Oscillation Propagation Analysis of Grid-Connected Converter System with New eVSG Control Patterns
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel control strategy named eVSG is proposed. Compared to VSGs, eVSGs exhibit superior performance in both weak and strong grids, as well as in grids with low and high inertia levels.
- An MPME model for the eVSG system is proposed to analyze the motion of frequency and assess the synchronizing stability of the eVSG system from a physical perspective.
- A novel modeling method is introduced to evaluate the OP effect between P and f from a physical perspective for both VSG and eVSG systems. This method addresses the limitations of conventional approaches, which cannot effectively analyze the P-f OP effect in VSG systems.
- The effectiveness of the proposed eVSG strategy and the modeling method is thoroughly validated through simulations and experiments.
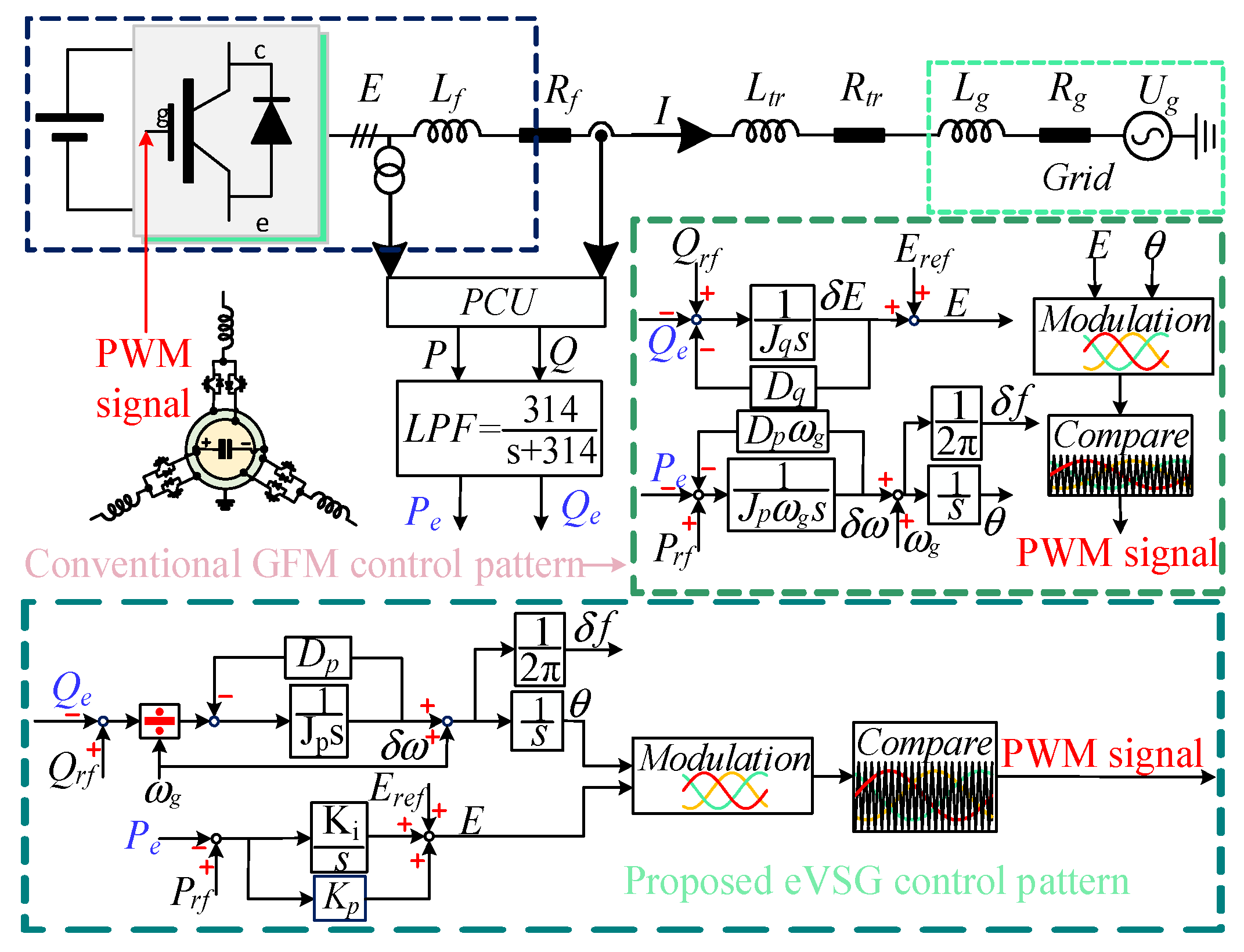
2. Modeling of Proposed Grid-Forming Pattern
2.1. Operation Principle of Proposed Grid-Forming Pattern
2.2. Proposed MPME Model for eVSGs
2.3. Case Study Based on the MPME Mode
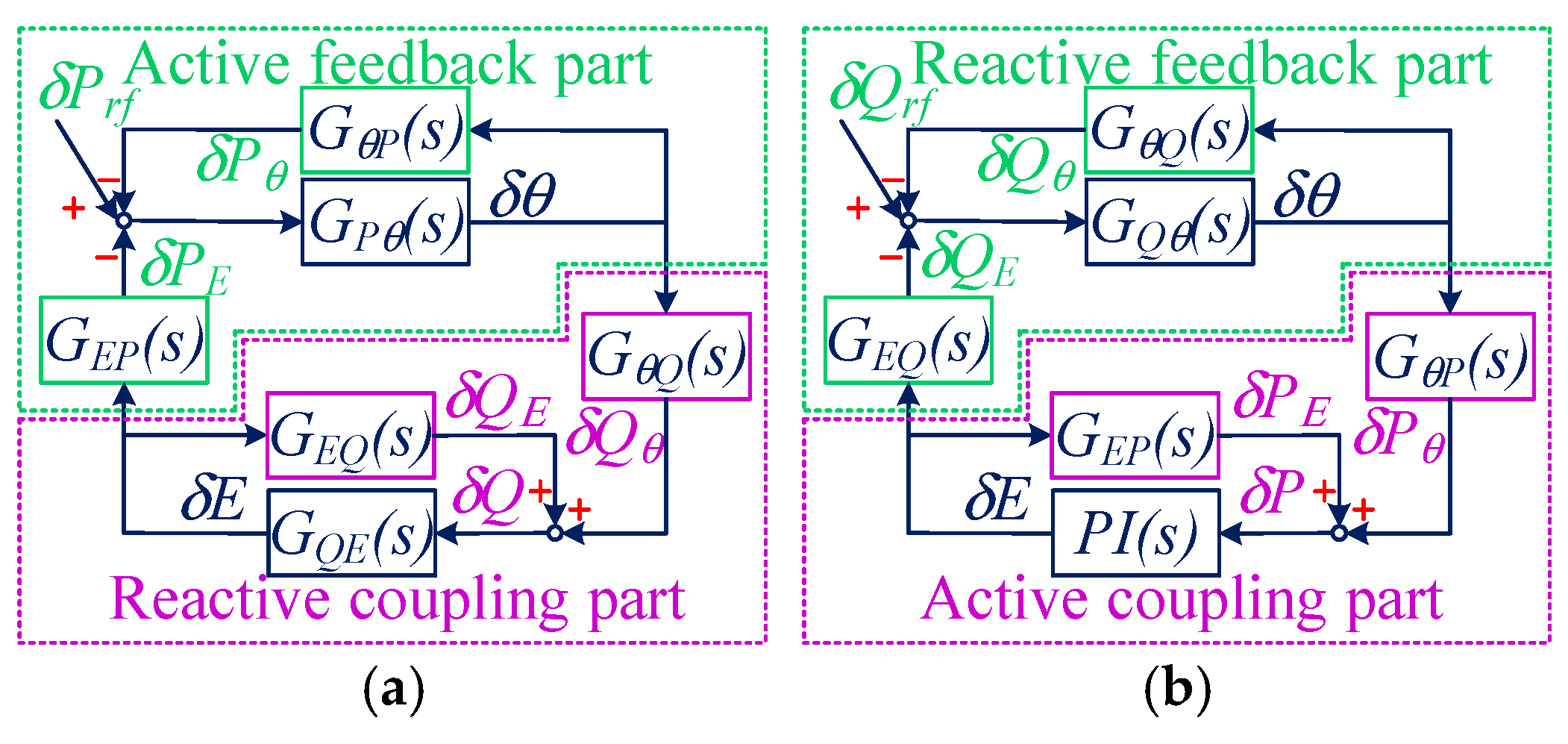
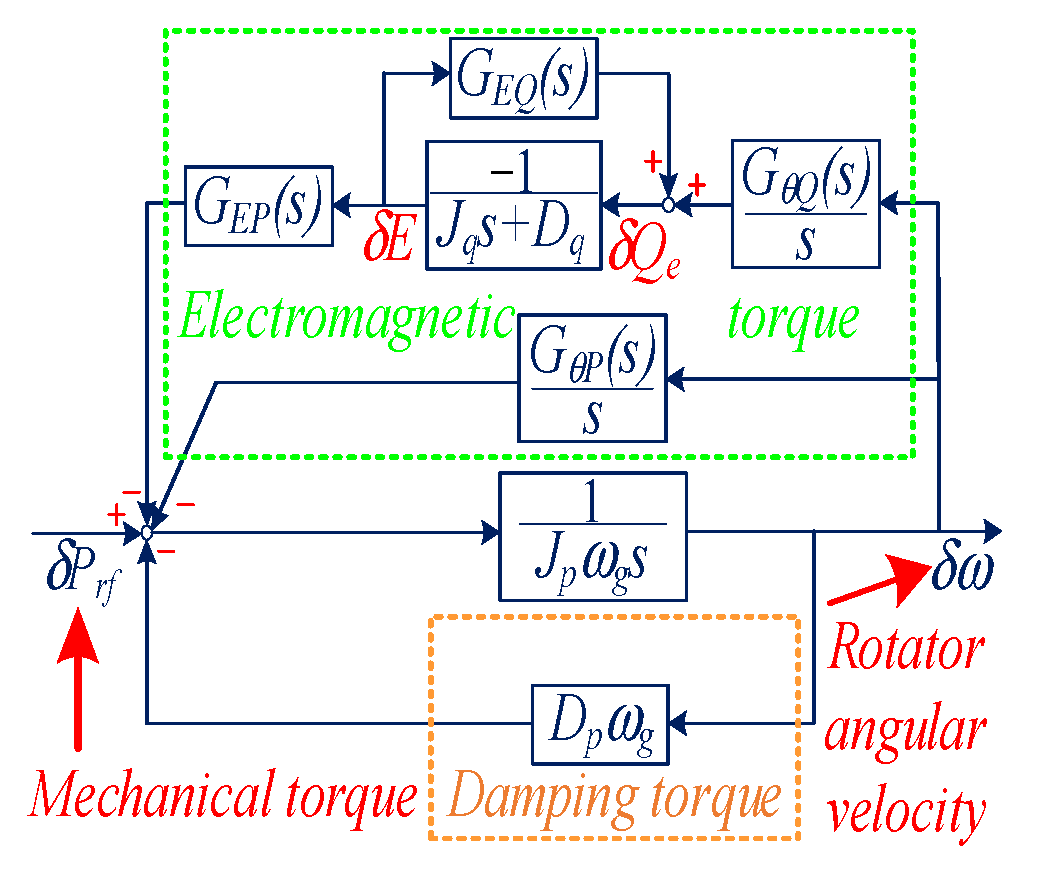
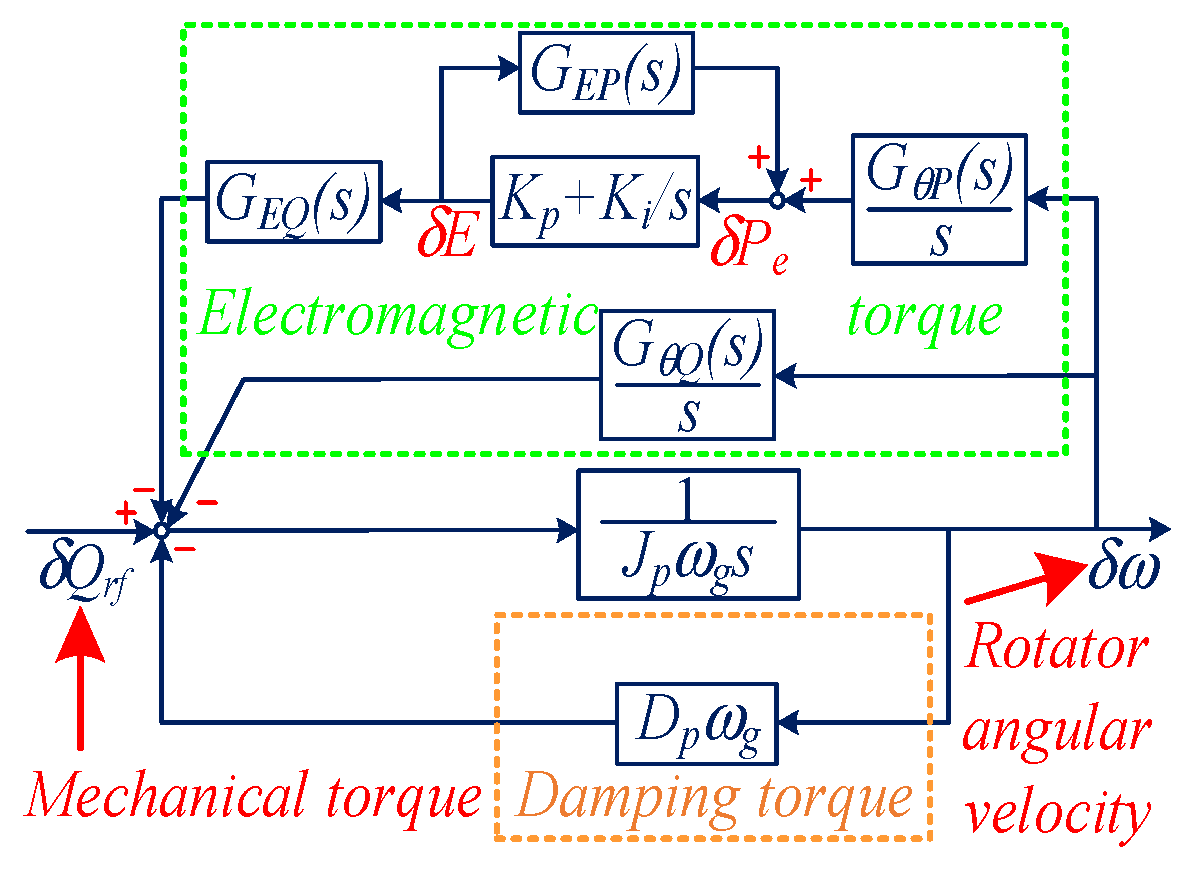
3. Oscillation Propagation Analysis for eVSG Strategy
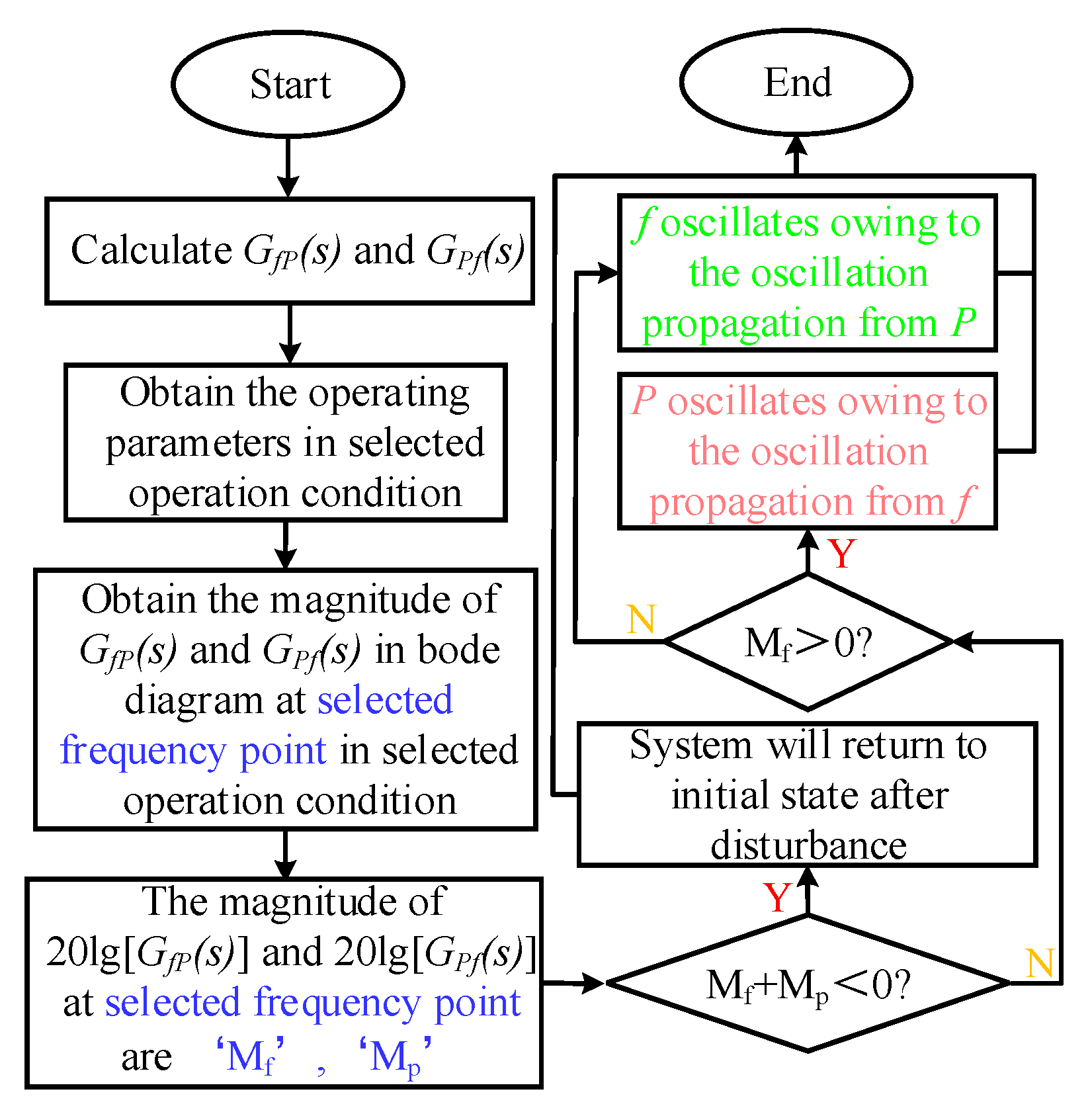
3.1. Establishment of Modeling for Oscillation Propagation
3.2. Oscillation Propagation Bewteen Frequency and Active Power
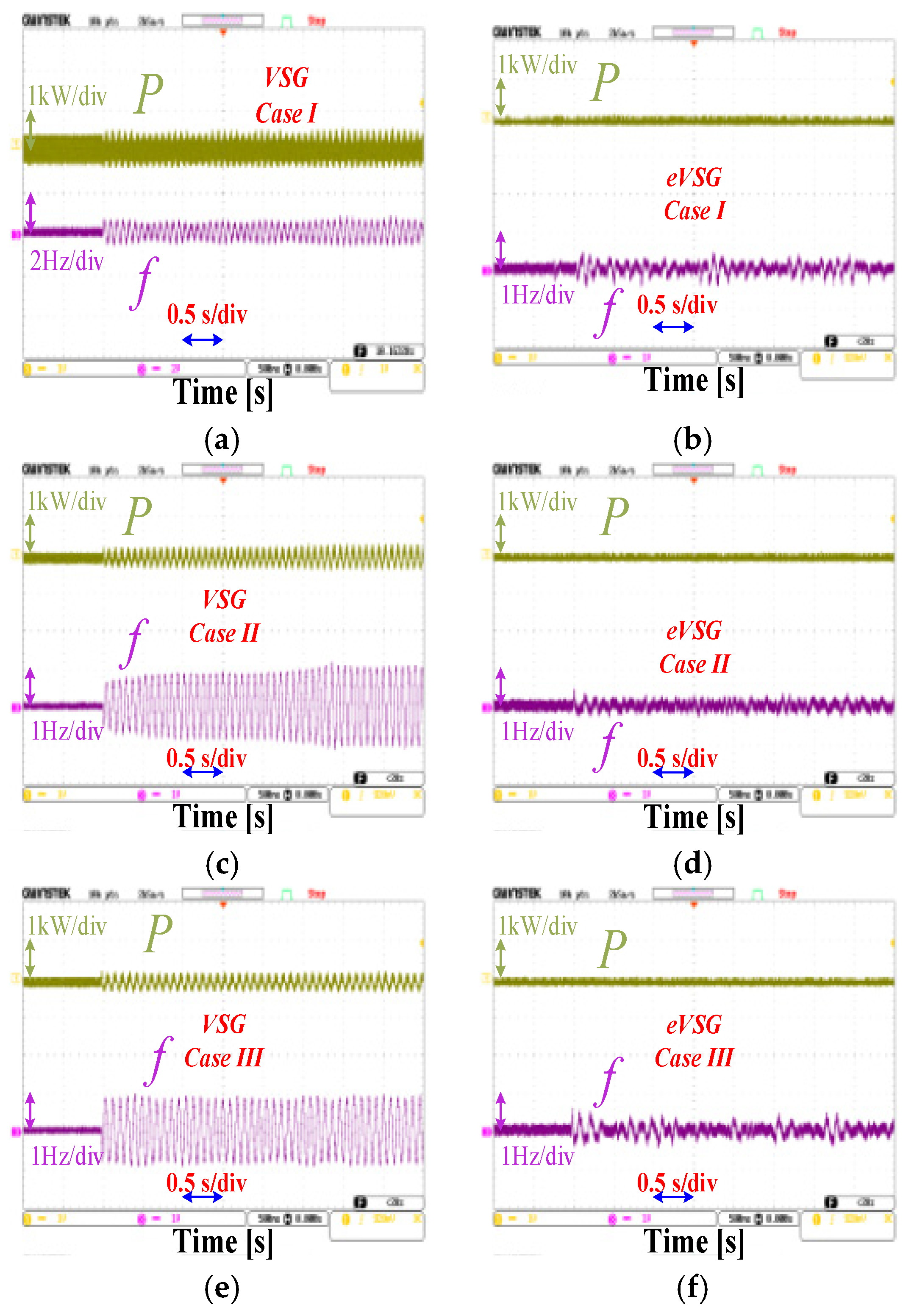
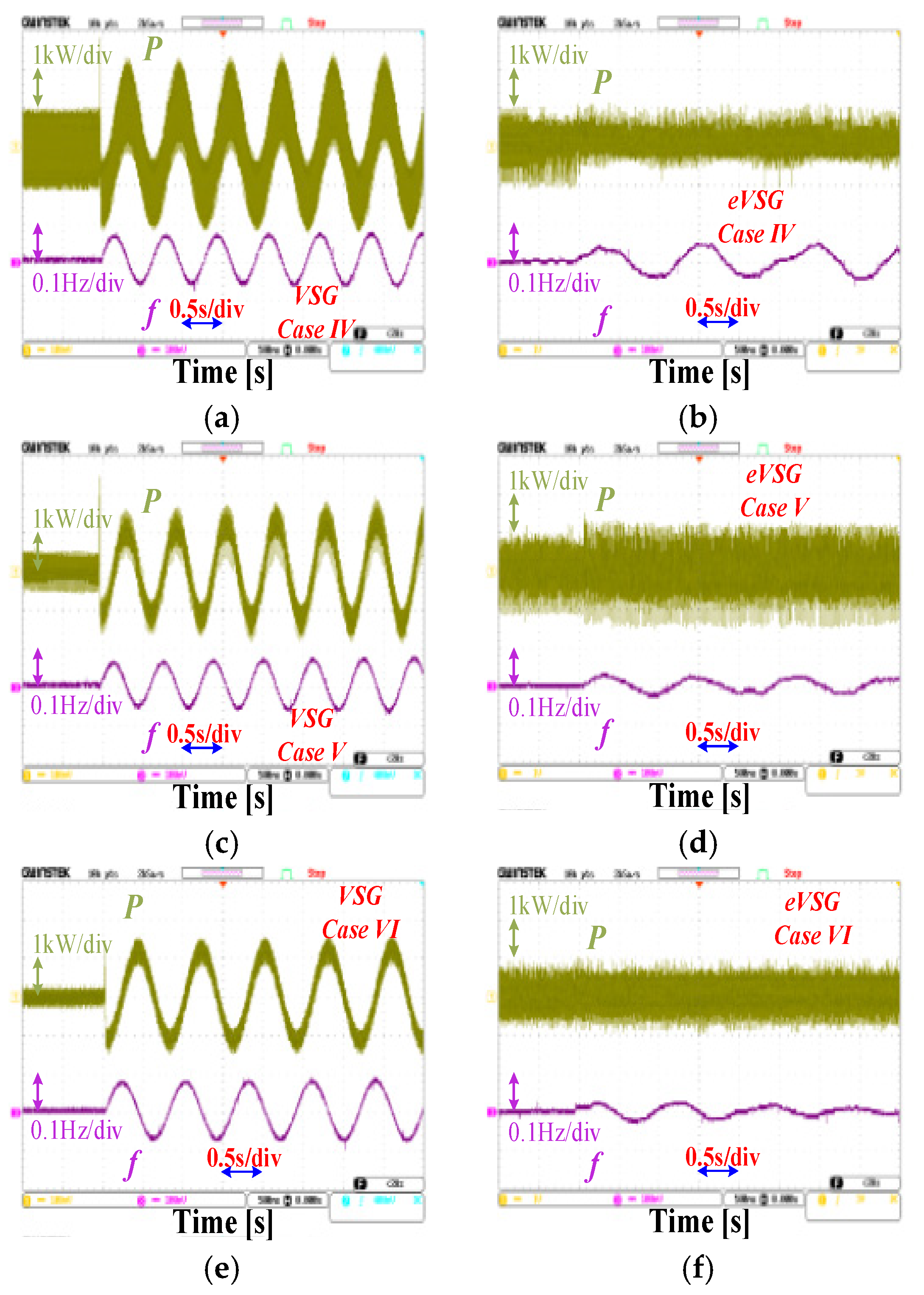
3.3. Case Studies
4. Experimental Verification
5. Conclusions
- By comparison of the VSG and eVSG systems from a perspective of oscillation and its transfer, it can be concluded that, in a wide range of grid inertia levels (Jp from 0.0125 to 1) and grid-tied systems, the eVSG strategy has significantly better performance on robustness than the VSG strategy when suffering same disturbance.
- Oscillation will occur when system has a negative stability margin, and the direction of oscillation propagation between P and f can be judged by the proposed framework and analytical method, also the degree of oscillation can be judged by the proposed framework.
- The simulations and experiment results also illustrated that whether in a strong grid, weak grid, high inertia level grid or low inertia level grid, grid-tied systems with the eVSG strategy had better performance on robustness compared with the conventional VSG strategy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Du, W.; Fu, Q.; Wang, H.F. Power system small-signal angular stability affected by virtual synchronous generators. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 34, 3209–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourmohammad, M.; Toulabi, M.; Ranjbar, A.M. Application of state feedback controller to ensure robust d-stable operation of virtual synchronous generators. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán-Pérez, J.; Rodríguez-Cabero, A.; Prodanovic, M. Design and analysis of virtual synchronous machines in inductive and resistive weak grids. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 1818–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauricio, J.M.; Leon, A.E. Improving small-signal stability of power systems with significant converter-interfaced generation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2020, 35, 2904–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xie, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, Z.; Lin, G.; Guo, J. Admittance-Based Stability Analysis of Current-Controlled VSG Considering the Frequency Coupling Characteristics. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2023, 11, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Sun, Y.; Lin, J.; Chen, S.; Su, M. P/Q-ω/V Admittance Modeling and Oscillation Analysis for Multi-VSG Grid-Connected System. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2023, 38, 5849–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, L.; Luo, A.; Zhou, X.; He, Z.; Yang, L.; Xie, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M. Sequence Impedance Modeling and Stability Comparative Analysis of Voltage-Controlled VSGs and Current-Controlled VSGs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 6460–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Shuai, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhou, X.; Yan, K.; Luo, A. Impedance-Based Harmonic Current Suppression Method for VSG Connected to Distorted Grid. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 5490–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Blaabjerg, F. Mechanism Analysis for Oscillation Transferring in Grid-Forming Virtual Synchronous Generator Connected to Power Network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2025, 72, 8715–8720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, Y.; Du, Y.; Gao, X.; Yang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Blaabjerg, F. Self-Stability and Induced-Stability Analysis for Frequency and Voltage in Grid-Forming VSG System With Generic Magnitude-Phase Model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 12328–12338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Mijatovic, N.; Dragicevic, T. Frequency Stability Assessment of Grid-Forming VSG in Framework of MPME With Feedforward Decoupling Control Strategy. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 6903–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Murashov, I.; Xu, J.; Aleshina, A.; Blaabjerg, F. Generalized stabilizer-oriented design for GFVSG integrated into weak-stiffness power networks. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2022, 37, 4958–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wu, M.; Zhang, W.; Dragičević, T. New framework of RoCoF-FD for wideband stability evaluation in renewable energy generators with virtual impedance control. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2022, 13, 3570–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Chen, Y.; Liao, S.; Wu, W.; Zhou, L.; Xie, Z.; Wang, X. Analysis and Mitigation of Low-Frequency Interactions Between the Source and Load Virtual Synchronous Machine in an Islanded Microgrid. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 3732–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sun, D.; Song, P.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, F.; Tian, Y. Influence of Virtual Synchronous Generators on Low Frequency Oscillations. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 8, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Xu, Y.; Yuan, C.; Jia, J. A Unified Method of Frequency Oscillation Characteristic Analysis for Multi-VSG Grid-Connected System. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2022, 37, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Blaabjerg, F. Modeling for Oscillation Propagation With Frequency-Voltage Coupling Effect in Grid-Connected Virtual Synchronous Generator. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 40, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Li, C.; Ghias, A.M.M.; Blaabjerg, F. Dynamic Coupling Mechanism Analysis Between Voltage and Frequency in Virtual Synchronous Generator System. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2024, 39, 2365–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, J.; Gao, C.; Li, G.; Wang, K. Low-frequency Oscillations and Resonance Analysis of VSG-controlled PMSG-based Wind Generation Systems. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean 2025, 13, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Zhu, D.; Zou, X.; Jiang, B.; Peng, L.; Kang, Y. Power Coupling Mechanism Analysis and Improved Decoupling Control for Virtual Synchronous Generator. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 3028–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chaudhary, S.K.; Tinajero, G.D.; Xu, L.; Bakar, N.N.A.; Vasquez, J.C.; Guerrero, J.M. A Reference-Feedforward-Based Damping Method for Virtual Synchronous Generator Control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 7566–7571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yu, P.; Hu, W.; Wang, Y.; Shu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Blaabjerg, F. Phase Feedforward Damping Control Method for Virtual Synchronous Generators. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 9790–9806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipoor, J.; Miura, Y.; Ise, T. Power System Stabilization Using Virtual Synchronous Generator With Alternating Moment of Inertia. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2015, 3, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Liao, S.; Xu, Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, H.; Cao, S. Impedance-Based Adaptively Reshaping Method for Enhancing Nonlinear Load Sharing and Voltage Quality in Islanded Microgrids With Virtual Synchronous Generator. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2022, 13, 2568–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, X. A Mode-Adaptive Power-Angle Control Method for Transient Stability Enhancement of Virtual Synchronous Generators. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 8, 1034–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Xu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Li, M. Coordinated VSG Control of Photovoltaic/Battery System for Maximum Power Output and Grid Supporting. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2022, 12, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo-Ossa, D.D.; Sanabria-Torres, E.A.; Vasquez-Plaza, J.D.; Rodriguez-Martinez, O.F.; Garzon-Rivera, O.D.; Andrade, F. Novel Rotated Virtual Synchronous Generator Control for Power-Sharing in Microgrids with Complex Line Impedance. Electronics 2023, 12, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


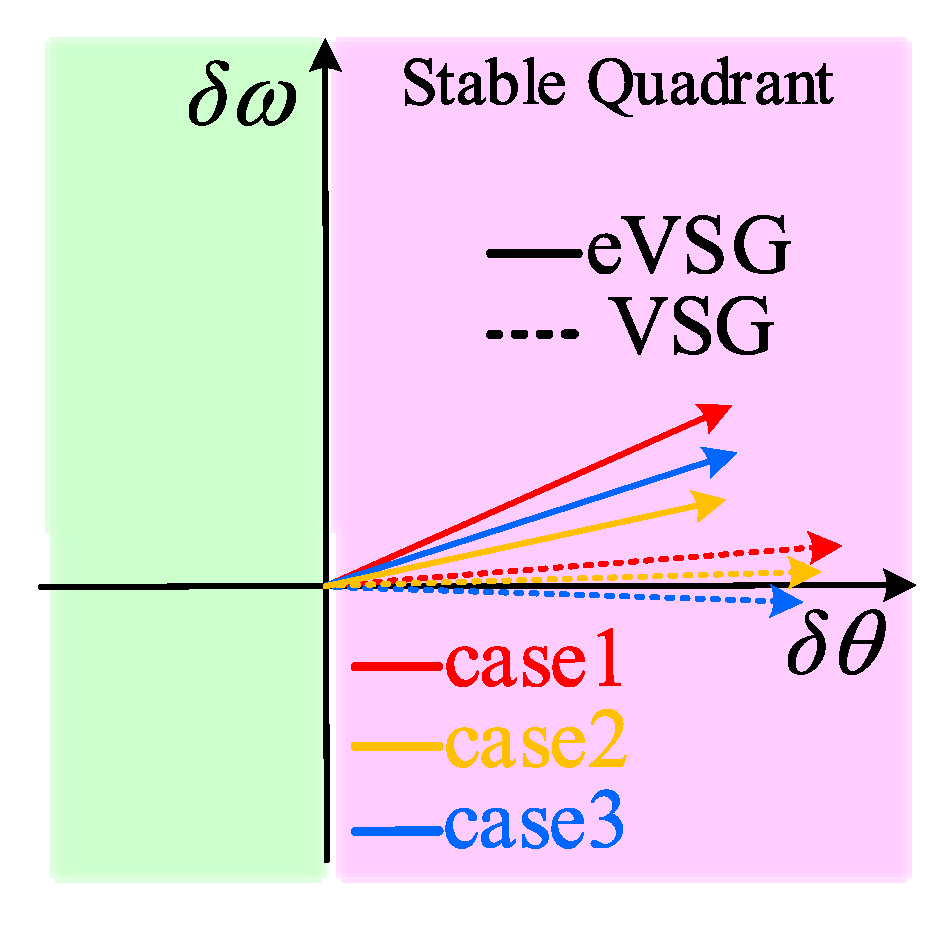
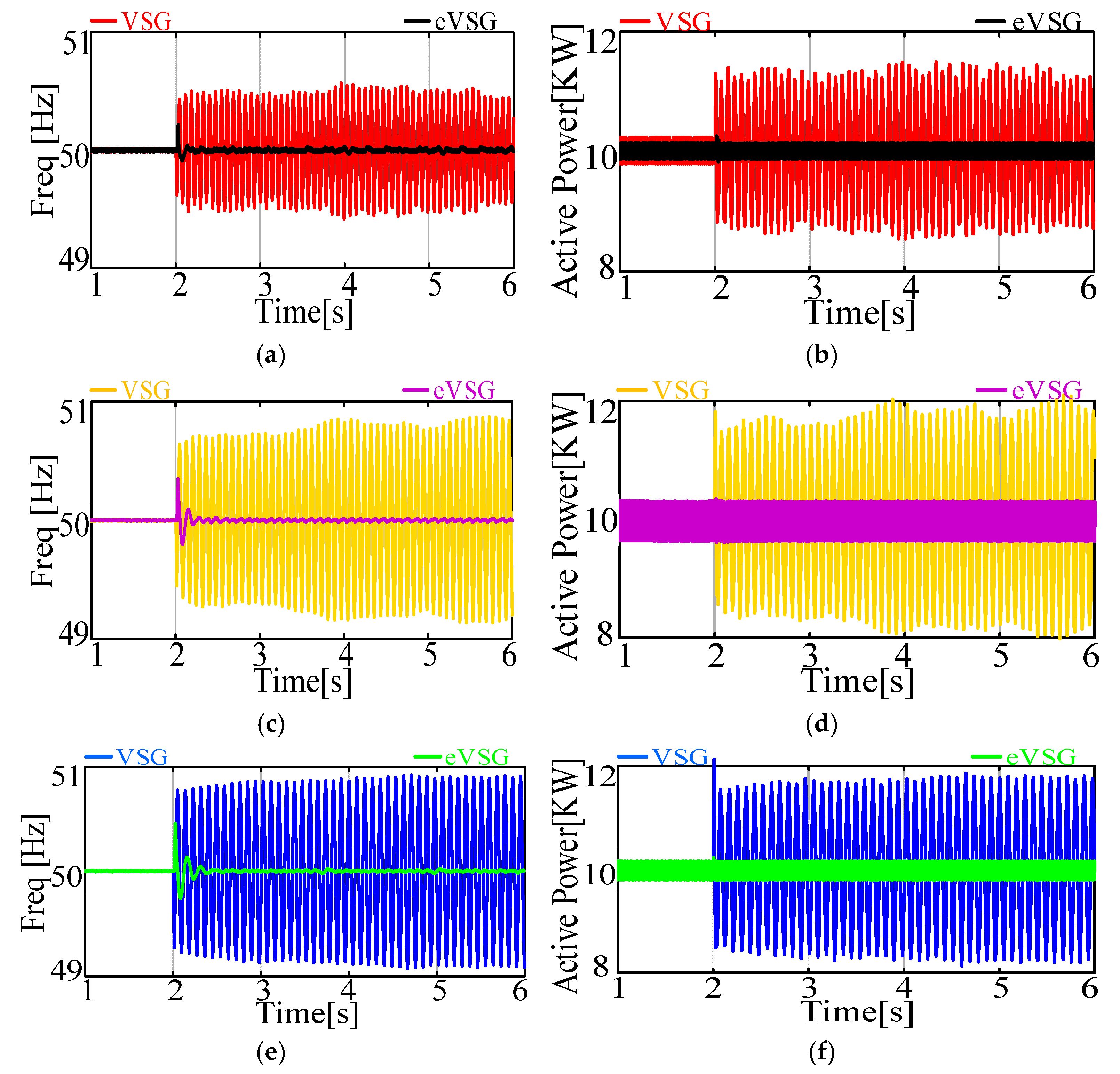


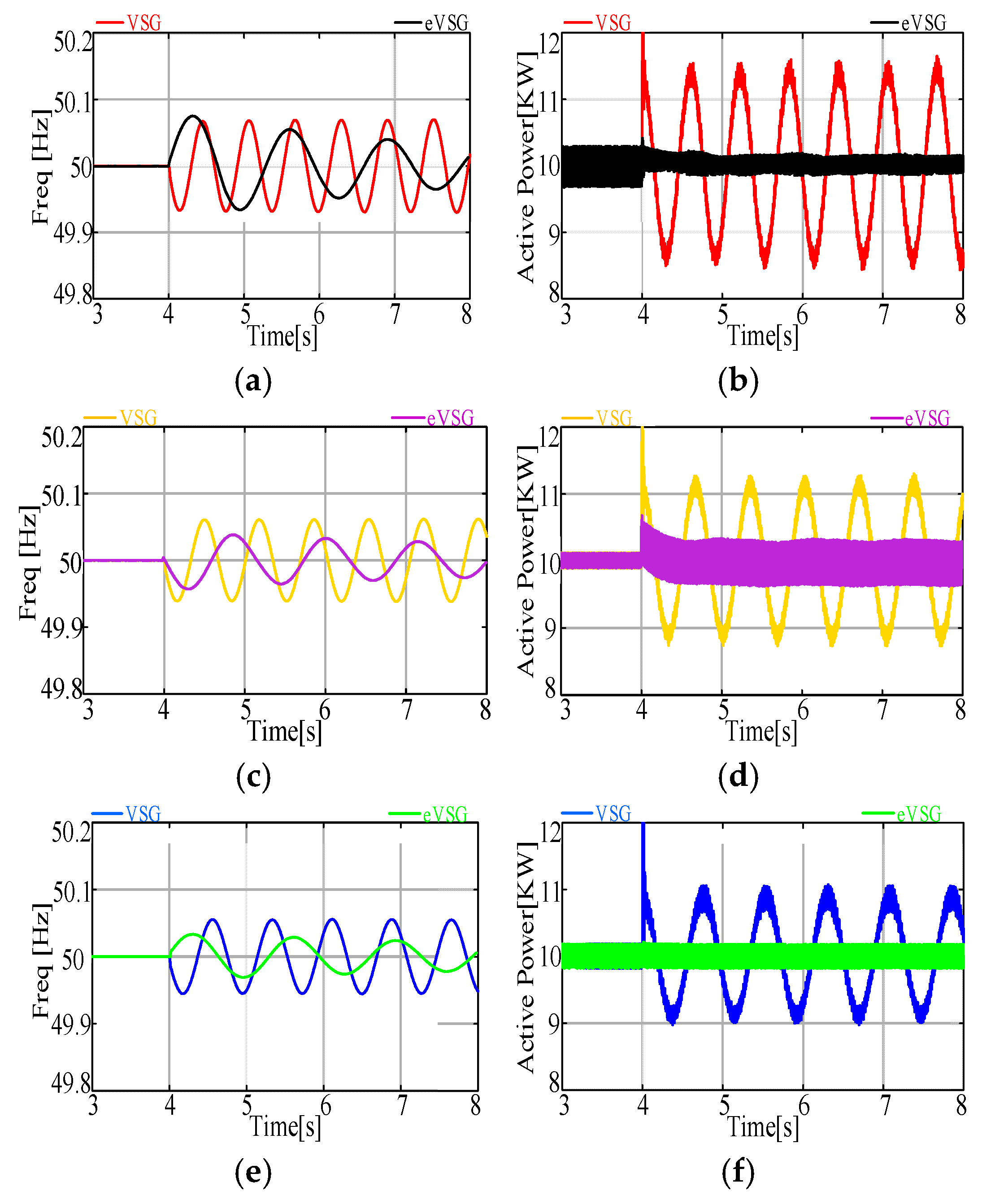
| Case I | Case II | Case III | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rf/Ω | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Lf/mH | 4.4 | 4.4 | 4.4 |
| Rtr/Ω | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Ltr/mH | 4.6 | 4.6 | 4.6 |
| SCR | 4.326 | 2.6 | 1.62 |
| Jp | 0.0125 | 0.0125 | 0.0125 |
| Dp | 0.499 | 0.41 | 0.317 |
| Jq/Ki | 0.25/0.1 | 0.25/0.1 | 0.25/0.1 |
| Dq/Kp | 520/0.5 | 520/0.5 | 520/0.5 |
| ωg | 100π | 100π | 100π |
| Eref | 311.127 | 311.127 | 311.127 |
| Power level | 10 kW | 10 kW | 10 kW |
| VSG | eVSG | |
|---|---|---|
| Case I | (89.2, 360.342) | (78.5, 28.521) |
| Case II | (87.6, 360.2826) | (78.5, 25.3) |
| Case III | (85.7, 359.9056) | (77.6, 18.987) |
| VSG | eVSG | |
|---|---|---|
| Case I | (85.5, 0.342) | (38.8, 35.2) |
| Case II | (78, 0.279) | (38.7, 29.7) |
| Case III | (70.2, −0.0952) | (39.7, 20.9) |
| Case VI | Case V | Case VI | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rf/Ω | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Lf/mH | 4.4 | 4.4 | 4.4 |
| Rtr/Ω | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Ltr/mH | 4.6 | 4.6 | 4.6 |
| SCR | 4.326 | 2.6 | 1.62 |
| Jp | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Dp | 0.497 | 0.421 | 0.323 |
| Jq/Ki | 0.5/0.1 | 0.5/0.1 | 0.5/0.1 |
| Dq/Kp | 987/0.5 | 987/0.5 | 987/0.5 |
| ωg | 100π | 100π | 100π |
| Eref | 311.127 | 311.127 | 311.127 |
| Power level | 10 kW | 10 kW | 10 kW |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Xu, B.; Li, J.; Xie, Y.; Ma, W. Oscillation Propagation Analysis of Grid-Connected Converter System with New eVSG Control Patterns. Electronics 2025, 14, 3850. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193850
Zhang H, Xu B, Li J, Xie Y, Ma W. Oscillation Propagation Analysis of Grid-Connected Converter System with New eVSG Control Patterns. Electronics. 2025; 14(19):3850. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193850
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hong, Bin Xu, Jinzhong Li, Yuguang Xie, and Wei Ma. 2025. "Oscillation Propagation Analysis of Grid-Connected Converter System with New eVSG Control Patterns" Electronics 14, no. 19: 3850. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193850
APA StyleZhang, H., Xu, B., Li, J., Xie, Y., & Ma, W. (2025). Oscillation Propagation Analysis of Grid-Connected Converter System with New eVSG Control Patterns. Electronics, 14(19), 3850. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193850






