Integrated Soft-Sensor Model for Wastewater Treatment Process with Collaborative Calibration Strategy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
3. Self-Organizing Fuzzy Neural Network with Feature Extraction Layer
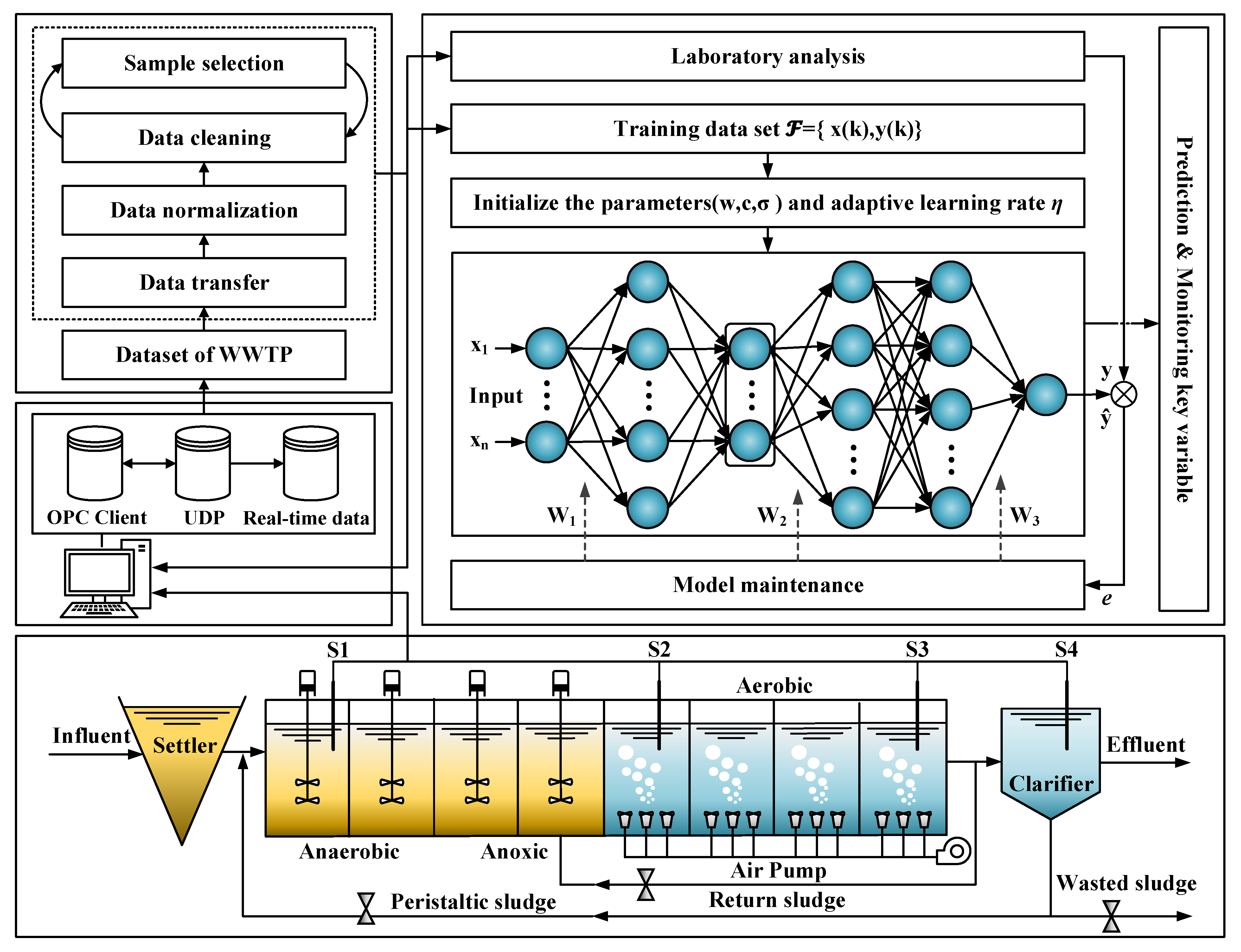
3.1. Framework of Integrated Soft-Sensor
3.1.1. Data Acquisition
3.1.2. Data Preprocessing
3.1.3. Model Design
3.1.4. Model Maintenance
3.2. Feature-Based Fuzzy Neural Network
3.2.1. Feature Extraction Method
| Algorithm 1: The variable selection method. |
| 1: Input: Dataset: ; 2: Output: Optimal feature set X; 3: Set ← “Network trained with dataset A” 4: for k = m down to 1 5: For each compute , Equation (11), and let ; 6: X ← , “Remove variable that has the lowest ”; 7: Set ← “Network updated by removing the input and adjusting the remaining weights according to Equation (12), and ”. 8: Calculate the mutual information of X and C; 9: If “Control the amount of feature selection by threshold ”; break; 10: Return the feature subset X as the selected subset; |
3.2.2. Self-Organizing Mechanism
3.3. Collaborative Optimization Algorithm
4. Simulation Studies
4.1. Experimental Settings
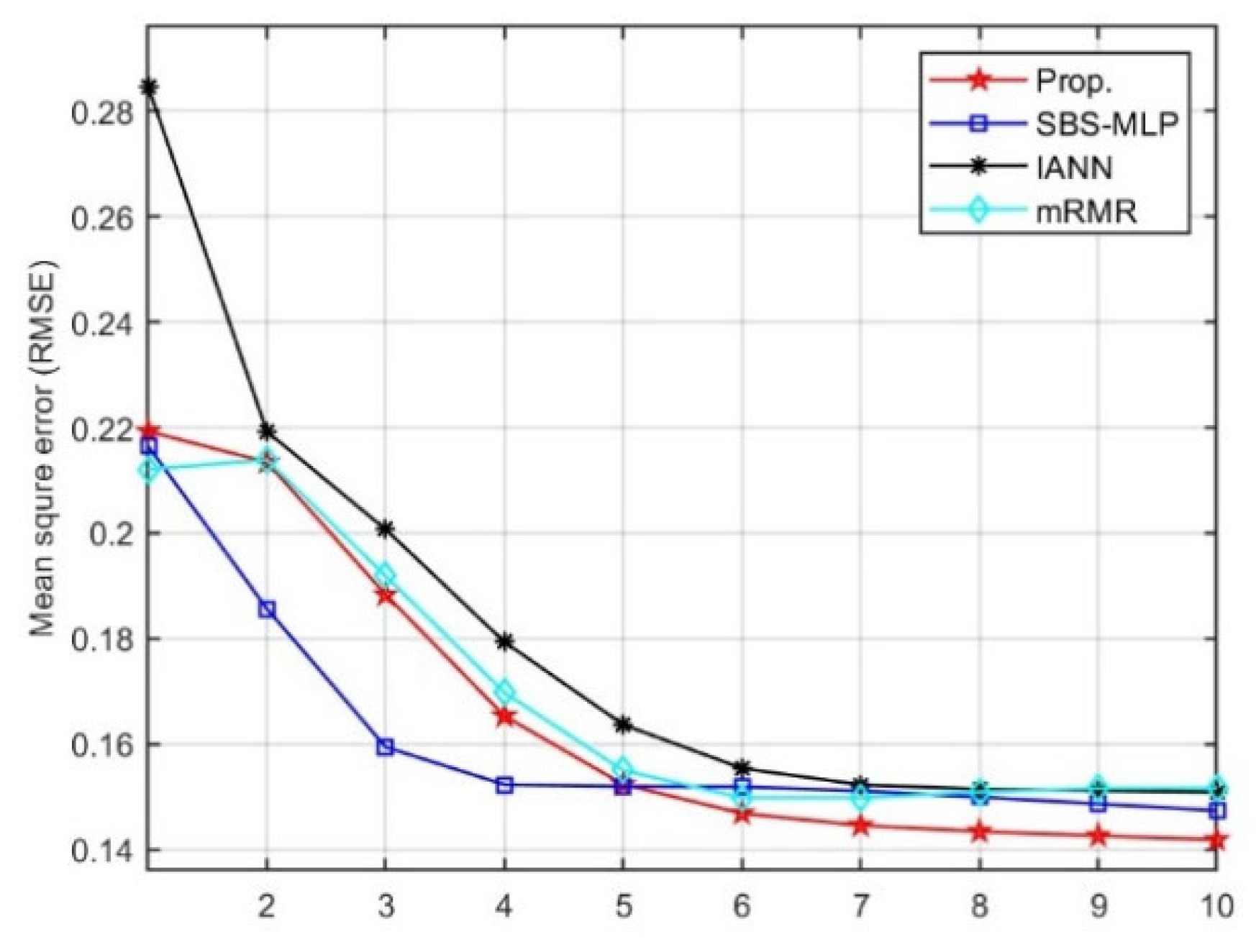
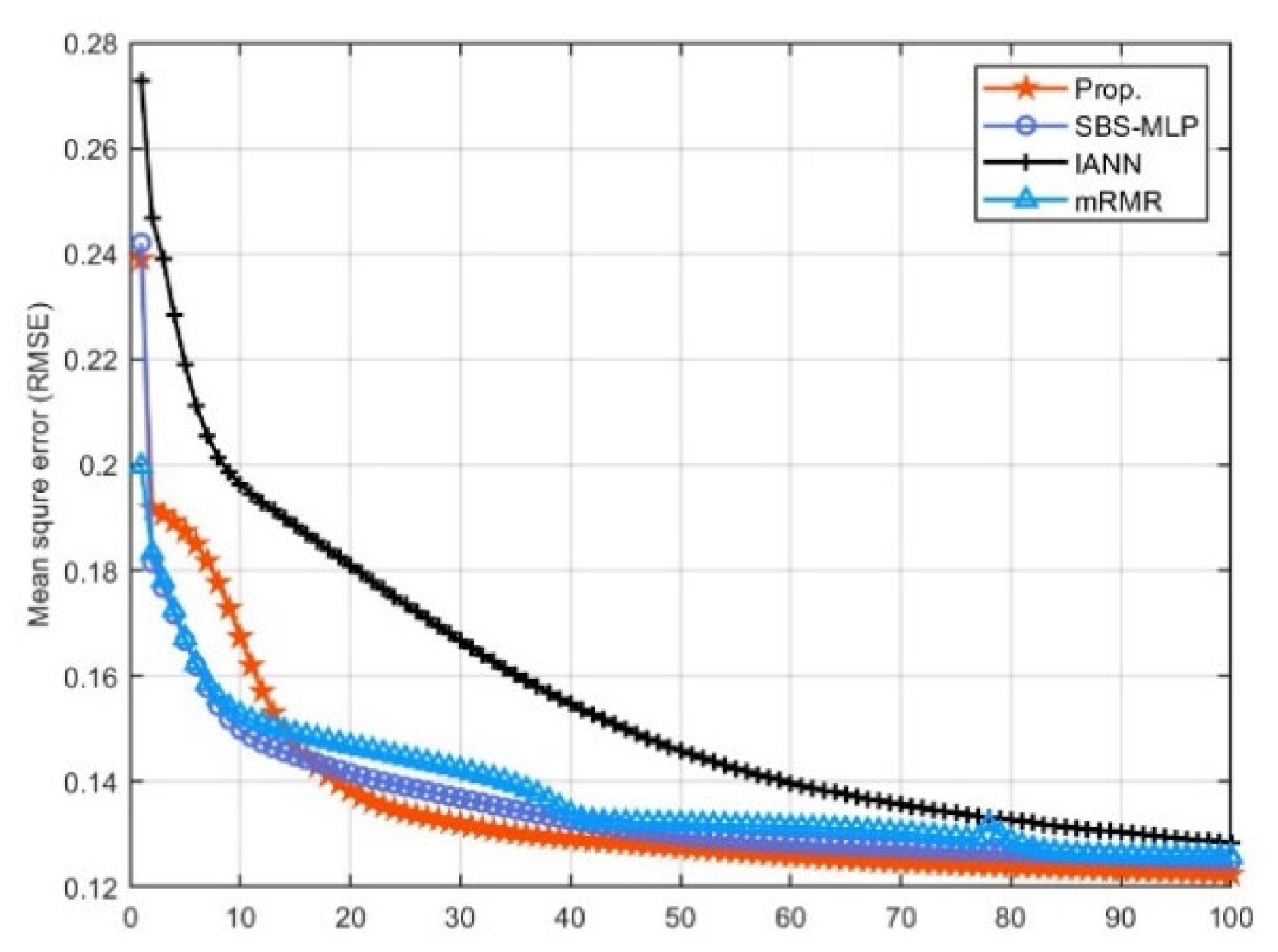
4.2. Experiment I: Comparison of Feature Extraction
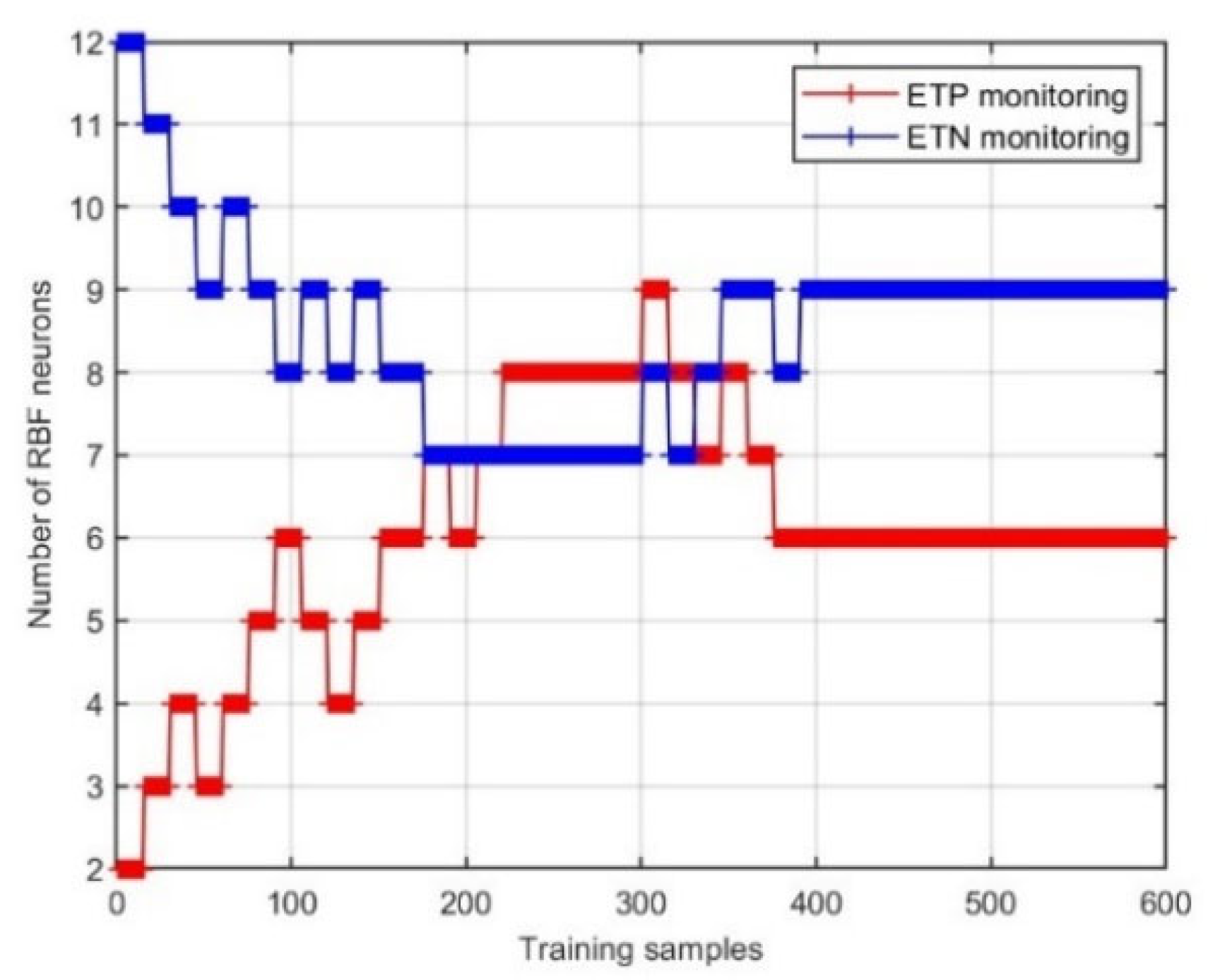
4.3. Experiment II: Comparison of Self-Organizing Algorithms
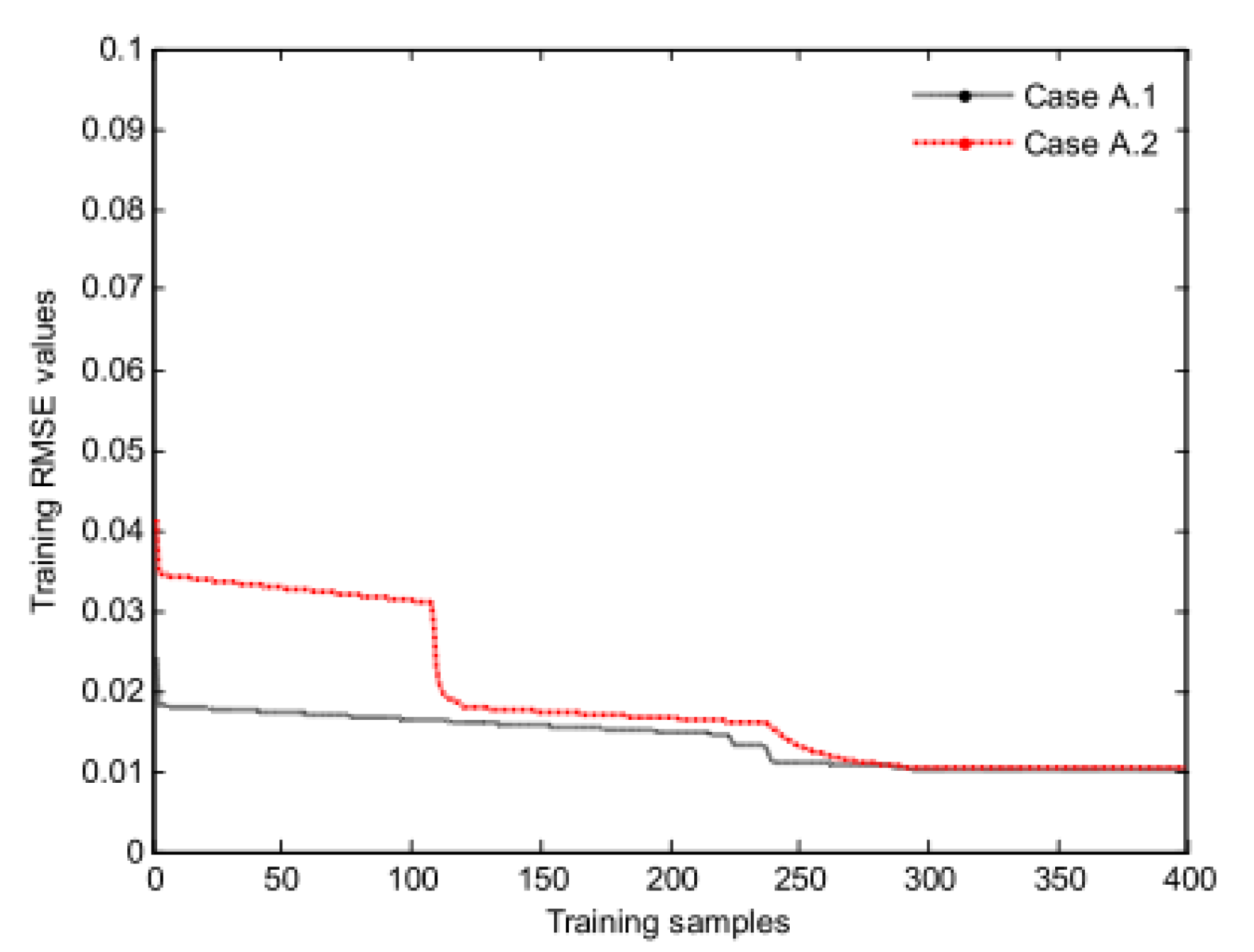
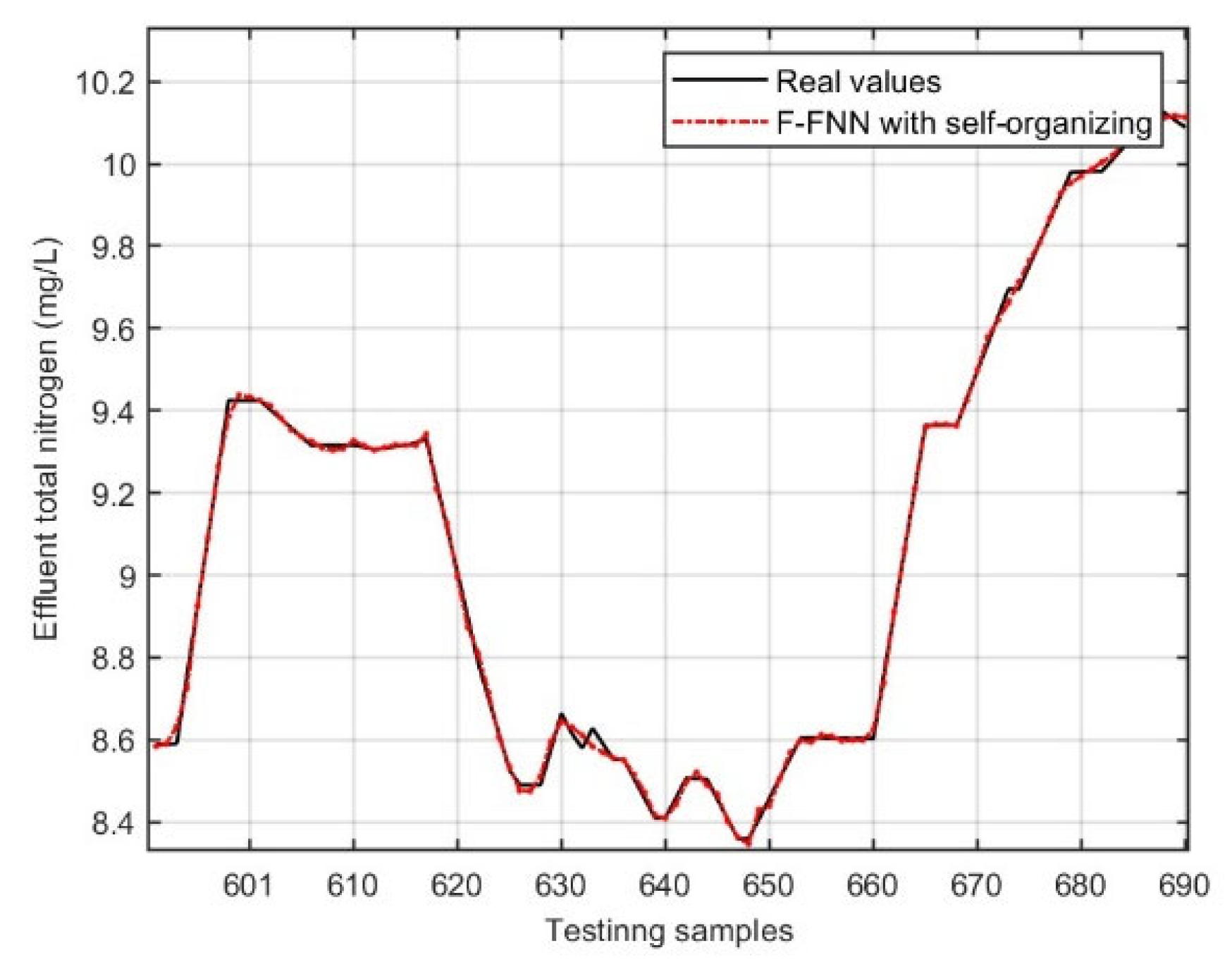
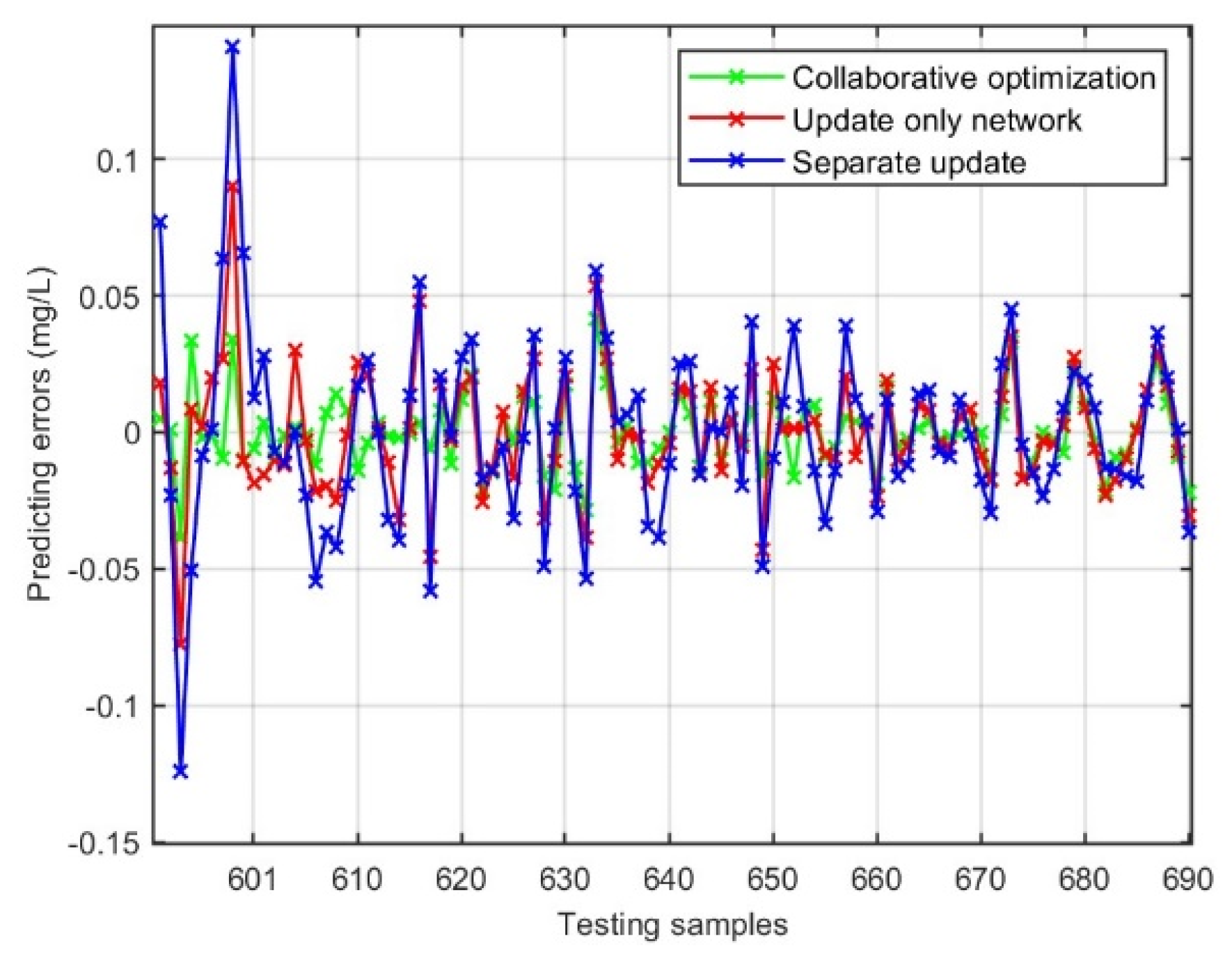
4.4. Experiment III: Comparison of Parameter Update Mode
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, R.; Han, J.; Shen, G.; Hao, Z.; Han, Y.; Xiong, W.; Liang, B.; Gao, S.; Yang, M.; Sun, Y.; et al. The threat of PPCPs from WWTP and solutions of advanced reduction coupled treatment processes with pilot-scale. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 498, 139782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.-T.; Xu, K.; Ding, T.; You, A.-J.; Hu, J.-W.; Hua, L.; Gan, Z.-W.; Hu, L.-F. Kitchen waste composting leachate stimulates endogenous simultaneous nitrifying and denitrifying pathways in WWTPs. Environ. Res. 2025, 285, 122588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Yu, L.-F.; Yu, T.; Fan, Y.; An, M.-Z.; Tian, X. Flow partitioning strategy for partial denitrification and anammox (PD/A) implementation: Simultaneous treatment of raw sewage and secondary effluent in WWTPs. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 77, 108276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.-F.; Zhang, J.-N.; Li, W.-J. PCA-based sensor drift fault detection with distribution adaptation in wastewater treatment process. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2025, 22, 10071–10083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.-G.; Xu, Z.-A.; Wang, J.-J. A novel set-based discrete particle swarm optimization for wastewater treatment process effluent scheduling. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2024, 54, 5394–5406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.-L.; Sui, E.-G.; Wang, W.; He, R. Soft sensor development based on hybrid modeling with ensemble learning for multimode batch processes. IEEE Sens. J. 2025, 25, 15588–15597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.-W.; Li, T.-Z.; Dong, X.-H.; Dang, X.-C. Semi-supervised soft sensor modeling based on ensemble learning with pseudo label optimization. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 2524818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.-F.; Xu, N.; Ye, L.-J.; Wang, K.; Shen, F.-F.; Wang, Y.-L. Attention-Based Interval Aided Networks for Data Modeling of Heterogeneous Sampling Sequences with Missing Values in Process Industry. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 5253–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba-Alawi, A.-H.; Kim, J. Dual-stage soft sensor-based fault reconstruction and effluent prediction toward a sustainable wastewater treatment plant using attention fusion deep learning model. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.-L.; Turcato, A.-C.; Sestito, G.-S. A soft sensor edge-based approach to fault diagnosis for piping systems. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2024, 97, 102618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.-N.; Yang, H.-W.; Cao, H.-C.M.; Xu, D.-Z. A missing data imputation method for industrial soft sensor modeling. J. Process Control. 2025, 152, 103485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.-S.; Feng, D.-Z.; Yang, F. A promising nonlinear dimensionality reduction method: Kernel-based within class collaborative preserving discriminant projection. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2020, 27, 2034–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louifi, A.; Kouadri, A.; Harkat, M.-F.; Bensmail, A.; Mansouri, M. Sensor fault detection in uncertain large-scale systems using interval-valued PCA technique. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 25, 3119–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.-H.; Luo, J.-Y.; Kong, X.-Y.; Xu, Z.-Y. Orthogonal multi-block dynamic PLS for quality-related process monitoring. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2023, 21, 3421–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.-J.; Alias, A.-H.; Haron, N.-A.; Bakar, N.-A. Development of a hoisting safety risk framework based on the stamp theory and PLS-sem method. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 122998–123017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Emran, M.; AlQudah, A.-A.; Abbasi, G.-A.; Al-Sharafi, M.-A.; Iranmanesh, M. Determinants of using ai-based chatbots for knowledge sharing: Evidence from PLS-SEM and fuzzy sets (fsQCA). IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2023, 71, 4985–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, J.-H.; Hair, J.-F. Explaining and predicting new retail market and consumer behavior habits using partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2025, 87, 104446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briscik, M.; Dillies, M.-A.; Déjean, S. Improvement of variables interpretability in kernel PCA. BMC Bioinform. 2023, 24, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, T.-K.; Negi, A.; Banka, H. 14-Dimensionality reduction using PCAs in feature partitioning framework. In Statistical Modeling in Machine Learning; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 269–286. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Yan, X.-F. Related and independent variable fault detection based on KPCA and SVDD. J. Process Control. 2016, 39, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.-G.; Tian, X.-M.; Chen, S. Deep principal component analysis based on layerwise feature extraction and its application to nonlinear process monitoring. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2019, 27, 2526–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.-B.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Zhou, D.-H. Key-performance-indicator-related process monitoring based on improved kernel partial least squares. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 2626–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Jiao, J.-F. A kernel least squares based approach for nonlinear quality-related fault detection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 64, 3195–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.-H.; Song, Z.-H. Generalized semi supervised self-optimizing kernel model for quality-related industrial process monitoring. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 10876–10886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Dairi, A.; Harrou, F.; Sun, Y.; Leiknes, T. Monitoring Influent Conditions of Wastewater Treatment Plants by Nonlinear Data-Based Techniques. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 108827–108837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouzari, M.; Pahlavani, P.; Izaditame, F.; Bigdeli, B. Estimating the chemical oxygen demand of petrochemical wastewater treatment plants using linear and nonlinear statistical models—A case study. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 129465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelsson, O.; Lindblom, E.-U.; Djupsjö, K.; Kanders, L.; Corominas, L. Mobility data for reduced uncertainties in model-based WWTP design. Water Res. X 2025, 29, 100418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.-B.; Liu, R.-B.; Zhu, K.-Y.; Hao, X.-D. Variable emission factors of CH4 and N2O from WWTPs: A model-based analysis on available data. Environ. Res. 2025, 264, 120380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Bai, L.-M.; Yu, H.-R.; Qu, F.-S. Comparison of interpretable machine learning models and mechanistic model for predicting effluent nitrogen in WWTP. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 77, 108344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadou, S.; Kokkinos, P.-A.; Kyzas, G.-Z.; Kalavrouziotis, I.-K. Fit-for-purpose WWTP unmanned aerial systems: A game changer towards an integrated and sustainable management strategy. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 949, 174966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuccoli, N.; Fatone, F.; Sgroi, M.; Eusebi, A.-L.; Rosati, R.; Screpanti, L.; Mancini, A.; Scaradozzi, D. Forecasting and early warning system for wastewater treatment plant sensors using multitask and LSTM neural networks: A Simulated and Real-World Case Study. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2025, 198, 109103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihály, N.-B.; Vasile, A.-V.; Cristea, M. Artificial neural networks-based identification of the WWTP DO sensor types of faults. In Computer Aided Chemical Engineering; Kokossis, A.C., Georgiadis, M.C., Pistikopoulos, E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; Volume 52, pp. 1879–1884. [Google Scholar]
- Karadimos, P.; Anthopoulos, L. Development of artificial neural networks for predicting the construction costs of WWTPs in Greece. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2025, 263, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.-J.; Yang, Z.; Chang, F.; Zhao, K. Prediction of the first weighting from the working face roof in a coal mine based on a GA-BP neural network. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourani, V.; Elkiran, G.; Abba, S.I. Wastewater treatment plant performance analysis using artificial intelligence-an ensemble approach. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 2064–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.-K.; Yadav, M.; Singh, V.; Padhiyar, H.; Kumar, V.; Bhatia, S.-K.; Show, P.-L. Artificial intelligence and machine learning-based monitoring and design of biological wastewater treatment systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 369, 128486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Pooi, C.-K.; Tan, K.-M.; Huang, S.-J.; Shi, X.-Q.; Ng, H.-Y. A novel long short-term memory artificial neural network (LSTM)-based soft-sensor to monitor and forecast wastewater treatment performance. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 54, 104041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.-F.; Chen, D.; Yang, C.; Li, D. Double-Layer Fuzzy Neural Network Based Optimal Control for Wastewater Treatment Process. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2025, 33, 2062–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Han, H.; Yang, H.; Qiao, J. Knowledge-Aided and Data-Driven Fuzzy Decision Making for Sludge Bulking. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2023, 31, 1189–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, L.-M.; Qiao, J.-F. A self-organizing fuzzy neural network with hybrid learning algorithm for nonlinear system modeling. Inf. Sci. 2023, 642, 119145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, P.-V. Fuzzy neural networks and neuro-fuzzy networks: A review the main techniques and applications used in the literature. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 92, 106275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, M.-K.; Ettwig, K.-F.; Vannecke, T.-P.; Stultiens, K.; Bogdan, A.; Kartal, B.; Volcke, E.-I.-P. Modelling simultaneous anaerobic methane and ammonium removal in a granular sludge reactor. Water Res. 2015, 73, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrou, F.; Cheng, T.; Sun, Y.; Leiknes, T.; Ghaffour, N. A Data-Driven Soft Sensor to Forecast Energy Consumption in Wastewater Treatment Plants: A Case Study. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 4908–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.-F.; Xue, A.; Yang, Y.; Cao, W.; Hu, X.-J.; Cao, G.-L.; Gu, J.-H.; Zhang, L.; Geng, X.-L. Deep learning based soft sensor for microbial wastewater treatment efficiency prediction. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 56, 104259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, K.-Y.; Sung, M.-J.; Gupta, P.-Y.; D'sa, J.; Tariq, F.-M.; Isele, D.; Bae, S.-J. IANN-MPPI: Interaction-aware neural network-enhanced model predictive path integral approach for autonomous driving. Comput. Sci. 2025, arXiv:2507.11940. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q. A Survey on Multi-Task Learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2022, 34, 5586–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergio, R.-G.; Iago, L.; David, M.-R.; Verónica, B.-C.; José, M.-B.; Francisco, H.; Amparo, A.-B. Fast-mRMR: Fast minimum redundancy maximum relevance algorithm for high-dimensional big data. Intell. Syst. 2016, 32, 134–152. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.-H.; Sun, J.; Yao, K.-S.; Xu, M.; Cao, Y. A variable selection method based on mutual information and variance inflation factor. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 268, 1386–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Lu, Y.-Q.; Qin, J.-C. A dynamic MLP-based DDoS attack detection method using feature selection and feedback. Comput. Secur. 2020, 88, 101645. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.-G.; Zhang, L.; Wu, X.-L.; Qiao, J.-F. An efficient second-order algorithm for self-organizing fuzzy neural networks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2017, 49, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, A.-T.; Er, M.-J.; Li, X.; Lim, B.-S. Sequential fuzzy clustering based dynamic fuzzy neural network for fault diagnosis and prognosis. Neurocomputing 2016, 196, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Chen, C.-P. Fuzzy Broad Learning System: A Novel Neuro-Fuzzy Model for Regression and Classification. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 50, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yang, C.; Chen, C.-P. Optimal Robot–Environment Interaction Under Broad Fuzzy Neural Adaptive Control. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 51, 3824–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
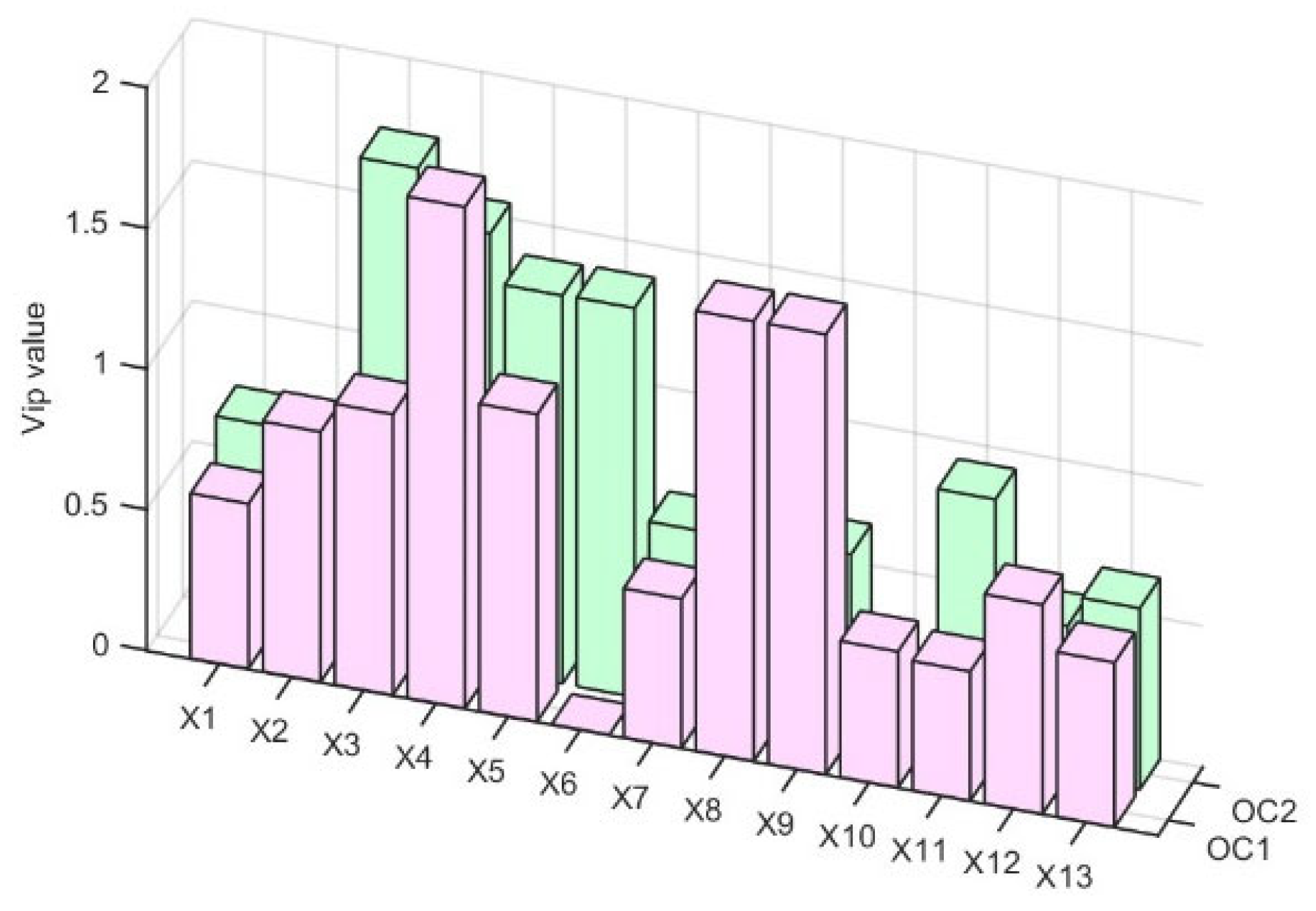
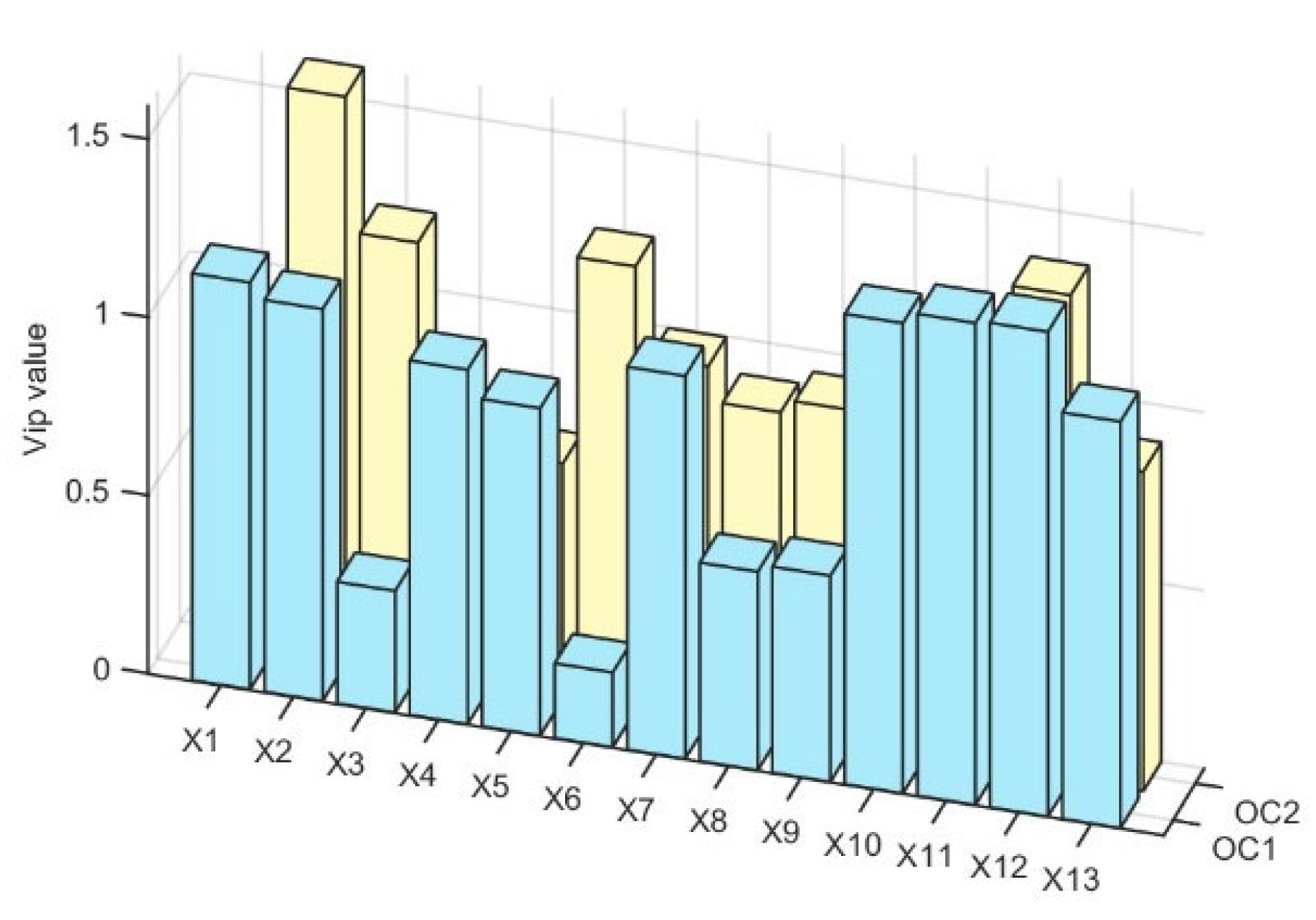
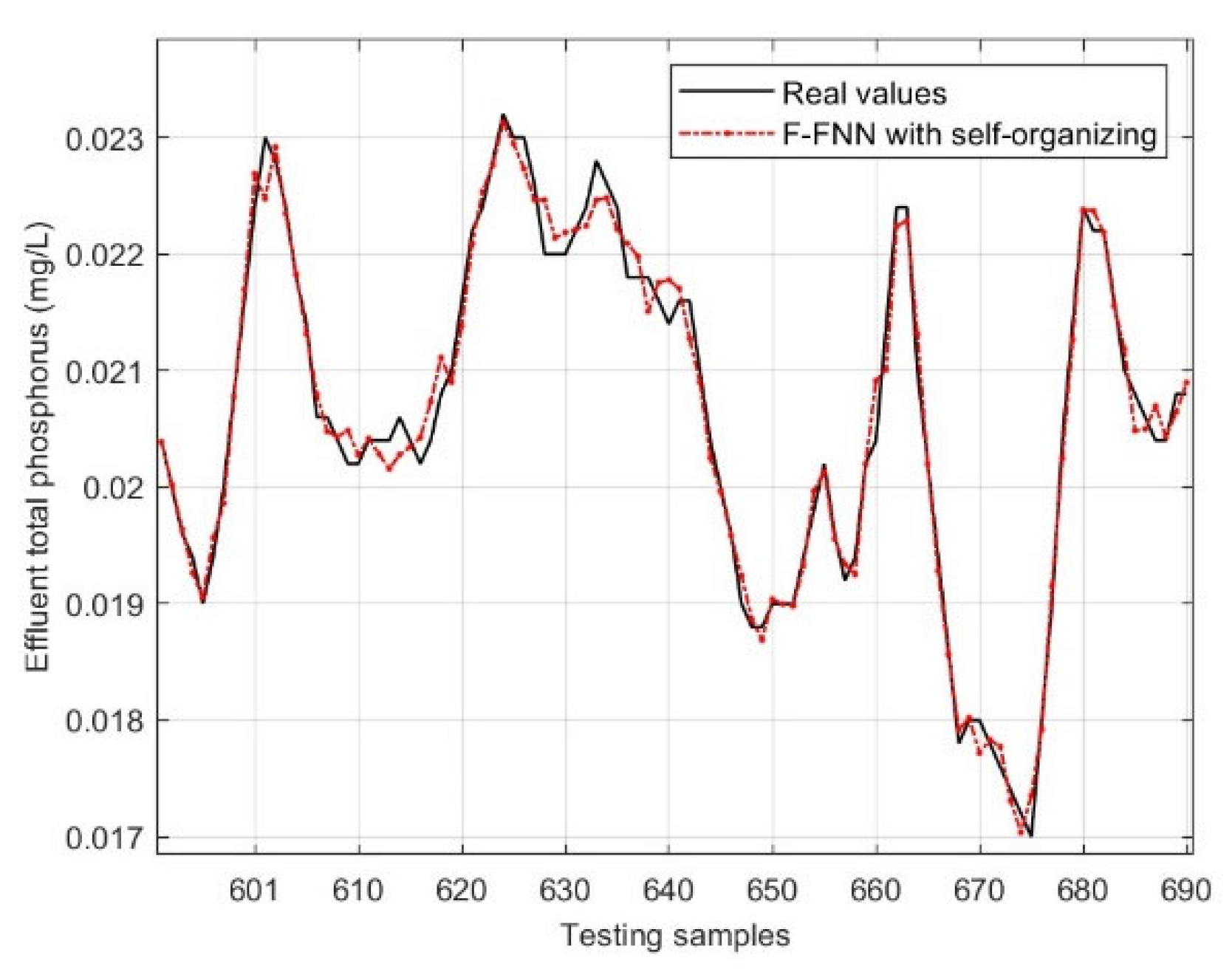
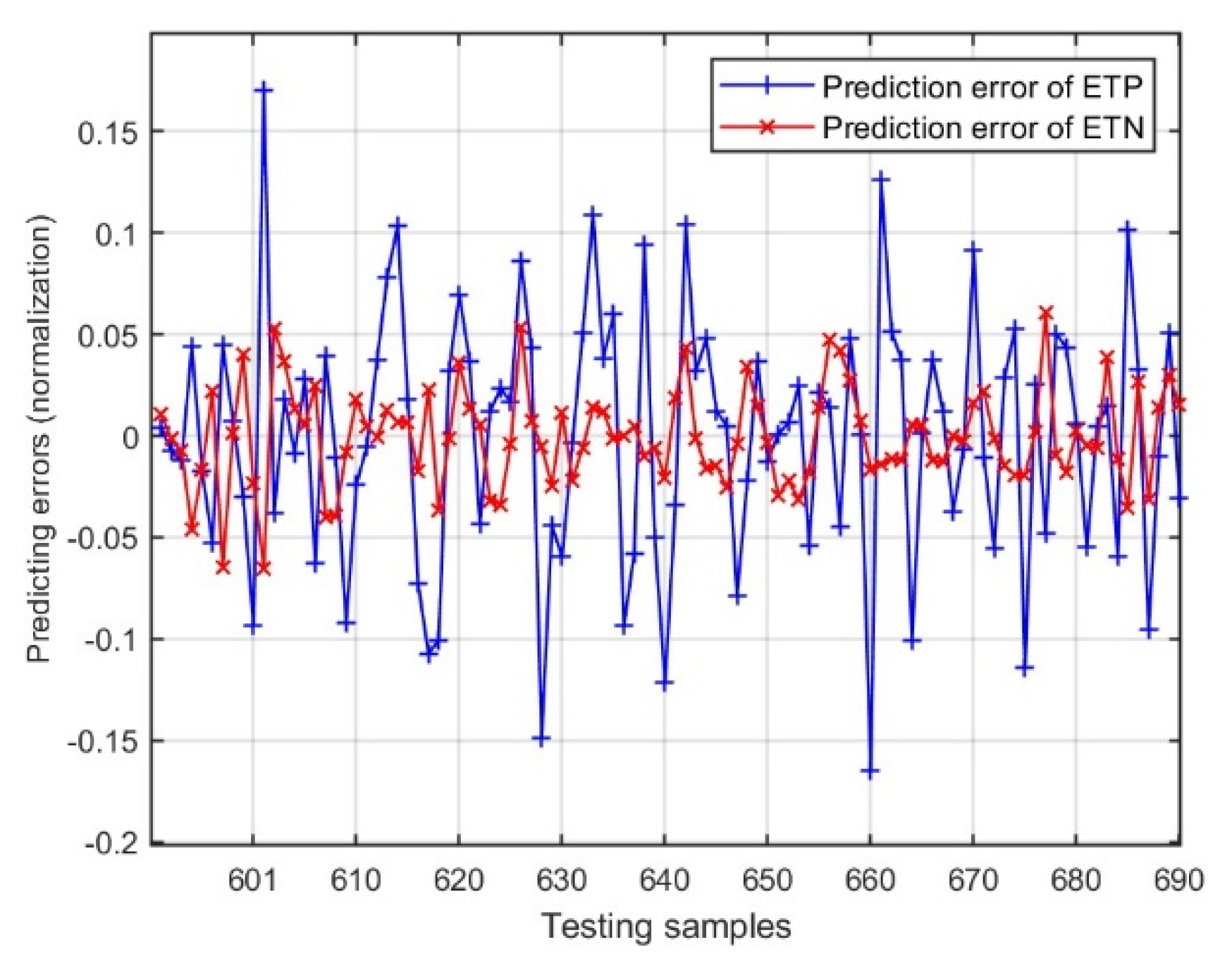
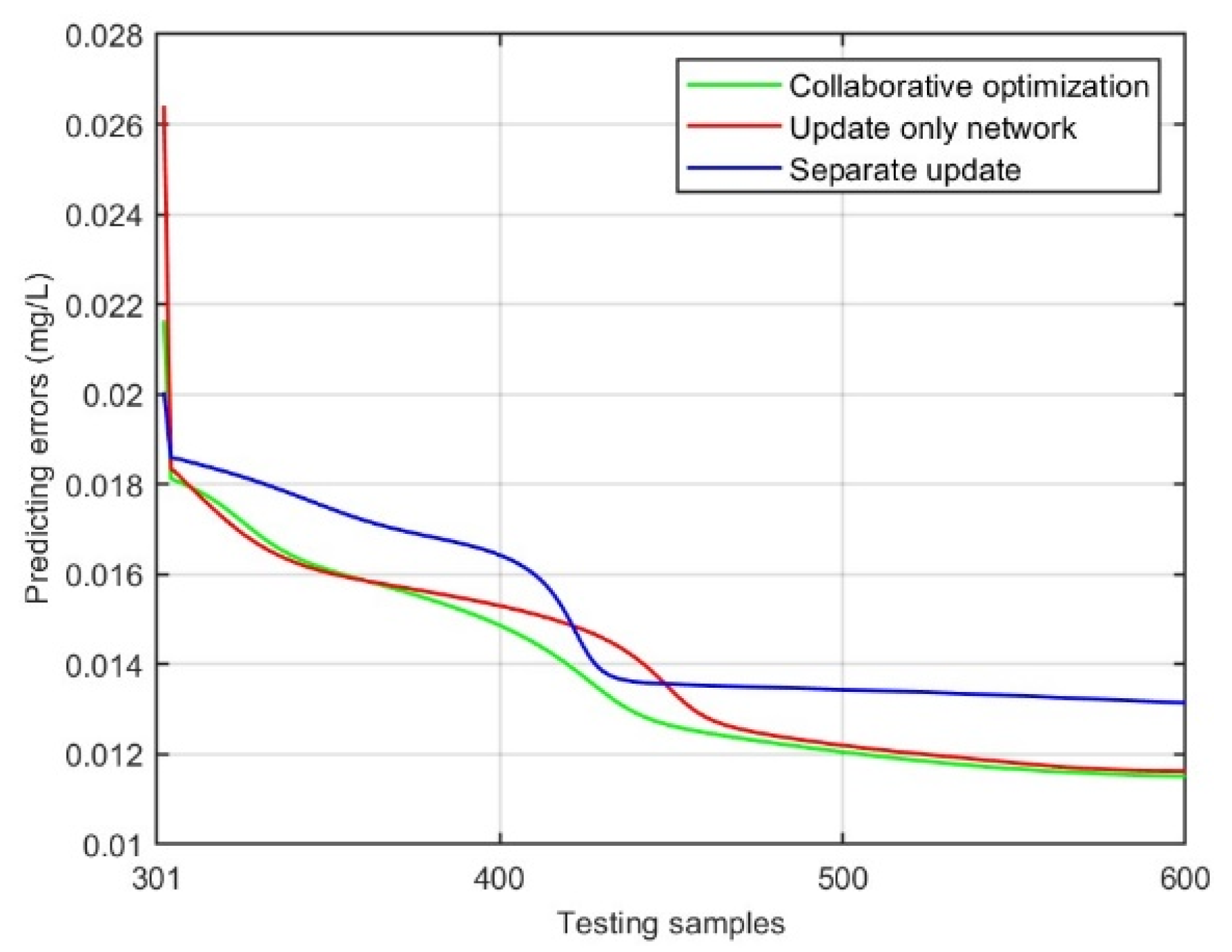
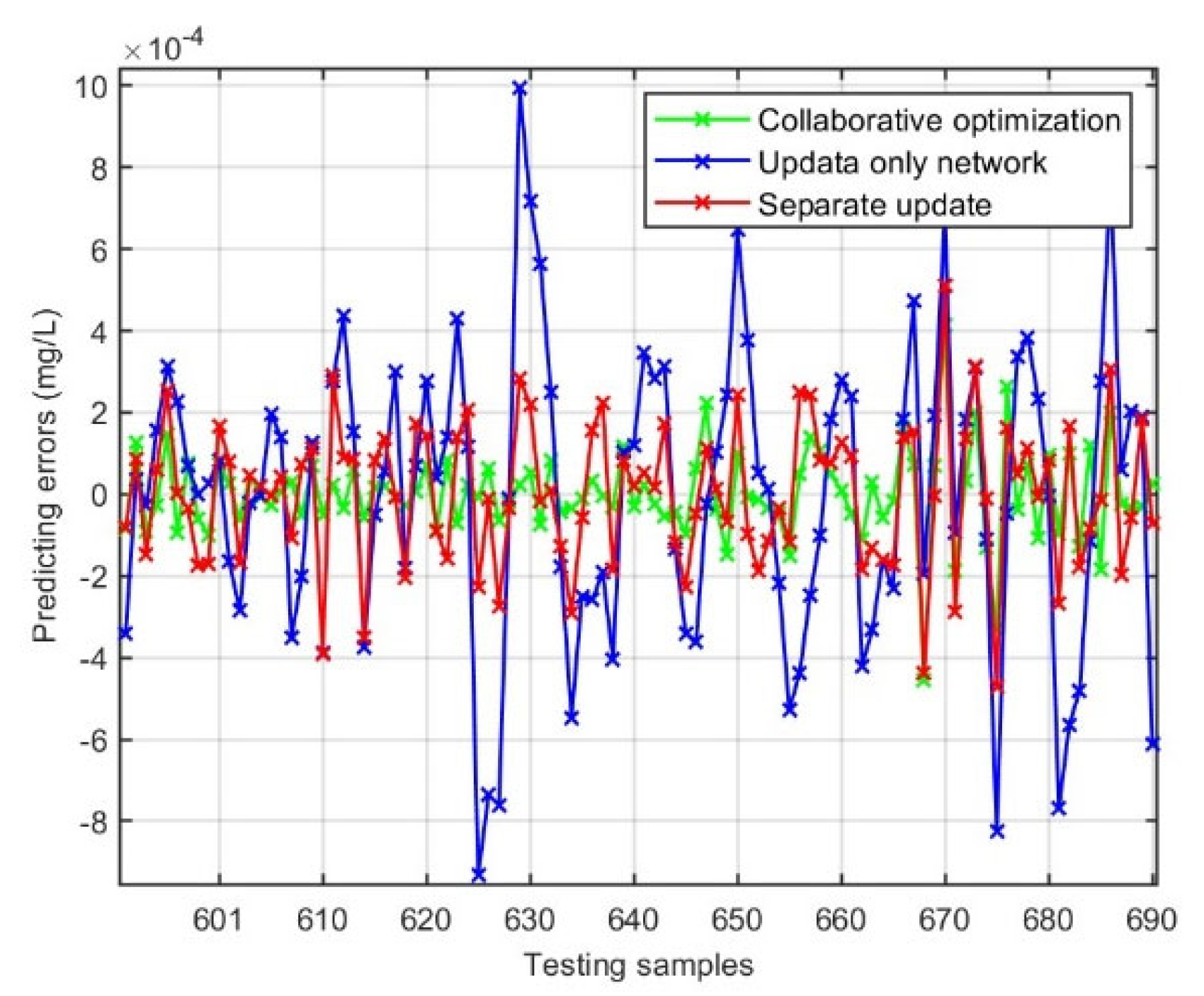
| Variable | Description | Unit | Collecting Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | Inlet flow | LMP | Influent Tank |
| X2 | Temperature | °C | Tank A |
| X3 | ORP1 | mV | Anaerobic tank (tank A) |
| X4 | ORP2 | mV | Anoxic tank (tank A) |
| X5 | MLSS1 | mg/L | Anoxic tank (tank A) |
| X6 | NO3-N | mg/L | Anoxic tank (tank A) |
| X7 | NH4-N | mg/L | Aerobic tank (tank A) |
| X8 | DO1 | mg/L | Aerobic tank (tank A) |
| X9 | ORP3 | mV | Anaerobic tank (tank B) |
| X10 | MLSS2 | mg/L | Anoxic tank (tank B) |
| X11 | NO3-N | mg/L | Anoxic tank (tank B) |
| X12 | DO2 | mg/L | Aerobic tank (tank B) |
| X13 | pH | – | Settler |
| Yd1 | TP | mg/L | Settler (effluent) |
| Yd2 | TN | mg/L | Settler (effluent) |
| Algorithm | Task A: Effluent Total Phosphorus Monitoring | Task B: Effluent Total Nitrogen Monitoring | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ⎸S⎹ | CPU Time(s) | Testing RMSE | CC | ⎸S⎹ | CPU Time(s) | Testing RMSE | CC | |
| Prop. | 7-6 | 4.1 | 0.1417 | 0.84 | 6-8 | 38.4 | 0.1221 | 0.8657 |
| IANN | 9-8 | 6.7 | 0.1586 | 0.82 | 7-9 | 47.6 | 0.1286 | 0.8406 |
| SBS-MLP | 7-6 | 105 | 0.1498 | 0.87 | 6-8 | 116.3 | 0.1237 | 0.8708 |
| NMIFS | 7-6 | 0.125 | 0.1531 | 0.83 | 6-8 | 10.21 | 0.1262 | 0.8539 |
| mRMR | 7-6 | 0.139 | 0.1567 | 0.84 | 6-8 | 8.9 | 0.1257 | 0.8572 |
| Algorithm | Task A: Effluent Total Phosphorus Monitoring | Task B: Effluent Total Nitrogen Monitoring | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Final RBF Neurons | CPU Time(s) | Testing RMSE | Testing APE | No. of Final RBF Neurons | CPU Time(s) | Testing RMSE | Testing APE | |
| Prop. | 6 | 21.61 | 0.0152 | 0.0043 | 9 | 52.21 | 0.133 | 0.052 |
| Prop (fixed structure) | 2 | 24.55 | 0.0232 | 0.0102 | 12 | 40.12 | 0.198 | 0.083 |
| SOA-FNN | 6 | 11.27 | 0.0105 | 0.0031 | 9 | 28.64 | 0.057 | 0.010 |
| DFNN | 6 | 36.55 | 0.0124 | 0.0039 | 8 | 82.12 | 0.165 | 0.067 |
| GDFNN | 8 | 42.33 | 0.0217 | 0.0084 | 9 | 142.67 | 0.178 | 0.081 |
| GP-FNN | 6 | 28.24 | 0.0105 | 0.0046 | 9 | 89.31 | 0.182 | 0.092 |
| SOFMLS | 8 | 29.36 | 0.0120 | 0.0095 | 9 | 78.63 | 0.193 | 0.098 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, X. Integrated Soft-Sensor Model for Wastewater Treatment Process with Collaborative Calibration Strategy. Electronics 2025, 14, 4506. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224506
Yang Y, Zhao Y, Wu X. Integrated Soft-Sensor Model for Wastewater Treatment Process with Collaborative Calibration Strategy. Electronics. 2025; 14(22):4506. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224506
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yanxia, Yan Zhao, and Xiaolong Wu. 2025. "Integrated Soft-Sensor Model for Wastewater Treatment Process with Collaborative Calibration Strategy" Electronics 14, no. 22: 4506. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224506
APA StyleYang, Y., Zhao, Y., & Wu, X. (2025). Integrated Soft-Sensor Model for Wastewater Treatment Process with Collaborative Calibration Strategy. Electronics, 14(22), 4506. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224506







