Non-Singular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control of 6-PUS Parallel Systems Based on Adaptive Disturbance Estimation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The dynamical equation of the mechanism is derived in detail using the principle of virtual work. The parallel mechanism has a complex structure, and its dynamics derivation is simple and easy to understand compared with the traditional Newton–Euler method and Lagrange method.
- An improved NFTSM controller is designed, which can effectively cope with the effects of modeling errors and unknown external perturbations. The experimental results show that the error converges to 0 within 0.5 s, realizing high-precision trajectory tracking, and the controller stabilizes the output driving force, which will help to enhance the training effect.
2. Problems
3. Mechanical Dynamics Analysis
3.1. Speed Analysis
3.2. Acceleration Analysis
3.3. Establishment of the Jacobi Matrix
3.4. Establishment of Dynamics Equations
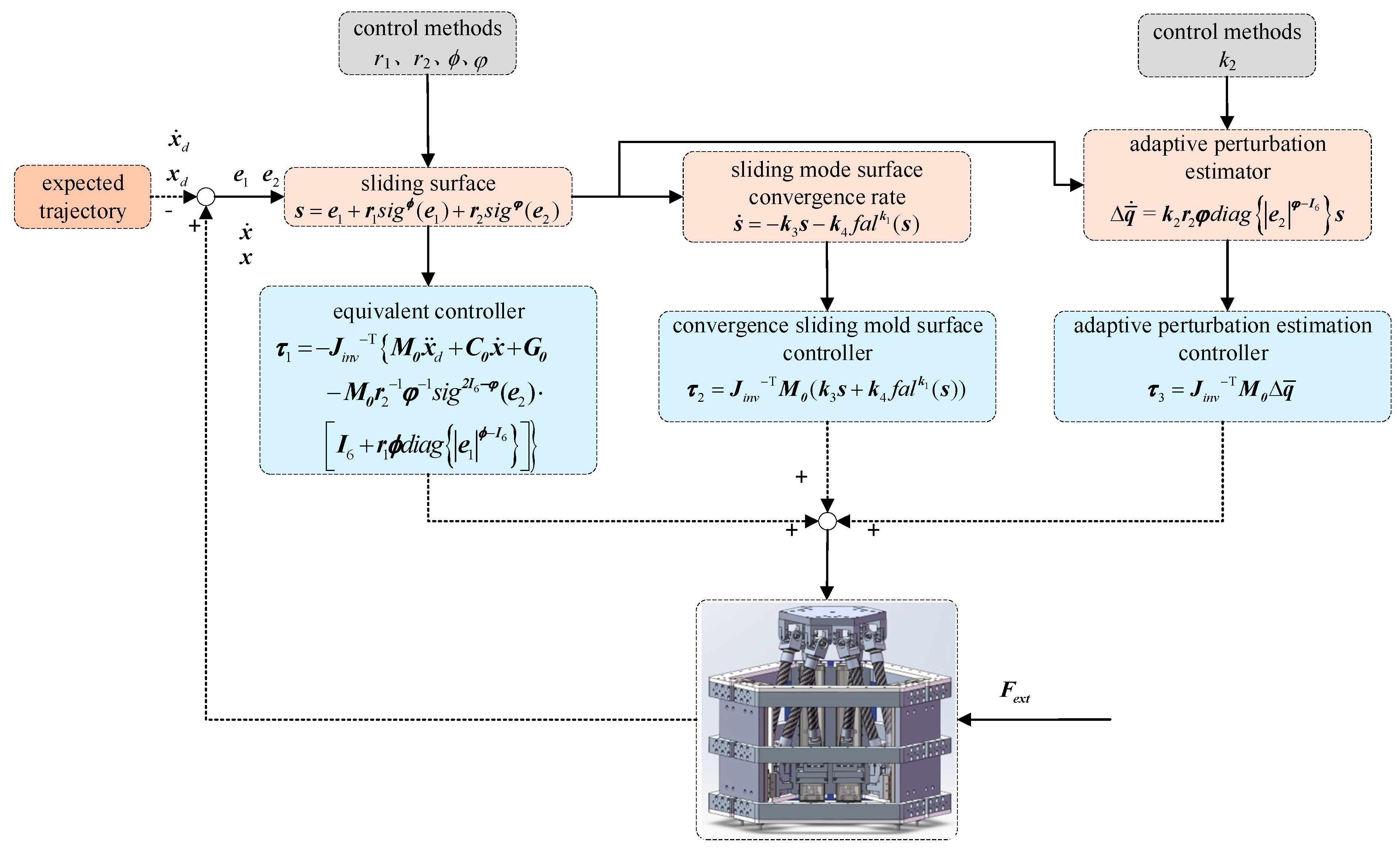
4. Research on Non-Singular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control Strategy Based on Adaptive Disturbance Estimation
4.1. Controller Design
4.2. Proof of Stability of the Controller
5. Experiments
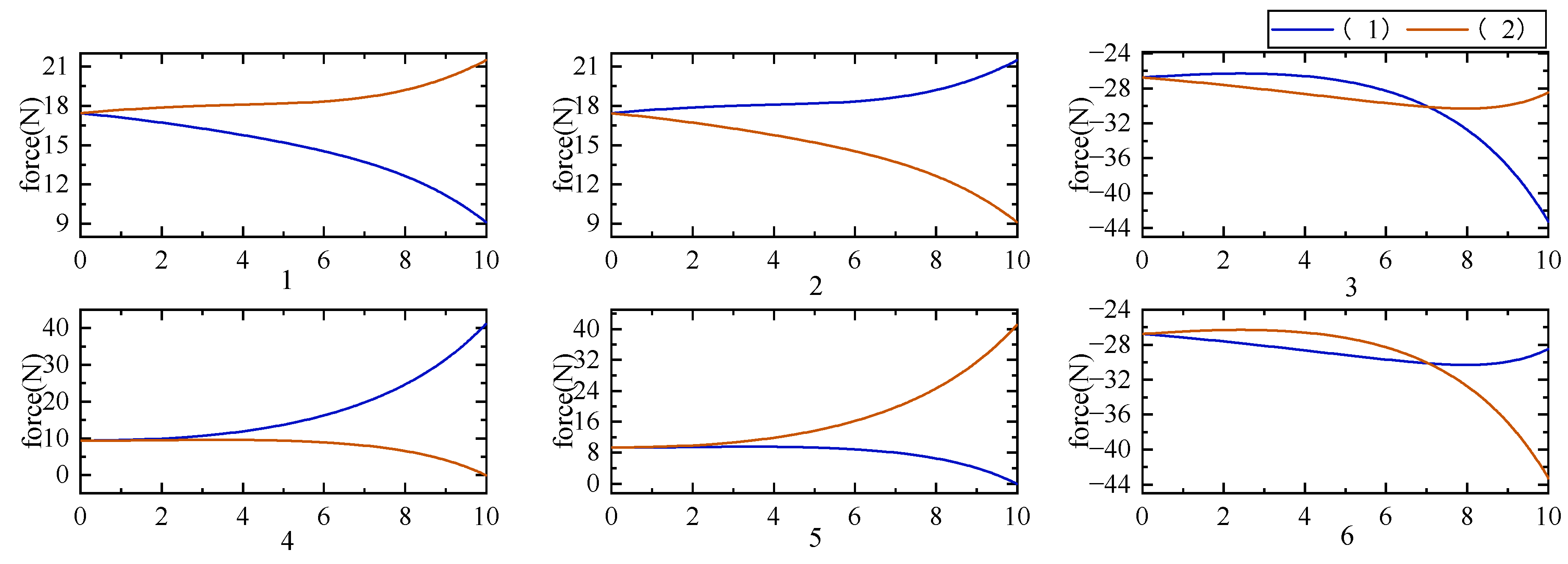
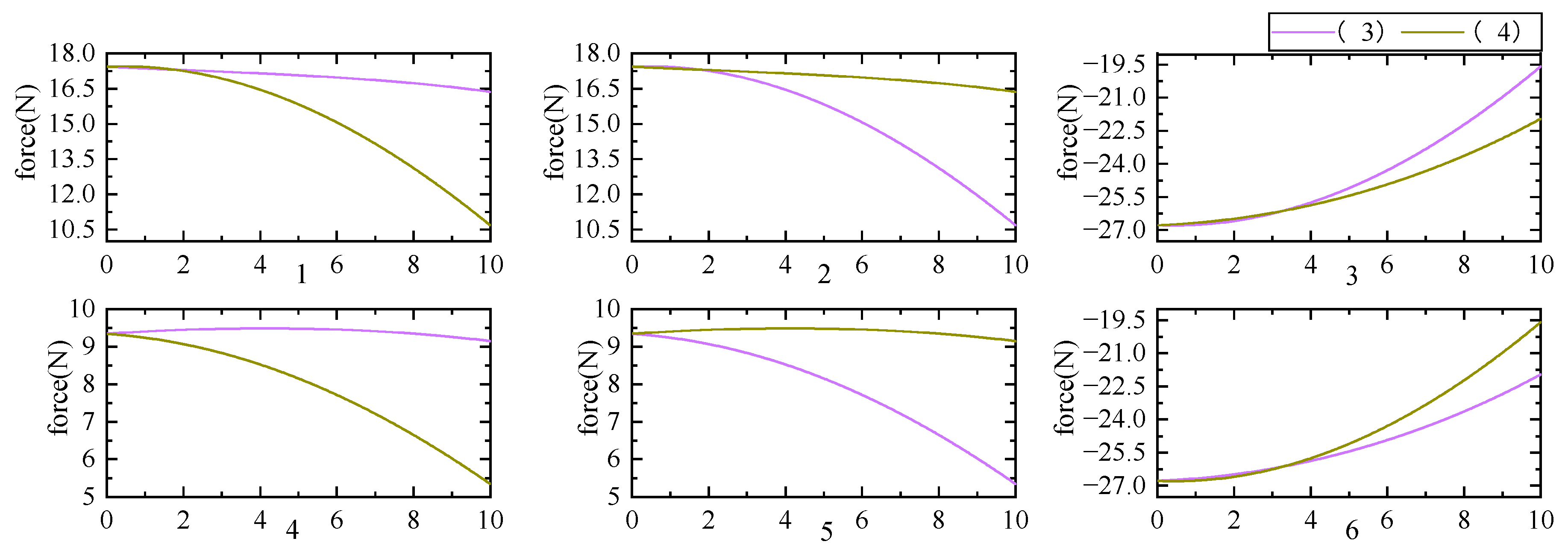
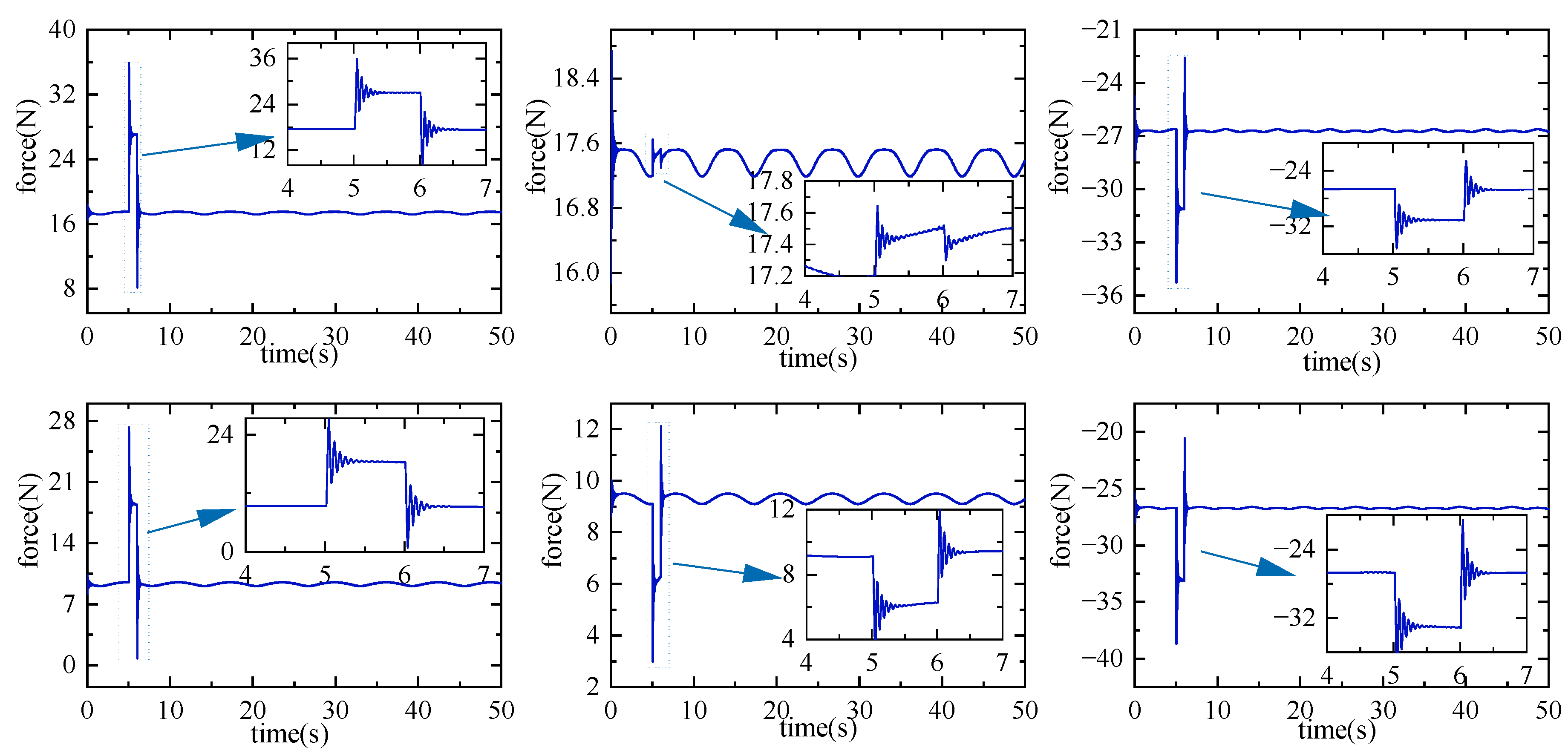
5.1. Dynamics Numerical Simulation Experiment
5.2. Controller Simulation Experiment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SMC | sliding mode control |
| TSMC | terminal sliding mode control |
| FTSM | fast terminal sliding mode control |
| NFTSM | non-singular fast terminal sliding mode control |
| ESO | extended state observer |
| ADE-NFTSM | non-singular fast terminal sliding mode control based on adaptive disturbance estimation |
References
- Patel, P.; Baier, J.; Baranov, E.; Khurana, E.; Gambrah-Sampaney, C.; Johnson, A.; Monokwane, B.; Bearden, D.R. Health beliefs regarding pediatric cerebral palsy among caregivers in Botswana: A qualitative study. Child Care Health Dev. 2017, 43, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanon, M.A.; Pacheco, R.L.; Latorraca, C.d.O.C.; Martimbianco, A.L.C.; Pachito, D.V.; Riera, R. Neurodevelopmental Treatment (Bobath) for Children With Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review. J. Child Neurol. 2019, 34, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakzewski, L.; Ziviani, J.; Boyd, R.N. Delivering Evidence-Based Upper Limb Rehabilitation for Children with Cerebral Palsy: Barriers and Enablers Identified by Three Pediatric Teams. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2013, 34, 368–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiFazio, R.L.; Vessey, J.A.; Miller, P.E.; Snyder, B.D.; Shore, B.J. Health-related quality of life and caregiver burden after hip reconstruction and spinal fusion in children with spastic cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2021, 64, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shea, J.; Nunally, K.D.; Miller, P.E.; Difazio, R.; Matheney, T.H.; Snyder, B.; Shore, B.J. Hip Reconstruction in Nonambulatory Children With Cerebral Palsy: Identifying Risk Factors Associated With Postoperative Complications and Prolonged Length of Stay. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2020, 40, e972–e977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shore, B.J.; Shrader, M.W.; Narayanan, U.; Miller, F.; Graham, H.K.; Mulpuri, K. Hip Surveillance for Children With Cerebral Palsy: A Survey of the POSNA Membership. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2017, 37, e409–e414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, L.-W. Solving the Inverse Dynamics of a Stewart-Gough Manipulator by the Principle of Virtual Work. J. Mech. Des. 2000, 122, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejri, S.; Gagnol, V.; Le, T.-P.; Sabourin, L.; Ray, P.; Paultre, P. Dynamic characterization of machining robot and stability analysis. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 82, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, C.M.; Guida, D. Forward and Inverse Dynamics of a Unicycle-Like Mobile Robot. Machines 2019, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess-Coelho, T.A.; Orsino, R.M.M.; Malvezzi, F. Modular modelling methodology applied to the dynamic analysis of parallel mechanisms. Mech. Mach. Theory 2021, 161, 104332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunquan, L.; Rui, W. Closed-form Dynamic Equations of the 6-RSS Parallel Mechanism through the Newton-Euler Approach. In Proceedings of the 2011 Third International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation, Shangshai, China, 6–7 January 2011; pp. 712–715. [Google Scholar]
- Bascetta, L.; Ferretti, G.; Scaglioni, B. Closed form Newton–Euler dynamic model of flexible manipulators. Robotica 2015, 35, 1006–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staicu, S.; Zhang, D. A novel dynamic modelling approach for parallel mechanisms analysis. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2008, 24, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, B.; Zhao, X. Dynamic Analysis of a New Type of Asymmetrical Parallel Mechanism Based on Lagrange Method. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 428, 012074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatif, H.; Heimann, B. Computational efficient inverse dynamics of 6-DOF fully parallel manipulators by using the Lagrangian formalism. Mech. Mach. Theory 2009, 44, 192–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrammehr, S.; Nahavandi, S.; Abdi, H. Closed-form dynamics of a hexarot parallel manipulator by means of the principle of virtual work. Acta Mech. Sin. 2018, 34, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.Q.; Li, G.Y. NN-PID Adaptive Control for 6_PUS Parallel Mechanism. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 226–228, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Karki, H. Modeling simulation & control of 6-DOF Parallel Manipulator using PID controller and compensator. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2014, 47, 421–428. [Google Scholar]
- Vo, A.T.; Kang, H.-J. A Novel Fault-Tolerant Control Method for Robot Manipulators Based on Non-Singular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control and Disturbance Observer. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 109388–109400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobayen, S.; Tchier, F. A novel robust adaptive second-order sliding mode tracking control technique for uncertain dynamical systems with matched and unmatched disturbances. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2017, 15, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Fadili, Y.; Berrada, Y.; Boumhidi, I. Improved sliding mode control law for wind power systems. Int. J. Dyn. Control 2024, 12, 3354–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zheng, J.; Shao, K.; Zhao, H.; Man, Z.; Sun, Z. Adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control of uncertain nonholonomic wheeled mobile robot with external disturbance and actuator saturation. Inf. Sci. 2024, 663, 120303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, L.; Fang, X. High-Order Fast Nonsingular Terminal Sliding Mode Control of Permanent Magnet Linear Motor Based on Double Disturbance Observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 3696–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.-T. Non-Negative Adaptive Mechanism-Based Sliding Mode Control for Parallel Manipulators with Uncertainties. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2023, 74, 2771–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobayen, S.; Mostafavi, S.; Fekih, A. Non-Singular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control With Disturbance Observer for Underactuated Robotic Manipulators. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 198067–198077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, T. Fault-Tolerant Control of Tidal Stream Turbines: Non-Singular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode and Adaptive Robust Method. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukattaya, M.; Mezghani, N.; Damak, T. Adaptive nonsingular fast terminal sliding-mode control for the tracking problem of uncertain dynamical systems. ISA Trans. 2018, 77, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, A.T.; Kang, H.-J. An Adaptive Neural Non-Singular Fast-Terminal Sliding-Mode Control for Industrial Robotic Manipulators. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, J.; Abbas, M.; Dwivedy, S.K. Design and validation of a pediatric gait assistance exoskeleton system with fast non-singular terminal sliding mode controller. Med. Eng. Phys. 2024, 123, 104080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oghabi, E.; Kardehi Moghaddam, R.; Kobravi, H.R. Adaptive interval type-2 fuzzy neural network nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode control for cable-driven parallel robots. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 136, 108963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Guo, X.; Meng, W.; Ai, Q.; Hu, J. Design and Control of a Reconfigurable Upper Limb Rehabilitation Exoskeleton With Soft Modular Joints. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 166815–166824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Zhai, J. Adaptive second-order fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode control for robotic manipulators. ISA Trans. 2019, 90, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, R.; Chen, L. Dual power non-singular fast terminal sliding mode fault-tolerant vibration-attenuation control of the flexible space robot subjected to actuator faults. Acta Mech. 2023, 235, 1255–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, H.; Jin, D.; Wang, A.; Liu, L. Disturbance observer based non-singular fast terminal sliding mode control of permanent magnet synchronous motors. J. Power Electron. 2023, 24, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yue, X.; Zhang, J.; Shi, K. Active Disturbance Rejection Control for Delayed Electromagnetic Docking of Spacecraft in Elliptical Orbits. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2022, 58, 2257–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hajjami, L.; Mellouli, E.M.; Berrada, M. Robust adaptive non-singular fast terminal sliding-mode lateral control for an uncertain ego vehicle at the lane-change maneuver subjected to abrupt change. Int. J. Dyn. Control 2021, 9, 1765–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Gu, X.; Liu, L.; Guo, Y. Finite time extended state observer based nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode control of flexible-joint manipulators with unknown disturbance. J. Frankl. Inst. 2023, 360, 18–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, B.; Liu, C.; Yue, X. Integrated Predictor-Observer Feedback Control for Vibration Mitigation of Large-Scale Spacecraft with Unbounded Input Time Delay. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.; Guo, X.; Liang, W.; Fang, P. Forward Kinematics Analysis of 6-PUS Parallel Mechanism based on Optimized BP-NR Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Tianjin, China, 4–7 August 2024; pp. 1440–1446. [Google Scholar]
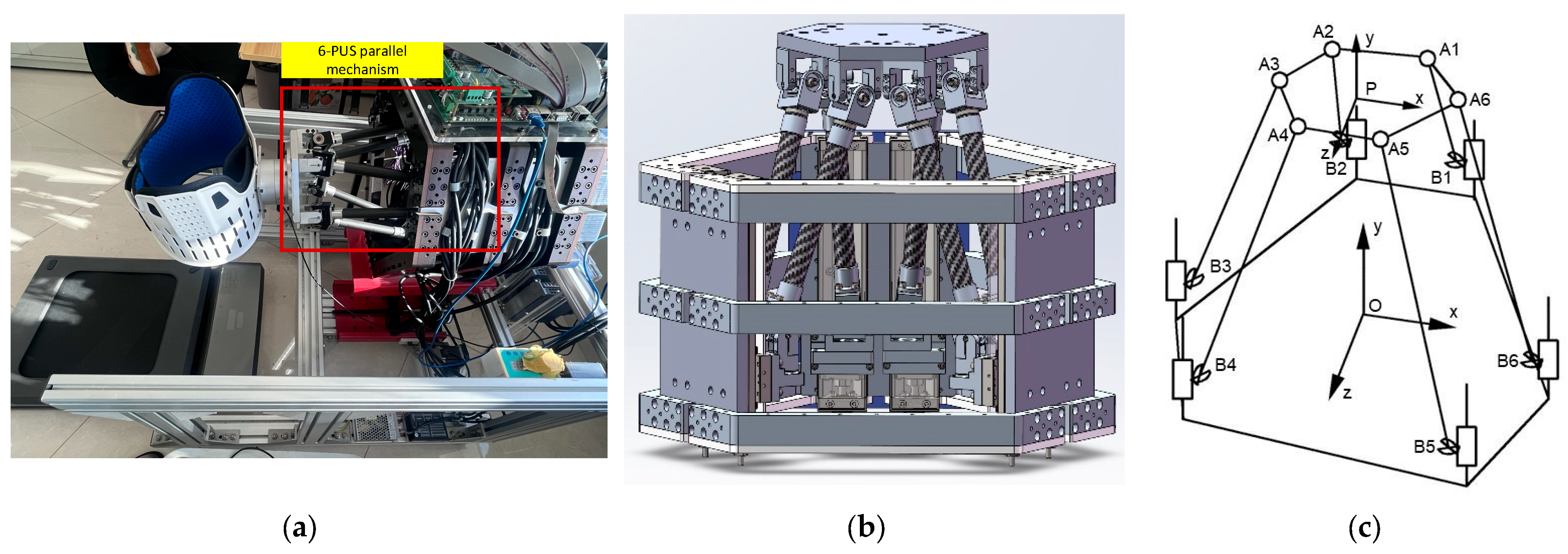
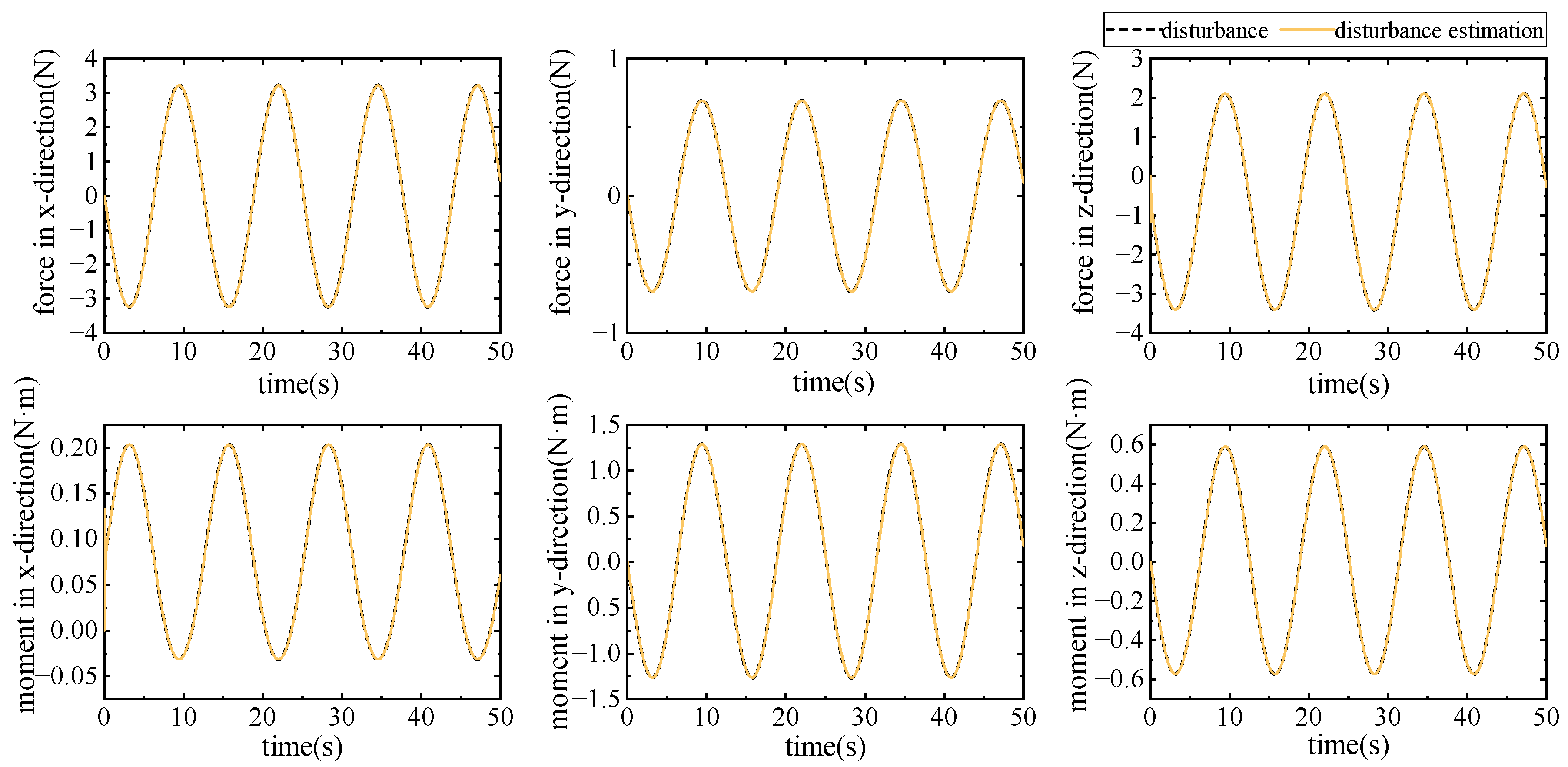
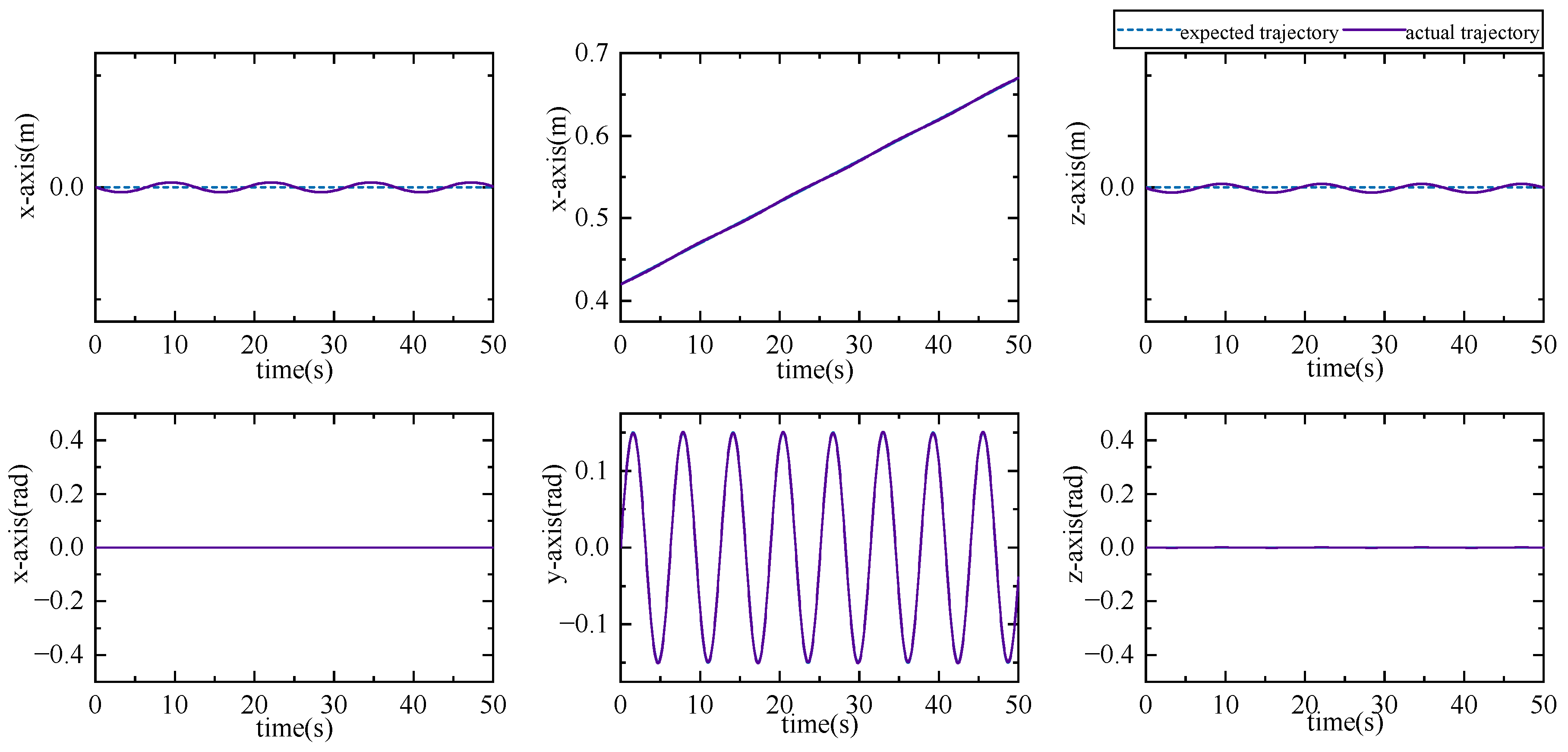


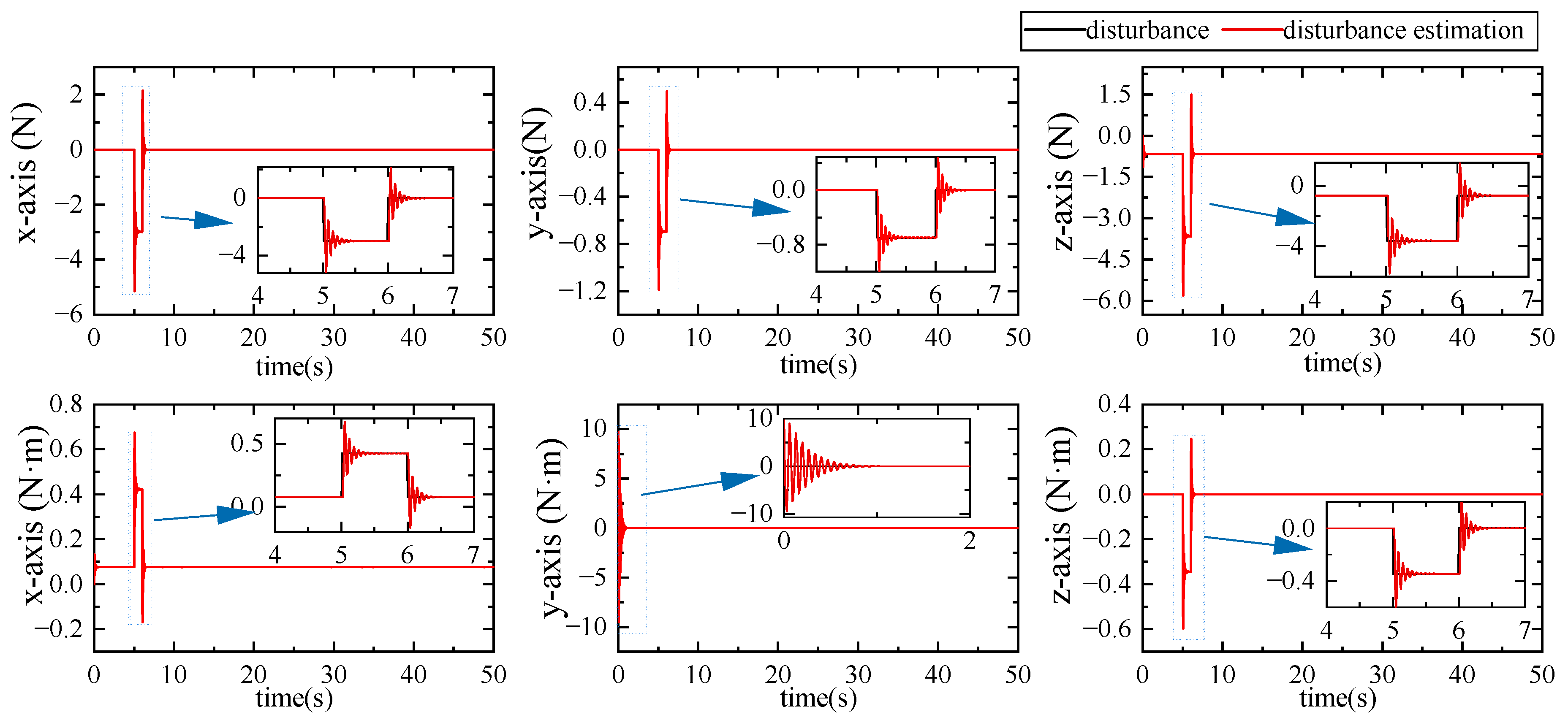

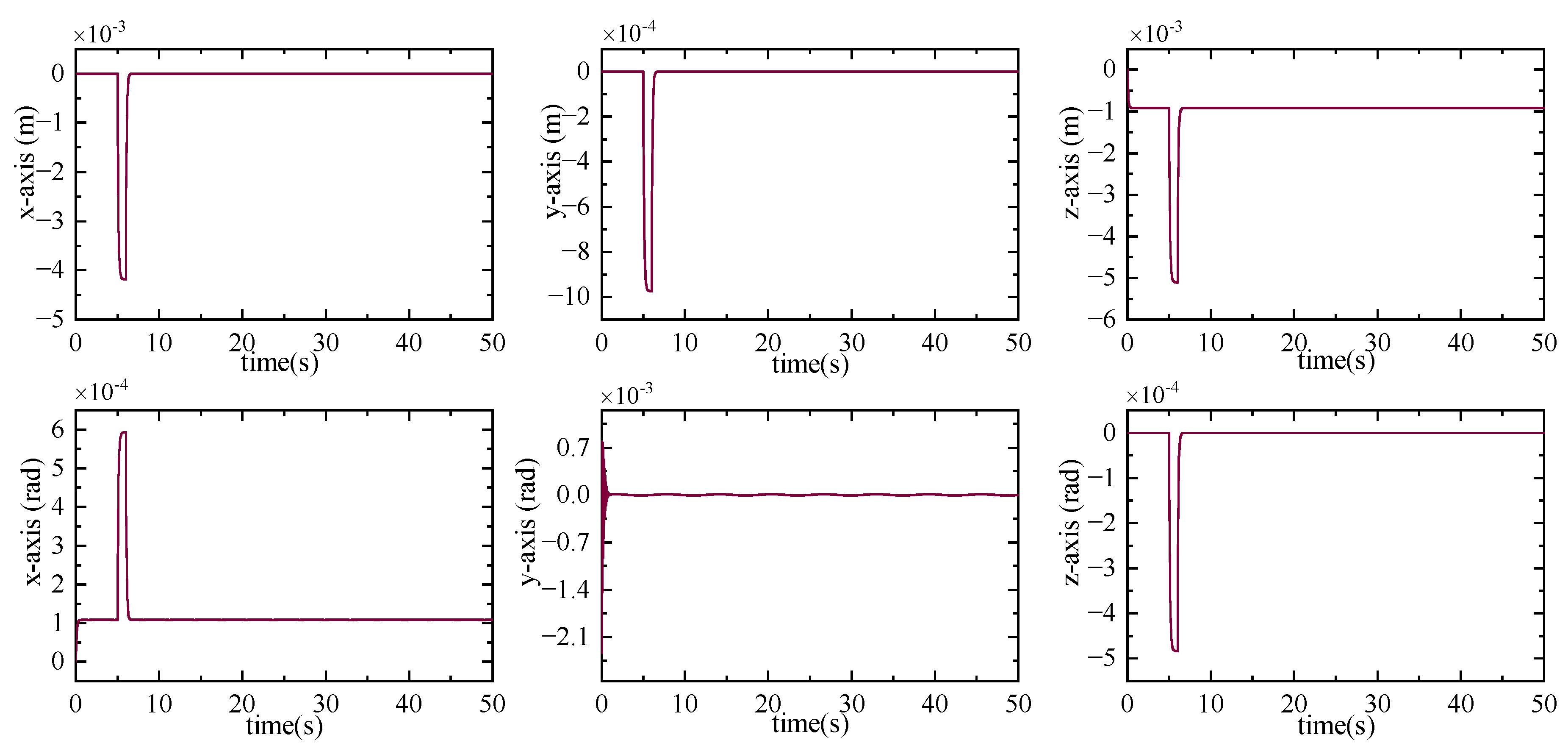
(mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 133.68 | −24.99 | 73.53 | 61.38 | −51.30 | 420 | 258.2 |
| 2 | 133.68 | 24.99 | 73.53 | 61.38 | 51.30 | 420 | 258.2 |
| 3 | −45.19 | 128.27 | 73.53 | 13.74 | 78.81 | 420 | 258.2 |
| 4 | −88.48 | 103.27 | 73.53 | −75.12 | 27.50 | 420 | 258.2 |
| 5 | −88.48 | −103.27 | 73.53 | −75.12 | −27.50 | 420 | 258.2 |
| 6 | −45.19 | −128.27 | 73.53 | 13.74 | −78.81 | 420 | 258.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, W.; Guo, X.; Lan, Z.; Liang, W. Non-Singular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control of 6-PUS Parallel Systems Based on Adaptive Disturbance Estimation. Electronics 2025, 14, 1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14061111
Niu W, Guo X, Lan Z, Liang W. Non-Singular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control of 6-PUS Parallel Systems Based on Adaptive Disturbance Estimation. Electronics. 2025; 14(6):1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14061111
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Wenjing, Xin Guo, Zhi Lan, and Wenyuan Liang. 2025. "Non-Singular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control of 6-PUS Parallel Systems Based on Adaptive Disturbance Estimation" Electronics 14, no. 6: 1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14061111
APA StyleNiu, W., Guo, X., Lan, Z., & Liang, W. (2025). Non-Singular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control of 6-PUS Parallel Systems Based on Adaptive Disturbance Estimation. Electronics, 14(6), 1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14061111






