Abstract
Steganalysis is a critical research direction in the field of information security. Traditional approaches typically employ convolution operations for feature extraction, followed by classification on noise residuals. However, since steganographic signals are inherently weak, convolution alone cannot fully capture their characteristics. To address this limitation, we propose a steganalysis method based on relationship mining, termed RMNet, which leverages positional relationships of steganographic signals for detection. Specifically, features are modeled as graph nodes, where both locally focused and globally adaptive dynamic adjacency matrices guide the propagation paths of these nodes. Meanwhile, the results are further constrained in the feature space, encouraging intra-class compactness and inter-class separability, thereby increasing inter-class separability of positional features and yielding a more discriminative decision boundary. Additionally, to counter signal attenuation during network propagation, we introduce a multi-scale perception module with cross-attention fusion. Experimental results demonstrate that RMNet achieves performance comparable to state-of-the-art models on the BOSSbase and BOWS2 datasets, while offering superior generalization capability.
1. Introduction
Image steganography is a technique that invisibly embeds secret information into image carriers to enable covert communication. The counterpart of steganography is image steganalysis, which aims to detect any hidden information being transmitted among different entities [1]. These two technologies evolve in an adversarial manner, driving mutual advancements.
Current steganalysis techniques can be broadly categorized into two groups: traditional methods reliant on hand-crafted features and modern approaches based on deep learning [2]. Traditional methods primarily depend on manually designed prior knowledge, which limits their transferability. In recent years, convolutional neural network (CNN)-based steganalysis methods have developed rapidly. These approaches leverage convolution operations to automatically extract and amplify steganographic signals while suppressing semantic information, thereby achieving superior accuracy and generalization compared to traditional techniques. Representative models in this category include Yedroudj-Net [3], SRNet [4], GBRAS-Net [5], SiaStegNet [6], LWENet [7], Luo-Net [8], DFNet [9], and Wei’s model [10].
Although CNN-based steganalysis networks have achieved remarkable progress, they still suffer from inherent limitations. Specifically, stacked convolutions can have insufficient receptive fields, causing over-sensitivity to local features and a lack of global attention. This drawback can trap the models in local analysis. Steganalysis analyzes noise residuals, which are highly dependent on their spatial distribution.Consequently, investigating both the local and global distributions of steganographic signals is particularly critical.
Graph neural networks (GNNs) [11] have emerged with global relation modeling as their distinctive advantage. In domains such as social networks, knowledge graphs, and fine-grained image classification, several cutting-edge studies [12,13,14,15] have demonstrated the strong capability of GNNs in global relationship mining. To better leverage the global information of steganographic signals, we propose a relationship-mining-based steganalysis framework, termed RMNet, which incorporates APPNP [16] to enhance interaction among graph nodes, enabling features to retain local details while also capturing global representations. The proposed approach integrates shallow and deep features through a cross-attention fusion mechanism, and further employs a distance-adaptive adjacency matrix to guide the APPNP algorithm. In this design, nodes closer to the current node are assigned higher dynamic weights, while distant nodes are adaptively weighted. The resulting features preserve local information while showing strong global characteristics. Moreover, to further improve the generalization ability of the model, we introduce a feature clustering and distance constraint module to guide the distribution of features in the representation space. The main contributions of this work can be summarized as follows:
- We propose a steganalysis approach that leverages relationship mining, where local-focused and globally adaptive patterns are employed to guide graph relation modeling and capture global features. In the feature space, feature clustering and contrastive learning are incorporated to enlarge inter-class global differences, thereby generating a more discriminative decision boundary and maximizing the utilization of global relationships for classification.
- We analyze the characteristics of features at different layers in traditional convolutional networks. To balance the large receptive field but insufficient local detail of deep features with the small receptive field but fine-grained detail of shallow features, we propose a cross-attention method between deep and shallow features. In this approach, deep features guide shallow features to obtain representations that not only maintain a large receptive field but also preserve sufficient local details.
- We conduct extensive experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. Ablation studies are performed to verify the contribution of each module, and visualization analyses are provided to further illustrate the performance of our model.
2. Related Work
In this section, we review the development of steganalysis and discuss several representative methods that exploit spatial positional relationships for analysis.
2.1. Development of Steganalysis
Steganalysis development has two stages: early hand-crafted features and recent deep learning methods.Early steganalysis methods primarily relied on manually designed statistical attributes of features [17], with representative approaches including rich models and ensemble-based methods [18,19,20]. However, these approaches were inherently constrained by the limitations of hand-crafted feature descriptors [21]. With the rapid progress of deep learning, CNN-based steganalysis methods have gradually become mainstream. CNNs use convolution to automatically extract features, reducing reliance on manual engineering. Qian et al. [22] were the first to introduce CNNs into this domain, proposing a three-part architecture consisting of high-pass filtering, convolutional feature extraction, and fully connected classification, which achieved performance comparable to traditional methods. Since then, a variety of advanced networks have emerged. XuNet [23] was the first to combine residual networks with spatial pyramid pooling. SRNet [4] introduced residual connections and non-fixed filters. SiaStegNet employed a parameter-sharing Siamese network structure. LWENet [7] integrated depthwise separable convolution, multiple normalization techniques, and global pooling for multi-view classification. SAANet [24] was the first to incorporate attention-augmented convolution. Tong et al. [9] proposed J-DFNet and S-DFNet, which combine residual and dense paths with coordinate attention mechanisms.
Although CNN-based steganalysis models have already achieved high levels of accuracy, they still suffer from certain limitations, such as the loss of feature details caused by convolutional stacking and insufficient utilization of the global spatial information of steganographic signals. These limitations remain major bottlenecks preventing CNNs from achieving even higher accuracy.
2.2. Development of Relationship Mining Techniques
Relationship mining, via GNNs, excels at modeling structured information and capturing global dependencies [11]. Its core is modeling element relationships, where message-passing allows nodes to acquire global and neighborhood context. In the field of fine-grained classification, Bera et al. [14] proposed a method that combines GNNs with attention mechanisms. By exploiting spatial relation-aware feature transformation and attention-based contextual modeling, their approach significantly improved the accuracy of fine-grained image classification. Sikdar et al. [15] further advanced this direction by constructing both inter-region and intra-region graphs to promote high-order feature interactions. Without requiring part-level bounding box annotations, their method automatically captured long-range dependencies and local details across different regions of objects, thereby achieving substantial improvements in classification accuracy.
However, the application of GNNs in the field of steganalysis remains underexplored. Liu et al. [25] conducted a preliminary study on employing GNNs for steganalysis. Their method transformed images into graph structures, extracted node features using shallow CNNs, and applied a graph attention network (GAT) [26] to learn global representations for distinguishing between cover and stego images. Subsequently, Liu et al. [27] extended this approach to the JPEG domain by partially removing pooling layers and setting the convolution stride to 1, in order to prevent the weakening of steganographic signals in deeper feature layers. Nonetheless, this method lacked further performance comparisons with more advanced models. These attempts showed GNNs’ advantages for global analysis but failed to resolve two key issues: signal attenuation in deep features and localized clustering patterns.
3. Method
3.1. Overview
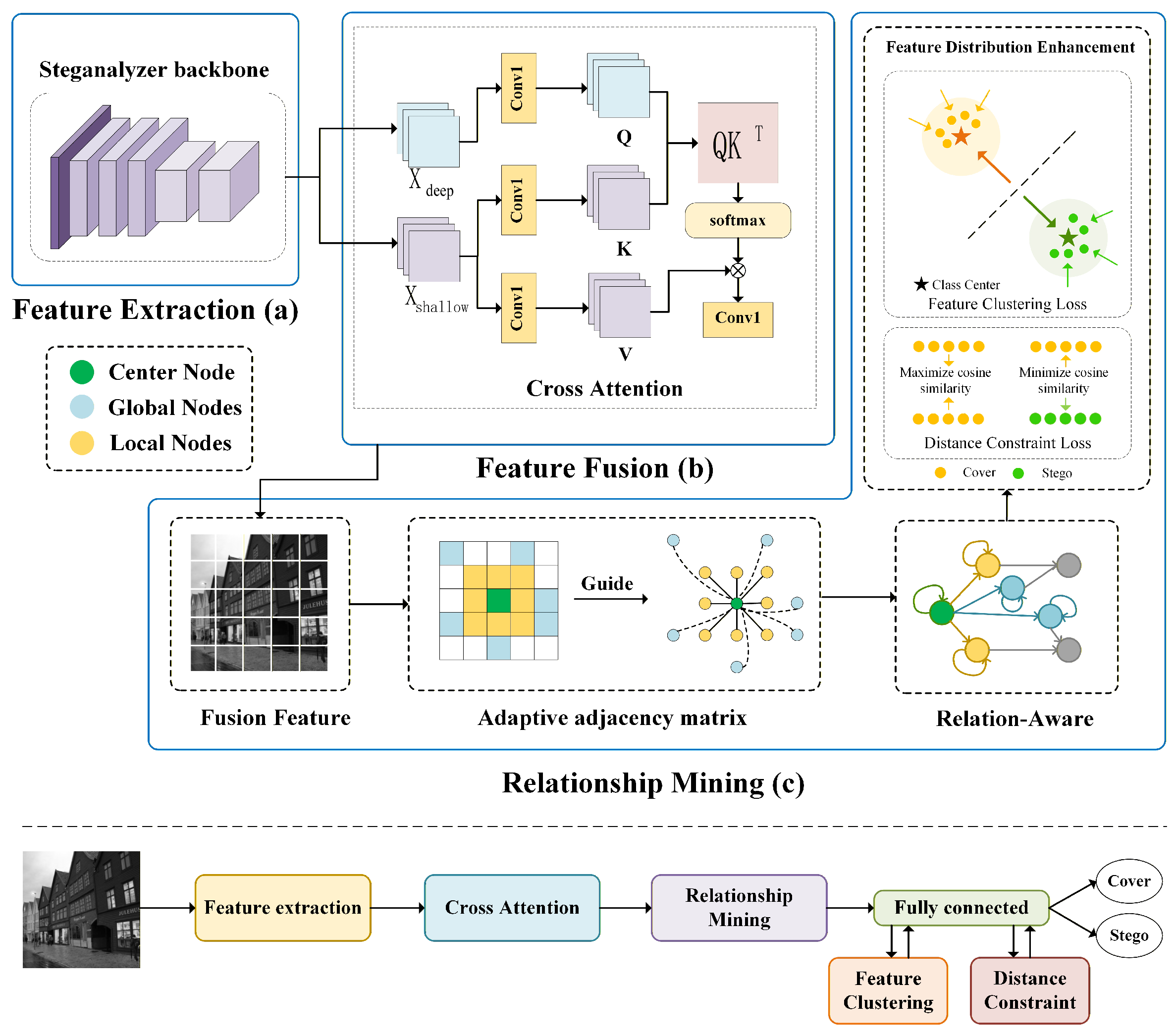
The proposed framework (Figure 1) has three main components: the Feature Extraction Module, the Feature Fusion Module, and the Relationship Mining Module. The Feature Extraction Module employs LWENet as the backbone network to extract steganographic features. The Feature Fusion Module integrates shallow and deep features obtained from the extraction stage, preserving their respective advantages. Building upon the fused representations, the Relationship Mining Module converts features into graph nodes and computes graph relations to obtain global feature representations. The implementations of the Feature Fusion Module and the Relationship Mining Module are described in detail in Section 3.2 and Section 3.3, respectively.
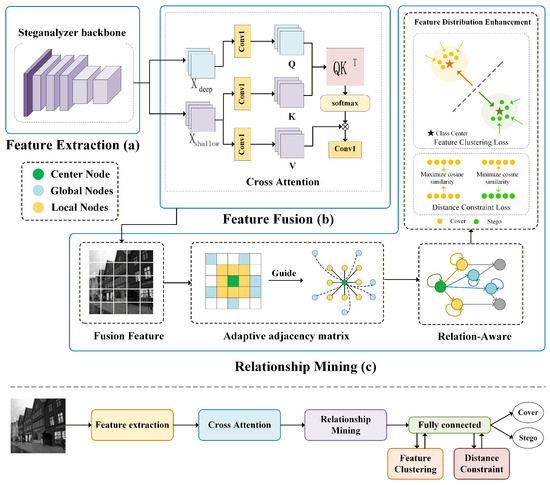
Figure 1.
The architecture of the RMNet network: (a) Backbone network for feature extraction, (b) Feature Fusion Module, (c) Relationship Mining Module.
3.2. Feature Fusion Module
The attention mechanism [28] is a core deep learning component due to its feature selection capability. In convolution-based steganalysis, classification is typically performed using deep features, which capture global representations, while the fine-grained local details contained in shallow features are often lost. To achieve an effective integration of local details and global context, we propose a cross-attention-based Feature Fusion Module, as illustrated in part (b) of Figure 1. Building upon the self-attention mechanism, we modify the usage of queries (q), keys (k), and values (v) to design a cross-attention mechanism tailored specifically for steganalysis.
Given the deep features as queries , the shallow features as keys , and the shallow features as values (where B denotes the batch size, C the number of channels, and the spatial resolution), the features are first projected through linear transformations to obtain Query, Key, and Value:
where , , and are learnable convolutional weights. For multi-head attention, the features are divided into heads, each with a dimension of :
After reshaping, the cross-scale similarity between deep features and shallow features is computed as:
where is a scaling factor. The similarity matrix S is normalized using the softmax function:
The detailed information from shallow features is then aggregated with the attention weights:
Finally, the aggregated representation is reshaped back to the original spatial format and fused through a convolution:
3.3. Relationship Mining Module
The core of steganalysis lies in analyzing the noise residuals between cover and stego images, which are inherently dependent on the spatial distribution of steganographic signals. Therefore, investigating both the local and global distributions of these signals is particularly important. To enable the network to make more effective use of global steganographic information, we propose a Relationship Mining Module, as illustrated in part (c) of Figure 1. This module leverages the interaction modeling capability of graph neural networks to capture global representations of features. It is composed of three components: an adaptive adjacency matrix, relation-aware learning, and feature distribution enhancement.
3.3.1. Adaptive Adjacency Matrix
Steganographic signals are typically embedded into textured regions. These regions exhibit certain local continuity, while the overall distribution tends to be scattered. Thus, emphasizing only global connections while ignoring local structures may obscure weak but important steganographic traces. Based on this observation, we propose a dynamic adjacency matrix that combines local and global connections among graph nodes, ensuring that features can preserve local consistency while also capturing global representations.
For the adjacency matrix, we define the local neighborhood for each graph node i. For any node , a local full connection is adopted as follows:
When node j falls outside the local neighborhood , we further adopt a dynamic adjacency strategy. Specifically, we compute the cosine similarity between node i and node j, normalized to the range :
where and denote the feature vectors of nodes i and j, respectively. We then preserve connections with stronger global relevance by keeping values greater than a threshold , while setting the others to zero. This yields the adaptive global adjacency:
Finally, the overall adjacency matrix is obtained by combining the local and global components:
3.3.2. Relation-Aware
The adjacency matrix specifies the connectivity of graph nodes. For a given feature graph , where B is the batch size, C is the number of channels, and denotes the spatial dimension, we adapt the Approximate Personalized Propagation of Neural Predictions (APPNP) message-passing algorithm [16]. APPNP achieves linear computational complexity by approximating topic-sensitive PageRank through power iteration. The initial feature representation is defined as:
and the iterative process of Approximate Personalized PageRank propagation is given by:
where is the symmetrically normalized adjacency matrix, is the diagonal degree matrix of , is the teleport probability, and denotes the propagation steps.
The final graph representation is obtained as:
Based on , node features are aggregated to obtain the representation for subsequent classification:
3.3.3. Feature Distribution Enhancement
To enlarge the global differences between different classes, we introduce the ideas of feature clustering and contrastive learning. This compacts intra-class features and separates inter-class features, yielding more discriminative representations and a clearer decision boundary. These two strategies are formulated with separate loss functions.
(1) Feature clustering loss: We encourage same-class features to cluster densely around their class center, while enlarging inter-class distances. This reduces intra-class distances and increases inter-class separability, thereby improving the model’s ability to learn discriminative features. Let denote the set of class centers, where p is the number of classes and m is the feature dimension. For a batch of extracted features, the clustering loss is defined as:
where b is the batch size, represents the feature extracted by the network, m is the feature dimension, is the class center, and is a normalization factor.
(2) Distance constraint loss: Inspired by contrastive learning, we enforce a distance constraint between similar and dissimilar features. Specifically, we minimize the distance among features of the same class, while maximizing the distance among features of different classes. This enhances inter-class separability and promotes more discriminative learning. The distance constraint loss is formulated as:
where b is the batch size, denotes the label, is the temperature parameter controlling the smoothness, and is the cosine similarity function.
Finally, the overall loss L consists of the traditional cross-entropy loss , the feature clustering loss , and the distance constraint loss :
where , , and are weighting coefficients for the three losses.
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
The datasets used in this work are derived from two sources, namely BOSSbase1.01 [29] and BOWS2 [30]. Both BOSSbase and BOWS2 contain 10,000 high-quality images, allowing effective evaluation in an ideal setting.
We combine BOSSbase1.01 and BOWS2 into a single dataset, which consists of 20,000 images. All images are resized to pixels using MATLAB R2021b, and the dataset is split into training, validation, and test sets with a ratio of 14:1:5. Notably, all 10,000 images from BOWS2 are used for training. This dataset setup primarily simulates the ideal case of distinguishing between cover and stego samples. To generate stego images, we adopt three widely used adaptive steganographic algorithms: WOW [31], S-UNIWARD [32], and Hill [33].
4.2. Experimental Environment
Our backbone network LWENet follows the same configuration as the original model [7]. The weight decay and momentum values were set to 0.0005 and 0.9, respectively. L2 regularization was disabled for the bias terms in all convolutional and fully connected layers. The learning rate was initialized at 0.01 and reduced by a factor of 10 at the 80th, 140th, and 180th epochs, with a total of 200 training epochs.
The Relationship Mining Module is implemented with an APPNP layer (, ), where edge weights modulate the message-passing intensities to achieve a balance between local feature preservation and neighborhood aggregation. A sigmoid activation function is applied to the outputs. All models were implemented using Python 3.8 and PyTorch 2.0.1, and experiments were conducted on an NVIDIA RTX 3090 GPU.
4.3. Comparison with Other Approaches
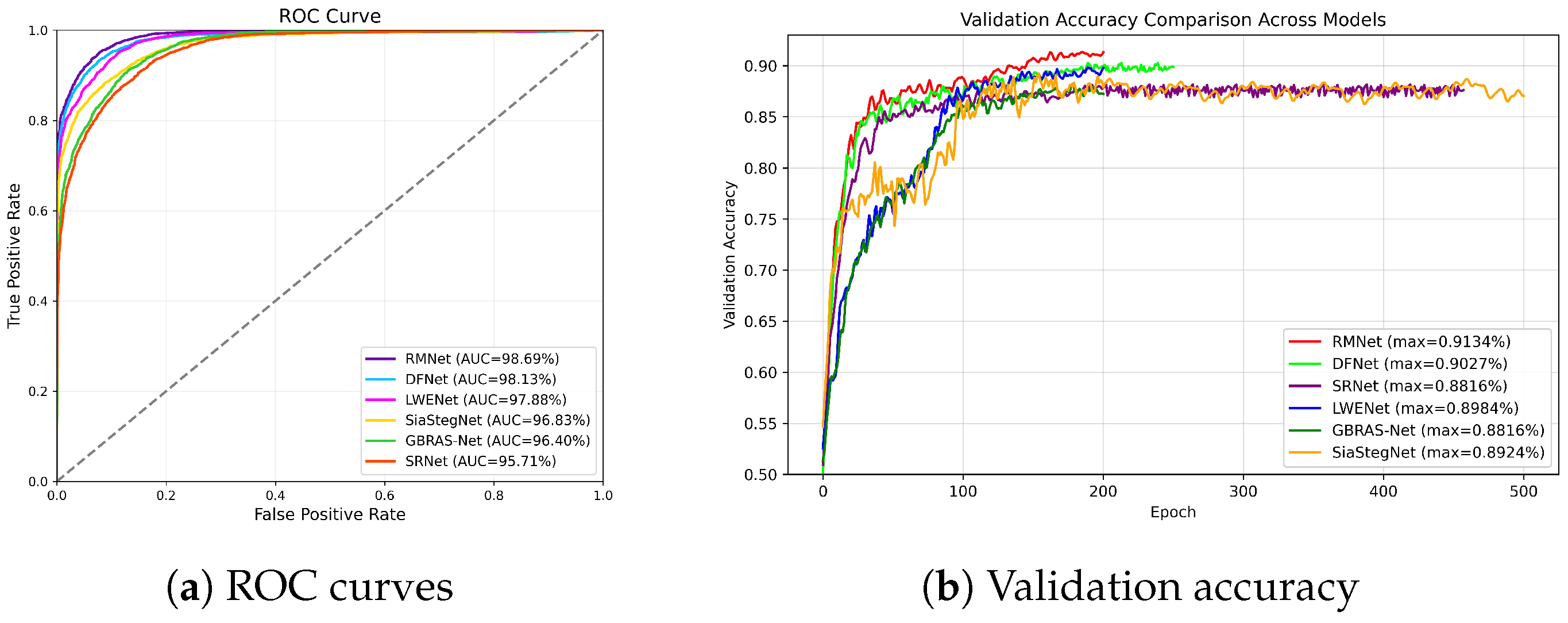
We compare RMNet with several recently proposed state-of-the-art models, including SRNet [4], GBRAS-Net [5], SiaStegNet [6], LWENet [7], and DFNet [9]. As shown in Table 1, our proposed method achieves the highest detection accuracy across the three steganographic algorithms at 0.4 bpp, 0.3 bpp, and 0.2 bpp. In particular, RMNet outperforms LWENet by up to 1.17%, DFNet by 0.62%, SiaStegNet by 6.62%, GBRAS-Net by 5.43%, and SRNet by 4.71%. At 0.1 bpp, RMNet obtains the best accuracy on the Hill algorithm, while achieving the second-best results on WOW and S-UNIWARD. As shown in Figure 2a, the ROC curves demonstrate the performance of six models on the Hill steganographic algorithm at 0.4 bpp. RMNet attains the largest area under the ROC curve, suggesting that it achieves the best detection performance among all compared models. As shown in Figure 2b, the validation accuracy evolves steadily with increasing epochs, where RMNet likewise attains the highest performance among all evaluated models.

Table 1.
Comparison of detection accuracy (%) of different models on BOSSbase & BOWS2 datasets at various embedding rates. Bold indicates the highest accuracy under the same algorithm.
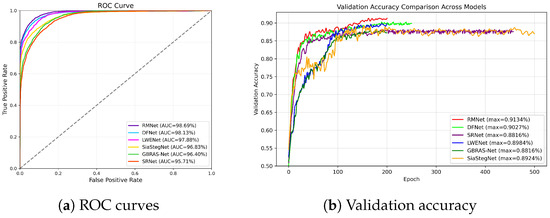
Figure 2.
Performance comparison: (a) ROC curves for Hill at 0.4 bpp. (b) Validation accuracy for WOW at 0.4 bpp.
4.4. Model Generalization Performance
We evaluate generalization by testing on mismatched steganographic algorithms. Specifically, six models—LWENet, DFNet, SiaStegNet, GBRAS-Net, SRNet, and RMNet—are trained on datasets generated using the same 0.4 bpp S-UNIWARD algorithm, and then tested on datasets generated by WOW, HUGO, MiPOD, and Hill algorithms to assess their generalization capability. As shown in Table 2, all models exhibit varying degrees of accuracy degradation when detecting cross-algorithm steganography. Nevertheless, our proposed RMNet consistently maintains the highest detection performance across all cases.

Table 2.
Detection accuracy (%) of different models under mismatched training-testing scenarios on BOSSbase & BOWS2 datasets (training on 0.4 bpp S-UNIWARD). Bold indicates the highest accuracy under the same algorithm.
4.5. Detailed Exploration of the Relationship Mining Module
4.5.1. Investigation of Graph Node Partitioning
In the Relationship Mining Module, converting two-dimensional feature maps into graph-structured data is a critical step. The number of node partitions serves as an important hyperparameter. Too few partitions causes information loss via pooling; too many increases computational complexity and hinders effective global relation modeling. To investigate the optimal partitioning strategy, we conducted the experiments summarized in Table 3. The results indicate that, within a reasonable complexity range, partitioning the feature map into nodes yields the best overall performance.

Table 3.
Exploration of graph node partitioning on the BOSSbase & BOWS2 datasets (Detection accuracy %). Bold indicates the highest accuracy under the same algorithm.
4.5.2. On the Local Fully-Connected Range in the Adjacency Matrix
To investigate the impact of the local fully-connected range (R) in the adjacency matrix on model performance, we designed comparative experiments ranging from purely dynamic connections () to global full connections (). As shown in Table 4, the size of the local range R has a significant influence on performance. When , the model achieves the best performance under all test conditions, with accuracy markedly higher than other configurations. This indicates that a moderate local fully-connected range is crucial. Both (no local connections) and excessively large R values lead to performance degradation, thereby validating the effectiveness of our proposed hybrid strategy of “local full connection with global dynamic connection”. An excessively large R introduces redundant weak connections as noise, while too small an R fails to sufficiently exploit essential local relationships.

Table 4.
On the local range of the adjacency matrix, where R = num indicates that all nodes within a distance of num from the current node are treated as fully connected. The dataset is BOSSbase & BOWS2 (Detection accuracy %). Bold indicates the highest accuracy under the same algorithm.
4.5.3. Investigation of the Threshold for Dynamic Connections
In addition, we conducted experiments on the threshold in the global dynamic connections. This threshold determines the connection condition between the current node and nodes outside its local region. As increases, only nodes with stronger similarity retain their connection weights, while those with similarity lower than are considered weak connections and set to zero to prevent interference with global features. The experimental results in Table 5 indicate that a higher filtering threshold is effective. Specifically, can filter out a large number of weak connections with low similarity, thereby avoiding the introduction of irrelevant noise and ensuring that the preserved global connections correspond to strongly related nodes. Consequently, the message passing process becomes more efficient and precise.

Table 5.
Selection of the global threshold on BOSSbase & BOWS2 (Detection accuracy %). Bold indicates the highest accuracy under the same algorithm.
4.5.4. Comparison Between RMNet and Vision Transformer-Based Steganalysis Models
According to the experimental results presented in Table 6, the RMNet model based on relationship mining demonstrates significantly superior detection performance compared with the Vision Transformer–based Luo-Net. This finding empirically substantiates the advantage of relationship mining techniques: by explicitly modeling the local dependencies among pixels through a graph-structured representation, RMNet can more directly and efficiently capture the subtle statistical perturbations introduced by steganographic operations. Consequently, it exhibits stronger robustness and higher detection accuracy when confronted with complex image content. In contrast, although Vision Transformer (ViT) models possess powerful global modeling capabilities, their attention mechanisms tend to be more susceptible to interference from semantic information in images, thereby reducing their efficiency in distinguishing weak steganographic signals from strong background content.

Table 6.
Comparison between Vision Transformer–based Luo-Net and relationship mining–based RMNet under different steganographic algorithms (Detection accuracy %). Bold indicates the highest accuracy under the same algorithm.
4.5.5. Investigation of the Teleport Probability and the Loss Function Weights in Graph Computation
We conducted an in-depth investigation into the teleport probability () used in the graph computation process. A higher value of indicates that each node has a greater tendency to retain its own information during propagation, while a lower value implies that the node relies more heavily on the information aggregated from its neighboring nodes. As shown in Table 7, the model achieves its best performance when , indicating that the most effective message propagation occurs when neighboring information dominates and self-information serves as auxiliary support. This result underscores the importance of maintaining an appropriate balance between self-retention and neighborhood dependency in relationship mining–based graph learning frameworks.

Table 7.
Discussion on the selection of teleport probability and loss weights , , and on BOSSbase & BOWS2 (Detection accuracy %). Bold indicates the highest accuracy under the same algorithm.
In the feature distribution enhancement module, we investigated the relationship among the weight coefficients of the cross-entropy loss, the feature distribution loss, and the distance constraint loss, denoted as , and , respectively. According to the data presented in Table 7, the model achieves the highest detection accuracy when the three weights are approximately equal. This observation indicates that the model performs best when these three loss components contribute jointly and uniformly to the gradient optimization process.
4.6. Visualization and Complexity Analysis
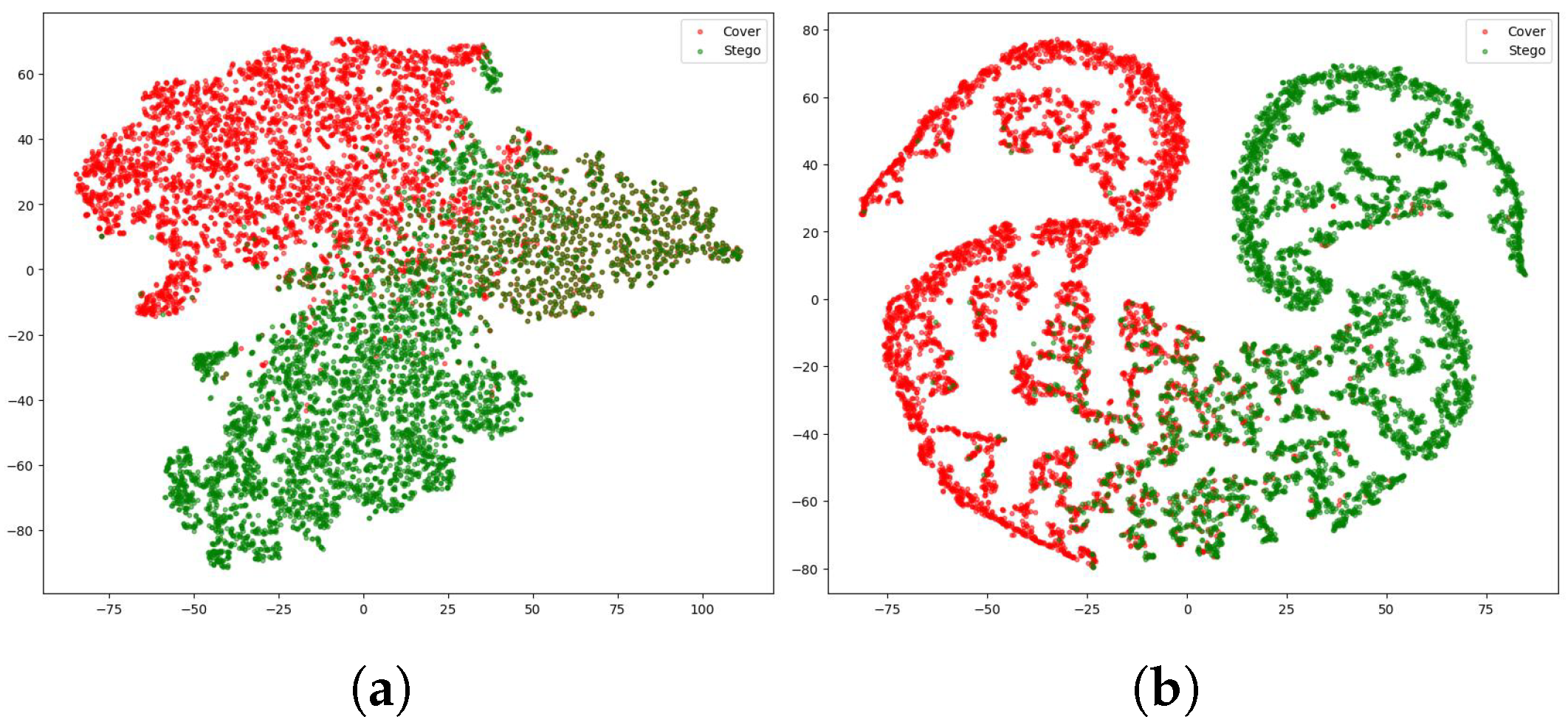
We use t-SNE to visualize feature discriminability, as class separation reflects the learned representations. We compared the t-SNE visualizations of features learned by the baseline model and by our model with the feature fusion and relationship mining modules. As shown in Figure 3, after applying the feature fusion and relationship mining modules, the distributions of the Cover and Stego features in the reduced-dimensional space are significantly optimized. Compared to Figure 3a, the overlapping and confusing regions near the class decision boundaries in RMNet are greatly reduced, demonstrating that the proposed modules are capable of learning more discriminative feature representations.
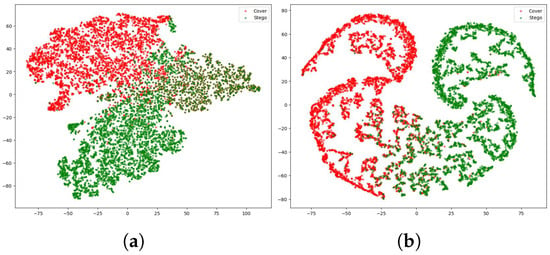
Figure 3.
(a) t-SNE visualization of features learned by the baseline model. (b) t-SNE visualization of features learned by RMNet, showing improved class separability between Cover and Stego samples.
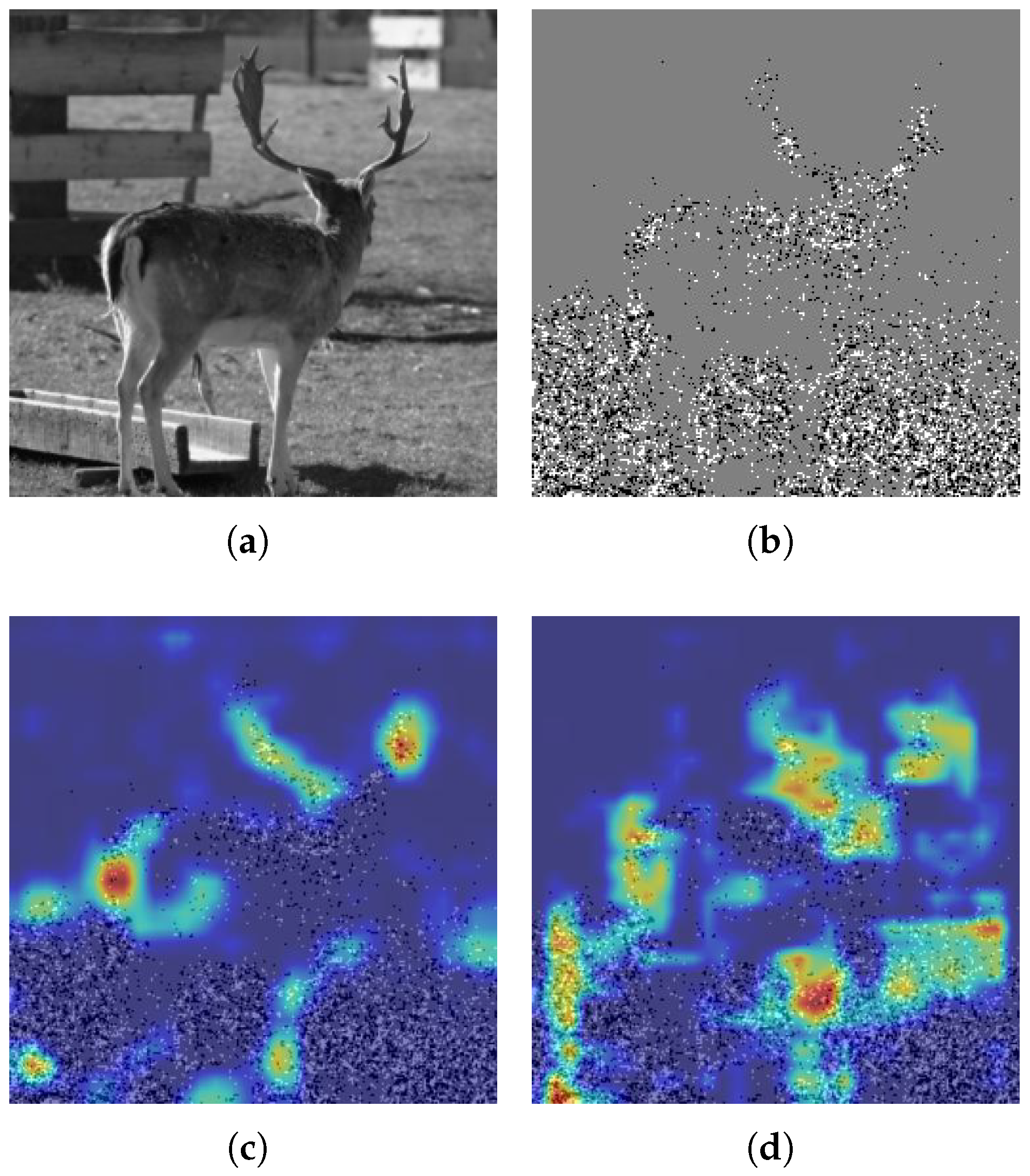
In addition, we employed the Grad-CAM [34] technique to visualize the regions of the images that the model attends to. In Grad-CAM, warmer colors indicate stronger attention from the model. As shown in Figure 4, compared with the heatmaps of the backbone network in Figure 4c, the heatmaps of RMNet in Figure 4d focus more on the regions where steganographic information is embedded, thereby improving detection accuracy. This further validates the effectiveness of our proposed framework.
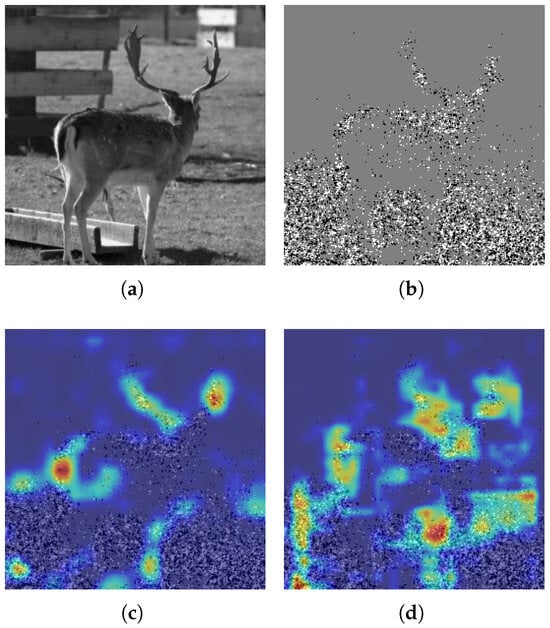
Figure 4.
Grad-CAM visualization of RMNet compared with backbone network LWENet after introducing the relationship mining technique. (a) Original image. (b) Stego image. (c) LWENet embedding heatmap. (d) RMNet embedding heatmap.
Model complexity is a key performance indicator. We evaluated each model’s training time and parameters to assess efficiency. According to the data presented in Table 8, the proposed RMNet contains slightly more parameters (0.91 million) than DFNet, LWENet, and SiaStegNet. However, it requires less training time than SiaStegNet and DFNet, while simultaneously achieving higher detection accuracy with only a marginal increase in parameters. This demonstrates the efficiency advantage of the proposed model in terms of both computational cost and training effectiveness.

Table 8.
Comparison of training time and number of parameters between the proposed model and other methods. Bold indicates the highest accuracy under the same algorithm.
4.7. Ablation Studies
4.7.1. Effectiveness of the Feature Fusion Module
As shown in Table 9, we compared the performance differences before and after introducing the Feature Fusion Module. The experimental results demonstrate that incorporating the Feature Fusion Module consistently improves performance under all test conditions. This validates the module’s effectiveness. The cross-attention mechanism effectively integrates shallow local details with deep global semantics, thereby enhancing the strength of steganographic signals and improving classification performance.

Table 9.
Ablation experiment on the Feature Fusion Module. The dataset is BOSSbase & BOWS2 (Detection accuracy %). Bold indicates the highest accuracy under the same algorithm.
4.7.2. Effectiveness of the Relationship Mining Module
To further analyze the role of the Relationship Mining Module, we designed four comparative experiments in Table 10: Model 1 represents the baseline model; Model 2 incorporates only the relation-aware component; Model 3 incorporates only the feature distribution enhancement component; and Model 4 includes the complete Relationship Mining Module (combining both relation-aware and feature distribution enhancement). The experimental results demonstrate that progressively adding module components leads to consistent performance improvements. Using only the relation-aware component (Model 2) or only the feature distribution enhancement component (Model 3) provides certain gains, but the complete module (Model 4) achieves the best overall performance. This indicates a synergy between the two components: the relation-aware component captures spatial dependencies via the adaptive adjacency matrix, while the feature distribution enhancement component optimizes global representations. Their combination enables more effective modeling of the spatial distribution characteristics of steganographic signals, thereby improving detection performance.

Table 10.
Ablation experiment on the Relationship Mining Module. The dataset is BOSSbase & BOWS2 (Detection accuracy %). Bold indicates the highest accuracy under the same algorithm.
4.8. Performance on the Alaska #2 Dataset
To further verify the effectiveness of the proposed model, we also conducted experiments on the ALASKA#2 dataset [35], which is more representative of real-world scenarios since the images are collected from various devices. This dataset enables us to evaluate the model’s detection capability under more complex conditions. Specifically, we selected 10,000 grayscale images, resized them to , and split them into training, validation, and testing sets with a ratio of 6:2:2. As shown in Table 11, the proposed model also achieves the best detection performance on the ALASKA#2 dataset.

Table 11.
Comparison of detection accuracy (%) of different models on ALASKA#2 datasets. Bold indicates the highest accuracy under the same algorithm.
5. Conclusions
We proposed a novel relation-mining steganalysis model to address CNN limitations in capturing global spatial dependencies. The core of the proposed model lies in two innovative modules: the Feature Fusion Module (FFM) and the Relation Mining Module (RMM). The FFM leverages a cross-attention mechanism to effectively integrate the complementary strengths of deep and shallow convolutional features. The RMM employs graph-based techniques to achieve global feature modeling, with an adaptive adjacency matrix strategy that ensures a balance between local and global properties. Furthermore, a feature distribution enhancement mechanism within the RMM further amplifies global feature distinctions, thereby improving overall model performance.
Ablation studies validated each component, and we compared our approach with state-of-the-art models. Performance was evaluated on accuracy, generalization, and complexity, using t-SNE and Grad-CAM visualizations. Experimental results demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art detection performance on the BOWS2, BOSSbase, and ALASKA#2 datasets.
In future work, we plan to extend this relation mining framework to the domain of few-shot steganalysis, aiming to further improve existing methods and achieve competitive or even superior performance with substantially fewer training samples.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.Y. and Y.Y.; methodology, R.Y.; software, R.Y.; validation, R.Y. and X.M.; formal analysis, R.Y.; investigation, R.Y.; resources, Y.Y. and L.Z.; data curation, R.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, R.Y.; writing—review and editing, X.M. and Y.Y.; visualization, R.Y.; supervision, Y.Y. and L.Z.; project administration, Y.Y.; funding acquisition, Y.Y. and L.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 72293583, Grant No. 72293580), the Opening Project of Police Integration Computing Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (No. JWRH202401002), and the 111 Project (Grant No. B21049).
Data Availability Statement
To prove the reliability of our experimental results, we have released the source code to https://github.com/Yang-Da-xiong/RMNet (accessed on 1 November 2025).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Farooq, N.; Selwal, A. Image steganalysis using deep learning: A systematic review and open research challenges. J. Ambient Intell. Human Comput. 2023, 14, 7761–7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Li, B.; Li, W.; Barni, M.; Tondi, B.; Liu, X. Constructing an intrinsically robust steganalyzer via learning neighboring feature relationships and self-adversarial adjustment. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2024, 19, 9390–9405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yedroudj, M.; Comby, F.; Chaumont, M. Yedroudj-Net: An efficient CNN for spatial steganalysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 2092–2096.
- Boroumand, M.; Chen, M.; Fridrich, J. Deep residual network for steganalysis of digital images. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2019, 14, 1181–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinel, T.-S.; Brayan, A.A.H.; Alejandro, B.O.M.; Alejandro, M.R.; Daniel, A.G.; Alejandro, A.G.; Alejandro Buenaventura, B.J.; Simon, O.-A.; Gustavo, I.; Raúl, R.-P.; et al. JGBRAS-Net: A convolutional neural network architecture for spatial image steganalysis. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 14340–14350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, X. A Siamese CNN for image steganalysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2021, 16, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, S.; Chen, M.; Yu, L.; Sun, S. Lightweight and effective deep image steganalysis network. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2022, 29, 1888–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Wei, P.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, X.; Qian, Z.; Li, S. Image steganalysis with convolutional vision transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 3089–3093.
- Fu, T.; Chen, L.; Jiang, Y.; Jia, J.; Fu, Z. Image steganalysis based on dual-path enhancement and fractal downsampling. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2025, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Luo, W.; Huang, J. Color image steganalysis based on pixel difference convolution and enhanced transformer with selective pooling. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2024, 19, 9970–9983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference Learning Representations (ICLR), Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, K.; Lee, Y.-C.; Nambi, S.; Salian, A.; Shah, S.; Kim, S.-W.; Kumar, S. A survey of graph neural networks for social recommender systems. ACM Comput. Surv. 2024, 56, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Kumar, Y.J.; Sing, G.O.; Song, F.; Wang, J. A comprehensive survey of graph neural networks for knowledge graphs. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 75729–75741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, A.; Wharton, Z.; Liu, Y.; Bessis, N.; Behera, A. SR-GNN: Spatial relation-aware graph neural network for fine-grained image categorization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 6017–6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikdar, A.; Liu, Y.; Kedarisetty, S.; Zhao, Y.; Ahmed, A.; Behera, A. Interweaving insights: High-order feature interaction for fine-grained visual recognition. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2025, 133, 1755–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klicpera, J.; Bojchevski, A.; Günnemann, S. Predict then propagate: Graph neural networks meet personalized PageRank. In Proceedings of the International Conference Learning Representations (ICLR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, S.; Farid, H. Detecting hidden messages using higher-order statistics and support vector machines. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Information Hiding, Berlin, Germany, 7–9 October 2002; pp. 340–354. [Google Scholar]
- Fridrich, J.; Kodovsky, J. Rich models for steganalysis of digital images. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2012, 7, 868–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodovsky, J.; Fridrich, J.; Holub, V. Ensemble classifiers for steganalysis of digital media. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2012, 7, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Li, H.; Luo, W.; Huang, J. Adaptive steganalysis based on embedding probabilities of pixels. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2016, 11, 734–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Ni, J.; Yi, Y. Deep learning hierarchical representations for image steganalysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2017, 12, 2545–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Dong, J.; Wang, W.; Tan, T. Learning and transferring representations for image steganalysis using convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference Image Processing (ICIP), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 2752–2756. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Wu, H.Z.; Shi, Y.Q. Structural design of convolutional neural networks for steganalysis. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, M.; Ke, Y.; Bi, X.; Kong, Y. Image steganalysis based on attention augmented convolution. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 19471–19490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhou, L.; Wu, H. Graph representation learning for spatial image steganalysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE 24th International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing (MMSP), Shanghai, China, 26–28 September 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Velickovic, P.; Cucurull, G.; Casanova, A.; Romero, A.; Lio, P.; Bengio, Y. Graph attention networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.10903. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Wu, H. JPEG steganalysis based on steganographic feature enhancement and graph attention learning. J. Electron. Imaging 2023, 32, 033032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Bas, P.; Filler, T.; Pevný, T. Break our steganographic system: The ins and outs of organizing BOSS. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Information Hiding, Prague, Czech Republic, 18–20 May 2011; pp. 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Bas, P.; Furon, T. BOWS-2. 2007. Available online: https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/kb3ngxfmjw/1 (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- Holub, V.; Fridrich, J. Designing steganographic distortion using directional filters. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security (WIFS), Costa Adeje, Spain, 2–5 December 2012; pp. 234–239. [Google Scholar]
- Holub, V.; Fridrich, J.; Denemark, T. Universal distortion function for steganography in an arbitrary domain. EURASIP J. Inf. Secur. 2014, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, M.; Huang, J.; Li, X. A new cost function for spatial image steganography. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference Image Processing (ICIP), Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 4206–4210. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 128, 336–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogranne, R.; Giboulot, Q.; Bas, P. The ALASKA steganalysis challenge: A first step towards steganalysis. In Proceedings of the ACM Workshop on Information Hiding and Multimedia Security, Paris, France, 3–5 July 2019; pp. 125–137. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).