A Rapid and Self-Contained Calibration Method for MIMUs Based on Residual Velocity Measurement
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- The Kalman filter based on residual velocity measurement is proposed to estimate the MIMU parameters.
- (2)
- A specific rotation path is designed to guarantee the observability of all parameters.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Parameters in MIMU Output Model
2.2. Parameters’ Estimation by Kalman Filter Based on Residual Velocity Measurement
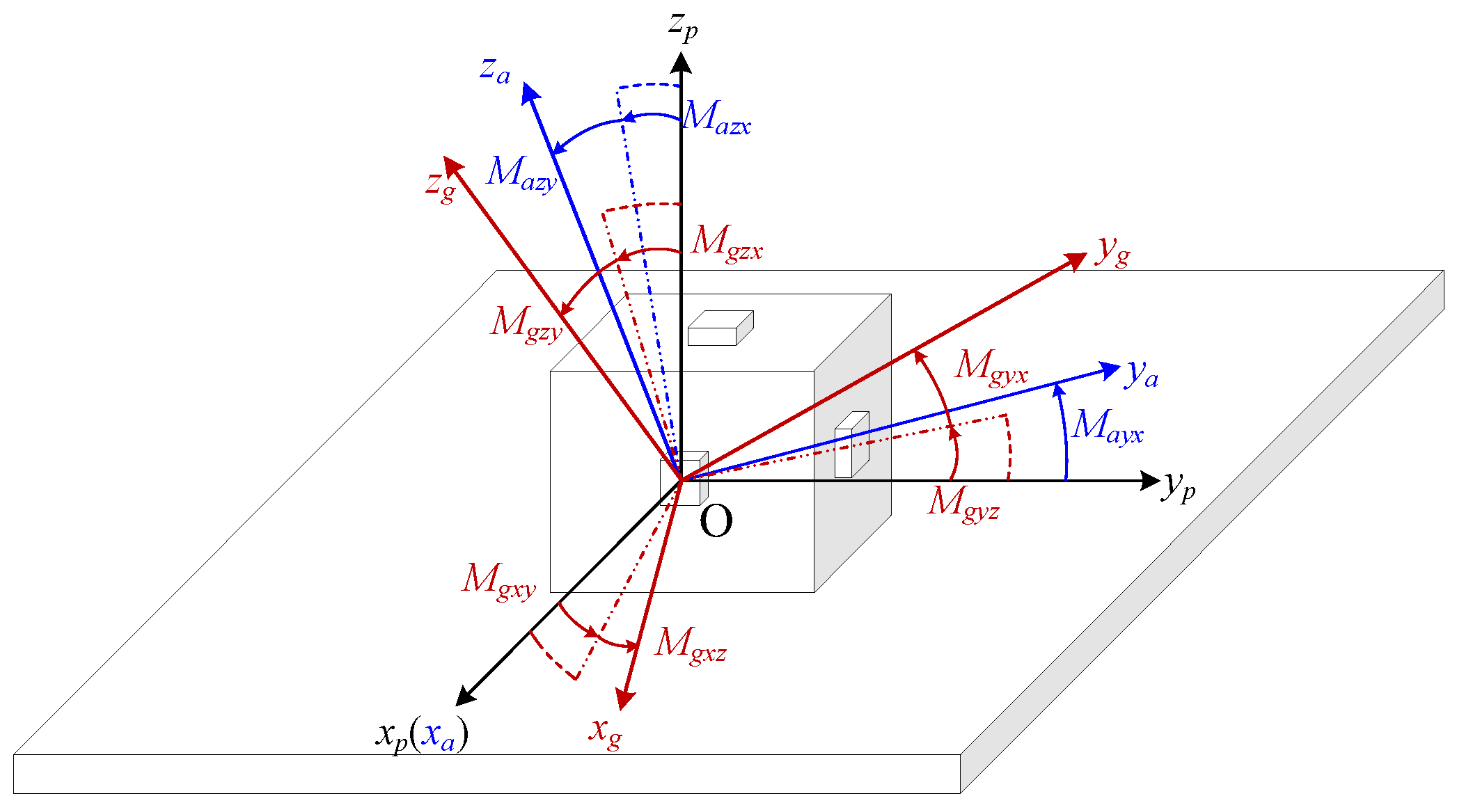
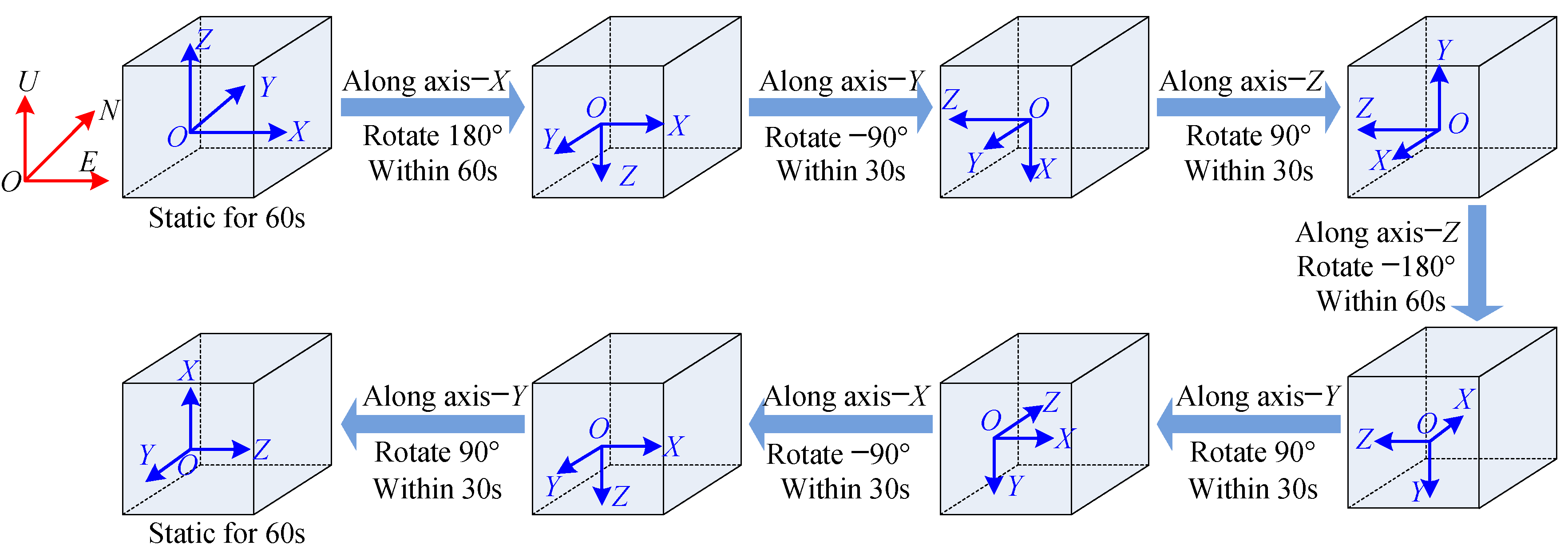
2.3. Oriented Rotation for the Self-Contained Calibration
2.3.1. Oriented Rotation Scheme Design
2.3.2. Observability Analysis for Oriented Rotation
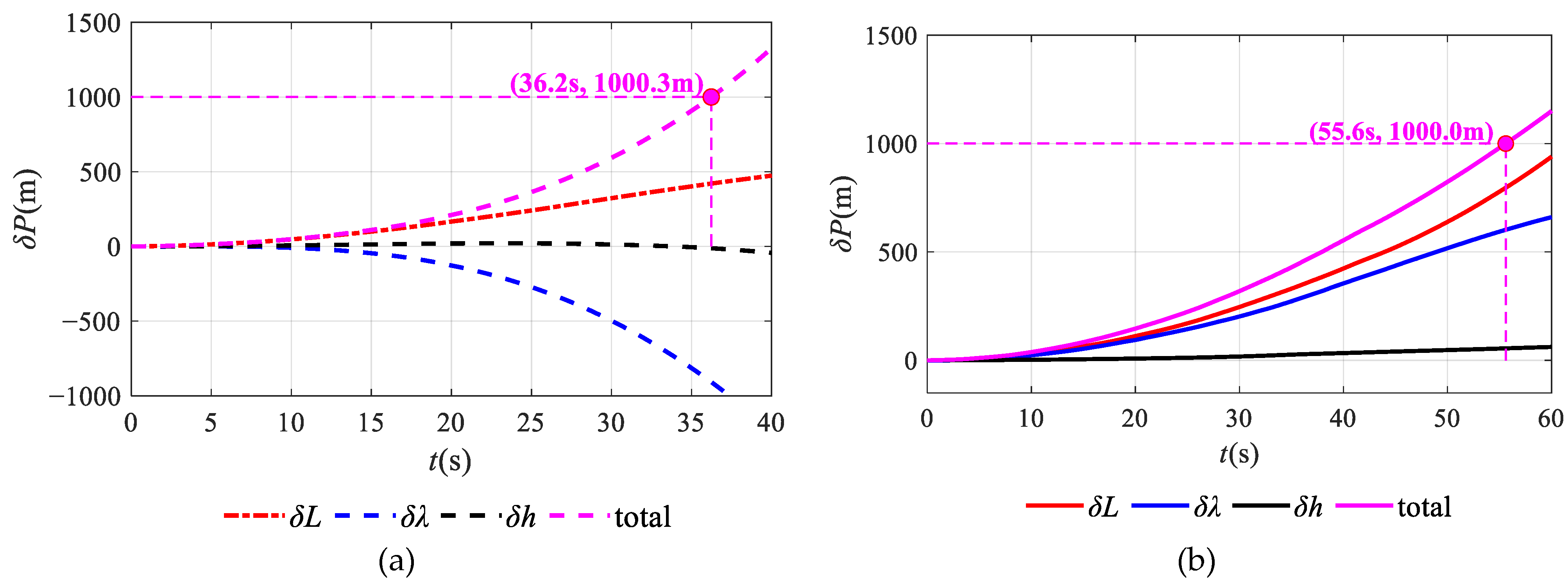
3. Simulation and Experiment Analysis
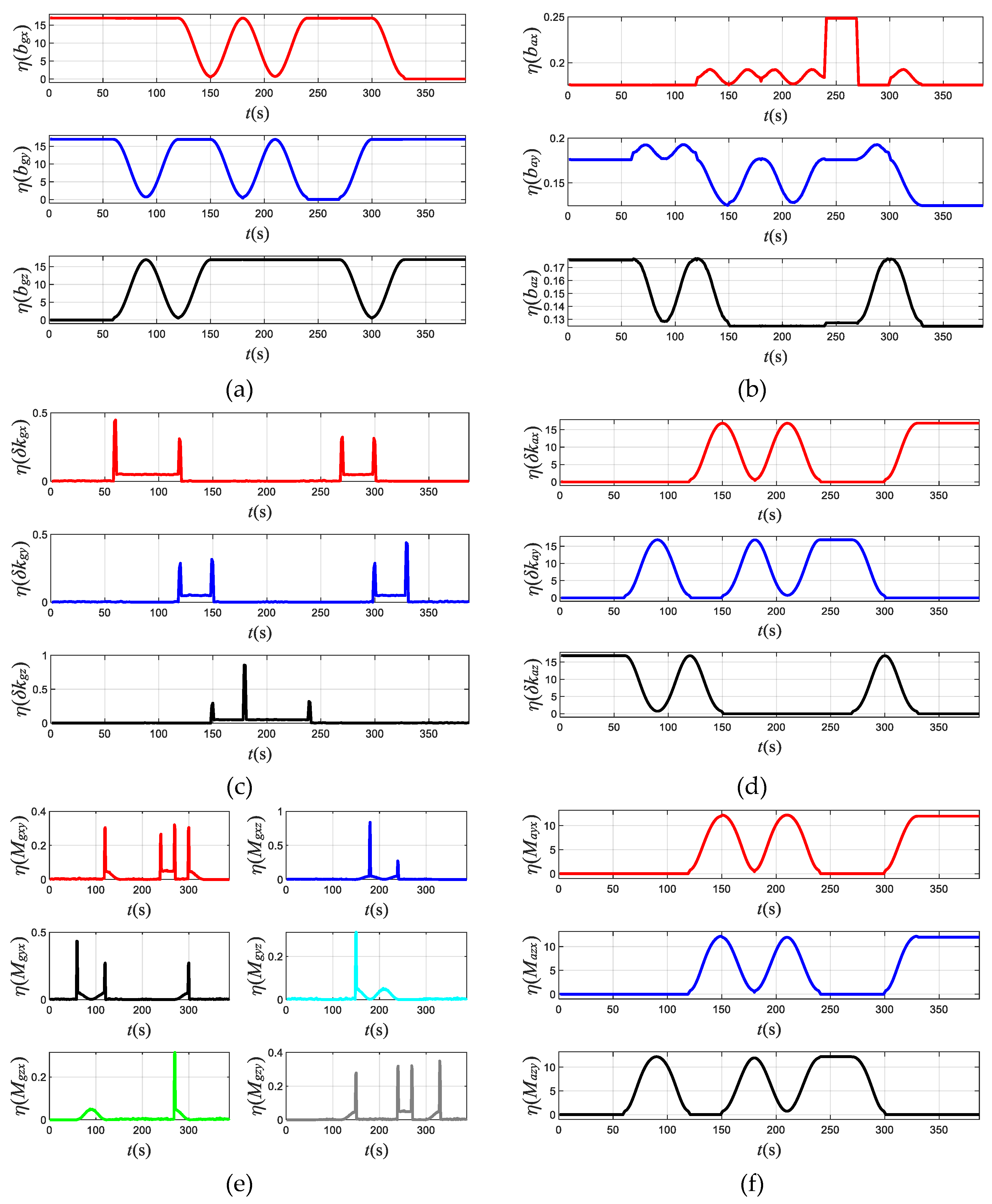
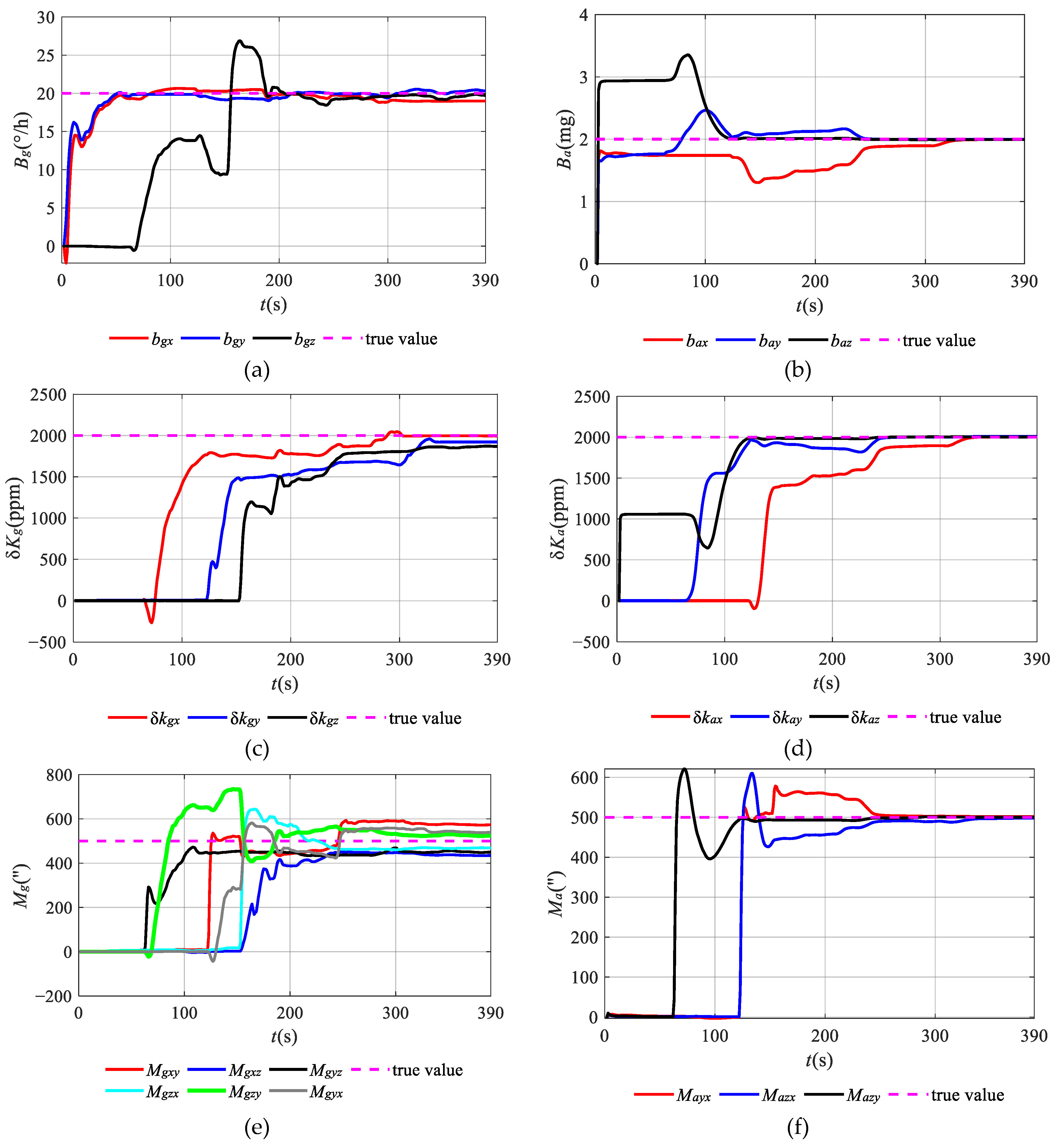
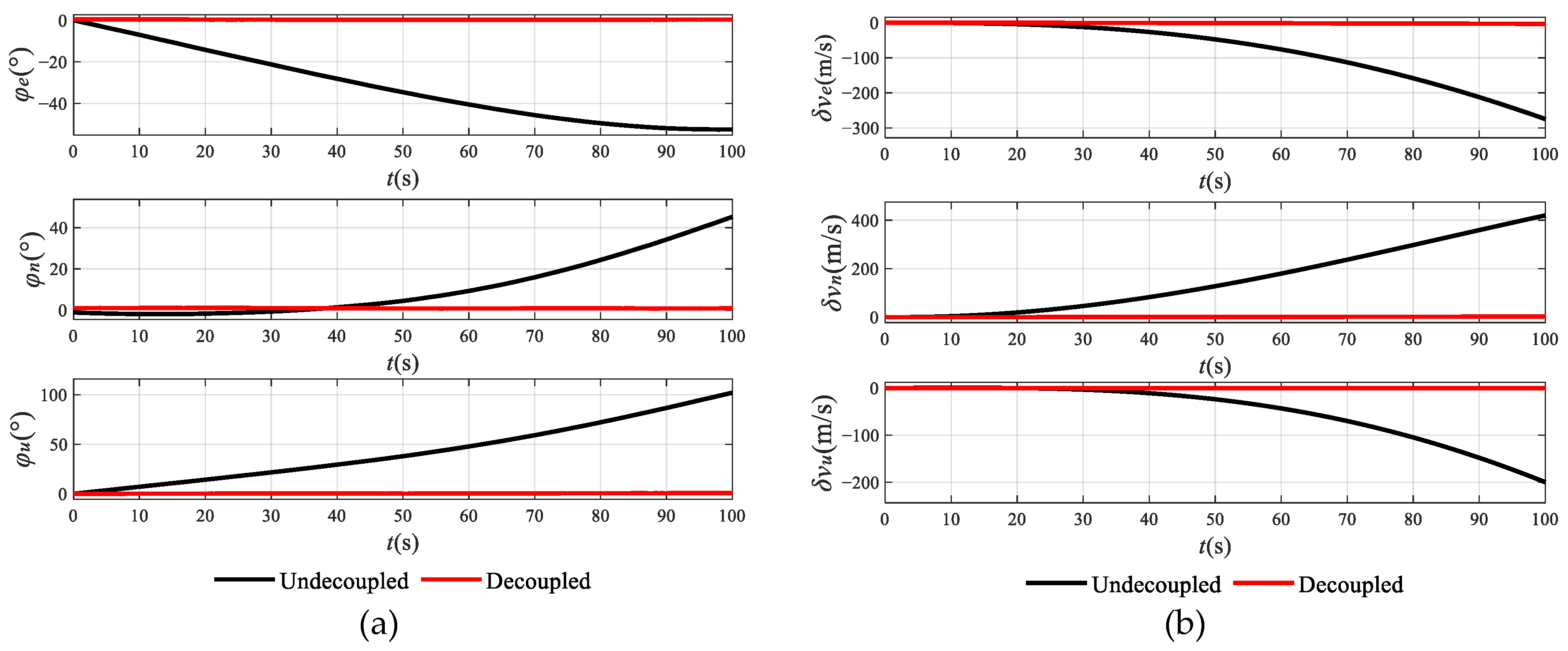
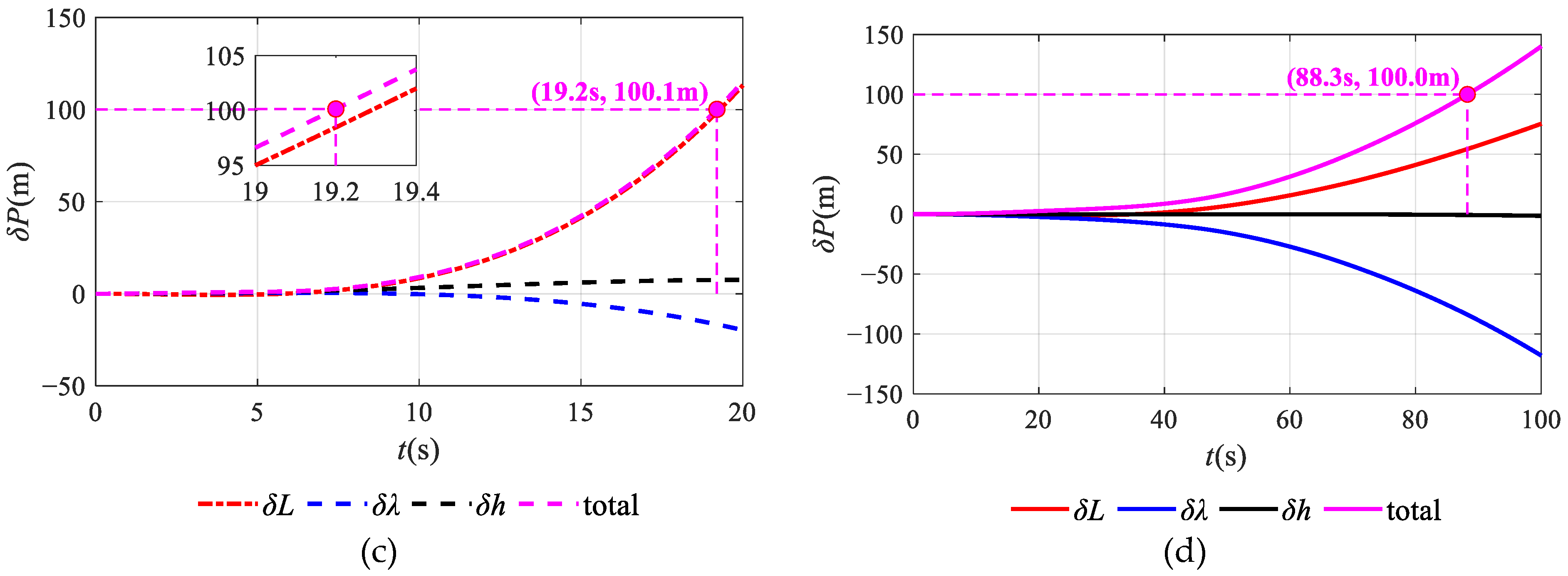
3.1. Numerical Simulation
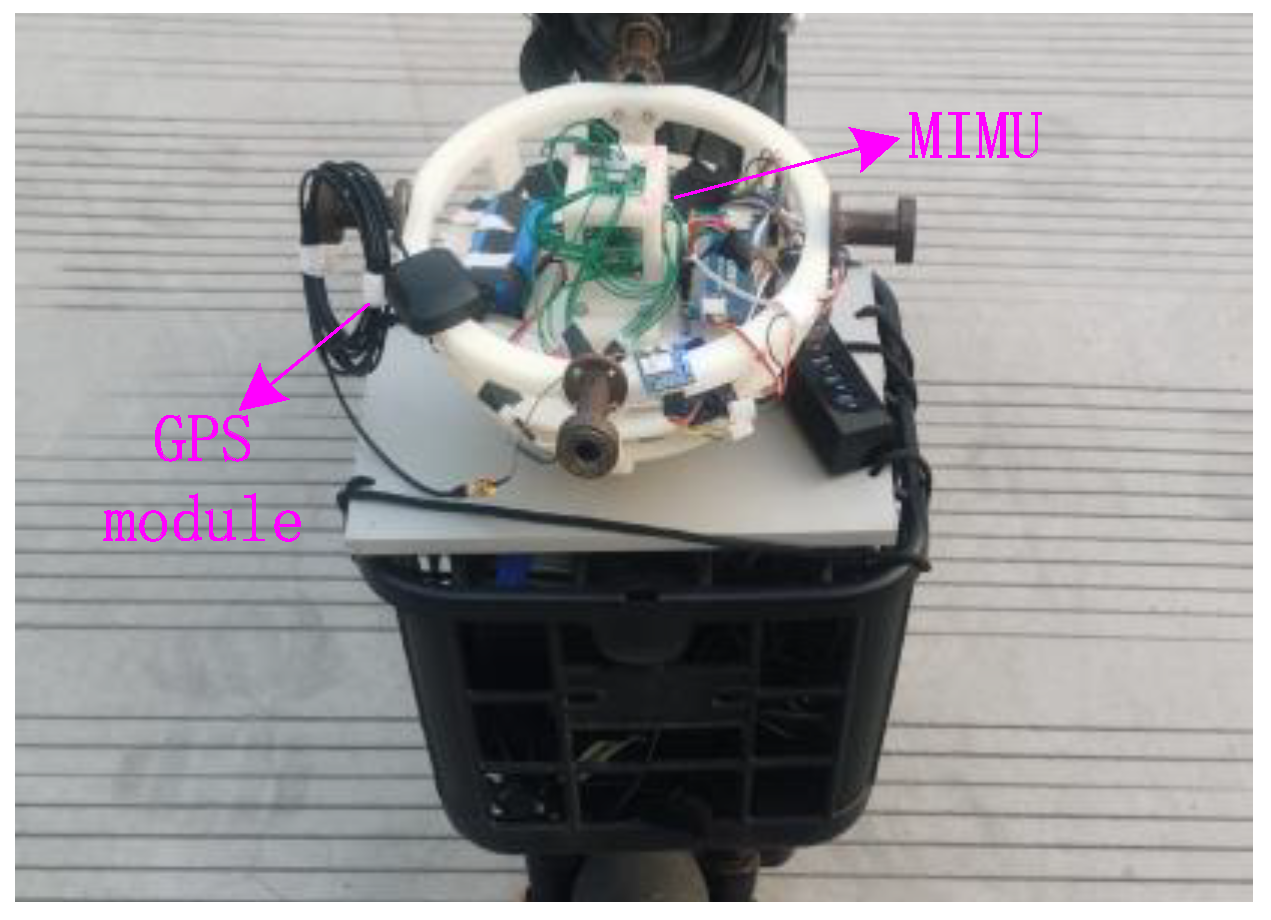
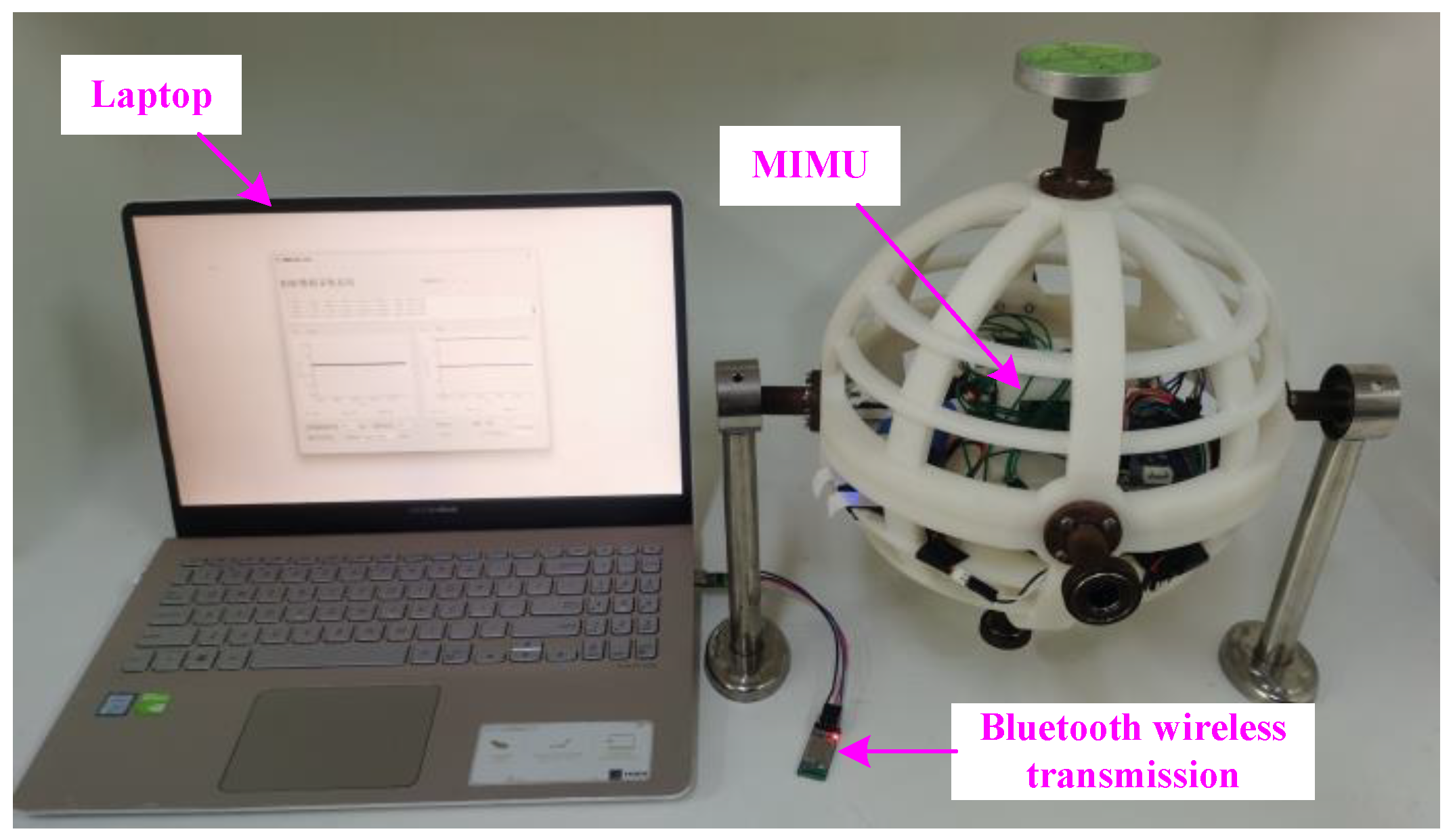
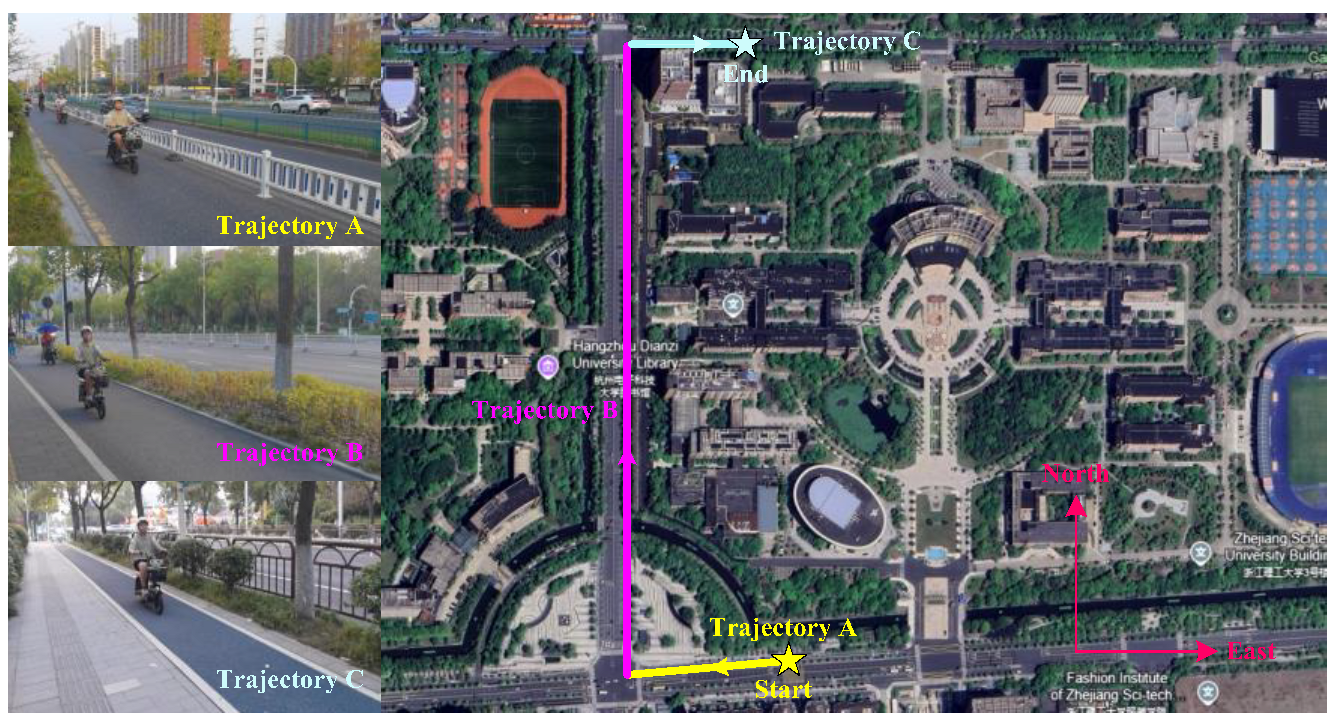
3.2. Experiment Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stefanoni, M.; Kovács, I.; Sarcevic, P.; Odry, Á. A Survey on the Main Techniques Adopted in Indoor and Outdoor Localization. Electronics 2025, 14, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yuan, M.; Wang, L.; Tang, H.; Niu, X. A robust and efficient IMU array/GNSS data fusion algorithm. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 26278–26289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Jiang, J.; Yan, P.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, Z. A Novel Three-Dimensional Positioning Method for Foot-Mounted Pedestrian Navigation System Using Low-Cost Inertial Sensor. Electronics 2023, 12, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfadel, D.; Haessig, D. Accelerometer Bias Estimation for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Using Extended Kalman Filter-Based Vision-Aided Navigation. Electronics 2025, 14, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Wang, Z.; Xing, L.; Gao, C. A MEMS IMU gyroscope calibration method based on deep learning. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1003009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xie, Y.; Yu, X.; Fan, H.; Wei, G.; Wang, L.; Fan, Z.; Wang, G.; Luo, H. A system-level calibration method including temperature-related error coefficients for a strapdown inertial navigation system. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2021, 32, 115117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunson, B.; Wang, J. Analytical framework for online calibration of sensor systematic errors under the generic multisensor integration strategy. Sensors 2025, 25, 3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wei, S.; Su, G.; Wang, J.; Lu, J. An improved fast self-calibration method for hybrid inertial navigation system under stationary condition. Sensors 2018, 18, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, L.; Duan, T. A novel hybrid calibration method for FOG-based IMU. Measurement 2019, 147, 106900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Tan, M.; Wang, X.; Liang, W.; Gao, S.; Chen, Z. Research on IMU calibration model based on polar decomposition. Micromachines 2023, 14, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harindranath, A.; Arora, M. Effect of sensor noise characteristics and calibration errors on the choice of IMU-sensor fusion algorithms. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2024, 379, 115850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, X.; Gu, N.; Shang, H.; Zhang, H. MEMS inertial sensor calibration technology: Current status and future trends. Micromachines 2022, 13, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Zhu, S.; Liu, F.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Xiao, X.; Gao, R.; Zhang, Z. Help you locate the car: A smartphone-based car-finding system in underground parking lot. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 7107–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Deng, Z.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, P. Coriolis-based heading estimation for pedestrian inertial localization based on MEMS MIMU. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 27509–27517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Tan, M.; Guo, Q.; Wu, C. An improved system-level calibration method of strapdown inertial navigation system based on matrix factorization. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 14986–14996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Li, L.; Hu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Xue, B.; Wu, J.; Liu, M. Robust equipment-free calibration of low-cost inertial measurement units. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 73, 9506712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, U.; Golnaraghi, F. An algorithm for the in-field calibration of a MEMS IMU. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 7479–7486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Xu, A.; Xu, X.; Liu, M. Modeling and compensation of inertial sensor errors in measurement systems. Electronics 2023, 12, 2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Xu, X.; Ye, H.; Zhang, L. A model-based and efficient parameters correction method for low-cost MEMS IMU. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2024, 36, 015036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.S.; Al-Gayem, Q. Three-axes MEMS calibration using Kalman filter and Delaunay triangulation algorithm. Appl. Comput. Intell. Soft Comput. 2023, 2023, 7658064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Wang, L.; Hu, Y.; Li, P.; Zu, Y. Optimal path planning method for IMU system-level calibration based on improved Dijkstra’s algorithm. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 11364–11376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Jlailaty, H.; Celik, A.; Mansour, M.M.; Eltawil, A.M. IMU hand calibration for low-cost MEMS inertial sensors. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 7505516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Nie, G. A novel method for improving the long-term stability of inertial devices based on model prediction. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2025, 228, 112492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodarahmi, M.; Maihami, V. A Review on Kalman Filter Models. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2023, 30, 727–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tang, H.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, X. PO-KF: A pose-only representation-based Kalman filter for visual inertial odometry. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 14856–14875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sun, Z.; Chen, H.; Chu, J.; Song, J. A barometer-enhanced state adaptive indirect Kalman filter for 3-D indoor navigation. IEEE Sens. J. 2025, 25, 19816–19824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simak, V.; Andel, J.; Nemec, D.; Kekelak, J. Online calibration of inertial sensors based on error backpropagation. Sensors 2024, 24, 7525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Sun, W.; Gao, Y. Improving observability of an inertial system by rotary motions of an IMU. Sensors 2017, 17, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Han, L.; Dong, X.; Li, Q.; Ren, Z. A quantitative method for observability analysis and its application in SINS cali-bration. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 105881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshen-Meskin, D.; Bar-Itzhack, I.Y. Observability analysis of piece-wise constant systems. I. Theory. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1992, 28, 1056–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajiyev, C.; Cilden-Guler, D. Attitude and gyro bias estimation by SVD-aided EKF. Measurement 2022, 205, 112209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Li, Q.; Liang, W.; Zhao, H. A system-level calibration method for SINS based on observability analysis. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 32871–32883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameters | Values | |
|---|---|---|
| Initial velocities | (0 m/s, 0 m/s, 0 m/s) | |
| Initial positions | (120.350440°, 30.314850°, 0 m) | |
| Initial misalignment angles | (0°, 0°, 0°) | |
| Initial matrix of P | P0(1, 1), P0(2, 2), P0(3, 3) | (0.1°)2 |
| P0(4, 4), P0(5, 5), P0(6, 6) | (0.01 m/s)2 | |
| P0(7, 7), P0(8, 8), P0(9, 9) | (0.1 m)2 | |
| P0(10, 10), P0(11, 11), P0(12, 12) | (100°/h)2 | |
| P0(13, 13), P0(14, 14), P0(15, 15) | (5 mg)2 | |
| P0(16, 16), P0(17, 17), P0(18, 18), P0(19, 19), P0(20, 20), P0(21, 21) | (6000 ppm)2 | |
| P0(22, 22), P0(23, 23), P0(24, 24), P0(25, 25), P0(26, 26), P0(27, 27), P0(28, 28), P0(29, 29), P0(30, 30) | (3000″)2 | |
| else | 0 | |
| Matrix of Q | Q(1, 1), Q(2, 2), Q(3, 3) | (0.36°/√h)2 |
| Q(4, 4), Q(5, 5), Q(6, 6) | (100 μg/√Hz)2 | |
| else | 0 | |
| Matrix of R | R(1, 1), R(2, 2), R(3, 3) | (0.01 m/s)2 |
| else | 0 | |
| Error Parameters of Each Sensor in MIMU | Parameter Value Settings | |
|---|---|---|
| Three-axis gyroscope parameters | Zero bias (°/h) | 20 |
| Scale factor error (ppm) | 2000 | |
| Non-orthogonal error (″) | 500 | |
| Angle random walk (°/√h) | 0.78 | |
| Three-axis accelerometer parameters | Zero bias (mg) | 2 |
| Scale factor error (ppm) | 2000 | |
| Non-orthogonal error (″) | 500 | |
| Velocity random walk (μg/√Hz) | 816 | |
| Gyroscope Parameters | Set Value | Estimated Value | Relative Error | Accelerometer Parameters | Set Value | Estimated Value | Relative Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bgx (°/h) | 20 | 18.98 | −5.10% | bax (mg) | 2 | 1.99 | −0.50% |
| bgy (°/h) | 20 | 20.19 | 0.95% | bay (mg) | 2 | 1.99 | −0.50% |
| bgz (°/h) | 20 | 19.52 | −2.40% | baz (mg) | 2 | 1.99 | −0.50% |
| δkgx (ppm) | 2000 | 1996.30 | −0.19% | δkax (ppm) | 2000 | 2005.04 | 0.25% |
| δkgy (ppm) | 2000 | 1921.70 | −3.92% | δkay (ppm) | 2000 | 2009.39 | 0.47% |
| δkgz (ppm) | 2000 | 1860.76 | −6.96% | δkaz (ppm) | 2000 | 2002.82 | 0.14% |
| Mgxy (″) | 500 | 574.42 | 14.88% | Mayx (″) | 500 | 501.89 | 0.38% |
| Mgxz (″) | 500 | 435.78 | −12.84% | Mazx (″) | 500 | 497.35 | −0.53% |
| Mgyx (″) | 500 | 451.94 | −9.61% | Mazy (″) | 500 | 500.09 | 0.02% |
| Mgyz (″) | 500 | 467.42 | −6.52% | ||||
| Mgzx (″) | 500 | 526.77 | 5.35% | ||||
| Mgzy (″) | 500 | 541.15 | 8.23% |
| Performance Specifications | Values for Each Axis (x, y, z) | |
|---|---|---|
| ADXRS453 | Full scale (°/sec) | ±300 |
| Bias instability (°/h) | 14.84/4.56/15.15 | |
| Angle random walk (°/√h) | 0.85/0.86/0.91 | |
| ADXL343 | Full scale (g) | ±16 |
| Bias instability (μg) | 101/57/46 | |
| Velocity random walk (μg/√Hz) | 561/459/425 | |
| Parameters in MIMU Output Model | Calibration Groups | Mean Value for Calibration | Standard Deviation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groups 1 | Groups 2 | Groups 3 | |||
| bgx (°/h) | −2456.51 | −2440.17 | −2444.80 | −2447.16 | 6.88 |
| bgy (°/h) | −335.21 | −310.00 | −290.45 | −311.89 | 18.32 |
| bgz (°/h) | 2588.04 | 2593.46 | 2602.90 | 2594.80 | 6.14 |
| δkgx (ppm) | −13,341.89 | −14,394.83 | −12,081.95 | −13,272.89 | 945.49 |
| δkgy (ppm) | −18,418.66 | −17,755.49 | −17,170.98 | −17,781.71 | 509.70 |
| δkgz (ppm) | −18,710.92 | −16,919.01 | −18,019.40 | −17,883.11 | 737.86 |
| Mgxy (′′) | −1979.05 | −2712.62 | −2559.65 | −2417.11 | 315.99 |
| Mgxz (′′) | 3530.53 | 2769.77 | 3644.30 | 3314.87 | 388.23 |
| Mgyx (′′) | 2965.19 | 3183.87 | 2635.60 | 2928.22 | 225.35 |
| Mgyz (′′) | −760.60 | −1603.20 | −763.82 | −1042.54 | 396.45 |
| Mgzx (′′) | −3438.19 | −2913.46 | −3243.23 | −3198.29 | 216.56 |
| Mgzy (′′) | 3802.91 | 3846.20 | 3602.60 | 3750.57 | 106.11 |
| bax (mg) | 45.33 | 45.44 | 43.79 | 44.85 | 0.75 |
| bay (mg) | 12.50 | 12.69 | 11.75 | 12.31 | 0.41 |
| baz (mg) | −2.14 | −2.22 | −1.95 | −2.10 | 0.11 |
| δkax (ppm) | −26,169.22 | −28,250.45 | −25,836.42 | −26752.03 | 1068.22 |
| δkay (ppm) | −11,391.84 | −13,111.82 | −10,844.88 | −11,782.85 | 965.89 |
| δkaz (ppm) | 8577.21 | 8272.67 | 8538.01 | 8462.63 | 135.27 |
| Mayx (′′) | −27.32 | 238.96 | −55.26 | 52.13 | 132.60 |
| Mazx (′′) | −1704.82 | −635.94 | −1867.02 | −1402.59 | 546.14 |
| Mazy (′′) | 350.77 | 575.16 | 430.40 | 452.11 | 92.88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, L.; Zhu, T.; Ma, J.; Xu, Y.; Luo, J. A Rapid and Self-Contained Calibration Method for MIMUs Based on Residual Velocity Measurement. Electronics 2025, 14, 4277. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214277
Xu L, Zhu T, Ma J, Xu Y, Luo J. A Rapid and Self-Contained Calibration Method for MIMUs Based on Residual Velocity Measurement. Electronics. 2025; 14(21):4277. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214277
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Ling, Tianyu Zhu, Jiangshan Ma, Yun Xu, and Jianbo Luo. 2025. "A Rapid and Self-Contained Calibration Method for MIMUs Based on Residual Velocity Measurement" Electronics 14, no. 21: 4277. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214277
APA StyleXu, L., Zhu, T., Ma, J., Xu, Y., & Luo, J. (2025). A Rapid and Self-Contained Calibration Method for MIMUs Based on Residual Velocity Measurement. Electronics, 14(21), 4277. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214277







