Spiking Neural Network-Based Bidirectional Associative Learning Circuit for Efficient Multibit Pattern Recall in Neuromorphic Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
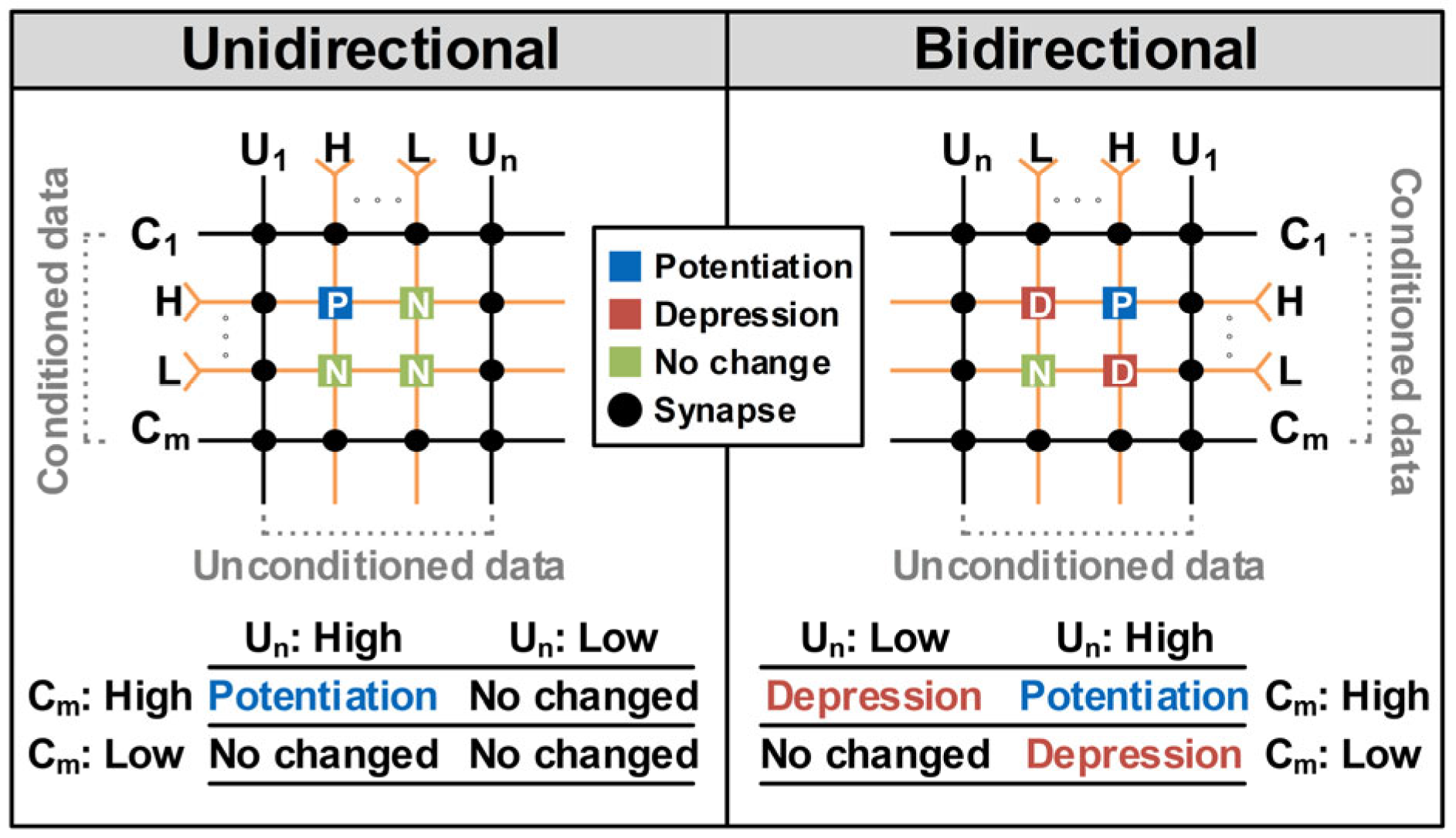
2.1. Mechanisms for Associative Learning Implementation
2.2. Python-Based Verification of Bidirectional Mechanism in Diverse Synaptic Environments
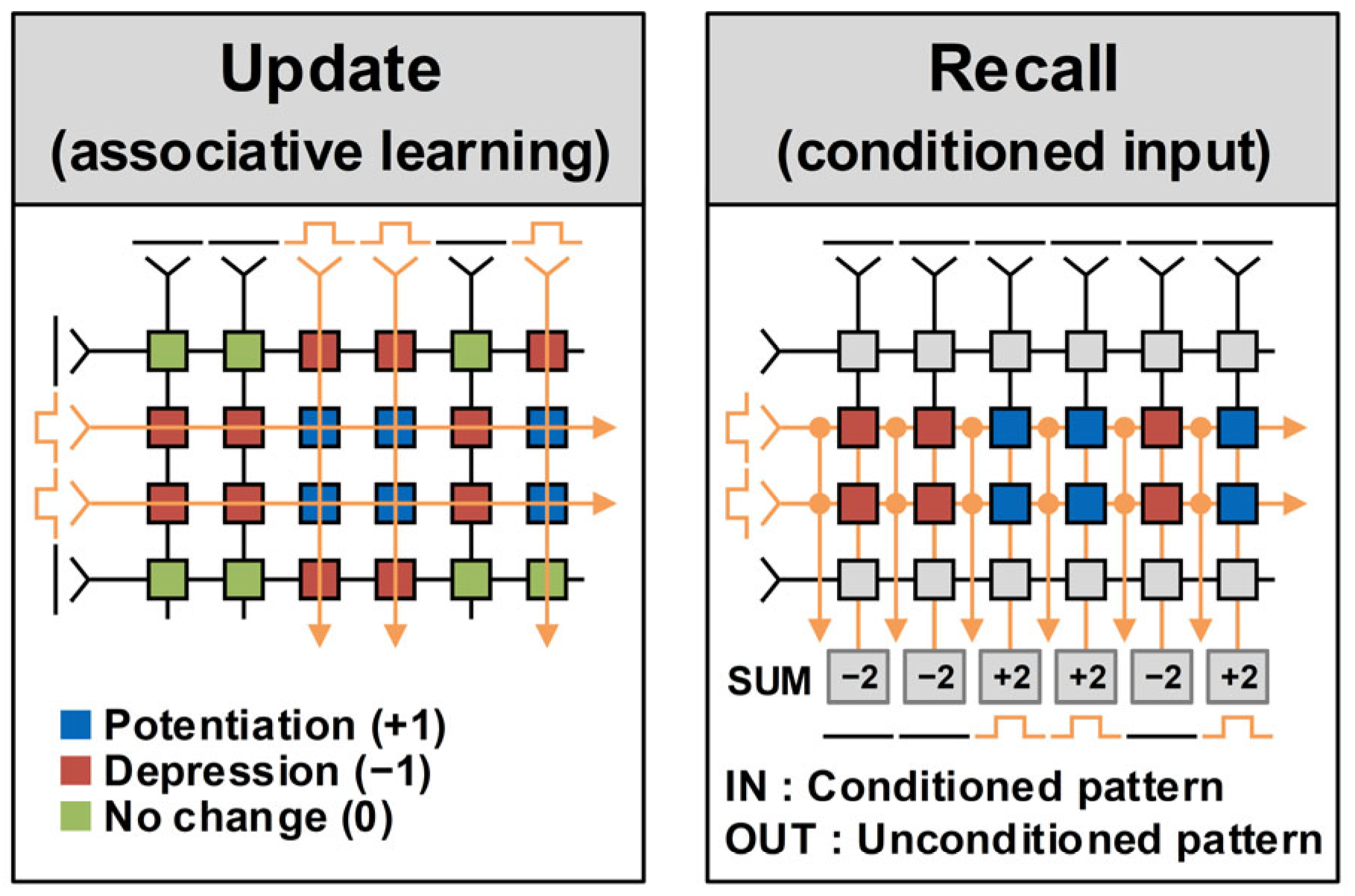
2.3. System Implementation of Pattern-Associative Learning
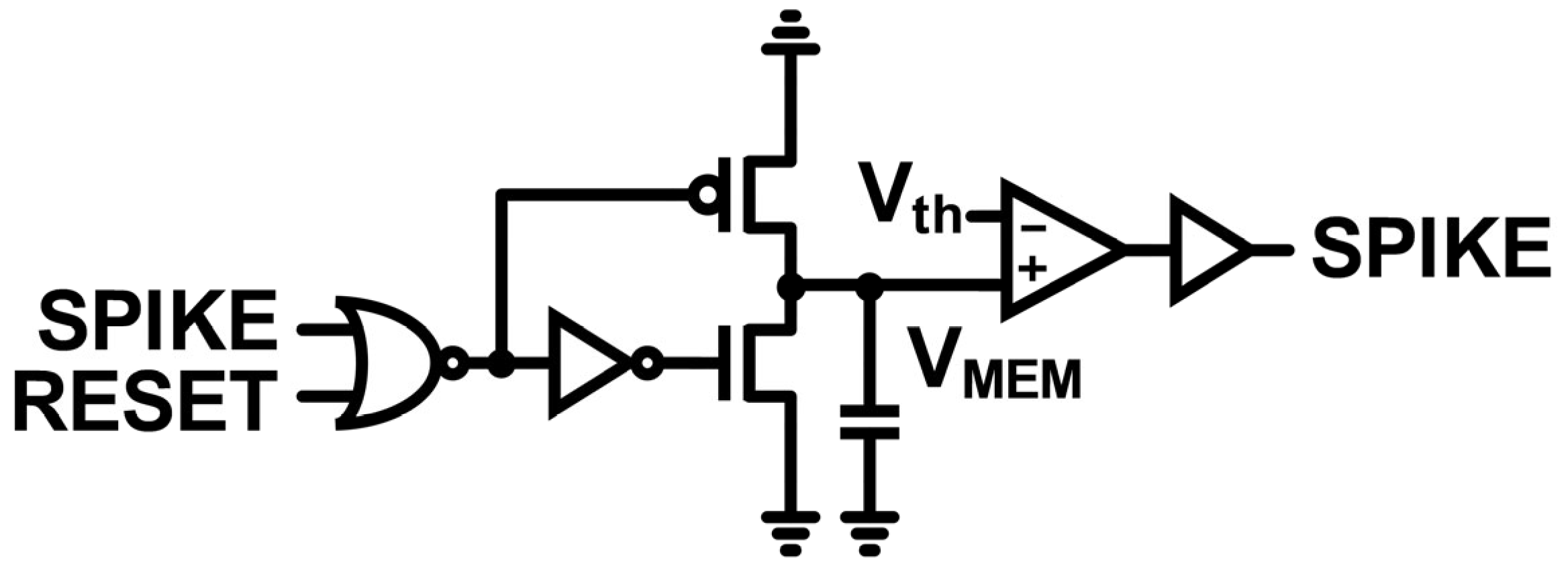
2.4. Implementation of Synapse and Neuron for Associative Learning
3. Results and Discussion
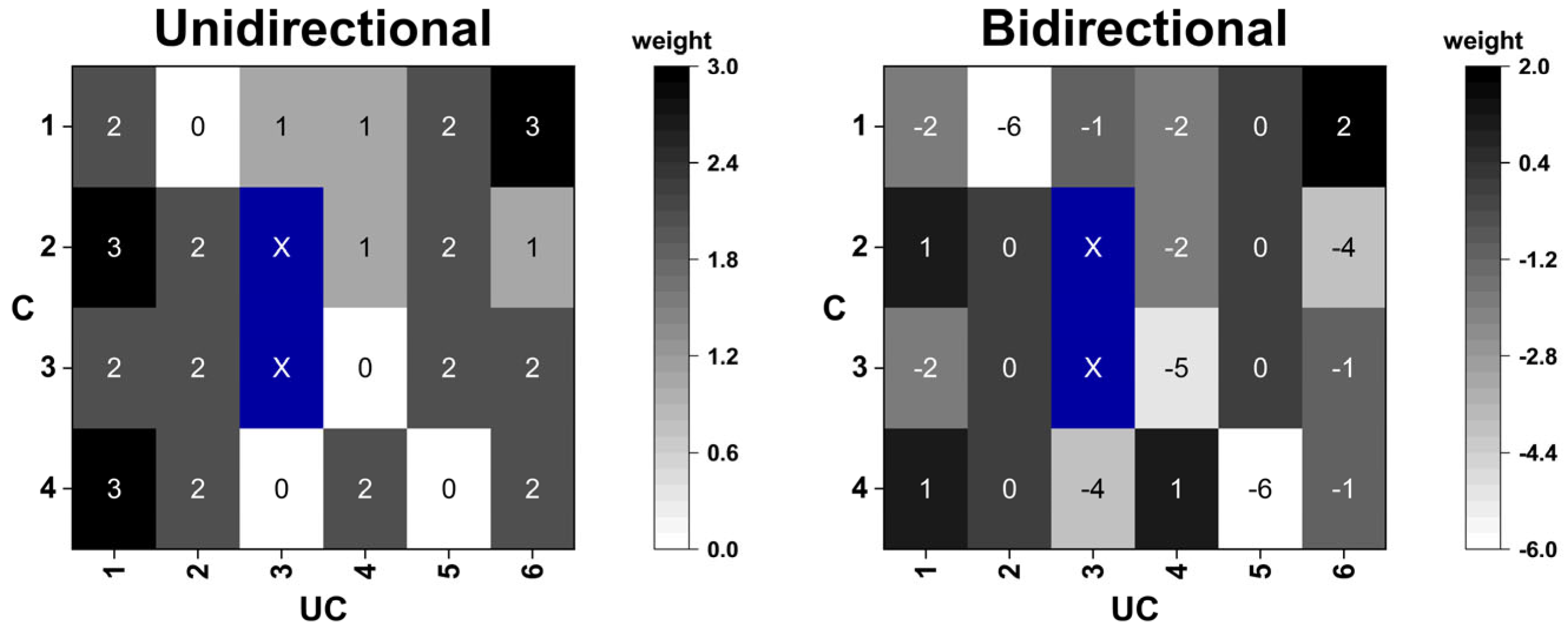
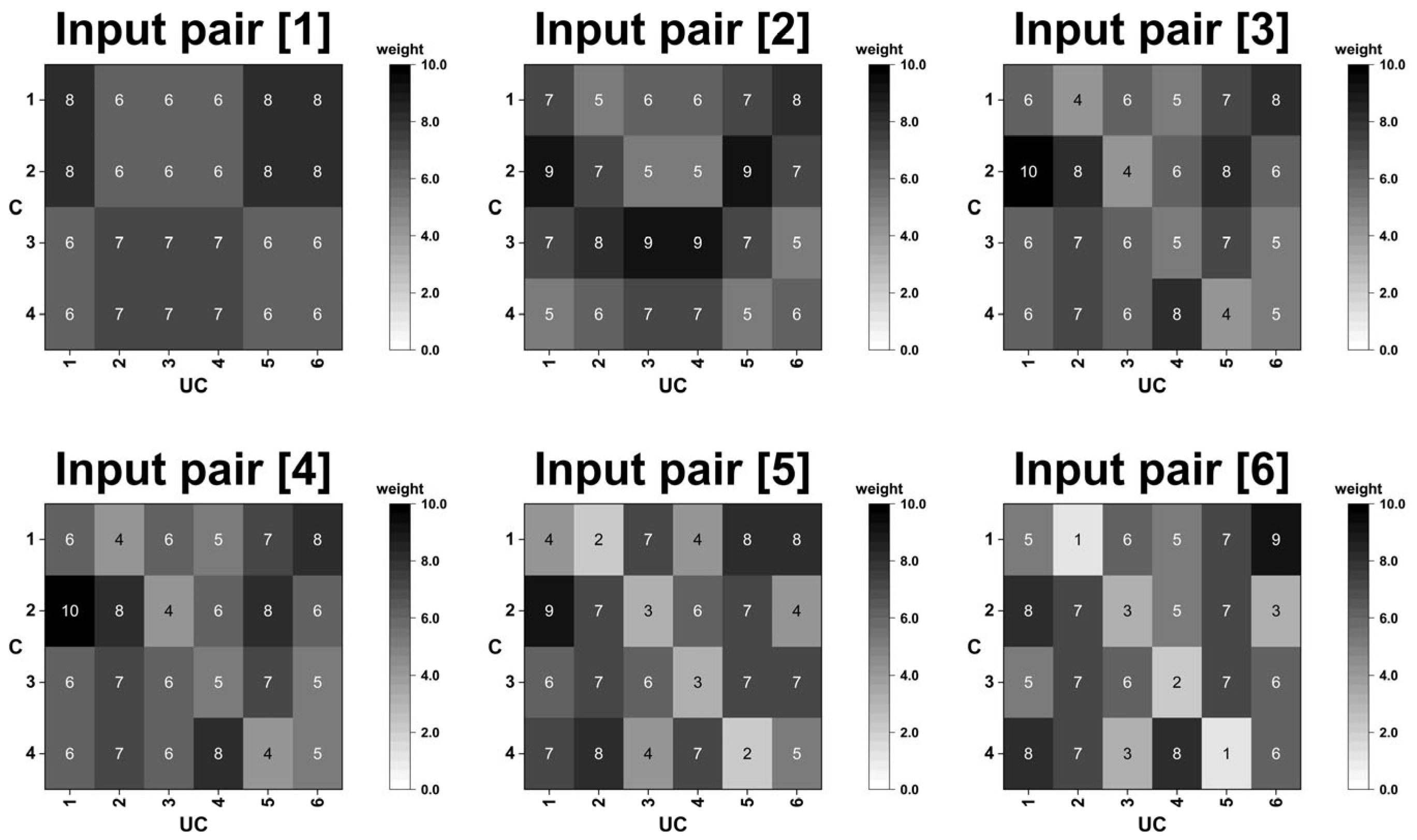
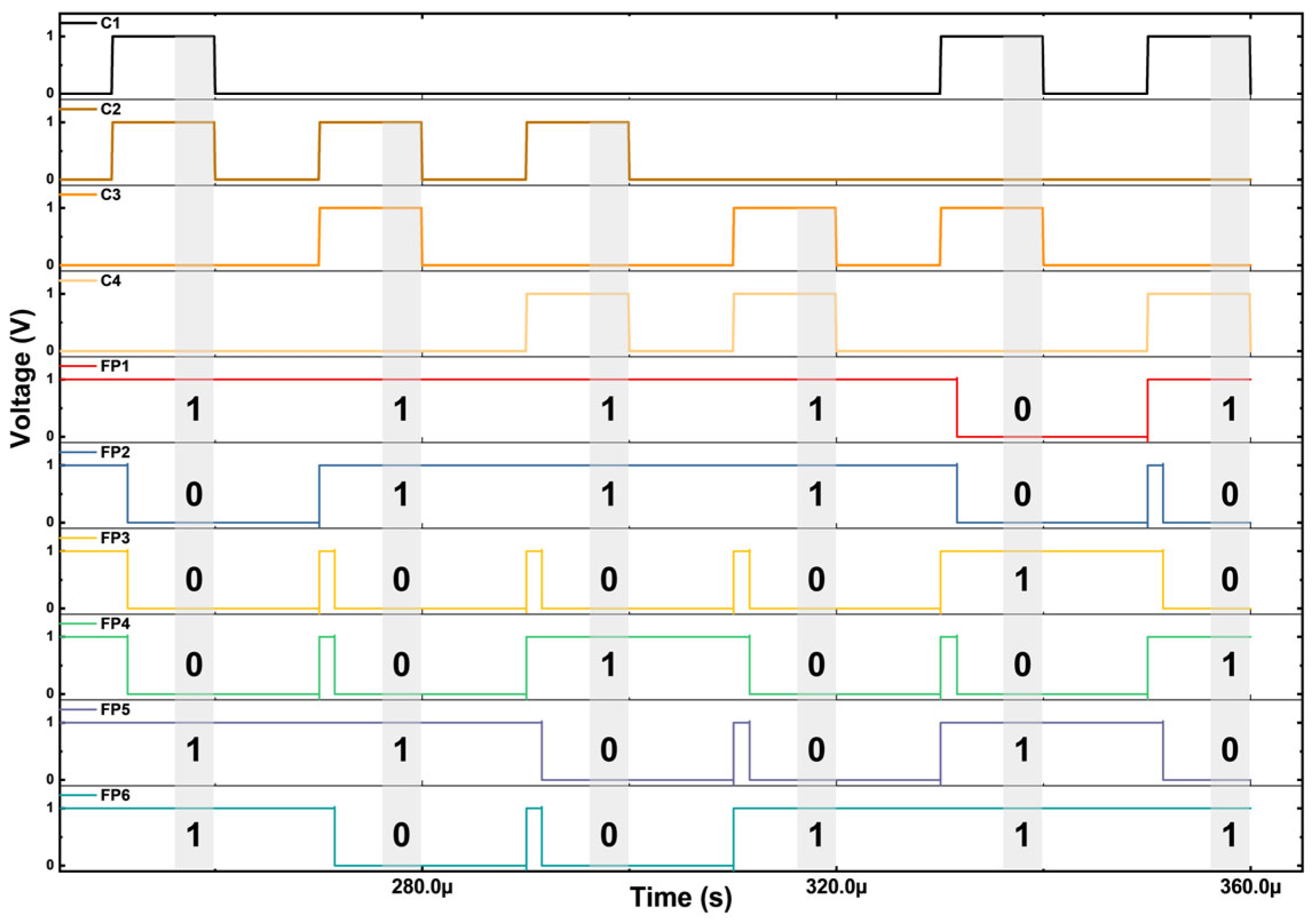
3.1. Cadence Simulation Results of Overall System Operation Under Ideal Synapse Condition
3.2. System Operation Under Conditions of Synapse Loss and Noisy Synaptic Weight States
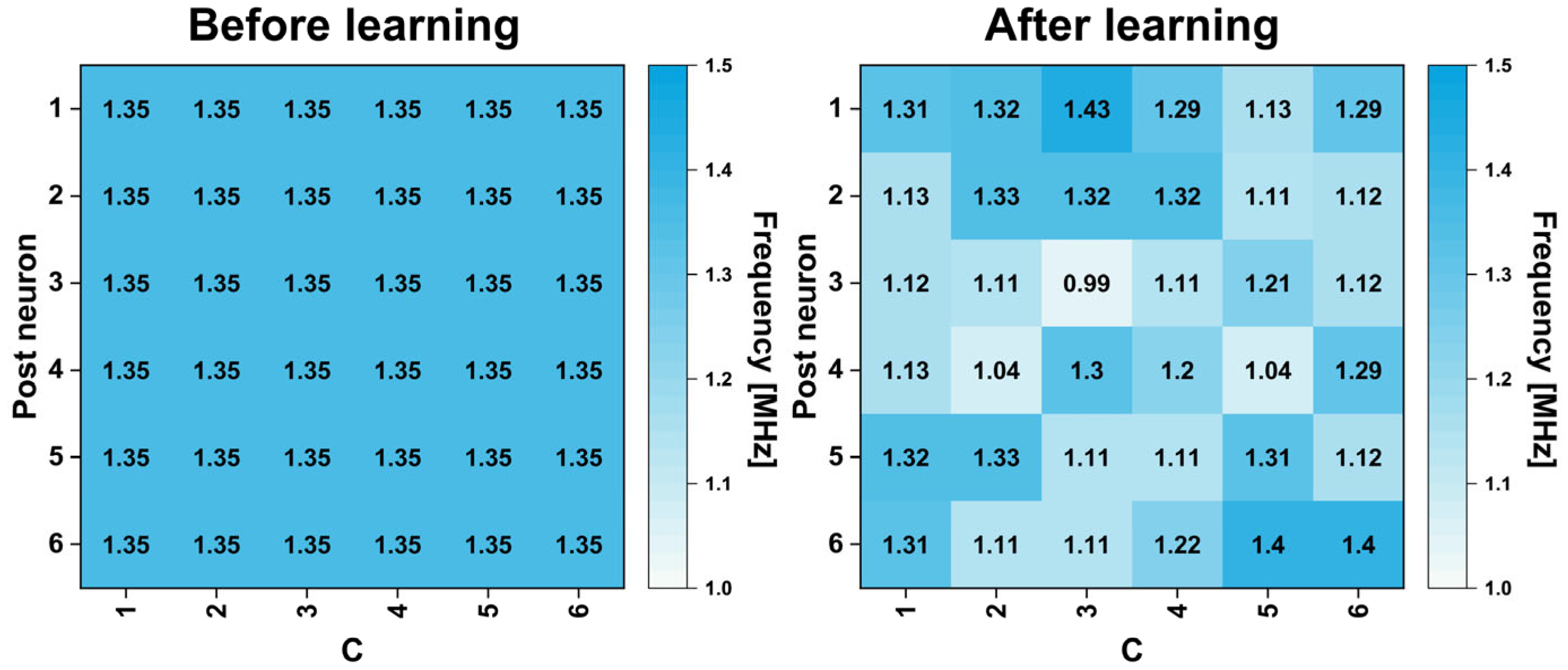
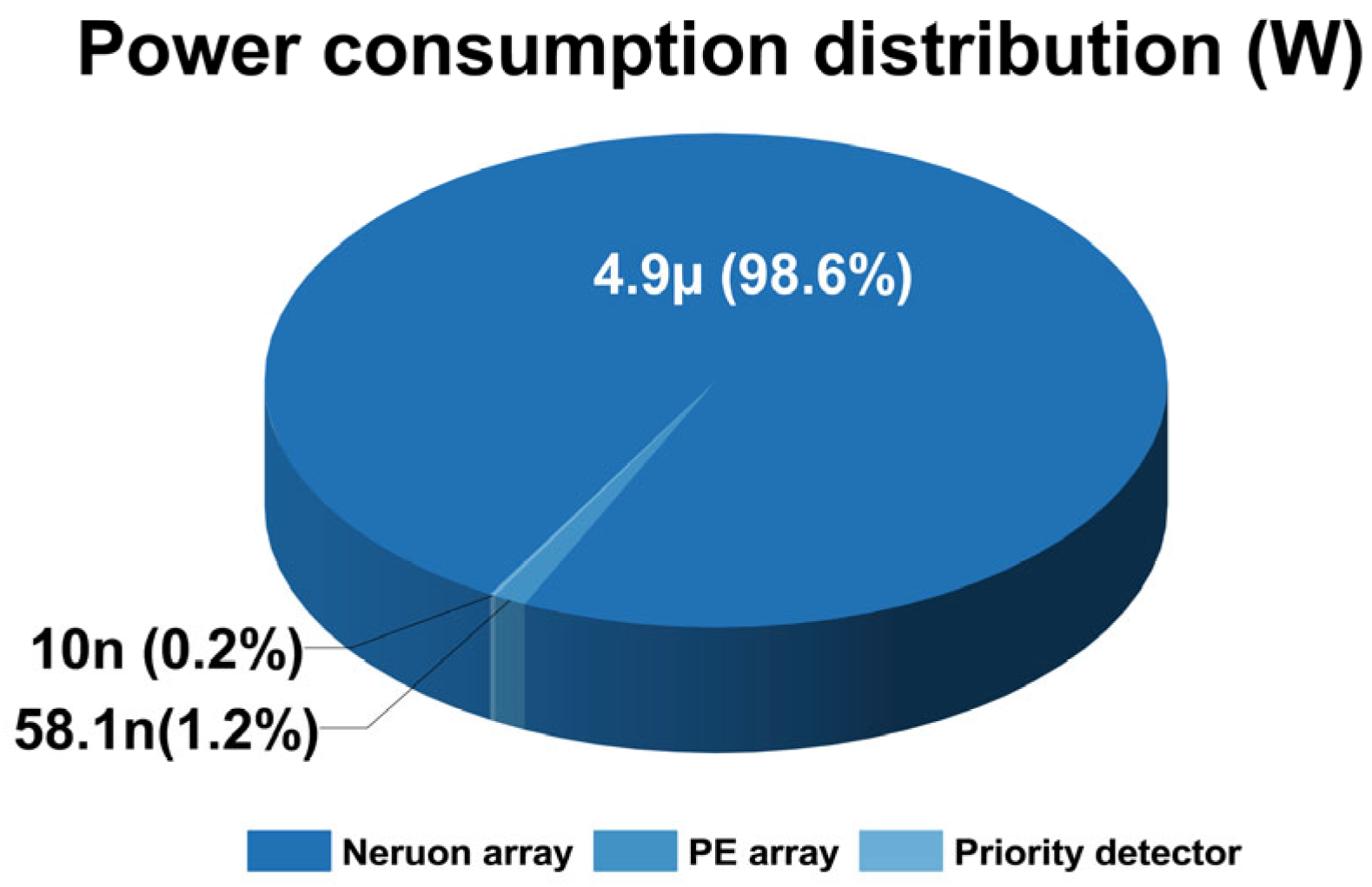
3.3. Measured Power of Proposed Associative Learning System
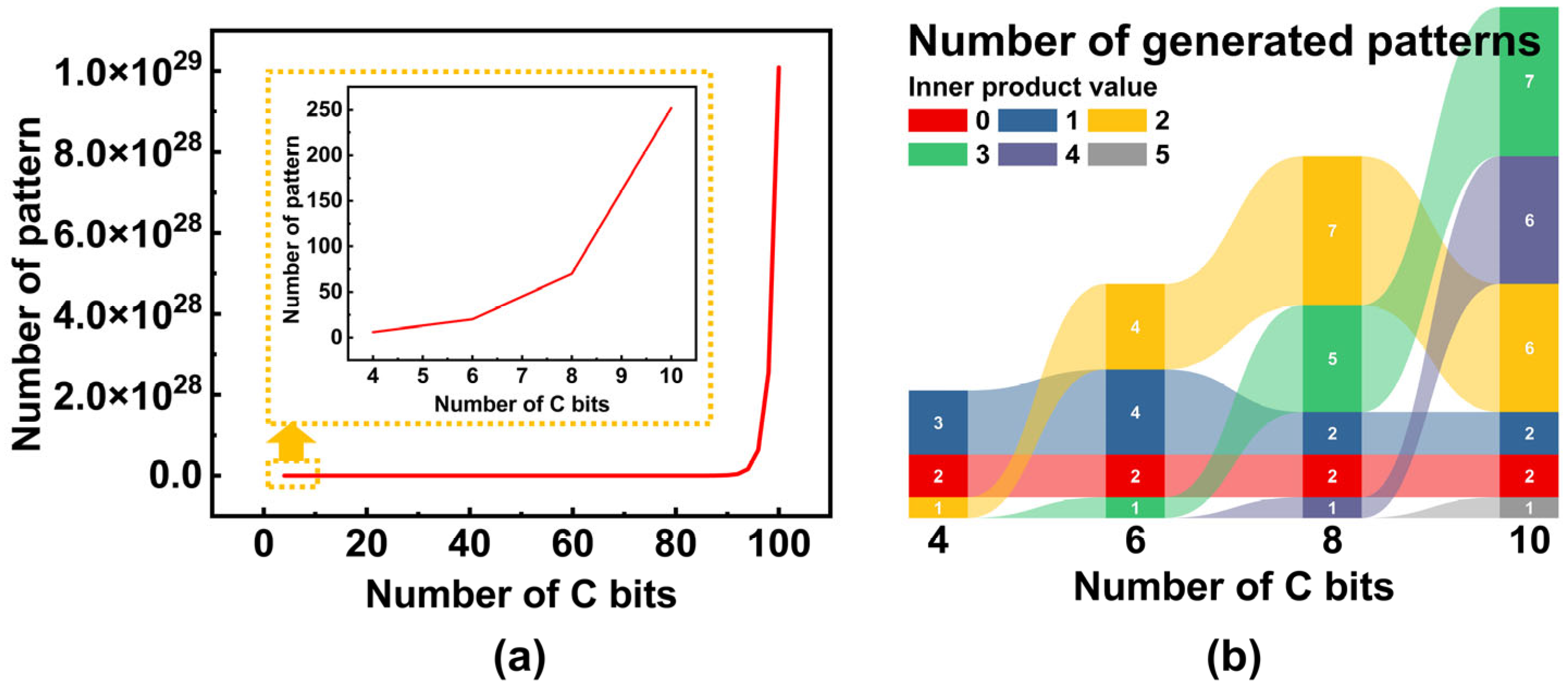
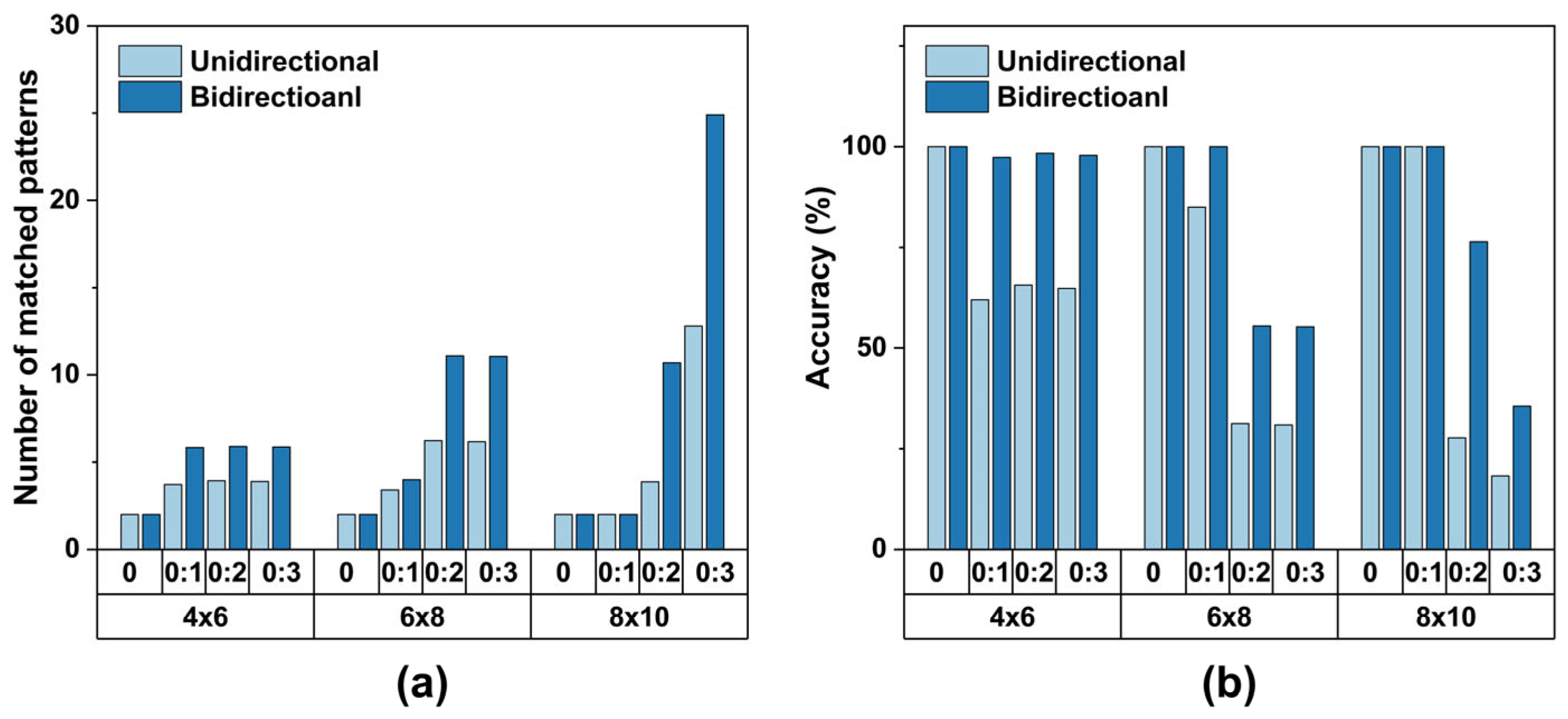
3.4. Examination of Memory Capacity and Recall Accuracy Under Array Scaling
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BOT | Bottom node of synapses |
| C | Conditioned |
| ERR | Error rate |
| PE | Processing element |
| RI | Relative improvement |
| SNN | Spiking neural network |
| T3H1 | Top 3 hot code |
| TOP | Top node of synapses |
| UC | Unconditioned |
References
- Takehara-Nishiuchi, K. Neuronal ensemble dynamics in associative learning. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2022, 73, 102530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.M.; Bouton, M.E. Theories of associative learning in animals. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2001, 52, 111–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zeng, Z.; Wen, S. A full-function Pavlov associative memory implementation with memristance changing circuit. Neurocomputing 2018, 272, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X. A Novel Memristor-Based Circuit Implementation of Full-Function Pavlov Associative Memory Accorded With Biological Feature. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2018, 65, 2210–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhao, K.; Dou, G. An associative memory circuit based on physical memristors. Neurocomputing 2022, 472, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, M.; Martin-Martinez, J.; Rodriguez, R.; Gonzalez, M.B.; Campabadal, F.; Nafria, M. An unsupervised and probabilistic approach to Pavlov’s dog experiment with OxRAM devices. Microelectron. Eng. 2019, 215, 111024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Han, J.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y. Memristor-based neural network circuit of pavlov associative memory with dual mode switching. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2021, 129, 153552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansvelder, H.D.; Verhoog, M.B.; Goriounova, N.A. Synaptic plasticity in human cortical circuits: Cellular mechanisms of learning and memory in the human brain? Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2019, 54, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, M.B. Synaptic Signaling in Learning and Memory. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 8, a016824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolibius, L.D.; Roux, F.; Parish, G.; Ter Wal, M.; Van Der Plas, M.; Chelvarajah, R.; Sawlani, V.; Rollings, D.T.; Lang, J.D.; Gollwitzer, S.; et al. Hippocampal neurons code individual episodic memories in humans. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2023, 7, 1968–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Wang, C.; Lin, H.; Sun, Y. A Memristive Spiking Neural Network Circuit with Selective Supervised Attention Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2023, 42, 2604–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, J.J.; Zhou, J.T.; Hu, S.G.; Yu, Q.; Chen, T.P.; Liu, Y. An Area- and Energy-Efficient Spiking Neural Network With Spike-Time-Dependent Plasticity Realized with SRAM Processing-in-Memory Macro and On-Chip Unsupervised Learning. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2023, 17, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, N.; Chakraborty, I.; Kosta, A.; Sengupta, A.; Ankit, A.; Panda, P.; Roy, K. Exploring Neuromorphic Computing Based on Spiking Neural Networks: Algorithms to Hardware. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 55, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanojevic, A.; Woźniak, S.; Bellec, G.; Cherubini, G.; Pantazi, A.; Gerstner, W. High-performance deep spiking neural networks with 0.3 spikes per neuron. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Lei, T.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Wong, M. Spiking Neural Network Based on Memory Capacitors and Metal-Oxide Thin-Film Transistors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2024, 71, 3965–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolls, E. Brain Computations and Connectivity; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, W.C.; Bliss, T.V.P.; Collingridge, G.L.; Morris, R.G.M. Long-term potentiation: 50 years on: Past, present and future. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2024, 379, 20230218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadiyal, K.; Ganesan, R.; Rastogi, A.; Thamankar, R. Bio-inspired artificial synapse for neuromorphic computing based on NiO nanoparticle thin film. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Abbas, H.; Choi, C.; Kim, S. Controllable analog resistive switching and synaptic characteristics in ZrO2/ZTO bilayer memristive device for neuromorphic systems. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 529, 147107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caya-Bissonnette, L.; Béïque, J.C. Half a century legacy of long-term potentiation. Curr. Biol. 2024, 34, R640–R662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayal, G.; Jinesh, K. Linear Weight Update and Large Synaptic Responses in Neuromorphic Devices Comprising Pulsed-Laser-Deposited BiFeO3. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2022, 4, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEliece, R.; Posner, E.; Rodemich, E.; Venkatesh, S. The capacity of the Hopfield associative memory. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1987, 33, 461–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treves, A.; Rolls, E. What determines the capacity of autoassociative memories in the brain? Netw. Comput. Neural Syst. 2009, 2, 371–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winocur, G.; Black, A.H. Cue-induced recall of a passive avoidance response by rats with hippocampal lesions. Physiol. Behav. 1978, 21, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusakov, D.A.; Savtchenko, L.P.; Latham, P.E. Noisy Synaptic Conductance: Bug or a Feature? Trends Neurosci. 2020, 43, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowsky, J.L.; Melnikova, T.; Fadale, D.J.; Xu, G.M.; Slunt, H.H.; Gonzales, V.; Younkin, L.H.; Younkin, S.G.; Borchelt, D.R.; Savonenko, A.V. Environmental enrichment mitigates cognitive deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 5217–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzioras, M.; McGeachan, R.I.; Durrant, C.S.; Spires-Jones, T.L. Synaptic degeneration in Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2023, 19, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuman, C.D.; Mitchell, J.P.; Johnston, J.T.; Parsa, M.; Kay, B.; Date, P.; Patton, R.M. Resilience and Robustness of Spiking Neural Networks for Neuromorphic Systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Glasgow, UK, 19–24 July 2020; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, D.E. The Spike-Timing Dependence of Plasticity. Neuron 2012, 75, 556–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvatinsky, S.; Talisveyberg, K.; Fliter, D.; Kolodny, A.; Weiser, U.C.; Friedman, E.G. Models of memristors for SPICE simulations. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 27th Convention of Electrical and Electronics Engineers in Israel, Eilat, Israel, 14–17 November 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Biolek, Z.; Biolek, D.; Biolková, V. SPICE Model of Memristor with Nonlinear Dopant Drift. Radioengineering 2009, 18, 210–214. [Google Scholar]
- Kvatinsky, S.; Ramadan, M.; Friedman, E.G.; Kolodny, A. VTEAM: A General Model for Voltage-Controlled Memristors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2015, 62, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvatinsky, S.; Friedman, E.G.; Kolodny, A.; Weiser, U.C. TEAM: ThrEshold Adaptive Memristor Model. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2013, 60, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Mathew, J.; Shafik, R.A.; Pradhan, D.K. Verilog-A Based Effective Complementary Resistive Switch Model for Simulations and Analysis. IEEE Embed. Syst. Lett. 2014, 6, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Abbas, Y.; Jeon, Y.R.; Sokolov, A.S.; Ku, B.; Choi, C. Engineering synaptic characteristics of TaOx/HfO2 bi-layered resistive switching device. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 415204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, S.; Simanjuntak, F.M.; Panda, D.; Tseng, T.Y. Enhanced Synaptic Linearity in ZnO-Based Invisible Memristive Synapse by Introducing Double Pulsing Scheme. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2019, 66, 4722–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folowosele, F.; Etienne-Cummings, R.; Hamilton, T.J. A CMOS switched capacitor implementation of the Mihalas-Niebur neuron. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference, Beijing, China, 26–28 November 2009; pp. 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Folowosele, F.; Hamilton, T.J.; Etienne-Cummings, R. Silicon modeling of the Mihalaş-Niebur neuron. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2011, 22, 1915–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriya, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Ono, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Yuminaka, Y.; Horio, Y.; Madrenas, J.; Sato, S. Analog VLSI Implementation of Subthreshold Spiking Neural Networks and Its Application to Reservoir Computing. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2025, 72, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuppunuthala, S.; Pasupureddi, V. 3.6-pJ/Spike, 30-Hz Silicon Neuron Circuit in 0.5-V, 65 nm CMOS for Spiking Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2023, 71, 2906–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Saxena, V.; Zhu, K.; Balagopal, S. A CMOS Spiking Neuron for Brain-Inspired Neural Networks With Resistive Synapses and In Situ Learning. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2015, 62, 1088–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, S.; Serb, A.; Prodromakis, T. Low-voltage programming of RRAM-based crossbar arrays using MOS parasitic diodes. Front. Nanotechnol. 2025, 7, 1587700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-S.; Kwon, D.-Y.; Choi, B.-D. High-Accuracy, Compact Scanning Method and Circuit for Resistive Sensor Arrays. Sensors 2016, 16, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Holleman, J.; Otis, B.P. Design of Ultra-Low Power Biopotential Amplifiers for Biosignal Acquisition Applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2012, 6, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, C.; Camuñas-Mesa, L.A.; Rosa, J.M.D.L.; Vianello, E.; Serrano-Gotarredona, T.; Linares-Barranco, B. Neuromorphic Low-Power Inference on Memristive Crossbars With On-Chip Offset Calibration. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 38043–38061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Choi, W.Y. Ultra-Low Static Power Circuits Addressing the Fan-Out Problem of Analog Neuron Circuits in Spiking Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 5248–5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



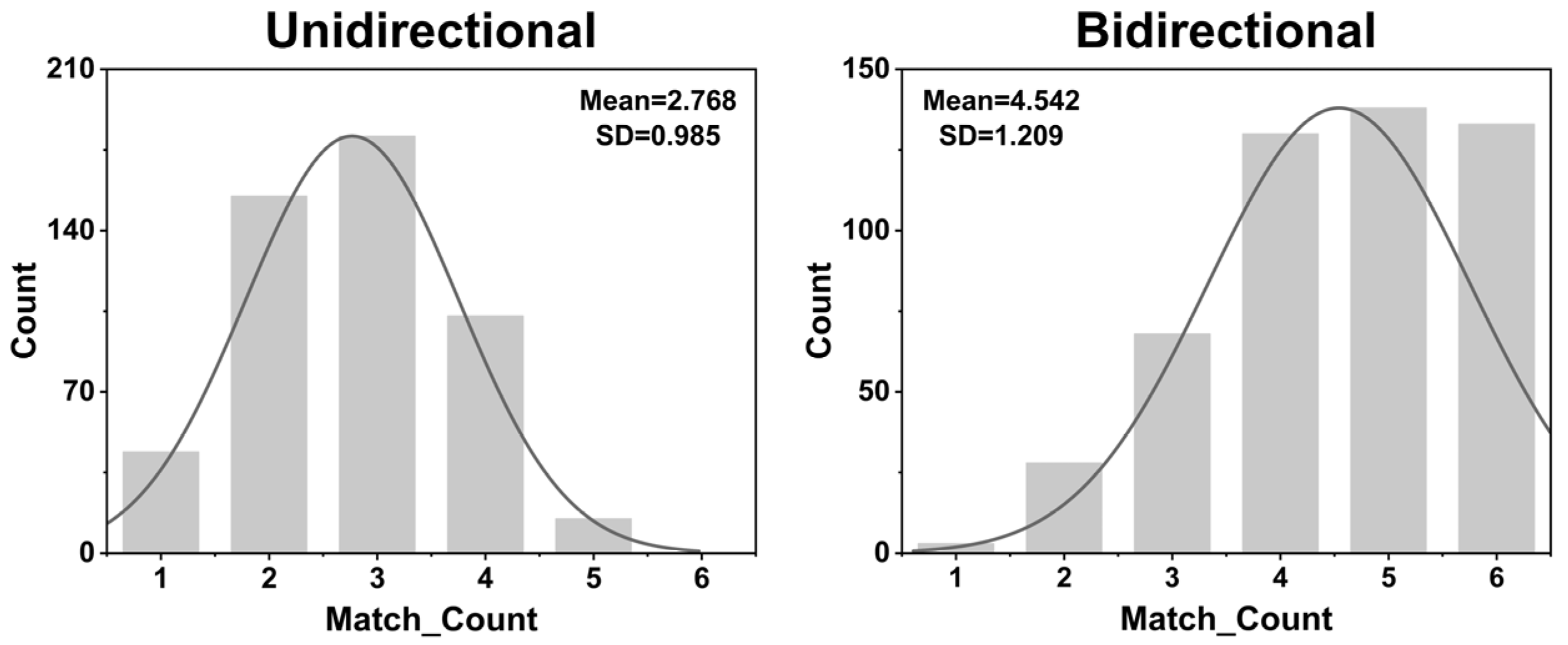

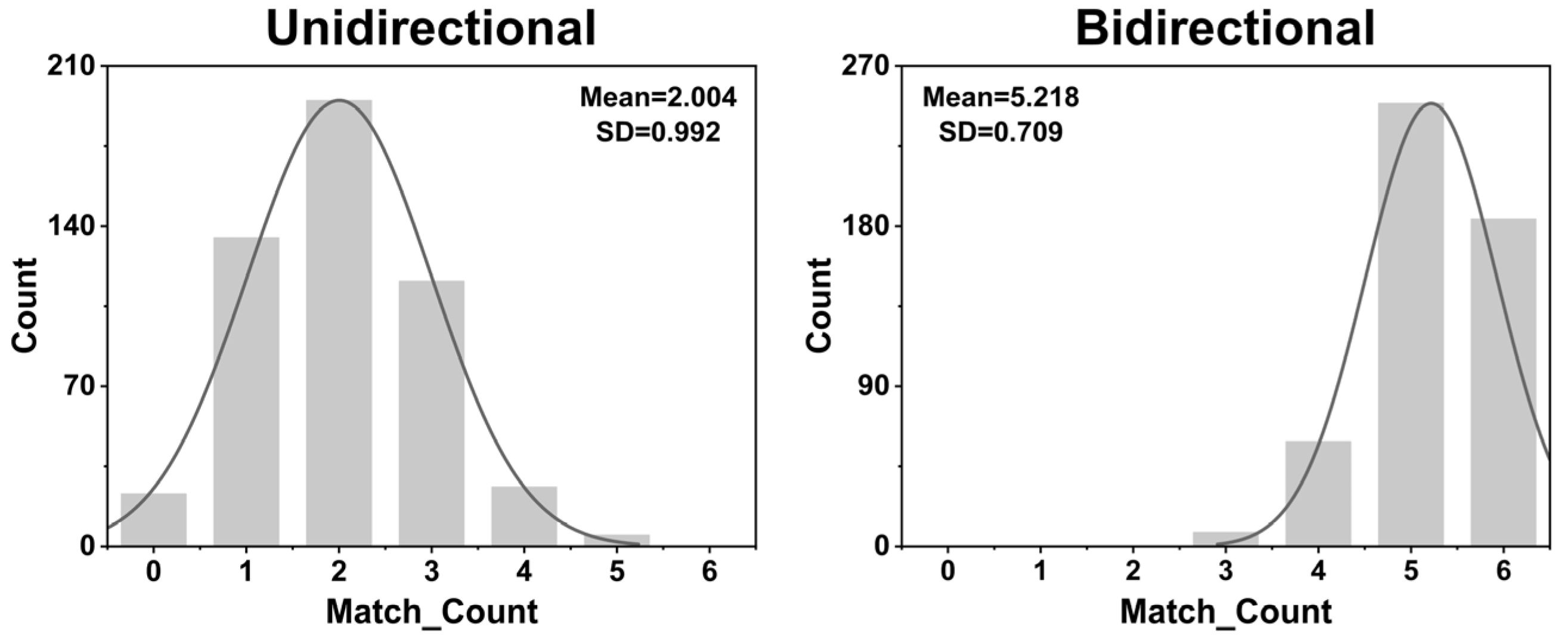
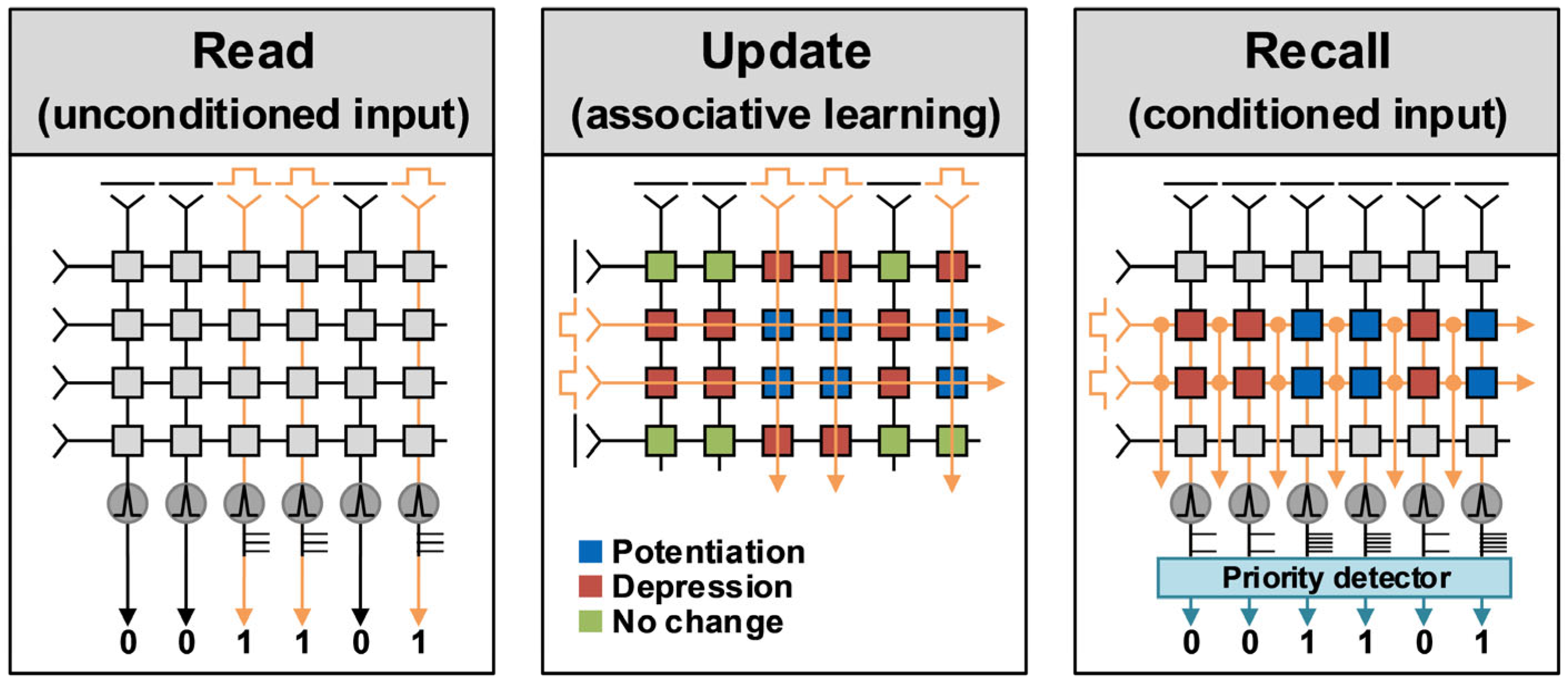


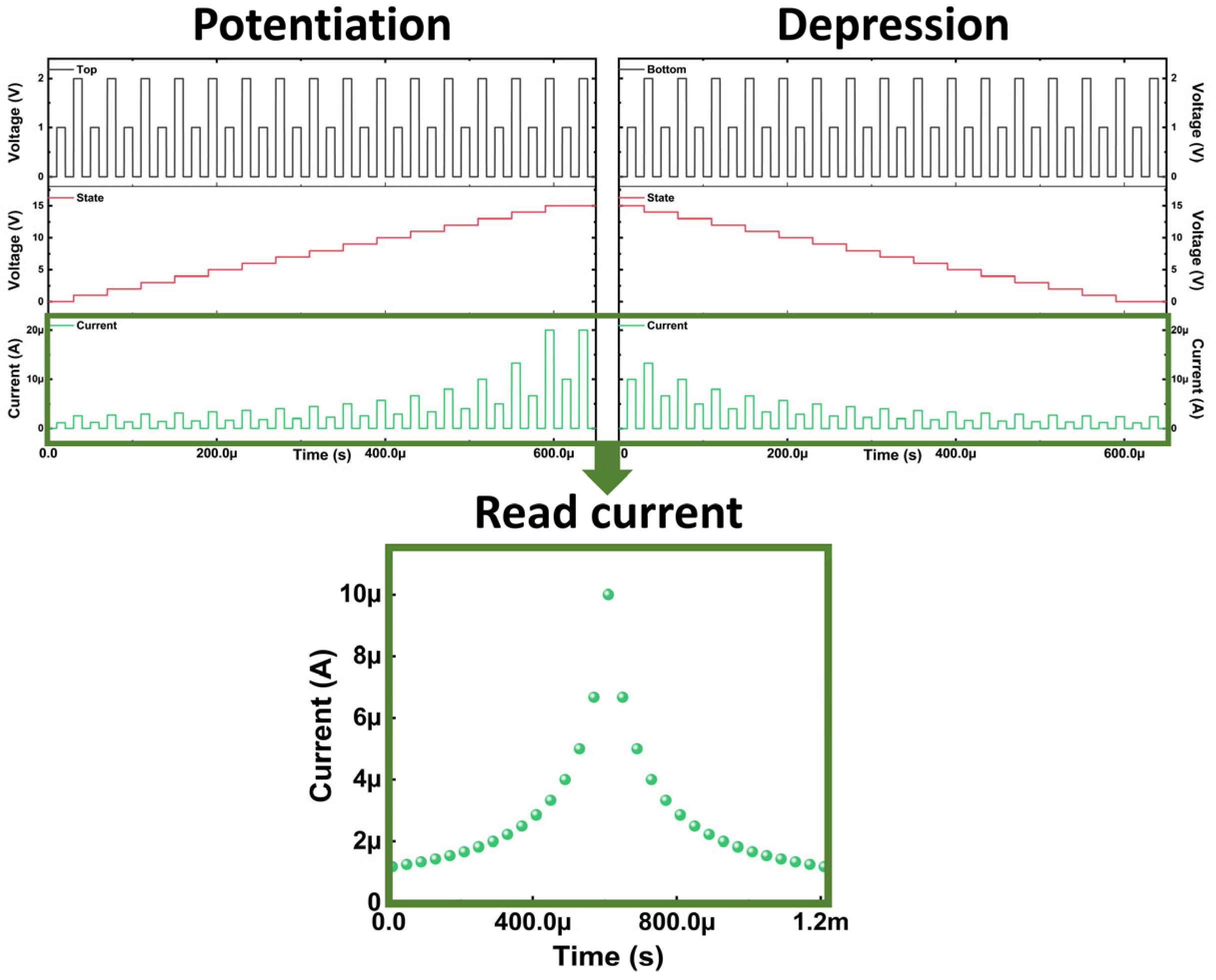




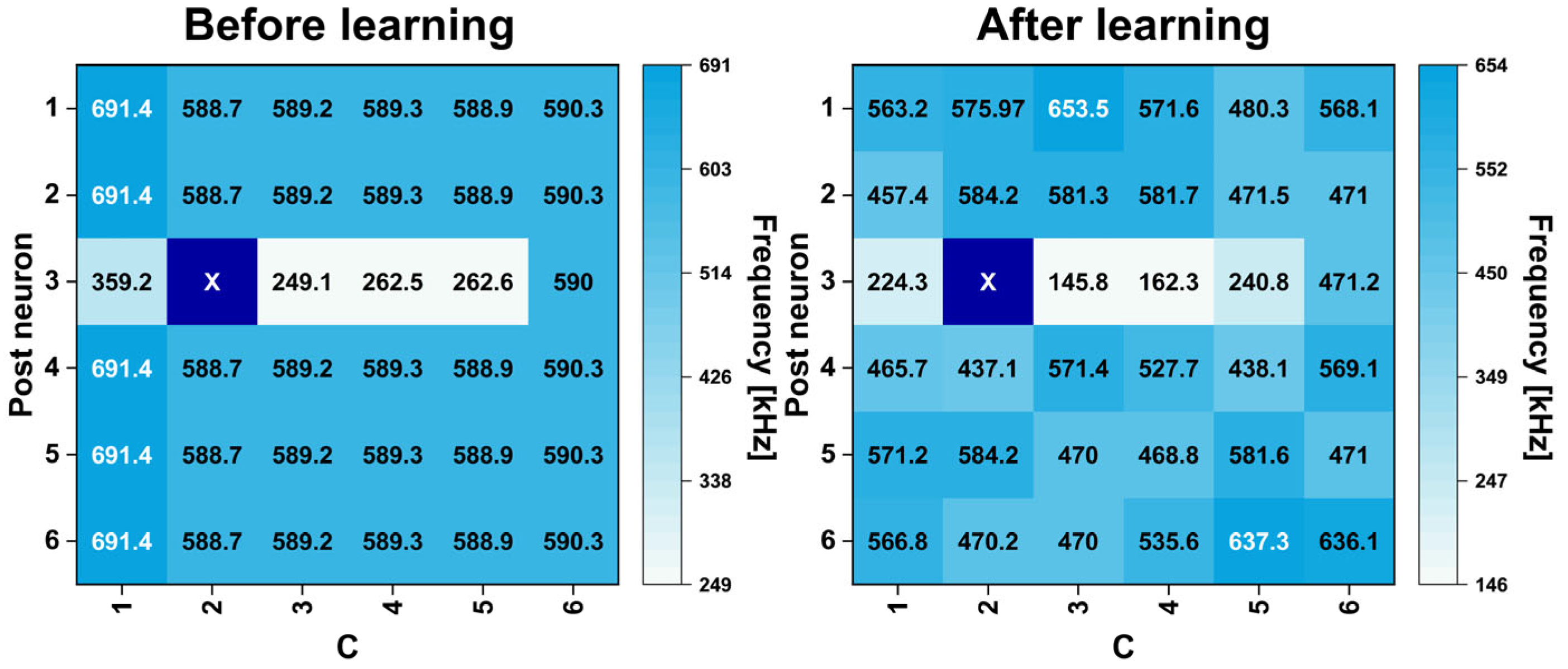
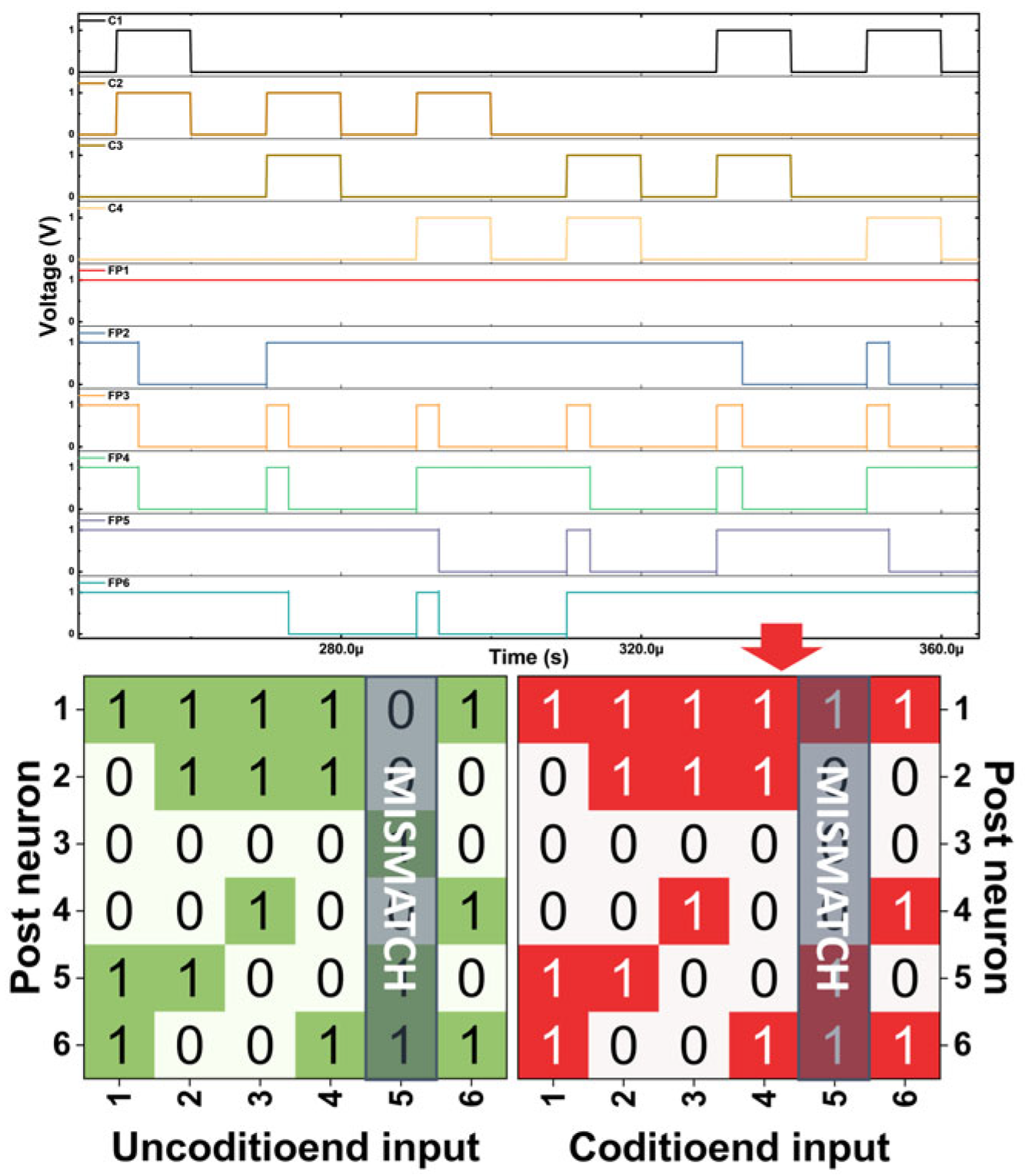
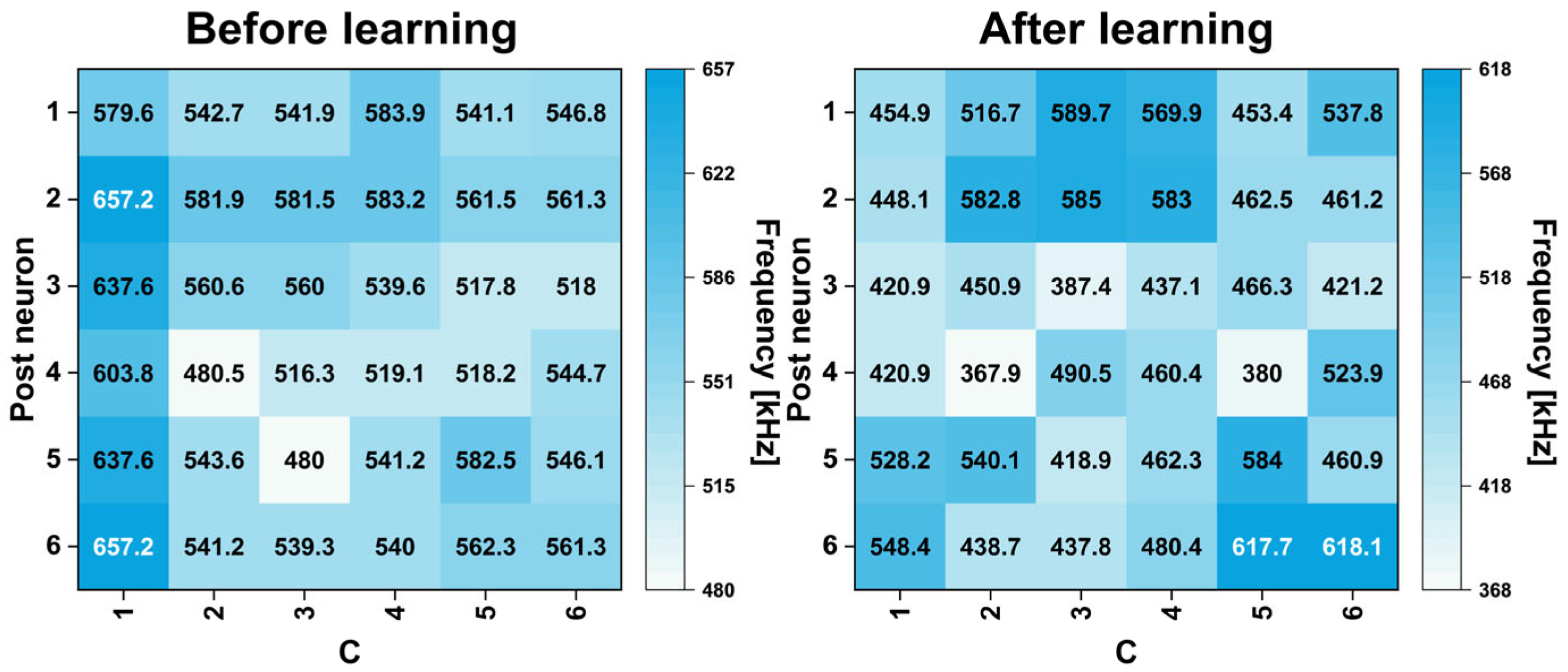




| Input | UC (Unconditioned) | C (Conditioned) |
|---|---|---|
| [LSB]–[MSB] | [LSB]–[MSB] | |
| {1} | 1 0 0 0 1 1 | 1 1 0 0 |
| {2} | 1 1 0 0 1 0 | 0 1 1 0 |
| {3} | 1 1 0 1 0 0 | 0 1 0 1 |
| {4} | 1 1 0 0 0 1 | 0 0 1 1 |
| {5} | 0 0 1 0 1 1 | 1 0 1 0 |
| {6} | 1 0 0 1 0 1 | 1 0 0 1 |
| In | Data | Unidirectional | Hit | Bidirectional | Hit | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C {1} | SUM | 5 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 4 | ✓ (1) | −1 | −6 | −5 | −4 | 0 | −2 | ✓ |
| T3H1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |||
| C {2} | SUM | 5 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 3 | ✓ | −1 | 0 | −5 | −7 | 0 | −5 | ✓ |
| T3H1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |||
| C {3} | SUM | 6 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 3 | ✕ (2) | 2 | 0 | −8 | −1 | −6 | −5 | ✓ |
| T3H1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |||
| C {4} | SUM | 5 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | ✓ | −1 | 0 | −5 | −4 | −6 | −2 | ✓ |
| T3H1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |||
| C {5} | SUM | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 5 | ✕ | −4 | −6 | −2 | −7 | 0 | 1 | ✓ |
| T3H1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |||
| C {6} | SUM | 5 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 5 | ✓ | −1 | −6 | −5 | −1 | −6 | 1 | ✓ |
| T3H1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |||
| In | Data | Unidirectional | Hit | Bidirectional | Hit | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C {1} | SUM | 5 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 4 | ✓ (1) | −1 | −6 | −1 | −4 | 0 | −2 | ✕ |
| T3H1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |||
| C {2} | SUM | 5 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 3 | ✓ | −1 | 0 | 0 | −7 | 0 | −5 | ✕ |
| T3H1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |||
| C {3} | SUM | 6 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 3 | ✕ (2) | 2 | 0 | −4 | −1 | −6 | −5 | ✓ |
| T3H1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |||
| C {4} | SUM | 5 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 4 | ✓ | −1 | 0 | −4 | −4 | −6 | −2 | ✓ |
| T3H1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |||
| C {5} | SUM | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 5 | ✕ | −4 | −6 | −1 | −7 | 0 | −1 | ✓ |
| T3H1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |||
| C {6} | SUM | 5 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 5 | ✓ | −1 | −6 | −5 | −1 | −6 | −1 | ✓ |
| T3H1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |||
| In | Data | Unidirectional | Hit | Bidirectional | Hit | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C {1} | SUM | 15 | 15 | 13 | 13 | 16 | 17 | ✕ | 9 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 12 | 11 | ✓ |
| T3H1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |||
| C {2} | SUM | 17 | 18 | 14 | 11 | 16 | 15 | ✓ (1) | 11 | 14 | 8 | 3 | 12 | 7 | ✓ |
| T3H1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |||
| C {3} | SUM | 18 | 18 | 13 | 14 | 12 | 15 | ✕ (2) | 14 | 14 | 5 | 10 | 5 | 7 | ✓ |
| T3H1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |||
| C {4} | SUM | 19 | 18 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 16 | ✓ | 13 | 14 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 10 | ✓ |
| T3H1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |||
| C {5} | SUM | 16 | 15 | 13 | 12 | 18 | 18 | ✕ | 8 | 7 | 9 | 4 | 14 | 14 | ✓ |
| T3H1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |||
| C {6} | SUM | 17 | 15 | 12 | 15 | 14 | 18 | ✕ | 11 | 7 | 6 | 11 | 7 | 14 | ✓ |
| T3H1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.J.; Lee, H.-M.; Jeong, Y.; Kwak, J.Y. Spiking Neural Network-Based Bidirectional Associative Learning Circuit for Efficient Multibit Pattern Recall in Neuromorphic Systems. Electronics 2025, 14, 3971. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193971
Kim MJ, Lee H-M, Jeong Y, Kwak JY. Spiking Neural Network-Based Bidirectional Associative Learning Circuit for Efficient Multibit Pattern Recall in Neuromorphic Systems. Electronics. 2025; 14(19):3971. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193971
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Min Jee, Hyung-Min Lee, YeonJoo Jeong, and Joon Young Kwak. 2025. "Spiking Neural Network-Based Bidirectional Associative Learning Circuit for Efficient Multibit Pattern Recall in Neuromorphic Systems" Electronics 14, no. 19: 3971. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193971
APA StyleKim, M. J., Lee, H.-M., Jeong, Y., & Kwak, J. Y. (2025). Spiking Neural Network-Based Bidirectional Associative Learning Circuit for Efficient Multibit Pattern Recall in Neuromorphic Systems. Electronics, 14(19), 3971. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193971







