GDCPlace: Geographic Distance Consistent Loss for Visual Place Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- To help models learn reasonable relationships between embedding of different localization in VPR, we propose GDCPlace, a classification loss function that holds similarity-distance constraint. To the best of our knowledge, this is also the first loss function designed specifically for training a classification proxy in a VPR retrieval model.
- (2)
- The mathematical analysis is presented to demonstrates the effectiveness of GDCPlace in a theoretical view.
- (3)
- We propose hard negative class mining through loss function design to help classification training with no overhead.
- (4)
- Experimental results show that GDCPlace outperforms previous classification loss functions and other SOTA methods in various VPR benchmarks. Experiments on ordinal classification further demonstrate its generalizability.
2. Related Works
2.1. Classification Loss for Retrieval
2.2. Visual Place Recognition
2.3. Hard Negative Mining
3. Methods
3.1. Problem Formulation
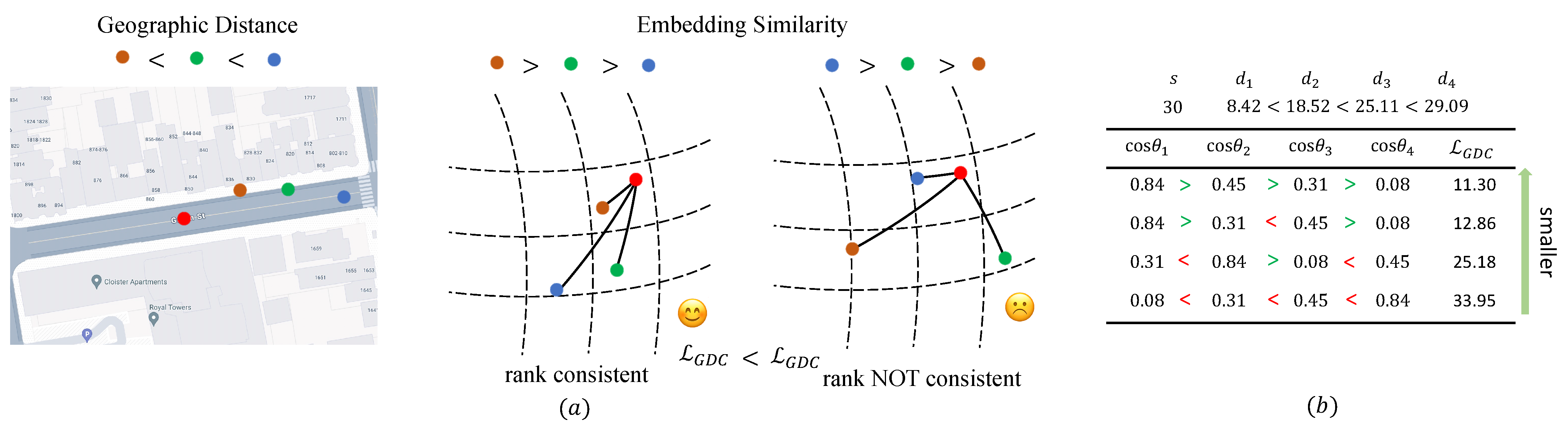
3.2. Geographic Distance Consistent Loss (GDCPlace)
3.3. Hard Negative Class Mining (HNCM)
3.4. Implementation of GDCPlace
4. Experiments
4.1. Common Settings
4.1.1. Experimental Platform
4.1.2. Datasets Selection
4.1.3. Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Comparison with Other Classification Loss Functions
4.2.1. Baseline Selection
4.2.2. Results
4.3. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
4.3.1. Baseline Selection
4.3.2. Vision Foundation Model
4.3.3. Results on ResNet50
4.3.4. Results on DINOv2
4.4. mAP Results of GDCPlace
4.5. Comparison with Janine’s Loss
4.6. Application to Ordinal Classification Task
4.7. Application to CosPlace
4.8. Ablation Studies
4.8.1. Ablation on HNCM
4.8.2. Ablation on Function h
4.9. Time Complexity of GDCPlace
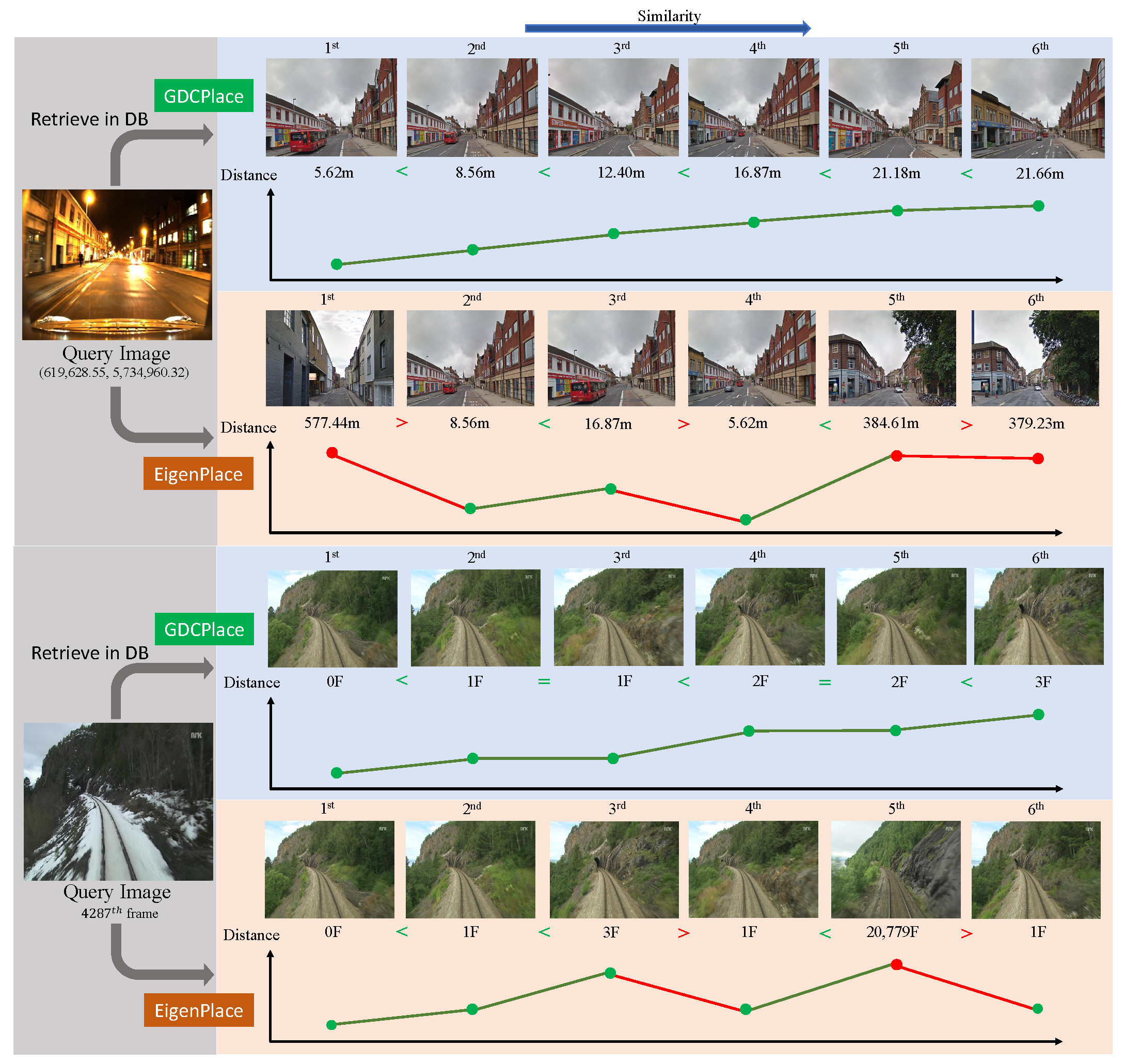
4.10. Qualitative Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VPR | Visual place recognition |
| SOTA | State of the art |
| GDC | Geographic distance consistent |
| HNM | Hard negative mining |
| HNCM | Hard negative class mining |
| mAP | Mean average precision |
| FOV | Field of view |
| SLAM | Simultaneous Localization and Mapping |
| PI | Pitts30k dataset |
| AM | AmsterTime dataset |
| EY | Eynsham dataset |
| TO | Tokyo-24/7 dataset |
| NL | Nordland dataset |
| SN | SVOX Night dataset |
| SO | SVOX Overcast dataset |
| SW | SVOX Snow dataset |
| SR | SVOX Rain dataset |
| SU | SVOX Sun dataset |
| MS | MSLS val dataset |
Appendix A. Proofs
Appendix A.1. Proof of Equations (2)–(5)
Appendix A.2. Proofs of Theorems, Corollaries, and Lemmata
Appendix B. Details on Map Partition for Classification Training
Appendix C. Additional Gradient Analysis

Appendix D. Datasets
Appendix E. Classification Loss Configurations
| NormFace [30] | SphereFace [45] | ArcFace [11] | CurricularFace [32] |
| , | , | ||
| AdaFace [31] | LM-Softmax [34] | MadaCos [85] | UniFace [33] |
| , , , | , | , , , |


References
- Keetha, N.; Mishra, A.; Karhade, J.; Jatavallabhula, K.M.; Scherer, S.; Krishna, M.; Garg, S. Anyloc: Towards universal visual place recognition. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 1286–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camara, L.G.; Gäbert, C.; Přeučil, L. Highly robust visual place recognition through spatial matching of CNN features. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 3748–3755. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Z.; Petillot, Y.; Lane, D.; Miao, Y.; Wang, S. TextPlace: Visual place recognition and topological localization through reading scene texts. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 2861–2870. [Google Scholar]
- Arandjelović, R.; Gronat, P.; Torii, A.; Pajdla, T.; Sivic, J. NetVLAD: CNN Architecture for Weakly Supervised Place Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 1437–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali-Bey, A.; Chaib-Draa, B.; Giguere, P. MixVPR: Feature mixing for visual place recognition. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2–7 January 2023; pp. 2998–3007. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Zhou, S.; Fu, J.; Wang, R.; Chen, S.; Zheng, N. StructVPR: Distill structural knowledge with weighting samples for visual place recognition. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 11217–11226. [Google Scholar]
- Ali-bey, A.; Chaib-draa, B.; Giguère, P. GSV-cities: Toward appropriate supervised visual place recognition. Neurocomputing 2022, 513, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivigno, G.; Berton, G.; Aragon, J.; Caputo, B.; Masone, C. Divide&Classify: Fine-Grained Classification for City-Wide Visual Geo-Localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 11142–11152. [Google Scholar]
- Muller-Budack, E.; Pustu-Iren, K.; Ewerth, R. Geolocation estimation of photos using a hierarchical model and scene classification. In Proceedings of theECCV 2018: 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 563–579. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Ji, X.; Gong, D.; Zhou, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, W. Large Margin Cosine Loss for Deep Face Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 5265–5274. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Guo, J.; Yang, J.; Xue, N.; Kotsia, I.; Zafeiriou, S. ArcFace: Additive Angular Margin Loss for Deep Face Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 5962–5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Chen, K.; Karpur, A.; Cui, Q.; Araujo, A.; Cao, B. Global Features are All You Need for Image Retrieval and Reranking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision 2023, Paris, France, 2–3 October 2023; pp. 11002–11012. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Seong, H.; Lee, S.; Kim, E. Correlation Verification for Image Retrieval. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Berton, G.; Masone, C.; Caputo, B. Rethinking visual geo-localization for large-scale applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 4878–4888. [Google Scholar]
- Berton, G.; Trivigno, G.; Caputo, B.; Masone, C. EigenPlaces: Training Viewpoint Robust Models for Visual Place Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 11080–11090. [Google Scholar]
- Thoma, J.; Paudel, D.P.; Gool, L.V. Soft contrastive learning for visual localization. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 11119–11130. [Google Scholar]
- Leyva-Vallina, M.; Strisciuglio, N.; Petkov, N. Regressing Transformers for Data-efficient Visual Place Recognition. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.16304. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, A.; Xie, W.; Kalogeiton, V.; Zisserman, A. Smooth-AP: Smoothing the path towards large-scale image retrieval. In Proceedings of the 16th European Conference (ECCV 2020), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 677–694. [Google Scholar]
- Revaud, J.; Almazán, J.; Rezende, R.S.; Souza, C.R.d. Learning with average precision: Training image retrieval with a listwise loss. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 5107–5116. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Z.; Zhou, M.; Wang, L.; Gao, X.; Hua, G. Ordinal Regression with Multiple Output CNN for Age Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4920–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.B.; Zhou, H.Y.; Wu, J.; Geng, X. Age Estimation Using Expectation of Label Distribution Learning. In Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 13–19 July 2018; pp. 712–718. [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava, A.; Gupta, A.; Girshick, R. Training region-based object detectors with online hard example mining. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 761–769. [Google Scholar]
- Henriques, J.F.; Carreira, J.; Caseiro, R.; Batista, J. Beyond hard negative mining: Efficient detector learning via block-circulant decomposition. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 2760–2767. [Google Scholar]
- Yildiz, B.; Khademi, S.; Siebes, R.M.; Van Gemert, J. AmsterTime: A visual place recognition benchmark dataset for severe domain shift. In Proceedings of the 2022 26th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Montreal, QC, Canada, 21–25 August 2022; pp. 2749–2755. [Google Scholar]
- Berton, G.M.; Paolicelli, V.; Masone, C.; Caputo, B. Adaptive-attentive geolocalization from few queries: A hybrid approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Virtual, 5–9 January 2021; pp. 2918–2927. [Google Scholar]
- Milford, M.J.; Wyeth, G.F. Mapping a suburb with a single camera using a biologically inspired SLAM system. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2008, 24, 1038–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torii, A.; Arandjelovic, R.; Sivic, J.; Okutomi, M.; Pajdla, T. 24/7 place recognition by view synthesis. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1808–1817. [Google Scholar]
- Warburg, F.; Hauberg, S.; Lopez-Antequera, M.; Gargallo, P.; Kuang, Y.; Civera, J. Mapillary street-level sequences: A dataset for lifelong place recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 2626–2635. [Google Scholar]
- Cummins, M.; Newman, P. Highly scalable appearance-only SLAM-FAB-MAP 2.0. In Robotics: Science and Systems; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Xiang, X.; Cheng, J.; Yuille, A.L. NormFace: L2 Hypersphere Embedding for Face Verification. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM international conference on Multimedia, Mountain View, CA, USA, 23–27 October 2017; pp. 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Jain, A.K.; Liu, X. AdaFace: Quality Adaptive Margin for Face Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 18750–18759. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tai, Y.; Liu, X.; Shen, P.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Huang, F. Curricularface: Adaptive curriculum learning loss for deep face recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 5901–5910. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Jia, X.; Li, Q.; Shen, L.; Duan, J. UniFace: Unified Cross-Entropy Loss for Deep Face Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 20730–20739. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, X.; Zhai, D.; Jiang, J.; Gao, X.; Ji, X. Learning Towards The Largest Margins. In International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). 2022. Available online: https://openreview.net/forum?id=hqkhcFHOeKD (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Oquab, M.; Darcet, T.; Moutakanni, T.; Vo, H.; Szafraniec, M.; Khalidov, V.; Fernandez, P.; Haziza, D.; Massa, F.; El-Nouby, A.; et al. Dinov2: Learning robust visual features without supervision. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.07193. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, Z.; Wei, X.; Liu, W.; Lu, X. Multi-Scale Aligned Spatial-Temporal Interaction for Video-Based Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Circuit Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 8536–8546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffer, E.; Ailon, N. Deep metric learning using triplet network. In Similarity-Based Pattern Recognition, Proceedings of the Third International Workshop, SIMBAD 2015, Copenhagen, Denmark, 12–14 October 2015; Proceedings 3; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 84–92. [Google Scholar]
- Khosla, P.; Teterwak, P.; Wang, C.; Sarna, A.; Tian, Y.; Isola, P.; Maschinot, A.; Liu, C.; Krishnan, D. Supervised contrastive learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 18661–18673. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Jia, X.; Zhou, J.; Shen, L.; Duan, J. UniTSFace: Unified Threshold Integrated Sample-to-Sample Loss for Face Recognition. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 32732–32747. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.Y.; Manmatha, R.; Smola, A.J.; Krahenbuhl, P. Sampling matters in deep embedding learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2840–2848. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Liu, T.; Gong, M.; Ding, C.; Tao, D. Correcting the triplet selection bias for triplet loss. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, ECCV 2018, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 71–87. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Shen, J. Triplet loss in siamese network for object tracking. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, ECCV 2018, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 459–474. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Qiao, Y. A discriminative feature learning approach for deep face recognition. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, ECCV 2016, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 499–515. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, X. Learning deep features via congenerous cosine loss for person recognition. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.06890. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Wen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Li, M.; Raj, B.; Song, L. SphereFace: Deep Hypersphere Embedding for Face Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Wen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Yang, M. Large-Margin Softmax Loss for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016; pp. 507–516. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.; Zhao, S.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, F. MagFace: A universal representation for face recognition and quality assessment. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 14225–14234. [Google Scholar]
- Kasarla, T.; Burghouts, G.; van Spengler, M.; van der Pol, E.; Cucchiara, R.; Mettes, P. Maximum class separation as inductive bias in one matrix. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 19553–19566. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Su, Y. Visual place recognition: A survey from deep learning perspective. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 113, 107760. [Google Scholar]
- Tsintotas, K.A.; Bampis, L.; Gasteratos, A. Visual Place Recognition for Simultaneous Localization and Mapping. In Autonomous—Vehicles Volume 2: Smart Vehicles; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 47–79. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Mao, J.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; Hu, X. A sequence-based visual place recognition method for aerial mobile robots. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1654, 012080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Qian, K. Robust place recognition based on salient landmarks screening and convolutional neural network features. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2020, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, Y. Global Localization in Large-Scale Point Clouds via Roll-Pitch-Yaw Invariant Place Recognition and Low-Overlap Global Registration. IEEE Trans. Circuit Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 3846–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rublee, E.; Rabaud, V.; Konolige, K.; Bradski, G. ORB: An efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 2564–2571. [Google Scholar]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; Volume 1, pp. 886–893. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar]
- Bay, H.; Tuytelaars, T.; Van Gool, L. SURF: Speeded up robust features. In Proceedings of the 9th European Conference on Computer Vision, Graz, Austria, 7–13 May 2006; pp. 404–417. [Google Scholar]
- Calonder, M.; Lepetit, V.; Strecha, C.; Fua, P. BRIEF: Binary robust independent elementary features. In Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, 5–11 September 2010; pp. 778–792. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhong, S.; Yan, L.; Cao, Z. An Embedded System-on-Chip Architecture for Real-time Visual Detection and Matching. IEEE Trans. Circuit Syst. Video Technol. 2014, 24, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, E.J.; Husain, S.S.; Bober-Irizar, M.; Bober, M. Deep Architectures and Ensembles for Semantic Video Classification. IEEE Trans. Circuit Syst. Video Technol. 2019, 29, 3568–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miech, A.; Laptev, I.; Sivic, J. Learnable pooling with context gating for video classification. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.06905. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhu, F.; Zhao, R.; Li, H. Self-supervising fine-grained region similarities for large-scale image localization. In Proceedings of the 16th European Conference (ECCV 2020), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 369–386. [Google Scholar]
- Radenović, F.; Iscen, A.; Tolias, G.; Avrithis, Y.; Chum, O. Revisiting oxford and paris: Large-scale image retrieval benchmarking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, P.H.; Weyand, T.; Sim, J.; Han, B. Cplanet: Enhancing image geolocalization by combinatorial partitioning of maps. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, ECCV 2018, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 536–551. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Schroff, F.; Kalenichenko, D.; Philbin, J. Facenet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 815–823. [Google Scholar]
- Hermans, A.; Beyer, L.; Leibe, B. In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.07737. [Google Scholar]
- Kalantidis, Y.; Sariyildiz, M.B.; Pion, N.; Weinzaepfel, P.; Larlus, D. Hard negative mixing for contrastive learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 21798–21809. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Zhu, Y.; Sohn, K.; Li, C.L.; Shin, J.; Lee, H. i-mix: A domain-agnostic strategy for contrastive representation learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.08887. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, C.Y.; Robinson, J.; Lin, Y.C.; Torralba, A.; Jegelka, S. Debiased contrastive learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 8765–8775. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, J.; Chuang, C.Y.; Sra, S.; Jegelka, S. Contrastive learning with hard negative samples. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.04592. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Chen, W.; Chen, T.; Yuan, Y.; Gong, C.; Chen, K.; Wang, Z. Self-pu: Self boosted and calibrated positive-unlabeled training. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning PMLR, Online, 13–18 July 2020; pp. 1510–1519. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Fan, H.; Wu, Y.; Xie, S.; Girshick, R. Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 9729–9738. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Fan, H.; Girshick, R.; He, K. Improved baselines with momentum contrastive learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.04297. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Xie, S.; He, K. An empirical study of training self-supervised vision transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 9640–9649. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, P.; Cao, Z.; Fan, S.; Yang, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, S. Hardness-aware Metric Learning with Cluster-guided Attention for Visual Place Recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuit Syst. Video Technol. 2025, 35, 367–379. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, T.Y.; Dollár, G. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Mercer, A.M. A variant of Jensen’s inequality. J. Inequalities Pure Appl. Math. 2003, 4, 73–74. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Lee, S.; Seong, H.; Kim, E. Revisiting Self-Similarity: Structural Embedding for Image Retrieval. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Cummins, M.; Newman, P. Appearance-only SLAM at large scale with FAB-MAP 2.0. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2011, 30, 1100–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Torii, A.; Sivic, J.; Pajdla, T.; Okutomi, M. Visual place recognition with repetitive structures. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 883–890. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.M.; Baatz, G.; Köser, K.; Tsai, S.S.; Vedantham, R.; Pylvänäinen, T.; Roimela, K.; Chen, X.; Bach, J.; Pollefeys, M.; et al. City-scale landmark identification on mobile devices. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2011, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 737–744. [Google Scholar]
- Weyand, T.; Araujo, A.; Cao, B.; Sim, J. Google landmarks dataset v2-a large-scale benchmark for instance-level recognition and retrieval. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Gao, X.; Ke, B.; Qiao, R.; Sun, X. Coarse-to-Fine: Learning Compact Discriminative Representation for Single-Stage Image Retrieval. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, R.; Marathe, A. Soft Labels for Ordinal Regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference On Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, J. Hybrid CNN-Transformer Features for Visual Place Recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuit Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Yang, L.; Chen, C.; Shah, M.; Shen, X.; Wang, H. R2former: Unified retrieval and reranking transformer for place recognition. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 19370–19380. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16 × 16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. In International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). 2021. Available online: https://openreview.net/forum?id=YicbFdNTTy (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Izquierdo, S.; Civera, J. Optimal transport aggregation for visual place recognition. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.15937. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, F.; Lan, X.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, D.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, C. CricaVPR: Cross-image Correlation-aware Representation Learning for Visual Place Recognition. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.19231. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Kong, A.W.K.; Goh, C.K. A Constrained Deep Neural Network for Ordinal Regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Song, Y.; Qi, H. Age progression/regression by conditional adversarial autoencoder. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 5810–5818. [Google Scholar]
- Moschoglou, S.; Papaioannou, A.; Sagonas, C.; Deng, J.; Kotsia, I.; Zafeiriou, S. Agedb: The first manually collected, in-the-wild age database. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 51–59. [Google Scholar]


| References | Training Strategies | Inference Strategies | Methods | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arandjelović et al. [4] | Sample-to-Sample | Retrieval | NetVLAD integrates a differentiable VLAD layer into a CNN, aggregating local features into a global descriptor. | High computational and memory requirements, along with sensitivity to variations in local features. |
| Ali-Bey et al. [5] | Sample-to-Sample | Retrieval | MixVPR fuses CNN feature maps using cascaded lightweight MLP blocks to generate compact global descriptors. | Its reliance on fixed pretrained backbones and MLP fusion can make it sensitive to noise. |
| Shen et al. [6] | Sample-to-Sample | Retrieval | StructVPR distills structural knowledge by dynamically weighting training samples to guide global descriptor learning. | Its effectiveness relies on accurate structural cues, making it potentially sensitive to noisy scene structures. |
| Ali-Bey et al. [7] | Sample-to-Sample | Retrieval | GSV-Cities introduces a large-scale, accurately labeled urban dataset to train VPR models | Its approach may be less effective in non-urban settings and relies on extensive, high-quality annotations. |
| Trivigno et al. [8] | Classification | Classification | Divide & Classify reformulates VPR task as a fine-grained classification task by partitioning dense urban maps into non-adjacent cells. | Its performance depends heavily on dense, well-distributed training data and may struggle with small-scale regions. |
| Muller-Budack et al. [9] | Classification | Classification | The method treats geolocalization as a classification task by hierarchically partitioning the Earth into cells and integrating scene context. | It suffers from ambiguity in scene content in defining effective partitions, reducing localization accuracy in transitional or unclear areas. |
| Berton et al. [14] | Classification | Retrieval | CosPlace reformulates visual geo-localization as a classification task by partitioning the city into discrete regions and training a CNN with an CosFace loss. | Its performance is highly sensitive to the partitioning strategy. Errors in defining region boundaries or ambiguous scene cues can lead to misclassifications. |
| Berton et al. [15] | Classification | Retrieval | EigenPlace trains a CNN to produce viewpoint-robust global descriptors by incorporating eigen-decomposition techniques that emphasize stable, discriminative features. | Its reliance on eigen-decomposition and the need for diverse, extensive training data can limit generalization and add computational complexity. |
| Method | Track | Multi-View | Frontal-View | AVG | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI | AM | EY | TO | NL | SN | SO | SW | SR | SU | MS | ||||
| NormFace [30] | Face | 90.6 | 41.3 | 90.0 | 88.3 | 58.4 | 40.3 | 88.2 | 87.2 | 85.2 | 41.3 | 86.8 | 72.5 | |
| SphereFace [45] | Face | 86.4 | 43.1 | 79.5 | 63.2 | 59.3 | 52.0 | 90.7 | 87.7 | 79.8 | 63.1 | 83.4 | 71.7 | |
| CosFace [10] | Face | 92.5 | 48.9 | 90.7 | 93.0 | 71.2 | 58.9 | 93.1 | 93.1 | 90.0 | 86.4 | 89.1 | 82.4 | |
| ArcFace [11] | Face | 89.2 | 40.5 | 83.2 | 91.2 | 64.2 | 46.1 | 82.8 | 90.2 | 83.6 | 81.4 | 85.7 | 76.2 | |
| CurricularFace [32] | Face | 92.3 | 47.1 | 90.8 | 91.4 | 68.8 | 61.6 | 93.7 | 93.6 | 90.6 | 84.4 | 89.1 | 82.1 | |
| AdaFace [31] | Face | 86.7 | 44.8 | 75.4 | 74.6 | 61.1 | 44.7 | 89.1 | 83.9 | 74.8 | 51.9 | 79.6 | 69.7 | |
| SORD [86] | Ordinal | 91.8 | 49.2 | 90.1 | 91.6 | 70.8 | 63.9 | 93.2 | 93.5 | 90.6 | 85.3 | 88.0 | 82.5 | |
| LM-Softmax [34] | General | 92.2 | 49.6 | 90.4 | 90.5 | 73.2 | 65.2 | 94.0 | 93.4 | 90.1 | 85.4 | 89.6 | 83.1 | |
| MadaCos [85] | Landmark | 91.7 | 46.8 | 90.6 | 90.8 | 68.8 | 61.4 | 95.0 | 93.6 | 90.3 | 85.1 | 88.5 | 82.1 | |
| Gem-AP [19] | Landmark | 90.6 | 45.1 | 88.6 | 91.5 | 68.2 | 54.1 | 91.9 | 92.0 | 86.4 | 82.9 | 85.0 | 79.7 | |
| UniFace [33] | Face | 92.2 | 46.5 | 90.6 | 91.4 | 65.5 | 61.2 | 94.2 | 94.0 | 91.5 | 84.7 | 88.1 | 81.8 | |
| GDCPlace | VPR | 92.6 | 51.6 | 90.9 | 92.1 | 77.6 | 70.1 | 95.0 | 94.4 | 90.8 | 86.8 | 89.6 | 84.7 | |
| Method | Backbone | Dim. | Multi-View | Frontal-View | AVG | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI | AM | EY | TO | NL | SN | SO | SW | SR | SU | MS | |||||
| Classification Training | |||||||||||||||
| D&C [8] | ResNet50 | 1280 | 84.6 | 17.5 | 87.2 | 60.0 | 11.9 | 4.7 | 69.3 | 57.7 | 55.1 | 42.5 | 69.6 | 50.9 | |
| CFCD [85] | ResNet50 | 512 | 62.2 | 28.8 | 76.3 | 54.9 | 6.1 | 16.8 | 60.8 | 50.9 | 39.3 | 25.6 | 50.7 | 42.9 | |
| CosPlace [14] | ResNet50 | 2048 | 90.9 | 47.7 | 90.0 | 87.3 | 71.9 | 50.7 | 92.2 | 92.0 | 87.0 | 78.5 | 87.4 | 79.6 | |
| EigenPlace [15] | ResNet50 | 2048 | 92.5 | 48.9 | 90.7 | 93.0 | 71.2 | 58.9 | 93.1 | 93.1 | 90.0 | 86.4 | 89.1 | 82.4 | |
| GDCPlace | ResNet50 | 2048 | 92.6 | 51.6 | 90.9 | 92.1 | 77.6 | 70.1 | 95.0 | 94.4 | 90.8 | 86.8 | 89.6 | 84.7 | |
| Sample-to-Sample Training | |||||||||||||||
| SFRS [62] | VGG16 | 4096 | 89.1 | 29.7 | 72.3 | 80.3 | 16.0 | 28.6 | 81.1 | 76.0 | 69.7 | 54.8 | 70.0 | 60.7 | |
| NetVLAD [4] | VGG16 | 4096 | 85.0 | 16.3 | 77.7 | 69.8 | 13.1 | 8.0 | 66.4 | 54.4 | 51.5 | 35.4 | 58.9 | 48.8 | |
| Former-global [88] | ResNet50 | 256 | 73.1 | 12.8 | 82.4 | 48.3 | 24.6 | 13.5 | 75.8 | 60.8 | 47.6 | 28.0 | 80.3 | 49.7 | |
| CNN-Transformer [87] | VGG16 + Swin-B | 4096 | 86.3 | - | - | 78.9 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| HCA [76] | VGG16 | 4096 | - | - | - | 86.7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 76.4 | - | |
| Conv-AP [7] | ResNet50 | 8192 | 90.5 | 35.0 | 87.6 | 72.1 | 62.9 | 43.4 | 91.9 | 91.0 | 82.8 | 80.4 | 82.4 | 74.5 | |
| MixVPR [5] | ResNet50 | 4096 | 91.5 | 40.2 | 89.4 | 85.1 | 76.2 | 64.4 | 96.2 | 96.8 | 91.5 | 84.8 | 87.2 | 82.1 | |
| Method | Backbone | Dim. | Multi-View | Frontal-View | AVG | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI | AM | EY | TO | NL | SN | SO | SW | SR | SU | MS | |||||
| Classification Training | |||||||||||||||
| EigenPlace [15] | DINOv2-B/14 | 2048 | 93.3 | 53.0 | 91.3 | 95.2 | 86.2 | 92.8 | 96.9 | 97.2 | 96.3 | 94.1 | 89.2 | 89.6 | |
| GDCPlace | DINOv2-B/14 | 2048 | 93.5 | 57.7 | 91.7 | 96.5 | 88.8 | 94.9 | 97.2 | 97.9 | 96.8 | 95.6 | 91.4 | 91.1 | |
| GDCPlace | DINOv2-B/14 | 8448 | 94.2 | 58.5 | 91.9 | 96.2 | 90.7 | 94.9 | 97.6 | 97.8 | 97.0 | 96.1 | 91.4 | 91.5 | |
| Sample-to-Sample Training | |||||||||||||||
| AnyLoc [1] | DINOv2-G/14 | 49152 | 87.5 | 43.9 | 87.5 | 91.4 | 35.7 | 76.5 | 91.9 | 88.0 | 85.6 | 86.5 | 70.3 | 76.8 | |
| SALAD [90] | DINOv2-B/14 | 8448 | 91.9 | 56.9 | 91.4 | 94.3 | 86.1 | 94.8 | 98.3 | 98.9 | 98.7 | 96.7 | 92.2 | 90.9 | |
| CricaVPR [91] | DINOv2-B/14 | 4096 | 94.9 | 64.7 | 91.6 | 93.0 | 90.7 | 85.1 | 96.7 | 96.0 | 95.0 | 93.8 | 90.0 | 90.1 | |
| Methods | Training Strategy | NordLand | SVOX Night | AmsterTime | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| @3 | @5 | @7 | @3 | @5 | @7 | @3 | @5 | @7 | ||
| CosPlace [14] | CLS | 60.8 | 51.8 | 44.6 | 40.1 | 31.8 | 26.0 | 54.8 | 56.2 | 56.7 |
| EigenPlace [15] | CLS | 57.0 | 46.8 | 39.4 | 47.7 | 34.1 | 27.6 | 56.0 | 57.1 | 57.7 |
| Conv-AP [7] | S2S | 49.1 | 40.4 | 34.3 | 31.6 | 24.3 | 19.5 | 40.5 | 41.9 | 42.4 |
| MixVPR [5] | S2S | 60.7 | 50.2 | 42.7 | 47.2 | 35.9 | 28.4 | 46.6 | 47.6 | 47.9 |
| GDCPlace | CLS | 63.6 | 52.8 | 44.8 | 54.6 | 42.3 | 33.7 | 58.3 | 59.7 | 60.0 |
| Methods | Tracks | NordLand | SVOX Night | AmsterTime | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| @3 | @5 | @7 | @3 | @5 | @7 | @3 | @5 | @7 | ||
| NormFace [30] | Face | 39.5 | 31.2 | 25.7 | 29.0 | 22.5 | 18.0 | 47.9 | 49.0 | 49.6 |
| SphereFace [45] | Face | 47.2 | 38.8 | 32.9 | 39.1 | 30.4 | 24.6 | 50.6 | 51.9 | 52.3 |
| CosFace [10] | Face | 60.8 | 51.8 | 44.6 | 40.1 | 31.8 | 26.0 | 54.8 | 56.2 | 56.7 |
| ArcFace [11] | Face | 38.9 | 31.7 | 26.8 | 19.3 | 14.6 | 11.7 | 45.3 | 46.6 | 47.2 |
| CurricularFace [32] | Face | 55.1 | 45.4 | 38.3 | 46.7 | 36.0 | 28.8 | 55.3 | 56.5 | 57.0 |
| AdaFace [31] | Face | 48.4 | 40.1 | 34.2 | 33.7 | 26.1 | 21.0 | 51.7 | 52.9 | 53.5 |
| SORD [86] | Ordinal | 61.2 | 50.6 | 43.2 | 51.4 | 39.8 | 32.4 | 58.0 | 57.6 | 59.4 |
| LM-Softmax [34] | General | 59.8 | 49.5 | 42.0 | 49.2 | 37.7 | 30.2 | 57.1 | 58.2 | 58.7 |
| MadaCos [85] | Landmark | 55.9 | 46.5 | 39.5 | 46.8 | 36.2 | 29.1 | 54.7 | 55.8 | 56.1 |
| GeM-AP [85] | Landmark | 58.2 | 47.9 | 41.5 | 48.7 | 37.8 | 31.2 | 56.2 | 57.2 | 58.0 |
| UniFace [33] | Face | 52.5 | 43.3 | 36.7 | 44.3 | 33.8 | 27.0 | 55.0 | 56.1 | 56.6 |
| GDCPlace | VPR | 63.6 | 52.8 | 44.8 | 54.6 | 42.3 | 33.7 | 58.3 | 59.7 | 60.0 |
| Formulation | Multi-View | Frontal-View | AVG | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NI | AM | EY | TO | NL | SN | SO | SW | SR | SU | MS | |||
| Janine’s Loss | 78.3 | 47.5 | 76.1 | 69.2 | 48.4 | 36.8 | 88.3 | 89.8 | 80.2 | 66.2 | 80.1 | 69.2 | |
| Janine’s Loss + HNCM | 89.9 | 51.6 | 89.2 | 81.6 | 51.3 | 44.7 | 92.4 | 92.2 | 87.4 | 78.3 | 86.6 | 76.8 | |
| GDCPlace | 92.6 | 51.6 | 90.9 | 92.1 | 77.6 | 70.1 | 95.0 | 94.4 | 90.8 | 86.8 | 89.6 | 84.7 | |
| Method | Regression [20] | Classification [92] | DLDL-v2 [21] | SORD [86] | OR-CNN [20] | GDCPlace |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTKFace | 4.78 | 4.95 | 4.67 | 4.77 | 4.64 | 4.59 |
| AgeDB | 6.72 | 7.29 | 6.89 | 6.86 | 6.68 | 6.55 |
| Method | Backbone | Dim. | Multi-View | Single-View | AVG | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI | AM | EY | TO | NL | SN | SO | SW | SR | SU | MS | |||||
| CosPlace | ResNet50 | 2048 | 90.9 | 47.7 | 90.0 | 87.3 | 71.9 | 50.7 | 92.2 | 92.0 | 87.0 | 78.5 | 87.4 | 79.6 | |
| CosPlace + GDCPlace | ResNet50 | 2048 | 91.5 | 50.2 | 90.0 | 89.5 | 75.8 | 54.2 | 93.0 | 93.5 | 87.8 | 79.0 | 88.0 | 81.1 | |
| K in HNCM | Pitts30k | Tokyo-24/7 | SVOX Night | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R@1 | R@5 | R@10 | R@1 | R@5 | R@10 | R@1 | R@5 | R@10 | |||
| 1 | 92.4 | 96.5 | 97.3 | 92.1 | 96.8 | 97.1 | 50.3 | 72.2 | 78.1 | ||
| 2 | 92.6 | 96.4 | 97.3 | 92.1 | 97.5 | 98.4 | 51.6 | 72.5 | 77.0 | ||
| 3 | 92.4 | 96.5 | 97.4 | 92.7 | 96.2 | 97.1 | 51.1 | 73.4 | 78.1 | ||
| 50 | 92.0 | 96.4 | 97.2 | 90.2 | 95.6 | 96.8 | 50.4 | 72.5 | 77.0 | ||
| No HNCM | 92.3 | 96.5 | 97.3 | 91.4 | 97.1 | 97.8 | 50.5 | 72.1 | 77.3 | ||
| in Function h | Pitts30k | Tokyo-24/7 | SVOX Night | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R@1 | R@5 | R@10 | R@1 | R@5 | R@10 | R@1 | R@5 | R@10 | |||
| 0.1 | 92.4 | 96.4 | 97.4 | 91.4 | 97.5 | 97.8 | 50.5 | 72.0 | 77.8 | ||
| 0.2 | 92.6 | 96.4 | 97.3 | 92.1 | 97.5 | 98.4 | 51.6 | 72.5 | 77.0 | ||
| 0.4 | 92.3 | 96.5 | 97.4 | 91.8 | 97.1 | 98.0 | 50.4 | 71.6 | 77.6 | ||
| 0.6 | 92.4 | 96.5 | 97.2 | 91.1 | 96.8 | 97.5 | 50.9 | 72.6 | 77.8 | ||
| 0.8 | 92.3 | 96.2 | 97.2 | 90.8 | 97.1 | 97.8 | 50.9 | 72.3 | 77.3 | ||
| in Function h | Pitts30k | Tokyo-24/7 | SVOX Night | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R@1 | R@5 | R@10 | R@1 | R@5 | R@10 | R@1 | R@5 | R@10 | |||
| 2 | 92.4 | 96.4 | 97.4 | 94.0 | 97.8 | 98.1 | 68.5 | 85.4 | 88.2 | ||
| 4 | 92.3 | 96.4 | 97.3 | 92.1 | 96.8 | 97.8 | 68.5 | 84.0 | 88.6 | ||
| 6 | 92.6 | 96.4 | 97.3 | 92.1 | 97.5 | 98.4 | 70.1 | 84.8 | 89.2 | ||
| 8 | 92.1 | 96.5 | 97.3 | 90.8 | 96.8 | 97.5 | 70.4 | 83.1 | 87.5 | ||
| 10 | 92.2 | 96.5 | 97.3 | 90.2 | 97.5 | 97.5 | 66.3 | 81.7 | 85.7 | ||
| Method | Time (min/5000 Steps) |
|---|---|
| EigenPlace | |
| GDCPlace |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, S.; Cui, Q. GDCPlace: Geographic Distance Consistent Loss for Visual Place Recognition. Electronics 2025, 14, 1418. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071418
Shao S, Cui Q. GDCPlace: Geographic Distance Consistent Loss for Visual Place Recognition. Electronics. 2025; 14(7):1418. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071418
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Shihao, and Qinghua Cui. 2025. "GDCPlace: Geographic Distance Consistent Loss for Visual Place Recognition" Electronics 14, no. 7: 1418. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071418
APA StyleShao, S., & Cui, Q. (2025). GDCPlace: Geographic Distance Consistent Loss for Visual Place Recognition. Electronics, 14(7), 1418. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071418






