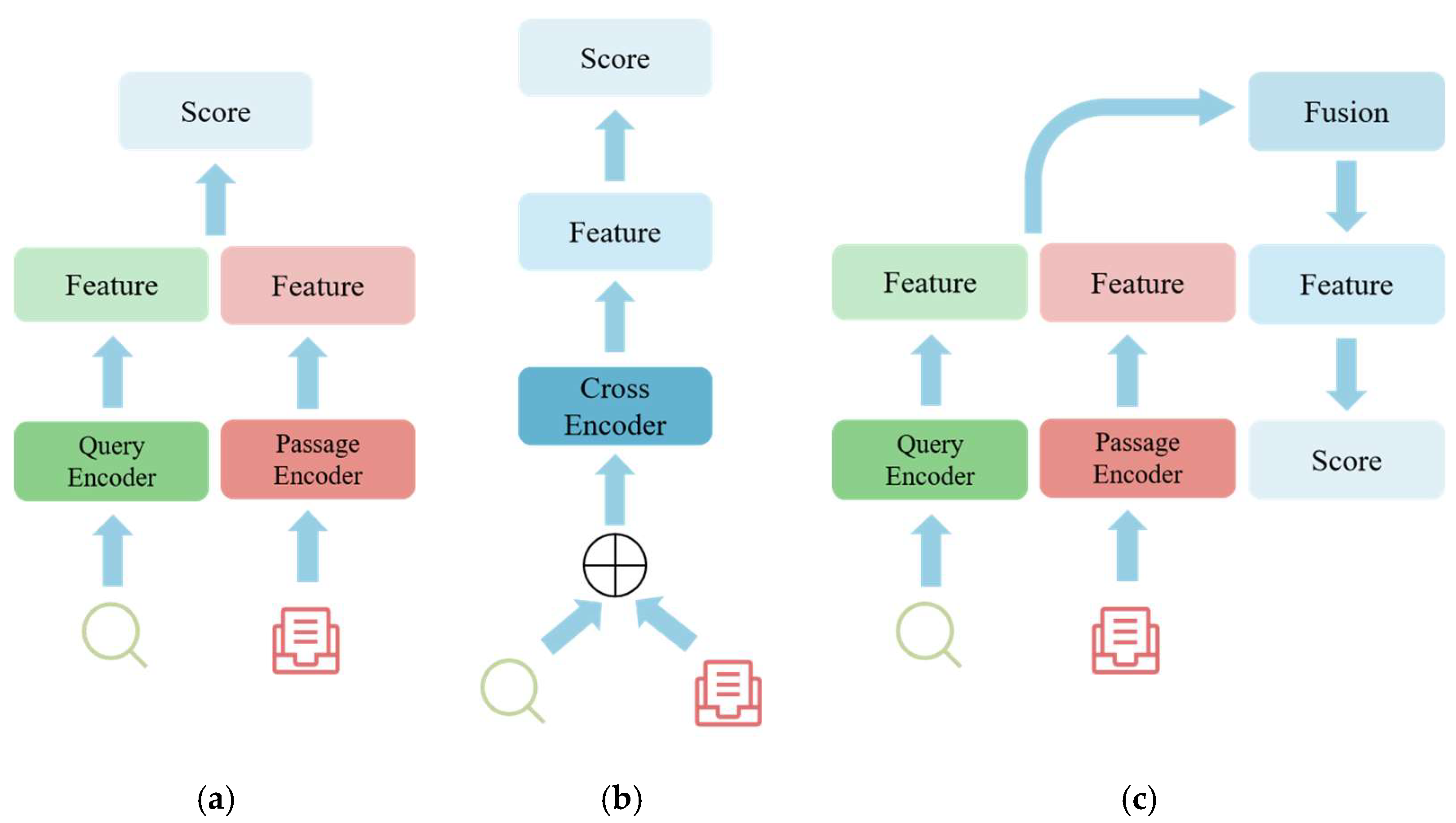
2.3.1. Dual-Encoder
2.3.2. Cross-Encoder
2.3.3. Late-Encoder
2.4. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
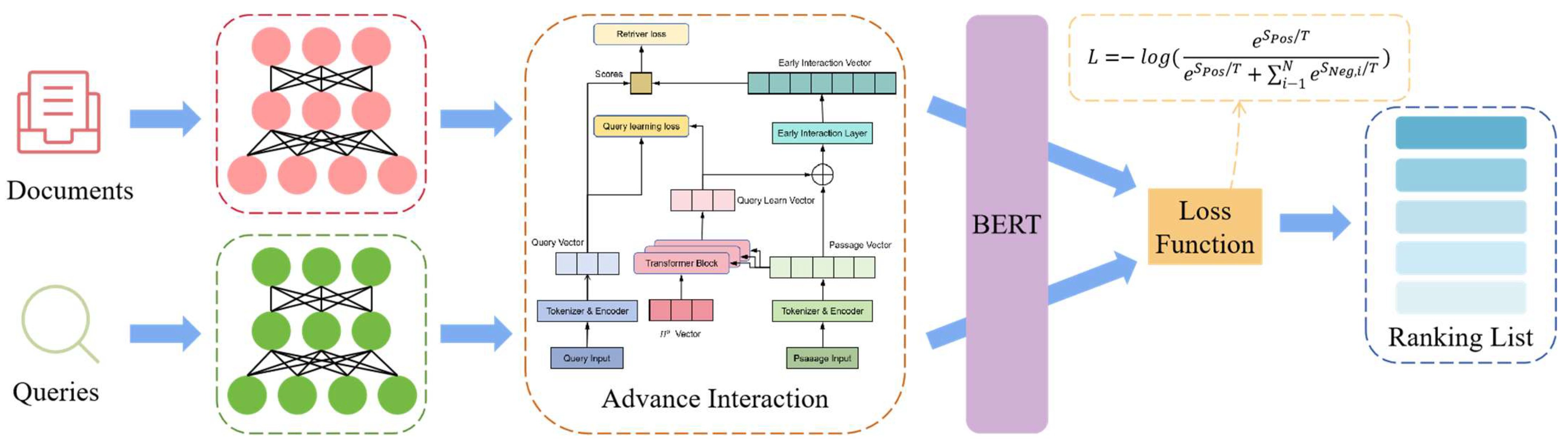
3. Optimization Algorithms for Twin-Tower Model
3.1. Advance Interaction of the Twin-Tower Model
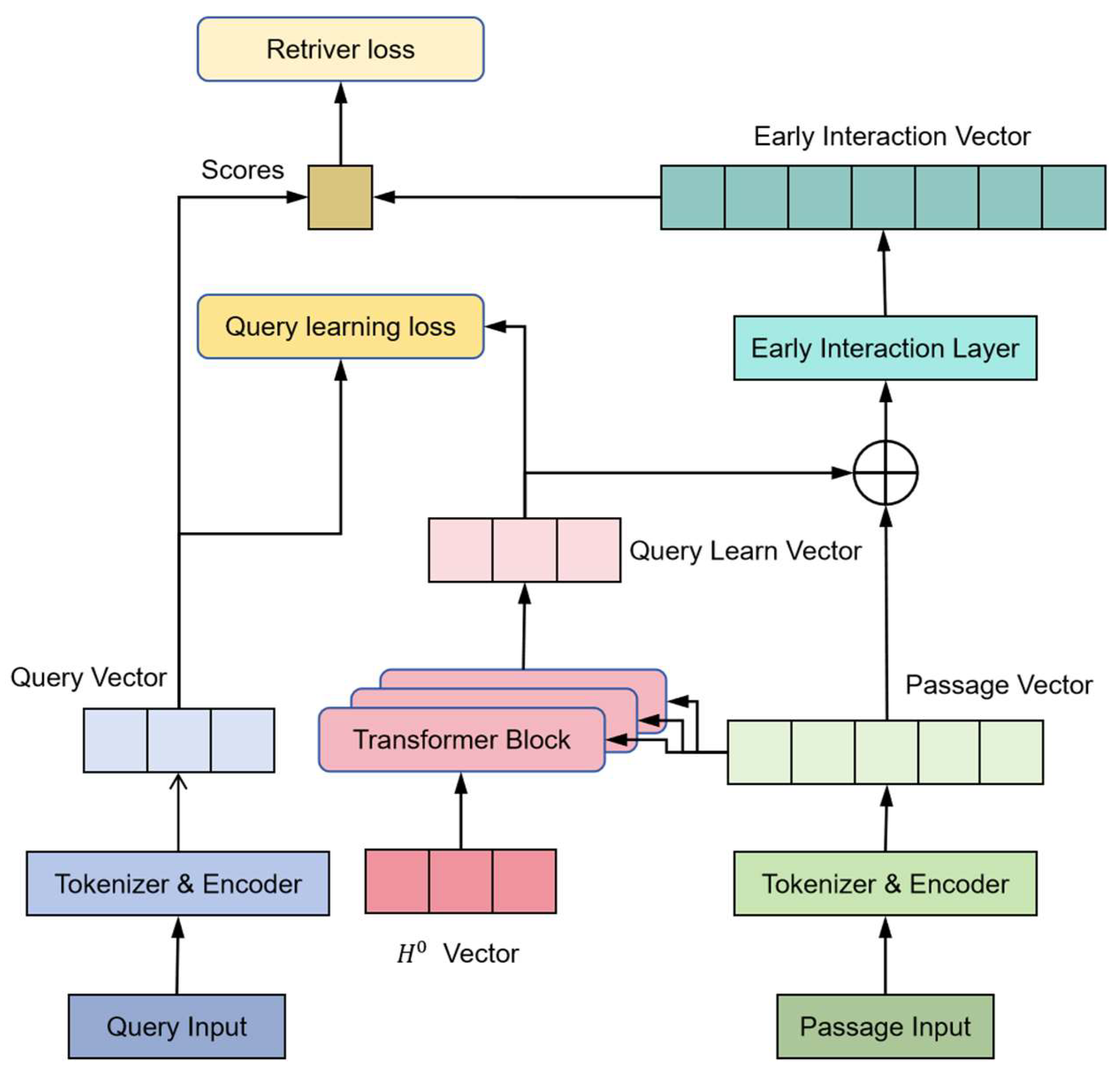
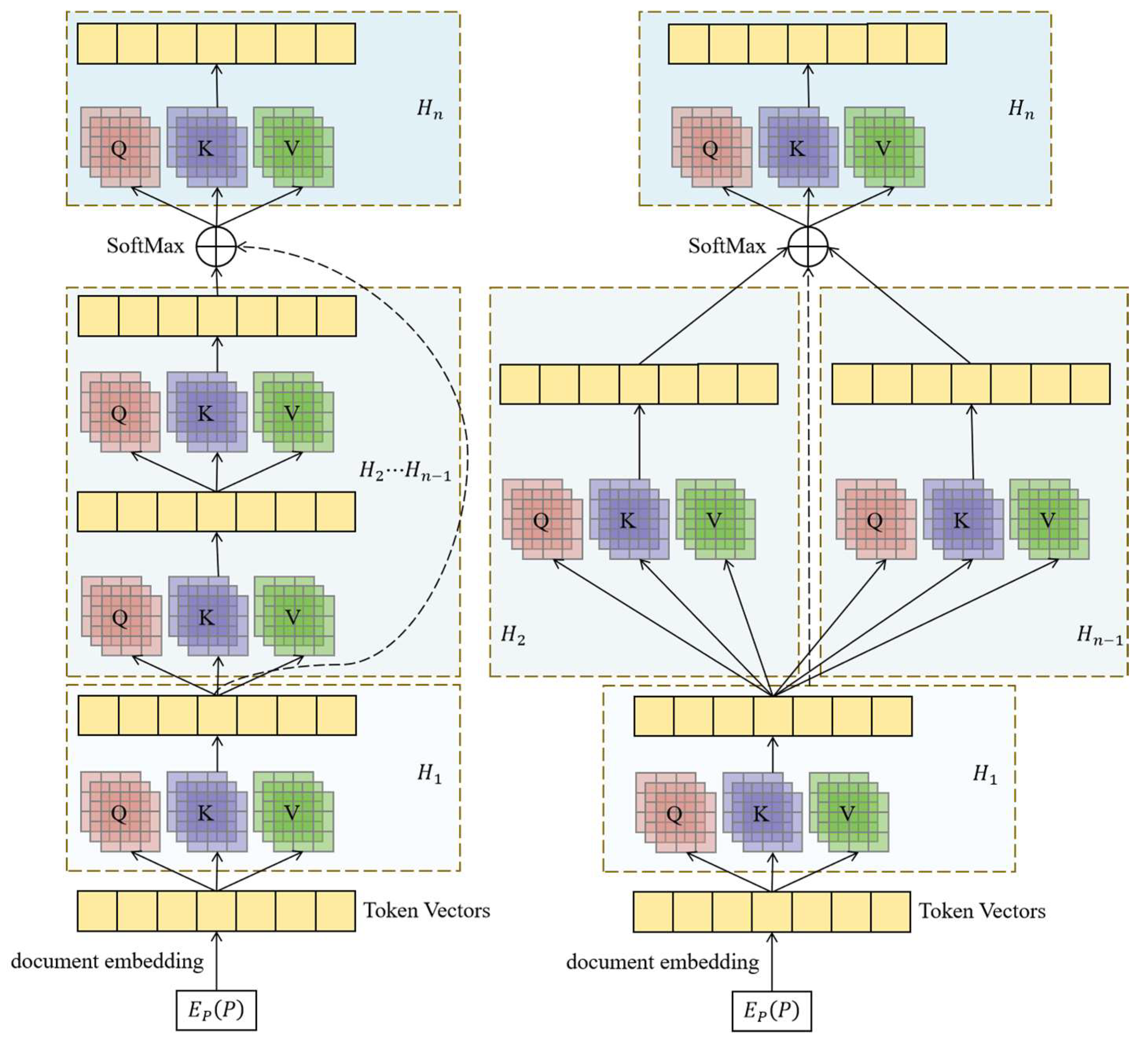
3.1.1. Embedding Layer
3.1.2. Inquiry Learning Layer
3.1.3. Early Interaction Layer
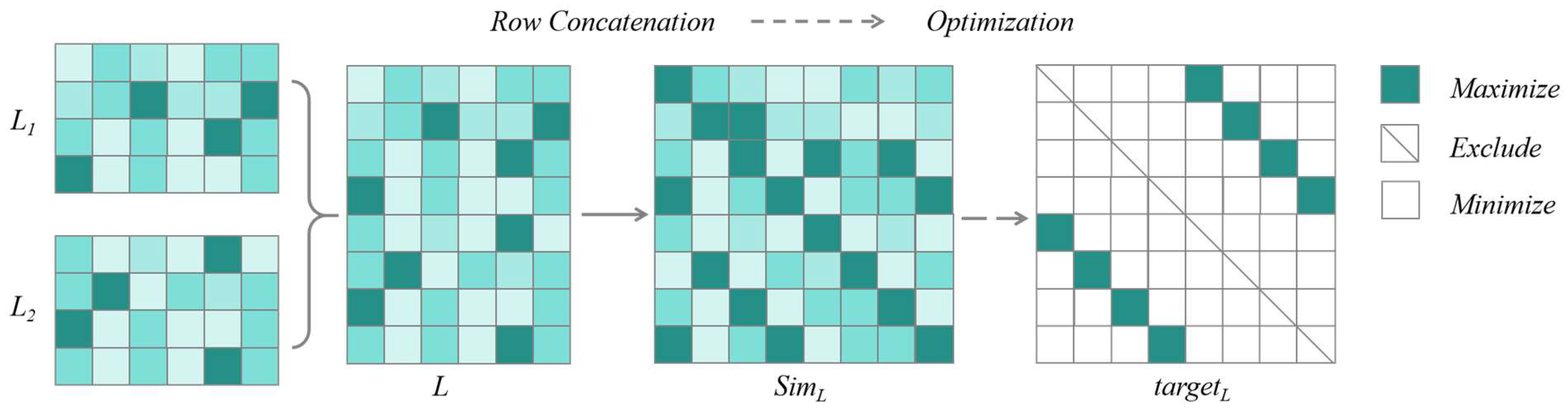
3.2. Optimization of Loss Function
4. Experiment
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Training Setups
4.4. Comparative Study
4.5. Ablation Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frommholz, I.; Liu, H.; Melucci, M. Bridging the Gap between Information Science, Information Retrieval and Data Science. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Bridging the Gap Between Information Science, Information Retrieval and Data Science (BIRDS 2020) Co-Located with 43rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval (SIGIR 2020), Xi’an, China, 30 July 2020; CEUR Workshop Proceedings. Volume 2741. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Z.; Xiong, C.; Callan, J.; Liu, Z. Convolutional Neural Networks for Soft-Matching N-Grams in Ad-hoc Search. In Proceedings of the Eleventh ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Marina Del Rey, CA, USA, 5–9 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Yan, Y.; Zhu, J.; Chen, X.; Gao, L.; Liu, Y.; Shi, W.; Lou, Y.; Wang, W.; Leng, J.; et al. Self-Supervised EEG Representation Learning with Contrastive Predictive Coding for Post-Stroke Patients. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2023, 33, 2350066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khang, N.H.G.; Nhat, N.M.; Quoc, T.N.; Hoang, V.T. Vietnamese Legal Text Retrieval based on Sparse and Dense Retrieval approaches. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 234, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Jia, W.; Piccardi, M.; Yu, P. Empowering large language models for automated clinical assessment with generation-augmented retrieval and hierarchical chain-of-thought. Artif. Intell. Med. 2025, 162, 103078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachan, D.S.; Lewis, M.; Yogatama, D.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Pineau, J.; Zaheer, M. Questions Are All You Need to Train a Dense Passage Retriever. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2023, 11, 600–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirasuna, V.Y.; Gradvohl, A.L.S. An optimized training approach for meteor detection with an attention mechanism to improve robustness on limited data. Astron. Comput. 2023, 45, 100753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Lu, Y.; Yao, Z.; Qu, F. Cross modal recipe retrieval with fine grained modal interaction. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.M.; Kwak, C.K.; Shin, H.J. HyFusER: Hybrid Multimodal Transformer for Emotion Recognition Using Dual Cross Modal Attention. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humeau, S.; Shuster, K.; Lachaux, M.A.; Weston, J. Poly-Encoders: Transformer Architectures and Pre-Training Strategies for Fast and Accurate Multi-Sentence Scoring. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.01969. [Google Scholar]
- MacAvaney, S.; Nardini, F.M.; Perego, R.; Tonellotto, N.; Goharian, N.; Frieder, O. Efficient Document Re-Ranking for Transformers by Precomputing Term Representations. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.14255. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Dai, Z.; Callan, J. Modularized Transfomer-based Ranking Framework. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Online, 16–20 November 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghali, M.-K.; Farrag, A.; Won, D.; Jin, Y. Enhancing knowledge retrieval with in-context learning and semantic search through generative AI. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2025, 311, 113047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ji, Z.; Pang, Y.; Han, J. Hierarchical and complementary experts transformer with momentum invariance for image-text retrieval. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2025, 309, 112912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, A.; Xu, J.; Shi, D. DCL-net: Dual-level correlation learning network for image–text retrieval. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2025, 122, 110000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, G.; Anderson, W.N.; Spies, C.N. Retrieval-augmented generation salvages poor performance from large language models in answering microbiology-specific multiple-choice questions. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2025, 63, e0162424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, Y.; Dehghani, M.; Bahri, D.; Metzler, D. Efficient Transformers: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 55, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, H.; Zakarya, M.; Ali, A.; Khan, A.A.; Qazani, M.R.C.; Al-Bahri, M.; Haleem, M. Energy efficient real-time tasks scheduling on high-performance edge-computing systems using genetic algorithm. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 54879–54892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Zhong, L.; Gao, M.; Wen, J.; Wu, Y. Multi-views contrastive learning for dense text retrieval. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 274, 110624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Hui, K.; He, B.; Han, X.; Sun, L.; Yates, A. BERT-QE: Contextualized Query Expansion for Document Re-ranking. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP, Online, 16–20 November 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Kyutoku, H.; Doman, K.; Komamizu, T.; Ide, I.; Qian, J. Cross-modal recipe retrieval based on unified text encoder with fine-grained contrastive learning. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2024, 305, 112641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, F.; Suk, J.; Yue, Z. WordPPR: A Researcher-Driven Computational Keyword Selection Method for Text Data Retrieval from Digital Media. Commun. Methods Meas. 2023, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chu, H.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, F.; Hu, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, W. Dual-tower model with semantic perception and timespan-coupled hypergraph for next-basket recommendation. Neural Netw. 2025, 184, 107001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Wu, C.; Pan, S.; Li, K.; Liu, S.; Lv, Y.; Wang, S.; Luo, R. Determining the geographical origins of goji berries using the Twin-Tower model for Multi-Feature. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 227, 109571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Li, X.; Cai, B. Graph neural network recommendation algorithm based on improved dual tower model. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Yang, L.; Wu, J.; He, T. Automatic Joint Lesion Detection by enhancing local feature interaction. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2025, 121, 102509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Dong, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, S.; Liu, D. MFAR-Net: Multi-level feature interaction and Dual-Dimension adaptive reinforcement network for breast lesion segmentation in ultrasound images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 272, 126727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Gui, G.; Luo, B.; Yang, C.; Gui, W.; Chang, K. CSFIN: A lightweight network for camouflaged object detection via cross-stage feature interaction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 269, 126451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All You Need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Liu, Y.; Wen, S.; Chen, W.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y. DTI-MHAPR: Optimized drug-target interaction prediction via PCA-enhanced features and heterogeneous graph attention networks. BMC Bioinform. 2025, 26, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, S.; Niu, A.; Yan, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y. A multi-scale feature cross-dimensional interaction network for stereo image super-resolution. Multimed. Syst. 2025, 31, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Qu, P.; Li, H. A 3D medical image segmentation network based on gated attention blocks and dual-scale cross-attention mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Comparison Dimension | BM25 | DPR | ColBERT | Ghali et al. [13] | Yu et al. [19] | Zheng et al. [20] | Our Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model Structure | Sparse retrieval | Dual-tower LLMs | Dual-tower w/late interaction | Hybrid generative AI/semantic search | Multi-view contrastive | BERT query expansion | Dual-tower w/early interaction |
| Retrieval Efficiency | Fast, exact matches | Efficient | Efficient | Efficient | Efficient | Efficient | On par with DPR, real-time suitable |
| Semantic Understanding | Lexical matching | Pre-trained LLMs | Contextual interactions | Strong integration | Multi-view learning | BERT expansion | Deeper understanding |
| Data Utilization | Labeled data | Labeled data | Labeled data | Dynamic data | Data augmentation | Unsupervised | Optimized loss function |
| Flexibility | Simple tasks | Various tasks | Various tasks | Complex queries | Diverse data | Query expansion | Highly flexible |
| Application Scenarios | Keyword matching | Semantic tasks | Contextual tasks | Knowledge-intensive | Multi-view tasks | Query expansion | Real-time retrieval |
| Dataset | Field | Train Set | Test Set | Validation Set | Number of Document Sets |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NQ | Web | 152,148 | 6515 | 3610 | 2 M |
| TQA | Wikipedia | 78,785 | 8837 | 11,313 | 740 K |
| WQ | Wikipedia | 3417 | 361 | 2032 | - |
| MS MARCO | Web | 502,939 | 6333 | 6980 | 8.8 M |
| Parameter | Value | Instructions |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Rate | 3 × 10−5 | Controls the step size during optimization; determines how quickly the model learns from the data. |
| Batch Size (per GPU) | 32 | Number of training examples processed before the model updates its parameters. Larger batches improve training stability but require more memory. |
| Number of Epochs | 3 (early stopping) | Total number of passes through the entire training dataset. Early stopping prevents overfitting by halting training if validation performance plateaus. |
| Loss Function Weight | λ = 0.8 | Balances contributions from the ranking loss and query reconstruction loss, ensuring the model prioritizes relative similarity ranking. |
| Transformer Layers | 6 (encoder and decoder) | Number of Transformer layers in both the encoder and decoder modules, which capture contextual relationships between tokens. |
| Embedding Dimension | 768 | Dimensionality of the word embeddings and hidden states in the model. Higher dimensions capture richer semantic information but increase computational complexity. |
| Dropout Rate | 0.1 | Probability of randomly dropping neurons during training to prevent overfitting and improve generalization. |
| Optimizer | AdamW | Optimization algorithm used to update model parameters, combining the benefits of Adam and weight decay for better convergence. |
| Gradient Clipping | 1.0 | Technique to prevent exploding gradients by limiting the maximum value of gradients during backpropagation. |
| Document Token Length | 512 tokens | Maximum length of document segments, ensuring compatibility with the BERT model’s input constraints. |
| Query Token Length | 64 tokens | Maximum length of queries, balancing information retention with computational efficiency. |
| Random Seed | 42 | Fixed seed for random number generation to ensure deterministic behavior and reproducibility across experiments. |
| Retriever | Top-20 | Top-100 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NQ | TQA | WQ | NQ | TQA | WQ | |
| BM25 | 61.9 | 70.7 | 50.9 | 77.2 | 76.4 | 69.9 |
| DPR | 77.6 | 81.4 | 69.7 | 84.4 | 84.0 | 79.4 |
| ANCE | 80.9 | 81.0 | 69.4 | 85.7 | 85.3 | 80.6 |
| ColBERT | 81.3 | 81.9 | 70.9 | 86.1 | 86.9 | 80.5 |
| Ours | 82.2 | 82.2 | 76.8 | 87.4 | 88.1 | 82.2 |
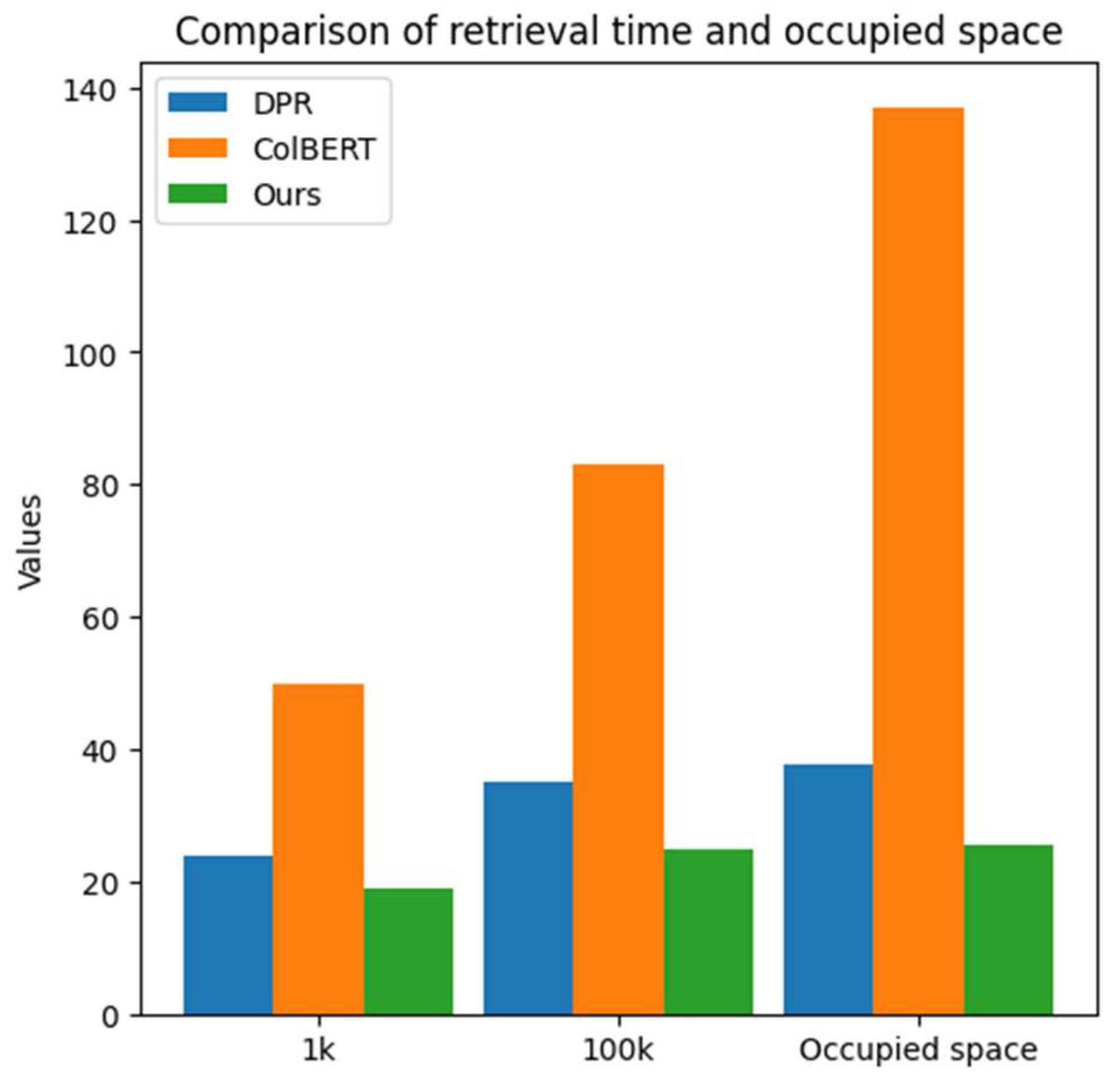
| Retriever | Number of Candidate Sets | Occupied Space (GB) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1k | 100k | ||
| DPR | 24 ms | 35 ms | 37.7 |
| ColBERT | 50 ms | 83 ms | 137 |
| Cross-encoder | 2.4 s | 4.0 m | - |
| Ours | 17 ms | 29 ms | 25.6 |
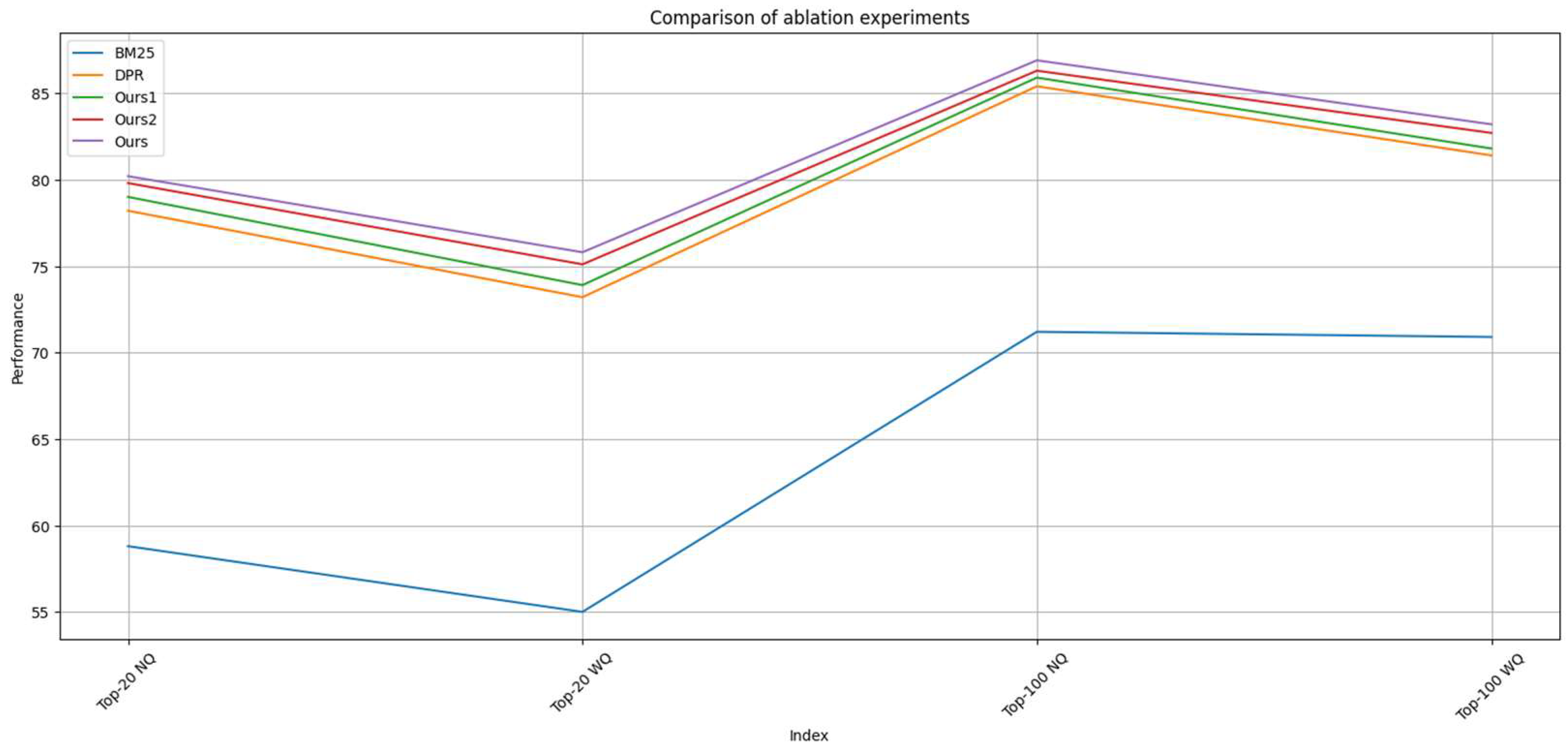
| Retriever | Top-20 | Top-100 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NQ | WQ | NQ | WQ | |
| BM25 | 58.8 | 55.0 | 71.2 | 70.9 |
| DPR | 78.2 | 73.2 | 85.4 | 81.4 |
| Ours1 | 79.0 | 73.9 | 85.9 | 81.8 |
| Ours2 | 79.8 | 75.1 | 86.3 | 82.7 |
| Ours | 80.2 | 75.8 | 86.9 | 83.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, G.; Xie, S.; Du, Y. Enhancing Retrieval-Oriented Twin-Tower Models with Advanced Interaction and Ranking-Optimized Loss Functions. Electronics 2025, 14, 1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14091796
Duan G, Xie S, Du Y. Enhancing Retrieval-Oriented Twin-Tower Models with Advanced Interaction and Ranking-Optimized Loss Functions. Electronics. 2025; 14(9):1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14091796
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Ganglong, Shanshan Xie, and Yutong Du. 2025. "Enhancing Retrieval-Oriented Twin-Tower Models with Advanced Interaction and Ranking-Optimized Loss Functions" Electronics 14, no. 9: 1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14091796
APA StyleDuan, G., Xie, S., & Du, Y. (2025). Enhancing Retrieval-Oriented Twin-Tower Models with Advanced Interaction and Ranking-Optimized Loss Functions. Electronics, 14(9), 1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14091796




