A Comparative Analysis of Single and Double RIS Deployment for Sensor Connectivity in L-Shaped Corridors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geometry and Simulation Setup
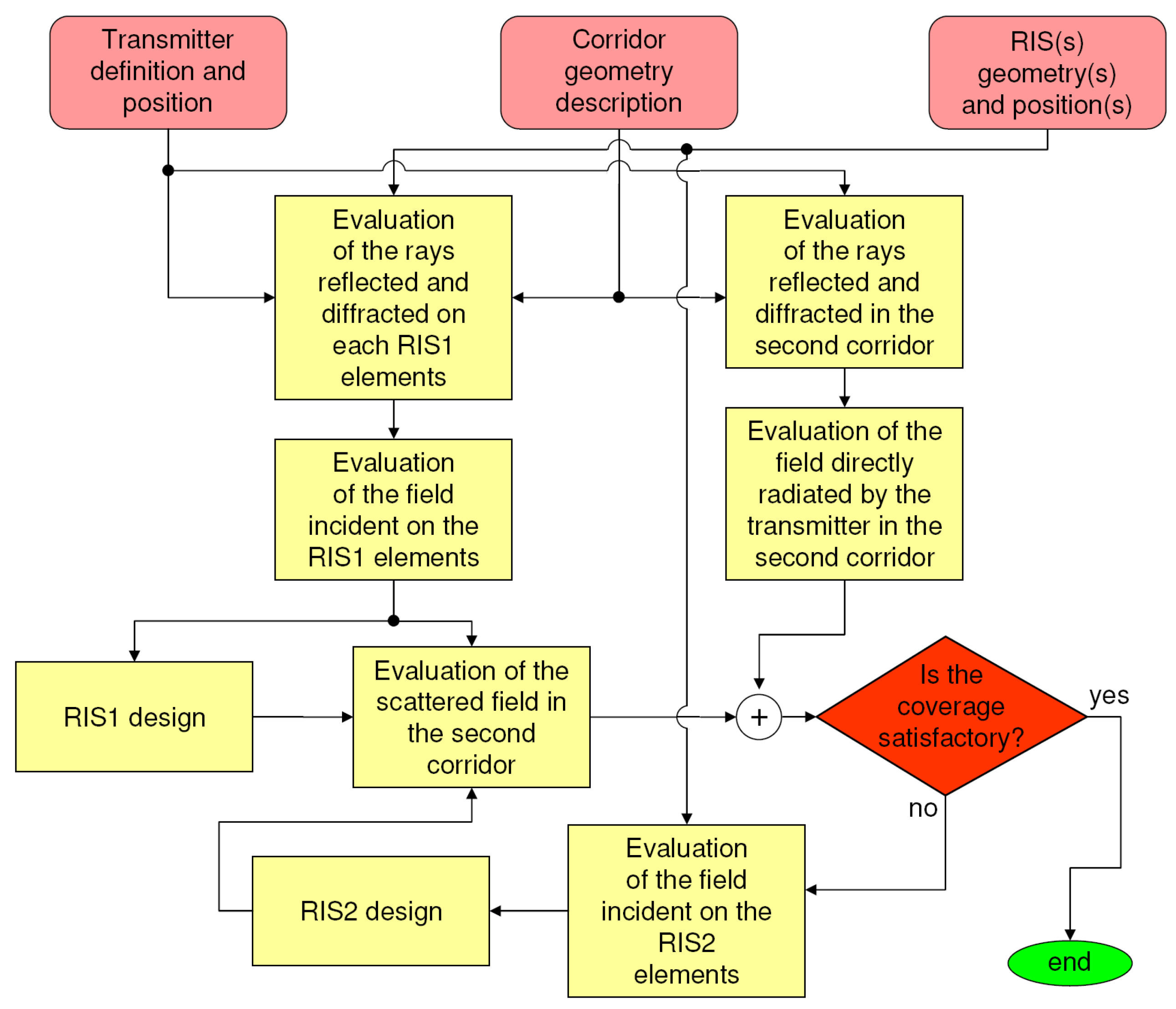
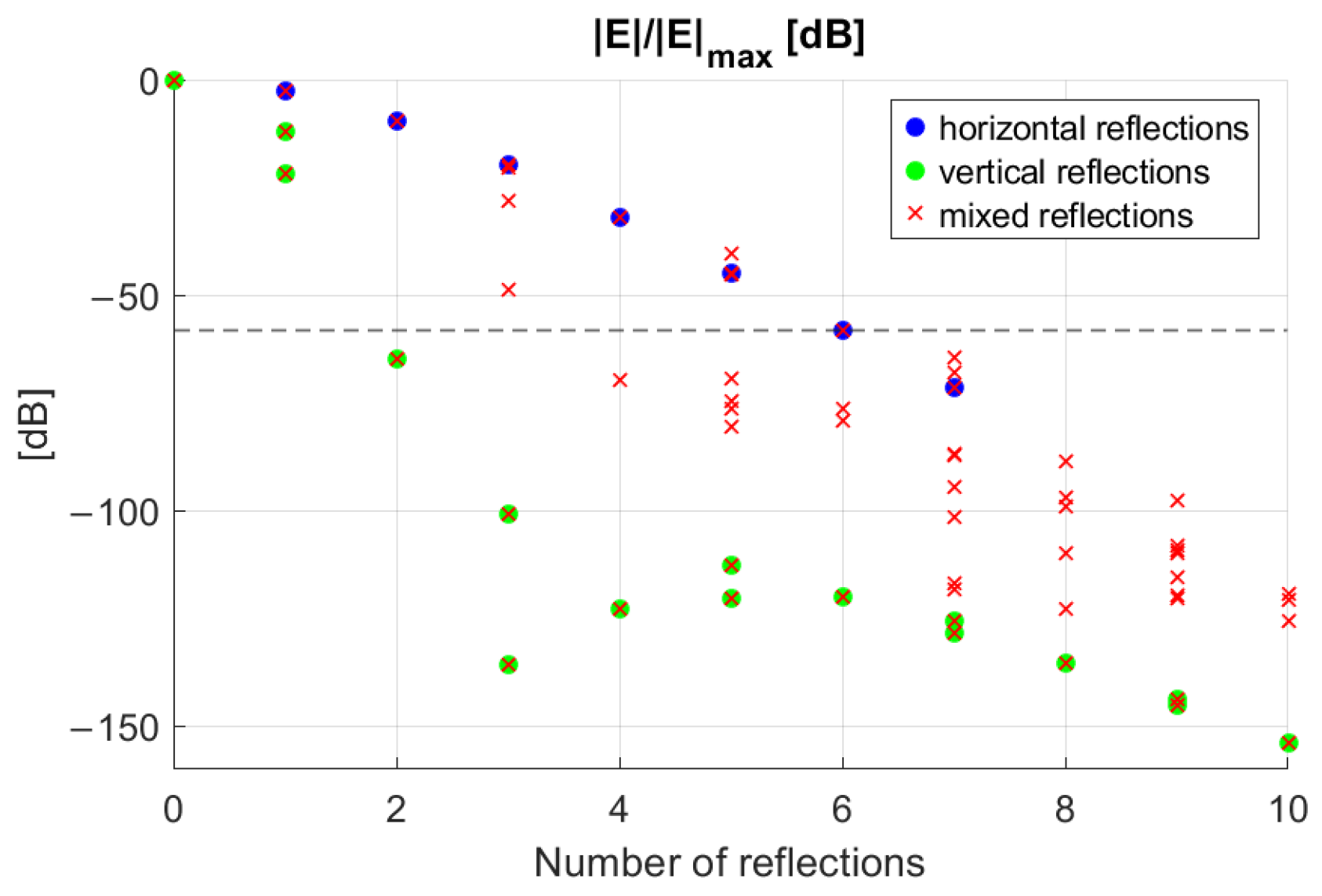
3. Ray-Tracing and Field Estimation Methodology
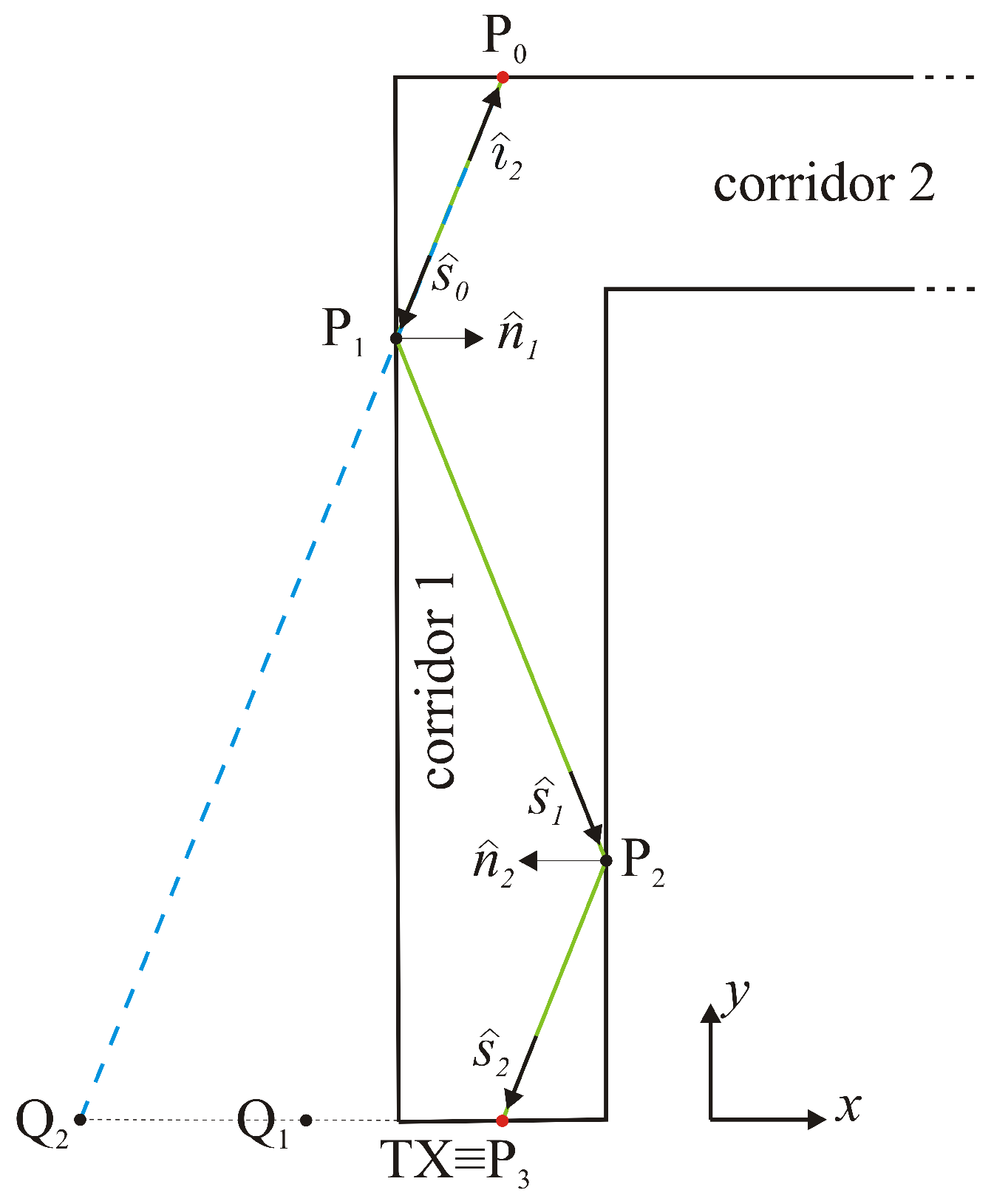
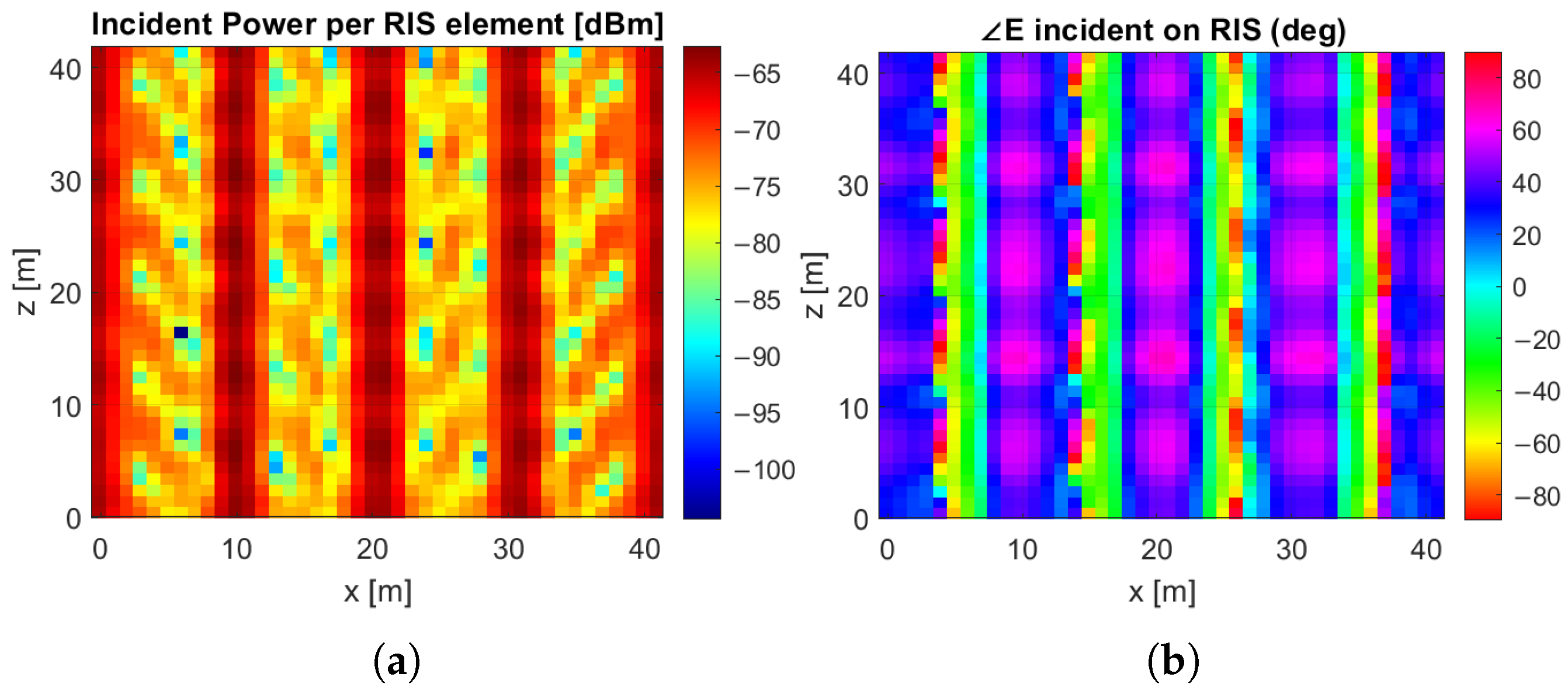
3.1. Incident Field Estimation at the RIS Location
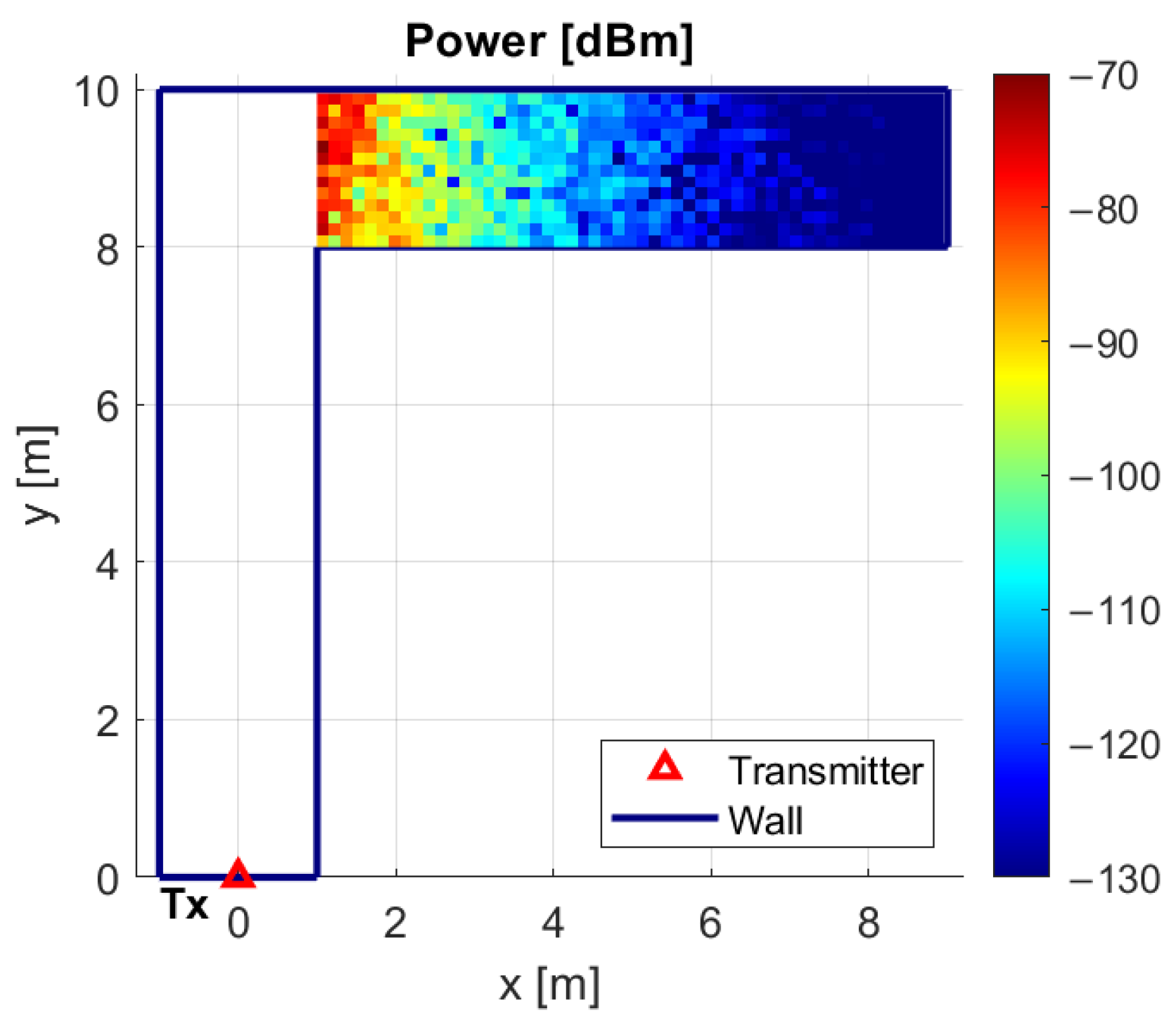
3.2. Field Estimation in the Shadowed Area
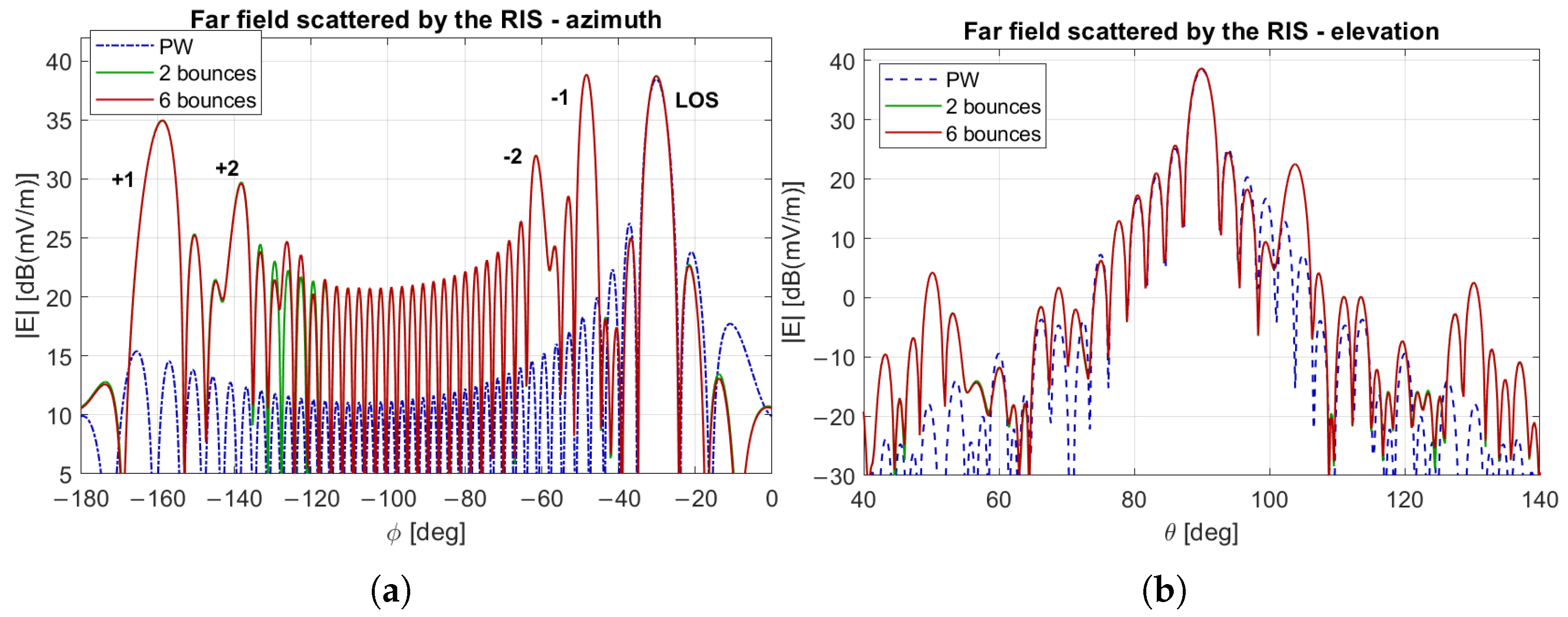
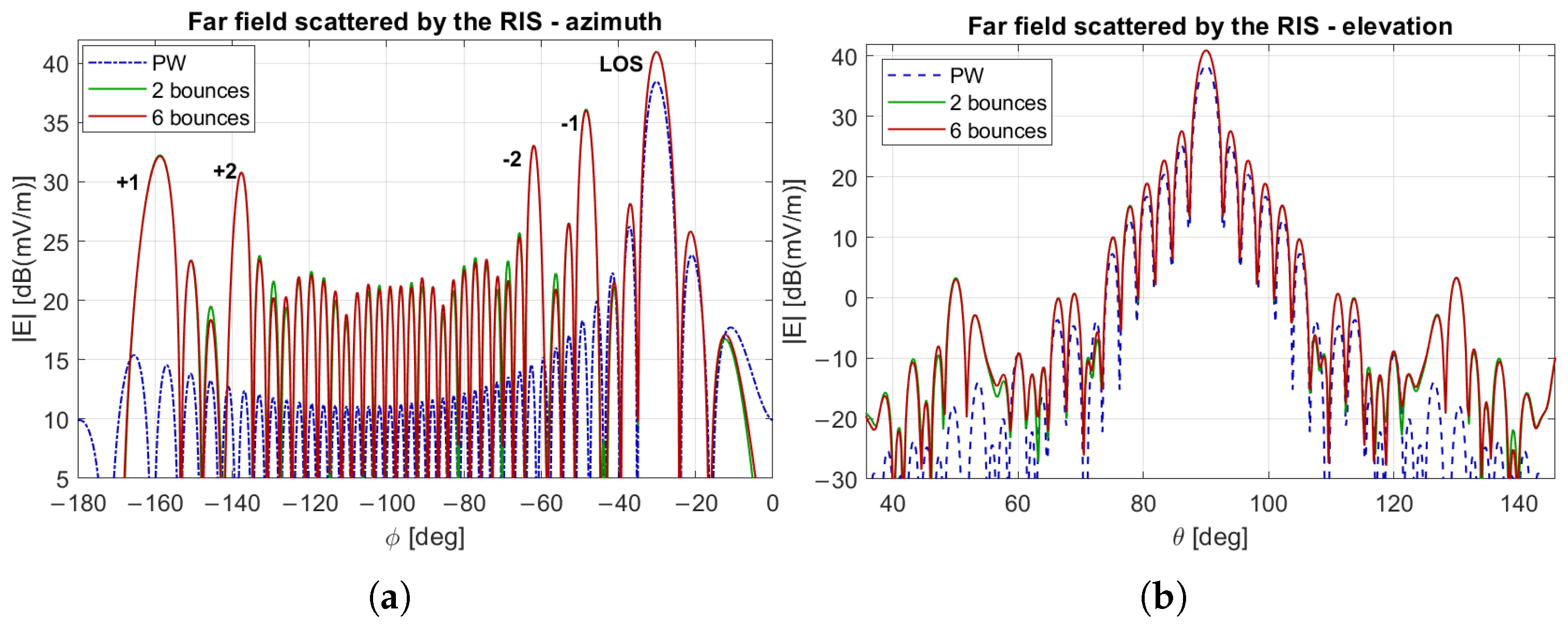
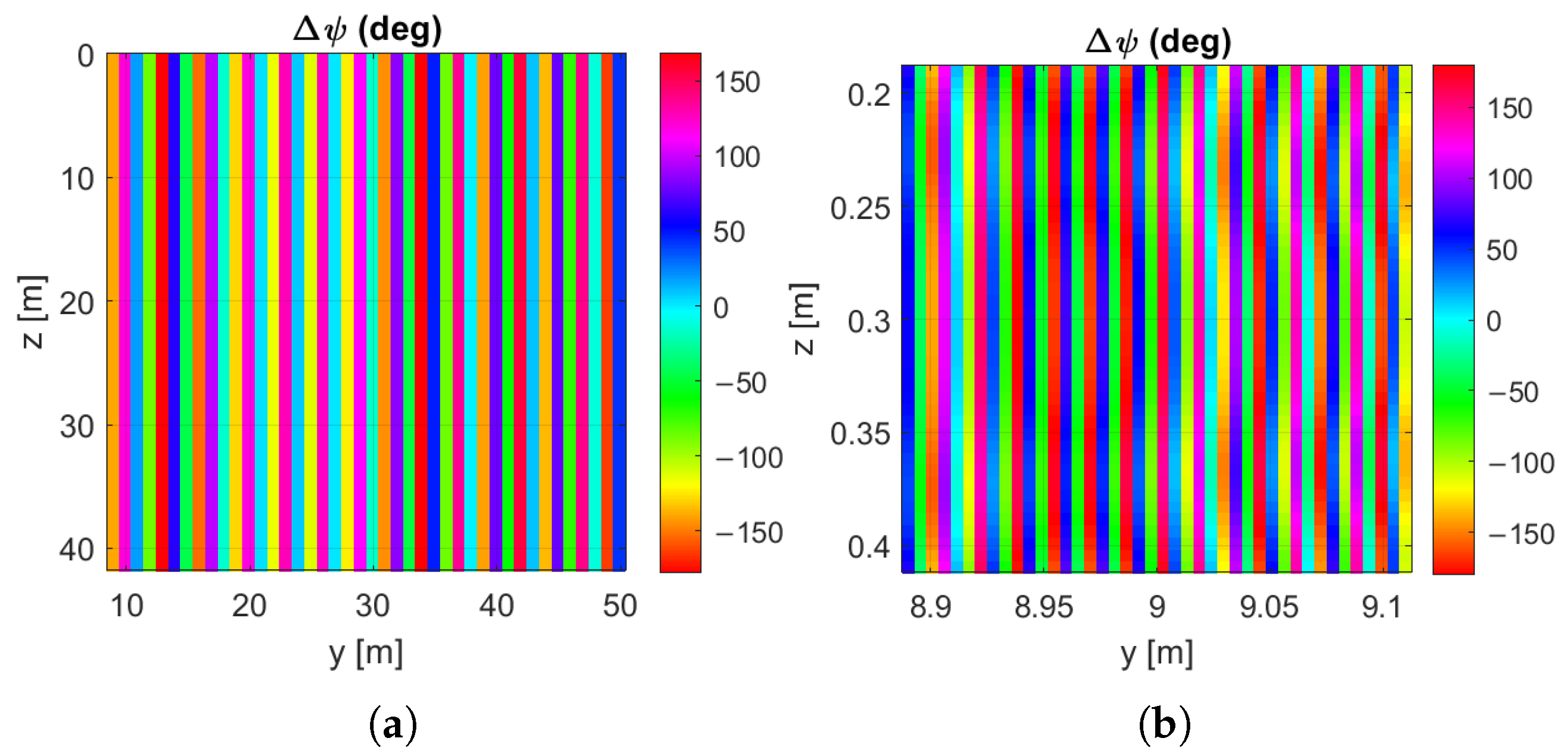
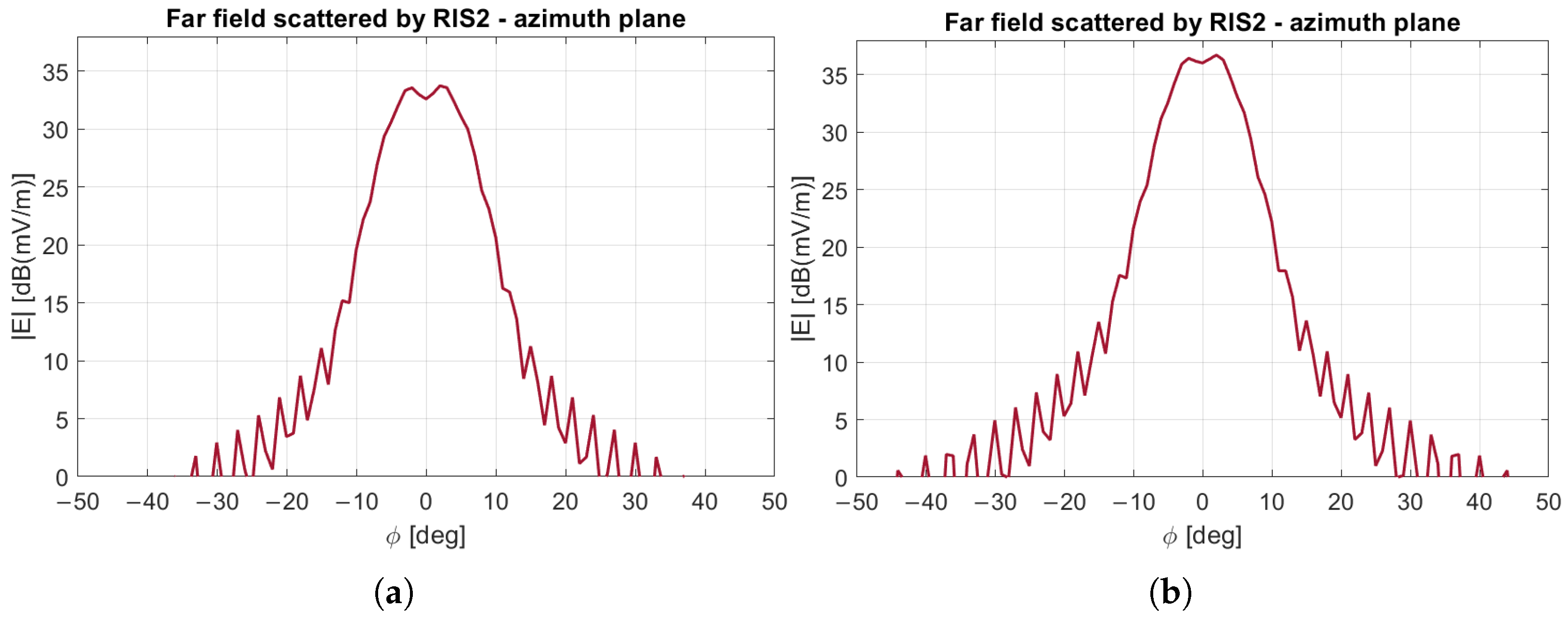
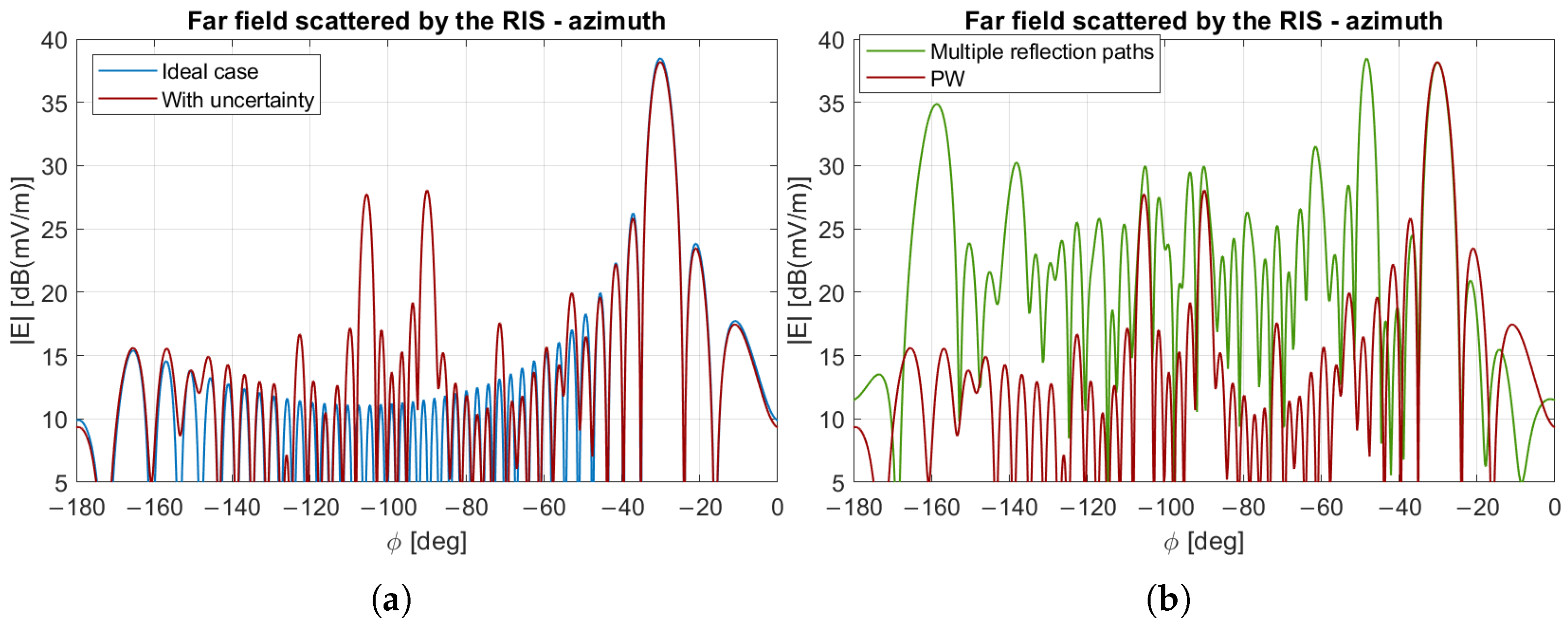
3.3. Evaluation of the Field Scattered by the RIS
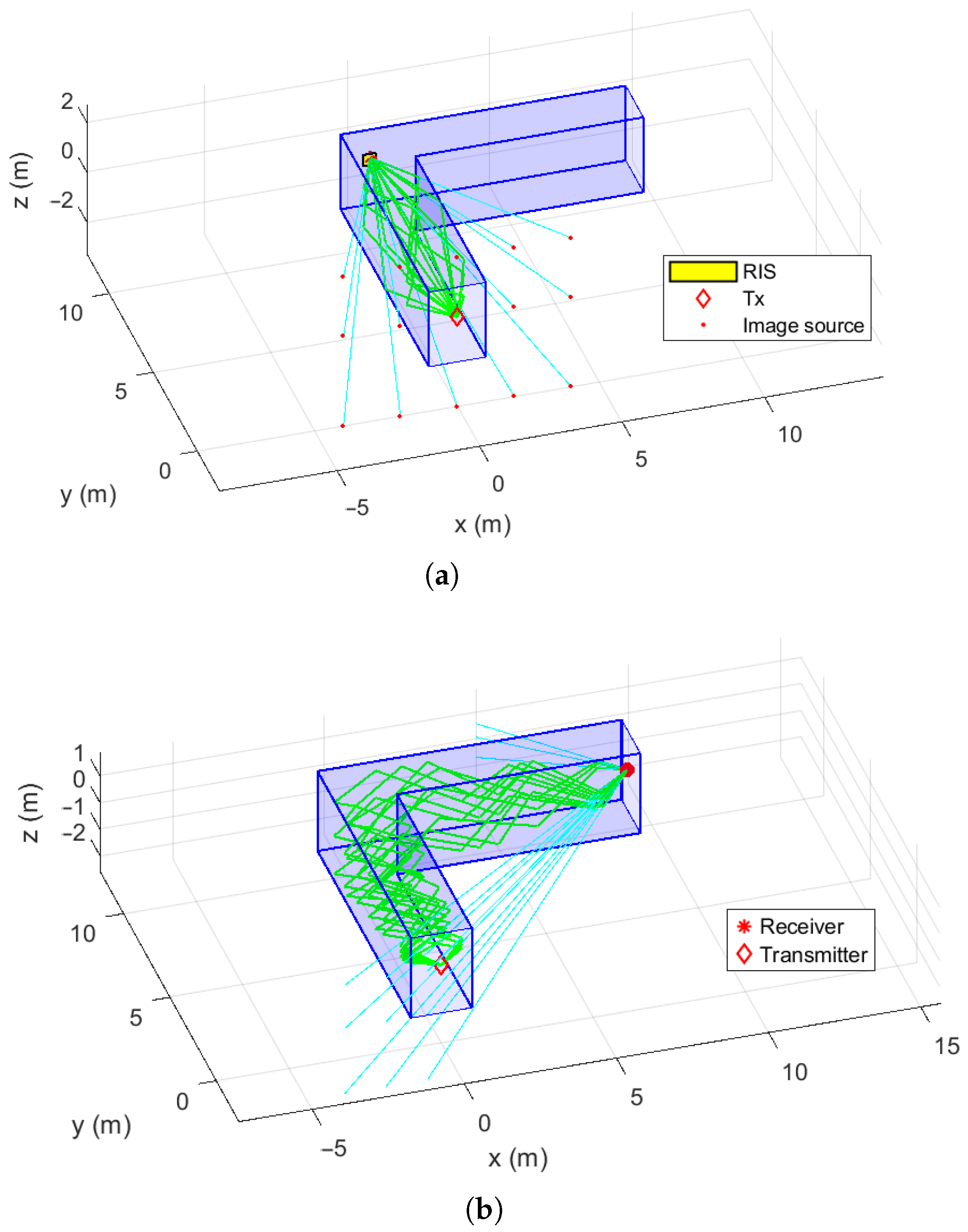
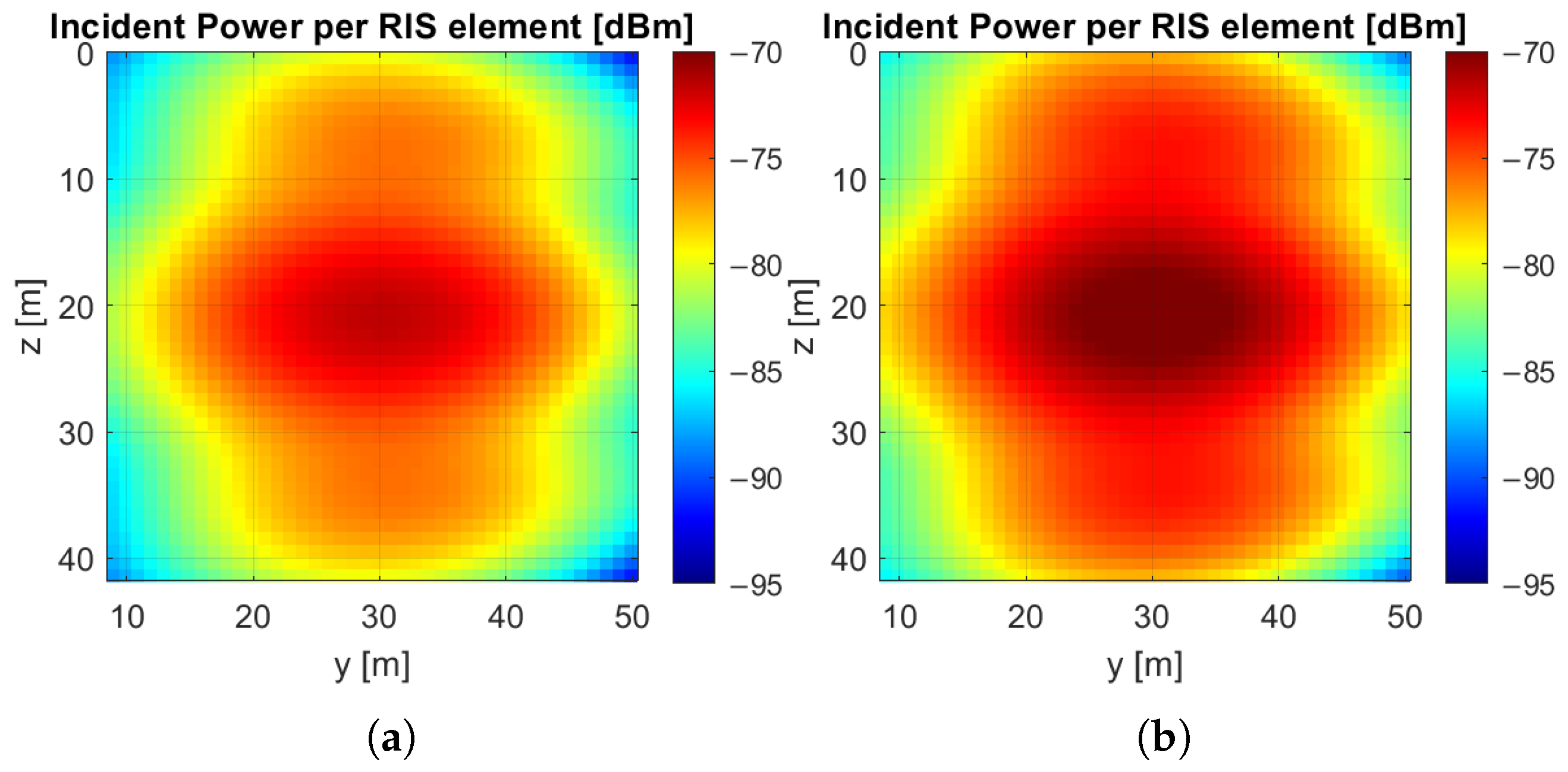
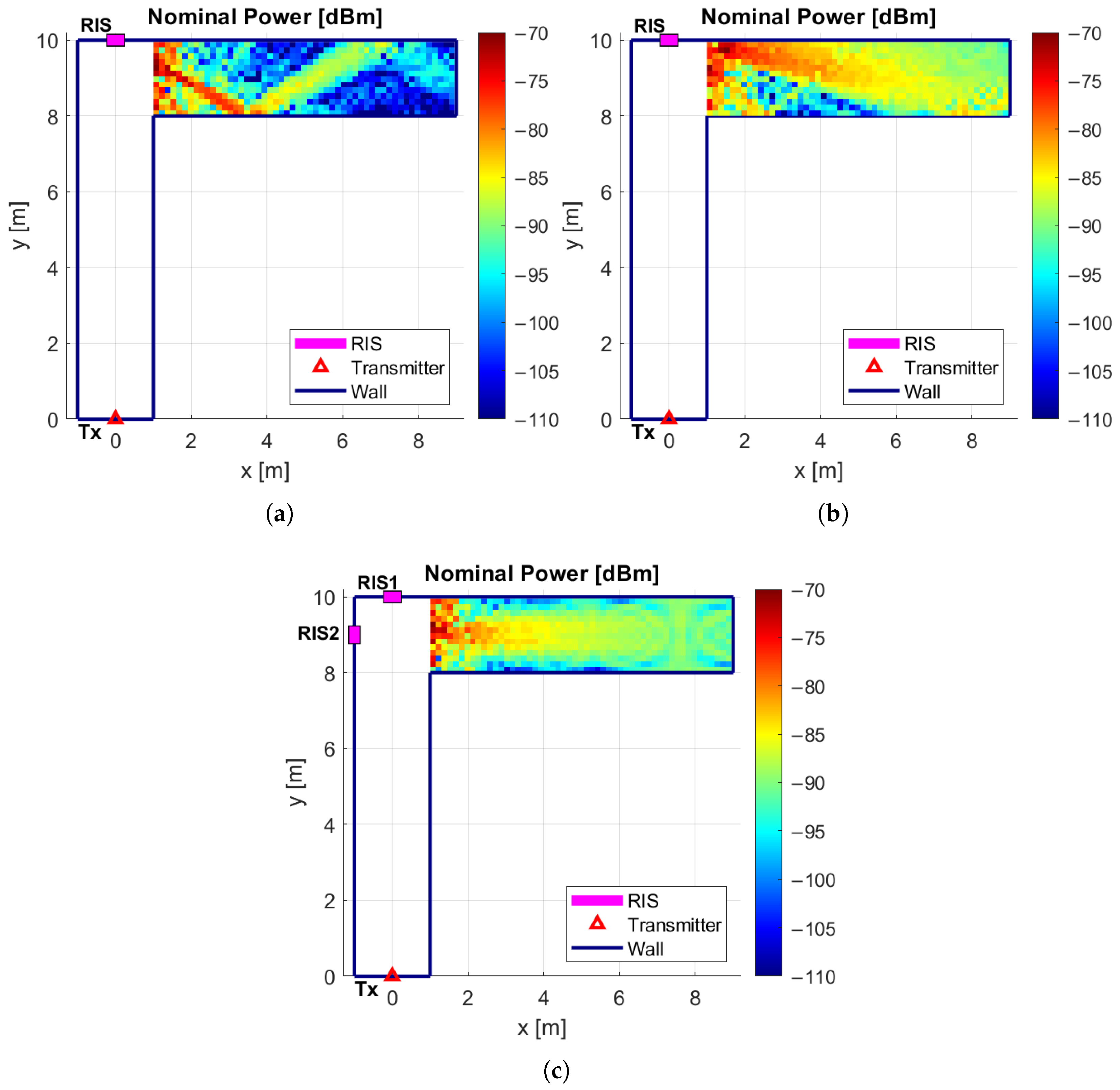
4. Double RIS Scenario and Coverage Performance Analysis
Coverage Performance Analysis
5. Computational Complexity
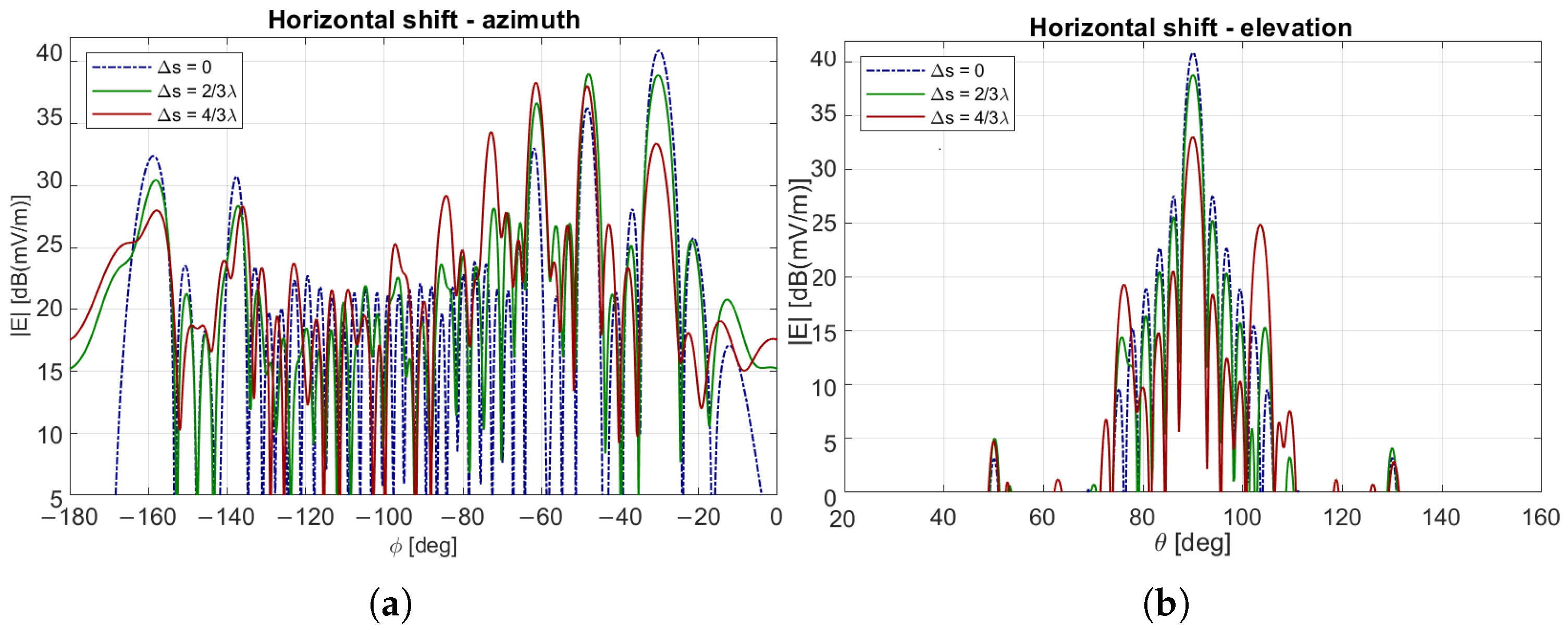
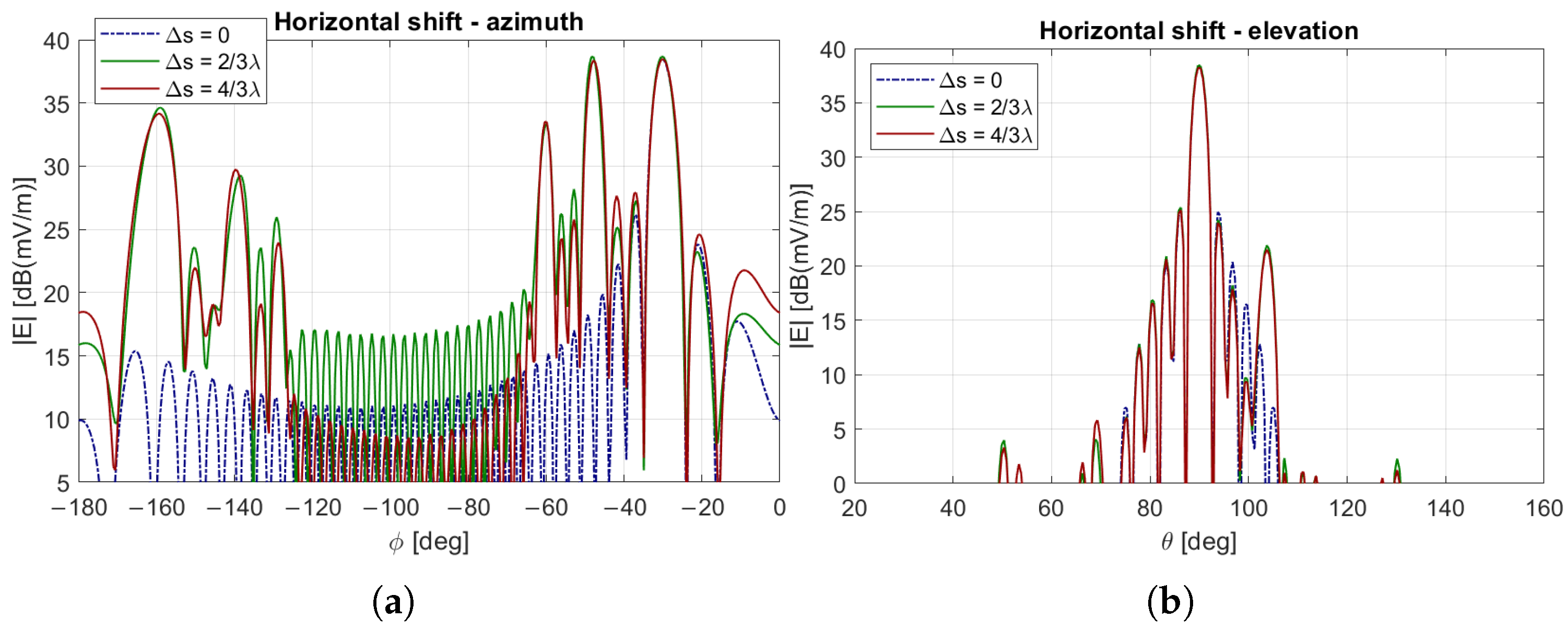
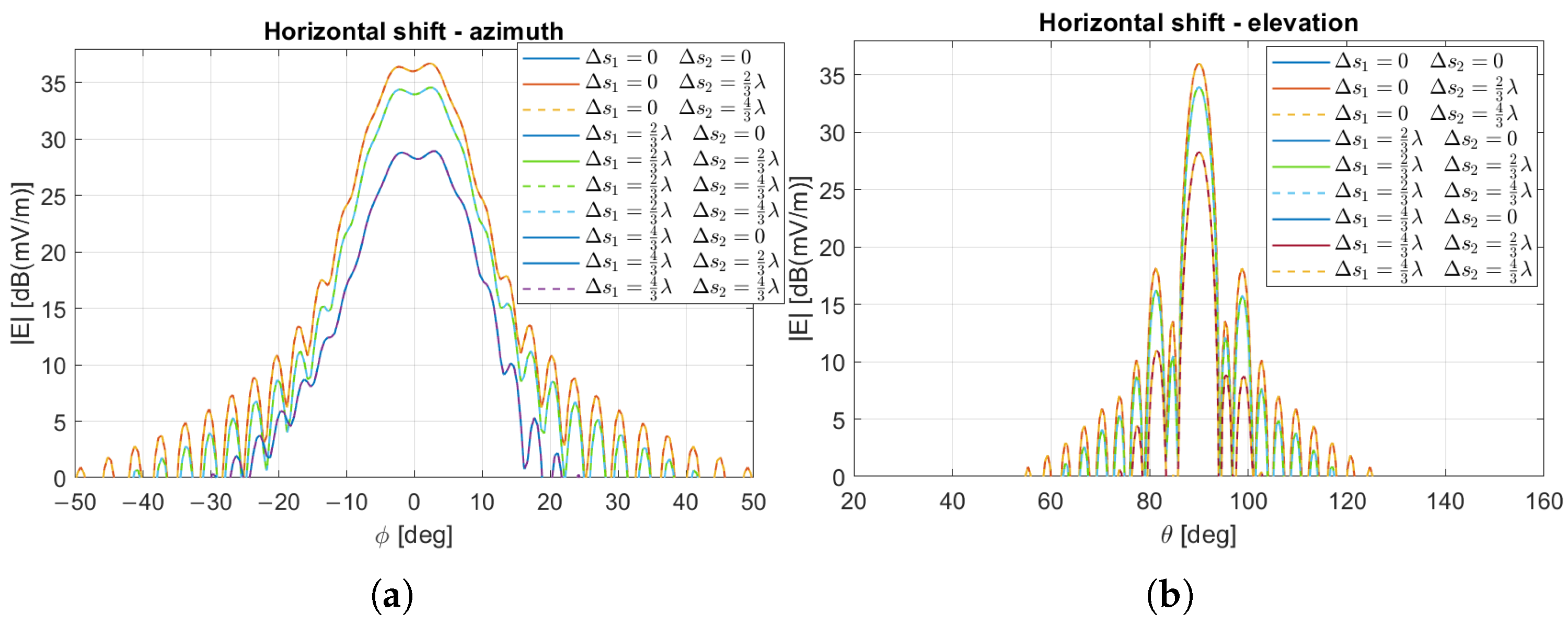
6. Uncertainty on the RIS Position
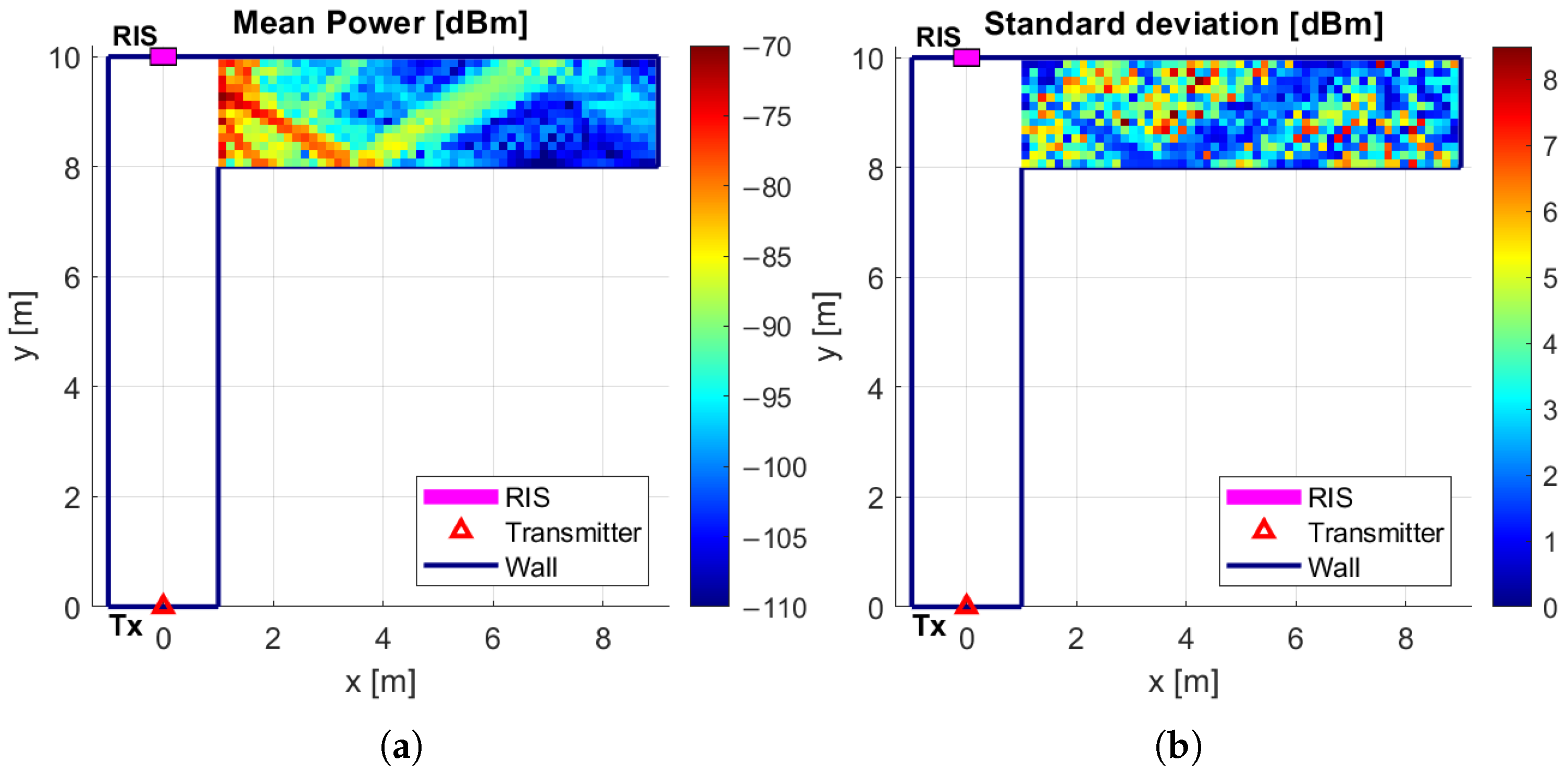
6.1. Single RIS Scenario
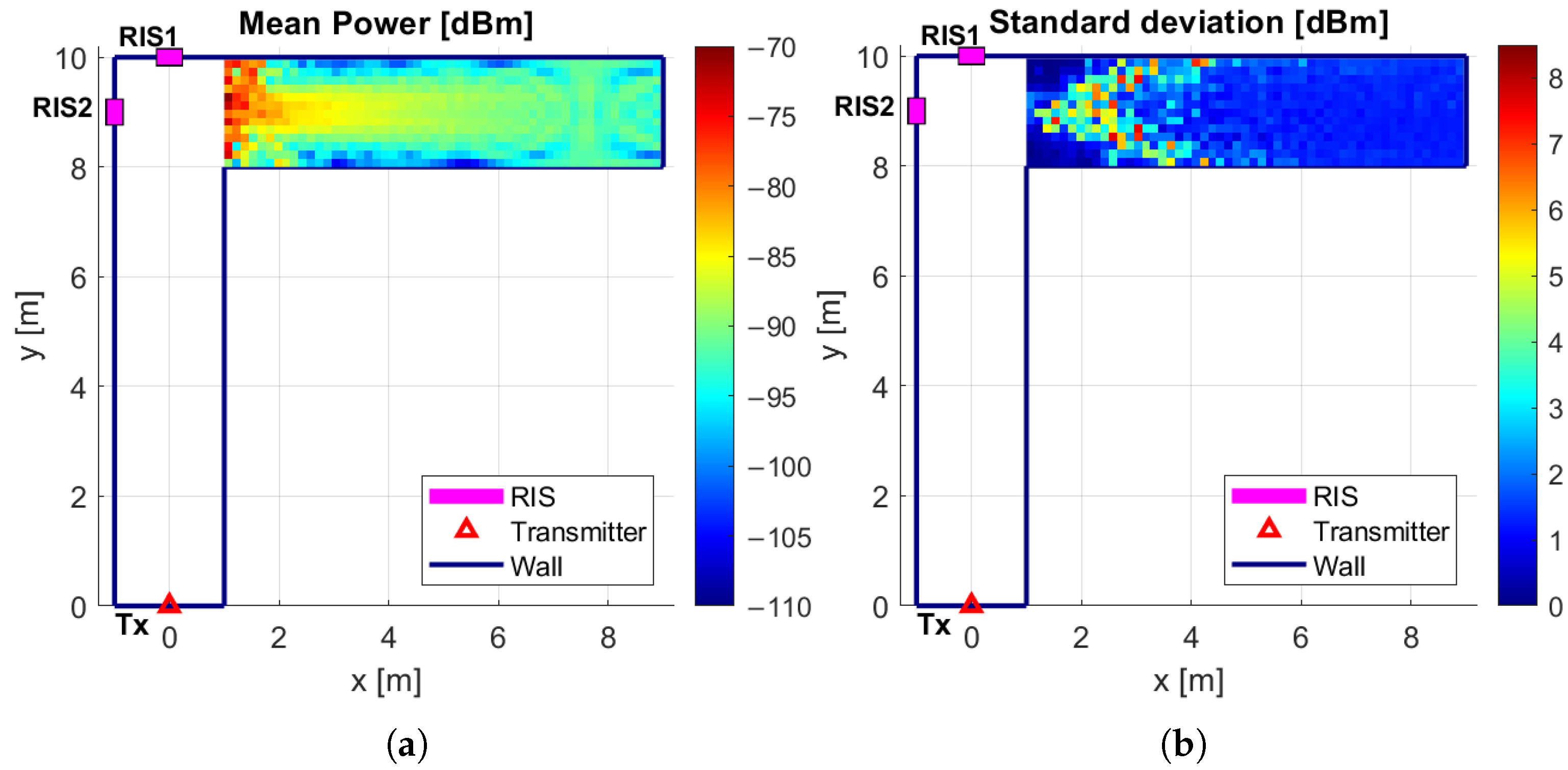
6.2. Double RIS Scenario
6.3. Statistical Analysis
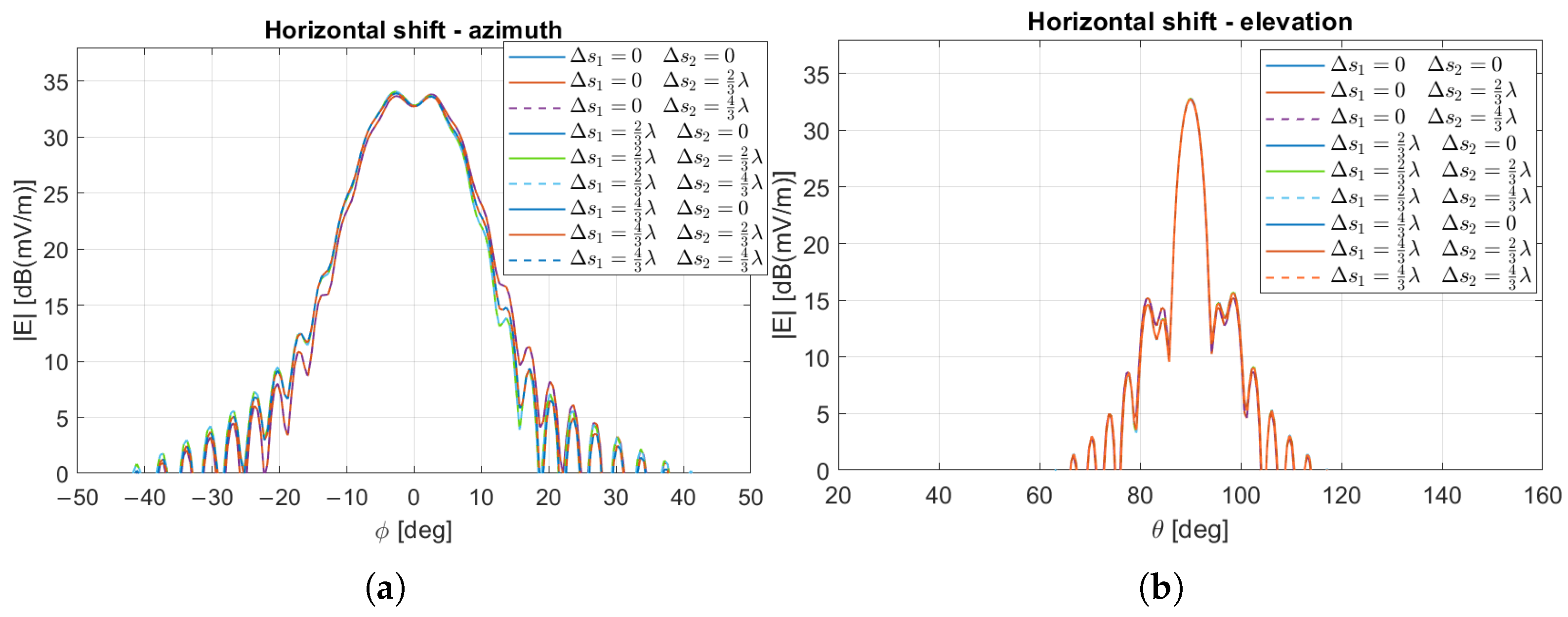
7. Manufacturing Uncertainty
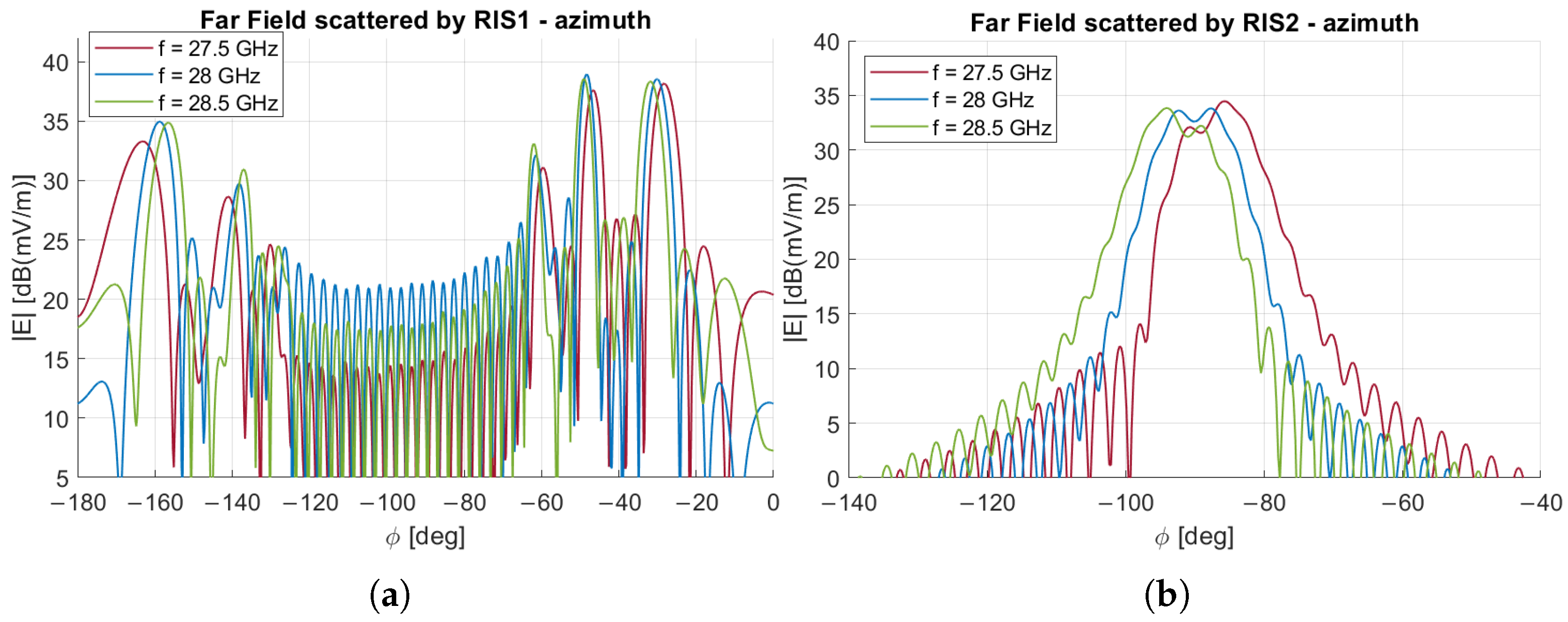
8. Frequency Behavior
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LoS | Line of Sight |
| NLoS | Non-line of Sight |
| RIS | Reflective Intelligent Surface |
| RT | Ray Tracing |
| UTD | Uniform Theory of Diffraction |
| WSN | Wireless Sensor Networks |
References
- Di Renzo, M.; Zappone, A.; Debbah, M.; Alouini, M.S.; Yuen, C.; de Rosny, J.; Tretyakov, S. Smart Radio Environments Empowered by Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces: How It Works, State of Research, and the Road Ahead. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2020, 38, 2450–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Lu, X.; Hoang, D.T.; Niyato, D.; Shu, L.; Kim, D.I.; Liang, Y.C. Toward Smart Wireless Communications via Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces: A Contemporary Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2020, 22, 2283–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, I.; Koo, I. Enhancing Throughput in IoT Networks: The Impact of Active RIS on Wireless Powered Communication Systems. Electronics 2024, 13, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freni, A.; Beccaria, M.; Mazzinghi, A.; Massaccesi, A.; Pirinoli, P. Low-Profile and Low-Visual Impact Smart Electromagnetic Curved Passive Skins for Enhancing Connectivity in Urban Scenarios. Electronics 2023, 12, 4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassouna, S.; Jamshed, M.A.; Rains, J.; Kazim, J.R.; Rehman, M.U.; Abualhayja, M.; Mohjazi, L.; Cui, T.J.; Imran, M.A.; Abbasi, Q.H. A survey on reconfigurable intelligent surfaces: Wireless communication perspective. IET Commun. 2023, 17, 497–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeisi, M.; Yildirim, I.; Ilter, M.C.; Gerami, M.; Basar, E. Plug-In RIS: A Novel Approach to Fully Passive Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2024, 23, 14776–14789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Shen, H.; Xu, W.; Zhao, C. Low-Cost Passive Beamforming for RIS-Aided Wideband OFDM Systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2022, 11, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, K.; Pan, C.; Ren, H.; Chai, K.K.; Elkashlan, M. Active RIS Versus Passive RIS: Which is Superior With the Same Power Budget? IEEE Commun. Lett. 2022, 26, 1150–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, B.; You, C.; Zhang, R. Intelligent Reflecting Surface-Aided Wireless Communications: A Tutorial. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2021, 69, 3313–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sejan, M.A.S.; Rahman, M.H.; Shin, B.-S.; Oh, J.-H.; You, Y.-H.; Song, H.-K. Machine Learning for Intelligent-Reflecting-Surface-Based Wireless Communication towards 6G: A Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuyyuru, S.K.; Hao, L.; Rupp, M.; Tretyakov, S.A.; Valkonen, R. Modeling RIS from Electromagnetic Principles to Communication Systems—Part I: Synthesis and Characterization of a Scalable Anomalous Reflector. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2024, 73, 1743–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mossallamy, M.A.; Zhang, H.; Song, L.; Seddik, K.G.; Han, Z.; Li, G.Y. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for wireless communications: Principles, challenges, and opportunities. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2020, 6, 990–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, I.P. Reviews Based on the Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Technical Issues. Electronics 2023, 12, 4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Z.; Iskander, M.F. Ray tracing for radio propagation modeling: Principles and applications. IEEE Access 2015, 3, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Ai, B.; Guan, K.; Wang, L.; Zhong, Z.; Kürner, T. The design and applications of high-performance ray-tracing simulation platform for 5G and beyond wireless communications: A tutorial. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 21, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuschini, F.; Vitucci, E.M.; Barbiroli, M.; Falciasecca, G.; Degli-Esposti, V. Ray tracing propagation modeling for future small-cell and indoor applications: A review of current techniques. Radio Sci. 2015, 50, 469–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eertmans, J.; di Cicco, N.; Oestges, C.; Jacques, L.; Vitucci, E.M.; Degli-Esposti, V. Towards Generative Ray Path Sampling for Faster Point-to-Point Ray Tracing. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning for Communication and Networking (ICMLCN), Barcelona, Spain, 26–29 May 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitucci, E.M.; Albani, M.; Kodra, S.; Barbiroli, M.; Degli-Esposti, V. An Efficient Ray-Based Modeling Approach for Scattering From Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2024, 72, 2673–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelifi, M.; Lioce, S.; Saucez, D.; Dabbous, W. To RIS or not to RIS: A ray-tracing study of RIS-assisted indoor 5G communications. In Proceedings of the EUSIPCO 2025—33rd European Signal Processing Conference, European Association for Signal Processing (EURASIP), Palerme, Italy, 8–12 September 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Wang, C.X.; Sun, Y.; Huang, J.; Zheng, F.C. A Novel Ray Tracing Based 6G RIS Wireless Channel Model and RIS Deployment Studies in Indoor Scenarios. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 33rd Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Kyoto, Japan, 12–15 September 2022; pp. 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitucci, E.M.; Fabiani, M.; Degli-Esposti, V. Use of a Realistic Ray- Based Model for the Evaluation of Indoor RF Coverage Solutions Using Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces. Electronics 2023, 12, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozar, D.M.; Targonski, S.D.; Syrigos, H.D. Design of millimeter wave microstrip reflectarrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1997, 45, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degli-Esposti, V.; Vitucci, E.M.; Renzo, M.D.; Tretyakov, S.A. Reradiation and Scattering From a Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface: A General Macroscopic Model. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2022, 70, 8691–8706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawaja, W.; Ozdemir, O.; Erden, F.; Ozturk, E.; Guvenc, I. Multiple Ray Received Power Modeling for mmWave Indoor and Outdoor Scenarios. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2020, 14, 1825–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Long, D.G. Microwave Radar and Radiometric Remote Sensing; The University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Ding, J.; Bian, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Zhong, Z.; Yu, J. Reflection Characteristics Measurements of Indoor Wireless Link in D-Band. Sensors 2022, 22, 6908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhekov, S.S.; Franek, O.; Pedersen, G.F. Dielectric Properties of Common Building Materials for Ultrawideband Propagation Studies [Measurements Corner]. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2020, 62, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouyoumjian, R.G.; Pathak, P.H. A Uniform Geometrical Theory of Diffraction for an Edge in a Perfectly Conducting Surface. Proc. IEEE 1974, 62, 1448–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luebbers, R.J. Finite Conductivity Uniform GTD Versus Knife Edge Diffraction in Prediction of Propagation Path Loss. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1984, 32, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carluccio, G.; Puggelli, F.; Albani, M. Generalization of UTD double diffraction to the case of impenetrable wedges with relatively general boundary conditions. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 3829–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratton, J.A. Electromagnetic Theory; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1941. [Google Scholar]
- Carluccio, G.; Mazzinghi, A.; Freni, A. Design of complementary reflectarray. Electron. Lett. 2014, 50, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, L.; Gillard, R.; Peris, F.; Loison, R.; Legay, H.; Girard, E. The phoenix cell: A new reflectarray cell with large bandwidth and rebirth capabilities. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2011, 10, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansys HFSS. 2025. Available online: https://www.ansys.com/products/electronics/ansys-hfss (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Beccaria, M.; Massaccesi, A.; Lumia, M.; Addamo, G.; Freni, A.; Pirinoli, P. Ka-Band Reflectarray with Cylindrical Dielectric Unit Cells: Optimized Additive Manufacturing and High-Permittivity Material Characterization. Sensors 2025, 25, 5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
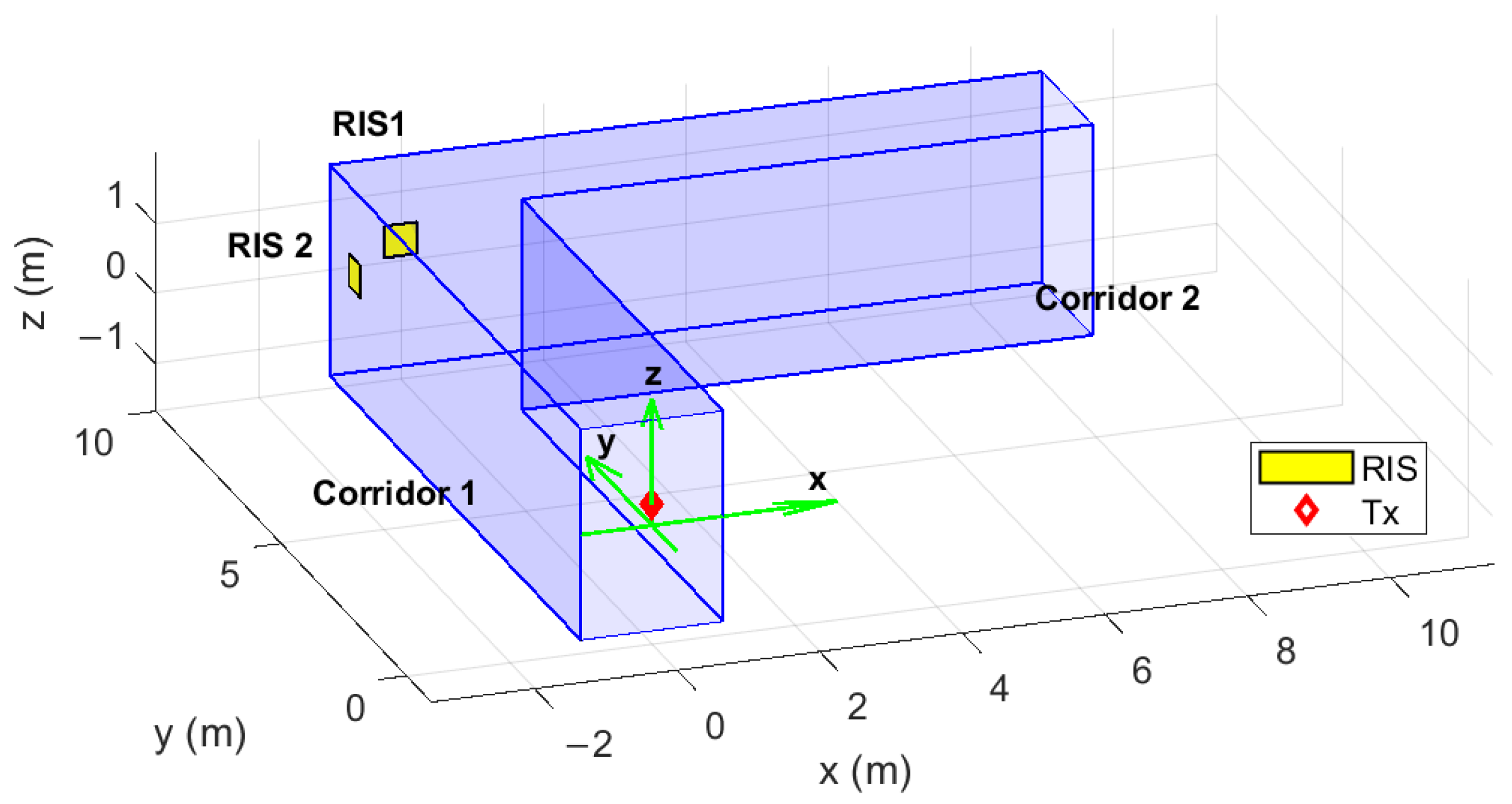

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| frequency (wavelength) | GHz ( mm) |
| RIS’s dimensions | cm2 (i.e., ) |
| periodicity of the lattice | mm (i.e., ) |
| RIS 1 centre | m |
| RIS 2 centre | m |
| wall parameters | , , |
| dimensions of each corridor’s segment | m, m, m |
| maximum number of reflections | , , |
| Configuration | Avg. Received Power [dBm] | Power Std. Dev. [dB] | Coverage Gain vs. No-RIS [%] 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| No RIS (Baseline) | −114.7 | 16.8 | – |
| Single RIS (60°) | −93.3 | 9.8 | 46 |
| Single RIS (80°) | −87.3 | 6.2 | 74 |
| Double-RIS (Proposed) | −88.0 | 6.4 | 76 |
| Max. Reflection Order | First Stage (s) | Second Stage (s) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline scenario (no RIS) | 12 | - | 0.53 |
| Single-RIS configuration | |||
| 42 × 42 elements | 3 | 17 | 4.5 |
| per unit cell | 3 | 0.0096 | 0.0029 |
| 42 × 42 elements | 6 | 82 | 22 |
| per unit cell | 6 | 0.0465 | 0.0125 |
| Double-RIS configuration | |||
| 42 × 42 elements | 3 | 69 | 9.8 |
| per unit cell | 3 | 0.0391 | 0.0073 |
| 42 × 42 elements | 6 | 116 | 45 |
| per unit cell | 6 | 0.0658 | 0.0255 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Burladean, A.; Freni, A.; Pirinoli, P.; Mazzinghi, A. A Comparative Analysis of Single and Double RIS Deployment for Sensor Connectivity in L-Shaped Corridors. Electronics 2025, 14, 4777. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14234777
Burladean A, Freni A, Pirinoli P, Mazzinghi A. A Comparative Analysis of Single and Double RIS Deployment for Sensor Connectivity in L-Shaped Corridors. Electronics. 2025; 14(23):4777. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14234777
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurladean, Ana, Angelo Freni, Paola Pirinoli, and Agnese Mazzinghi. 2025. "A Comparative Analysis of Single and Double RIS Deployment for Sensor Connectivity in L-Shaped Corridors" Electronics 14, no. 23: 4777. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14234777
APA StyleBurladean, A., Freni, A., Pirinoli, P., & Mazzinghi, A. (2025). A Comparative Analysis of Single and Double RIS Deployment for Sensor Connectivity in L-Shaped Corridors. Electronics, 14(23), 4777. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14234777








