ACE-Net: A Fine-Grained Deepfake Detection Model with Multimodal Emotional Consistency
Abstract
1. Introduction
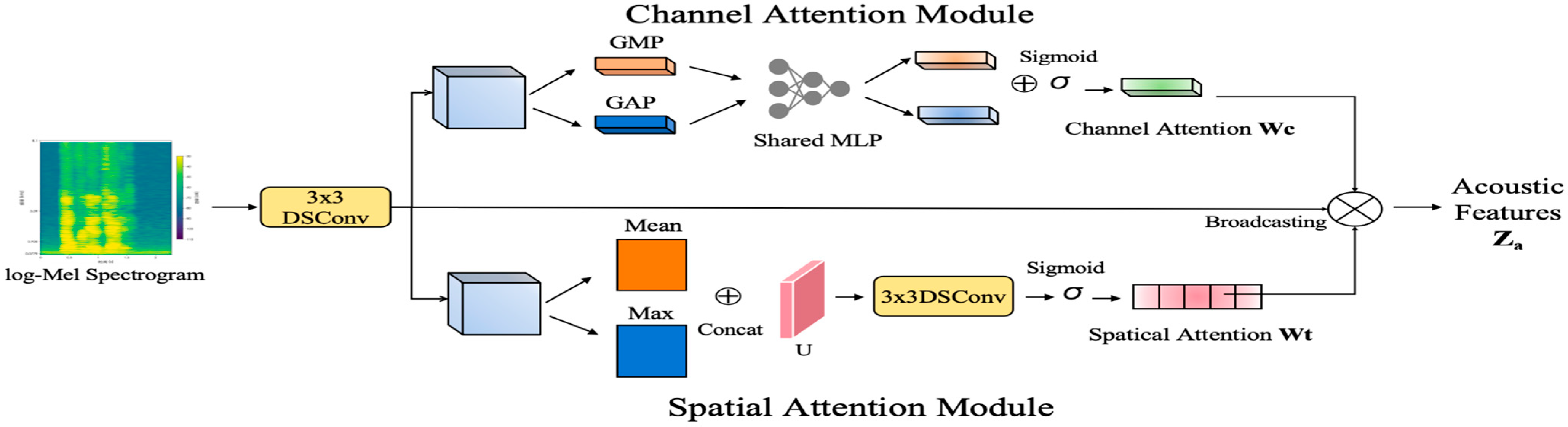
- We develop a lightweight Multi-grained Depthwise Convolutional Network (MDCNN) equipped with a parallel channel-spatial attention mechanism. This network captures emotionally salient peaks by combining global and local pooling strategies and efficiently models spatio-temporal correlations in the time-frequency domain using depthwise separable convolutions, thereby achieving refined, multi-scale perception of acoustic features.
- We design a Coarse-to-Fine visual emotional dynamics frame selection strategy, which integrates motion analysis based on optical flow with an expression verification perception head based on MobileNetV3. This two-stage mechanism rapidly discards static and redundant segments, focusing computational resources on keyframes with the most intense emotional expressions, thereby significantly improving the efficiency and precision of visual feature extraction.
- We propose an emotional consistency discriminator based on multi-aspect feature fusion and deep learning. Our method first constructs a comprehensive feature representation by combining three complementary operations: concatenation, difference, and product. This multi-aspect vector, which encodes aggregation, conflict, and synergy signals, is then fed into a deep, non-linear discriminator (MLP). This allows the model to learn complex semantic correlations from the data directly, significantly enhancing its performance and generalization capability.
2. Related Works
2.1. Visual Modality Detection Methods
2.2. Audio Modality Detection Methods
2.3. Multimodal Emotional Consistency Detection Methods
3. Methods
3.1. Overall Framework
3.2. Speech–Text Emotion Feature Extraction Module
3.2.1. MDCNN Acoustic Branch
3.2.2. Bidirectional Cross-Modal Attention Mechanism
3.3. Dynamic–Temporal Facial Emotion Feature Extraction Module
3.3.1. Keyframe Selection
3.3.2. Lightweight Spatiotemporal Feature Extraction
3.4. Multimodal Emotional Consistency Discrimination
3.5. Training Strategy
3.6. Computational Efficiency Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Experimental Datasets and Forgery Synthesis
4.1.1. Design Principles
- Decoupled Two-Stage Training. Our training process, detailed in Section 3.5, separates feature learning on genuine data from consistency learning on mixed data to ensure a focus on semantic relationships.
- Controlled Forgery Generation. We generate different types of forgeries to act as experimental controls, allowing us to isolate and test for specific inconsistencies. The detailed synthesis methods are described in Section 4.1.2.
4.1.2. Forgery Synthesis
4.1.3. Data Preprocessing
4.2. Experimental Setup
4.2.1. Model Parameters and Training Configuration
4.2.2. Evaluation Strategy and Metrics
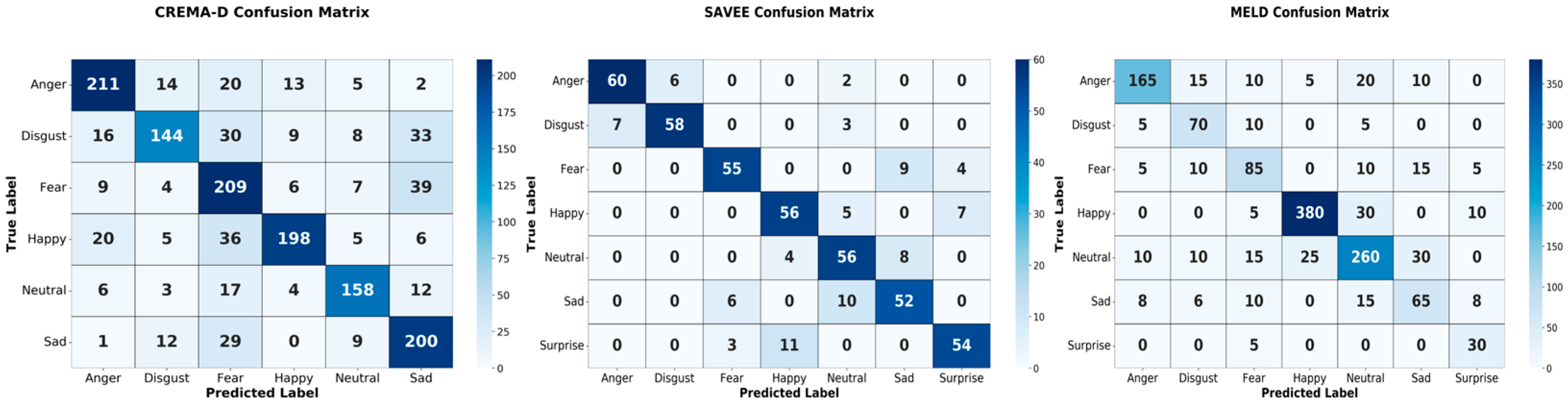
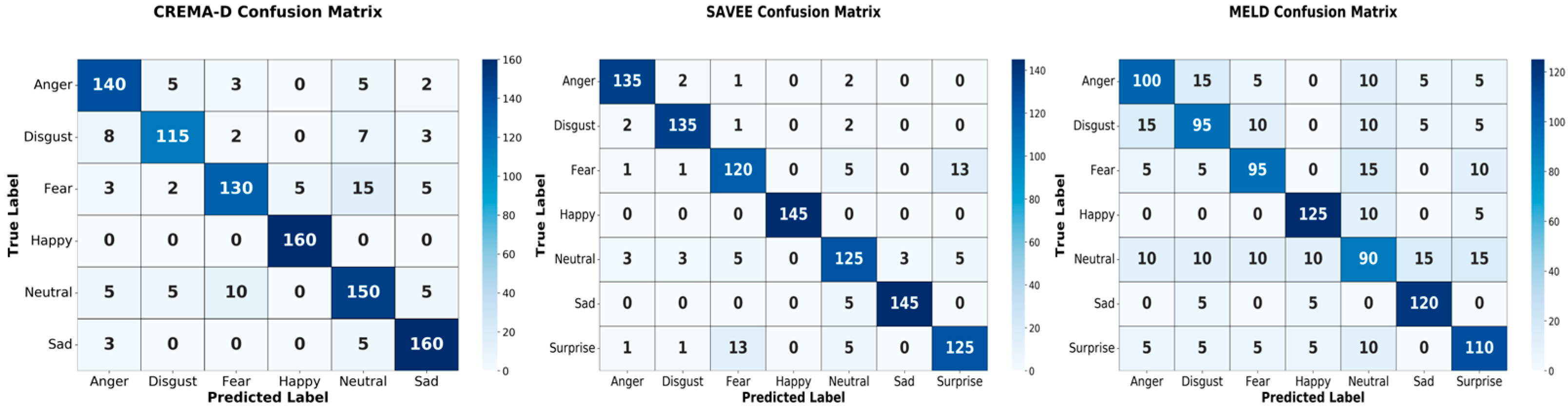
4.3. Emotion Recognition Results Analysis
4.3.1. Speech–Text Model Experimental Results and Analysis
4.3.2. Facial Emotion Recognition Results and Analysis
4.4. Forgery Detection Results Analysis
4.4.1. Performance on Different Forgery Types
4.4.2. Ablation Study
4.4.3. Comparison with Existing Methods
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE-Net | Affective Consistency Evaluation Network |
| ASR | Automatic Speech Recognition |
| AUC | Area Under the ROC Curve |
| BERT | Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers |
| CBAM | Convolutional Block Attention Module |
| DWConv | Depthwise Convolution |
| DSC | Depthwise Separable Convolution |
| FV-LiteNet | Facial Visual Lite Network |
| MACs | Multiply–Accumulate Operations |
| MDCNN | Multi-granularity-attention Depthwise Convolutional Network |
| MLP | Multi-Layer Perceptron |
References
- Croitoru, F.A.; Hondru, V.; Ionescu, R.T.; Shah, M. Diffusion models in vision: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 10850–10869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, J.; Hua, M.; He, Q.; Yi, Z.; Liu, Y. Region-aware face swapping. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 7632–7641. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.K.; Xu, S.K.; Zhang, S.H.; Chen, Q. Survey on deep adversarial visual generation. J. Image Graph. 2021, 26, 2751–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Y.; Li, X.H.; Hu, Z. A review of deepfake face generation and detection techniques. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2025, 53, 85–103. [Google Scholar]
- Koujan, M.R.; Doukas, M.C.; Roussos, A.; Zafeiriou, S. Head2head: Video-based neural head synthesis. In Proceedings of the 2020 15th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 16–20 November 2020; pp. 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, P.Y.; Dai, S.T.; Bai, J.; Gao, X. Bimodal emotion recognition with speech and facial image. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2024, 46, 4542–4552. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Yamagishi, J.; Echizen, I. Capsule-forensics: Using capsule networks to detect forged images and videos. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 2307–2311. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bao, J.; Zhou, W.; Wang, W.; Li, H. Altfreezing for more general video face forgery detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 4129–4138. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Zhou, W.; Chen, D.; Wei, T.; Zhang, W.; Yu, N. Multi-attentional deepfake detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 2185–2194. [Google Scholar]
- Rossler, A.; Cozzolino, D.; Verdoliva, L.; Riess, C.; Thies, J.; Nießner, M. Faceforensics++: Learning to detect manipulated facial images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Xiao, Z.; Li, S.; Lin, F.; Li, J.; Ge, S. Learning natural consistency representation for face forgery video detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 407–424. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Xu, X.; Chao, W. A public and large-scale expert information fusion method and its application: Mining public opinion via sentiment analysis and measuring public dynamic reliability. Inf. Fusion 2022, 78, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Tan, P.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, C. Speech emotion recognition using emotion perception spectral feature. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2021, 33, e5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Chen, X.; Huang, S.; Xiong, G.; Yan, K.; Zhou, X. Federal learning edge network based sentiment analysis combating global COVID-19. Comput. Commun. 2023, 204, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Liu, M.; Cao, M. Multi-modality behavioral influence analysis for personalized recommendations in health social media environment. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2019, 6, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T. Deepfake generation and detection, a survey. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 6259–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Yu, W.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Tay, F.E.H.; Feng, J.; Yan, S. Tokens-to-token vit: Training vision transformers from scratch on imagenet. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 558–567. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Xu, C. GhostNet: More features from cheap operations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1580–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Zhou, X.; Yu, L.; Shen, L.; Yu, S. Double biologically inspired transform network for robust palmprint recognition. Neurocomputing 2019, 337, 24–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liang, W.; Kevin, I.; Wang, K.; Wang, H.; Yang, L.T.; Jin, Q. Deep-learning-enhanced human activity recognition for Internet of Healthcare Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 6429–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.; Mermelstein, P. Comparison of parametric representations for monosyllabic word recognition in continuously spoken sentences. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1980, 28, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atal, B.S.; Schroeder, M.R. Adaptive predictive coding of speech signals. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1970, 49, 1973–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, T.M.; Gunawan, T.S.; Qadri, S.A.A.; Kartiwi, M.; Ambikairajah, E. A comprehensive review of speech emotion recognition systems. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 47795–47814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinpelu, S.; Viriri, S.; Adegun, A. An enhanced speech emotion recognition using vision transformer. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nfissi, A.; Bouachir, W.; Bouguila, N.; Sadouk, L. CNN-N-GRU: End-to-end speech emotion recognition from raw waveform signal using CNNs and gated recurrent unit networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 21st IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications, Nassau, Bahamas, 12–15 December 2022; pp. 699–702. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.C.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, H.Y.; Mao, X.N. Speech enhancement based on deep complex gated dilated recurrent convolutional network. J. China Acad. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2025, 20, 194–202. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.A.; Muller, B.; Yu, B.; Stenetorp, P.; Gales, M.; Aharoni, R.; Andreae, C.; Gales, D.; Wang, Y.; King, S. Spirit-lm: Interleaved spoken and written language model. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2025, 13, 30–51. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Liang, W. CNN-RNN based intelligent recommendation for online medical pre-diagnosis support. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2020, 18, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, M.; Kou, G.; Dong, Y.; Chiclana, F. Bounded confidence evolution of opinions and actions in social networks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 7017–7028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.J.; Cai, C.G.; Pan, B.; Wang, P. A multi-agent linguistic-style large group decision-making method considering public expectations. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2021, 14, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Qin, J.J.; Yu, Y.; Hao, X.K. Audio-visual emotion recognition based on improved ConvMixer and dynamic focal loss. Acta Electron. Sin. 2024, 52, 2824–2835. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.; Zheng, B.; Paul, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, Z.; Sun, J.; Liu, S. Exploring the deep fusion of large language models and diffusion transformers for text-to-image synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 15–21 June 2025; pp. 28586–28595. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, S. Correlation-split and Recombination-sort Interaction Networks for air quality forecasting. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 145, 110544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Guo, Y.; Wang, T.; Dou, Y.; Cao, Y.; Tao, D. Voice-face homogeneity tells deepfake. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2023, 20, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Qi, M.J.; Zhan, Z.Y.; Qu, L.G.; Nie, X.S.; Nie, L.Q. A survey on image-text matching research based on deep learning. Chin. J. Comput. 2023, 46, 2370–2399. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Jiang, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, M. An integrated PCA-DAEGCN model for movie recommendation in the social Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 9410–9418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustubioglu, A.; Ustubioglu, B.; Ulutas, G. Mel spectrogram-based audio forgery detection using CNN. Signal Image Video Process. 2023, 17, 2211–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, X. Truthful resource trading for dependent task offloading in heterogeneous edge computing. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2022, 133, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Makhmudov, F.; Kutlimuratov, A.; Akhmedov, F.; Ostonov, A.; Islmuratov, S. Modeling speech emotion recognition via attention-oriented parallel CNN encoders. Electronics 2022, 11, 4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Fan, Z.; Zhu, S.; Dai, Q.; Tan, P. Cascade cost volume for high-resolution multi-view stereo and stereo matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 2495–2504. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Mahendren, J.; Bukhari, S.; Iqbal, S. Multimodal Emotion Recognition via the Fusion of Mamba and Liquid Neural Networks with Cross-Modal Alignment. Electronics 2025, 14, 3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qian, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y. Illumination-Aware Cross-Modality Differential Fusion Multispectral Pedestrian Detection. Electronics 2023, 12, 3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Du, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Q.F.; Lee, C.H. Information fusion in attention networks using adaptive and multi-level factorized bilinear pooling for audio-visual emotion recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2021, 29, 2617–2629. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, D.; Garcia-Romero, D.; Sell, G.; Povey, D.; Khudanpur, S. X-vectors: Robust DNN embeddings for speaker recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 5329–5333. [Google Scholar]
- Ku, H.; Dong, W. Face recognition based on MTCNN and convolutional neural network. Front. Signal Process. 2020, 4, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcfee, B.; Raffel, C.; Liang, D.; Ellis, D.P.W.; McVicar, M.; Battenberg, E.; Nieto, O. librosa: Audio and music signal analysis in python. In Proceedings of the 14th Python in Science Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 6–12 July 2015; pp. 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Maountzouris, K.; Perikos, I.; Hatzilygeroudis, I. Speech emotion recognition using convolutional neural networks with attention mechanism. Electronics 2023, 12, 4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Han, D.K.; Ko, H. Fusion-ConvBERT: Parallel convolution and BERT fusion for speech emotion recognition. Sensors 2020, 20, 6688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahonen, T.; Hadid, A.; Pietikainen, M. Face description with local binary patterns: Application to face recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2006, 28, 2037–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afchar, D.; Nozick, V.; Yamagishi, J.; Echizen, I. MesoNet: A compact facial video forgery detection network. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security, Hong Kong, China, 11–13 December 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Bao, J.; Zhang, T.; Yang, H.; Chen, D.; Wen, F.; Guo, B. Face X-ray for more general face forgery detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 5001–5010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.; Han, X.; Morariu, V.I.; Davis, L.S. Two-stream neural networks for tampered face detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1831–1839. [Google Scholar]
- Todisco, M.; Delgado, H.; Evans, N. Constant Q cepstral coefficients: A spoofing countermeasure for automatic speaker verification. Comput. Speech Lang. 2017, 45, 516–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, H.; Patino, J.; Todisco, M.; Nautsch, A.; Evans, N.; Larcher, A. End-to-end anti-spoofing with RawNet2. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 6369–6373. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, H.; Guo, Q.; Juefei-Xu, F.; Xie, X.; Ma, L.; Feng, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J. DeepRhythm: Exposing deepfakes with attentional visual heartbeat rhythms. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 4318–4327. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, T.; Bhattacharya, U.; Chandra, R.; Bera, A.; Manocha, D. Emotions don’t lie: An audio-visual deepfake detection method using affective cues. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 2823–2832. [Google Scholar]
- Chugh, K.; Gupta, P.; Dhall, A.; Subramanian, R. Not made for each other-Audio-visual dissonance-based deepfake detection and localization. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 439–447. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Gui, W. VAE-based interpretable latent variable model for process monitoring. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 35, 6075–6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Liu, A.; Mao, X.; Li, F. An intelligent charging scheme maximizing the utility for rechargeable network in smart city. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2021, 77, 101457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lv, P.; Wang, H.; Shi, C. SAR-U-Net: Squeeze-and-Excitation Block and Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling Based Residual U-Net for Automatic Liver Segmentation in CT. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 208, 106268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Component | Efficiency Source | Params (M) | Analytical Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
| MDCNN | 3 × 3 DSC; GAP + GMP (r = 8) | 0.019 | ≈1/9 MACs vs. standard 3 × 3 |
| Keyframe-based | K keyframes instead of all T | – | ×(K/T) ≈ 0.07–0.13 |
| FV-LiteNet | Truncated GhostNet; last two SE removed | 1.2 | – |
| Fusion | Small inverted MLP on 4d-dim fused vector | 0.59 | – |
| Model | CREMA-D | SAVEE | MELD |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | 62.15 | 68.25 | 55.48 |
| CNN + GRU | 65.83 | 71.98 | 58.01 |
| CNN + BERT | 70.29 | 76.54 | 64.33 |
| MDCNN | 74.67 | 80.25 | 68.92 |
| Model | CREMA-D | SAVEE | MELD |
|---|---|---|---|
| LBP + SVM | 88.10 | 82.45 | 54.18 |
| FV-LiteNet | 86.83 | 90.15 | 71.77 |
| Dataset | Pairing Type | ACC | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAVEE | Genuine Pairs | 91.2 | 90.8 | 92 | 91.4 | 0.95 |
| SAVEE | Emotion Tampering | 85.6 | 86.5 | 84.2 | 85.3 | 0.91 |
| SAVEE | Cross-Identity Spliced Forgery | 88.1 | 87.6 | 89 | 88.3 | 0.92 |
| CREMA-D | Genuine Pairs | 90.5 | 90.9 | 90.2 | 90.5 | 0.95 |
| CREMA-D | Emotion-Tampering | 86.2 | 88.1 | 86 | 87 | 0.92 |
| CREMA-D | Cross-Identity Spliced Forgery | 88.9 | 88.5 | 89.4 | 88.9 | 0.94 |
| MELD | Genuine Pairs | 75.1 | 76.0 | 74.8 | 75.4 | 0.82 |
| MELD | Emotion-Tampering | 70.4 | 71.2 | 70.0 | 70.6 | 0.77 |
| MELD | Cross-Identity Spliced Forgery | 73.2 | 72.8 | 73.8 | 73.3 | 0.80 |
| Pairing Type | Fusion Method | ACC | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emotion Tampering | Concatenation+ Difference + Product | 87.2 | 88.1 | 86 | 87 | 0.92 |
| Emotion Tampering | Concatenation+ Difference | 85.9 | 86.3 | 85.2 | 85.7 | 0.9 |
| Emotion Tampering | Concatenation | 82.5 | 83.1 | 82.0 | 82.5 | 0.88 |
| Cross-Identity Spliced Forgery | Concatenation+ Difference + Product | 90.3 | 89.8 | 91.2 | 90.5 | 0.94 |
| Cross-Identity Spliced Forgery | Concatenation+ Difference | 89.1 | 89.6 | 88.3 | 88.9 | 0.93 |
| Cross-Identity Spliced Forgery | Concatenation | 85.1 | 84.8 | 85.5 | 85.1 | 0.90 |
| Category | Method | Dataset |
|---|---|---|
| DFDC | ||
| Visual—Artifact/Texture | MesoNet-4 | 0.753 |
| Face X-ray | 0.809 | |
| Two-stream CNN | 0.614 | |
| Audio—Acoustic Artifact | CQCC-GMM | 0.523 |
| RawNet2 | 0.718 | |
| Multimodal—High-level Semantics | DeepRhythm | 0.745 |
| Siamese | 0.844 | |
| MDS | 0.915 | |
| Ours | ACE-Net | 0.921 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, S.; Chen, X.; Sheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Yu, S. ACE-Net: A Fine-Grained Deepfake Detection Model with Multimodal Emotional Consistency. Electronics 2025, 14, 4420. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224420
Yu S, Chen X, Sheng Y, Zhang H, Li X, Yu S. ACE-Net: A Fine-Grained Deepfake Detection Model with Multimodal Emotional Consistency. Electronics. 2025; 14(22):4420. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224420
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Shaoqian, Xingyu Chen, Yuzhe Sheng, Han Zhang, Xinlong Li, and Sijia Yu. 2025. "ACE-Net: A Fine-Grained Deepfake Detection Model with Multimodal Emotional Consistency" Electronics 14, no. 22: 4420. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224420
APA StyleYu, S., Chen, X., Sheng, Y., Zhang, H., Li, X., & Yu, S. (2025). ACE-Net: A Fine-Grained Deepfake Detection Model with Multimodal Emotional Consistency. Electronics, 14(22), 4420. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224420





