Research on Calibration Method of Triaxial Magnetometer Based on Improved PSO-Ellipsoid Fitting Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Sensor fabrication errors, including sensitivity errors, non-orthogonality errors, and zero-offset errors caused by material properties and machining precision limitations;
- Environmental interference errors, primarily stemming from hard-iron interference generated by the vehicle’s ferromagnetic materials and soft-iron interference arising from the magnetization of surrounding magnetic substances under external magnetic fields [3].
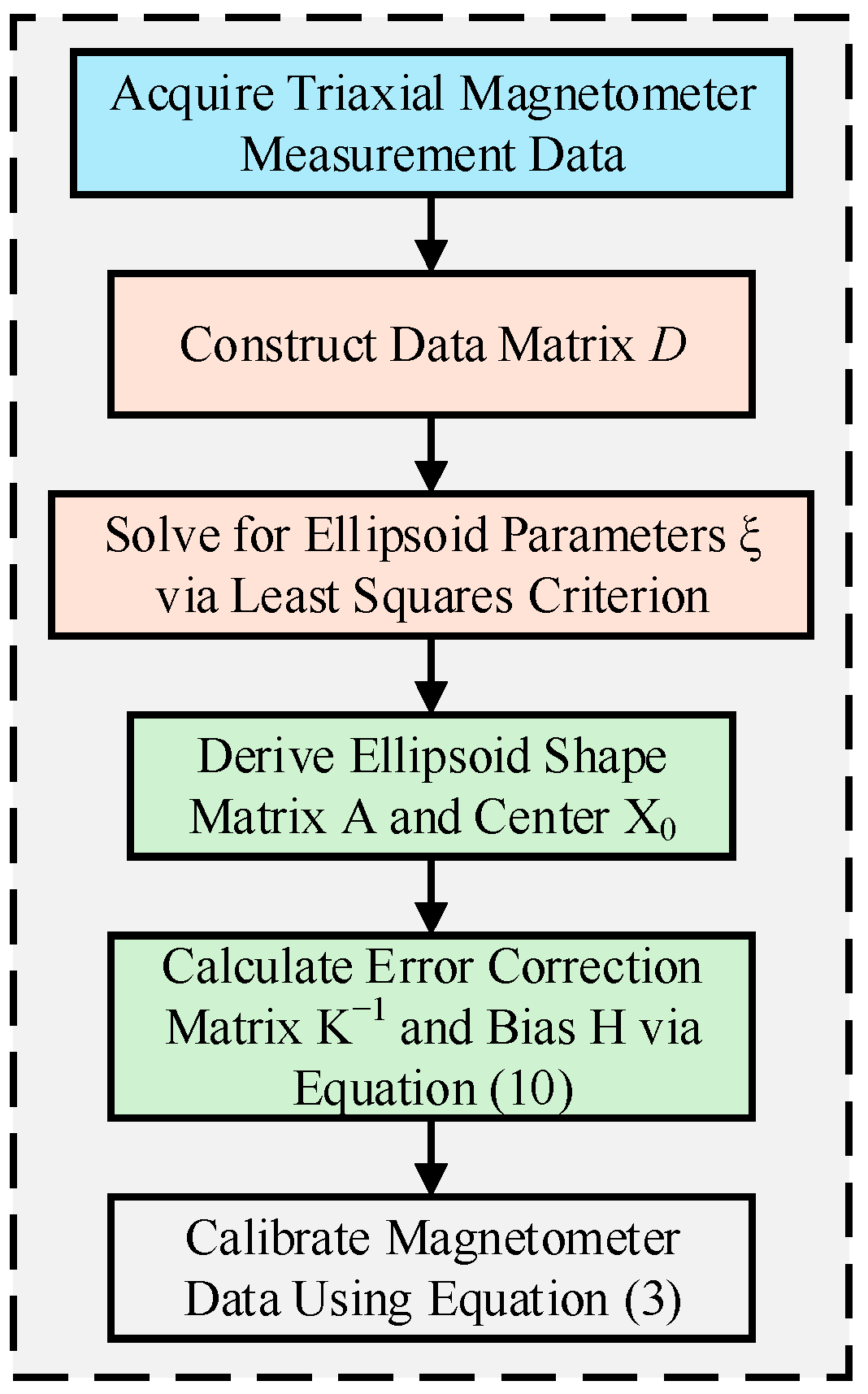
2. Error Model and Ellipsoid Fitting Algorithm
2.1. Error Model of Triaxial Magnetometer
2.2. Ellipsoid Fitting Algorithm
3. Ellipsoid Fitting Algorithm Based on Dynamic Hierarchical Elite-Guided Particle Swarm Optimization
3.1. Conventional PSO Algorithm
3.2. Enhancement Strategies for Dynamic Hierarchical Elite-Guided Particle Swarm Optimization
3.2.1. Dynamic Hierarchical Mechanism
3.2.2. Elite Guidance Strategy
- Elite Layer
- Ordinary Layer
3.2.3. Adaptive Inertia Weight Adjustment
3.2.4. Ellipsoid Constraints
- If Equation (22) is satisfied, the current solution is retained;
- If Equation (22) is violated, the particle position is stochastically perturbed with minor amplitude;
- This mechanism guarantees precise ellipsoid model fitting via DHEPSO;
- Figure 2 illustrates the complete workflow of the DHEPSO algorithm.
3.3. Ellipsoid Fitting Algorithm Based on DHEPSO
3.3.1. Fitness Function
3.3.2. DHEPSO Parameter Initialization
4. Simulation Experiment Validation
4.1. Simulated Data Generation and Experimental Setup
4.2. Introduction and Analysis of Comparison Algorithms
4.2.1. TSLPSO
4.2.2. MPSO
4.2.3. AWPSO
4.2.4. Comparative Analysis
4.3. Sensitivity Analysis of DHEPSO Parameters
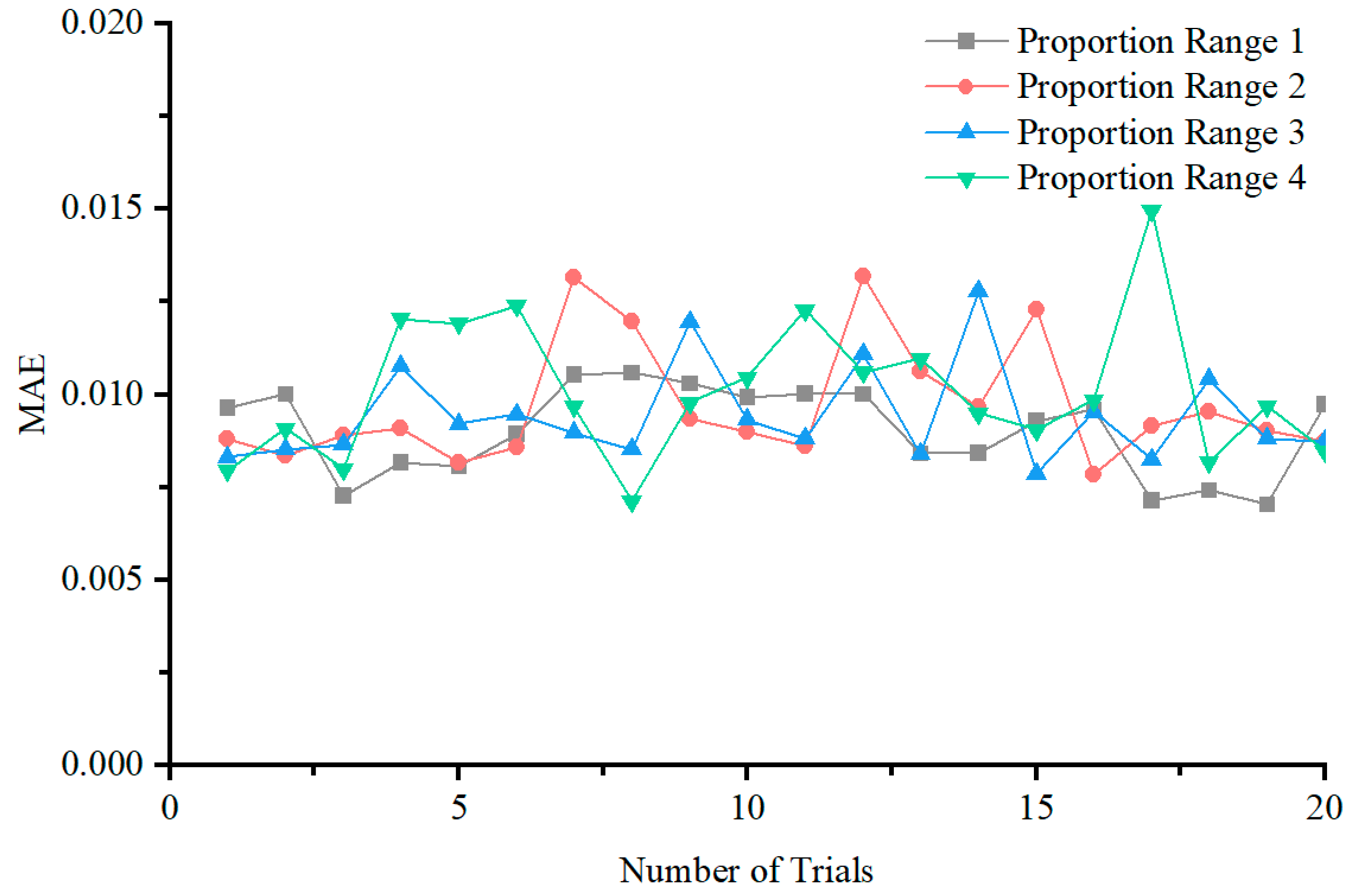
4.3.1. Elite Proportion
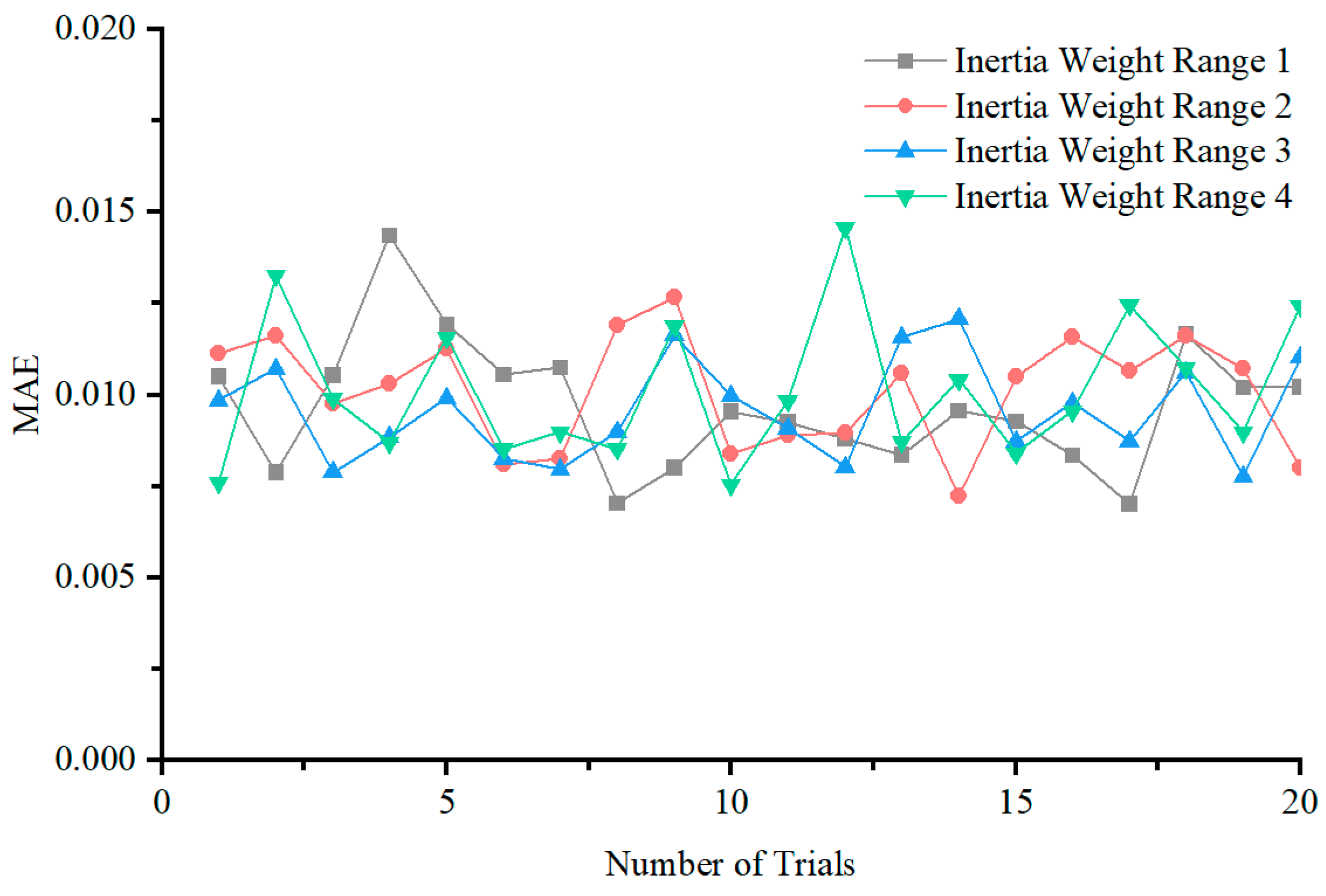
4.3.2. Inertia Weight
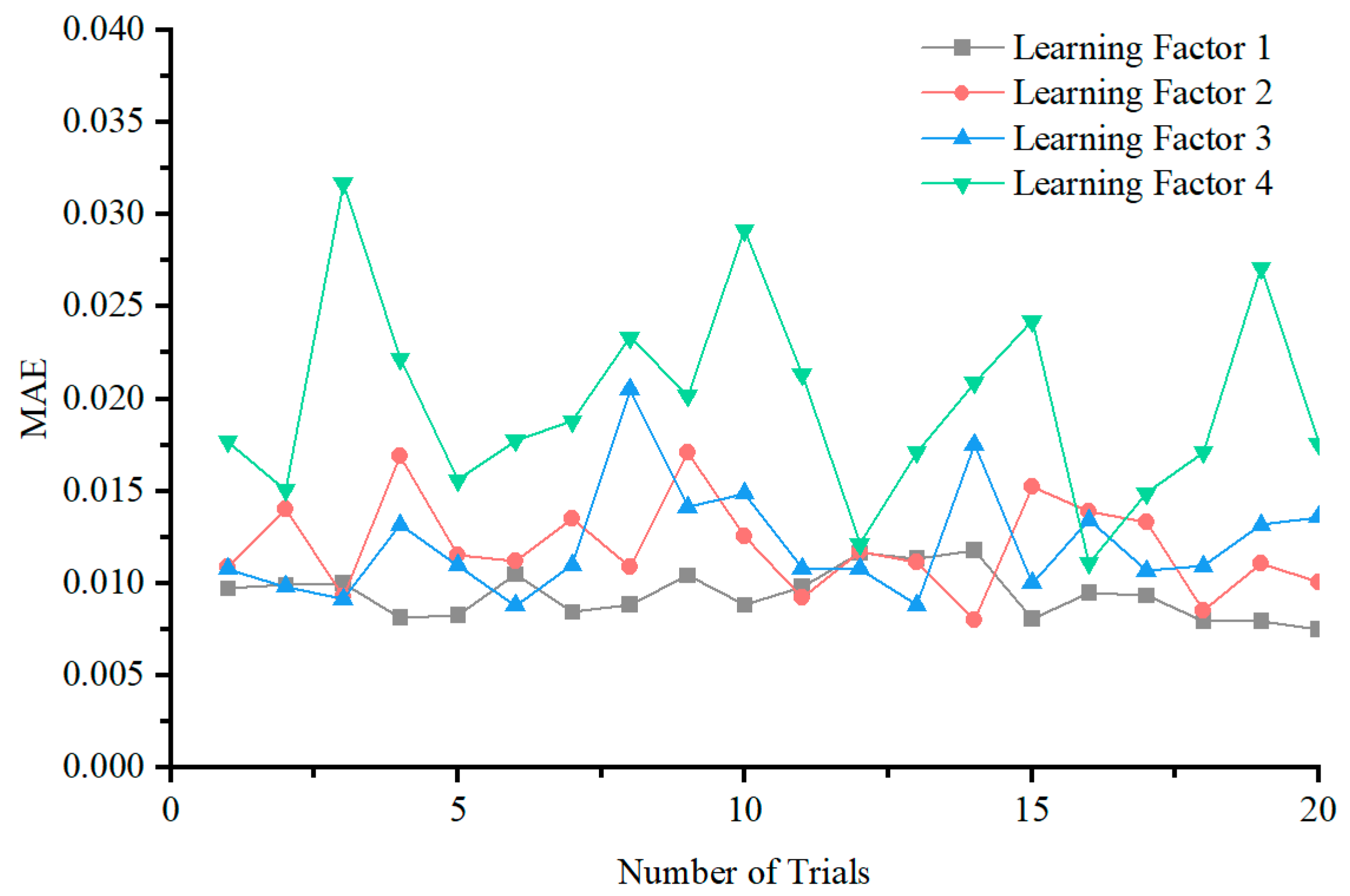
4.3.3. Learning Factor
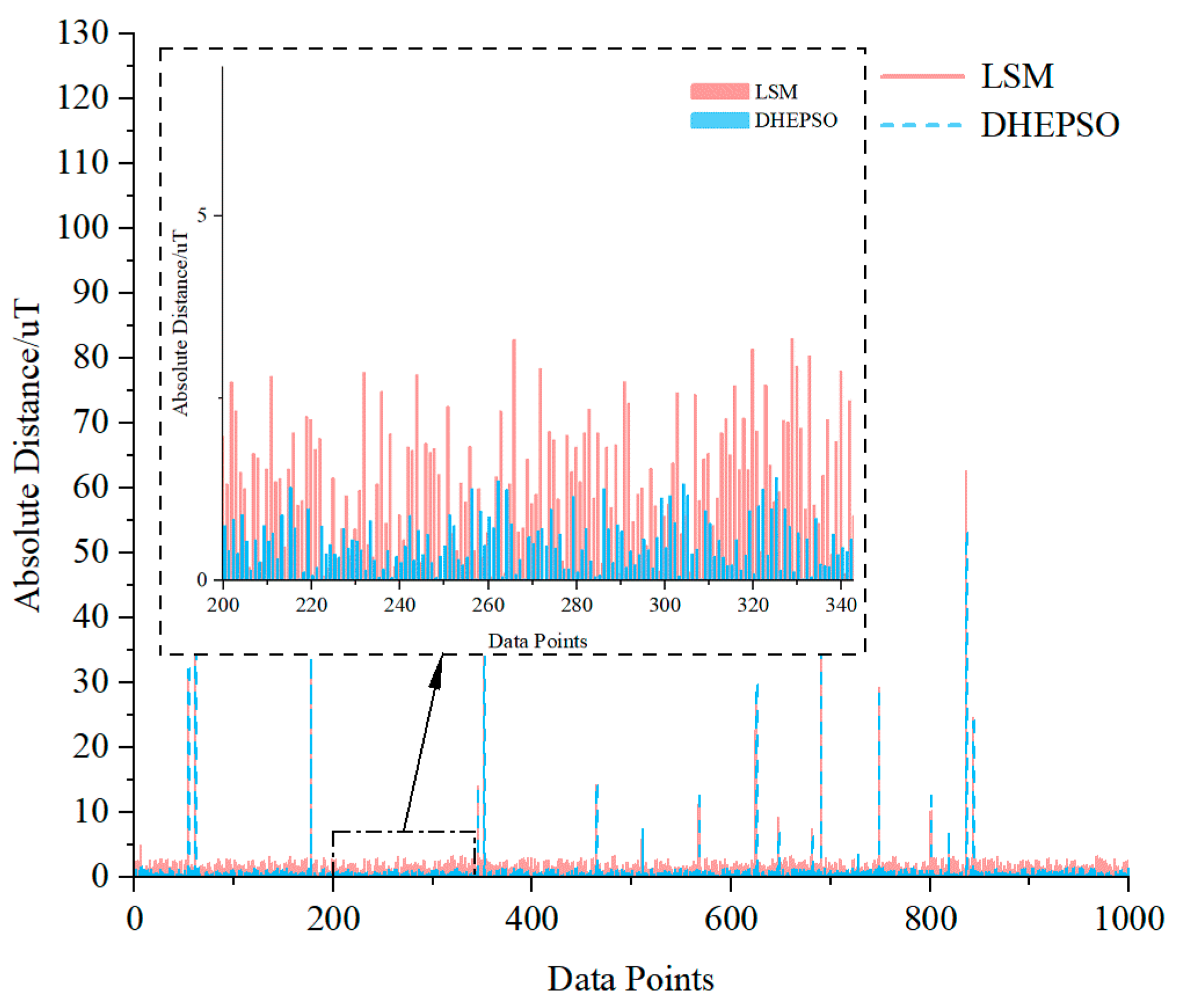
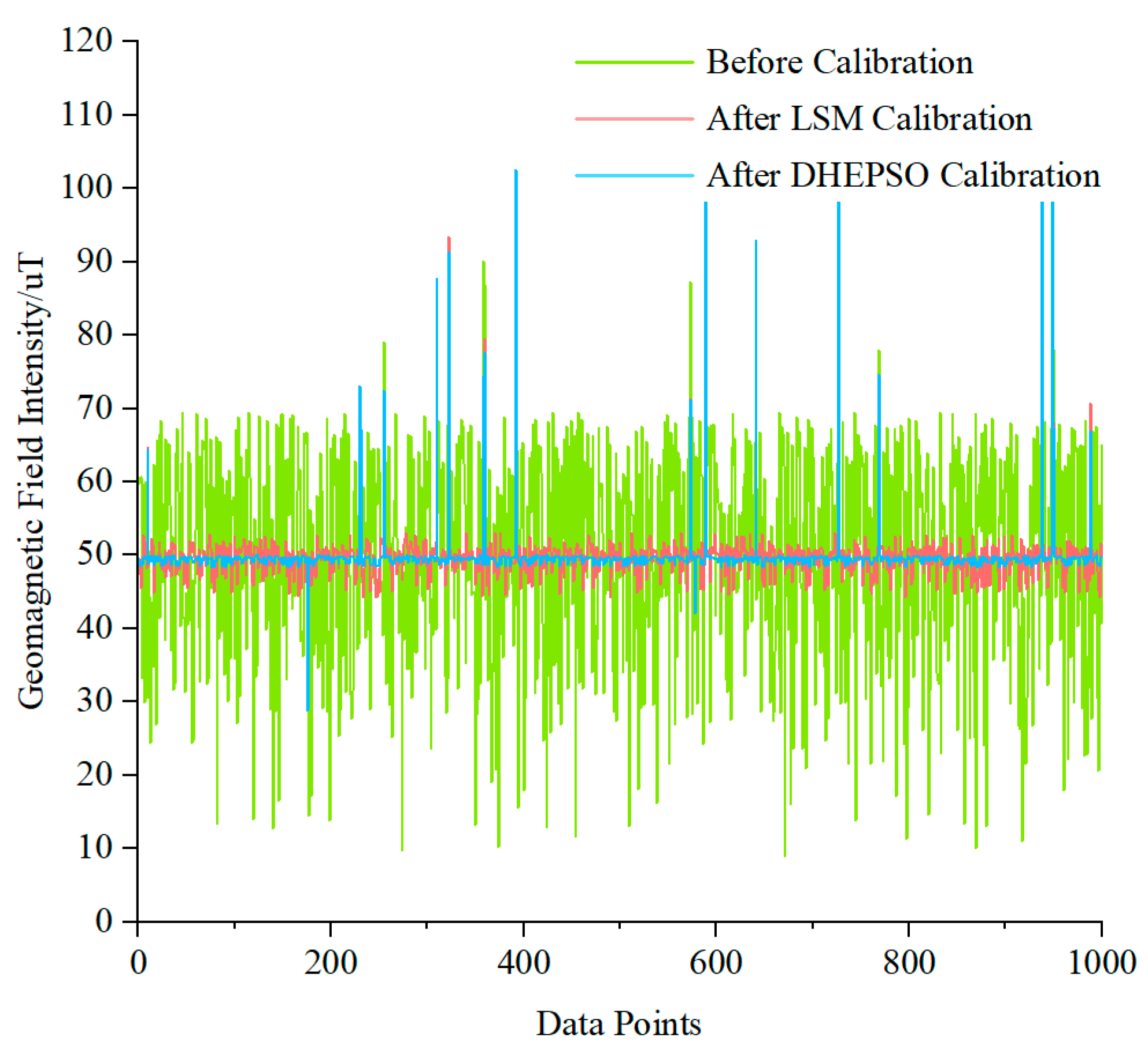
4.4. Comparative Analysis of DHEPSO and LSM
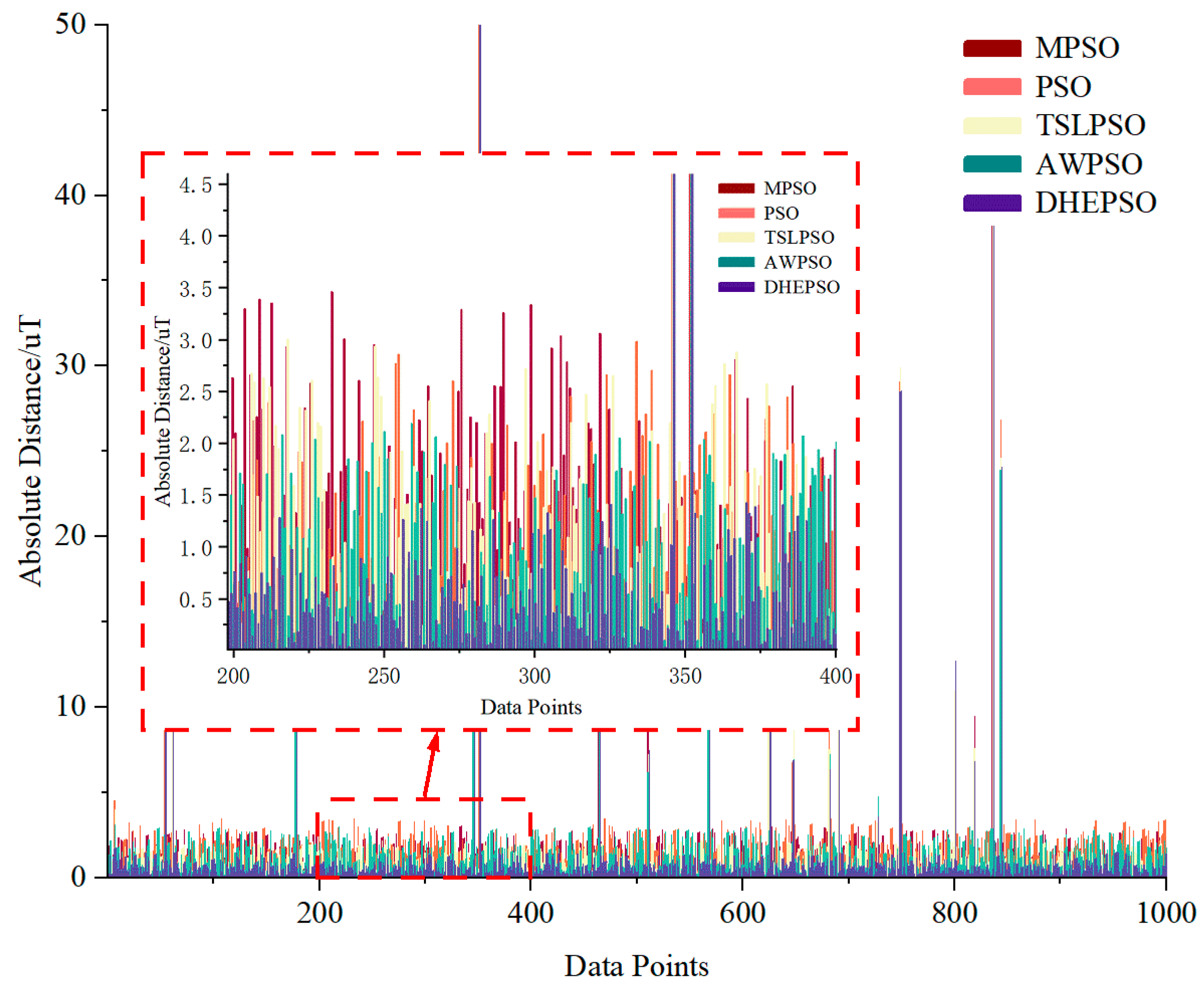
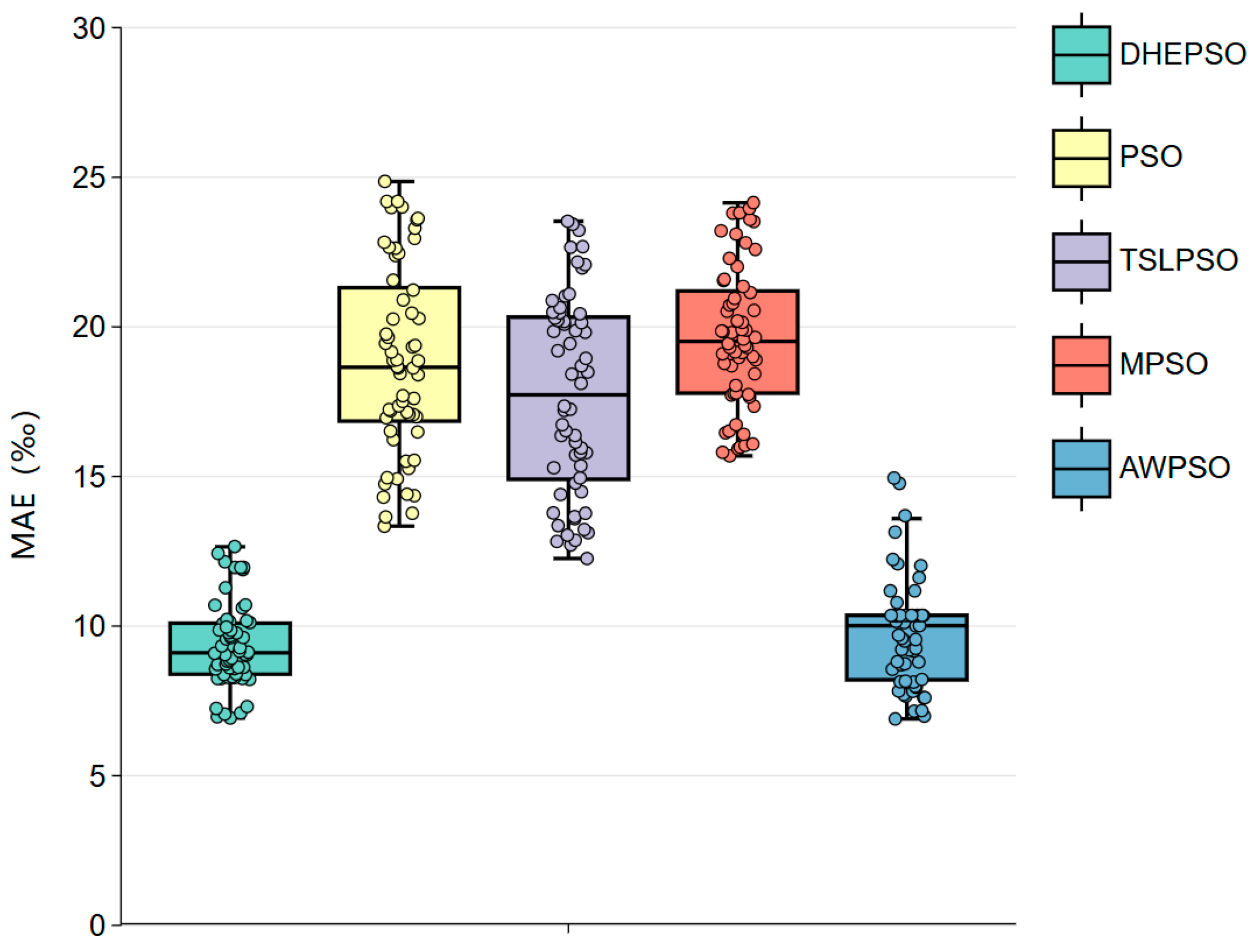
4.5. Comparative Analysis of PSO Variants
5. Conclusions
- Enhanced anti-interference capability: compared to the LSM-based ellipsoid fitting algorithm, the DHEPSO-based algorithm demonstrates superior resistance to outlier interference, higher fitting precision, and robust stability when processing outlier-contaminated data, effectively mitigating the impact of outliers on calibration processes.
- Accelerated convergence performance: the DHEPSO algorithm achieves faster convergence than the traditional PSO, TSLPSO, MPSO, and AWPSO, efficiently locating global optima in ellipsoid fitting tasks, thereby exhibiting significant advantages in parameter optimization mechanisms.
- Improved consistency and reliability: multiple independent experiments confirm that the DHEPSO-based algorithm outperforms comparative methods in median error and IQR, demonstrating enhanced reliability and consistency.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sadaf, M.; Iqbal, Z.; Javed, A.R.; Saba, I.; Krichen, M.; Majeed, S.; Raza, A. Connected and automated vehicles: Infrastructure, applications, security, critical challenges, and future aspects. Technologies 2023, 11, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hua, M.; Deng, Z.; Meng, Z.; Huang, Y.; Hu, C.; Song, S.; Gao, L.; Liu, C.; Shuai, B.; et al. A systematic survey of control techniques and applications in connected and automated vehicles. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 21892–21916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Zhang, X.; Wei, X.; Luo, Z.; Cao, J. A Fast Calibration and Compensation Method for Magnetometers in Strap-Down Spinning Projectiles. Sensors 2018, 18, 4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Wang, L. Study and Numerical Simulation of the Standardizing Method of Geomagnetic Sensor. J. Proj. Rocket. Missiles Guid. 2018, 38, 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, Z.W.; Gao, K.; Chu, Z.W.; Lin, W.; Lin, X.H. A Calibration Method of Magnetic Compass Based on Non-iterative Ellipsoid Fitting. Instrum. Technol. 2020, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.B.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhang, W.; Yao, X.T. Calibration Method for Measurement Error Parameters of Three-Axis Magnetic Sensors. J. Gun Launch Control 2025, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhimin, L.I.; Jizhou, L.A.; Pin, L.Y. Experimental design for rapid calibration of three-axis magnetic sensors based on ellipsoidal fitting. Exp. Technol. Manag. 2023, 40, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, X.; Song, Z.; Xi, X. Error calibration of three axis magnetometer based on Global Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference of IEEE Region 10 (TENCON 2013), Xi’an, China, 22–25 October 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, S.; Xu, C.; Chen, H.; Xiao, S.; Tang, X.; Li, Y. Correction method of three-Axis magnetic sensor based on DA–LM. Metals 2022, 12, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yan, S.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Yan, Y. Partition beetles antennae search algorithm for magnetic sensor calibration optimization. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 5967–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.L.; Lin, C.S. Calibration Coefficients Solving of Three-Axis Magnetic Sensor Based on Genetic Algorithm. J. Detect. Control 2017, 39, 42–45+51. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Luo, S.; Wan, C.; Chen, D.; Pan, M.; Luo, F. Calibration of three-axis magnetometers with differential evolution algorithm. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 346, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wang, P.; Shen, H. Magnetometer error compensation algorithm based on immune adaptation particle swarm optimization algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Sensing, Measurement & Data Analytics in the era of Artificial Intelligence (ICSMD), Nanjing, China, 21–23 October 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Hu, X.; Wu, M. Calibration of three-axis magnetometer using stretching particle swarm optimization algorithm. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2012, 62, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Zhang, X.; Hao, Y. An intelligent ellipsoid calibration method based on the grey wolf algorithm for magnetic compass. J. Bionic Eng. 2021, 18, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafi, M.R.S.; Narm, H.G.; Kalat, A.A. Calibration of fluxgate sensor using least square method and particle swarm optimization algorithm. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 570, 170364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerrise, F.; Sosanya, A.S.; Neary, P. Physics-informed calibration of aeromagnetic compensation in magnetic navigation systems using liquid time-constant networks. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.09631. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, D.; Li, Y.; Jin, M.; Guo, Y.; Meng, F.; Liu, Q. Data-Driven Calibration of Tri-axial Magnetic Sensors. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2025, 36, 035117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowart, J., III; Petrich, J. Three-dimensional magnetometer calibration using higher order models embedded into neural networks. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2025, 186, 104903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zikmund, A.; Janosek, M.; Ulvr, M.; Kupec, J. Precise calibration method for triaxial magnetometers not requiring earth’s field compensation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2015, 64, 1242–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei, S.A.H.; Gluhak, A.; Tafazolli, R. A fast calibration method for triaxial magnetometers. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2013, 62, 2929–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chi, C.; Cheng, P.; Chen, J. An aeromagnetic compensation strategy for large uavs. Sensors 2024, 24, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Guo, Y.; Ye, L.; Han, T.; Su, S.W. Experimental Design for the Inclination based Linear Magnetometers Calibration Method. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 1005609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingbeil, L.; Eling, C.; Zimmermann, F.; Kuhlmann, H. Magnetic field sensor calibration for attitude determination. J. Appl. Geod. 2014, 8, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Tan, X. Improved ellipsoid fitting aided geomagnetic sensor calibration algorithm. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2024, 35, 076302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Wu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Nie, J.; Li, W.; Gao, Q. An improved method for the magnetometer calibration based on ellipsoid fitting. In Proceedings of the 2019 12th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Biomedical Engineering and Informatics (CISP-BMEI), Suzhou, China, 19–21 October 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- An, L.L.; Wang, L.M.; Zhong, Y. Ellipsoid fitting compensation method for three-axis magnetometer on projectile. Transducer Microsyst. Technol. 2020, 39, 4–6+13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Yao, M.L.; Shen, X.W. Research on Field Calibration Method for MEMS Accelerometer Based on Support Ellipsoid Fitting. Acta Armamentarii 2020, 41, 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez-Ochoa, D.D.; Pérez-Domínguez, L.A.; Martínez-Gómez, E.A.; Luviano-Cruz, D. PSO, a swarm intelligence-based evolutionary algorithm as a decision-making strategy: A review. Symmetry 2022, 14, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharwat, A.; Schenck, W. A conceptual and practical comparison of PSO-style optimization algorithms. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 167, 114430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Saihjpal, V.; Singh, N.; Singh, S.B. An overview of variants and advancements of PSO algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Gao, W.; Liu, N.; Song, C. Low-discrepancy sequence initialized particle swarm optimization algorithm with high-order nonlinear time-varying inertia weight. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 29, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, W.; Wu, J.; Zhao, K. Calibration method of magnetic and inertial sensors based on Newton iteration and ellipsoid fitting. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2020, 41, 142–149. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Su, Z.; Liu, F.; Li, C.; Li, Q. Magnetometer-based phase shifting ratio method for high spinning projectile’s attitude measurement. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 22509–22522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, F.; Walczak, B. Particle swarm optimization (PSO). A tutorial. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2015, 149, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Cui, Q.; Shi, X.; Ge, H.; Zhan, Z.H.; Lee, H.P.; Liang, Y.; Tai, R.; Wu, C. Particle swarm optimization based on dimensional learning strategy. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2019, 45, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, X.W.; Tu, L.P. A modified particle swarm optimization using adaptive strategy. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 152, 113353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Zeng, N.; Hone, K.; Liu, X. A novel sigmoid-function-based adaptive weighted particle swarm optimizer. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 51, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


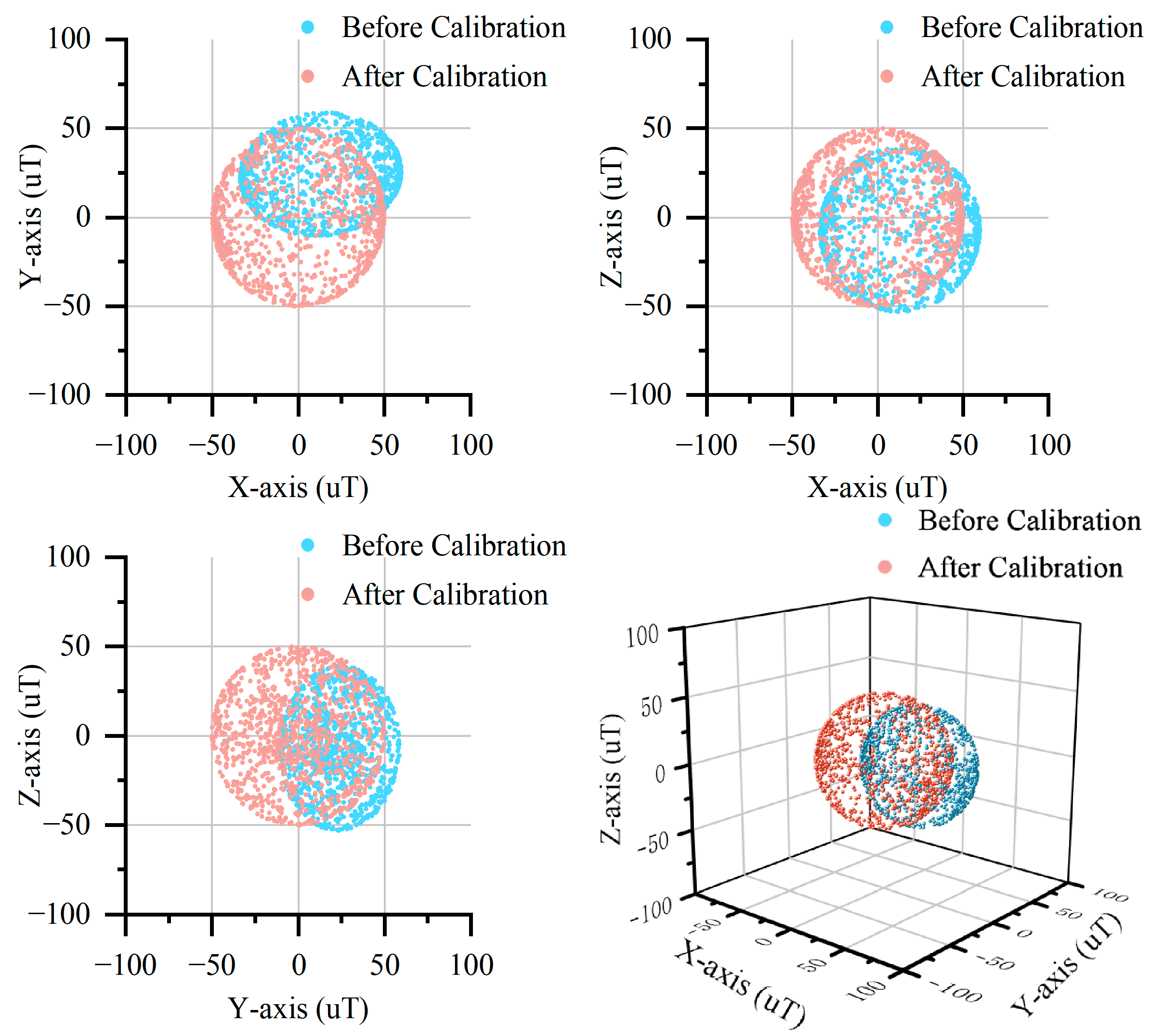
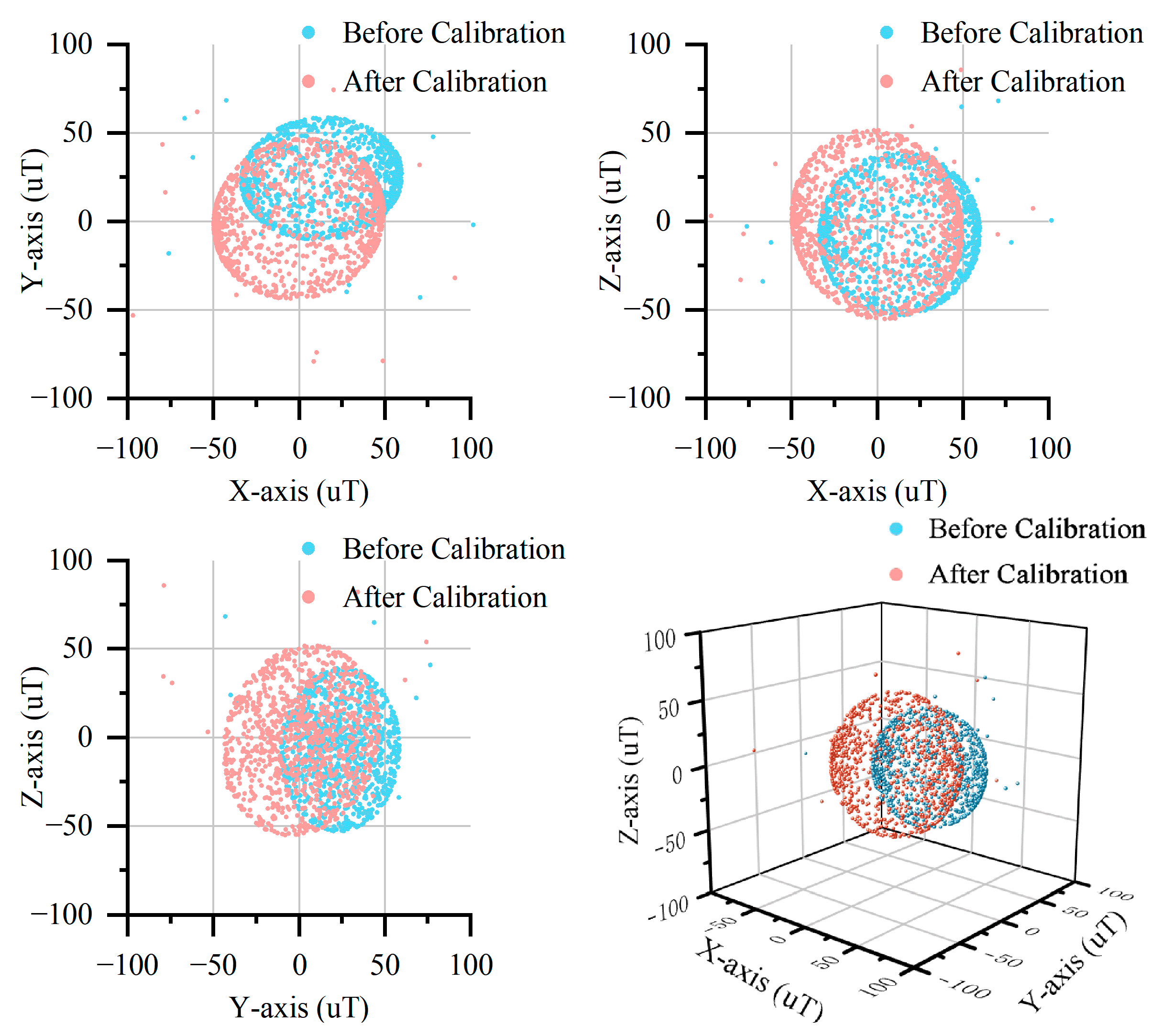
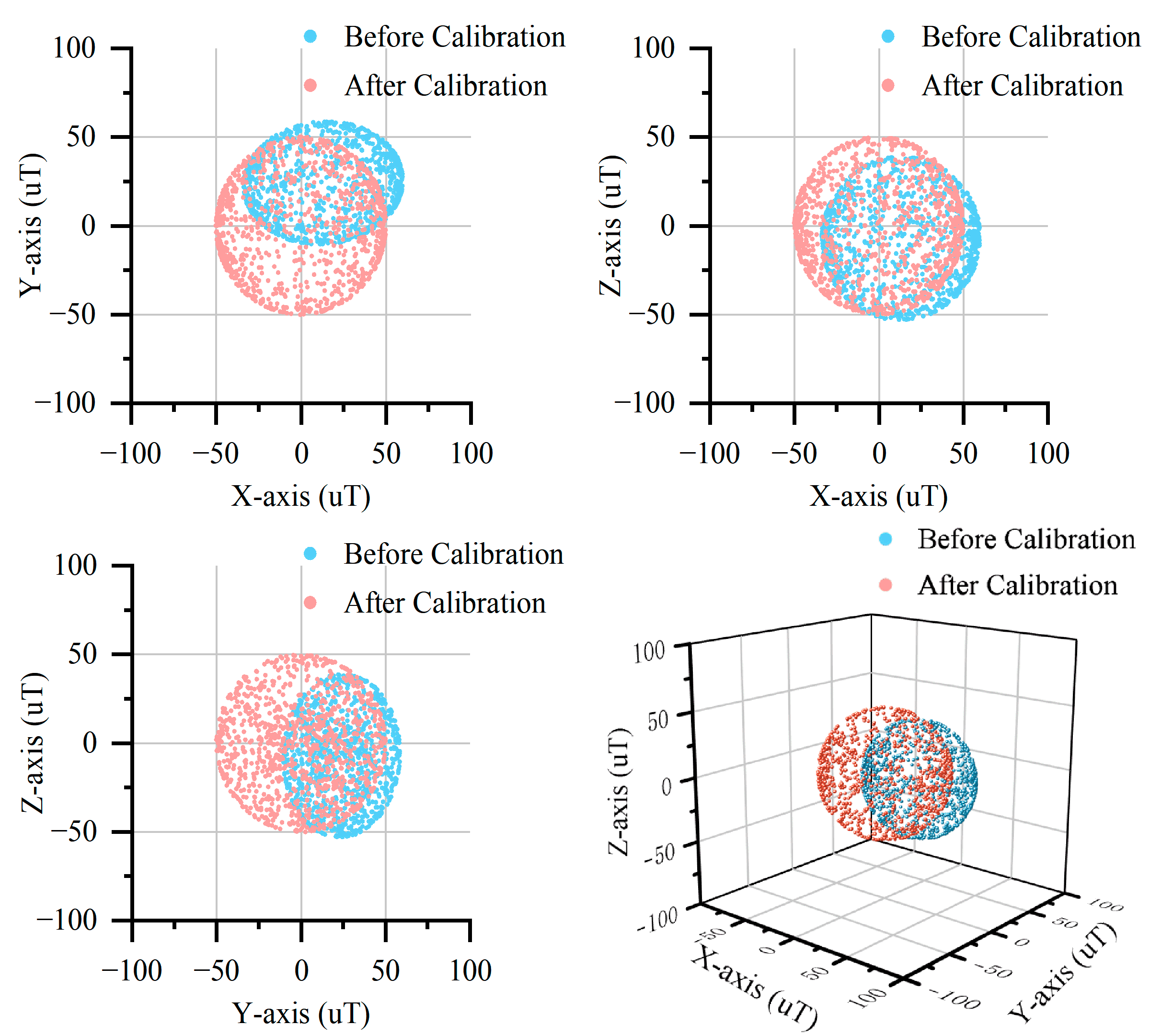
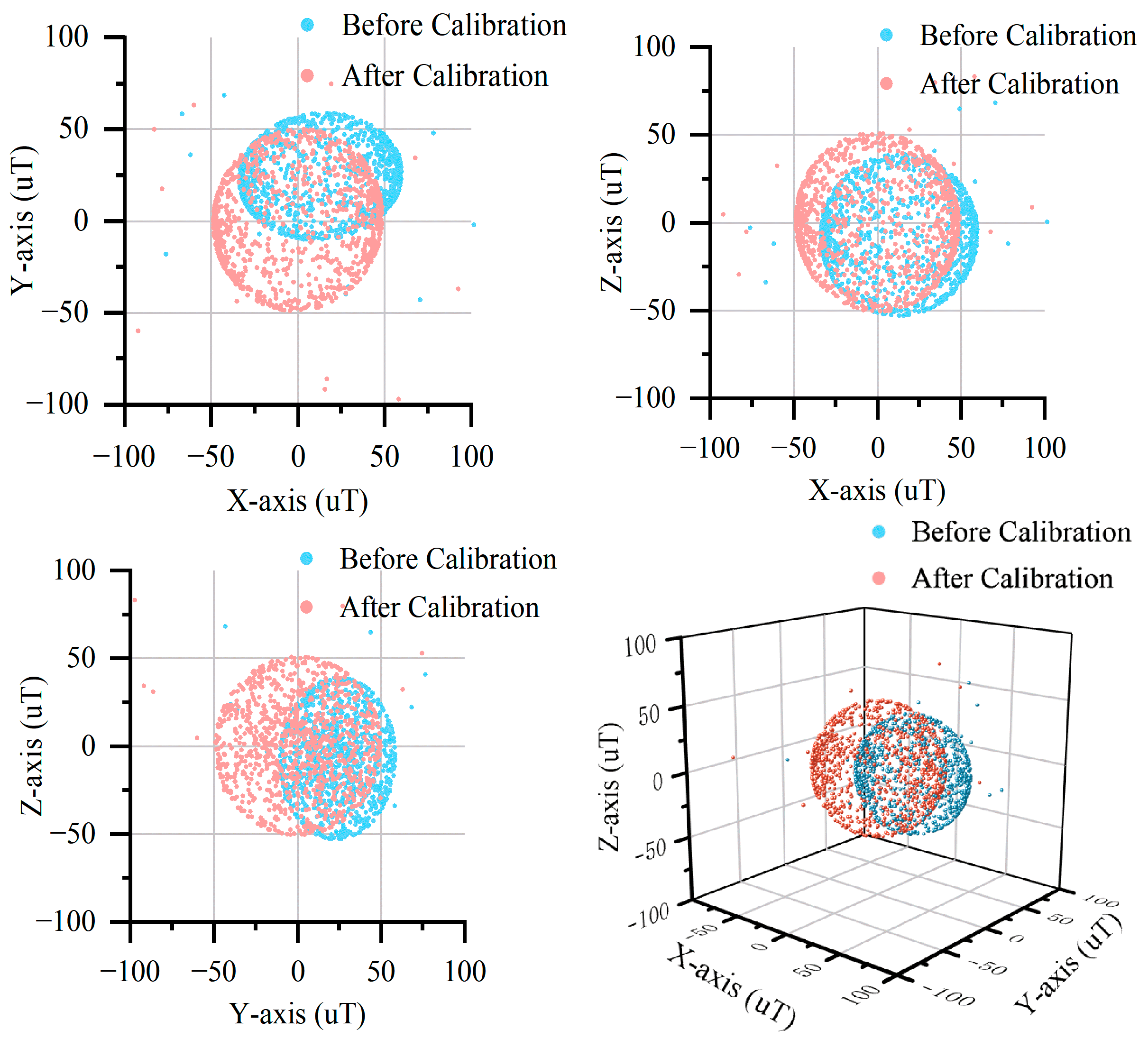

| Parameter Name | Symbol | Value/Range |
|---|---|---|
| Population Size | 100 | |
| Parameter Dimension | 10 | |
| Maximum Iterations | 500 | |
| Inertia Weight | [0.5, 0.7] | |
| Minimum Elite Proportion | 0.05 | |
| Maximum Elite Proportion | 0.15 | |
| Elite Layer Individual Learning Factor | 2.0 | |
| Elite Layer Swarm Learning Factor | 1.5 | |
| Ordinary Layer Individual Learning Factor | 1.5 | |
| Ordinary Layer Swarm Learning Factor | 2.0 | |
| Elite Guidance Term Learning Factor | 0.1 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Geomagnetic Field Intensity/µT | 50 |
| Magnetic Declination/° | −5.8 |
| Magnetic Inclination/° | 49.0 |
| Sensitivity Error | |
| Non-Orthogonality Error | |
| Zero-Offset Error/µT | |
| Soft-Iron Interference | |
| Hard-Iron Interference/µT |
| Parameter Set | Value |
|---|---|
| Proportion Range 1 | (0.05, 0.15) |
| Proportion Range 2 | (0.04, 0.2) |
| Proportion Range 3 | (0.03, 0.3) |
| Proportion Range 4 | (0.02, 0.4) |
| Parameter Set | Value |
|---|---|
| Inertia Weight Range 1 | (0.5, 0.7) |
| Inertia Weight Range 2 | (0.4, 0.8) |
| Inertia Weight Range 3 | (0.3, 0.9) |
| Inertia Weight Range 4 | (0.2, 1.0) |
| Parameter Set | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Factor 1 | 2.0 | |
| 1.5 | ||
| 1.5 | ||
| 2.0 | ||
| Learning Factor 2 | 2.5 | |
| 1.5 | ||
| 1.5 | ||
| 2.5 | ||
| Learning Factor 3 | 2.8 | |
| 1.2 | ||
| 1.2 | ||
| 2.8 | ||
| Learning Factor 4 | 2.5 | |
| 2.0 | ||
| 2.0 | ||
| 2.5 | ||
| Algorithm | Parameters |
|---|---|
| PSO | |
| TSLPSO | |
| MPSO | |
| AWPSO |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, J.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, G. Research on Calibration Method of Triaxial Magnetometer Based on Improved PSO-Ellipsoid Fitting Algorithm. Electronics 2025, 14, 1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14091778
Guan J, Chen Z, Jiang G. Research on Calibration Method of Triaxial Magnetometer Based on Improved PSO-Ellipsoid Fitting Algorithm. Electronics. 2025; 14(9):1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14091778
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Jun, Zhihui Chen, and Guilin Jiang. 2025. "Research on Calibration Method of Triaxial Magnetometer Based on Improved PSO-Ellipsoid Fitting Algorithm" Electronics 14, no. 9: 1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14091778
APA StyleGuan, J., Chen, Z., & Jiang, G. (2025). Research on Calibration Method of Triaxial Magnetometer Based on Improved PSO-Ellipsoid Fitting Algorithm. Electronics, 14(9), 1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14091778






