A Flexible Multi-Core Hardware Architecture for Stereo-Based Depth Estimation CNNs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Algorithms
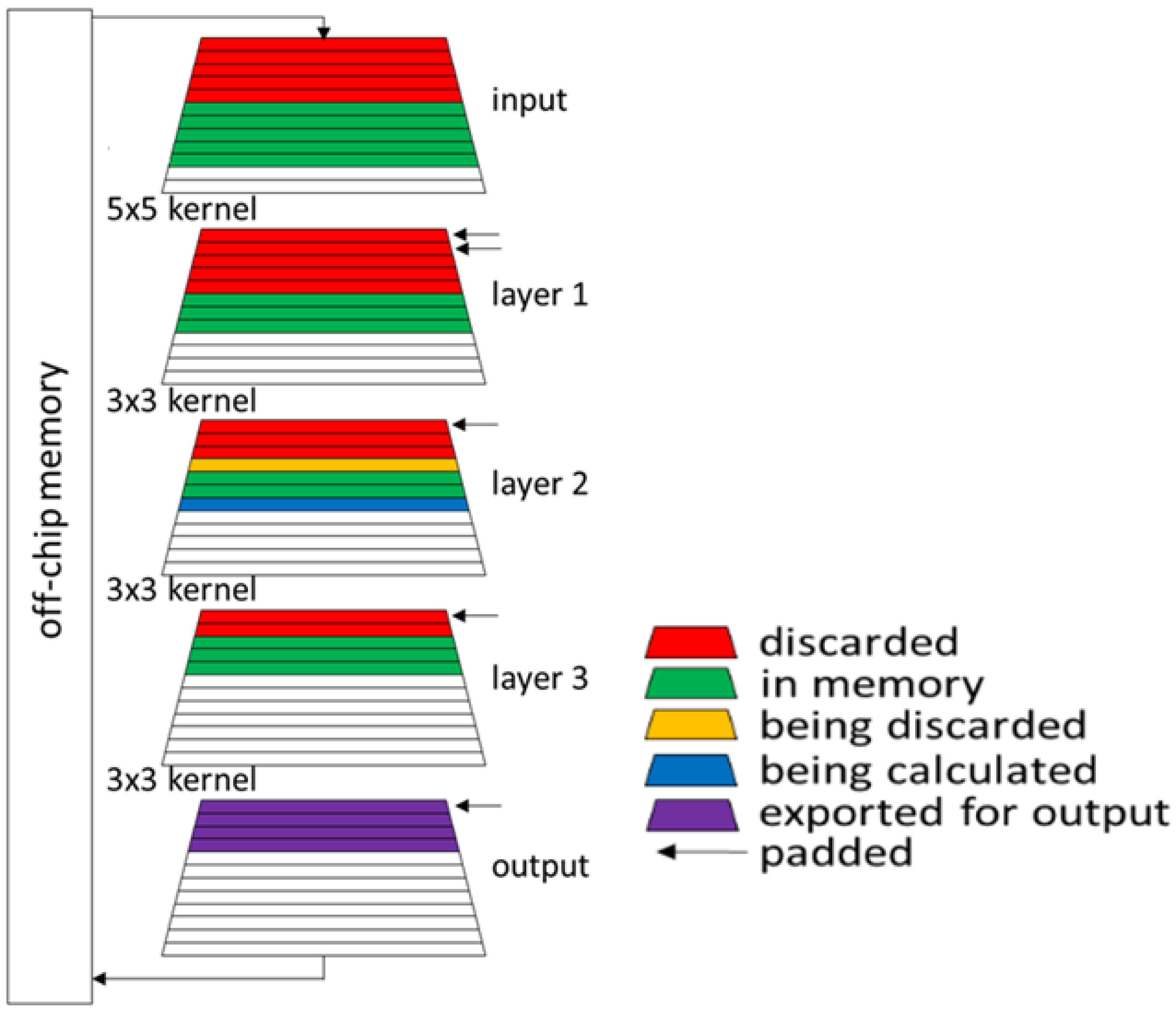
2.2. Hardware: Concept of Depth-First
3. Hardware Architecture
3.1. Introduction
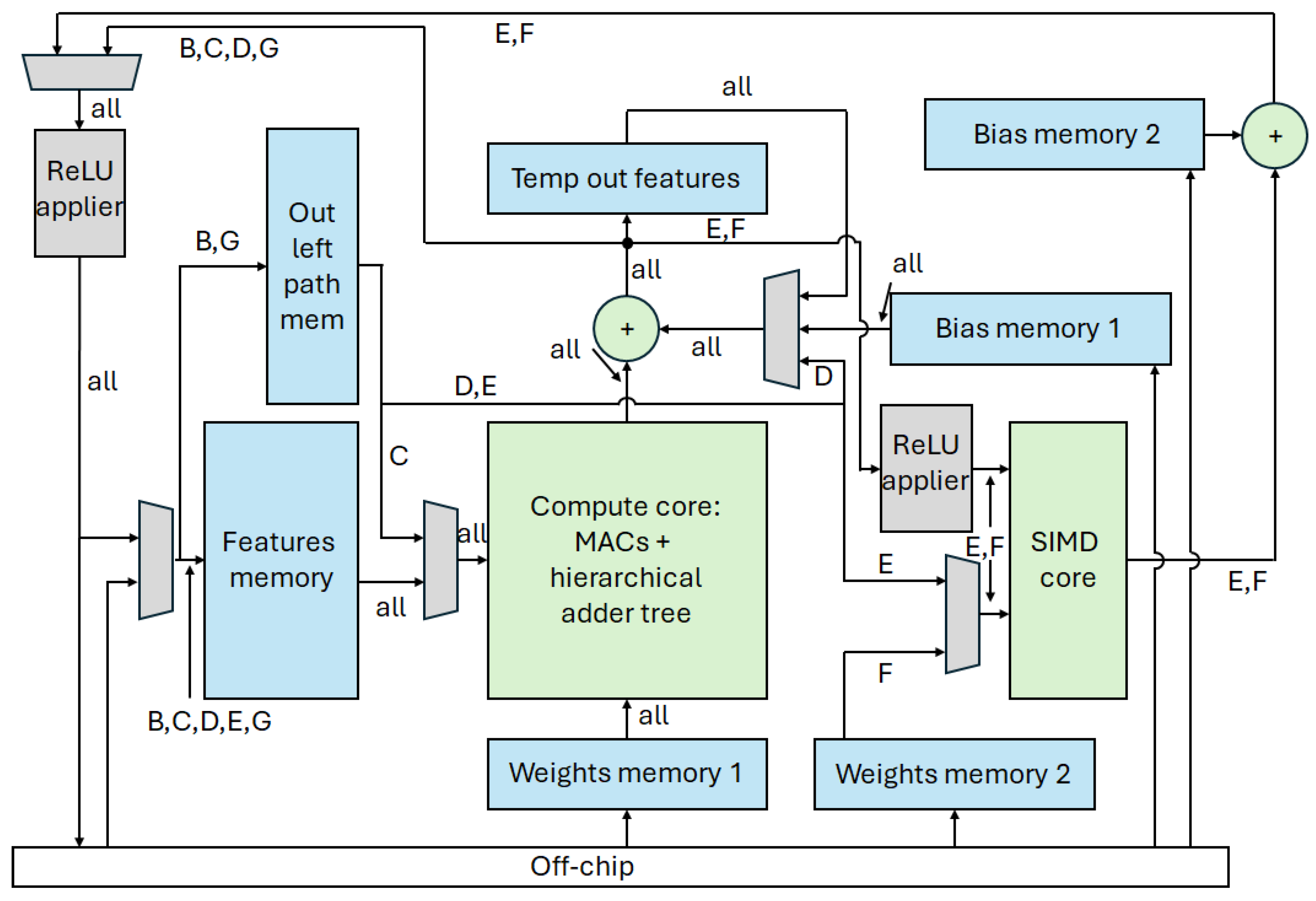
3.2. Overview of the Architecture Datapath
3.3. Compute Core
3.4. SIMD Core
3.5. Other Adders
3.6. ReLU Operator
3.7. Memories
4. Scheduling on Hardware
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Stand-Alone Convolutional Layer: Depth-First
| Algorithm 1 Scheduling for Section 4.2 |
|
4.3. Concatenation of Stereo Paths
4.4. Addition of Stereo Paths
4.5. Multiplication of Stereo Paths
| Algorithm 2 Scheduling for Section 4.4 |
|
4.6. Final Convolutional Layers of Network
4.7. First Convolutional Layer of Network
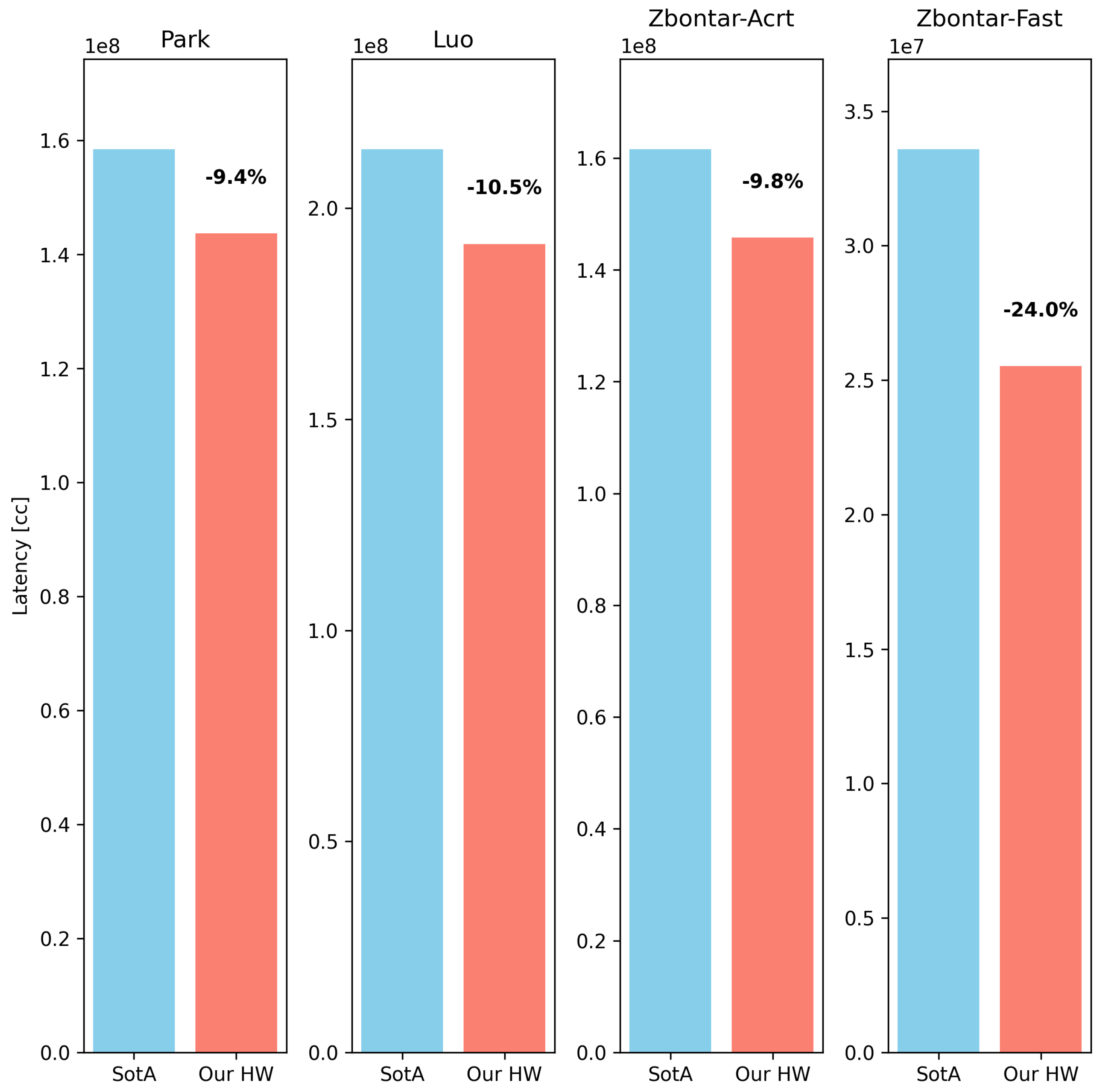
5. Case Study
- Which network architecture benefits the most from the proposed design?
- How does the size of the main core array influence the performance?
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ponrani, M.A.; Ezhilarasi, P.; Rajeshkannan, S. Robust stereo depth estimation in autonomous vehicle applications by the integration of planar constraints using ghost residual attention networks. Signal Image Video Process. 2025, 19, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemsaram, N.; Das, A.; Dubbelman, G. A stereo perception framework for autonomous vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 91st Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2020-Spring), Antwerp, Belgium, 25–28 May 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, S.; Yang, X.; Xiang, Y.; Yu, J.; Ding, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Efficient and Hardware-Friendly Online Adaptation for Deep Stereo Depth Estimation on Embedded Robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2025, 10, 4308–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Pan, W.; Wang, Z.; Mao, M.; Zhang, G.; Bao, H.; Tan, P.; Cui, Z. Dps-net: Deep polarimetric stereo depth estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–3 October 2023; pp. 3569–3579. [Google Scholar]
- Laga, H.; Jospin, L.V.; Boussaid, F.; Bennamoun, M. A survey on deep learning techniques for stereo-based depth estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 1738–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolyanskiy, N.; Kamenev, A.; Birchfield, S. On the importance of stereo for accurate depth estimation: An efficient semi-supervised deep neural network approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 1007–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; An, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J. Visual attention-based self-supervised absolute depth estimation using geometric priors in autonomous driving. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 11998–12005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Lee, K.M. Look wider to match image patches with convolutional neural networks. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 24, 1788–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Schwing, A.G.; Urtasun, R. Efficient deep learning for stereo matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 5695–5703. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Huang, H.; Zhang, X. Efficient stereo matching leveraging deep local and context information. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 18745–18755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satushe, V.; Vyas, V. Use of CNNs for Estimating Depth from Stereo Images. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart Computing and Communication, Bali, Indonesia, 25–27 July 2024; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 45–58. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilera, C.A.; Aguilera, C.; Navarro, C.A.; Sappa, A.D. Fast CNN stereo depth estimation through embedded GPU devices. Sensors 2020, 20, 3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zou, Y.; Lv, J.; Cao, Y.; Yu, H. Lightweight Self-Supervised Monocular Depth Estimation Through CNN and Transformer Integration. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 167934–167943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Nex, F.; Vosselman, G.; Kerle, N. Lite-mono: A lightweight cnn and transformer architecture for self-supervised monocular depth estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 18537–18546. [Google Scholar]
- Goetschalckx, K.; Verhelst, M. Breaking high-resolution CNN bandwidth barriers with enhanced depth-first execution. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2019, 9, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colleman, S.; Verhelst, M. High-utilization, high-flexibility depth-first CNN coprocessor for image pixel processing on FPGA. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2021, 29, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symons, A.; Mei, L.; Colleman, S.; Houshm, P.; Karl, S.; Verhelst, M. Stream: A Modeling Framework for Fine-grained Layer Fusion on Multi-core DNN Accelerators. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Symposium on Performance Analysis of Systems and Software (ISPASS), Raleigh, NC, USA, 23–25 April 2023; pp. 355–357. [Google Scholar]
- Žbontar, J.; LeCun, Y. Stereo matching by training a convolutional neural network to compare image patches. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2016, 17, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zbontar, J.; LeCun, Y. Computing the stereo matching cost with a convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1592–1599. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Fischer, P.; Ilg, E.; Hausser, P.; Hazirbas, C.; Golkov, V.; van der Smagt, P.; Cremers, D.; Brox, T. Flownet: Learning optical flow with convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 2758–2766. [Google Scholar]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Colleman, S.; Nardi-Dei, A.; Geilen, M.C.W.; Stuijk, S.; Goedemé, T. A Flexible Multi-Core Hardware Architecture for Stereo-Based Depth Estimation CNNs. Electronics 2025, 14, 4425. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224425
Colleman S, Nardi-Dei A, Geilen MCW, Stuijk S, Goedemé T. A Flexible Multi-Core Hardware Architecture for Stereo-Based Depth Estimation CNNs. Electronics. 2025; 14(22):4425. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224425
Chicago/Turabian StyleColleman, Steven, Andrea Nardi-Dei, Marc C. W. Geilen, Sander Stuijk, and Toon Goedemé. 2025. "A Flexible Multi-Core Hardware Architecture for Stereo-Based Depth Estimation CNNs" Electronics 14, no. 22: 4425. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224425
APA StyleColleman, S., Nardi-Dei, A., Geilen, M. C. W., Stuijk, S., & Goedemé, T. (2025). A Flexible Multi-Core Hardware Architecture for Stereo-Based Depth Estimation CNNs. Electronics, 14(22), 4425. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224425






