Aging-Aware Character Recognition with E-Textile Inputs
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A deep kernel-based two-sample test method for data distribution validation. A deep neural network is used to extract a feature representation of the high-dimensional image data, under which the source domain and target domain can be well separated, and thus obtain a well-parameterized kernel.
- A Gabor domain adaptation technique for handwritten character recognition, with a newly designed Gabor orientation convolution introduced for consideration of transformation invariance.
- A series of experiments to demonstrate the feasibility of proposed techniques.
2. Related Work
2.1. Interaction with E-Textile
2.2. Character Recognition
2.3. Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
3. Data Preparation
3.1. Data Collecting
3.2. Data Pre-Processing
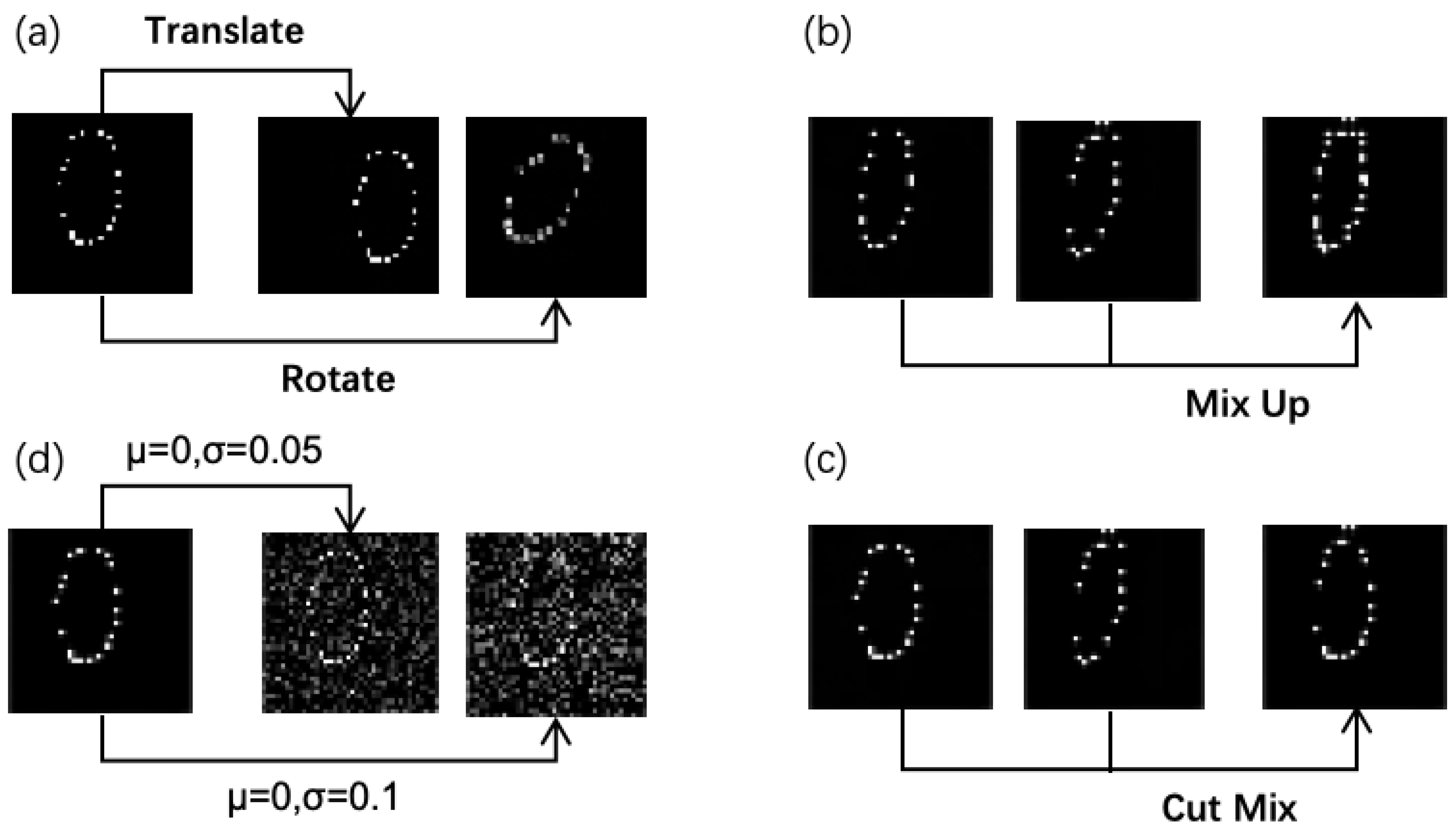
3.3. Data Augmentation
4. Data Distribution Analysis
4.1. Problem Formulation
4.2. Deep Kernel Test
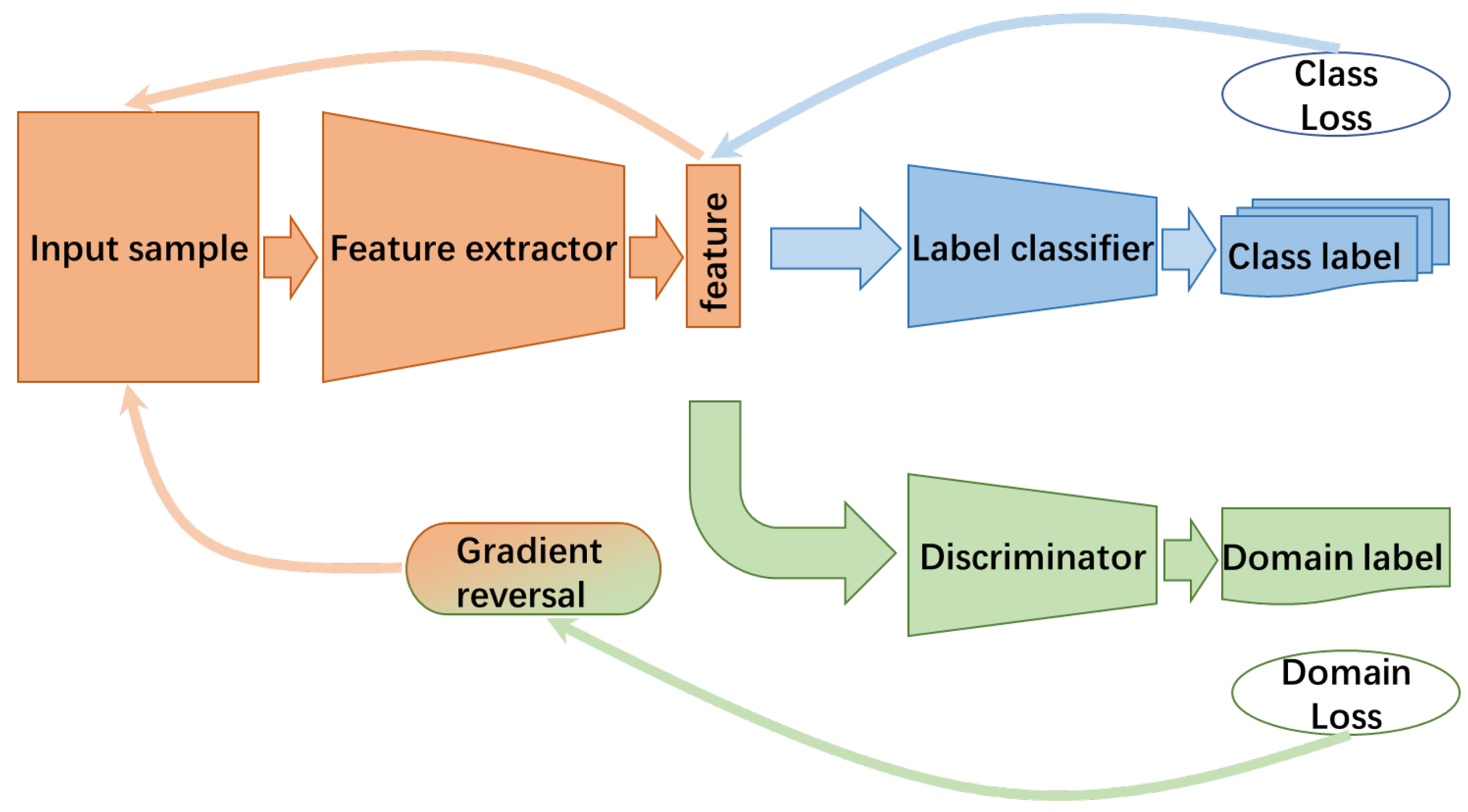
5. Aging-Aware Character Recognition with Gabor Domain Adaptation
6. Experimental Results
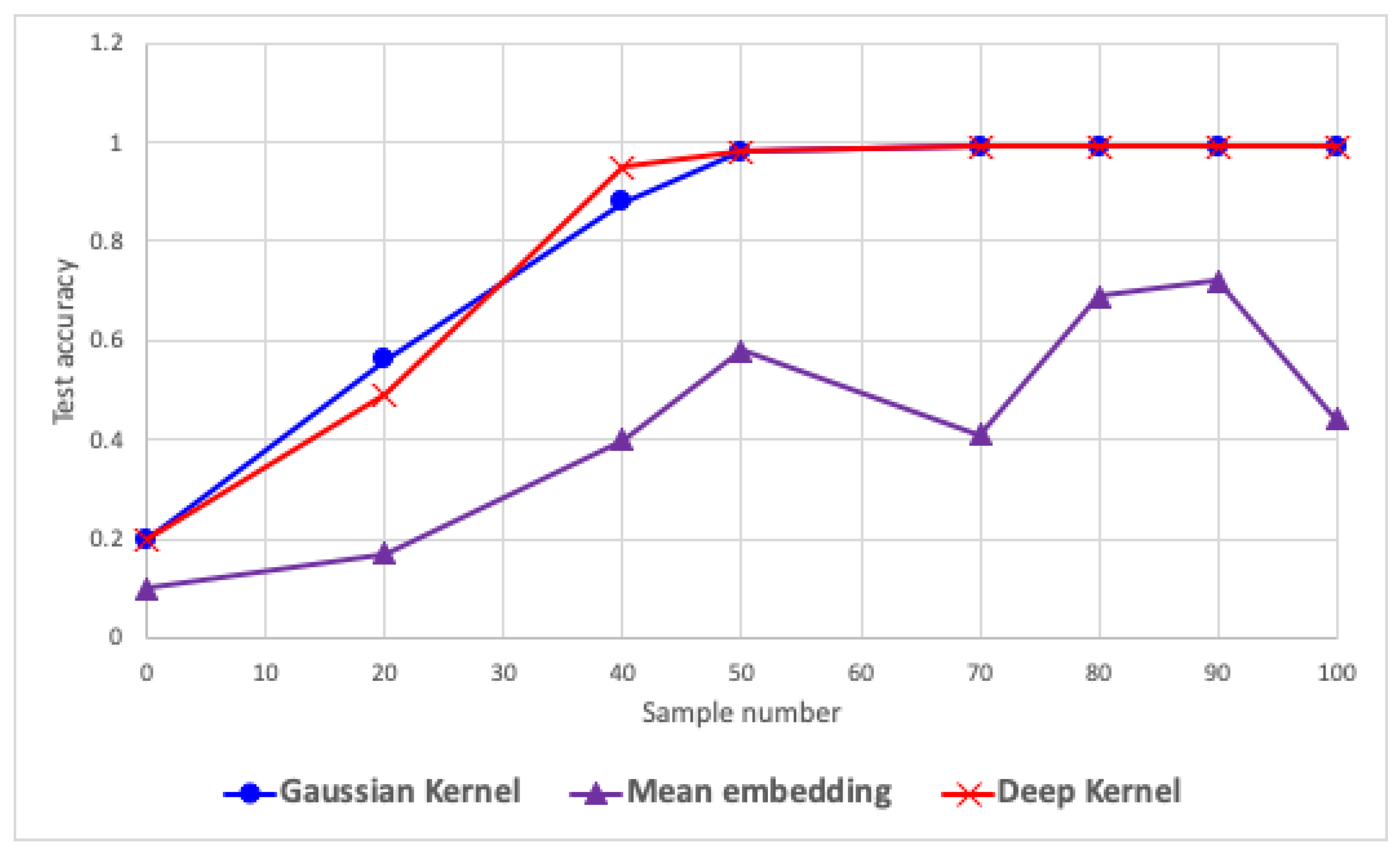
6.1. Data Distribution
6.2. Character Recognition
- Different datasets: We investigated the transfer of knowledge learned from the SSDA dataset to the STDA dataset, denoted as SSDA → STDA, and other combinations including USPS → QMNIST, MNIST → QMNIST, and MNIST + EMNIST → SSDA + STDA.
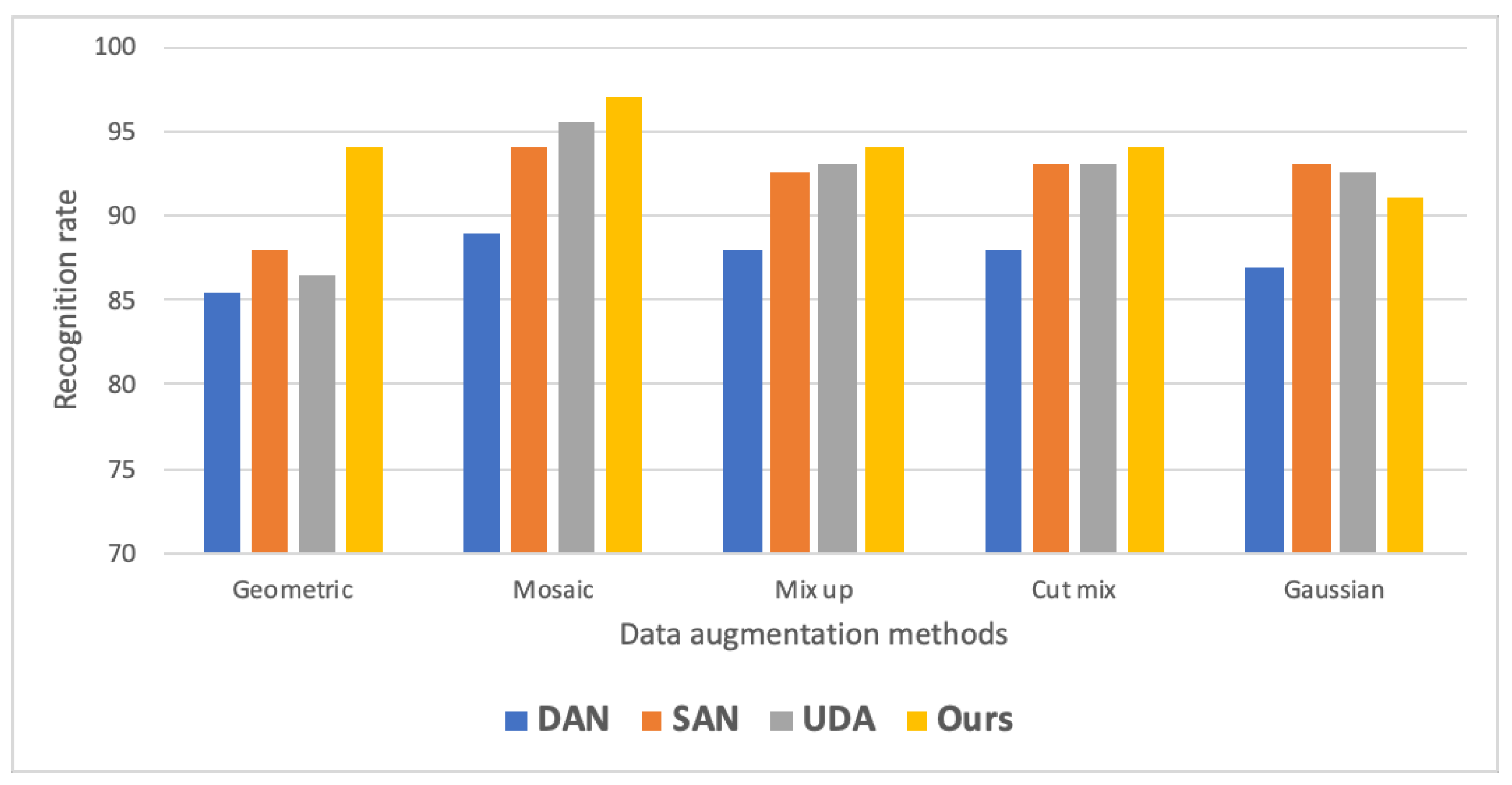
- Different data augmentation: We augmented real samples from the source domain in various ways, as mentioned in Section 3.3, for the task SSDA → STDA, to determine the optimal augmentation strategy for our model.
- Different distribution measures: We investigated the optimal distribution measurement for our model in the SSDA → STDA task by adjusting the loss according to different distribution metrics.
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, L.H.; Braud, T.; Zhou, P.; Wang, L.; Xu, D.; Lin, Z.; Kumar, A.; Bermejo, C.; Hui, P. All one needs to know about metaverse: A complete survey on technological singularity, virtual ecosystem, and research agenda. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.05352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kienzle, W.; Ma, Y.; Ng, S.S.; Benko, H.; Harrison, C. ActiTouch: Robust touch detection for on-skin AR/VR interfaces. In Proceedings of the 32nd Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, New Orleans, LA, USA, 20–23 October 2019; pp. 1151–1159. [Google Scholar]
- Hachisu, T.; Bourreau, B.; Suzuki, K. Enhancedtouchx: Smart bracelets for augmenting interpersonal touch interactions. In Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Glasgow, UK, 4–9 May 2019; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Yu, C.; Yi, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, S. Blindtype: Eyes-free text entry on handheld touchpad by leveraging thumb’s muscle memory. In Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Whitmire, E.; Jain, M.; Jain, D.; Nelson, G.; Karkar, R.; Patel, S.; Goel, M. Digitouch: Reconfigurable thumb-to-finger input and text entry on head-mounted displays. In Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Gu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yi, X.; Luo, H.; Shi, Y. Tap, dwell or gesture? exploring head-based text entry techniques for hmds. In Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 6–11 May 2017; pp. 4479–4488. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, D.; Foong, P.S.; Zhao, S.; Liu, C.; Janaka, N.; Erusu, V. Eyeditor: Towards on-the-go heads-up text editing using voice and manual input. In Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 April 2020; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, L.; Xiong, T.; Zhang, H.; Guo, S.; Chen, X.; Gong, J.; Lin, J.; Qin, Y. TouchEditor: Interaction Design and Evaluation of a Flexible Touchpad for Text Editing of Head-Mounted Displays in Speech-unfriendly Environments. In Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2024; Volume 7, pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhan, L.; Guo, S.; Zhang, M.; Lin, J.; Qin, Y.; Fu, H. Handwriting Velcro: Endowing AR Glasses with Personalized and Posture-adaptive Text Input Using Flexible Touch Sensor. In Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2023; Volume 6, pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Biermaier, C.; Bechtold, T.; Pham, T. Towards the functional ageing of electrically conductive and sensing textiles: A review. Sensors 2021, 21, 5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Chen, X.; Mehmood, A.; Raivio, L.; Huttunen, H.; Raumonen, P.; Virkki, J. ClothFace: A batteryless RFID-based textile platform for handwriting recognition. Sensors 2020, 20, 4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, G.N.; Ali, A.; Collie, S. Textile sensors for wearable applications: A comprehensive review. Cellulose 2020, 27, 6103–6131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parzer, P.; Perteneder, F.; Probst, K.; Rendl, C.; Leong, J.; Schuetz, S.; Vogl, A.; Schwoediauer, R.; Kaltenbrunner, M.; Bauer, S. Resi: A highly flexible, pressure-sensitive, imperceptible textile interface based on resistive yarns. In Proceedings of the 31st Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, Berlin, Germany, 14 October 2018; pp. 745–756. [Google Scholar]
- Mikkonen, J.; Townsend, R. Frequency-based design of smart textiles. In Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Glasgow, UK, 4–9 May 2019; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.Y.; Qi, S.; Chen, J.; Shang, M.; Gong, J.; Seyed, T.; Yang, X.D. Fabriccio: Touchless Gestural Input on Interactive Fabrics. In Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 April 2020; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Geissler, D.; Faulhaber, M.; Gleiss, C.E.; Zahn, E.F.; Ray, L.S.S.; Gamarra, D.; Rey, V.F.; Suh, S.; Bian, S. MoCaPose: Motion Capturing with Textile-integrated Capacitive Sensors in Loose-fitting Smart Garments. In Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2023; Volume 7, pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ku, P.S.; Huang, K.; Kao, C.H.L. Patch-O: Deformable Woven Patches for On-body Actuation. In Proceedings of the 2022 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 29 April–5 May 2022; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Wan, Q.; Deng, W.; Guo, T.; Cheng, J. Smart-Sleeve: A wearable textile pressure sensor array for human activity recognition. Sensors 2022, 22, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorsandi, P.M.; Jones, L.; Davoodnia, V.; Lampen, T.J.; Conrad, A.; Etemad, A.; Nabil, S. FabriCar: Enriching the User Experience of In-Car Media Interactions with Ubiquitous Vehicle Interiors using E-textile Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2023 ACM Designing Interactive Systems Conference, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 10–14 July 2023; pp. 1438–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia, A.; Mughrabi, M.H.; Abdlkarim, D.; Di Luca, M.; Gonzalez-Franco, M.; Ahuja, K.; Seifi, H. Text Entry for XR Trove (TEXT): Collecting and Analyzing Techniques for Text Input in XR. In CHI ’25, Proceedings of the 2025 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Yokohama, Japan, 26 April–1 May 2025; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihara, A.S.; Nakajima, K.; Kake, A.; Ishimaru, K.; Osugi, K.; Naruse, Y. Advantage of handwriting over typing on learning words: Evidence from an N400 event-related potential index. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 679191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keysers, D.; Deselaers, T.; Gollan, C.; Ney, H. Deformation models for image recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 29, 1422–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCoste, D.; Schölkopf, B. Training invariant support vector machines. Mach. Learn. 2002, 46, 161–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, M.D.; Tissera, M.D.; Vladusich, T.; van Schaik, A.; Tapson, J. Fast, simple and accurate handwritten digit classification by training shallow neural network classifiers with the ‘extreme learning machine’algorithm. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciresan, D.C.; Meier, U.; Gambardella, L.M.; Schmidhuber, J. Convolutional neural network committees for handwritten character classification. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Beijing, China, 18–21 September 2011; pp. 1135–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Moczulski, M.; Denil, M.; Freitas, N.D.; Smola, A.; Song, L.; Wang, Z. Deep fried convnets. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1476–1483. [Google Scholar]
- Hertel, L.; Barth, E.; Käster, T.; Martinetz, T. Deep convolutional neural networks as generic feature extractors. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Killarney, Ireland, 12–17 July 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hull, J.J. A database for handwritten text recognition research. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1994, 16, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L. The mnist database of handwritten digit images for machine learning research [best of the web]. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2012, 29, 141–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, G.; Afshar, S.; Tapson, J.; Schaik, A.V. EMNIST: Extending MNIST to handwritten letters. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Anchorage, AK, USA, 14–19 May 2017; pp. 2921–2926. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, C.; Bottou, L. Cold case: The lost mnist digits. In Proceedings of the NIPS’19: 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Donahue, J.; Jia, Y.; Vinyals, O.; Hoffman, J.; Zhang, N.; Tzeng, E.; Darrell, T. Decaf: A deep convolutional activation feature for generic visual recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Beijing, China, 21–26 June 2014; pp. 647–655. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, R.; Chen, W.; Yang, S.; Song, J.; Lin, L.; Xie, D.; Pu, S.; Wang, X.; Song, M.; Zhuang, Y. Slimmable domain adaptation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 7141–7150. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Y.; Yu, Z.; Liu, X.; Kumar, B.; Wang, J. Confidence regularized self-training. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 5982–5991. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Feng, Z.; Gu, Q.; Cheng, G.; Lu, X.; Shi, J.; Ma, L. Uncertainty-aware consistency regularization for cross-domain semantic segmentation. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2022, 221, 103448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, T.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Wen, F. Prototypical pseudo label denoising and target structure learning for domain adaptive semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 12414–12424. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, A.; Han, Y.; Zhu, L.; Yang, Y. Instance-invariant domain adaptive object detection via progressive disentanglement. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 4178–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schölkopf, B.; Smola, A.J. Learning with Kernels: Support Vector Machines, Regularization, Optimization, and Beyond; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gretton, A.; Borgwardt, K.M.; Rasch, M.J.; Schölkopf, B.; Smola, A. A kernel two-sample test. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2012, 13, 723–773. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Xu, W.; Lu, J.; Zhang, G.; Gretton, A.; Sutherland, D.J. Learning deep kernels for non-parametric two-sample tests. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Online, 13–18 July 2020; pp. 6316–6326. [Google Scholar]
- Wenliang, L.; Sutherland, D.J.; Strathmann, H.; Gretton, A. Learning deep kernels for exponential family densities. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 6737–6746. [Google Scholar]
- Ganin, Y.; Lempitsky, V. Unsupervised domain adaptation by backpropagation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 1180–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Ye, Q.; Qiu, Q.; Jiao, J. Oriented response networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 519–528. [Google Scholar]
- Kwolek, B. Face detection using convolutional neural networks and Gabor filters. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, Warsaw, Poland, 11–15 September 2005; pp. 551–556. [Google Scholar]
- Calderon, A.; Roa, S.; Victorino, J. Handwritten digit recognition using convolutional neural networks and gabor filters. Proc. Int. Congr. Comput. Intell. 2003, 42, 9-441. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.Y.; Morgan, N. Robust CNN-based speech recognition with Gabor filter kernels. In Proceedings of the Fifteenth Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Singapore, 14–18 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gabor, D. Theory of communication. Part 1: The analysis of information. J. Inst. Electr. Eng.-Part III Radio Commun. Eng. 1946, 93, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Munoz, C.; Rios-Vila, A.; Calvo-Zaragoza, J. Handwritten Text Recognition: A Survey. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.08417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jordan, M. Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 97–105. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Long, M.; Wang, J.; Jordan, M.I. Partial transfer learning with selective adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 2724–2732. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Guo, Z.; Li, S.; Xing, F.; You, J.; Kuo, C.C.J.; El Fakhri, G.; Woo, J. Adversarial unsupervised domain adaptation with conditional and label shift: Infer, align and iterate. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10367–10376. [Google Scholar]



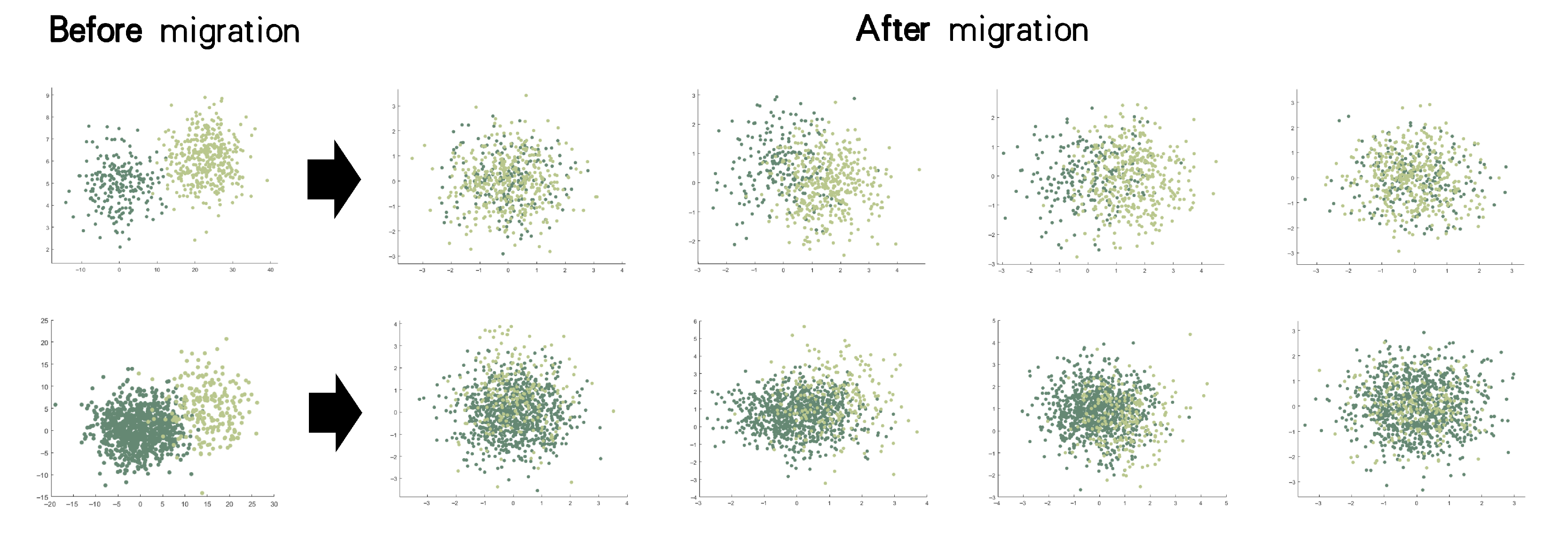
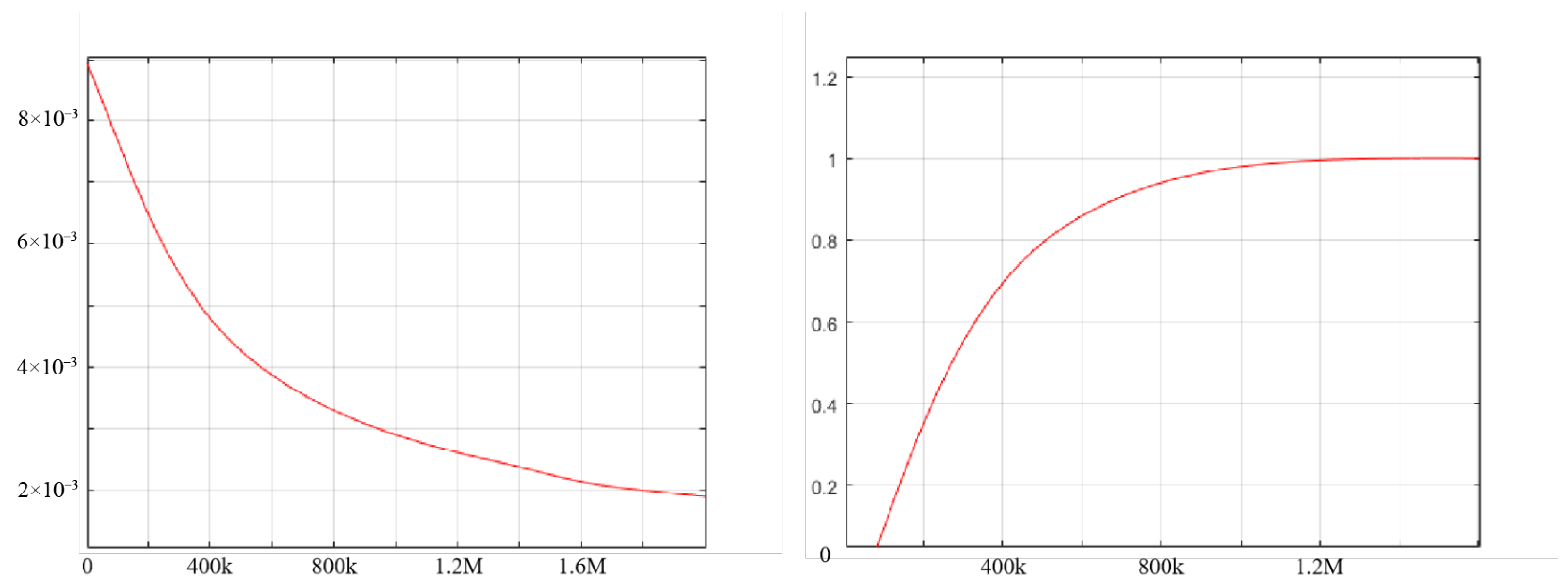
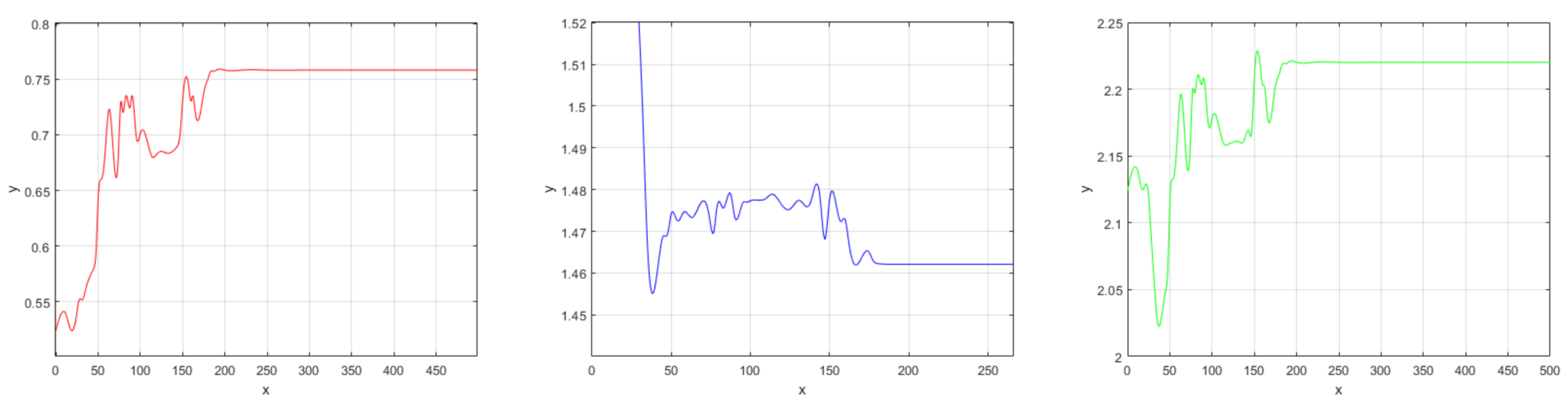
| Datasets | Gaussian Kernel | Mean Embedding |
|---|---|---|
| USPS | √ | × |
| MNIST | √ | √ |
| SA | √ | √ |
| N | Mean Embedding | Gaussian Kernel | Deep Kernel |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 0.555 ± 0.044 | ||
| 400 | 0.996 ± 0.004 | ||
| 600 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | ||
| 800 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | ||
| 1000 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | ||
| Avg |
| Tasks | Methods | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| SSDA → STDA | DAN [51] | 62.3 ± 4.22 |
| SSDA → STDA | SAN [52] | 69.5 ± 2.48 |
| SSDA → STDA | UDA [53] | 73.7 ± 0.83 |
| SSDA → STDA | A2TEXT | 75.6 ± 1.25 |
| USPS → QMNIST | DAN | 74.7 ± 1.28 |
| USPS → QMNIST | SAN | 78.1 ± 1.91 |
| USPS → QMNIST | UDA | 78.8 ± 0.69 |
| USPS → QMNIST | A2TEXT | 80.4 ± 1.82 |
| MNIST → QMNIST | DAN | 76.7 ± 1.58 |
| MNIST → QMNIST | SAN | 79.2 ± 1.13 |
| MNIST → QMNIST | UDA | 80.5 ± 0.97 |
| MNIST → QMNIST | A2TEXT | 82.1 ± 1.08 |
| MNIST + EMNSIT → SSDA + STDA | DAN | 68.4 ± 0.91 |
| MNIST + EMNSIT → SSDA + STDA | SAN | 69.8 ± 0.63 |
| MNIST + EMNSIT → SSDA + STDA | UDA | 73.5 ± 0.55 |
| MNIST + EMNSIT → SSDA + STDA | A2TEXT | 77.8 ± 0.93 |
| Data Enhancement Methods | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| Geometric | 88.6 ± 2.3 |
| Mosaic | 96.9 ± 0.5 |
| Mix up | 94.2 ± 1.1 |
| Cut Mix | 94.4 ± 0.7 |
| Gaussian | 90.7 ± 1.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, J.; Rong, Y.; Cheng, Y.; He, C. Aging-Aware Character Recognition with E-Textile Inputs. Electronics 2025, 14, 3964. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193964
Lin J, Rong Y, Cheng Y, He C. Aging-Aware Character Recognition with E-Textile Inputs. Electronics. 2025; 14(19):3964. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193964
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Juncong, Yujun Rong, Yao Cheng, and Chenkang He. 2025. "Aging-Aware Character Recognition with E-Textile Inputs" Electronics 14, no. 19: 3964. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193964
APA StyleLin, J., Rong, Y., Cheng, Y., & He, C. (2025). Aging-Aware Character Recognition with E-Textile Inputs. Electronics, 14(19), 3964. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193964





