Abstract
Next- generation wireless communications are projected to integrate reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) to perpetrate enhanced spectral and energy efficiencies. To quantify the performance of RIS-aided wireless networks, the statistics of a single random variable plus the sum of double random variables becomes a core approach to reflect how communication links from RISs improve wireless-based systems versus direct ones. With this in mind, the work applies the statistics of a single random variable plus the sum of double random variables in the secure performance of RIS-based non-orthogonal multi-access (NOMA) systems with the presence of untrusted users. We propose a new communication strategy by jointly considering NOMA encoding and RIS’s phase shift design to enhance the communication of legitimate nodes while degrading the channel capacity of untrusted elements but with sufficient power resources for signal recovery. Following that, we analyze and derive the closed-form expressions of the secrecy effective capacity (SEC) and secrecy outage probability (SOP). All analyses are supported by extensive Monte Carlo simulation outcomes, which facilitate an understanding of system communication behavior, such as the transmit signal-to-noise ratio, the number of RIS elements, the power allocation coefficients, the target data rate of the communication channels, and secure data rate. Finally, the results demonstrate that our proposed communication can be improved significantly with an increase in the number of RIS elements, irrespective of the presence of untrusted proximate or distant users.
1. Introduction
1.1. Backgrounds and Concerns
Recently, the shift to massive interconnected Internet of Thing (IoT) devices has resulted in several challenges for the fifth-generation (5G) and sixth-generation (6G) wireless infrastructure networks, mainly in spectral efficiency, energy consumption, and communication latency [1,2]. However, increased interactions among unsynchronized networks introduce several emerging flaws in security from physical-layer perspectives, especially in coexistence networks with frequent access element changes [3] and when employing advanced learning approaches in collecting network data to serve optimizing network communications, like distributed learning [4] or generative artificial intelligent (GAI) [5]. In this game, any party can become an unauthorized entity, potentially stealing information or disrupting network operations.
With spectrum scarcity due to massive connectivity and outdated orthogonal multiple access (OMA) technologies, new multiple access methods like non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) have emerged [6]. NOMA allows simultaneous communication with shared resources by focusing on the power domain and arranging signals based on channel gains [7] or service priorities [8]. In downlink NOMA, weaker channels or higher priorities obtain more power, which is reversed in uplink NOMA [9]. However, the receiver side must employ successive interference cancellation (SIC) mechanisms to recover the broadcast symbol and cancel the interference between users in decreasing power order. Due to its advantages, NOMA has been extensively studied, addressing research challenges [10], opportunities [11], and its interplay with emerging technologies [12].
Besides NOMA technology, reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs), also known as intelligent reflecting surfaces, have recently attracted significant attention from both scientific and industrial communities due to their ability to alter the wireless propagation medium [13,14]. This feature enables manageable wireless transmission, mitigating issues like deep fading and blockages. Additionally, RISs can perform better than costly relay nodes by increasing the reflective elements [15]. In structure terms, an RIS consists of low-cost passive elements that vary phase shift and amplitude through a programmable microcontroller. Early studies on RISs have focused on myths and critical questions [16], fundamentals of physics, propagation, and path loss modeling [17], as well as initial prototyping, adaptive beamforming, and indoor/outdoor field trials [18]. Subsequent research includes tutorials [19], single-reflection to multi-reflection design and optimization [20], and channel estimation and practical passive beamforming design [21]. Additionally, RIS applications span various contexts, such as cooperative communications [22], short-packet communication [23,24,25], ambient backscatter [26], hardware impairments [27], aerial RISs [28], wireless power transfer [29], two-way communication [30], millimeter-wave communication [31,32], multi-hop RIS-aided relaying [33], imperfect channel estimation [34,35], and energy/rate-reliability trade-offs [36].
On the other hand, physical layer security (PLS) enhances information security by leveraging unique communication channel characteristics, complementing traditional cryptographic methods. It exploits the differences between the channels used by legitimate users and eavesdroppers, achieving perfect security if the legitimate channel is superior [37]. Techniques to improve PLS include relaying, which uses intermediate nodes to enhance diversity gain and coverage, making it harder for eavesdroppers to intercept signals [38]. Other methods include artificial noise generation, which adds random noise to confuse eavesdroppers; beamforming, which focuses the signal in a specific direction; and cooperative jamming, where friendly nodes generate interference to protect communications [39]. PLS research covers various topics, including security and reliability trade-offs in two-way half-duplex wireless relaying networks [40] as well as secure communication using rateless codes under the effects of interference and hardware impairments [41].
1.2. State of the Art
With the ongoing headway of NOMA applications, research on NOMA in PLS has gained considerable attention. For example, the work in [42] investigated the PLS performance of amplify-and-forward (AF) versus decode-and-forward (DF) protocols in cooperative NOMA systems, where using AF schemes shows worse secrecy outage probability (SOP) than the DF one. In [43], a cognitive radio-inspired NOMA scheme was designed to manage the interferences among secondary users while ensuring primary users’ quality of services. In [44], three friendly energy harvesting (EH) jammer selection schemes were proposed to enhance SOP performance, including the random, maximal, and opportunistic EH jammer selection schemes. In [45], the authors proposed to secure cooperative communication in large-scale NOMA networks by exploiting a full-duplex operation at nearby NOMA users as friendly jammers to generate artificial noise to confuse eavesdroppers. In [46], a joint power allocation and beamforming scheme was introduced to protect trusted far users when selecting untrusted nearby users for the NOMA pairing process. In [47], the authors investigated the performance of active reconfigurable repeater-assisted NOMA networks with the presence of not only untrusted users but also external eavesdroppers, focusing on deriving theoretical analysis first and then optimizing PLS performance.
Similarly, there is also a variety of works investigating RISs in PLS in recent years. While the work in [48] investigated the PLS performance of downlink RIS-aided networks with random user location in the surveillance of a multi-antenna eavesdropper, the work in [49] designed a joint RIS beamforming and power allocation sub-optimal scheme to combat the eavesdropping of untrusted users on the information of far-end users. In contrast, the work in [50] proposed three wireless-powered communication RIS systems to degrade the quality reception of passive eavesdroppers for IoT applications. In [51], the authors considered the promise of RISs in cognitive networks to not only improve PLS performance but also resolve the spectrum scarcity.
Of course, the interaction between NOMA and RISs in PLS has certainly been studied in the literature. For instance, the work in [52] investigated the SOP performance of multi-group pairing in NOMA communication, where RISs are deployed to enhance the performance of distant NOMA users. In [53], the authors studied the impact of residual transceiver hardware impairment characteristics on the SOP performance of the actual transceiver equipment, whereas the work in [54] analyzed the SOP of RISs with hardware limitations operating via a 1-bit coding scheme. In addition to that, the work in [55] inspected the SOP performance of a combination of radio frequency and free space optical connections in dual-hop transmission to guarantee the confidentiality of information while preventing unauthorized access. Meanwhile, the work in [56] comprehensively examined the SOP performance of the downlink and uplink NOMA scenario with a pernicious eavesdropper. On the other hand, the work in [57] proposed to use active RIS architecture to compensate for SOP performance loss due to the double fading phenomenon in cascaded RIS channels. At the same time, the authors in [58] proposed two protocols, namely the time-switching protocol and energy splitting, to simultaneously charge batteryless devices and secure legitimate transmission. The work in [59] focused on analyzing the marginal distributions of the legitimate receiving vehicles’ channels in vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication systems with double RIS implementations, thereby gaining more insights into secrecy performance. Meanwhile, the authors in [60] proposed to deploy multiple aerial RIS platforms with two strategies of optimal and sub-optimal aerial RIS selection in order to maximize the secrecy capacity. To do so, they first derived analytical expressions for the SOP and probability of non-zero secrecy capacity to capture PLS performance and then jointly optimize the cooperation of aerial RIS locations and their phase shifts to achieve the secrecy capacity maximization. Recently, the authors in [61] proposed to exploit a mathematical SOP frame to assist in optimizing the power allocation resource and the number of RIS elements to enhance PLS performance.
1.3. Motivations and Contributions
One may be worried about the efficacy of the research on the PLS performance of RIS-based NOMA systems in the literature, as elaborated above, since most of the works only investigate PLS with the presence of external eavesdroppers, with very little study on untrusted users. However, in practice, the presence of untrusted near users might introduce a big flaw in security if they are paired with trusted users [46,49]. Therefore, the concern of random untrusted users in NOMA pairing in RIS-based systems remains an open question, which is the main focus of this work. Moreover, investigating the performance of RIS-secured NOMA systems mostly relies on a certain fading model with and without direct channel communication, lacking a generalized mathematical evaluation framework. Until now, to the best of the authors’ knowledge, there are only three published works highlighting the applications of statistics of two produced variables’ sums, including [62], Nakagami-m random vectors [63], and generalized double variables’ form [64], whereas the statistics of the sum of single variable plus two variables has only one published work in [65] covering the sum of single and double variables. Explicitly, the application of the statistics of a single random variable (RV) plus the sum of double RVs has not been discussed in the literature, especially in the context of security performance. Table 1 summarizes the main differences, contributions of the considered work with the state-of-the-art.

Table 1.
Comparison of the proposed scheme with other works.
The following covers the summary of this work’s contributions in light of previously explained motivations:
- We provide a comprehensive review of the statistics of a single random variable plus the sum of double RVs, including an analysis of the cumulative distribution function (CDF) and/or the probability density function (PDF) for cascaded channels with an optimal RIS phase shifter. This plays a core approach in guiding how to analyze the performance analysis of RIS-aided networks in general and RIS-secured systems in particular.
- We propose a novel communication strategy that combines the mutual benefits of NOMA encoding and an RIS phase shifter by allocating higher power levels for untrusted nodes while optimally configuring the RIS phase shifter. This helps achieve the following three goals: enhancing legitimate channel quality, serving untrusted nodes, and reducing leaks of eavesdropping activities.
- In addition to that, we provide detailed guidance on how to achieve the CDF and PDF for cascaded channels with random RIS phase shifters, which lays the foundation for measuring the impacts of untrusted parties.
- Capitalizing on the CDF and PDF in modeling channel characteristics, we derive closed-form expressions for the secrecy effective capacity and SOP, considering both exact and asymptotic analysis in high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) regions. This serves as an effective way for probing key insights into system designs, such as the secrecy ergodic slope or diversity order gain.
- Through simulation results based on the Monte Carlo method, we not only demonstrate the efficacy of our proposed communication method in favor of RIS-secured undertaking but also exhibit several impacts of system parameters, which reflects the importance of choosing a resource power allocation policy and transmission target data rate.
1.4. Review of the Statistics of Single Random Variable Plus the Sum of Double Random Variables
This section reviews the statistical analysis of a single RV plus the sum of double RVs, focusing on how to derive the PDF and/or CDF under different distribution types.
In recent years, the problem of finding CDF/PDF for a single RV plus the sum of double RVs was identified as a common topic in wireless communications, especially in the field of RISs [62,63,64,65,66]. Specifically, if Z, , and are, respectively, the channels of links from source information to the destination, from source information to the k-th element of RISs, and from the k-th element of RISs to the destination, the end-to-end channel gain received by the destination takes the form
The common method to have the CDF/PDF of U is to fit it into Gamma distribution [64], with the shape parameter and the inverse scale , which can be expressed as
where and denote the expectation and variance operators of RV U, respectively. Having obtained and in hand, the CDF and PDF of U can be written as
where , , and are, respectively, the Gamma function, lower-incomplete Gamma function, and upper-incomplete Gamma function.
In what follows, we will guide a simple method when dealing with different popular distribution types, including Rayleigh fading, Nakagami-m fading, and Rician fading. It is worth noting that our analysis is not limited to the case where . Moreover, Z has the same type of fading but can extend to the case of different types of fading statuses, for example, is Rayleigh, is Nakagami-m, and Z is Rician fading.
1.4.1. Rayleigh Fading Environment
For the Rayleigh fading medium, the PDF of variable with inverse scale can be given as in [67,68,69] as
Based on this, the n-th moment of V can be derived as
which is obtained using the aid of ([70] Equation (3.326.2)). Having obtained (6) in hand, we can fit V into the Gamma distribution with
Since ([70] Equation (8.338.2)) and ([70] Equation (8.338.1)), we can rewrite and as
Note that if and , we can rewrite and as
1.4.2. Nakagami-m Fading Environment
For the Nakagami-m fading medium, the PDF of variable with shape and inverse scale can be given as in [55,60] as
1.4.3. Rician Fading Environment
For the Rician fading medium, the PDF of variable having the Rician factor K and scale parameter can be given as in [71,72,73] as
where is the modified Bessel function of the first kind with the zero order.
From (13), the n-th moment of V can be derived in terms of the confluent hypergeometric function as
which is obtained by first exchanging variable , then applying the standard form in ([70] Equation (6.643.2)), and finally using two transformations as in ([70] Equations (9.220.2) and (9.210.1)).
Having (14) in hand, we can fit V into the Gamma distribution, similar to two previous fading considerations.
2. System Model
2.1. Model Description
Let us consider an RIS-assisted NOMA system, including one source node (), one trustworthy user—Bob (), one untrustworthy user—Willie (), and one RIS (). In terms of setups, all nodes are single antenna devices and the RIS has L programmable elements, indexed by . Due to long-distance communication, the source node employs the NOMA protocol to communicate with both Bob and Willie, and its superimposed signal is encoded as the form of , where , with P being the source transmit power and and being the power allocation (PA) coefficients of signals of Bob () and Willie (), respectively.
Denote , , and by the channel vectors from the source to the RIS, from the RIS to Willie, and from RIS to Bob, respectively. and are direct links from the source to Will and Bob, respectively. is the diagonal matrix at RIS, with , where is the phase shifter of the l-th RIS element and uniformly distributes within [64].
Under NOMA transmission, the signals received by Bob and Willie will have the form
where are the additive white Gaussian noises with zero mean and variance .
Since Bob is a trustworthy user while Willie is an untrustworthy one, we consider configuring the phase shifter at the RIS so that the cascaded channel from the source node to Bob is maximized while that from the source to Willie is arbitrary. Accordingly, the phase shifter at the RIS is configured with the criterion
where is the phase of channel h. Moreover, to better protect Bob’s information, we apply the modified NOMA protocol wherein Bob’s signal is allocated a power level lower than that of Will, i.e., , and we provide the necessary information from Willie for Bob to perform the SIC process [46]. It is worth noting that a joint consideration of an RIS phase shifter and NOMA allocation yields two advantages:
- Bob has optimal cascaded channel gains to perform SIC in descending power order.
- Bob’s information is protected better from Willie’s eavesdropping since the signal strength of Bob () is much lower than that of Willie (). If Willie wants to optimally wiretap Bob’s information (), he needs to perform SIC to first decode their signal (), then remove their signal from the received signal using SIC to obtain Bob’s signal (), and finally intercept Bob’s information ().
Based on the above observation, it is clear that the proposed scheme can be adopted in various scenarios. For instance, in securing Internet of Vehicle (IoV) communications, RISs can be effectively combined with NOMA transmission to enhance the PLS by creating reflecting paths that strengthen legitimate signals and weaken signals received by potential eavesdroppers. Specifically, an RIS deployed on roadside infrastructure could dynamically adjust to route signals only to authorized vehicles while scattering the signals away from potential eavesdroppers. Another practical example is protecting multi-user communications systems, where RISs can provide an extra layer of security by combining NOMA pairing processing to serve two users per cluster. Moreover, with RISs aiding in directing signals, the primary user can maximally enhance its received signal while minimizing the ability for internal eavesdroppers to intercept the data.
To provide a better security observation, this work will focus on the worst-case scenario when Willie tries to wiretap Bob’s information using the SIC mechanism. Let us assume perfect channel state information at the terminals. (Obtaining accurate channel state information can be achieved using some common techniques. First, in pilot-assisted channel estimation, pilot signals or training sequences are sent by the transmitter, which the receiver uses to estimate the channel. This method involves inserting known symbols (pilots) into the transmitted signal. These pilots then help the receiver to measure and estimate the channel’s characteristics accurately. Second, with least squares and minimum mean square error methods, these approaches are frequently used statistical techniques for channel estimation. Compared to minimum mean square error methods, least square methods are simpler and require less computational power but need more pilot signals and lower performance in noisy conditions. Third, regarding blind and semi-blind estimates, blind estimation does not require pilot signals and can be used when there are no pilots available but has less accuracy compared to pilot-assisted methods) and derive the signal-plus-interference-to-noise ratios (SINRs) achieved at node via a perfect SIC process (In this study, we consider a perfect SIC process for performance evaluation to establish a theoretical benchmark, showcasing the maximum potential of a system in ideal conditions. This approach also facilitates relatively secure performance metrics by providing a consistent baseline, enabling easier comparison across different configurations and innovations. Moreover, it yields theoretical insights into secure capacity limits and secrecy outage performance, facilitating the development of robust communication protocols and standards) as
where is the short notation of the cascaded channel gain at node , with
From this formulation, we can see that the randomness of and causes the RV . Thus, to evaluate the system performance, it is necessary to find out the CDF of the PDF of the RVs . Details are outlined in the following:
2.2. Legitimate Channels of Link Sources: RIS and Bob
As for the case of , the distribution of can be derived similar to Section 1.4.3 (i.e., Gamma distribution). Let . Since , the PDF of can be derived as
Making use of ([70] Equation (3.351.2)), the CDF of can be derived as
2.3. Eavesdropping Channels of Link Sources: RIS and Willie
As for the case of , the distribution of is obtained by two following steps:
- Step 1: Denote by , with . Let us rewrite Q asSince the weighted sum of a uniform RV is a uniform RV, is uniformly distributed within . Accordingly, we can derive the following:
- Step 2: Making use of the relation between circularly symmetric complex Gaussian noise, we can map into the exponential distribution with inverse variance , i.e.,Making use of ([70] Equation (3.351.2)), the CDF of can be derived as
3. Performance Evaluation Framework
In this section, we will evaluate the secure performance of the considered system.
According to [37], the secrecy rate of legitimate transmission under an eavesdropping activity is defined as the difference between the main channel capacity and wiretap channel capacity . Mathematically, the secrecy rate that an eavesdropper wiretaps the legitimate signal can be written as
Linking this definition with the considered system, the secrecy rate of Bob’s information can be derived as
3.1. SEC Analysis
Let be the target rate for decoding . Thus, the SEC that Willie wiretaps based on the SIC process can be derived as referenced in [29] for the case of effective capacity as
where the first probability on the right-hand side (RHS) indicates the probability that Willie fails to decode while the second one is the complementary probability. Herein, the SEC can be interpreted as follows: if Willie fails to decode , represented by the probability on the RHS , the SINR for decoding at Willie will turn to zero, leading to the term to be converged to and with the average secrecy capacity being .
The probability can be derived using the formulated SINR in (18) as
where .
Meanwhile, the term can be derived as
Herein, we solve the integral of by first employing the following transformations:
Next, we apply the standard form in ([74] Equation (07.34.21.0013.01 )) to solve . Meanwhile, the standard form in ([70] Equation (4.337)) to directly address .
Gathering all the above analyses together, we obtain the following Lemma:
Lemma 1.
Conditioned on , the SEC that Willie wiretaps based on the SIC process can be derived as
where
and
To understand the SEC performance trend at the high-SNR case (i.e., ), where the noise becomes negligible, we next focus on the asymptotic SEC. Specifically, under the fact that as , we make use of as to approximate as
Next, under the fact that as , we can approximate and as
Now, applying the aid of ([70] Equation (4.352)), we obtain the following:
Thus, at a high SNR, the SEC with that Willie wiretaps based on the SIC process with can be approximated as
herein, if we further let , the SEC will converge to a constant value
3.2. SOP Analysis
Given the secure target rate for protecting , the SOP that Willie wiretaps based on the SIC process can be derived as referenced in [47] for the case of the untrusted user as
where the probability in the RHS indicates the probability that Willie successfully decodes their information but fails to decode Bob’s information.
To achieve the SOP in (52), we start by invoking the formulated SINR in (18) and the formulated secrecy rate in (35). The second probability in the RHS of (52) can be derived as
Now, using the PDF of in (32) and CDF of in (22), we can rewrite the SOP expression as
which is achieved using variable exchange and .
Next, we apply the Heaviside step transfer function for the integral above to obtain
where the last step is obtained using the following transformations:
Finally, applying the standard form as in ([25] Equation (51)), we can achieve a solution for .
From the above analysis, we obtain the following theorem:
Theorem 1.
Exact closed-form expressions for the SOP that Willie wiretaps based on the SIC process can be derived as
where
To obtain insights into the performance and reliability of secure communication systems in the high-SNR case (i.e., ), we study the asymptotic SOP next. By understanding SOPs in these asymptotic modes, one can draw theoretical boundaries, identify potential weaknesses, and design more robust and efficient protocols that ensure security even in the most challenging situations. This analysis also simplifies complex performance metrics, making it easier to evaluate and compare different system designs. Specifically, we make use of as to approximate in (53) as
Herein, we can see that if is set to zero, can be rewritten in terms of the Parabolic cylinder function as
which is achieved by making use of ([70] Equation (6.454)). Since is a constant value, increasing the SNR does not improve the SOP performance at a high SNR.
4. Numerical Results and Discussion
This section quantifies the theoretical analysis regarding the SOP performance of the considered system, where the Monte Carlo simulation method is utilized. Specifically, we randomly generate a sample for channels and . Then, we compute the SINRs as in (18). Finally, we evaluate the SEC and SOP by injecting the SINRs into (36) and (52), and then we take the average. In this work, all results are implemented using Matlab software with version 2023b on a computer simulation. For each set of system parameters, the average running time is 11.1363 s for SOP simulation results, 4.6461 s for SOP analytical results, 1.827821 s for SEC simulation results, and 0.2779 s for SEC analytical results. For the sake of notation, we use (sim.) to denote the simulation result. Parameters used for this section are listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Main parameters for simulations.
In Figure 1, we plot the PDF and CDF for and under different settings of RIS elements (). The left-hand-side parts (a,c,e) show the CDF of , where the curves increase with an increase in the target input, revealing higher input values x. Conversely, the right-hand-side parts (b,d,f) represent the PDF of , where the curves decrease with an increase in the target input, revealing higher input values x. Overall, it can be seen that the simulation outputs, represented by markers, are closely consistent with the analytical approximation results, represented by solid lines, confirming the accuracy of the approximation approach.
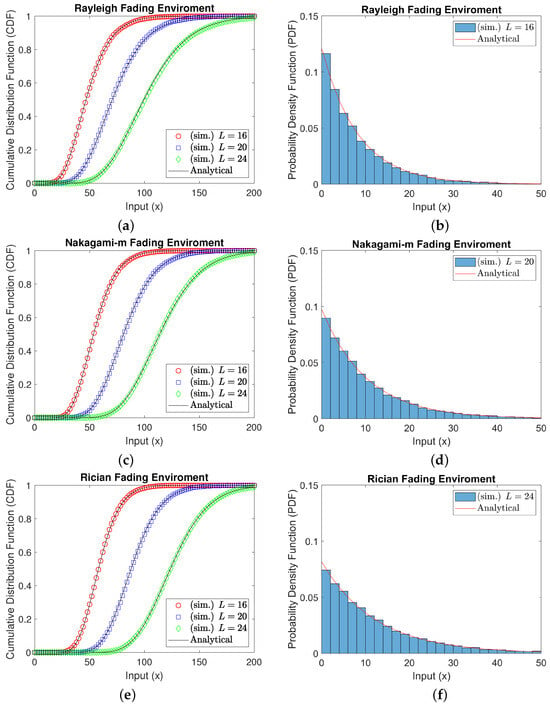
Figure 1.
PDF and CDF validation under different settings of RIS elements. (a,c,e) illustrate the CDF of and (b,d,f) show the PDF of under different settings of RIS elements and channel distributions.
In Figure 2, we plot the SOP performance as a function of the SNR (in sub-figure (a)) and power allocation coefficient (in sub-figure (b)) under three common channels models (Rayleigh, Nakagami-m, and Rician). It is observed from Figure 2a that the SOP results follow an increasing trend with a small SNR value, return to a decreasing trend with a moderate SNR, and finally become saturated at high SNR regions, returning to a zero diversity order for secure performance. Notably, all channel models have the same performance behavior, where the Rician model displays the lowest SOP performance, followed by Nakagami-m and Rayleigh. As for the SNR setting at 5 dB (for example), from Figure 2b, we get that the larger the power allocation level for Willie’s signal, the higher the SOP performance. This justifies that Willie’s signal reception is increased, increasing the chance to wiretap Bob’s information. Again, it can be found that the analytical results closely match the simulated results, verifying the developed mathematical solutions.
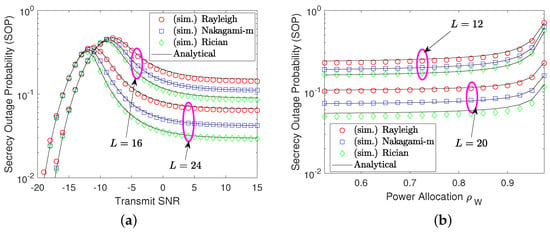
Figure 2.
SOP performance against transmit SNR and power allocation. (a) shows the SOP with respect to (w.r.t.) the SNR and (b) illustrates the SOP w.r.t. power allocation coefficient .
Next, in Figure 3, we explore the SOP performance as a function of the target data rates, including one for Willie’s rate and the other for Bob’s secure rate , with varying RIS elements from 12 to 20. Under the transmit SNR of 5 dB, we can obtain some insights from the figures. First, the SOP performance in Figure 3a tends to be stable with a small value of and then becomes zero when is larger than 1.7 bps/Hz, at which Willie fails to decode its information, yielding information protection that is better than Bob’s. This highlights the positive impact of transmission data on secure performance but harms Willie’s service quality. Second, the SOP performance in Figure 3b increases with a higher secure rate requirement, demonstrating the risk of information leakage. However, we observe that the higher the number of RIS elements, the smaller the SOP performance. This improvement is due to the superior signal-focusing capabilities of RISs to Bob’s expectation, instead of Willie’s.
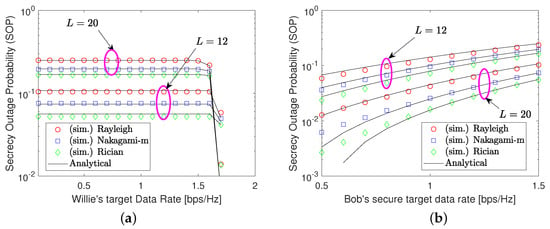
Figure 3.
SOP performance against target rate transmission. (a) shows the SOP w.r.t. the Willie’s target data rates and (b) illustrates the SOP regarding the Bob’s secure rate .
In Figure 4, we plot the SEC performance as a function of the transmit SNR and power allocation coefficient, as well as different numbers of RIS elements. As observed, the analysis reveals several key insights. First, across all channel models in Figure 4a, the SEC curves shift to the RHS as the transmit SNR increases, where the SEC becomes saturated as exceeds 15 dB; however, it can be further improved with an increase in RIS elements. Second, the SEC’s performance in Figure 4a has a decreasing trend with an increase in the power allocation coefficient , which can be interpreted as the same reason as SOP analysis.
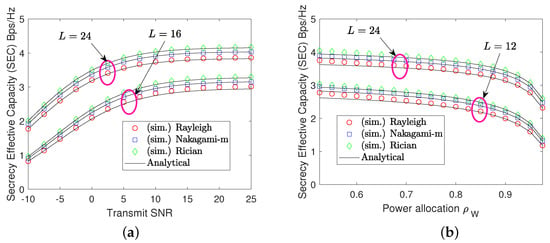
Figure 4.
SEC performance against transmit SNR and power allocation. (a) shows the SEC with respect to (w.r.t.) the SNR and (b) illustrates the SEC w.r.t. power allocation coefficient .
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we studied the performance of RIS-secured NOMA systems, where a joint design of power allocation and RIS’s phase shift alignment are proposed to deal with untrusted users in NOMA transmission. Focusing on three common channel models, we provided a generalized closed-form expression for the SEC and SOP performance. Through numerical results, it was demonstrated that our developed mathematical frameworks can highly predict simulation results. Additionally, it was also shown that increasing the number of RIS elements could indeed significantly boost SEC and SOP performance.
Future studies could focus on further improving the performance of RIS-secured NOMA systems with potential directions, including multiple transceiver transmissions with beamforming designs, active or hybrid active-and-passive RIS operations, multiple eavesdropper scenarios with collaborative monitoring situations, and issues of optimizing resource power allocation to minimize SOP or maximize SEC—subject to OP constraints of users—or address the trade-off between reliability and security performance, involving intercept probability and outage probability.
Author Contributions
P.T.T. and S.-Q.N. proposed the idea for this study and the system model; B.V.M. implemented the methodology and software; A.-T.L. and T.T.D. were responsible for data curation; L.-T.T. wrote the original draft; L.R. supervised this work. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ton Duc Thang University under grant number FOSTECT.2023.14.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest related to the publication of this paper.
References
- Mahdi, M.N.; Ahmad, A.R.; Qassim, Q.S.; Natiq, H.; Subhi, M.A.; Mahmoud, M. From 5G to 6G Technology: Meets Energy, Internet-of-Things and Machine Learning: A Survey. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sufyan, A.; Khan, K.B.; Khashan, O.A.; Mir, T.; Mir, U. From 5G to beyond 5G: A Comprehensive Survey of Wireless Network Evolution, Challenges, and Promising Technologies. Electronics 2023, 12, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouedi, O.; Vu, T.H.; Sacco, A.; Nguyen, D.C.; Piamrat, K.; Marchetto, G.; Pham, Q.V. A Survey on Intelligent Internet of Things: Applications, Security, Privacy, and Future Directions. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.; Huynh-The, T.; Do-Duy, T.; Vu, T.H.; Hwang, W.J.; Pham, Q.V. Applications of Distributed Machine Learning for the Internet-of-Things: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2024, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.H.; Jagatheesaperumal, S.K.; Nguyen, M.D.; Van Huynh, N.; Kim, S.; Pham, Q.V. Applications of Generative AI (GAI) for Mobile and Wireless Networking: A Survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, A.T.; Vu, T.H.; Duy, T.T.; Tu, L.T.; Voznak, M. Analysis of PHY-Layer Security and Covert Communication in Hybrid Power-Frequency Multiple Access Systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2024, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Benjebbour, A.; Kishiyama, Y.; Nakamura, T. System-level performance evaluation of downlink non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA). In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 24th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), London, UK, 8–11 September 2013; pp. 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, M.M.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Khairy, M.M. Power allocation strategies for Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Selected Topics in Mobile & Wireless Networking (MoWNeT), Cairo, Egypt, 11–13 April 2016; pp. 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Elkashlan, M.; Ding, Z.; Nallanathan, A.; Hanzo, L. Nonorthogonal Multiple Access for 5G and Beyond. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 2347–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Vu, T.H.; Tu, L.T.; Duy, T.T.; Nguyen, Q.S.; da Costa, D.B. A Low-Complexity Relaying Protocol for Cooperative Short-Packet NOMA-Based Spectrum Sharing Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 9044–9049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Wang, B.; Ding, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S.; Hanzo, L. A Survey of Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access for 5G. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 2294–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezi, M.; Baduge, G.A.A.; Liu, Y.; Arafa, A.; Fang, F.; Ding, Z. Interplay Between NOMA and Other Emerging Technologies: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2019, 5, 900–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnson, E.; Wymeersch, H.; Matthiesen, B.; Popovski, P.; Sanguinetti, L.; De Carvalho, E. Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces: A signal processing perspective with wireless applications. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2022, 39, 135–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Chien, T.; Papazafeiropoulos, A.K.; Tu, L.T.; Chopra, R.; Chatzinotas, S.; Ottersten, B. Outage Probability Analysis of IRS-Assisted Systems Under Spatially Correlated Channels. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 1815–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnson, E.; Özdogan, Ö.; Larsson, E.G. Intelligent Reflecting Surface Versus Decode-and-Forward: How Large Surfaces are Needed to Beat Relaying? IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2019, 9, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnson, E.; Özdogan, Ö.; Larsson, E.G. Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces: Three Myths and Two Critical Questions. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2021, 58, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdogan, Ö.; Björnson, E.; Larsson, E.G. Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces: Physics, Propagation, and Pathloss Modeling. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2019, 9, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Yin, H.; Tan, L.; Cao, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, K.; Zhang, K.; Björnson, E. RIS-Aided Wireless Communications: Prototyping, Adaptive Beamforming, and Indoor/Outdoor Field Trials. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2021, 69, 8627–8640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, B.; You, C.; Zhang, R. Intelligent Reflecting Surface-Aided Wireless Communications: A Tutorial. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2021, 69, 3313–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, W.; Zheng, B.; You, C.; Zhang, R. Intelligent Reflecting Surface-Aided Wireless Networks: From Single-Reflection to Multireflection Design and Optimization. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 1380–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; You, C.; Mei, W.; Zhang, R. A Survey on Channel Estimation and Practical Passive Beamforming Design for Intelligent Reflecting Surface Aided Wireless Communications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2022, 24, 1035–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.C.; Hoang, T.M.; Tran, P.T.; Nguyen, T.N.; Phan, V.D.; Minh, V.; Voznak, M. Cooperative Communications for Improving the Performance of Bidirectional Full-Duplex System With Multiple Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 134733–134742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.H.; Nguyen, T.V.; da Costa, D.B.; Kim, S. Intelligent Reflecting Surface-Aided Short-Packet Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 4500–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.H.; Nguyen, T.V.; Pham, Q.V.; da Costa, D.B.; Kim, S. STAR-RIS-Enabled Short-Packet NOMA Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 13764–13769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, D.T.; Nguyen, T.N.; Le, A.T.; Phan, V.D.; Voznak, M. Holographic Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-Aided Downlink NOMA IoT Networks in Short-Packet Communication. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 65266–65277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, A.T.; Nguyen, T.N.; Tu, L.T.; Tran, T.P.; Duy, T.T.; Voznak, M.; Ding, Z. Performance Analysis of RIS-Assisted Ambient Backscatter Communication Systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2023, 13, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.N.; Vinh, N.V.; Nguyen, B.C.; Minh, B.V. On performance of RIS-aided bidirectional full-duplex systems with combining of imperfect conditions. Wirel. Netw. 2024, 30, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phu, L.S.; Nguyen, T.N.; Voznak, M.; Nguyen, B.C.; Hoang, T.M.; Minh, B.V.; Tran, P.T. Improving the Capacity of NOMA Network Using Multiple Aerial Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 107958–107971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.H.; Jee, A.; da Costa, D.B.; Kim, S. STAR-RIS Empowered NOMA Systems with Caching and SWIPT. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2023, 5, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.H.; Pham, Q.V.; Nguyen, T.T.; da Costa, D.B.; Kim, S. Enhancing RIS-Aided Two-Way Full-Duplex Communication With Nonorthogonal Multiple Access. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 19963–19977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, D.T.; Nguyen, B.C.; Lam, S.C.; Van Vinh, N.; Nguyen, T.N. SER performance of millimeter-wave communications with multiple reconfigurable intelligent surfaces and transmit antenna selection. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2023, 160, 154517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, X.N.; Nguyen, B.C.; Thi, T.D.; Van Vinh, N.; Minh, B.V.; Kim, T.; Nguyen, T.N.; Le, A.V. Enhancing data rate and energy efficiency of NOMA systems using reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for millimeter-wave communications. Digit. Signal Process. 2024, 151, 104553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, P.M.; Kien, N.T.; Duy, T.T.; An, N.H.; Tung, N.T.; Le, A.V. Performance Evaluation Of Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Aided Multi-Hop Relaying Schemes With Short Packet Communication. Adv. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2024, 22, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.H.; Kim, S. Performance Analysis of Full-Duplex Two-Way RIS-Based Systems With Imperfect CSI and Discrete Phase-Shift Design. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2022, 27, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.Q.; Le, A.T.; Thien, H.T.; Kharel, R. Outage Performance Analysis of STAR-RIS-NOMA Networks under Imperfect CSI. Adv. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2024, 22, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.H.; Nguyen, T.N.; Nguyen, T.T.; Kim, S. Hybrid Active-Passive STAR-RIS-based NOMA Systems: Energy/Rate-Reliability Trade-offs and Rate Adaptation. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2024, 14, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyner, A.D. The wire-tap channel. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1975, 54, 1355–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanenga, A.; Mapunda, G.A.; Jacob, T.M.L.; Marata, L.; Basutli, B.; Chuma, J.M. An Overview of Key Technologies in Physical Layer Security. Entropy 2020, 22, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, M.; Tu, L.T.; Minh, B.V.; Nguyen, Q.S.; Rejfek, L.; Lee, B.M. Security and Reliability Analysis of the Power Splitting-Based Relaying in Wireless Sensors Network. Sensors 2024, 24, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, D.H.; Nguyen, T.N.; Tran, M.H.; Li, X.; Tran, P.T.; Voznak, M. Security and reliability analysis of a two-way half-duplex wireless relaying network using partial relay selection and hybrid TPSR energy harvesting at relay nodes. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 187165–187181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran Tin, P.; Nguyen, T.N.; Sang, N.Q.; Trung Duy, T.; Tran, P.T.; Voznak, M. Rateless codes-based secure communication employing transmit antenna selection and harvest-to-jam under joint effect of interference and hardware impairments. Entropy 2019, 21, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Yang, L.; Alouini, M.S. Physical Layer Security for Cooperative NOMA Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 4645–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Yang, W.; Pan, G.; Cai, Y.; Song, Y. Physical Layer Security in Cognitive Radio Inspired NOMA Network. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2019, 13, 700–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Wang, B.; Ding, H.; Lv, L.; Dong, R.; Cheng, T. Improving Physical Layer Security of Uplink NOMA via Energy Harvesting Jammers. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2020, 16, 786–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Yue, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Dai, X. Enhancing Physical Layer Security With Artificial Noise in Large-Scale NOMA Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 2349–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.H.; Pham, Q.V.; da Costa, D.B.; Debbah, M.; Kim, S. Physical-Layer Security in Short-Packet NOMA Systems with Untrusted Near Users. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Rome, Italy, 28 May–1 June 2023; p. 2023-01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, A.T.; Vu, T.H.; Tu, N.H.; Nguyen, T.N.; Tu, L.T.; Voznak, M. Active Reconfigurable Repeater-Assisted NOMA Networks in Internet-of-Things: Reliability, Security, and Covertness. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Du, H.; Sun, Q.; Ai, B.; Ng, D.W.K. Physical Layer Security Enhancement With Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-Aided Networks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2021, 16, 3480–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, C.; Jia, F.; Ge, J.; Gong, F. Improving Physical Layer Security for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Aided NOMA 6G Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 4451–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Ding, H.; Lv, L.; Su, Z.; Tao, J.; Gong, F. Physical-Layer Security for Intelligent-Reflecting-Surface-Aided Wireless-Powered Communication Systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 18097–18110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshafa, M.H.; Ngatched, T.M.N.; Ahmed, M.H. RIS-Aided Physical Layer Security Improvement in Underlay Cognitive Radio Networks. IEEE Syst. J. 2023, 17, 6437–6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yuan, Y. Secrecy outage probability analysis for RIS-assisted NOMA systems. Electron. Lett. 2020, 56, 1254–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Li, M.; Yang, X.; Alturki, R.; Alshehri, M.D.; Khan, F. Impact of Residual Hardware Impairment on the IoT Secrecy Performance of RIS-Assisted NOMA Networks. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 42583–42592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Yue, X.; Wang, X.; Dai, X.; Zou, R.; Essaaidi, M. Intelligent Reflecting Surface Aided Secure Communications for NOMA Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 71, 2761–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Badrudduza, A.S.M.; Islam, S.M.R.; Islam, S.H.; Ibrahim, M.; Abdullah-Al-Wadud, M. Enhancing Physical Layer Secrecy Performance for RIS-Assisted RF-FSO Mixed Wireless System. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 127737–127753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, S.P.; Nguyen, H.N.; Nguyen, N.T.; Van, C.H.; Le, A.T.; Voznak, M. Physical layer security analysis of IRS-based downlink and uplink NOMA networks. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2023, 2023, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pei, Y.; Yue, X.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Z. Secure Communication of Active RIS Assisted NOMA Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2023, 23, 4489–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yi, W.; Wu, X.; Nallanathan, A. Physical Layer Security for STAR-RIS-NOMA: A Stochastic Geometry Approach. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2023, 23, 6030–6044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadi, F.R.; Kaveh, M.; Wong, K.K.; Martín, D. Physical Layer Security Performance of Cooperative Dual-RIS-Aided V2V NOMA Communications. IEEE Syst. J. 2024, 18, 2074–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshafa, M.H.; Ahmed, G.; Ngatched, T.M.N.; Di Renzo, M. Aerial Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces-Enabled Secured Wireless Communications: Performance Analysis and Optimization. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2024, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, A.T.; Hieu, T.D.; Nguyen, T.N.; Le, T.L.; Nguyen, S.Q.; Partila, P. Physical layer security analysis for RIS-aided NOMA systems with non-colluding eavesdroppers. Comput. Commun. 2024, 219, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badarneh, O.S. Statistics of the Product of Two α-F Variates with Applications. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 1761–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegos, S.A.; Tyrovolas, D.; Diamantoulakis, P.D.; Liaskos, C.K.; Karagiannidis, G.K. On the Distribution of the Sum of Double-Nakagami-m random vectors and application in randomly reconfigurable surfaces. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 7297–7307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.V.; Tran, P.T.; Pham, T.-H.T.; Le, A.T.; Le, S.-P.; Partila, P. Statistics of the Sum of Double Random Variables and Their Applications in Performance Analysis and Optimization of Simultaneously Transmitting and Reflecting Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-Assisted Non-Orthogonal Multi-Access Systems. Sensors 2024, 24, 6148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, H.S.; Lourenço, G.B.L.C.; Queiroz, W.J.L.; Oliveira, A.S.R.; Madeiro, F.; Badarneh, O.S. On the Sum of α-F and Double α-F VariatesWith Application to MRC and RIS. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2022, 26, 2894–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Chien, T.; Tu, L.T.; Khalid, W.; Yu, H.; Chatzinotas, S.; Di Renzo, M. RIS-Assisted Wireless Communications: Long-Term Versus Short-Term Phase Shift Designs. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2024, 72, 1175–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.N.; Tran, P.T.; Vozňák, M. Power splitting–based energy-harvesting protocol for wireless-powered communication networks with a bidirectional relay. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2018, 31, e3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.N.; Minh, T.H.Q.; Tran, P.T.; Voznak, M.; Duy, T.T.; Nguyen, T.L.; Tin, P.T. Performance enhancement for energy harvesting based two-way relay protocols in wireless ad-hoc networks with partial and full relay selection methods. Ad Hoc Netw. 2019, 84, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.M.; Nguyen, B.C.; Thang, N.N.; Tran, M.; Tran, P.T. Performance and optimal analysis of time-switching energy harvesting protocol for MIMO full-duplex decode-and-forward wireless relay networks with various transmitter and receiver diversity techniques. J. Frankl. Inst. 2020, 357, 13205–13230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, A.; Zwillinger, D. Table of Integrals, Series, and Products; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.N.; Tran Tin, P.; Ha, D.H.; Voznak, M.; Tran, P.T.; Tran, M.; Nguyen, T.L. Hybrid TSR–PSR alternate energy harvesting relay network over Rician fading channels: Outage probability and SER analysis. Sensors 2018, 18, 3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.N.; Quang Minh, T.H.; Tran, P.T.; Vozňák, M. Energy harvesting over Rician fading channel: A performance analysis for half-duplex bidirectional sensor networks under hardware impairments. Sensors 2018, 18, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.N.; Tran, P.T.; Minh, T.H.Q.; Voznak, M.; Sevcik, L. Two-way half duplex decode and forward relaying network with hardware impairment over Rician fading channel: System performance analysis. Elektron. Elektrotechnika 2018, 24, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer G-Function: Integration. Wolfram Research. Available online: http://functions.wolfram.com/07.34.21.0013.01 (accessed on 30 December 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).