LTSPICE Memristor Neuron with a Modified Transfer Function Based on Memristor Model with Parasitic Parameters †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Memristors, Modeling, and LTSPICE Implementation
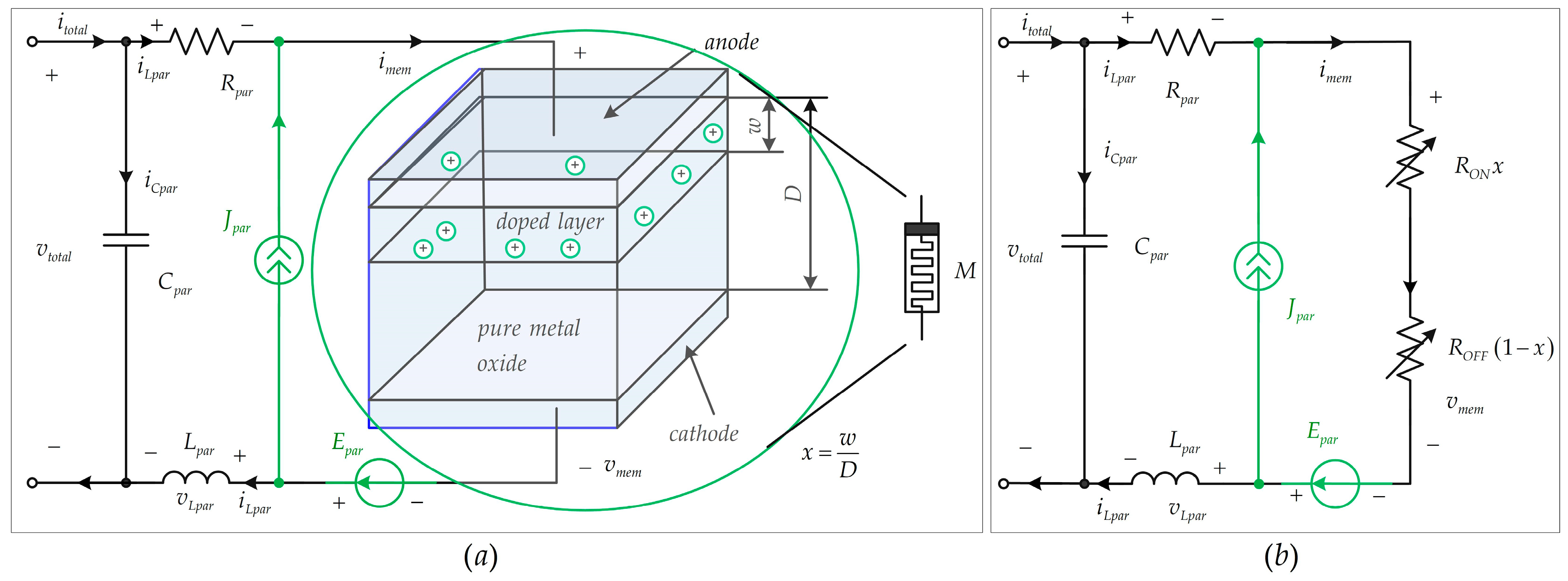
2.1. Structure of Memristor Elements and Their Operation
2.2. Memristor Modeling
2.3. The Proposed Memristor Model (B6m)
3. Experimental Investigation, Adjustment in MATLAB–Simulink, and Generation and Analysis of the Corresponding LTSPICE Memristor Model
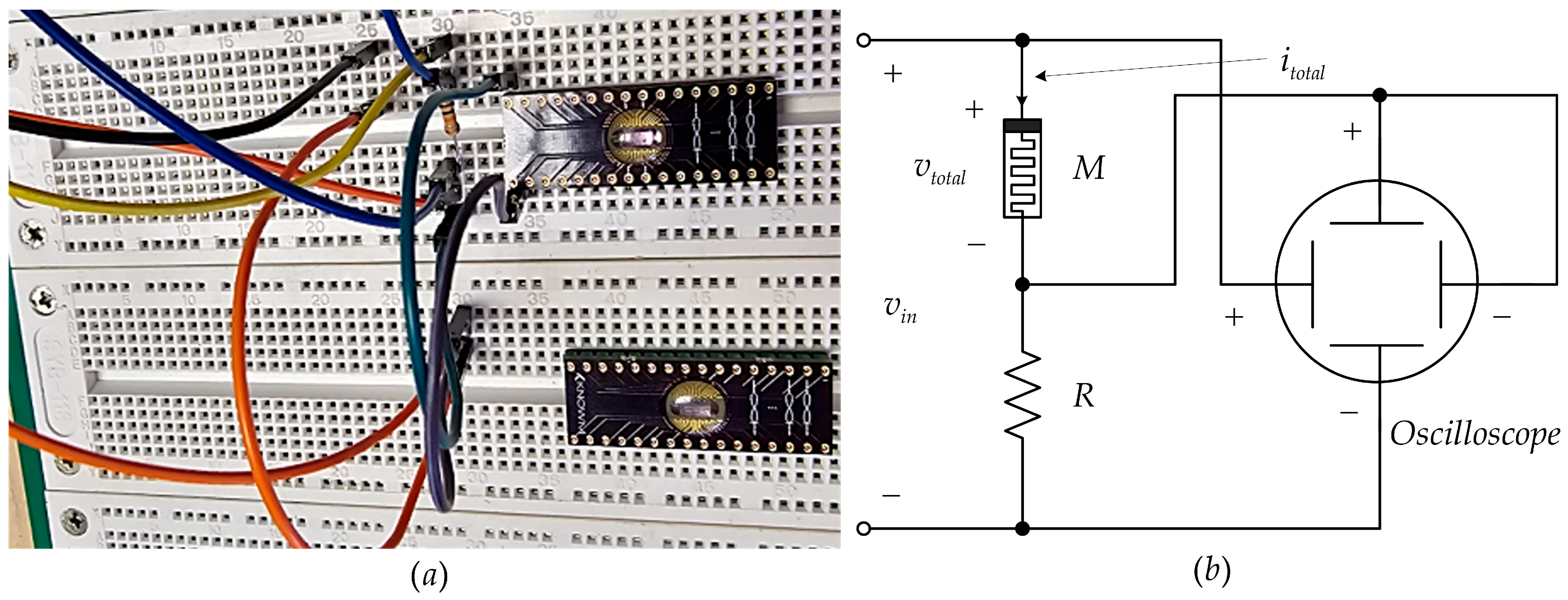
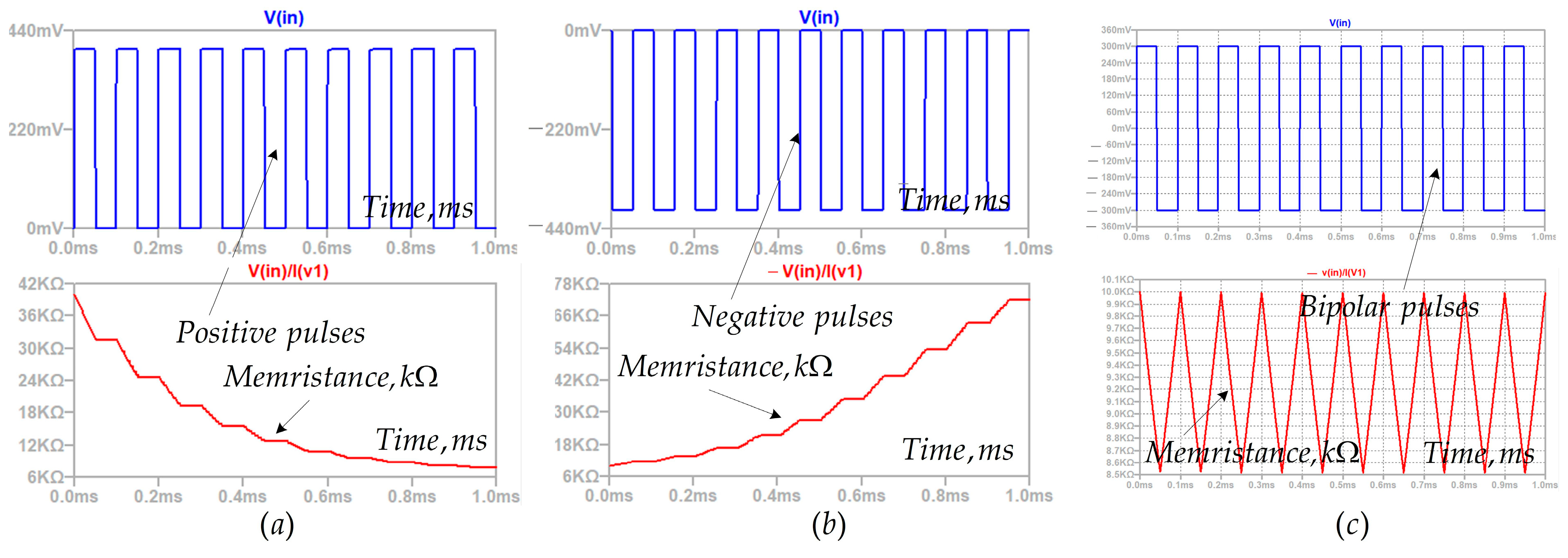
3.1. Experimental Measurements
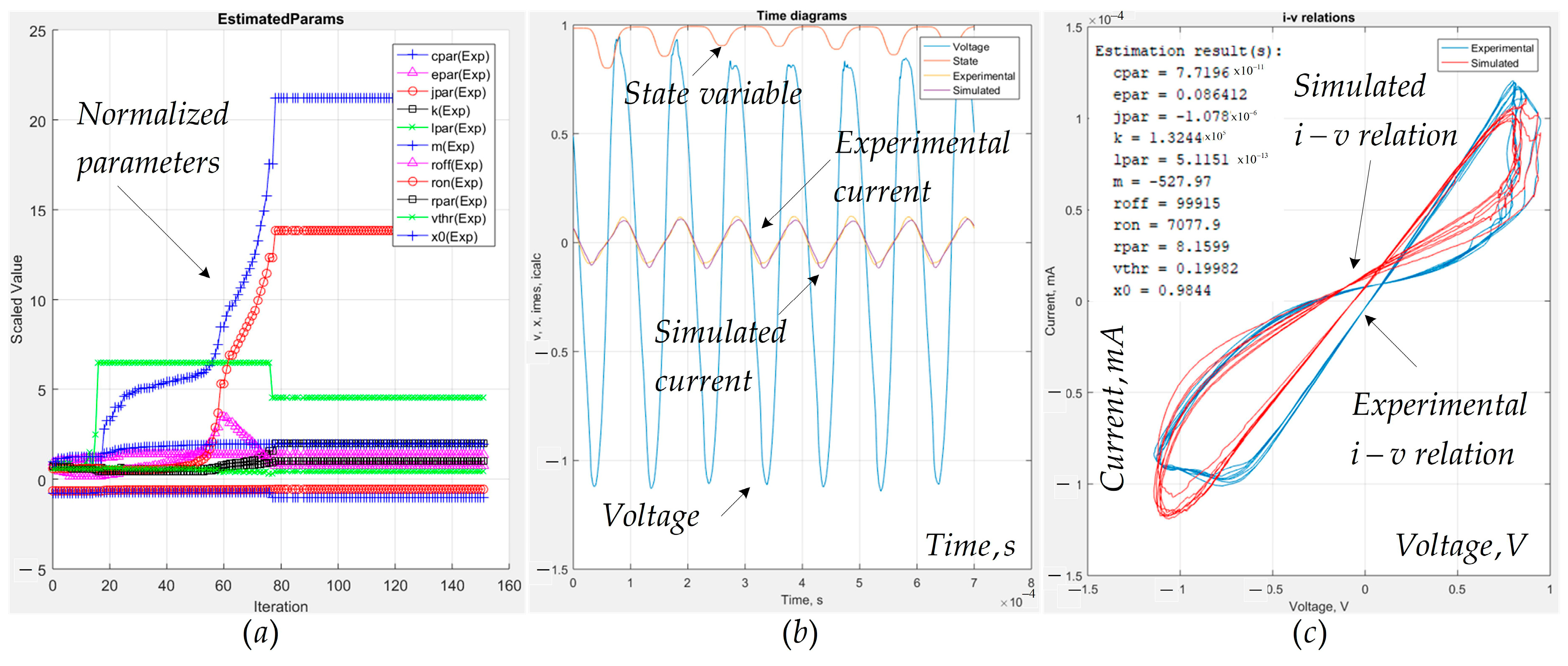
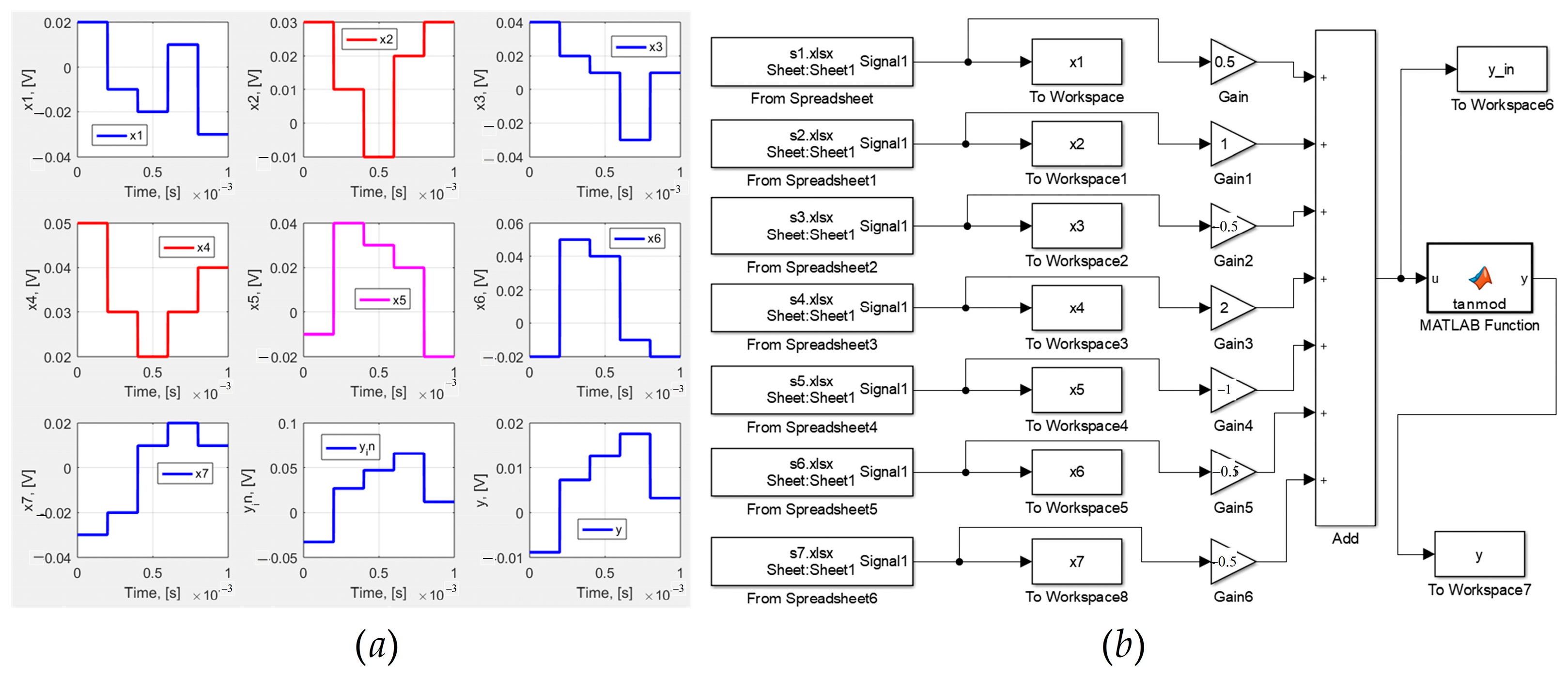
3.2. Adjustment of the Proposed Memristor Model in MATLAB–Simulink, According to the Experimental Data of Knowm Memristors [19]
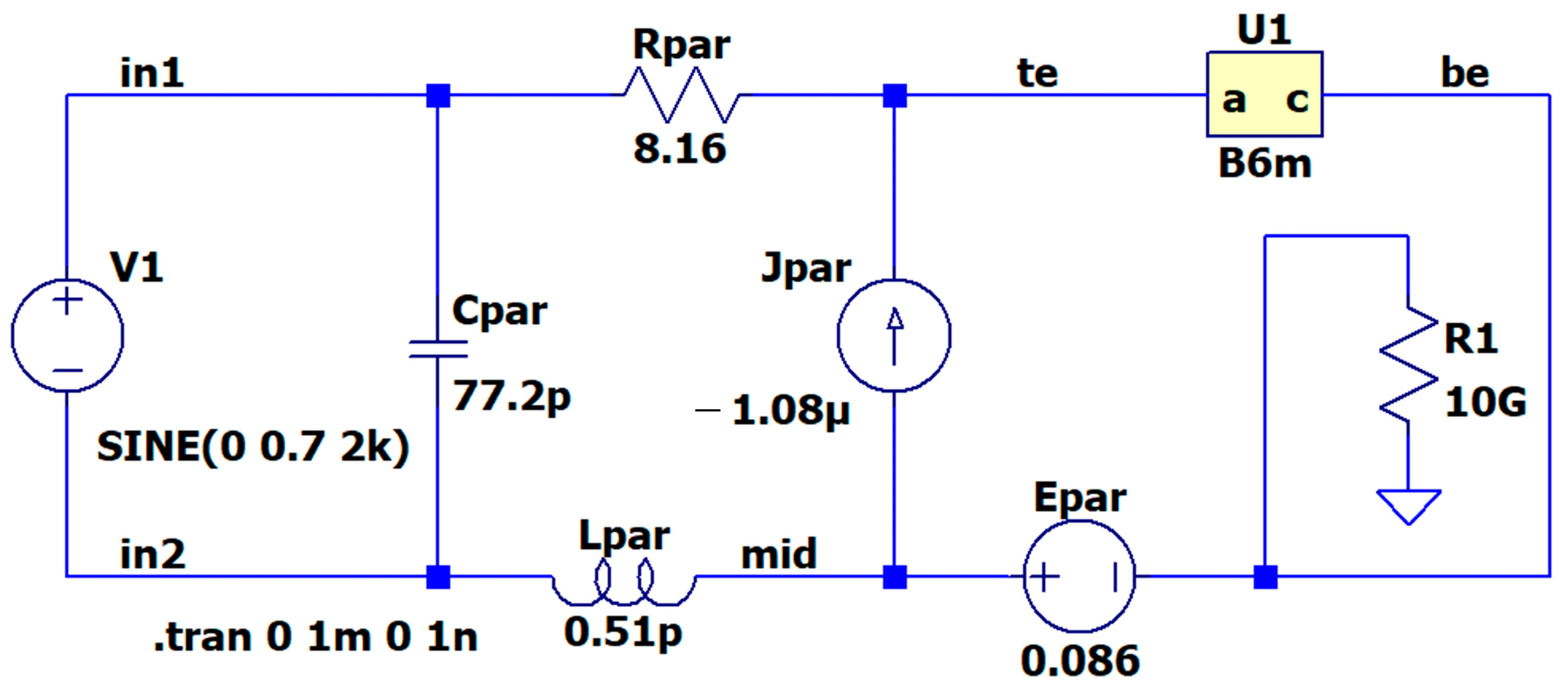
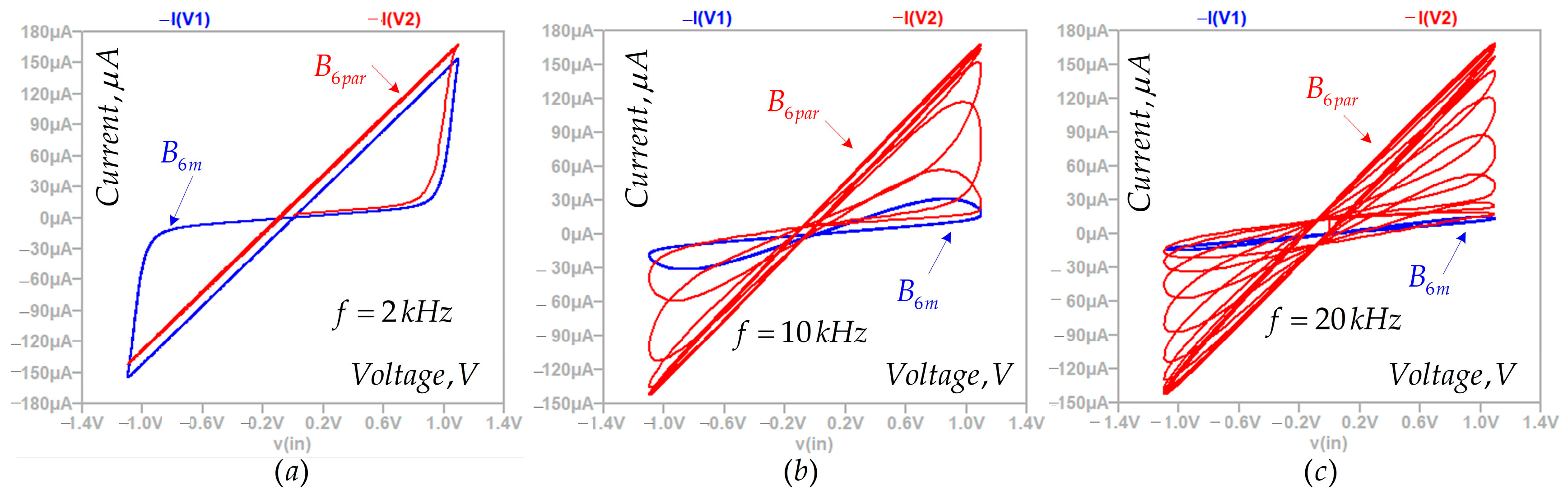
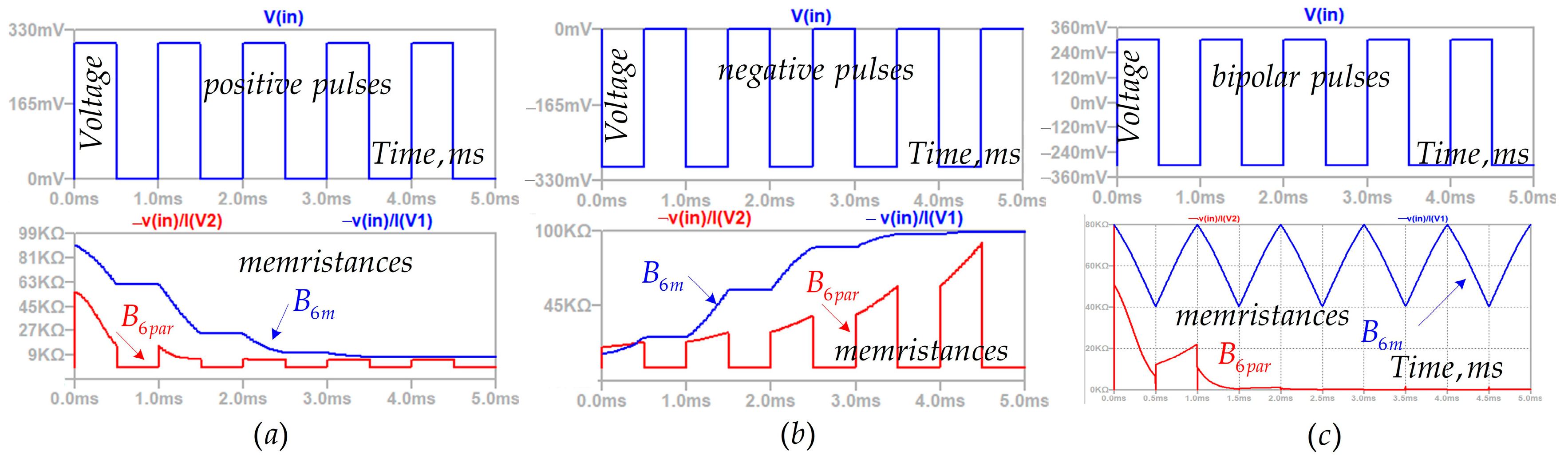
3.3. Generation and Analysis of the Corresponding LTSPICE Memristor Models
- . subckt B6m a c Y
- .params m0=10e3 ron=7077.9 roff=99.915e3 k=132.44e3 vthr=0.1998
- C1 Y 0 {1}
- . IC V(Y)={(roff-m0)/(roff-ron)}
- R1 Y 0 10G
- G2 0 Y value={(k*pow(V(a,c),3)*(V(Y)*(1-V(Y))))*(1/(1+exp(−527.987*(abs(V(a,c))-vthr))))}
- G1 a c value={V(a,c)*((1/(ron*(V(Y))+roff*(1-V(Y)))))}
- .ends B6m
- 9.
- .subckt b6par in1 in2
- 10.
- Cpar in1 in2 77.2p
- 11.
- Rpar te in1 8.16
- 12.
- Lpar mid in2 0.51p
- 13.
- I§Jpar mid te −1.08µ
- 14.
- V§Epar mid be 0.086
- 15.
- XU1 te be B6m
- 16.
- R1 be 0 10G
- 17.
- .lib C:\Users\StoyanKirilov\Desktop\LTSPICE_MODELS\b6m.cir
- 18.
- .backanno
- 19.
- .ends b6par
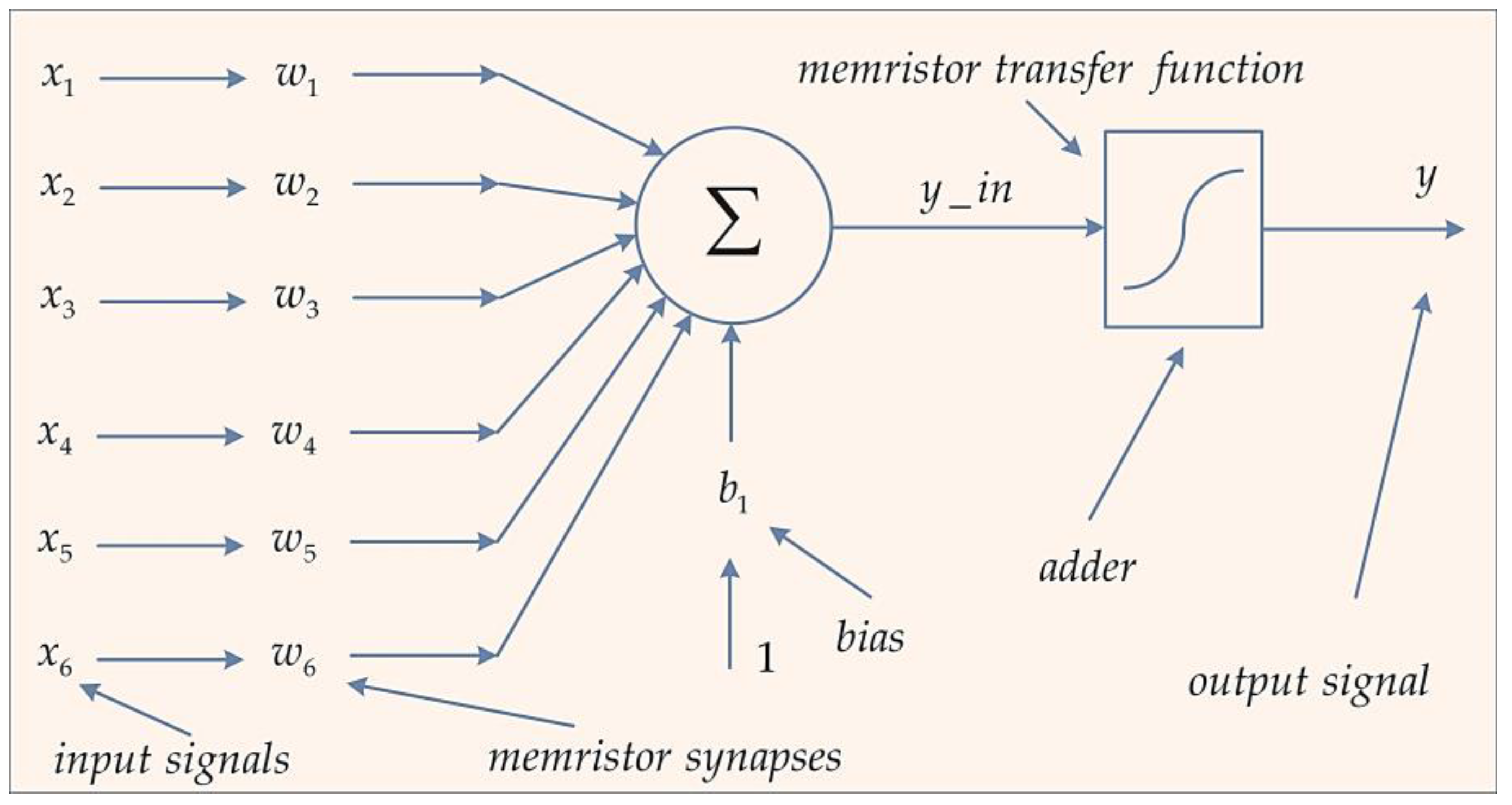
4. The Suggested Memristor-Based Artificial Neuron
4.1. The Structure of a Simple Memristor-Based Artificial Neuron
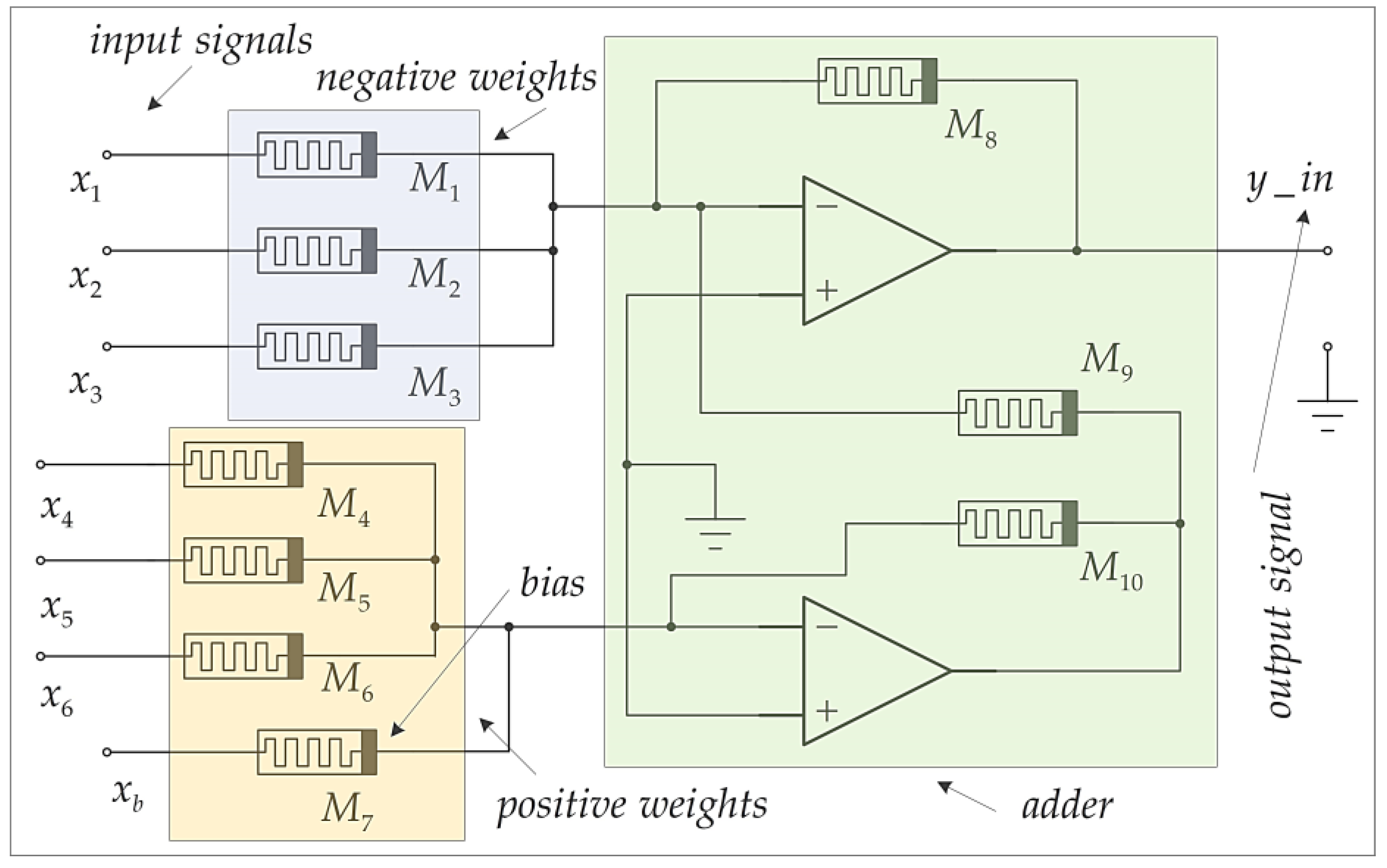
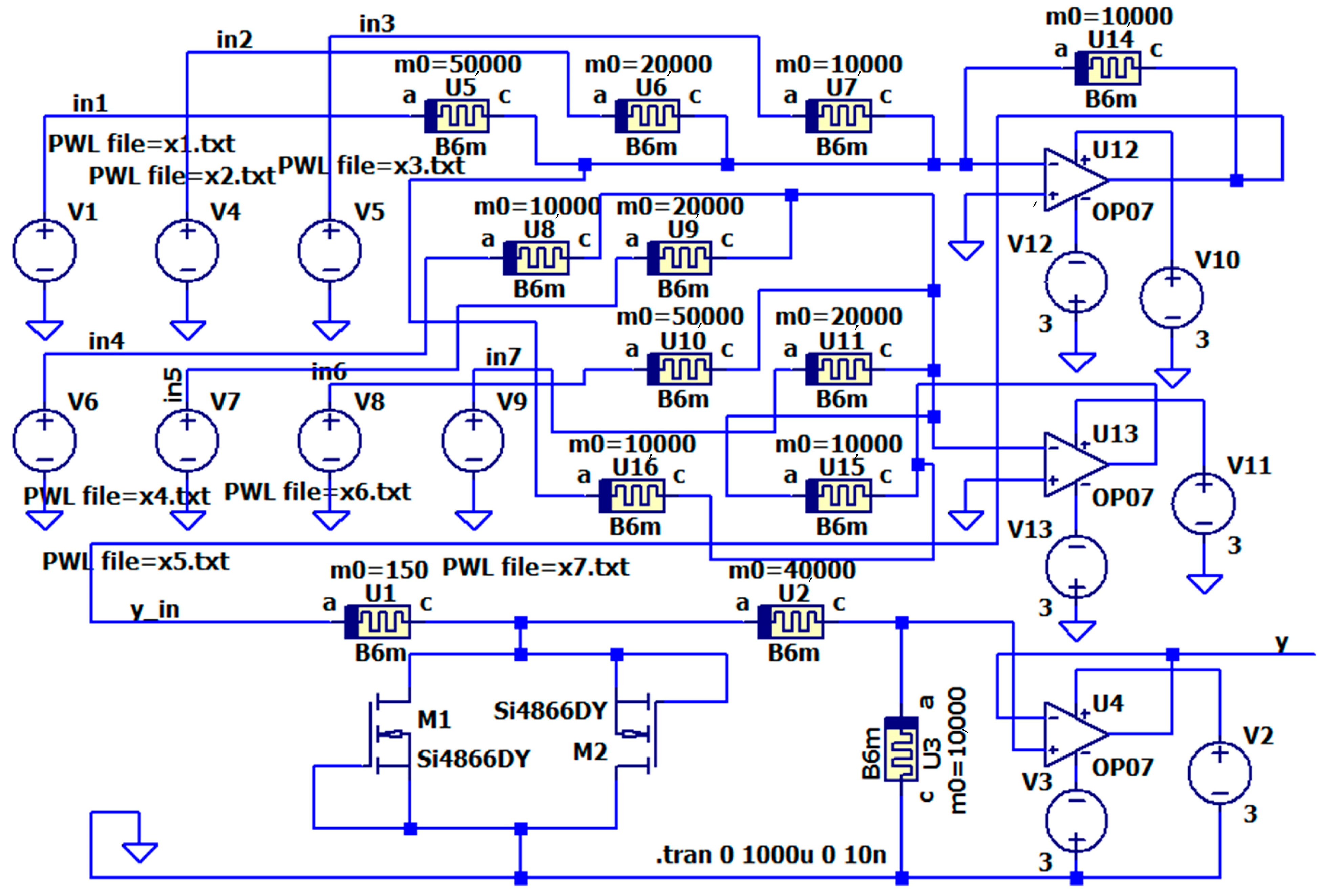
4.2. The Realization of Memristor Adder and Synaptic Connections
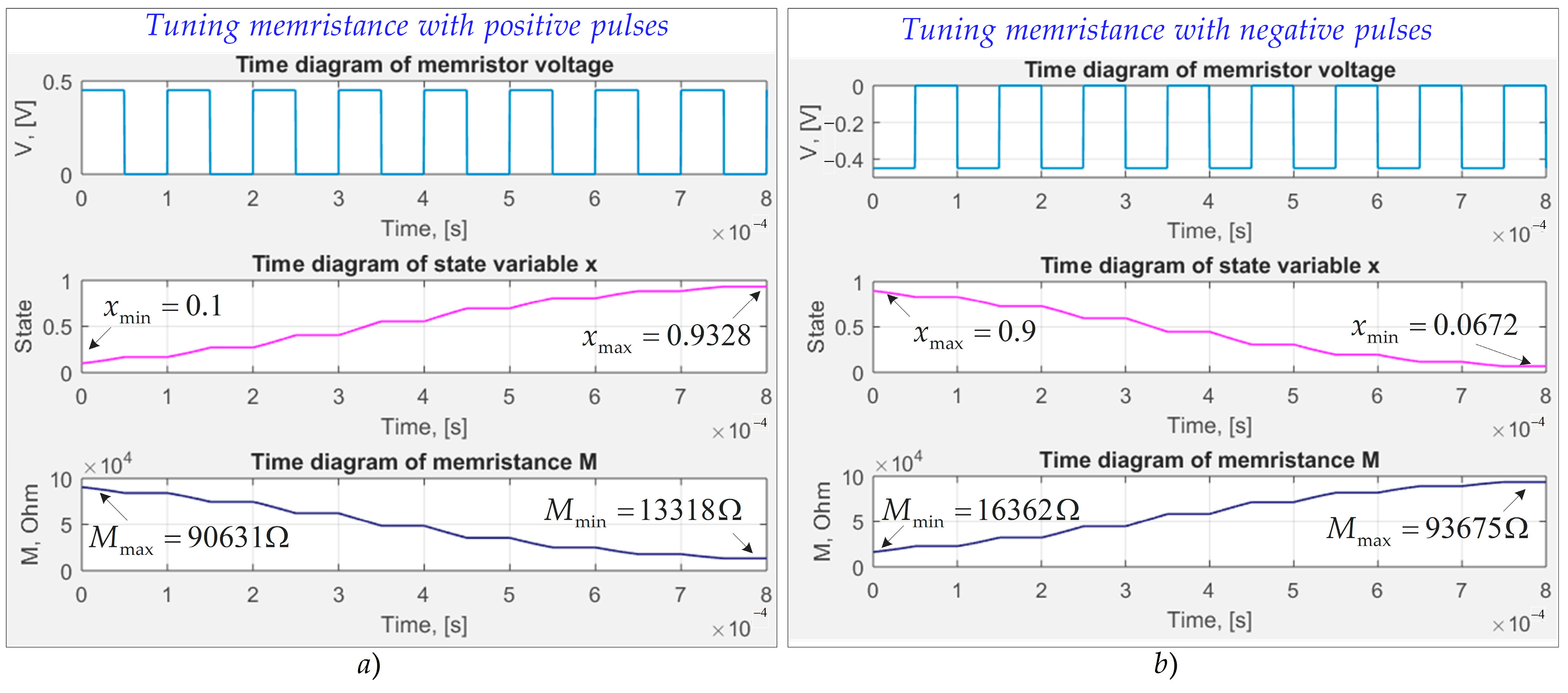
4.3. Synaptic Weights Adjustment
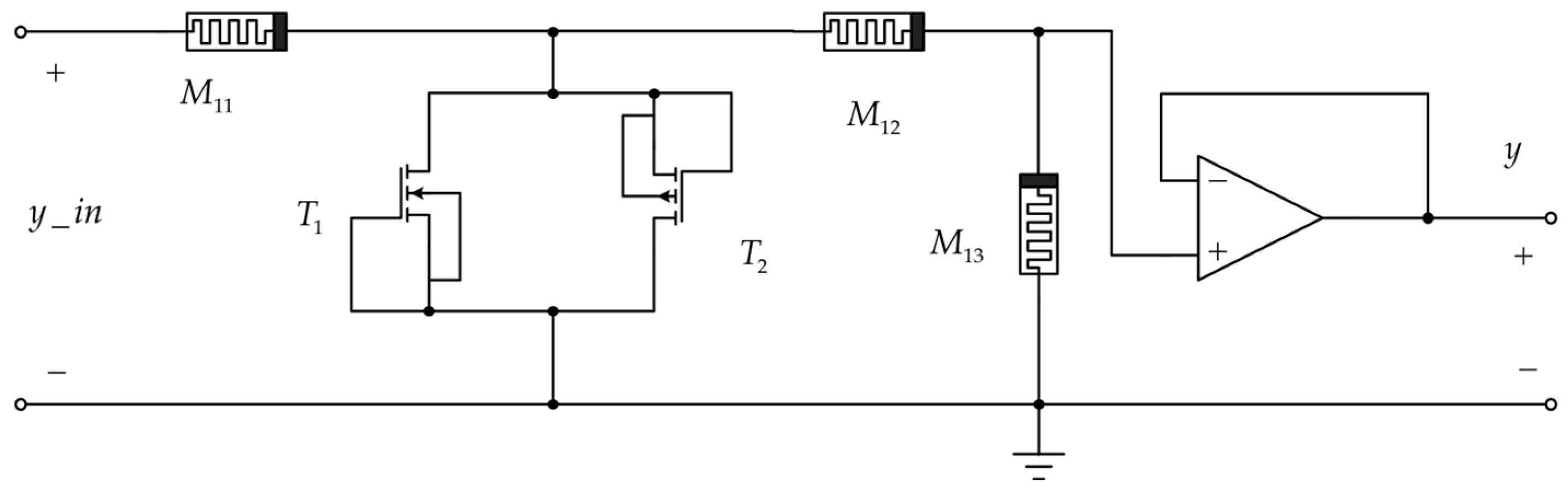
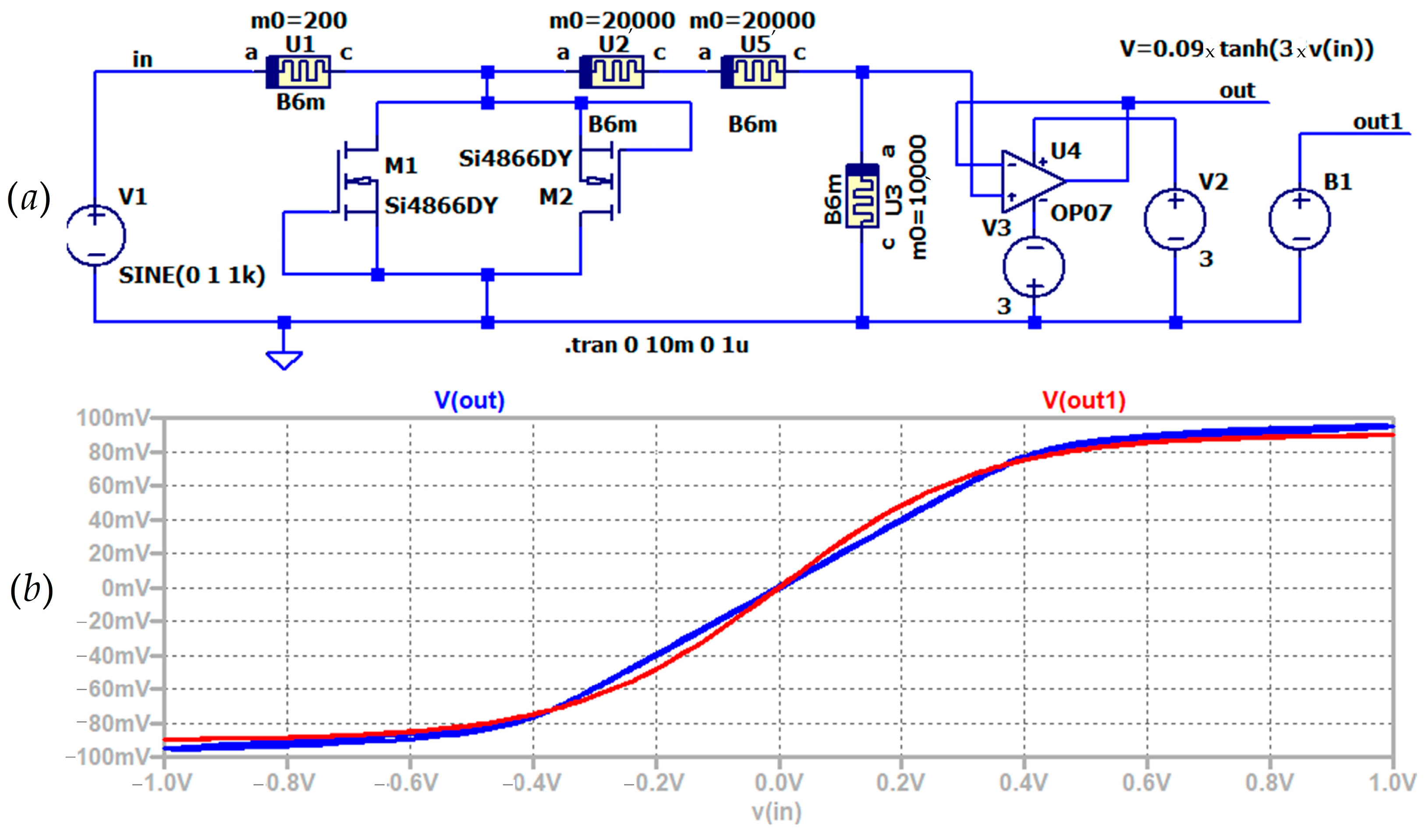
4.4. A Modified Transfer Function, Based on Memristors and MOS Transistors
5. Comparison and Analysis of Derived Results
A Comparison of the Results Derived in MATLAB–Simulink and LTSPICE
6. Discussion [11,13,16]
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MOS | Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Transistor |
| CMOS | Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Technologies |
| KCL | Kirchhoff Current Law |
| KVL | Kirchhoff Voltage Law |
| SPICE | Simulation Program with Integrated Circuits Emphasis |
| LTspice | Linear Technology SPICE software |
| MATLAB | MATrix LABoratory software |
| RAM | Random Access Memory |
| SSD | Solid-State Disk Drive |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| CAD | Computer-Aided Design Software |
| DC | Direct Current components |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
References
- Aggarwal, C. Neural Networks and Deep Learning; Springer International Publishing AG: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; p. 497. ISBN 978-3-319-94463-0. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Yan, X. Advances in memristor-based neural networks. Front. Nanotechnol. 2021, 3, 645995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Zhao, L.; Wang, X. Novel circuit designs of memristor synapse and neuron. Neurocomputing 2019, 330, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Song, L.; Chen, W.; Wang, G.; Hao, E.; Li, C.; Hu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Nathan, A.; Hu, G.; et al. Memristor-Based Intelligent Human-Like Neural Computing. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2023, 9, 2200877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strukov, D.B.; Snider, G.S.; Stewart, D.R.; Williams, S. The missing memristor found. Nature 2008, 453, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirilov, S.; Mladenov, V. A Simple LTSPICE Memristor Neuron with a Modified Transfer Function. In Proceedings of the 2024 13th International Conference on Modern Circuits and Systems Technologies (MOCAST), Sofia, Bulgaria, 28–30 June 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.P.; Yang, C.; Kim, H.; Chua, L.O. Memristor bridge synapse-based neural network and its learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2012, 23, 1426–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, S.; Xie, X.; Yan, Z.; Huang, T.; Zeng, Z. General memristor with applications in multilayer neural networks. Neural Netw. 2018, 103, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biolek, Z.; Biolek, D.; Biolkova, V. SPICE Model of Memristor with Nonlinear Dopant Drift. Radioengineering 2009, 18, 210–214. [Google Scholar]
- Kolka, Z.; Biolkova, V.; Biolek, D. Simplified SPICE model of TiO2 Memristor. In Proceedings of the International Conference MEMRISYS, Paphos, Cyprus, 8–10 November 2015; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Mladenov, V. A Unified and Open LTSPICE Memristor Model Library. MDPI Electron. 2021, 10, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyeva, E.B.; Azarov, V.A. Comparative Analysis of Memristor Models with a Window Function Described in LTspice. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Conference of Russian Young Researchers in Electrical and Electronic Engineering (ElConRus), Moscow, Russia, 26–29 January 2021; pp. 1097–1101. [Google Scholar]
- Dautovic, S.; Samardzic, N.; Juhas, A.; Ascoli, A.; Tetzlaff, R. Simscape and LTspice models of HP ideal generic memristor based on finite closed form solution for window functions. In Proceedings of the 2021 ICECS Conference, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 28 November–1 December 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sah, M.P.; Yang, C.; Kim, H.; Muthuswamy, B.; Jevtic, J.; Chua, L. A generic model of memristors with parasitic components. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 2015, 62, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsenov, G.T.; Kirilov, S.; Mladenov, V. SPICE memristor model based on estimate from measured data. COMPEL—Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. [CrossRef]
- Ascoli, A.; Tetzlaff, R.; Biolek, Z.; Kolka, Z.; Biolkova, V.; Biolek, D. The Art of Finding Accurate Memristor Model Solutions. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circ. Syst. 2015, 5, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, D.A.; Joujou, M.K.; Khaddaj, S.I.; Kabalan, K.Y. A learning approach to circuitry problems using MATLAB and PSPICE. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON), Marrakech, Morocco, 17–20 April 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, K.A. Self-directed channel memristor for high temperature operation. Microelectron. J. 2017, 59, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarz, K.; Garda, B. Measurement and Modeling of Self-Directed Channel (SDC) Memristors: An Extensive Study. Energies 2017, 17, 5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtonen, E.; Laiho, M. CNN using memristors for neighborhood connections. In Proceeding of the Conference CNNA, Berkeley, CA, USA, 3–5 February 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Joglekar, Y.N.; Wolf, S.J. The elusive memristor: Properties of basic electrical circuits. Eur. J. Phys. 2009, 30, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodromakis, T.; Peh, B.P.; Papavassiliou, C.; Toumazou, C. A versatile memristor model with nonlinear dopant kinetics. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2011, 58, 3099–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharab, A.; Guenther, R. An Introduction to Numerical Methods: A MATLAB® Approach; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; p. 631. ISBN 9781315107042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P. Matlab Deep Learning. In With Machine Learning, Neural Networks and Artificial Intelligence; APress: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-14842-28456. [Google Scholar]
- Zhevnenko, D.A.; Meshchaninov, F.P.; Kozhevnikov, V.S.; Shamin, E.S.; Telminov, O.A.; Gornev, E.S. Research and Development of Parameter Extraction Approaches for Memristor Models. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shooshtari, M.; Kim, S.Y.; Pahlavan, S.; Rivera-Sierra, G.; Través, M.J.; Serrano-Gotarredona, T.; Bisquert, J.; Linares-Barranco, B. Advancing Logic Circuits With Halide Perovskite Memristors for Next-Generation Digital Systems. SmartMat 2025, 6, e70032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slipko, V.A.; Pershin, Y.V.; Di Ventra, M. Changing the state of a memristive system with white noise. Phys. Rev. E—Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2023, 87, 042103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Han, J.E.; Beckmann, K.; Cady, N.; Sambandamurthy, G. Noise Spectroscopy and Electrical Transport In NbO2 Memristors with Dual Resistive Switching. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2025, 11, 2400877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
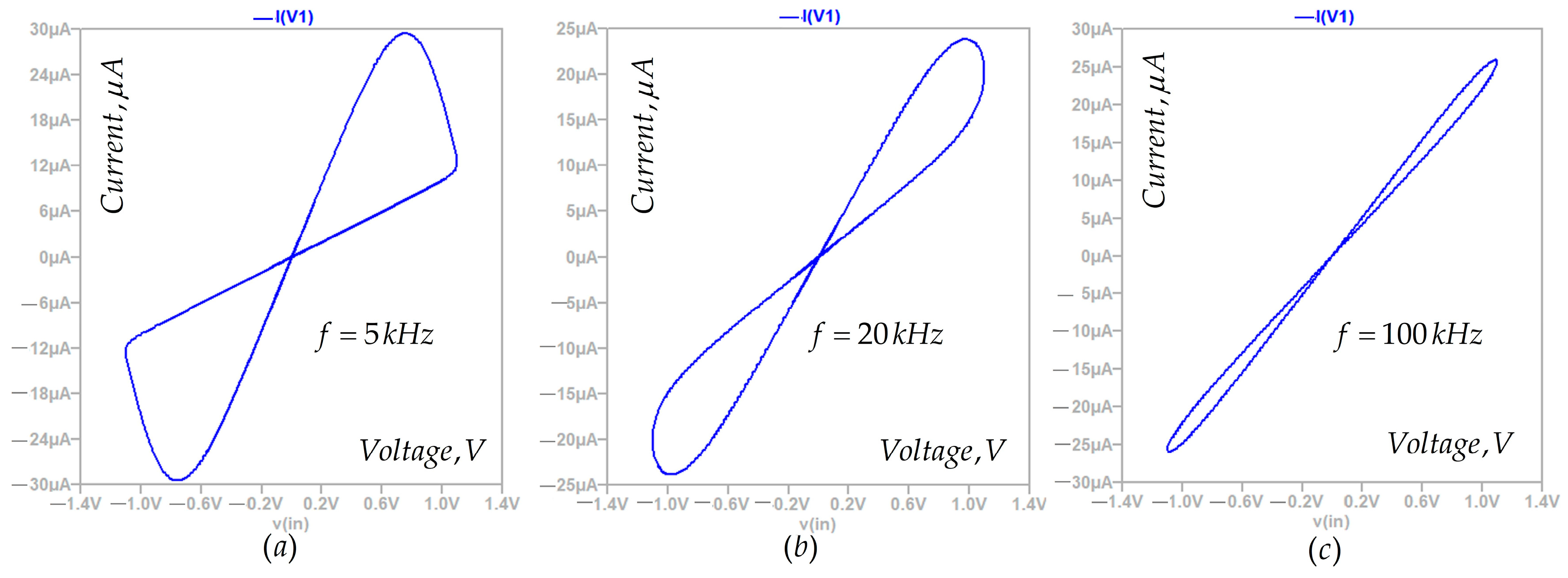
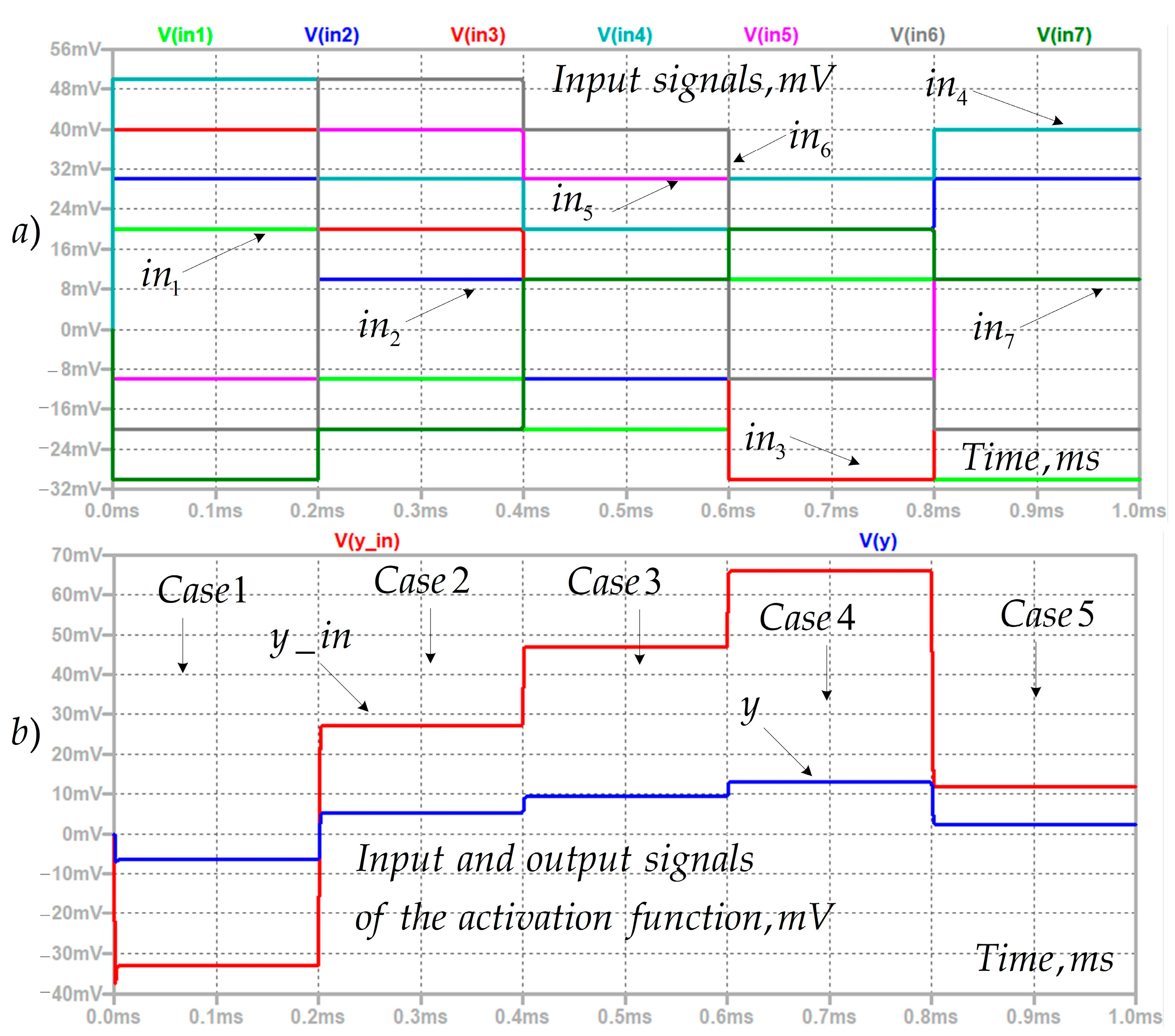
| Case | vin1, mV | vin2, mV | vin3, mV | vin4, mV | vin5, mV | vin6, mV | vb, mV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | −10 | −20 | −30 |
| II | −10 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | −20 |
| III | −20 | −10 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 10 |
| IV | 10 | 20 | −30 | 30 | 20 | −10 | 20 |
| V | −30 | 30 | 10 | 40 | −20 | −20 | 10 |
| Synapse | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | −0.2 | −0.5 | −1 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.5 |
| M, kΩ | 50 | 20 | 10 | 10 | 20 | 50 | 20 |
| Case | Y_in MATLAB–Simulink mV | Y_in LTSpice mV | Relative Error Between Y_in MATLAB and Y_in LTSPICE, % | Y MATLAB–Simulink, mV | Y LTSpice mV | Relative Error Between Y MATLAB and Y_in LTSPICE, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | −33 | −33.03 | 0.091 | −8.88 | −8.57 | 3.49 |
| II | 37 | 37.4 | 1.08 | 7.27 | 7.4 | 1.79 |
| III | 47 | 47 | 0 | 12.6 | 11.89 | 5.63 |
| IV | 66 | 66 | 0 | 17.6 | 17.16 | 2.5 |
| V | 12.2 | 12 | 1.67 | 3.24 | 3.1 | 4.32 |
| Synapse | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial values of the synaptic weights | −0.2 | −0.5 | −1 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.5 |
| Initial values of the memristances, kΩ | 50 | 20 | 10 | 10 | 20 | 50 | 20 |
| Weights achieved according to model B6m | −0.23 | −0.68 | −1.45 | 1.45 | 0.68 | 0.23 | 0.68 |
| Memristances according to model B6m, kΩ | 43.9 | 14.6 | 6.9 | 6.9 | 14.6 | 43.9 | 14.6 |
| Weights achieved according to model B6par | −0.21 | −0.52 | −1.52 | 1.52 | 0.52 | 0.21 | 0.52 |
| Memristances according to model B6par, kΩ | 47.8 | 19.1 | 6.6 | 6.6 | 19.1 | 47.8 | 19.1 |
| Memristor Model | Complexity | Accuracy | Operating Frequency | Switching Properties | Simulation Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K3 [9] | low | average | average | satisfactory | 14.7 ms |
| K5 [20] | high | high | high | good | 17.2 ms |
| Knowm [18,19] | high | high | high | good | 17.9 ms |
| B6m [6] | low | high | high | good | 16.1 ms |
| B6par | high | average | average | satisfactory | 17.7 ms |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kirilov, S.; Mladenov, V. LTSPICE Memristor Neuron with a Modified Transfer Function Based on Memristor Model with Parasitic Parameters. Electronics 2025, 14, 4645. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14234645
Kirilov S, Mladenov V. LTSPICE Memristor Neuron with a Modified Transfer Function Based on Memristor Model with Parasitic Parameters. Electronics. 2025; 14(23):4645. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14234645
Chicago/Turabian StyleKirilov, Stoyan, and Valeri Mladenov. 2025. "LTSPICE Memristor Neuron with a Modified Transfer Function Based on Memristor Model with Parasitic Parameters" Electronics 14, no. 23: 4645. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14234645
APA StyleKirilov, S., & Mladenov, V. (2025). LTSPICE Memristor Neuron with a Modified Transfer Function Based on Memristor Model with Parasitic Parameters. Electronics, 14(23), 4645. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14234645







