Model-Free Current Controller for PMSM Based on Super-Twisting Sliding Mode Observer
Abstract
1. Introduction
- An ultralocal model is adopted to replace the traditional motor model, enabling model-free deadbeat control without relying on the motor model;
- An observer based on the super-twisting sliding mode algorithm is designed to estimate disturbances and predict currents, thereby enhancing the dynamic performance of current control and improving robustness to variations in electromagnetic parameters;
- A coefficient-adaptive method based on deadbeat current tracking is proposed to ensure rapid optimization when controller coefficients deviate from actual parameters, thereby eliminating dependence on inductance parameters.
2. Modeling of the PMSM
3. Traditional Deadbeat Predictive Current Controller
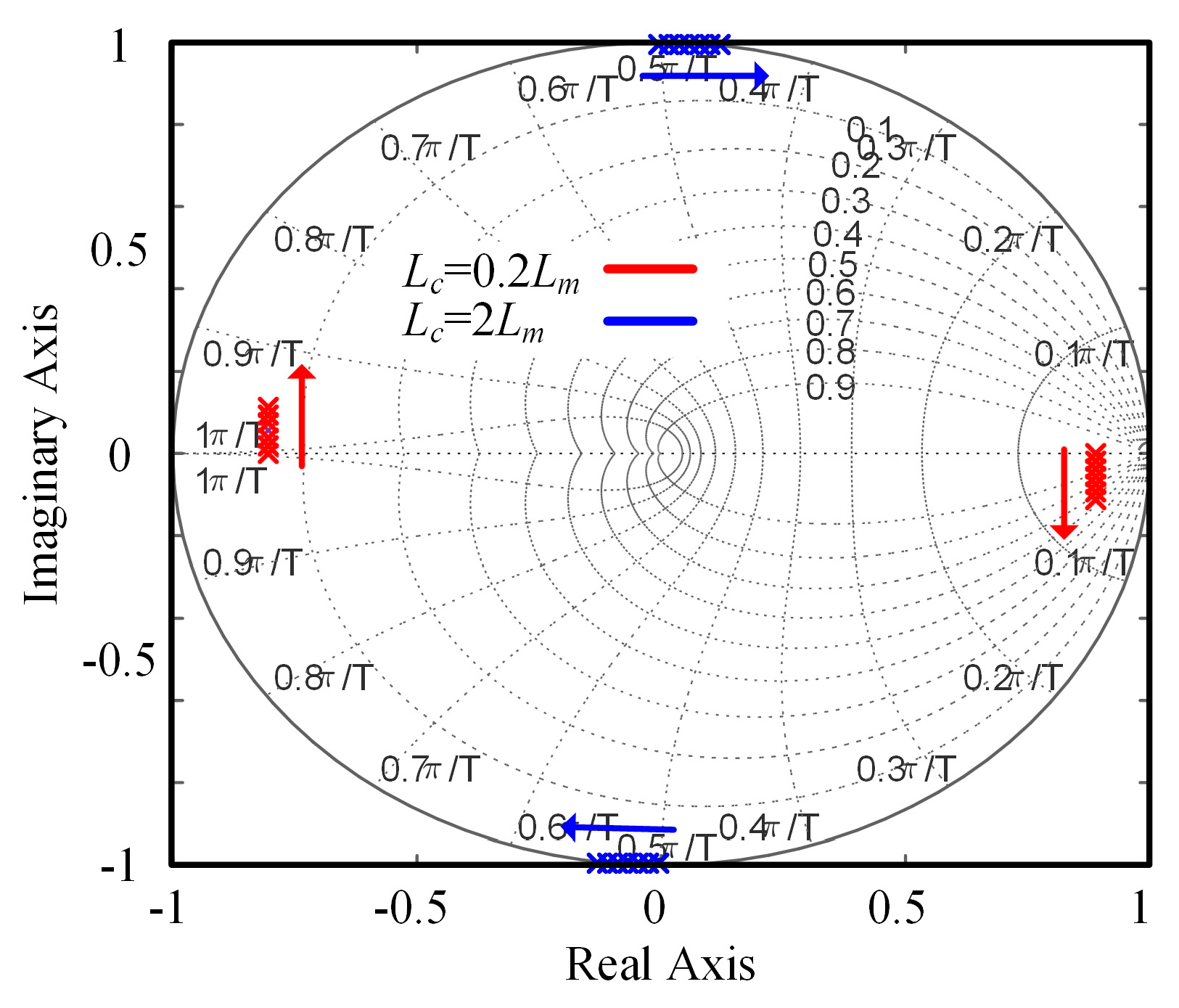
- When the controller inductance parameter is smaller than the actual inductance, the closed-loop poles deviate from the origin, resulting in a stable system but with degraded dynamic performance;
- When the controller inductance parameter is larger than the actual inductance, as the rotational speed increases, the closed-loop poles move closer to the boundary, leading to deteriorating stability;
- When the inductance parameter error exceeds twice the actual value, the system becomes unstable.
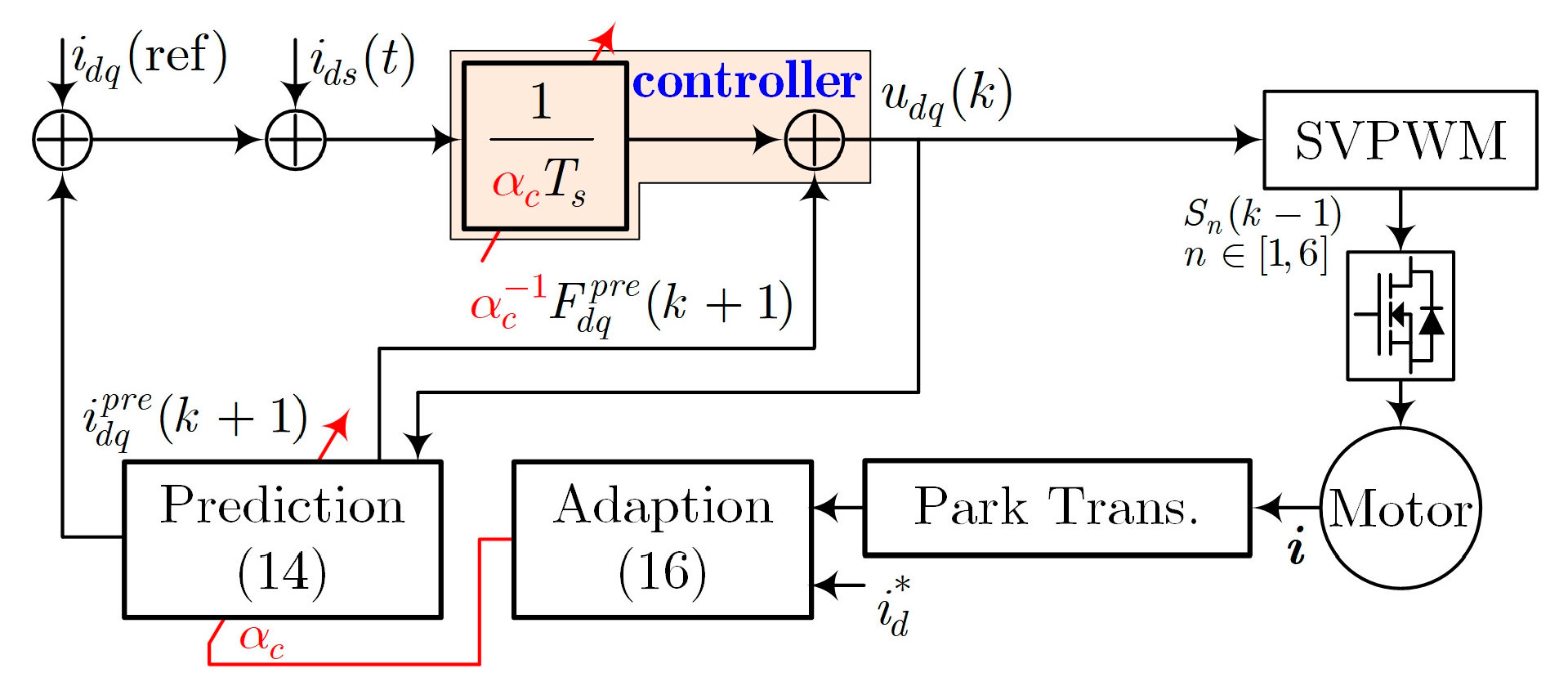
4. Proposed ST-MFCC
4.1. MFCC
4.2. Super-Twisting Sliding Mode Observer
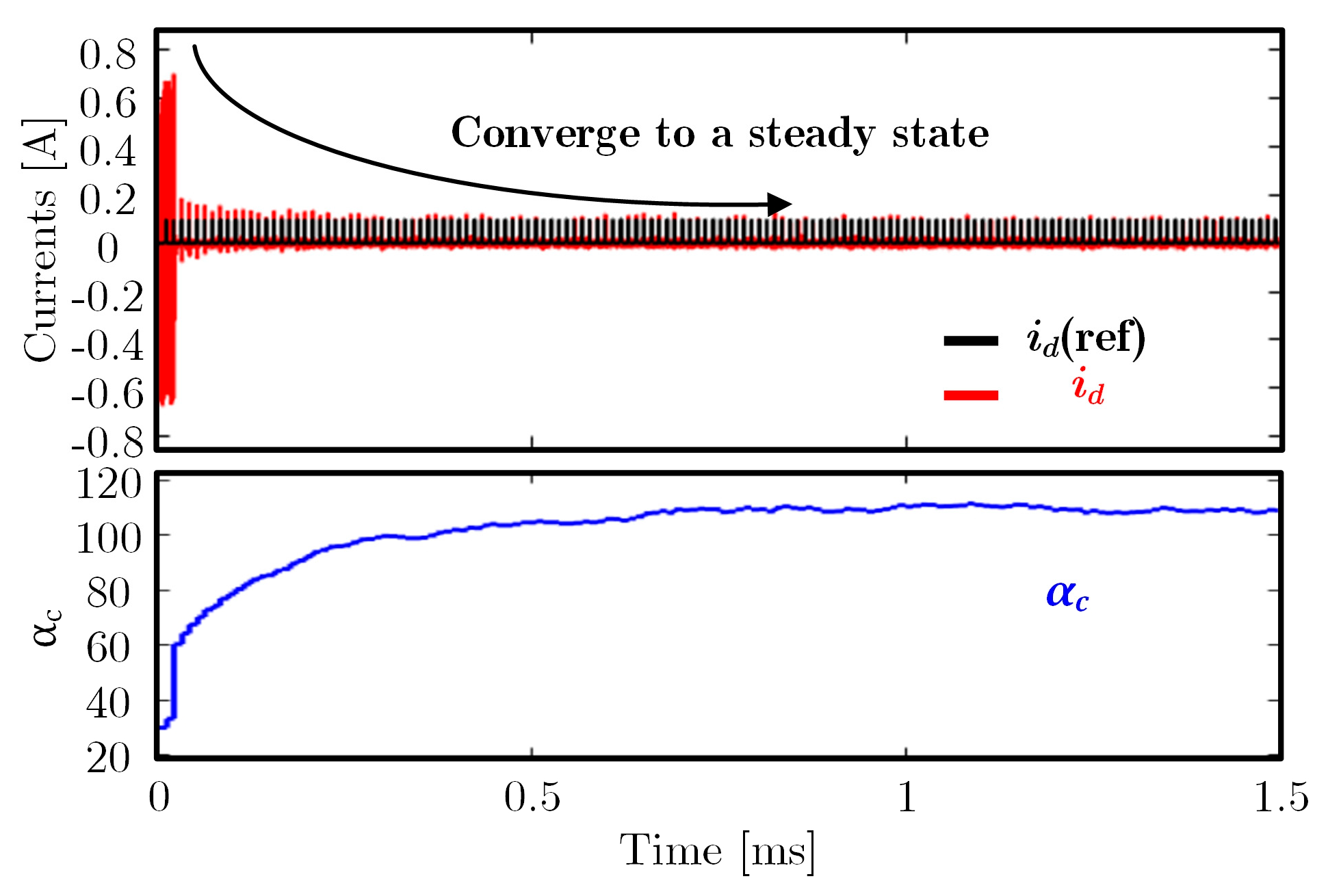
4.3. Adaption of the Coefficient
- When αc is greater than αm, the sampled current at k + 2 exceeds the reference value at k, resulting in overshoot;
- When αc is less than αm, the sampled current at k + 2 is less than the reference value at k, preventing fast tracking;
- When and only when αc equals αm, the sampled current at k + 2 equals the reference value at k, achieving deadbeat current control.
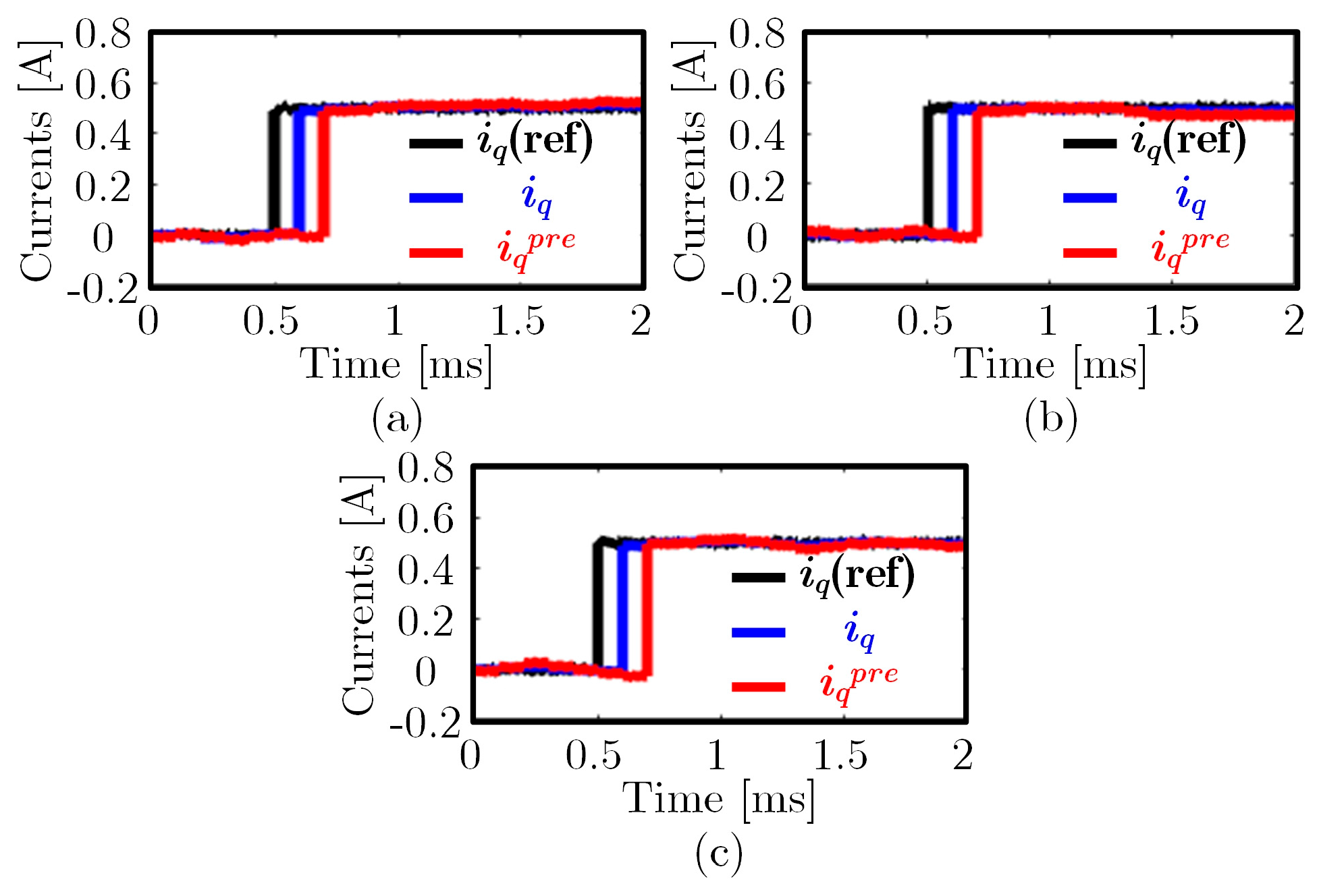
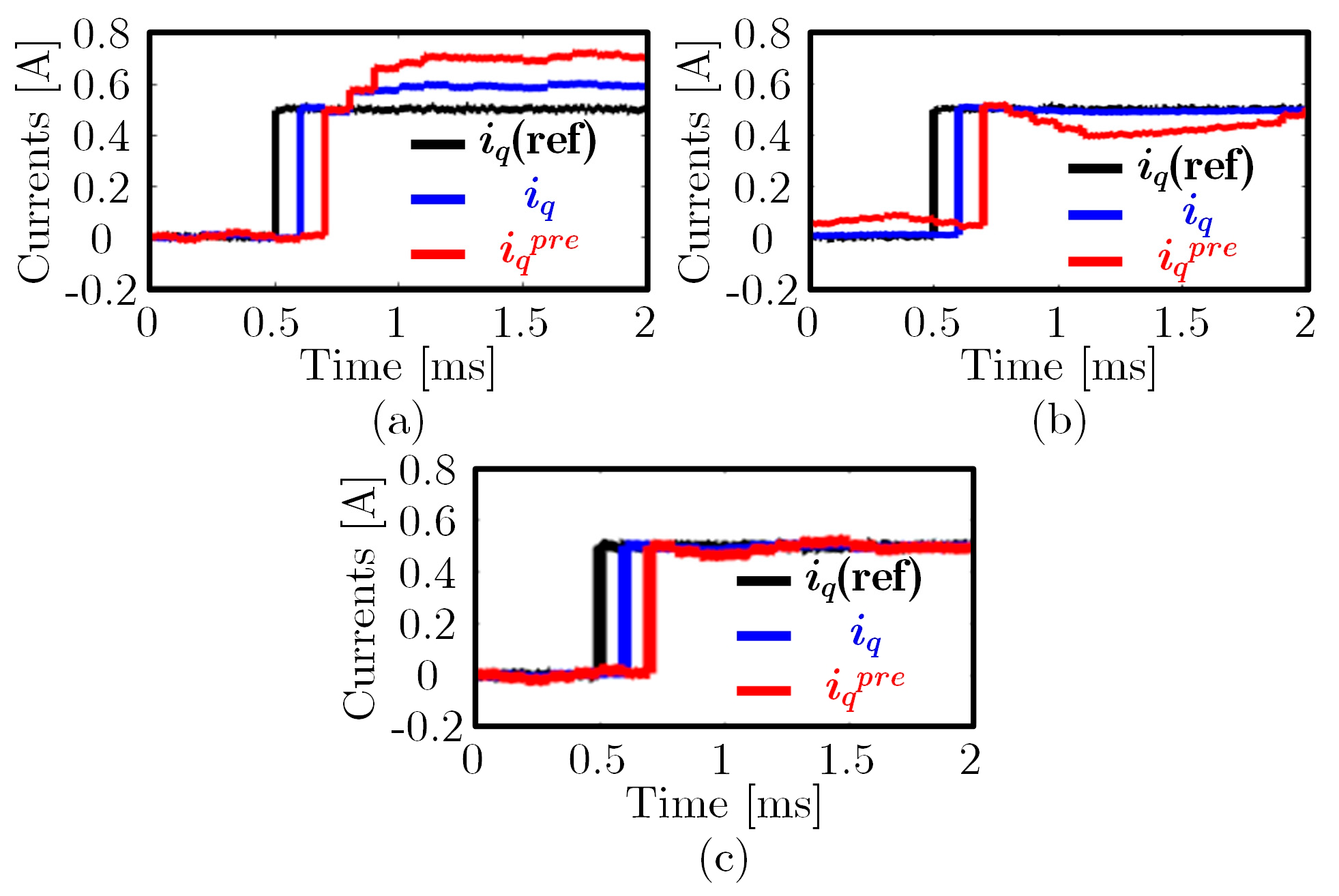
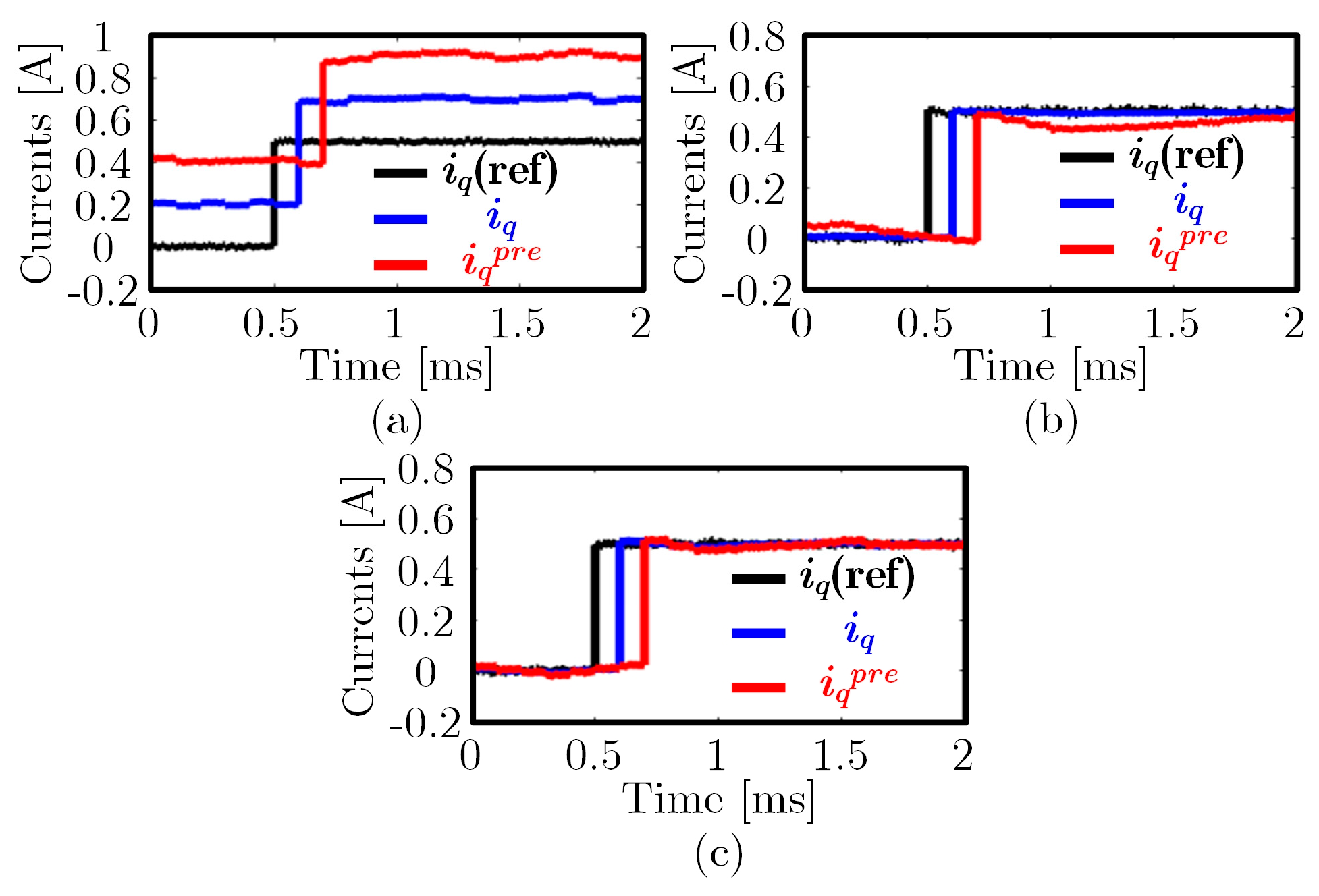
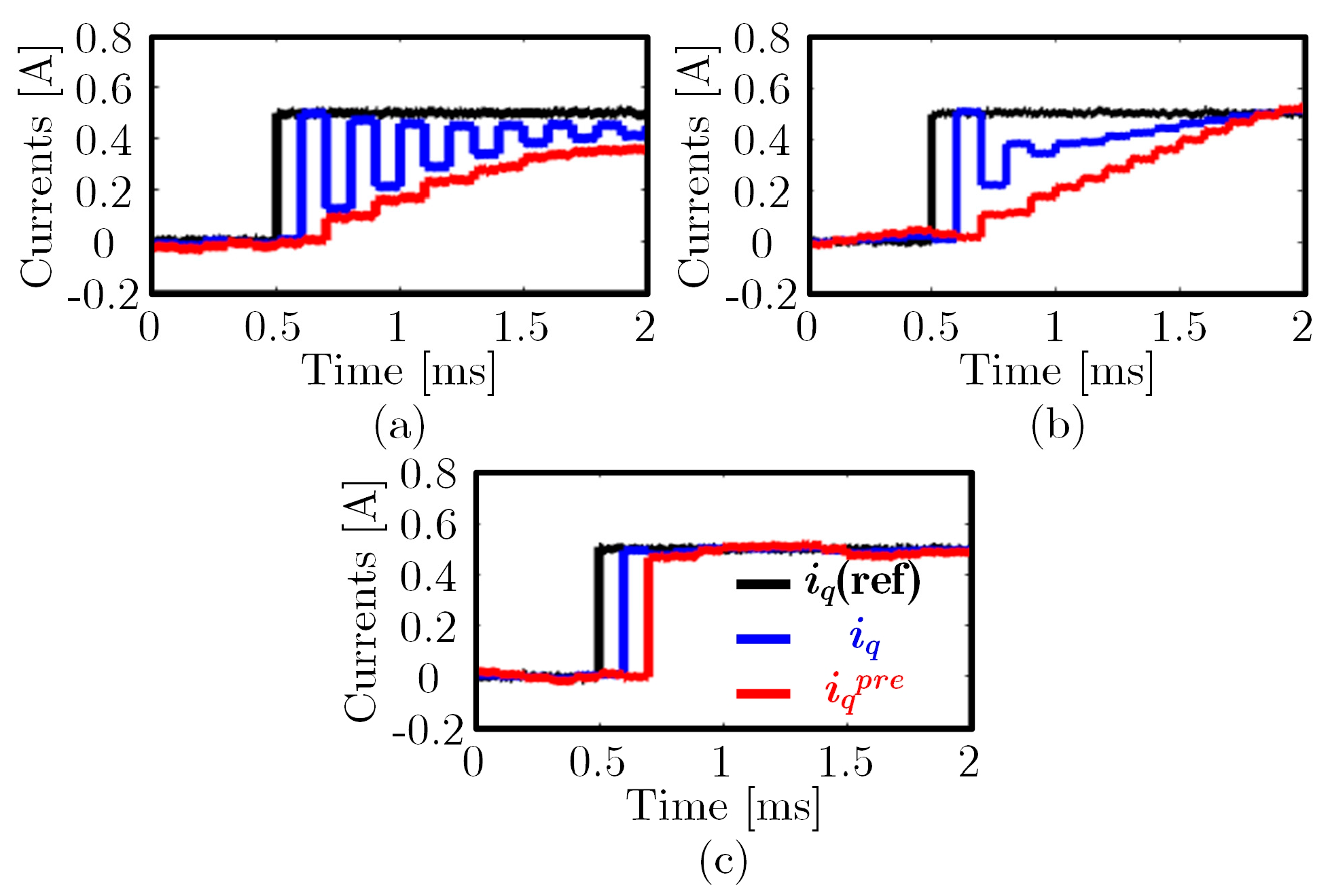
5. Experimental Results
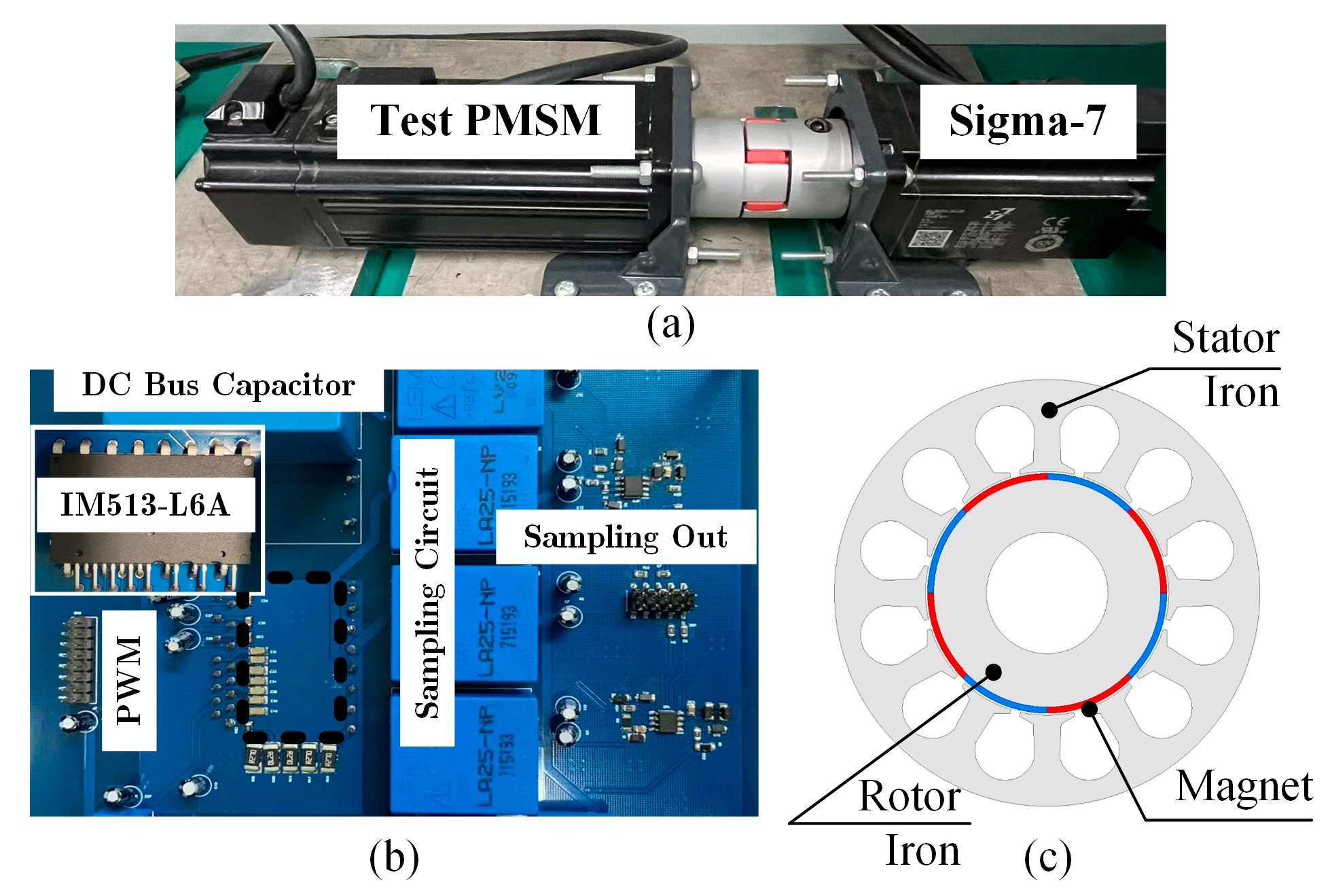
5.1. Introduction to the Experimental Platform
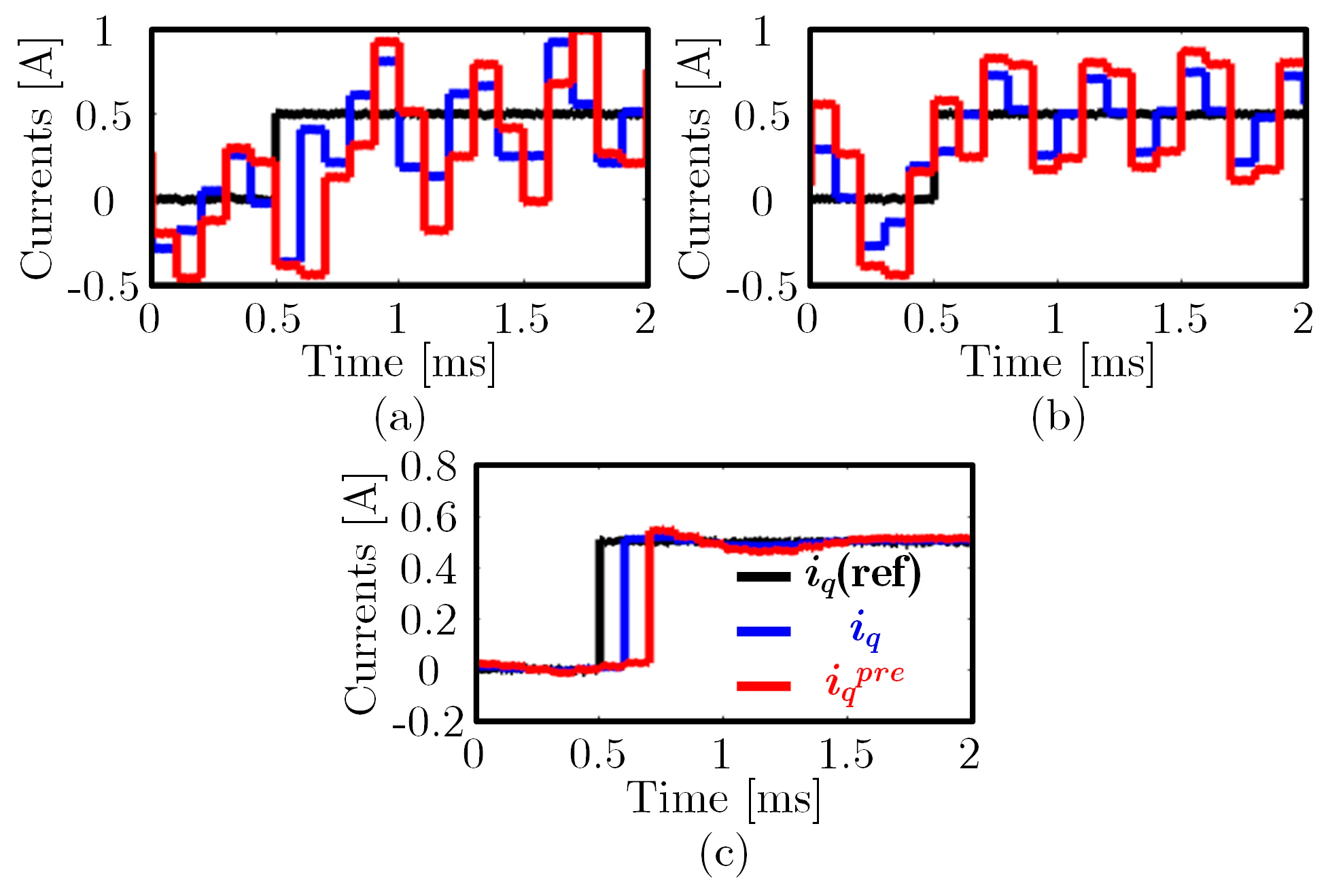
5.2. Experimental Comparison
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, M.; Gardner, M.C.; Toliyat, H.A. Design and Analysis of an Axial Flux Magnetically Geared Generator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Nakamura, K. Investigation of Magnetic Interaction of IPM-Type Magnetic-Geared Motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2021, 57, 8202005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Fan, Y.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Q. Parameter-Free Ultralocal Model-Based Deadbeat Predictive Current Control for PMVMs Using Finite-Time Gradient Method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 5549–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Kennel, R.M.; Espinoza, J.; Trincado, M.; Silva, C.A.; Rojas, C.A. High-Performance Control Strategies for Electrical Drives: An Experimental Assessment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Fan, Y.; Wang, W.; Lee, C.H.T.; Wang, Y. Sensorless Control for SynRM Drives Using a Pseudo-Random High-Frequency Triangular-Wave Current Signal Injection Scheme. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 7122–7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liang, J. A New Reaching Law for Antidisturbance Sliding-Mode Control of PMSM Speed Regulation System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 4117–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNabb, L.; Wang, L. An Improved Horizon-1 Finite-Control-Set Model-Predictive Current Control Design for an Induction Machine with Integrated Anti-Windup. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2023, 31, 985–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Kazmierkowski, M.P.; Espinoza, J.R.; Zanchetta, P.; Rub, H.A.; Young, H.A. State of the Art of Finite Control Set Model Predictive Control in Power Electronics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2013, 9, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liao, W.; Huang, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, M.; Li, C.; Huang, S. A Robust DPCC for IPMSM Based on a Full Parameter Identification Method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 7695–7705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, H. Two-Vector-Based Model Predictive Torque Control Without Weighting Factors for Induction Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 1381–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siami, M.; Khaburi, D.A.; Rodriguez, J. Torque Ripple Reduction of Predictive Torque Control for PMSM Drives with Parameter Mismatch. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 7160–7168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Chen, J. Improved Model-Free Deadbeat Predictive Current Controller for PMSMs Based on Ultralocal Model and H∞ Norm. Energies 2024, 17, 2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Fan, Y.; Mao, C. A Gain Design Method for a Linear Extended State Observers to Improve Robustness of Deadbeat Control. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 2231–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Wang, M.; Song, Z.; Liu, T. Robust Model Predictive Current Control of Three-Phase Voltage Source PWM Rectifier with Online Disturbance Observation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2012, 8, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, S.; Zou, J. Integral sliding mode control based deadbeat predictive current control for PMSM drives with disturbance rejection. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 2845–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhou, L.; Gao, W.; Wang, H.; Yang, C. Model-Free Coordinated Optimal Regulation for Rigidly Connected Dual-PMSM Systems via Adaptive Dynamic Programming. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2025, 12, 2138–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, S.; Huang, D. An Improved Model-Free Active Disturbance Rejection Deadbeat Predictive Current Control Method of PMSM Based on Data-Driven. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 9606–9616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, R.; Mao, J. Model-free control of surface mounted PMSM drivesystem. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, M.S.; Davari, S.A.; Nekoukar, V.; Garcia, C.; Rodriguez, J. A Robust Torque and Flux Prediction Model by a Modified Disturbance Rejection Method for Finite-Set Model-Predictive Control of Induction Motor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 9322–9333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fliess, M.; Join, C. Model-free control. Int. J. Control 2013, 86, 2228–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, L.; Xiong, L.; Zhou, Y.; Gou, F.; Huang, W. Hierarchical Robustness Strategy Combining Model-Free Prediction and Fixed-Time Control for Islanded AC Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2025, 16, 4380–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Huang, S.; Li, P.; Wang, Z.; Khan, M.W.; Niu, T. Hidden Markov Jump System Based Robust Control of Inverter-Fed Power Systems with Asynchronous Sliding Mode Observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2025; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levant, A. Sliding order and sliding accuracy in sliding mode control. Int. J. Control 1993, 58, 1247–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Li, J.; Qu, R.; Kong, W. Adaptive Second-Order Sliding-Mode Observer for PMSM Sensorless Control Considering VSI Nonlinearity. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 8994–9004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| (k + n)th, n = | 0 | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| id(ref) | 0 | 0 | |
| id(k) | 0 | 0 | (αm/αc) |
| Stator Resistance Rm | Inductance Lm | Sampling Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 1.6 Ω | 9 mH | 10 k |
| Permanent Magnet Flux ψm | Pole Pairs pn | Control Frequency |
| 0.006 Wb | 4 | 10 k |
| Parameter | DPCC | SMO-DPCC | ST-MFCC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step Time | accurate | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Rc = 10Rm | DC Bias | 2 | 2 | |
| ψc = 10ψm | DC Bias | 2 | 2 | |
| Lc = 0.2Lm | >15 | 15 | 2 | |
| Lc = 3Lm | Unstable | Unstable | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Chen, J. Model-Free Current Controller for PMSM Based on Super-Twisting Sliding Mode Observer. Electronics 2025, 14, 4542. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224542
Wang Y, Chen J. Model-Free Current Controller for PMSM Based on Super-Twisting Sliding Mode Observer. Electronics. 2025; 14(22):4542. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224542
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yining, and Junlei Chen. 2025. "Model-Free Current Controller for PMSM Based on Super-Twisting Sliding Mode Observer" Electronics 14, no. 22: 4542. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224542
APA StyleWang, Y., & Chen, J. (2025). Model-Free Current Controller for PMSM Based on Super-Twisting Sliding Mode Observer. Electronics, 14(22), 4542. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224542






