HRformer: A Hybrid Relational Transformer for Stock Time Series Forecasting
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Complex Temporal Patterns in Stock Data: Stock price movements are influenced by various internal temporal dynamics, including trend, cyclic, and volatility. These components exhibit distinct time dependencies, with trend capturing long-term movements, cyclic modeling periodic patterns, and volatility representing short-term irregular fluctuations. However, many existing methods fail to effectively extract all three types of temporal relationships, especially the time-varying nature of short-term volatility and its interaction with long-term trends and cycles. To enhance prediction performance, it is essential to model these temporal dependencies and their dynamic interactions over time.
- Inter-Stock Correlation Modeling: Stock price movements are often interdependent, with the behavior of one stock influencing others. Accurately capturing these cross-stock dependencies is essential for improving forecasting performance. Many existing methods inadequately model these inter-stock correlations, leading to incomplete representations of the market’s relational structure. By focusing on inter-stock correlation modeling, we can better understand the complex relationships between stocks and improve predictive accuracy across different market conditions.
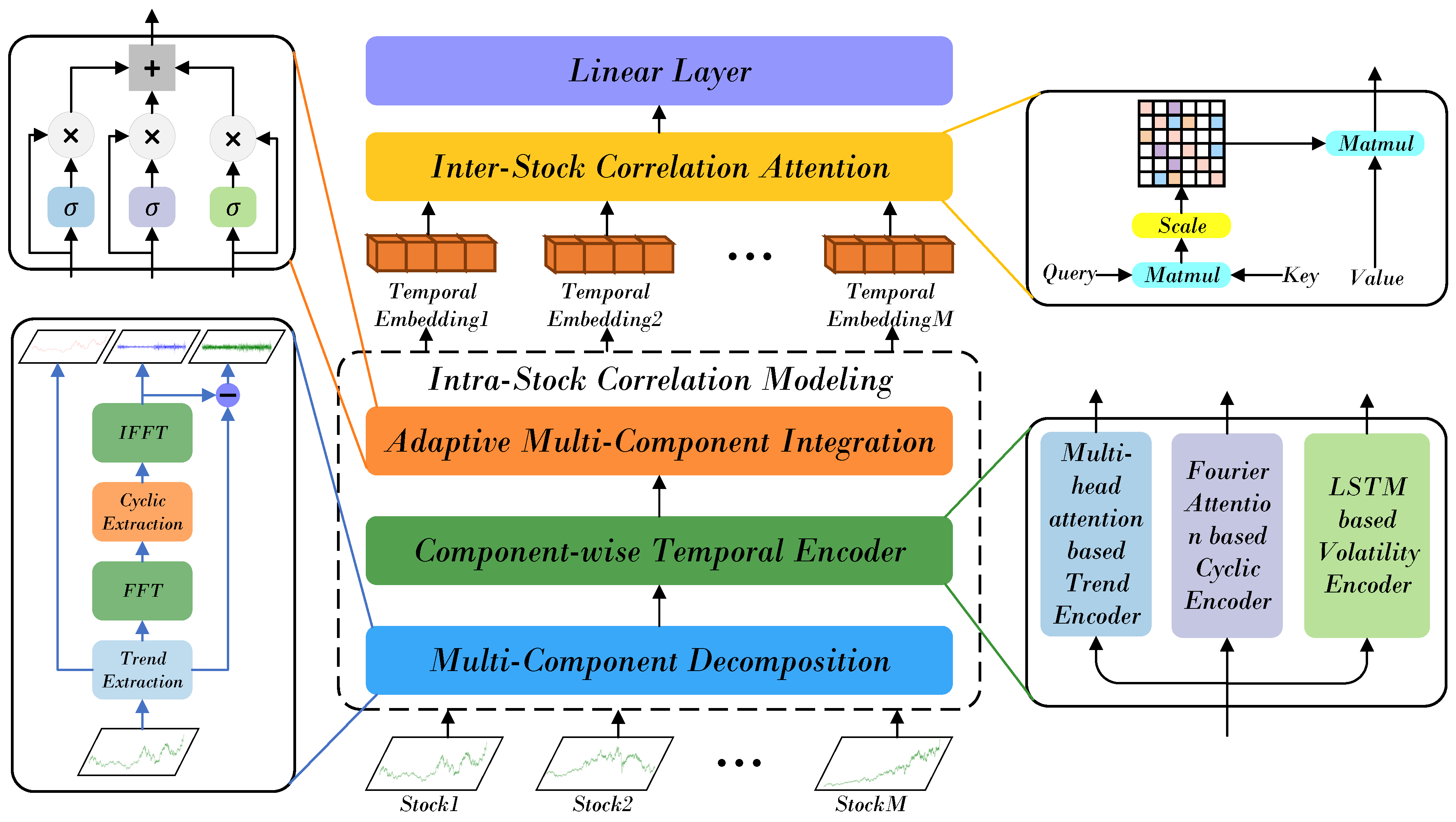
- We propose the HRformer, which jointly models intra-stock temporal dynamics and inter-stock correlations. The Multi-Component Decomposition Layer extracts trend, cyclic, and volatility components from each stock series, while the Adaptive Multi-Component Integration (AMCI) module dynamically balances their contributions. To capture cross-stock relationships, the Inter-Stock Correlation Attention (ISCA) applies multi-head attention to learn dependencies and market co-movements. By unifying component-wise modeling and correlation learning, HRformer effectively captures complex dependencies in stock time series and enhances forecasting performance across market conditions.
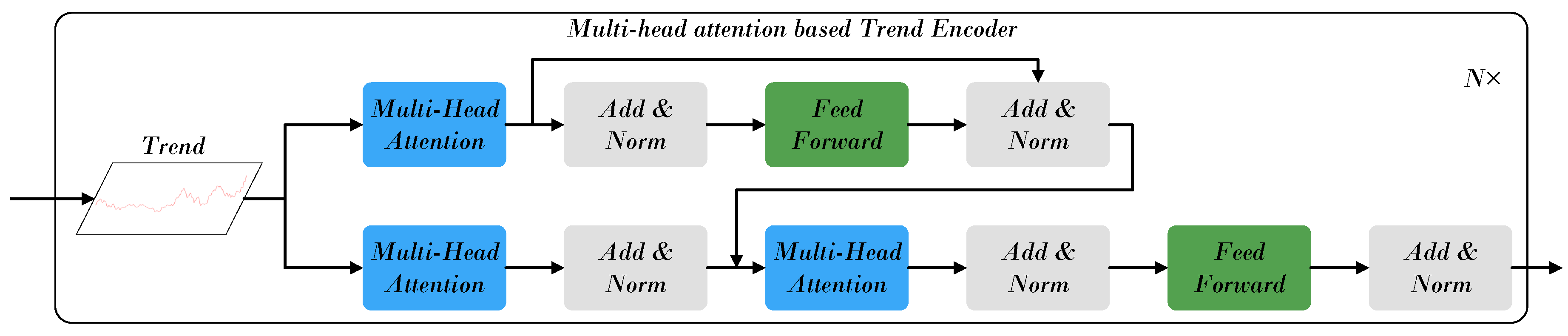
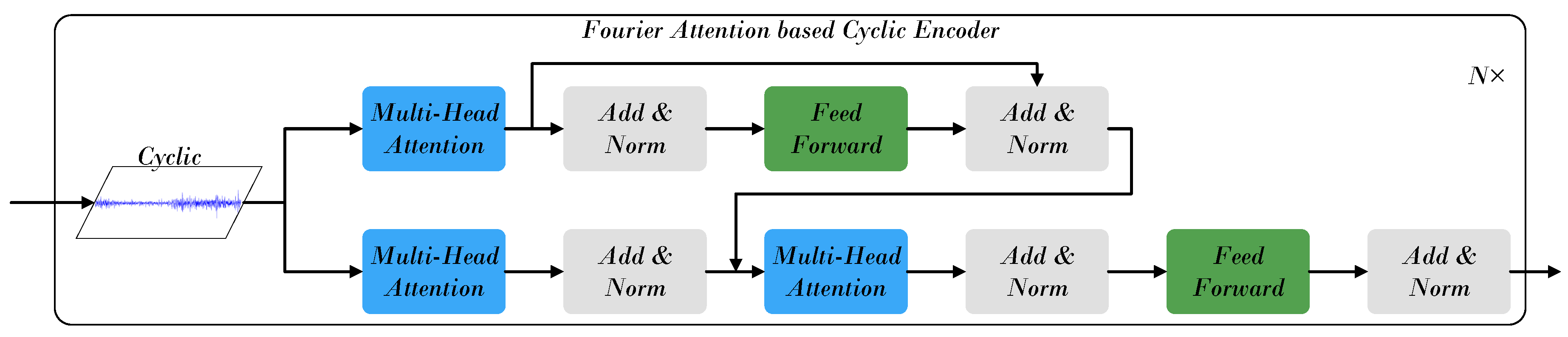
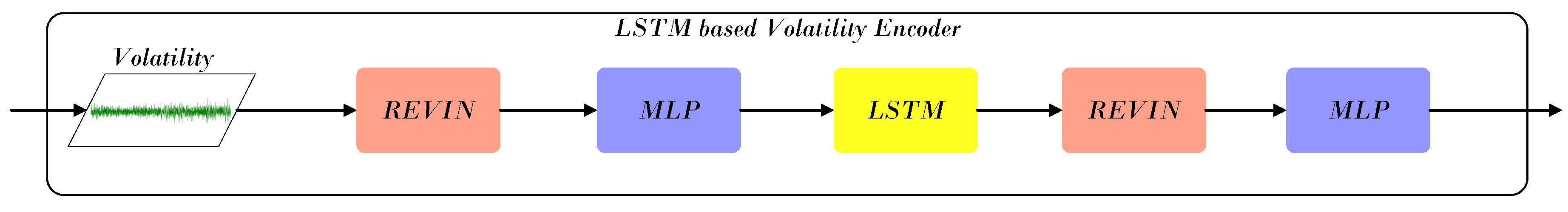
- The Component-wise Temporal Encoder (CTE) models intra-stock dynamics by processing trend, cyclic, and volatility components separately: a Transformer encoder captures long-term trends, frequency-enhanced attention models periodic patterns, and a RevIN–MLP–LSTM structure represents short-term fluctuations. The Adaptive Multi-Component Integration (AMCI) module then fuses these representations, while the Inter-Stock Correlation Attention (ISCA) captures cross-stock dependencies and market co-movements, forming a unified temporal–spatial representation.
- Comprehensive experiments and backtesting confirm that HRformer achieves superior predictive performance and practical robustness compared with representative stock forecasting models, while ablation studies validate the contribution of each module.
2. Related Work
2.1. Deep Learning Based Stock Trend Prediction
2.2. Decomposition-Based Time Series Forecasting Methods
2.3. Fusion Methods in Time Series Forecasting
3. Problem Formulation
4. Framework of HRformer
4.1. Multi-Component Decomposition Layer
4.2. Component-Wise Temporal Encoder
4.2.1. Trend Component Processing Module
4.2.2. Cyclic Component Processing Module
4.2.3. Volatility Component Processing Module
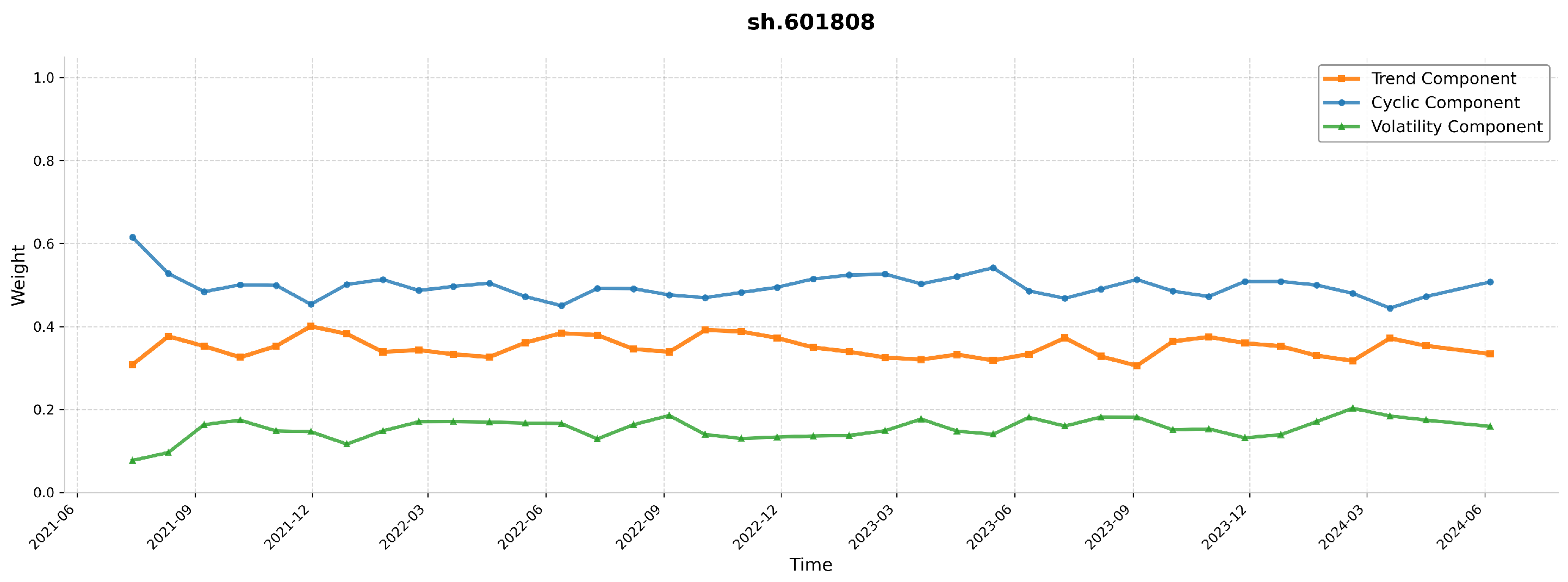
4.3. Adaptive Multi-Component Integration
4.4. Inter-Stock Correlation Attention
4.4.1. Multi-Head Attention Mechanism
4.4.2. Feed-Forward Network and Output Projection
5. Experiments
5.1. Datasets
5.2. Evaluation Metrics
- Accuracy:where TP, TN, FP, and FN denote true positives, true negatives, false positives, and false negatives.
- Precision:
- Recall:
- F1-score:
- Average Maximum Drawdown (AMDD): average of maximum peak-to-trough declines,where is the peak prior to a drawdown and is the subsequent trough.
- Sharpe Ratio (SR): annualized risk-adjusted return,where is portfolio return, is the risk-free rate, and is the standard deviation of excess returns.
- Annualized Return (AR): annualized profitability assuming 252 trading days,where and are initial and final portfolio values, and T is the holding length (days).
- Final Accumulated Portfolio Value (fAPV):
5.3. Compared Methods
- Transformer: standard self-attention model for global dependency modeling.
- FEDformer: frequency-enhanced decomposition with Transformer to capture global and local dependencies.
- StockMixer: integrates temporal and cross-sectional mixing to model stock-specific and market-wide signals.
- TDformer: temporal decomposition within a Transformer backbone for multi-scale dependency modeling.
- FourierGNN: combines Fourier analysis and graph neural networks to model periodic patterns and cross-stock relations.
- iTransformer: applies attention to transposed dimensions for multivariate dependency modeling.
- DLinear: linear heads over decomposed components for efficient long-horizon forecasting.
- edRVFL: extreme deep random vector functional link network with randomized layers and direct connections.
- TCN: dilated causal convolutions with residual blocks for parallel long-range sequence modeling.
5.4. Implementation Details
5.5. Backtesting Settings
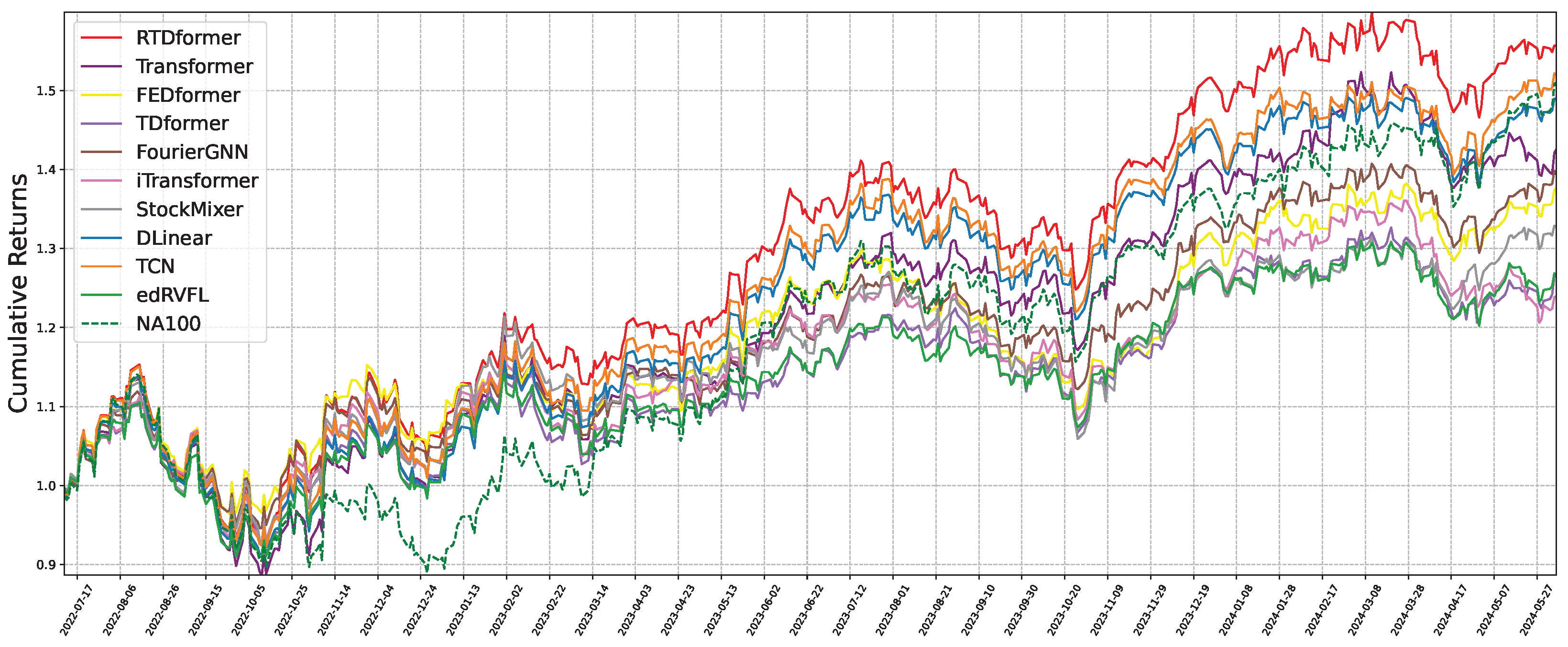
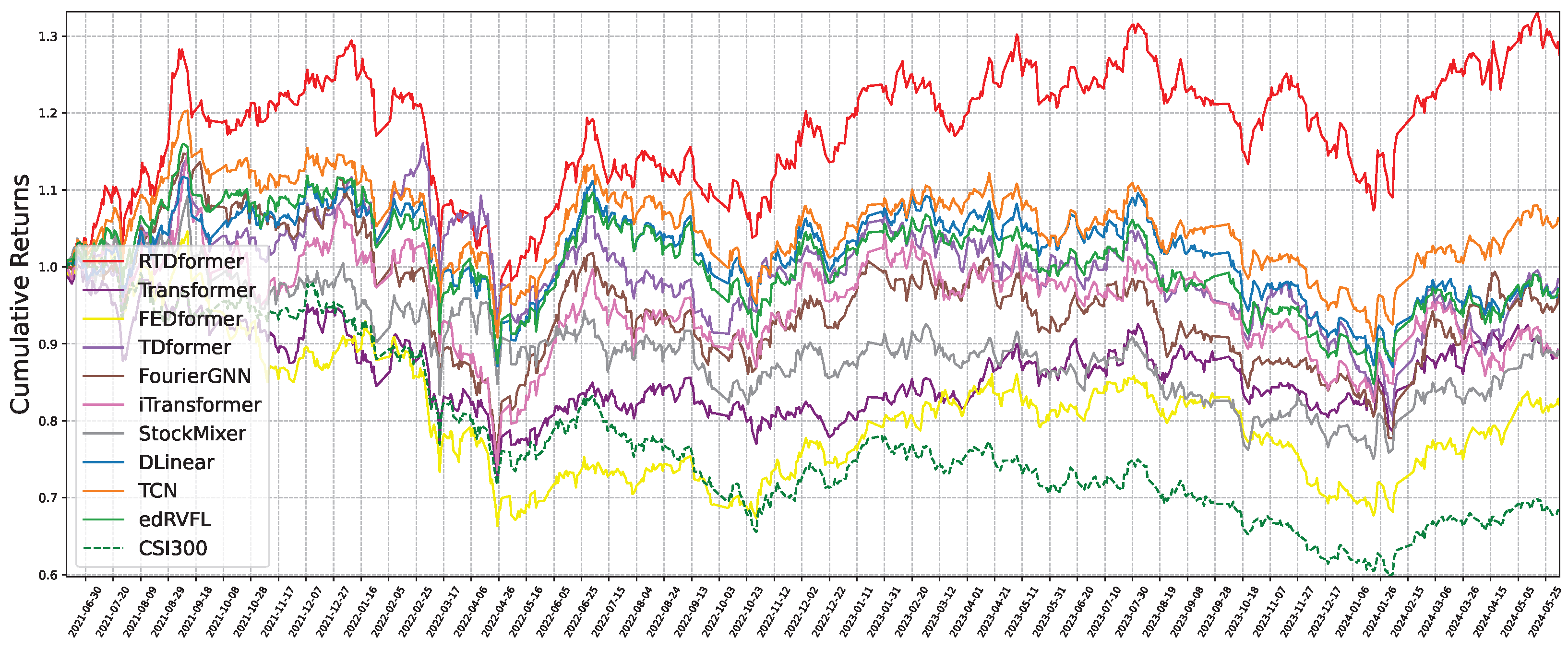
- Trading period: July 2022 to June 2024 for both CSI300 and NASDAQ100.
- Stock selection: top 10 (CSI300) or top 20 (NASDAQ100) by predicted rise probability at day t over the next 48 days.
6. Results and Analysis
6.1. Overall Performance
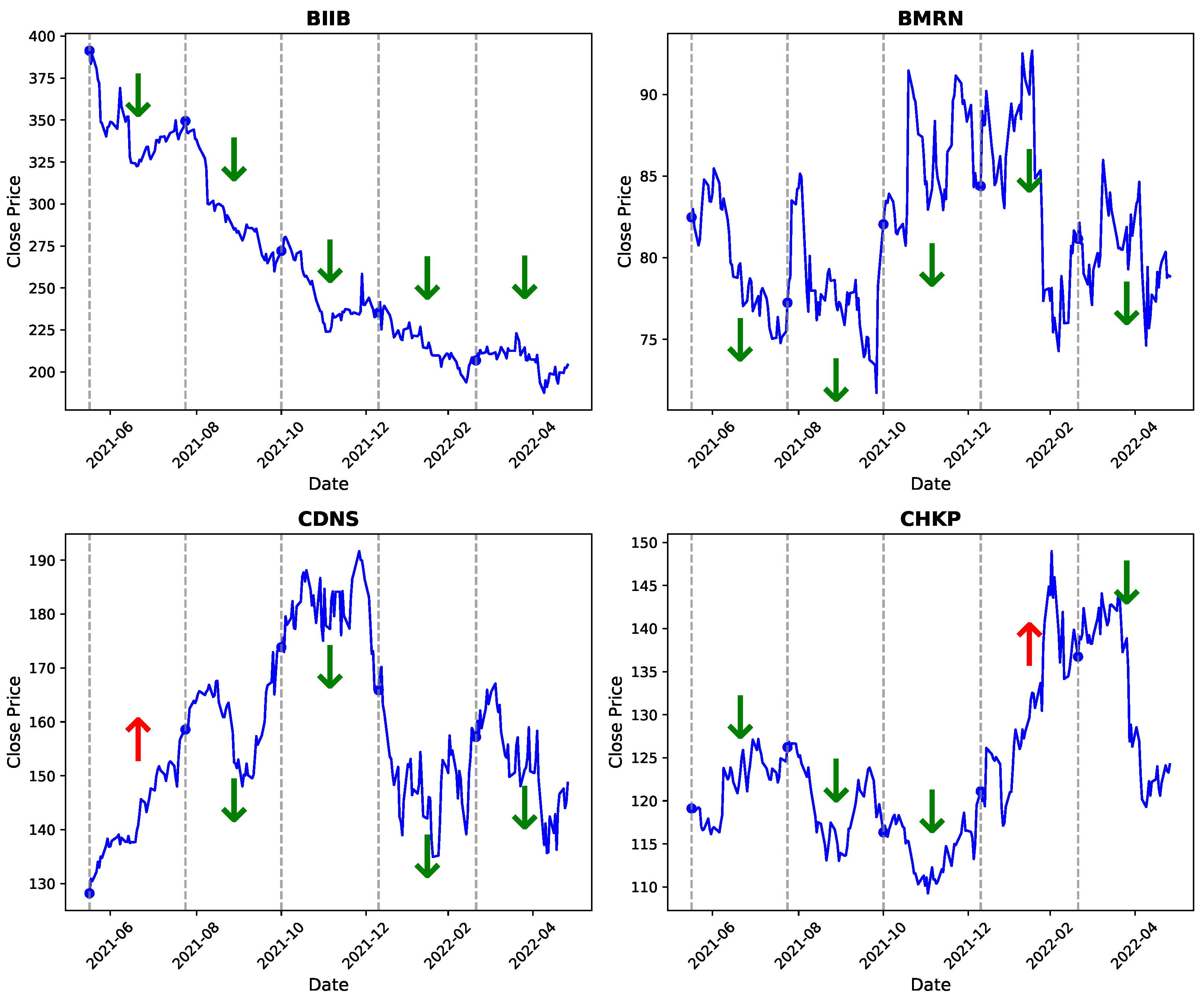
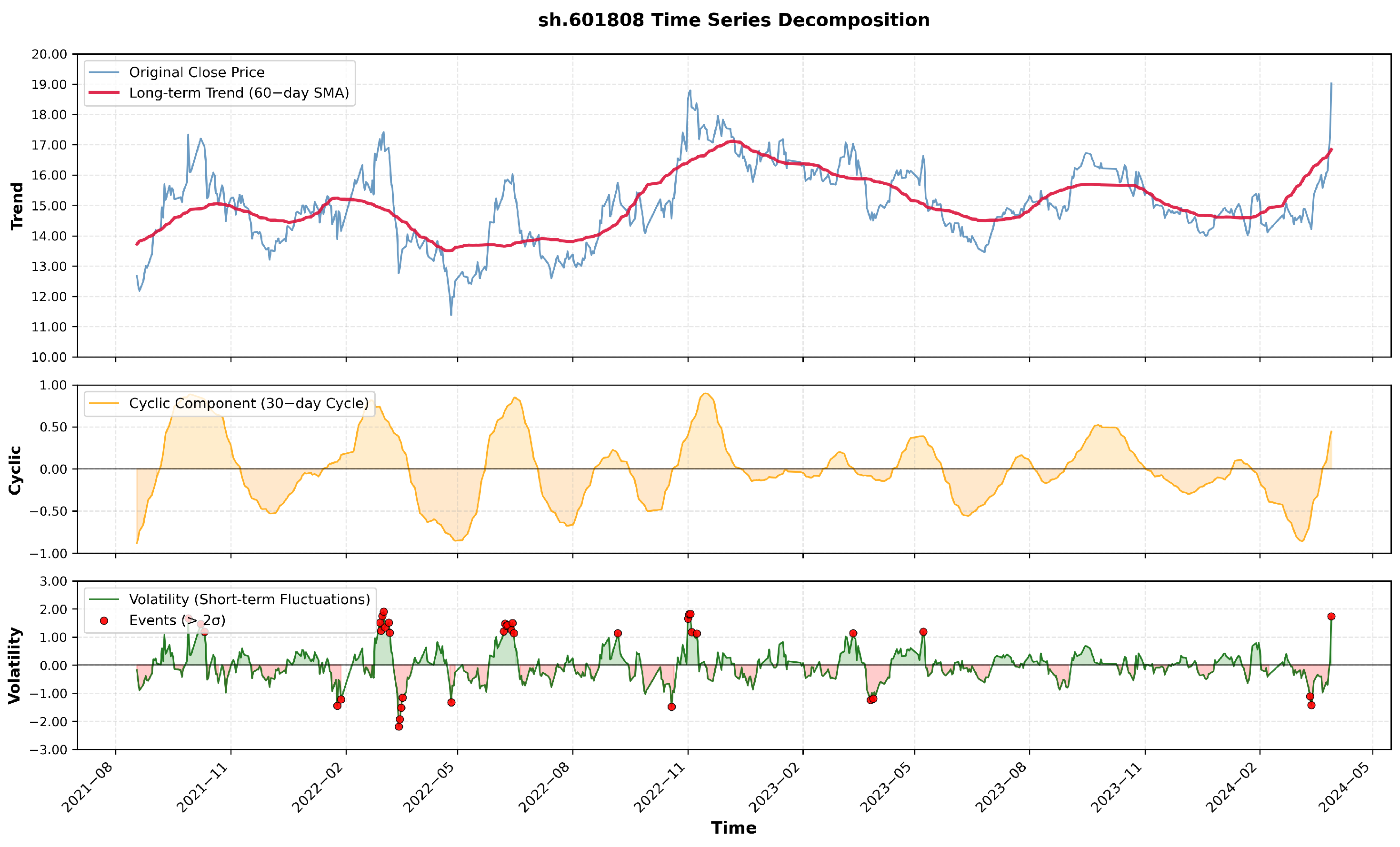
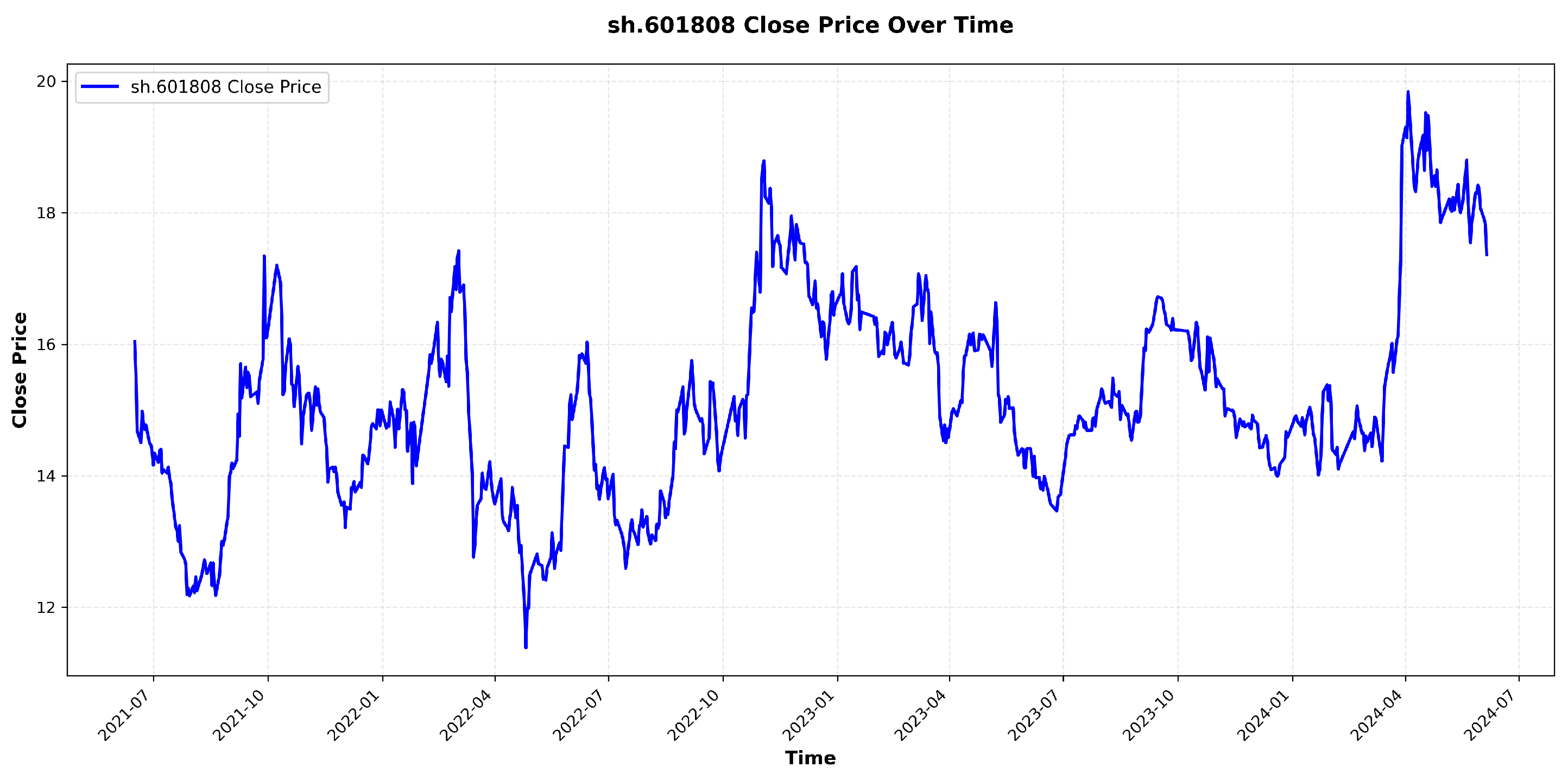
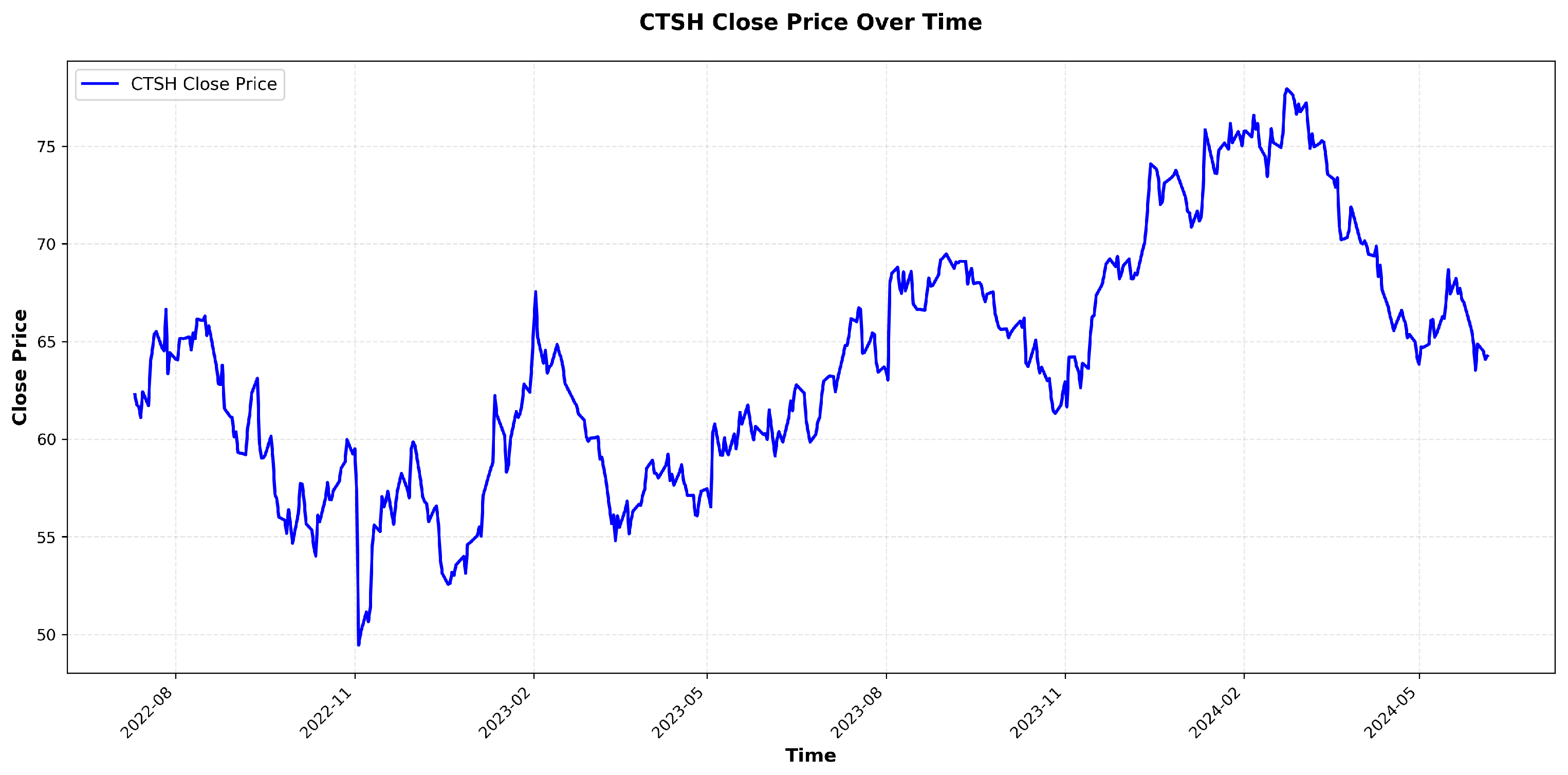
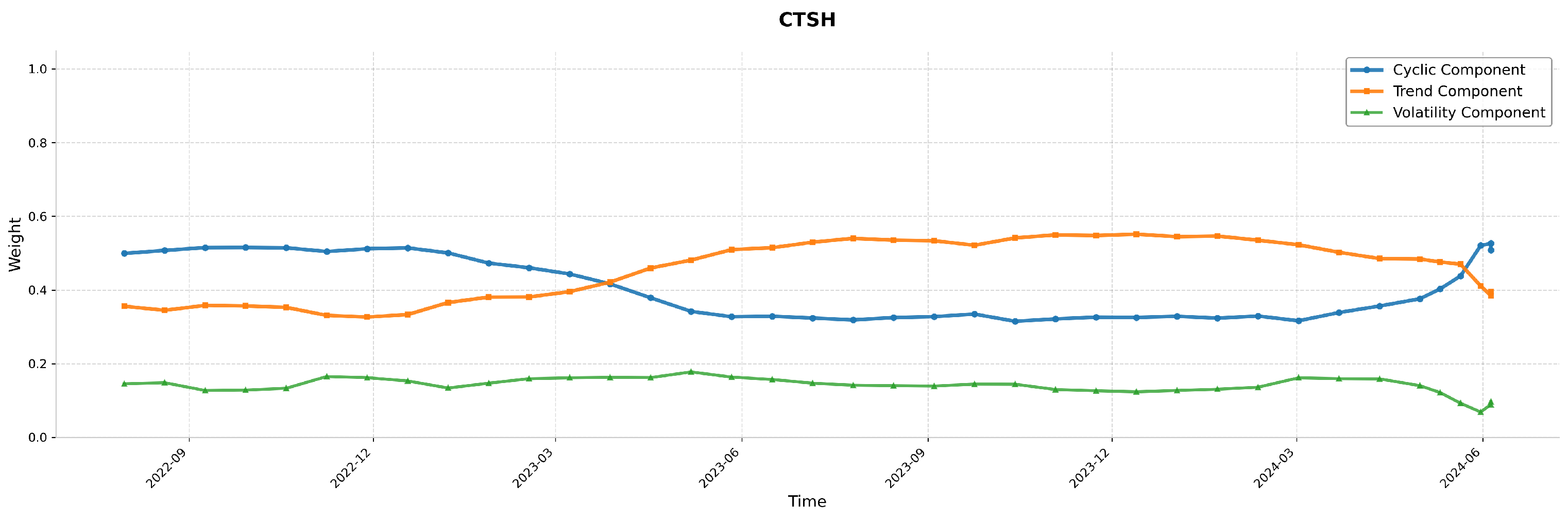
6.2. Visualization and Analysis of Stock Price Component Decomposition, Dynamic Weight Distribution, and Periodic Patterns
- Red upward arrows (↑): periods where HRformer predicted a price increase.
- Green downward arrows (↓): periods where HRformer predicted a price decrease.
6.3. Backtesting Performance
6.4. Statistical Analysis
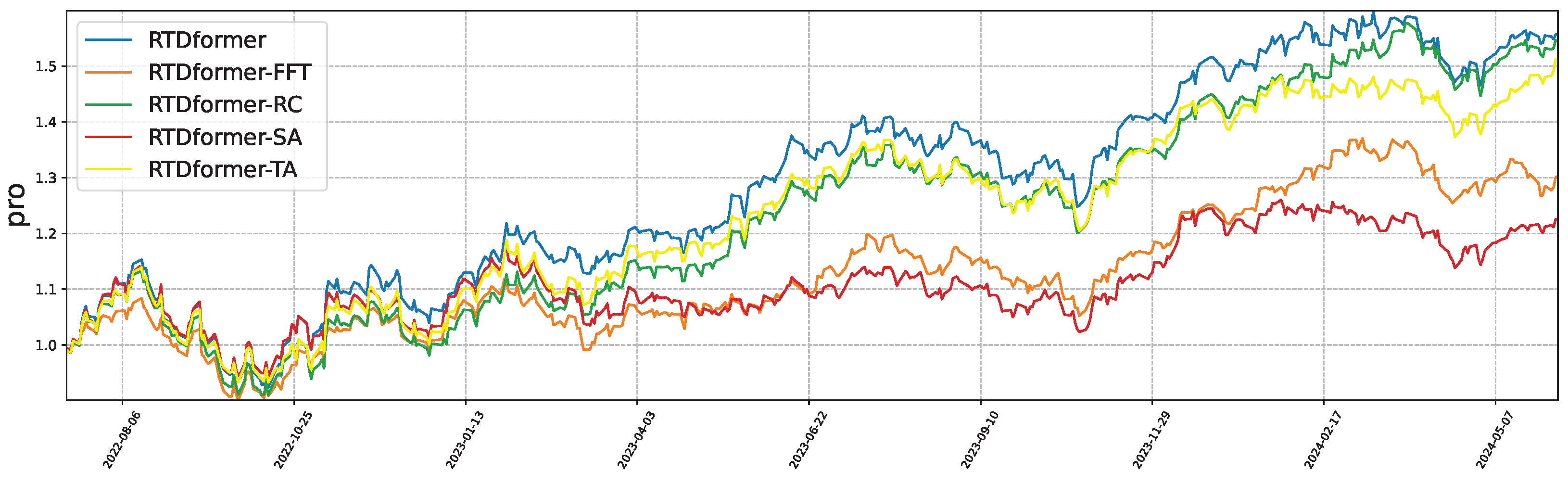
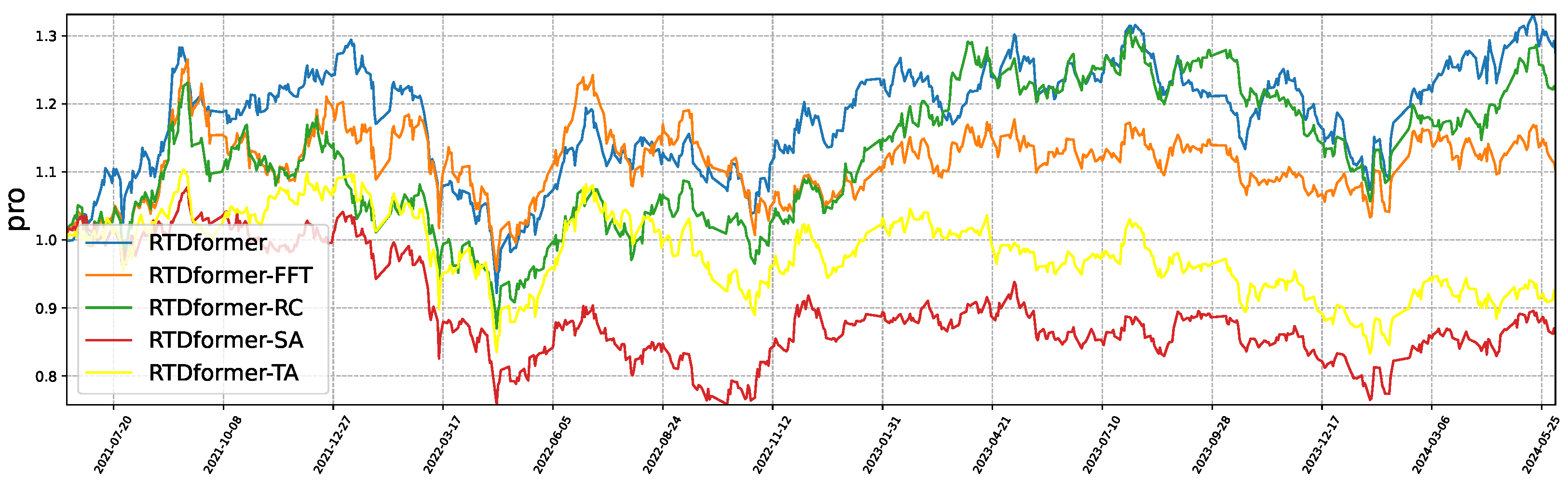
6.5. Ablation Study
- HRformer-FFT: remove FFT/IFFT within the Multi-Component Decomposition Layer to test the role of frequency–domain separation of cyclic and volatility components.
- HRformer-VC: remove the volatility component branch to evaluate the impact of short-term fluctuation modeling.
- HRformer-ISCA: remove the Inter-Stock Correlation Attention to test cross-stock spatial dependency modeling.
- HRformer-TA: replace attention in the Component-wise Temporal Encoder with an MLP to test temporal attention effectiveness.
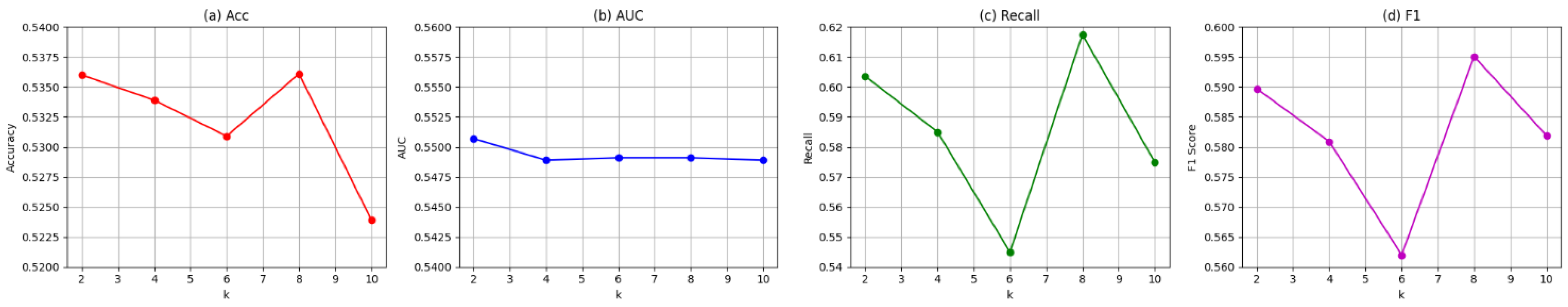
6.6. Parameter Analysis
6.7. Complexity Analysis
6.8. Performance Analysis
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Visualization of Attention Heatmaps Between Correlated Stocks
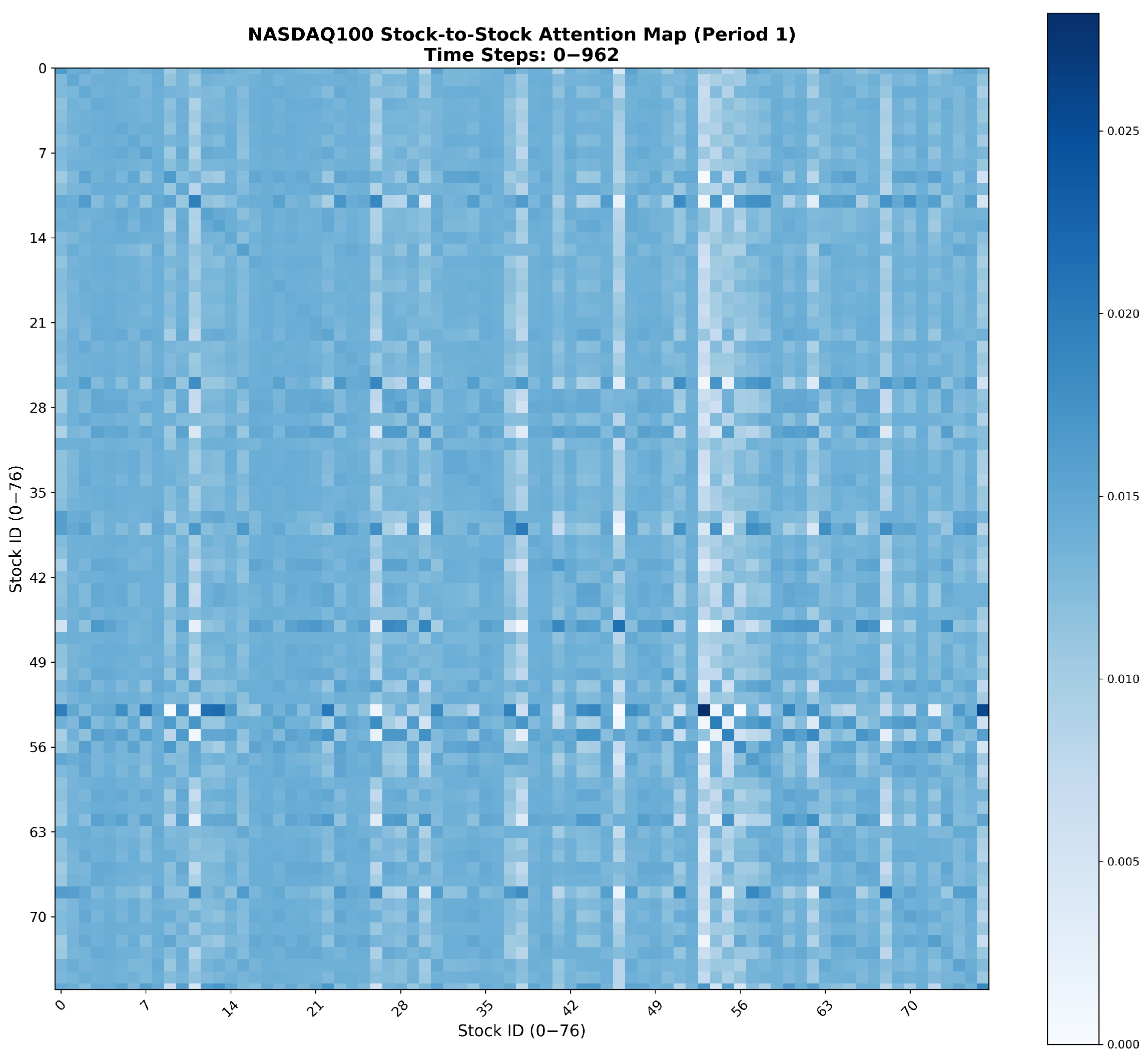
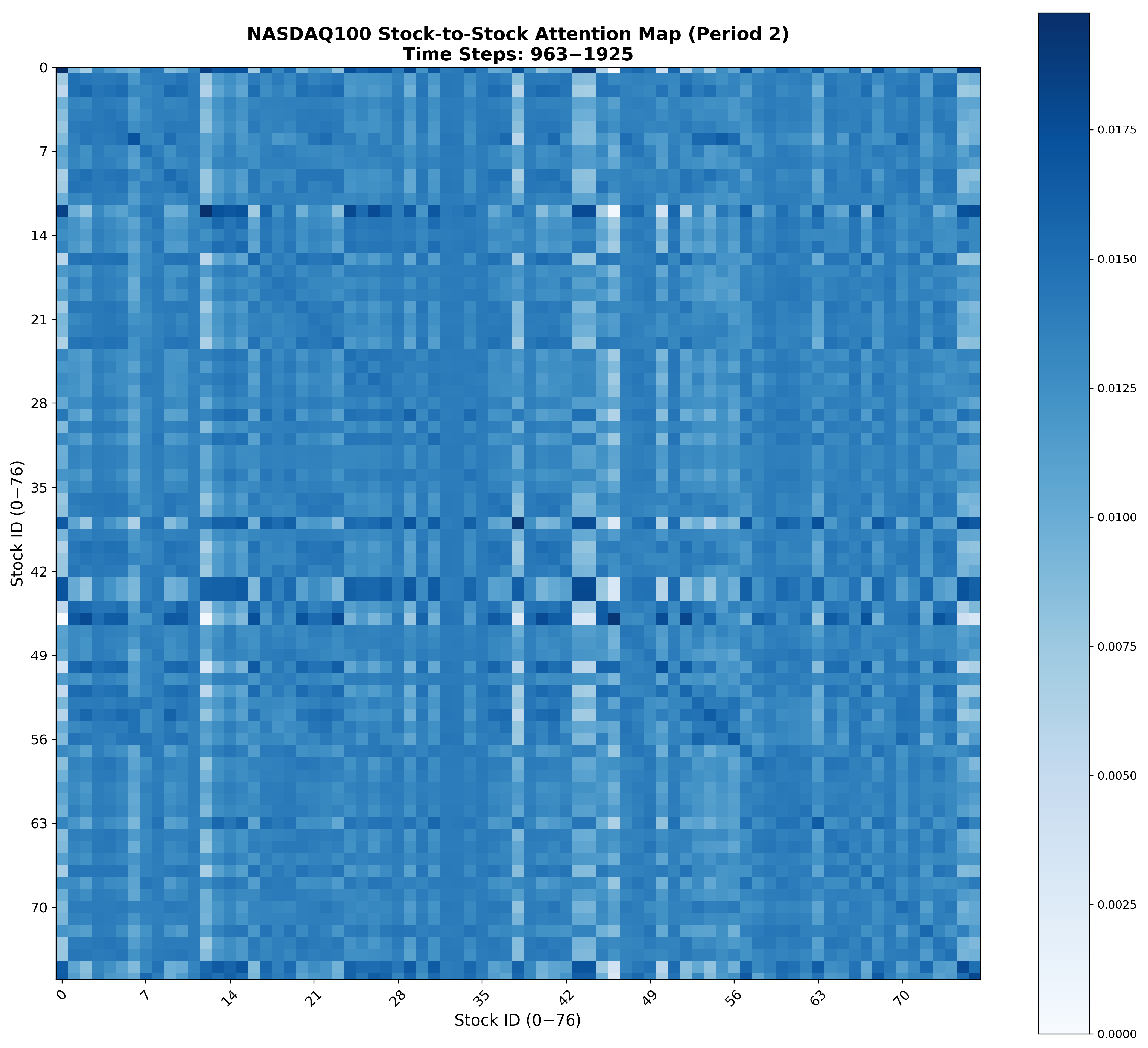
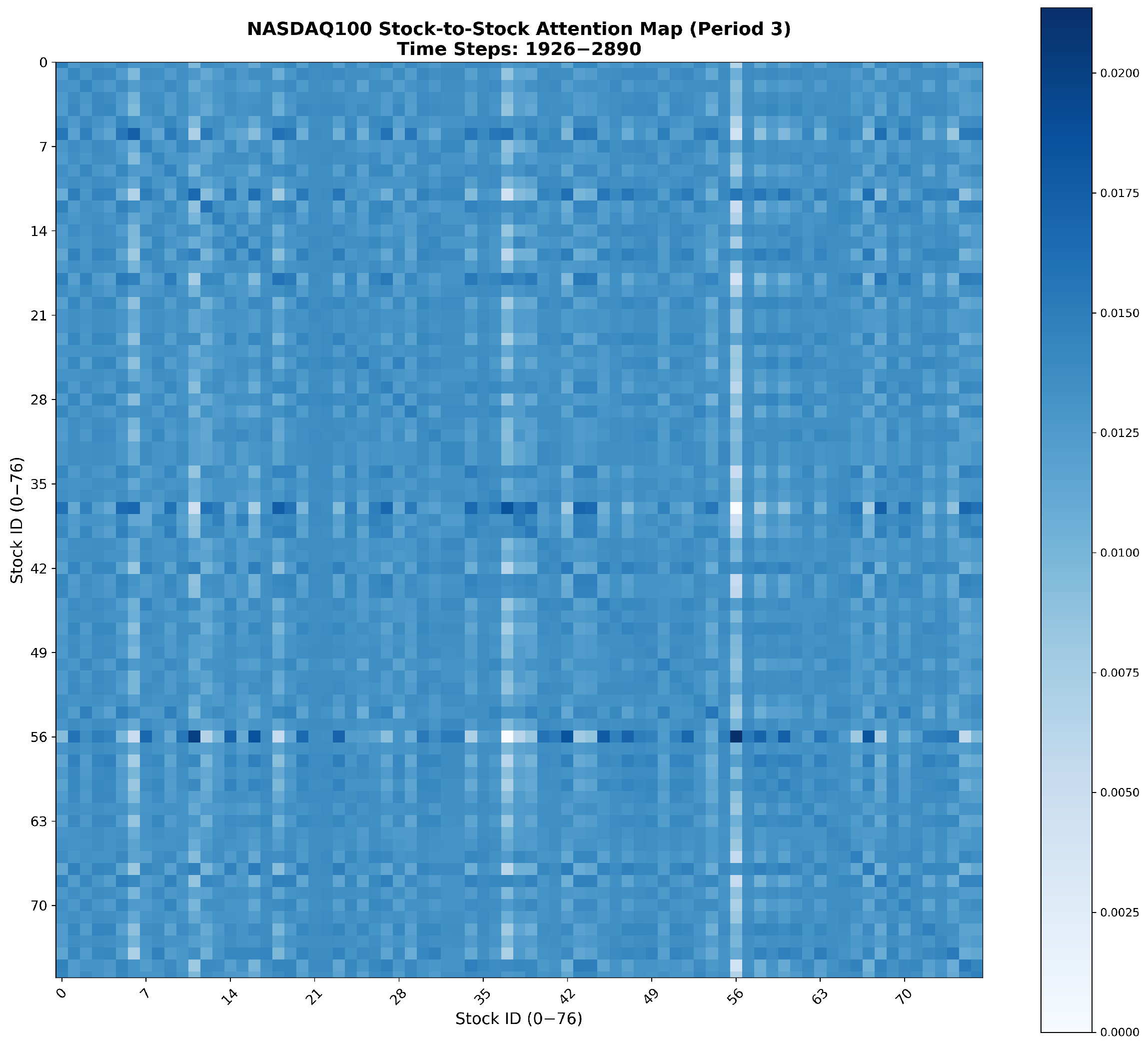
References
- Song, L.; Li, H.; Chen, S.; Gan, X.; Shi, B.; Ma, J.; Pan, Y.; Wang, X.; Shang, X. Multi-Scale Temporal Neural Network for Stock Trend Prediction Enhanced by Temporal Hyepredge Learning. In Proceedings of the IJCAI, Montreal, QC, Canada, 16–22 August 2025; pp. 3272–3280. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Zheng, J.; Yang, Z.; Chen, N.; Wu, D.O. Pleno-Alignment Framework for Stock Trend Prediction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2025, 36, 16604–16618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.; Chi, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, C. Robust stock trend prediction via volatility detection and hierarchical multi-relational hypergraph attention. Knowl. Based Syst. 2025, 329, 114283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Xie, L.; Du, Y.; Chen, S.; Wan, H.; Xu, H. Stock trend prediction based on dynamic hypergraph spatio-temporal network. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 154, 111329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Xie, L.; Liao, S.; Chen, S.; Wu, Y.; Xu, H. DTSMLA: A dynamic task scheduling multi-level attention model for stock ranking. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 243, 122956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Xie, L.; Chen, S.; Xu, H. Stock trend prediction based on industry relationships driven hypergraph attention networks. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 29448–29464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasarweh, M.; Alwadi, S. ARIMA model in predicting banking stock market data. Mod. Appl. Sci. 2018, 12, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotidis, T.; Stengos, T.; Vravosinos, O. The effects of markets, uncertainty and search intensity on bitcoin returns. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2019, 63, 220–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhu, X.; Huang, C.; Yang, X.; Wen, F.; Zhong, M. A new approach for stock price analysis and prediction based on SSA and SVM. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Decis. Mak. 2019, 18, 287–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Gao, R.; Suganthan, P.N.; Tanveer, M. Automated layer-wise solution for ensemble deep randomized feed-forward neural network. Neurocomputing 2022, 514, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Li, B.; Li, P.; Zhang, R. Research on stock trend prediction method based on optimized random forest. CAAI Trans. Intell. Technol. 2023, 8, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, T.; Asahi, Y. The Nikkei Stock Average Prediction by SVM. In Proceedings of the Human Interface and the Management of Information—Thematic Area, HIMI 2023, Held as Part of the 25th HCI International Conference, HCII 2023, Copenhagen, Denmark, 23–28 July 2023; Mori, H., Asahi, Y., Eds.; Proceedings, Part I; Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; Volume 14015, pp. 211–221. [Google Scholar]
- Kumbure, M.M.; Lohrmann, C.; Luukka, P.; Porras, J. Machine learning techniques and data for stock market forecasting: A literature review. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 197, 116659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, W.G.; Chen, Z. A novel graph convolutional feature based convolutional neural network for stock trend prediction. Inf. Sci. 2021, 556, 67–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Xie, L.; Xu, H. Multi-resolution Patch-based Fourier Graph Spectral Network for spatiotemporal time series forecasting. Neurocomputing 2025, 638, 130132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Xie, L. A Dynamic Stiefel Graph Neural Network for Efficient Spatio-Temporal Time Series Forecasting. In Proceedings of the IJCAI, Montreal, QC, Canada, 16–22 August 2025; pp. 7155–7163. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, X.; Zhang, X.; Luo, Z. Multi-scale local cues and hierarchical attention-based LSTM for stock price trend prediction. Neurocomputing 2022, 505, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhu, G.; Xiang, H. Artificial intelligent based day-ahead stock market profit forecasting. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 99, 107837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, U.; Bhattacharjee, V.; Bishnu, P.S. StockNet—GRU based stock index prediction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 207, 117986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhao, J. Temporal convolutional networks for anomaly detection in time series. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1213, 042050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ren, J.; Liang, H.; Gong, J.; Wang, B. Conducting stock market index prediction via the localized spatial–temporal convolutional network. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2023, 108, 108687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, S.; Peng, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, W. Informer: Beyond efficient transformer for long sequence time-series forecasting. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual, 19–21 May 2021; Volume 35, pp. 11106–11115. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Ma, Z.; Wen, Q.; Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Jin, R. Fedformer: Frequency enhanced decomposed transformer for long-term series forecasting. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Baltimore, MD, USA, 17–23 July 2022; pp. 27268–27286. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Jin, X.; Gopalswamy, K.; Gupta, G.; Park, Y.; Shi, X.; Wang, H.; Maddix, D.C.; Wang, Y. First De-Trend then Attend: Rethinking Attention for Time-Series Forecasting. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.08151. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, T.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H.; Wang, S.; Ma, L.; Long, M. itransformer: Inverted transformers are effective for time series forecasting. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.06625. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Long, M. Autoformer: Decomposition transformers with auto-correlation for long-term series forecasting. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 22419–22430. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, W.; Wu, X.; Chen, P.C.; Liu, J. LSTM network: A deep learning approach for short-term traffic forecast. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2017, 11, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, D.; Flunkert, V.; Gasthaus, J.; Januschowski, T. DeepAR: Probabilistic forecasting with autoregressive recurrent networks. Int. J. Forecast. 2020, 36, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, J. Crossformer: Transformer utilizing cross-dimension dependency for multivariate time series forecasting. In Proceedings of the The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations, Kigali, Rwanda, 1–5 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, Y.; Nguyen, N.H.; Sinthong, P.; Kalagnanam, J. A time series is worth 64 words: Long-term forecasting with transformers. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.14730. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Tan, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, H. A multimodal event-driven LSTM model for stock prediction using online news. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2020, 33, 3323–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Kaur, R.; Siddagangappa, S.; Rahimi, S.; Balch, T.; Veloso, M. Financial time series forecasting using cnn and transformer. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.04912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Wang, Z.; Pang, B.; Wang, J.; Liu, X. Wavelet Transformer: An Effective Method on Multiple Periodic Decomposition for Time Series Forecasting. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2025, 36, 14063–14077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhu, P.; Cheng, D.; Dai, T. Adaptive Multi-Scale Decomposition Framework for Time Series Forecasting. In Proceedings of the AAAI, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–27 February 2024; Walsh, T., Shah, J., Kolter, Z., Eds.; AAAI Press: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 2025; pp. 17359–17367. [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland, R.B.; Cleveland, W.S.; McRae, J.E.; Terpenning, I. STL: A seasonal-trend decomposition. J. Off. Stat 1990, 6, 3–73. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Hu, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J.; Long, M. Timesnet: Temporal 2d-variation modeling for general time series analysis. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.02186. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, A.; Chen, M.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Q. Are transformers effective for time series forecasting? In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Montréal, QC, Canada, 8–10 August 2023; Volume 37, pp. 11121–11128. [Google Scholar]
- Oreshkin, B.N.; Carpov, D.; Chapados, N.; Bengio, Y. N-BEATS: Neural basis expansion analysis for interpretable time series forecasting. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.10437. [Google Scholar]
- Challu, C.; Olivares, K.G.; Oreshkin, B.N.; Ramirez, F.G.; Canseco, M.M.; Dubrawski, A. Nhits: Neural hierarchical interpolation for time series forecasting. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Montréal, QC, Canada, 8–10 August 2023; Volume 37, pp. 6989–6997. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.; Du, L.; Liu, C.; Hu, Y.; Fang, F.; Ward, T. Multi-modal fusion for business process prediction in call center scenarios. Inf. Fusion 2024, 108, 102362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.H.; Bai, Y.L.; Yang, J.; Lu, Y.N. A hybrid prediction method based on empirical mode decomposition and multiple model fusion for chaotic time series. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 141, 110366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Wu, B.; Liu, P.; Li, N.; Bao, J.; Jiang, Y.; Xia, S.T. Periodicity decoupling framework for long-term series forecasting. In Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations, Vienna, Austria, 7–11 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.M.; Pereira, A.C.; De Oliveira, R.A. Stock market’s price movement prediction with LSTM neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Anchorage, AK, USA, 14–19 May 2017; pp. 1419–1426. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Wu, J.; Jiang, X.; Xu, K. Chart GCN: Learning chart information with a graph convolutional network for stock movement prediction. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 248, 108842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, W.; He, H.; Hu, L.; Wang, P.; An, N.; Cao, L.; Niu, Z. FourierGNN: Rethinking multivariate time series forecasting from a pure graph perspective. In Proceedings of the 37th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2023), New Orleans, LA, USA, 10–16 December 2023; Volume 36. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Shen, Y. StockMixer: A Simple Yet Strong MLP-Based Architecture for Stock Price Forecasting. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 8389–8397. [Google Scholar]
- Hewage, P.; Behera, A.; Trovati, M.; Pereira, E.; Ghahremani, M.; Palmieri, F.; Liu, Y. Temporal convolutional neural (TCN) network for an effective weather forecasting using time-series data from the local weather station. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 16453–16482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Chion, J.H.; Suganthan, P.N.; Katuwal, R.K. Ensemble deep random vector functional link neural network for regression. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2022, 53, 2604–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Dataset | Time Interval | Length | num_stocks | Label_0 | Label_1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSI300 | Train set | 4 January 2010–29 August 2017 | 1719 | 230 | 148,955 | 139,500 |
| Valid set | 30 August 2017–15 June 2021 | 873 | 230 | 70,267 | 72,023 | |
| Test set | 16 June 2021–5 June 2024 | 673 | 230 | 54,006 | 57,749 | |
| NASDAQ100 | Train set | 2 August 2010–1 August 2019 | 2124 | 77 | 70,257 | 104,225 |
| Valid set | 2 August 2019–10 July 2022 | 692 | 77 | 26,694 | 30,209 | |
| Test set | 11 July 2022–5 June 2024 | 433 | 77 | 18,569 | 18,391 |
| Model | SeqLen | Epoch | Head | Learning Rate | Hidden Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transformer [22] | 48 | 30 | 8 | 0.0002 | 512 |
| FEDformer [17] | 48 | 30 | 8 | 0.0002 | 512 |
| TDformer [36] | 48 | 30 | 8 | 0.0002 | 512 |
| FourierGNN [42] | 48 | 30 | 0 | 0.0002 | 64 |
| iTransformer [25] | 48 | 30 | 8 | 0.0002 | 512 |
| StockMixer [24] | 48 | 30 | 0 | 0.0002 | 512 |
| DLinear [31] | 48 | 30 | 0 | 0.0002 | 64 |
| TCN [20] | 48 | 30 | 0 | 0.0002 | 64 |
| edRVFL [21] | 48 | 30 | 0 | 0.0002 | 64 |
| HRformer | 48 | 30 | 8 | 0.0002 | 512 |
| Model | NASDAQ100 | CSI300 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC (↑) | PRE (↑) | REC (↑) | F1 (↑) | ACC (↑) | PRE (↑) | REC (↑) | F1 (↑) | |
| Transformer [29] | 53.51 | 61.54 | 61.11 | 61.33 | 51.44 | 52.76 | 51.97 | 52.36 |
| FEDformer [23] | 52.96 | 61.51 | 58.83 | 60.14 | 50.24 | 51.73 | 48.47 | 50.05 |
| TDformer [24] | 50.87 | 61.68 | 47.94 | 54.06 | 51.80 | 52.26 | 60.74 | 56.18 |
| FourierGNN [46] | 50.90 | 60.57 | 53.37 | 56.74 | 51.99 | 52.71 | 58.22 | 55.33 |
| iTransformer [25] | 46.86 | 57.45 | 45.65 | 50.88 | 49.87 | 51.22 | 57.67 | 54.25 |
| StockMixer [47] | 46.77 | 57.79 | 42.88 | 49.23 | 52.49 | 53.07 | 56.23 | 54.88 |
| DLinear [38] | 51.40 | 60.54 | 61.07 | 58.19 | 50.43 | 51.54 | 60.65 | 55.72 |
| TCN [48] | 51.98 | 59.98 | 61.84 | 58.75 | 52.10 | 52.98 | 61.00 | 50.71 |
| edRVFL [49] | 51.46 | 59.88 | 59.76 | 56.77 | 51.96 | 52.96 | 58.91 | 55.78 |
| HRformer | 54.91 | 61.76 | 66.15 | 63.88 | 52.61 | 53.36 | 61.95 | 57.33 |
| Model | NASDAQ100 | CSI300 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMDD (↓) | SR (↑) | AR (↑) | fAPV (↑) | AMDD (↓) | SR (↑) | AR (↑) | fAPV (↑) | |
| Transformer [29] | 16.53 | 142.50 | 20.47 | 142.58 | 24.03 | −50.77 | −4.01 | 88.96 |
| FEDformer [23] | 15.56 | 119.15 | 20.30 | 142.19 | 35.86 | −55.17 | −6.70 | 82.03 |
| TDformer [24] | 15.67 | 113.00 | 12.69 | 125.55 | 24.22 | −23.17 | −0.69 | 98.03 |
| FourierGNN [46] | 15.24 | 135.73 | 20.00 | 141.51 | 30.61 | −16.83 | −1.69 | 95.25 |
| iTransformer [25] | 15.59 | 111.12 | 12.00 | 124.10 | 29.48 | −13.67 | −3.92 | 89.20 |
| StockMixer [47] | 17.40 | 94.70 | 16.05 | 132.78 | 26.57 | −64.91 | −4.14 | 88.63 |
| DLinear [38] | 15.83 | 149.04 | 23.22 | 148.85 | 23.40 | −7.10 | −1.12 | 96.91 |
| TCN [48] | 16.00 | 151.47 | 24.55 | 151.93 | 24.59 | 3.62 | 1.68 | 105.98 |
| edRVFL [49] | 15.60 | 117.81 | 12.95 | 126.27 | 25.64 | −9.30 | −1.30 | 96.89 |
| HRformer | 15.53 | 153.54 | 26.18 | 155.72 | 22.32 | 53.98 | 8.88 | 127.53 |
| Model Comparison | ACC (↑) | PRE (↑) | F1 (↑) | ASR (↑) | AR (↑) | fAPV (↑) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRformer vs. Transformer | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| HRformer vs. FEDformer | 0.002 | 0.193 | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.023 | 0.023 |
| HRformer vs. TDformer | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.023 | 0.023 |
| HRformer vs. FourierGNN | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| HRformer vs. iTransformer | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| HRformer vs. StockMixer | 0.014 | 0.020 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| HRformer vs. DLinear | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.004 |
| HRformer vs. TCN | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| HRformer vs. edRVFL | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.004 |
| Model | Acc (↑) | Pre (↑) | Recall (↑) | F1 (↑) | AMDD (↓) | SR (↑) | AR (↑) | fAPV (↑) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRformer-FFT | 53.68 | 61.67 | 57.41 | 59.92 | 14.55 | 114.30 | 14.92 | 130.32 |
| HRformer-VC | 54.82 | 61.52 | 59.00 | 61.18 | 15.61 | 152.82 | 25.65 | 154.49 |
| HRformer-ISCA | 51.90 | 61.36 | 54.88 | 57.94 | 15.71 | 91.76 | 11.24 | 122.49 |
| HRformer-TA | 50.16 | 60.31 | 58.44 | 60.11 | 15.94 | 142.37 | 24.15 | 150.99 |
| HRformer | 54.91 | 61.76 | 66.15 | 63.88 | 15.53 | 153.54 | 26.18 | 155.72 |
| Model | Acc (↑) | Pre (↑) | Recall (↑) | F1 (↑) | AMDD (↓) | SR (↑) | AR (↑) | fAPV (↑) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRformer-FFT | 51.83 | 51.42 | 61.07 | 54.63 | 21.05 | 44.01 | 3.45 | 110.18 |
| HRformer-VC | 52.31 | 53.17 | 61.03 | 56.83 | 23.43 | 40.42 | 7.21 | 122.00 |
| HRformer-ISCA | 51.38 | 51.84 | 56.38 | 55.52 | 29.44 | −41.34 | −5.07 | 86.16 |
| HRformer-TA | 51.10 | 52.34 | 56.10 | 54.72 | 22.70 | −21.38 | −2.76 | 92.28 |
| HRformer | 52.61 | 53.36 | 61.95 | 57.33 | 22.32 | 53.98 | 8.88 | 127.53 |
| Model | Parameters | One-Epoch Training Time (s) |
|---|---|---|
| Transformer [22] | 10,532,872 | 32 |
| FEDformer [17] | 10,527,244 | 33 |
| TDformer [36] | 10,865,222 | 33 |
| FourierGNN [42] | 1,897,338 | 30 |
| iTransformer [24] | 6,380,090 | 27 |
| StockMixer [24] | 31,927 | 33 |
| DLinear [31] | 74,506 | 25 |
| TCN [20] | 40,410 | 23 |
| edRVFL [21] | 43,300 | 23 |
| HRformer | 22,462,014 | 42 |
| Model | Trainable Parameters | Training Time | Max GPU Memory | Batch Inference Latency | Per-Sample Latency | Throughput (Samples/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRformer | 22.43 M | 0.05 h | 3.26 GB | 0.0164 s | 0.000064 s | 15,640.82 |
| FEDformer | 10.53 M | 0.03 h | 1.98 GB | 0.0039 s | 0.000015 s | 65,701.67 |
| iTransformer | 6.35 M | 0.02 h | 0.19 GB | 0.0020 s | 0.000008 s | 125,617.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Wan, H.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Xie, L. HRformer: A Hybrid Relational Transformer for Stock Time Series Forecasting. Electronics 2025, 14, 4459. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224459
Xu H, Wan H, Wu Y, Zheng J, Xie L. HRformer: A Hybrid Relational Transformer for Stock Time Series Forecasting. Electronics. 2025; 14(22):4459. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224459
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Haijiao, Hongyang Wan, Yilin Wu, Jiankai Zheng, and Liang Xie. 2025. "HRformer: A Hybrid Relational Transformer for Stock Time Series Forecasting" Electronics 14, no. 22: 4459. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224459
APA StyleXu, H., Wan, H., Wu, Y., Zheng, J., & Xie, L. (2025). HRformer: A Hybrid Relational Transformer for Stock Time Series Forecasting. Electronics, 14(22), 4459. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224459






