Abstract
As societal perceptions of pet ownership shift, an increasing number of individuals are choosing to keep pets, leading to various challenges. In Taiwan, the growing population of stray dogs and cats is largely attributed to insufficient education and inadequate management practices among pet owners, posing public health and safety concerns. This issue primarily stems from a lack of understanding regarding proper pet care. In response, awareness of animal protection and life education has been gaining traction, drawing attention to these concerns. To address this, this study introduces an augmented reality (AR) pet care teaching system aimed at enhancing pet care knowledge through smartphones or tablets. Utilizing interactive AR technology, students are able to meet learning objectives related to pet care and foundational knowledge. This study adopts a quasi-experimental design and incorporates questionnaire surveys involving 61 college students and 8 teachers. The findings indicate that while both AR and traditional teaching methods are effective, the AR group exhibited superior learning outcomes. Furthermore, teacher feedback emphasized that the AR system fosters greater student engagement and significantly improves learning effectiveness.
1. Introduction
As Taiwanese society has evolved, perceptions of pet ownership have shifted significantly. In the 1950s, cats and dogs were primarily kept for practical purposes, such as guarding homes and controlling pests, fulfilling a protective role to ensure property safety. However, since the 1970s, motivations for keeping pets have gradually shifted toward emotional satisfaction, emphasizing companionship and entertainment. By the 1990s, the trend of keeping cats as household companions had grown, making them an essential part of family life [1]. Economic growth led to smaller living spaces, reducing the protective functions traditionally associated with pets. Concurrently, declining birth rates and population aging increased feelings of loneliness, further reinforcing the emotional and comforting roles pets play. Since 2018, Taiwan has officially entered the stage of an aging society and is predicted to enter a super-aged society in 2025 [2].
These societal changes have shifted the purpose of pet ownership from practical needs to emotional connections, with pets increasingly regarded as family members, playing a central role in modern households [3]. This shift is not unique to Taiwan; similar trends have been observed in other countries, particularly in regions experiencing demographic shifts and urbanization. For example, in Japan and South Korea, falling birth rates and aging populations have led to the rise of so-called companion animals, with pets often seen as substitutes for children or close family members. In Western countries such as the United States and Europe, pet humanization is also becoming more and more popular, and pet-related industries are expanding to accommodate this evolving relationship. These global trends highlight that the growing emotional significance of pets is a widespread phenomenon, driven by changing societal structures and demographic trends around the world.
The outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic had a profound impact on people’s lives, prompting many to adopt pets for emotional support. A 2021 study by Hoffman et al. [4] reported a noticeable increase in pet ownership during the COVID-19 pandemic, with dog ownership rising from 48% to 54% of households. This trend reflects the rise of the “companionship economy”, which has also created business opportunities. Since the spread of COVID-19 in Taiwan in 2020, the pet-related industry has continued to expand. Between 2018 and 2021, the sales of pet-related businesses in Taiwan grew annually, reaching NT$43.88 billion in 2021, with a growth rate of 11%. The pandemic has transformed lifestyles and consumption patterns, driving significant growth in pet products, healthcare, and related industries.
Pet ownership has become a growing trend in Taiwan, but it has also led to a rise in related issues. Abandonment of pets has become more prevalent, prompting increased attention from both the government and society toward the importance of animal protection and education. According to data from the Council of Agriculture, there were approximately 155,869 stray dogs in Taiwan in 2020, marking a 6.19% increase compared to 2018, highlighting the worsening stray animal problem. In 2021, public animal shelters nationwide housed 32,388 stray dogs and cats, with uncollected stray animals potentially threatening community safety. In addition to promoting pet registration, education to raise owners’ awareness of animal protection is essential to reduce abandonment and abuse. The government has also promoted spaying and neutering programs for owned and semi-owned cats through subsidies [5], aiming to reduce abandonment, euthanasia, and public health concerns.
Impulsive pet purchases are often driven by the appeal of an animal’s cute appearance, without fully considering the responsibilities and knowledge required for proper care. Such actions frequently lead to subsequent abandonment issues. To prevent this, prospective pet owners should first understand the responsibilities involved and acquire essential care knowledge [6]. The Agriculture Bureau recommends that owners carefully consider their lifestyle and living environment before deciding on a suitable pet. Educational programs or readiness surveys can help potential owners assess their ability to care for a pet. These measures promote responsible ownership, reduce abandonment rates and address related societal issues.
Insufficient knowledge about pet care can lead to a variety of problems, particularly regarding nutrition. Owners who are unfamiliar with pets’ dietary needs may inadvertently cause malnutrition or even death. Feeding pets inappropriate diets, such as those containing harmful ingredients or lacking proper nutritional balance, can lead to serious health problems [7]. Furthermore, as the pet population grows, the environmental impact of pet food production increases, leading to greater land and water consumption and higher carbon emissions [8].
Pet ownership also raises safety concerns. For example, failing to leash pets in public spaces can lead to traffic accidents or injuries [9,10]. Certain bacteria found in pets, like Capnocytophaga canimorsus, pose health risks. Free-roaming dogs and cats, especially during mating periods, can cause noise disturbances that affect nearby residents [11]. Moreover, high veterinary costs, especially without national health insurance coverage for pets, significantly increase owners’ financial burden, emphasizing the need for careful consideration of economic capability and long-term responsibility before adopting pets.
In 1998, Taiwan’s Ministry of Agriculture introduced the “Animal Protection Act”, signaling a pivotal change in Taiwan’s animal welfare policy. This legislation not only aims to prevent cruelty but also promotes respect for animal rights. The law has also served as a foundation for life education, integrating animal protection into the educational system. With the expansion of the educational curriculum, students gain a deeper understanding of biodiversity and ecosystems, fostering values that promote respect for life and social responsibility toward animal welfare.
According to recent data, pet ownership in Taiwan has significantly increased, with dogs and cats being the most commonly adopted companion animals [12]. Yan et al. [12] reported that, between 2012 and 2020, there was a growing public interest in adopting dogs and cats from animal shelters. Reflecting these trends, this study focuses on cats and dogs as primary subjects for developing educational content aimed at promoting responsible pet care. With increasing attention to animal-related education in Taiwan, pet ownership issues have become a significant topic of discussion. Given the high acceptance of digital products in modern society, digital learning methods that integrate the Internet and multimedia are emerging as mainstream educational trends [13,14]. However, several challenges remain in effectively promoting such educational programs:
- (1)
- Applicability of teaching materials: Learning experiences based solely on reading or auditory information often fail to create deep understanding and long-term retention. In contrast, hands-on experience or simulations are more effective in helping learners acquire knowledge and skills. Therefore, the reliance on image- or text-based materials may limit learning outcomes.
- (2)
- Limitations of teaching materials: learning with paper-based teaching materials often lacks interactivity, making it difficult for students to stay focused and motivated, which can negatively impact learning effectiveness.
- (3)
- Lack of knowledge dissemination: many social issues stem from deficiencies in character or inadequate education, reflecting that educational resources have not been adequately disseminated.
Addressing these challenges requires focusing on improving the applicability of teaching materials, overcoming the limitations of current resources, and enhancing the distribution of knowledge. Based on these potential challenges, this paper proposes the following research questions (RQs).
RQ1: Does the augmented reality (AR) teaching system effectively enhance students’ learning outcomes in pet knowledge courses?
Traditional learning methods that rely primarily on reading or auditory instruction may hinder students’ memory retention and comprehension, particularly when teaching materials lack interactivity, thus limiting learning effectiveness. In contrast, AR technology integrates virtual and real-world environments, providing an immersive and interactive learning experience. This approach allows students to engage in simulations and hands-on manipulation, which fosters a deeper understanding of the material and enhances memory retention. Additionally, AR technology has been shown to improve learners’ motivation and focus by making abstract concepts more concrete and easier to grasp, promoting long-term retention.
Recent studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of AR-based teaching systems in improving educational outcomes across various subjects. For example, Tsai et al. [15] developed and validated a virtual chemical laboratory for elementary natural science education, showing that interactive AR environments significantly enhance student engagement and understanding of scientific concepts. Similarly, Tsai and Lai [16] designed an AR-based teaching system for primary logic programming education, highlighting its effectiveness in improving student motivation and comprehension. In addition, a recent study [17] highlights that the sensor-based human−computer interaction and multimodal sensory feedback can improve the learning experience. Building on these findings, this study explores the application of AR systems in pet knowledge courses, investigating their potential to enhance student learning and engagement in biological and animal-related education.
RQ2: Can AR teaching materials effectively stimulate students’ motivation in pet knowledge courses?
Motivation plays a crucial role in fostering active engagement in learning, and a lack of motivation often results in challenges with sustained learning efforts. Research has shown that gamified learning significantly enhances student interest and motivation, making gamification an increasingly popular approach in education [18]. By integrating game elements into the learning process, gamified learning strategies have been widely used to improve knowledge retention in various subjects, including mathematics, language arts, natural sciences, as well as in enhancing problem-solving, strategic planning, and skill application.
To enhance engagement in pet knowledge courses, this study integrates various gamification mechanisms into AR-based teaching materials. These mechanisms include an interactive task system, where learners complete specific actions based on different tasks, and a virtual pet learning system, allowing students to choose and care for different types of pets. Each virtual pet represents a learning milestone, motivating students to stay engaged and progress through the curriculum. By combining these elements, this study aims to evaluate whether AR teaching materials with gamified components can effectively enhance students’ motivation and engagement in learning about pet care.
RQ3: Can the AR teaching system optimize the teaching equipment used in pet knowledge courses?
With technological advancements, the widespread accessibility of smartphones and tablets has enabled the rapid development and adoption of AR and Virtual Reality (VR) applications. These devices significantly lower the barriers to AR and VR technologies, allowing learners to easily interact with virtual objects via mobile devices, offering sensory experiences that are often difficult to achieve in conventional learning environments. The immersive and interactive nature of AR and VR-based teaching methods enhances learners’ engagement and focus, making them highly effective. As portable devices and wireless networks continue to expand, learners can access instructional content in a variety of contexts. This study seeks to explore whether the AR teaching system can optimize the use of teaching equipment in pet knowledge courses by leveraging these accessible technologies.
Based on the exploration of challenges in pet knowledge education and the literature review, this study proposes an AR-based pet care teaching system. The content of the system is grounded in the Taiwan Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (TSPCA) and animal protection laws, integrating AR technology with gamification design to enhance learners’ interest and focus, thereby improving learning outcomes. Learners can complete educational tasks and simulate pet care interactions through AR mobile games. This study compares the effectiveness of AR learning with traditional teaching materials and presents the following three main contributions:
- (1)
- Expansion of educational materials: the AR-based teaching system enables learners to acquire pet care knowledge via smartphones, overcoming the limitations of traditional materials and geographic constraints.
- (2)
- Curriculum design: the incorporation of AR features and gamification elements into pet knowledge courses is shown to effectively stimulate students’ motivation.
- (3)
- Optimization of teaching equipment: the system replaces traditional textbooks, offering a more accessible and convenient learning method through widely available mobile devices.
The research results indicate a significant difference in student progress between those using traditional textbooks and those using AR teaching materials in pet knowledge courses. The group utilizing AR teaching materials exhibited significantly better learning outcomes, demonstrating the positive influence of AR on educational effectiveness. Students expressed high satisfaction with AR learning, underscoring its role in boosting motivation. Moreover, teachers also showed strong support for the integration of AR into teaching, further validating the effectiveness of the AR-based pet care teaching system in enhancing educational experiences.
2. Research Method
Figure 1 illustrates the framework of the research method for this study. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed AR-based pet care teaching system, a quasi-experimental method and a questionnaire survey were employed. This approach was designed to assess the learning outcomes of participants. Multiple teachers and students were invited to engage with the virtual course, after which their feedback was collected through surveys. The results from test papers and questionnaires were gathered post-experiment for analysis. The following sections provide a detailed explanation of the participants, curriculum planning, research design, experimental procedures, and research tools used in the study. A comprehensive description of the AR teaching materials is provided in the subsequent section.
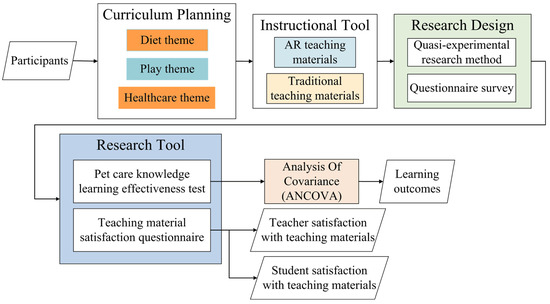
Figure 1.
Research method used in this study.
2.1. Participants
The participants in this study primarily consisted of university students aged 20–24, along with a small group of teaching staff. The sample included students from a university in New Taipei City, as well as university teaching assistants aged 25–29 and elementary school teachers. To account for variations in prior AR experience and interest in pet care, participants were surveyed regarding their familiarity with AR-based learning tools and their engagement with pet-related topics before the study. The study divided participants into two groups: an experimental group of 30 students and a control group of 31 students, resulting in a total of 61 students, all providing valid responses. Participants were assigned to these groups based on random assignment to avoid any potential selection bias and ensure balanced representation. In addition, feedback from 7 university teaching assistants and 1 elementary school teacher, totaling 8 teaching staff members, was analyzed regarding their experience with the AR teaching materials. Overall, the research involved 69 participants, with all 69 samples considered available for analysis.
2.2. Curriculum Planning
This study aimed to examine different teaching methods and incorporate new experiential approaches to enhance learners’ understanding of key concepts in pet care courses. The learning objectives and content are detailed as follows.
2.2.1. Learning Objectives
The AR pet care teaching system developed in this study integrates content from various public sources, including the TSPCA, animal protection laws, the “Pre-Life Education for Pet Ownership” online course provided by the New Taipei City Animal Protection Office, and other relevant resources organized by the researchers for student learning. The learning objectives are as follows:
- (1)
- Understanding knowledge related to pet diet and excretion: learners would gain insights into the dietary needs and waste management practices essential for pet care.
- (2)
- Understanding knowledge related to pet play and interaction: learners would explore the interaction and play behaviors typical of pets to better understand their emotional and physical needs.
- (3)
- Understanding knowledge related to pet medical and health care: learners would acquire knowledge of basic medical care, health management, and emergency response for pets.
By using the AR pet care teaching system, learners would interact with virtual pets, simulating real-world activities such as feeding, playing, and providing healthcare, thus enhancing their understanding of pet care responsibilities.
2.2.2. Learning Content
Learners engaging with the AR pet care system gained basic pet care knowledge through guided reading and interactive exercises. In the AR environment, they used virtual tools to perform tasks like feeding, playing, and attending to a pet’s health, providing a hands-on experience to reinforce learning. For the traditional teaching group, identical learning content was provided in a paper format. Students used paper-based worksheets to study the same pet knowledge covered in the AR system, ensuring consistency in the instructional material between both groups. Based on the planned learning objectives, the AR courses were organized around three main themes: diet, play, and healthcare. Table 1 presents a detailed course planning table, outlining these themes, their learning objectives, and the associated content.

Table 1.
Pet care course planning.
2.3. Research Design
This study employed a mixed-method approach, integrating both quasi-experimental research methods and survey methods to examine the effects of AR-based and traditional teaching methods on learning outcomes. Additionally, the study evaluated the satisfaction levels of students and teachers with the pet care teaching materials. The research design is outlined as follows.
2.3.1. Quasi-Experimental Research Method
The quasi-experimental research method bridges experimental and observational research by implementing intervention measures while lacking complete random assignment of participants. This approach is particularly suitable for real-world settings where true experimental conditions are difficult to achieve. To enhance both internal and external validity, statistical control techniques such as Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA) are employed. ANCOVA helps account for covariates, interfering variables that may influence outcomes, allowing for better isolation of the independent variables’ effects. In this study, potential confounding factors, such as technological proficiency and engagement with pet-related topics, were assessed through pre-test surveys. In addition, since the AR teaching materials were presented in Chinese, a language familiar to students, language proficiency was taken into account. Although individual learning motivation was not explicitly controlled, random assignment was used to balance potential motivational differences across groups.
Figure 2 illustrates the research design framework, where the key components of the quasi-experimental design are shown as follows:
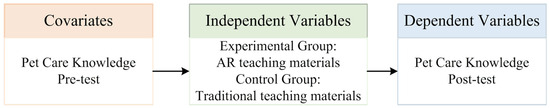
Figure 2.
Framework of the research design for this study.
- (1)
- Covariates: any external variables that may influence the participants’ learning performance (e.g., prior knowledge or motivation).
- (2)
- Independent variable: the different teaching methods (AR-based learning vs. traditional learning).
- (3)
- Dependent variable: the primary outcome, which is the learners’ performance and understanding in pet care knowledge.
Two groups were compared: the experimental group and the control group. In the experimental group, participants engaged with the pet care teaching system designed for the study, utilizing AR-based teaching materials. In the control group, participants relied on traditional paper-based teaching materials to complete the same course content. The purpose of this design was to investigate whether the immersive, interactive AR experience leads to better learning outcomes compared to traditional methods. By using a quasi-experimental approach, the study aimed to provide insights into the efficacy of innovative teaching technologies in educational contexts.
2.3.2. Questionnaire Survey
The questionnaire survey was only administered to the 38 participants in the experimental group, including 30 students and 8 teachers, as it was specifically designed to assess their experiences with the AR teaching system. The study limited the scope of the survey to the experimental group, aiming to focus on evaluating the actual application and user satisfaction of the AR teaching system. Since the control group did not interact with the AR system, they were not required to complete the questionnaire. Their role in the study was primarily to provide baseline data and serve as a comparative group for evaluating the learning outcomes of the experimental group.
A uniform satisfaction survey questionnaire was administered to both students and teachers to ensure consistency in the data collection process. This approach minimized data bias and facilitated the comparison of responses from different participant groups. Using the same set of questions allowed for an aligned analysis of the participants’ perspectives on the teaching materials and system, ensuring that both student and teacher feedback could be used to guide improvements in the system.
2.4. Experimental Procedure
Figure 3 illustrates the experimental procedure used in this study. Students were divided into two groups: an experimental group using the AR pet care teaching system and a control group relying on traditional teaching materials. The experiment lasted for 40 min and was conducted in three phases:
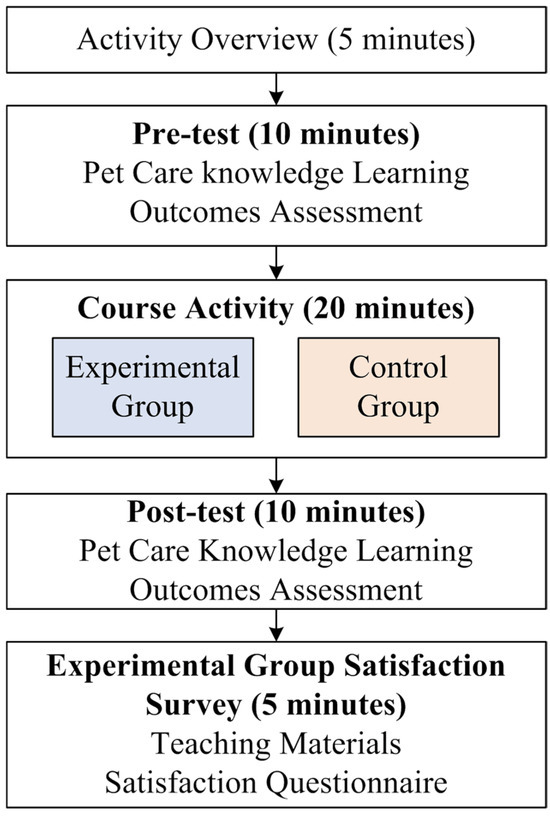
Figure 3.
Experimental procedure diagram.
- (1)
- Pre-test (10 min): A pre-test was administered to all participants to assess their baseline knowledge of pet care. This test served to measure the effectiveness of the AR system and traditional methods in improving pet knowledge.
- (2)
- Course activity (20 min): The experimental group engaged with the AR pet care teaching system, which allowed them to interact with virtual pets through various features. Participants were guided through pet care tasks, including feeding, playing, and identifying signs of illness in the virtual pets. Step-by-step instructions were provided to ensure they explored key functions of the AR system, such as scanning real-world objects to trigger pet-related scenarios and receiving real-time feedback on their actions. The control group used conventional paper-based materials to teach the same pet care topics, including text descriptions and graphic illustrations to reinforce students’ understanding.
- (3)
- Post-test (10 min): a post-test was conducted to evaluate the knowledge gained from the lesson activity in both groups, comparing the learning outcomes between the AR system and traditional teaching methods.
Additionally, students in the experimental group completed a satisfaction questionnaire following the post-test, evaluating their experience with the AR system. Teachers who used the AR teaching system on smartphones were also asked to fill out the satisfaction questionnaire and provide verbal feedback, offering insights into their acceptance and perceptions of the system. This comprehensive feedback from both students and teachers was used to refine the AR teaching materials and system.
2.5. Research Tools
The study used two primary research tools: the pet knowledge learning effectiveness test and the teaching material satisfaction questionnaire. Each tool is described in detail below.
2.5.1. Pet Knowledge Learning Effectiveness Test
The pet knowledge learning effectiveness test was developed with expert validation, with content reviewed and revised by specialists in the field. The test was administered without answers both prior to and following the instructional sessions, with questions rearranged between the pre-test and post-test phases. The pre-test assessed students’ prior knowledge, while the post-test evaluated the knowledge gained from the instructional materials.
2.5.2. Teaching Material Satisfaction Questionnaire
The teaching material satisfaction questionnaire, adapted from the “e-Learning Quality Satisfaction Standards” in the literature [19], served as the satisfaction measure for this experiment. It included aspects related to teaching material content, learning guidance, material design, and instructional media. The questionnaire employed a five-point Likert scale, where 5 represented “strongly agree”, 4 represented “agree”, 3 represented “somewhat agree”, 2 represented “disagree”, and 1 represented “strongly disagree”. Higher scores reflected greater satisfaction levels among respondents.
2.6. Data Analysis Methods
The data collected in this study were analyzed using SPSS 22 statistical software. The analysis focused on evaluating learning outcomes of the pet knowledge course and responses from the teaching material satisfaction questionnaire. Details of the data analysis methods are as follows.
2.6.1. Analysis of Learning Outcomes in the Pet Knowledge Course
The analysis of learning outcomes was conducted using ANCOVA, with different teaching materials as the independent variable, post-test learning outcome scores as the dependent variable, and pre-test scores as the covariate. Before applying ANCOVA, the assumption of homogeneity of regression slopes was assessed to confirm that regression coefficients were consistent across groups. This involved regression analysis to test for interaction between the covariate and the dependent variable within each group. If the assumption of homogeneity was satisfied, ANCOVA was applied at a significance level of 0.05. If violated, alternative methods of analysis were considered.
2.6.2. Analysis of the Teaching Material Satisfaction Survey
A satisfaction survey was conducted on students and teachers in the experimental group using the pet care teaching system. Descriptive statistical analysis was used to evaluate satisfaction levels with the course activities, providing insights into participants’ engagement and perception of the instructional materials.
Table 2 presents the reliability analysis of the satisfaction survey data collected from the experimental group, comprising 30 students. The overall reliability of this study was 0.863. The Cronbach’s α values for the four dimensions—teaching material content, learning guidance, teaching material design, and instructional media—were 0.883, 0.893, 0.871, and 0.843, respectively, indicating a moderate to high level of reliability.

Table 2.
Reliability analysis of the student teaching material satisfaction survey.
Table 3 presents the reliability analysis of the satisfaction survey data collected from the teacher group, with an overall reliability of 0.884. The Cronbach’s α values for teaching material content, learning guidance, teaching material design, and instructional media dimensions were 0.900, 0.783, 0.869, and 0.811, respectively, also indicating a moderate to high level of reliability.

Table 3.
Reliability analysis of the teacher teaching material satisfaction survey.
3. The Proposed System
This section outlines the teaching framework of the AR pet care teaching system, detailing its functionalities and the main learning objectives for each topic.
3.1. Concept of the AR-Based Pet Care Teaching System
The proposed AR-based pet care teaching system aims to provide students with an enriched learning experience that is different from the traditional teaching method. Figure 4 illustrates the differences between the two approaches. In Figure 4a, the traditional teaching method relies primarily on a classroom teacher and text-based or pictorial materials, which may constrain students’ comprehension of the content. Conversely, Figure 4b illustrates the AR-based teaching system, where students can choose a learning category through an interactive application and immerse themselves in an AR environment tailored to the lesson. Within this AR environment, students can engage with virtual objects and complete tasks linked to specific learning topics, thereby fostering a more dynamic and hands-on learning experience.
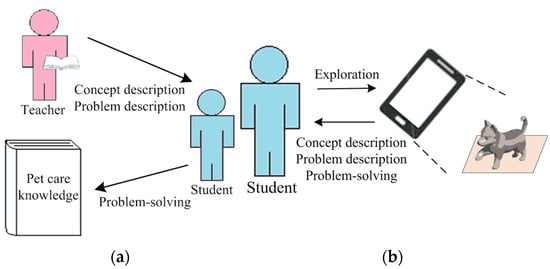
Figure 4.
Two teaching methods applied in the study: (a) a traditional teaching approach using text-based materials; and (b) an AR-based teaching method that integrates virtual objects for an interactive learning experience.
3.2. Design of the Pet Care Teaching System
3.2.1. Terminology Explanation
Pet Status Indicators
The pet status indicators are presented as visual metrics, allowing learners to easily observe changes in the pet’s condition during the simulated care process. These indicators include satiety, thirst, excretion, and mood. To address the needs reflected by these indicators, learners must interact with the pet using items from the virtual object library. Table 4 outlines the relationships between these interactions and the corresponding pet status indicators.

Table 4.
Relationship between course topics and status indicators.
Virtual Object Library
Aligned with the course objectives, the study developed various virtual objects, categorized into pet-related objects, food-related objects, and play-related objects. Interaction within the system is triggered when the pet objects collide with food or play objects, thus reinforcing the course content through active participation. The comprehensive list of virtual objects is provided in Table 5.

Table 5.
Comprehensive list of virtual objects.
Pet Status and Behavior
Figure 5 shows the design of pet behaviors corresponding to various scenarios and course content to reflect how virtual pets interact with learners. Autonomous behaviors refer to spontaneous actions performed by the pet in the environment that are influenced by their mood levels. These dynamic behaviors provide learners with a more realistic experience of the pet’s characteristics and needs, fostering a deeper comprehension of effective pet care. The pet’s status is continuously updated based on the status indicator values, representing the pet’s current state.
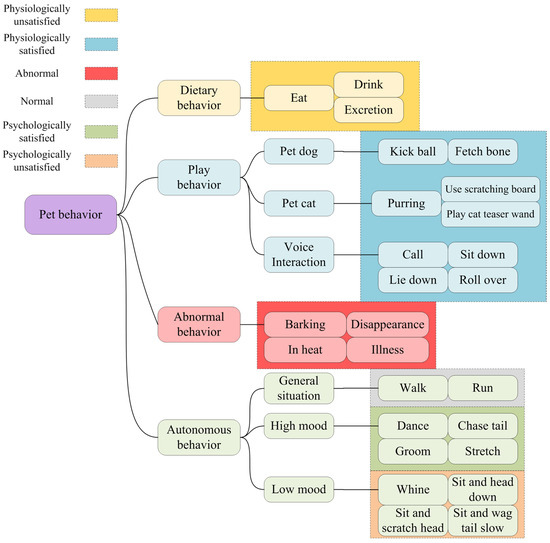
Figure 5.
Hierarchy diagram of pet behaviors.
3.2.2. Learning Points
The learning topics are structured progressively, beginning with the diet theme, followed by the play theme, and concluding with the healthcare theme, with each module increasing in complexity. Initially, learners start with basic feeding tasks, such as selecting appropriate food types for different pets. The play module introduces more interactive engagement, requiring learners to choose suitable toys and understand pet behavior cues. The final healthcare module presents the most complex tasks, where learners must identify signs of illness and administer basic care. Table 6 provides an overview of the key learning points for each theme. Learners are required to follow the instructional guidance to complete the course activities, with the correct execution of tasks confirmed through the behavior of the virtual pets. Errors are signaled through auditory feedback or behavioral cues from the pet, ensuring learners receive real-time corrective guidance before progressing to more advanced tasks.

Table 6.
Learning points for each theme.
3.2.3. Pet Care Teaching System
The pet care teaching system developed in this study is a mobile application for the Android platform, designed to facilitate autonomous learning of pet care knowledge and enable interactive, visualized operations in an AR environment. Figure 6 illustrates the system architecture, which comprises two primary components: the Android application (APP) and the AR module. Note that the proposed AR module is developed using Unity AR Foundation, which provides a robust and flexible AR framework by integrating ARCore and ARKit for cross-platform AR functionality.
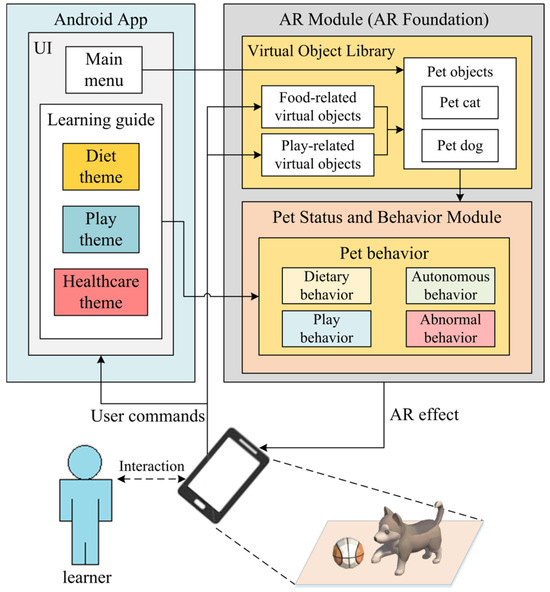
Figure 6.
Architecture of the proposed AR-based pet care teaching system.
The Android App implements a User Interface (UI) that includes both the main menu and a learning guide. Through the main menu, learners can select a desired learning category. Upon selection, corresponding virtual objects are displayed within the scene, allowing learners to engage with the course content. The learning guide offers textual descriptions for each learning theme, providing step-by-step guidance and emphasizing key learning points. Learners have the option to repeat the course content by using the reset button, which restores the virtual objects in the scene to their original positions. Additionally, if a pet becomes unwell due to incorrect actions, learners can utilize the hospital button to treat the pet and proceed with the course.
The AR module consists of a virtual object library and a pet status and behavior module. Its primary purpose is to display the pet’s behavior and autonomous interactions with virtual objects from the library. The virtual object library includes realistic virtual items, such as pets, food, and play-related objects, which learners can use to interact with the pet and complete the corresponding learning tasks. During the learning process, learners can use food-related virtual items to feed the pet, observe its eating behavior and gain fundamental knowledge about pet nutrition. They can also use play-related objects to engage with the pet, observe its play behavior and acquire basic knowledge about pet activities. The hospital button enables learners to treat the pet and observe any abnormal behaviors, providing essential insights into pet healthcare. To enhance the learning experience, the pet status and behavior module updates the virtual pet’s status, which directly affects its behavior. The next section provides a detailed explanation of how these behaviors are determined by the pet’s status.
3.2.4. Pet Status and Behavior Module
Figure 7 presents the architecture of the pet status and behavior module, which illustrates how learners can increase the pet’s status indicators through appropriate interactions, while incorrect actions or a lack of interaction leads to a decline in these indicators. The values of these status indicators determine the pet’s overall condition and behavior. The observed pet behaviors provide learners with insights into the consequences of their actions, thereby enhancing engagement and motivation through realistic visual effects. This design encourages learners to actively participate and engage in the learning process. By interacting with the virtual pet and observing its behavior throughout the course, learners acquire essential knowledge about pet care.
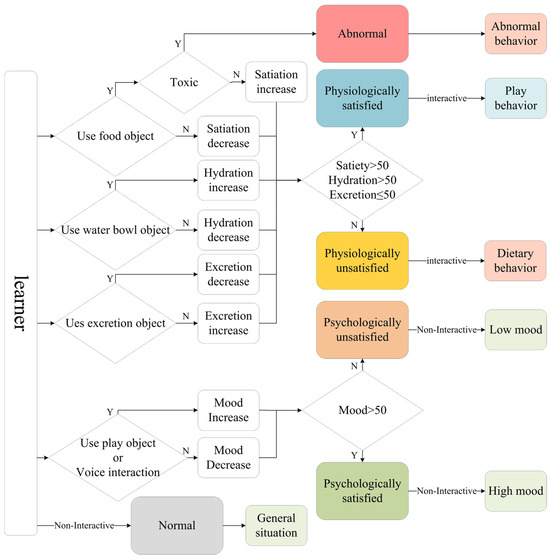
Figure 7.
Architecture of the pet status and behavior module.
Table 7 outlines the design of learner interactions with the pet. When the pet’s physiological needs are met, it enters a “physiologically satisfied” state; otherwise, it enters a “physiologically unsatisfied” state. In the unsatisfied state, the pet will only respond to food-related virtual objects. When in the satisfied state, learners can use play-related objects or the voice command function to interact with the pet. Note that the voice recognition feature is developed using the Android SpeechRecognizer API, enabling the system to recognize specific spoken commands such as “sit”, “lie down”, and “roll over”. The system processes these commands in real time based on the device’s default language settings. If a command is unclear or incorrect, the system provides feedback, prompting the user to repeat or adjust their input. This integration enhances the interactive experience by allowing natural voice-based engagement with the virtual pet.

Table 7.
Design of learner interactions and operations.
When utilizing play objects or engaging in voice interactions, the pet’s mood value increases, resulting in corresponding playful behaviors; conversely, a lack of interaction leads to a decrease in mood value. Under normal conditions, pets may walk or run within the scene. When the psychological needs of the pet are met, the pet enters a state of psychological satisfaction; if unmet, the pet transitions into a state of psychological dissatisfaction. In situations where the pet’s psychological needs are unmet and the learner does not interact with the pet, the pet will exhibit self-initiated behaviors indicative of low mood. Conversely, when the pet’s psychological needs are satisfied, it will demonstrate self-initiated behaviors indicative of a cheerful mood.
This system employs gamified teaching methods to stimulate learners’ motivation, allowing them to acquire knowledge and skills through the care of virtual pets. Learners must complete the content of various teaching units to care for the pets, with each unit designed to cover different learning objectives, enabling learners to naturally grasp knowledge through interaction. Additionally, the system provides immediate feedback based on learner performance, facilitating self-adjustment and continuous improvement. The use of gamified teaching not only enhances learner engagement but also strengthens their problem-solving abilities.
4. Experimental Results
This section presents the statistical analyses of the data collected from the experiments, focusing on participants’ learning outcomes and motivation. The results are provided as the foundation for the discussion in the next section, where we address each of the research questions (RQ1–RQ3) in detail. By first outlining the statistical findings here, we aim to support a clearer interpretation and discussion of how these results relate to the study’s research objectives.
4.1. Experimental Platform
The experiments were conducted using mid- to high-performance Android smartphones. The hardware specifications of the smartphones are presented in Table 8. Note that the proposed system was designed to perform optimally on hardware platforms that are equivalent to or more powerful than the Google Pixel 4.

Table 8.
Specifications of the experimental hardware platform.
4.2. Analysis of Covariance
This section explores the impact of the pet care teaching system applied to pet knowledge courses on university students’ learning outcomes. Students completed a pre-test on pet knowledge effectiveness before the course activities and a post-test after the activities to examine the influence of different instructional materials on learning outcomes.
Before conducting the ANCOVA, a homogeneity of regression coefficients test was performed to ensure that the regression models across different groups had similar regression coefficient structures. If the assumption of homogeneity of regression coefficients within groups is met, ANCOVA can be conducted. If not, alternative methods must be adopted. The results of the regression coefficient homogeneity test for this study are presented in Table 9.

Table 9.
Homogeneity of the regression slope test.
The analysis results indicate that the homogeneity test for learning effectiveness assessments under different instructional materials yielded an F-value of 1.668 and a p-value of 0.202, which is greater than 0.05. This confirms compliance with the assumptions necessary for ANCOVA, allowing for further analysis.
Descriptive statistics for pre- and post-test learning outcomes under different instructional materials are shown in Table 10. The control group had a pre-test mean score of 80.000 (SD = 8.066) and a post-test mean score of 85.420 (SD = 5.982), while the experimental group had a pre-test mean score of 78.970 (SD = 7.657) and a post-test mean score of 89.810 (SD = 5.735). For both groups, we calculated Cohen’s d for paired samples, which measures the effect size of the improvement within each group. The effect size for pre-to-post improvement was 1.60 (large) for the experimental group and 0.76 (moderate-large) for the control group, indicating that students using the AR-based system experienced significantly greater learning gains. These effect size values confirm that the AR intervention had a notable impact on learning outcomes.

Table 10.
Descriptive statistics.
After confirming the homogeneity of regression coefficients within groups, ANCOVA was conducted. The results of the ANCOVA are presented in Table 11, where the F-value is 9.013 and the p-value is 0.004, indicating a significant difference between the groups. The experimental group outperformed the control group in post-test scores, suggesting that different instructional materials result in significant differences in students’ post-test learning outcomes.

Table 11.
Analysis of covariance.
To control for baseline differences and improve the accuracy of the results, as shown in Table 12, the control group’s mean score was 85.474, while the experimental group’s mean score was 89.943. The standard deviations were 1.043 for the control group and 1.060 for the experimental group, indicating lower variability in sample means and greater stability of the results. The 95% confidence interval for the control group ranged from 83.386 to 87.562, while the experimental group’s 95% confidence interval ranged from 87.820 to 92.066. The narrower confidence interval and the lack of overlap between the two groups’ confidence intervals suggested that the differences between the groups were significant, indicating a substantial impact of the experiment on the results and more accurate mean estimations. After accounting for the influence of pre-test scores, the adjusted post-test mean score for the experimental group was higher than that of the control group, demonstrating that the experimental group provided greater assistance to students in learning outcomes.

Table 12.
Estimated marginal means.
4.3. Analysis of the Student Satisfaction Survey for Teaching Materials
The student satisfaction survey for teaching materials in this study was conducted after the instructional activities. The survey utilized a modified version of the “e-Learning Quality Satisfaction Standards” proposed in the literature [19] as the satisfaction scale for this experiment. The dimensions included teaching material content, learning guidance, teaching material design, and instructional media. The survey was designed using a five-point Likert scale, where a score of 5 indicates “strongly agree”, 4 indicates “agree”, 3 indicates “neutral”, 2 indicates “disagree”, and 1 indicates “strongly disagree”. Higher scores reflect greater satisfaction, while lower scores indicate less satisfaction.
Table 13 presents the results of the satisfaction survey regarding the AR teaching materials. The analysis indicates that the average satisfaction score for the content of the teaching materials within the pet care instructional system was 4.350, demonstrating that learners were highly satisfied with the information, narratives, and examples provided in the teaching materials. The average satisfaction score for learning guidance was 4.450, indicating that the learning guidance effectively facilitated learning and concentration. The average satisfaction score for material design was 4.700, suggesting that the AR instructional method was perceived as engaging and dynamic, thereby enhancing interactive learning. The average satisfaction score for teaching media was 4.607, reflecting a positive user experience regarding the convenience of operation and clarity of the steps involved in using the AR teaching materials. The overall satisfaction average score was 4.523, indicating that learners highly rated the AR teaching materials for enhancing their learning motivation and effectiveness. All satisfaction indicators maintained a standard deviation within 10% of the mean, signifying a high consistency in the data and stable results.

Table 13.
Student satisfaction survey for teaching materials.
4.4. Analysis of the Teacher Satisfaction Survey for Teaching Materials
The teacher satisfaction survey regarding the AR teaching materials is presented in Table 14. In terms of mean scores, the average score for material design was 4.720, indicating that teachers highly evaluated the teaching materials designed with AR technology, perceiving their interactivity and vividness as effectively enhancing the student learning experience. The average score for teaching media was 4.640, suggesting that teachers generally found the AR teaching materials to be user-friendly and supportive of instructional activities. The average score for learning guidance was 4.533, reflecting a high level of recognition from teachers regarding its organization and instructiveness, which aids students in focusing on learning objectives. However, the average score for content of the teaching materials was 4.333. Although this score remained within a high range, it was relatively lower, possibly indicating that there is room for improvement in terms of the amount of information presented or the clarity of the narratives.

Table 14.
Teacher satisfaction survey for teaching materials.
Regarding standard deviations, the standard deviation for teaching media was 0.260, demonstrating a consistent view among teachers regarding the operational convenience and user experience of the AR teaching materials, with the majority highly affirming their accessibility. The standard deviation for material design was 0.340, indicating that the evaluation of the AR teaching materials was relatively stable, with most teachers satisfied with their design and interactivity. The standard deviation for content of the teaching materials was 0.417, reflecting a general consensus among teachers regarding the satisfaction with the presentation of information, narrative style, and examples. Conversely, the standard deviation for learning guidance was 0.533, suggesting considerable variation in teacher satisfaction levels, which may reflect differing degrees of acceptance regarding the instructional methods among different teachers.
Remark: Although the satisfaction scores were high and the standard deviations were low, we recognize that a novelty effect could have influenced participants’ initial enthusiasm for the AR system. To reduce this, the survey was given after participants used the system for a sufficient amount of time. We also ensured that the survey was anonymous to encourage honest feedback, though response bias may still be a possibility. Furthermore, the small sample size may have led to biased results in the statistical analysis, limiting the generalizability of the findings. These factors should be considered as potential limitations of this study when interpreting the satisfaction results and overall study outcomes.
5. Discussion
Based on the experimental results and questionnaire analysis, the proposed AR teaching system has a positive impact on students’ learning outcomes and motivation. In terms of learning outcomes, while the test scores of the AR-based learning group showed a greater improvement than those of the traditional learning group, all students demonstrated significant progress in pet knowledge acquisition, independent of the teaching method used. Regarding learning motivation, the AR teaching approach was found to facilitate greater focus and interest among students. The results from the material satisfaction survey indicated that both students and teachers expressed a high level of satisfaction.
5.1. Response to RQ1
This study developed a pet care teaching system based on AR technology and gamification design. The implementation and evaluation results demonstrated that the AR-based teaching system significantly enhanced students’ learning outcomes in pet knowledge courses. The material satisfaction survey revealed that, compared to traditional teaching methods, students exhibited improved focus and interest. Therefore, the AR-based teaching system has a significantly positive effect on students’ learning outcomes.
However, this study primarily involved students with backgrounds in electrical engineering and assistant teachers, who generally have a higher acceptance of new technologies. This may have positively influenced the results. Future research should expand to include audiences from diverse disciplinary backgrounds to validate the effectiveness and acceptance of the AR-based teaching system across a broader population.
5.2. Response to RQ2
Several previous studies have developed instructional tools for animal-related education. For example, Sautière et al. [20] designed and implemented e-learning tools to enhance undergraduate students’ understanding of animal biology. Their approach focused on delivering educational content through multimedia tools, offering structured materials that support independent learning. Building on this foundation, our AR-based teaching system goes further by providing an immersive and interactive learning experience. Unlike traditional multimedia tools, our system allows students to actively engage with virtual pets by performing tasks such as feeding, playing, and managing their health. This hands-on, experiential approach promotes active learning and helps students apply their knowledge in realistic, practical scenarios.
Moreover, recent research highlights the advantages of AR in various educational fields. In science education, AR helps visualize complex biological processes; in medical training, it provides realistic patient simulations; and in language learning, it creates interactive conversation scenarios. Building on these advancements, our system incorporates real-time feedback and voice interaction to deliver an engaging and effective learning experience in pet care education. Compared with traditional pet-related teaching tools, our AR system offers a more dynamic, interactive platform that aligns with modern trends in AR-enhanced learning.
To increase students’ motivation, we integrated two interactive methods into our instructional design: virtual object interaction and voice commands. By combining AR technology with gamification, students can place virtual pets in real-world settings, observe their behaviors and respond to situational cues. This creates a realistic experience that encourages students to focus on the learning content.
In terms of interaction, students can drag virtual objects to feed or play with their pets. The virtual pets react immediately to these actions, helping students understand the pets’ needs through direct cause-and-effect learning. Additionally, the system supports voice commands, such as calling the pet’s name or instructing it to “sit”, allowing students to simulate real-life pet training. These features address the limitations of traditional 2D learning tools, which often rely on static images and basic click interactions. By integrating learning activities into the student’s environment and supporting two-way interaction with virtual pets, AR technology enables students to actively “do” rather than passively “observe”. This fosters deeper engagement and promotes experiential learning.
In summary, the AR-based instructional design not only increases students’ interest and attention during the learning process but also significantly improves their understanding and application of pet care knowledge.
5.3. Response to RQ3
The feedback from the teaching assistants and elementary school teachers involved in this study highlights several advantages of using AR instructional materials to enhance the learning process. Teachers observed that the AR-based teaching system made lessons more vivid, interactive, and engaging compared to traditional methods. Students showed higher levels of enthusiasm, participation, and immersion, which suggests that AR technology can effectively increase motivation and interest in learning activities. In addition, the portability and flexibility of the AR materials allow for educational activities to be conducted in different settings, reducing the dependence on fixed classroom resources.
However, some challenges were identified that need to be addressed to improve the system’s practicality and adaptability. For example, AR functionality can be affected by environmental conditions such as poor lighting or difficulties in detecting flat surfaces, which may limit its effectiveness in certain classroom settings. Future improvements in technology and system design should aim to overcome these limitations to ensure smoother integration into various learning environments. Moreover, although this study focused on college students, some elementary school teachers suggested that the current difficulty level and interaction design may not be fully suitable for younger learners. To make the system more age-appropriate, future adaptations could include simplifying the interface, reducing task complexity, and offering guided instructions tailored to different developmental stages. For younger students, intuitive controls and additional visual or audio prompts may help enhance usability and understanding.
In terms of practical classroom integration, teachers emphasized the importance of providing clear implementation guidelines. For instance, they recommended offering short training sessions for instructors (around 2–3 h) to familiarize them with the app’s functions and prepare them to assist students during activities. Additionally, classrooms would need to be equipped with compatible devices, such as tablets or smartphones that meet the system’s hardware requirements, to ensure optimal performance.
In summary, while the initial responses to the AR teaching system were positive, adjustments are necessary to make it more suitable for younger students and to facilitate its seamless use in daily classroom routines.
6. Conclusions and Future Work
In this study, we developed an AR-based teaching system focused on pet care, providing students with instructional materials to understand the essential aspects and potential costs of pet ownership. To enhance students’ learning outcomes and motivation, the proposed system incorporates three AR technology-based modules: the application module, the AR Foundation module, and the AR environment module. The application module involves the development of the user interface and the management of virtual objects. The AR Foundation module utilizes features such as plane detection, voice recognition, and image recognition to enrich the interactive learning experience. The AR environment module combines the application interface with thematic and spatial settings generated by AR Foundation, enabling learners to engage with virtual pet objects and view outcomes within the spatial environment of their mobile devices, thus making learning about pet care more engaging and practical.
The AR-based pet care teaching system proposed in this study has demonstrated a significant positive impact on enhancing students’ learning outcomes and motivation. Teachers have generally expressed high levels of satisfaction with the system, highlighting its ability to facilitate teaching in an intuitive manner while promoting engagement and interactivity. However, the system does present some limitations. Some teachers may require additional training to effectively adapt to the new technology, which could increase their workload. Additionally, students might face technical issues or limitations related to their mobile device systems when using AR teaching materials, potentially impacting their learning experiences and outcomes.
In future research, we will focus on enhancing the stability and compatibility of the AR system to ensure smooth operation on both Android and iOS devices. Furthermore, we plan to optimize the pet education content by adding more interactive and challenging tasks through gameplay, while also including topics like pet behavior training, basic emergency care, and responsible pet ownership to give students a more complete understanding of pet care. Since many students are also interested in pets beyond cats and dogs, such as fish and birds, we aim to expand the instructional materials to cover a wider variety of pets. This expansion will help meet different learning needs and keep students motivated. Moreover, as this system is currently a prototype designed for general users, future work may explore ways to improve accessibility, such as larger text, voice commands, and screen reader support, to make the system more inclusive. Additionally, we recognize the importance of objective evaluations beyond self-reported outcomes. Future work will include performance-based assessments, such as tasks that test how well students apply pet care skills, and long-term tests to measure knowledge retention. We also aim to involve a larger and more diverse group of participants from different age groups, education levels, and cultural backgrounds to better understand how the system works for different learners. Finally, we plan to explore the impact of different levels of gamification within the AR learning environment to ensure that game mechanics continue to enhance, rather than distract from, the learning experience. These enhancements will help provide a more comprehensive understanding of the AR system’s educational impact.
Author Contributions
: Conceptualization, T.-R.L.; methodology, T.-R.L. and C.-Y.T.; software, T.-R.L.; validation, T.-R.L.; formal analysis, T.-R.L.; investigation, T.-R.L. and C.-Y.T.; resources, C.-Y.T.; experimental data collection, T.-R.L.; writing—original draft preparation, C.-Y.T. and T.-R.L.; writing—review and editing, C.-Y.T.; visualization, T.-R.L.; supervision, C.-Y.T.; project administration, C.-Y.T.; funding acquisition, C.-Y.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Science and Technology Council of Taiwan under Grant NSTC 112-2221-E-032-036-MY2.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Chien, Y.-J. How Does the Dog Market Shape Roles and Values of Dogs?—A Case Study of the Commodification of Dogs in Taiwan after the 1950s. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the International Society for Anthrozoology, Tokyo, Japan, 4 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, Y.-C.; Chen, K.-C.; Chen, I.-F.; Liu, L.-H. A Study of the Key Sustainable Factors of Taiwan’s Community Care Centers. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, F. Human-Animal Bonds I: The Relational Significance of Companion Animals. Fam. Process 2009, 48, 462–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, C.L.; Thibault, M.; Hong, J. Characterizing Pet Acquisition and Retention during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 781403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotterell, J.L.; Rand, J.; Barnes, T.S.; Scotney, R. Impact of a Local Government Funded Free Cat Sterilization Program for Owned and Semi-Owned Cats. Animals 2024, 14, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, G.A.; Reeve, C.; Torjussen, A. Companion Animal Adoption and Relinquishment during the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Experiences of Animal Rescue Staff and Volunteers. Anim. Welf. 2024, 33, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Buff, P.R.; Carter, R.A.; Bauer, J.E.; Kersey, J.H. Natural Pet Food: A Review of Natural Diets and Their Impact on Canine and Feline Physiology. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 3781–3791. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yavor, K.M.; Lehmann, A.; Finkbeiner, M. Environmental Impacts of a Pet Dog: An LCA Case Study. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, Y. Who Is Liable if an Off-Leash Dog Causes an Accident? Weinberg Law Offices, 2023. Available online: https://www.weinberglawoffices.com/who-is-liable-if-off-leash-dog-causes-accident/ (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Shea, J. The Dangers of Unleashed Dogs. Shea Law Group, 2012. Available online: https://www.shealawgroup.com/the-dangers-of-unleashed-dogs/ (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Bellack, J.; Addressing Pet Nuisance Complaints in Rental Housing. Rent. Hous. J. 2025. Available online: https://rentalhousingjournal.com/addressing-pet-nuisance-complaints-in-rental-housing/ (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Yan, T.-Y.; Teng, K.T.-Y. Trends in Animal Shelter Management, Adoption, and Animal Death in Taiwan from 2012 to 2020. Animals 2023, 13, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-H. The Relationships between Learning Motivation, Learning Strategy, and Learning Performance of e-learning. J. Manag. Oper. 2017, 14, 68–86. [Google Scholar]
- Jhang, F.-M.; He, G.-H.; Wu, W.-L.; Li, J.-H.; Lin, H.-Y.; Xu, S.-Y. The Next Step for Paper Textbooks? Researching and Developing Digital Textbooks for Primary and Middle School Students. J. Textb. Res. 2023, 16, 151–182. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, C.-Y.; Ho, Y.-C.; Nisar, H. Design and Validation of a Virtual Chemical Laboratory—An Example of Natural Science in Elementary Education. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-Y.; Lai, Y.-C. Design and Validation of an Augmented Reality Teaching System for Primary Logic Programming Education. Sensors 2022, 22, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zendehdel, N.; Leu, M.C.; Yin, Z. A Gaze-Driven Manufacturing Assembly Assistant System with Integrated Step Recognition, Repetition Analysis, and Real-Time Feedback. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 144, 110076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, M.D. Murder on Grimm Isle: The Impact of Game Narrative Design in an Educational Game-Based Learning Environment. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2011, 42, 456–469. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.-E. National Digital Learning Technology Project and Integration Research on Cross-Disciplinary e-Learning. J. Educ. Res. 2004, 125, 126–132. [Google Scholar]
- Sautière, P.-E.; Blervacq, A.-S.; Vizioli, J. Production and Uses of e-Learning Tools for Animal Biology Education at University. Eur. Zool. J. 2019, 86, 63–78. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).