Integrating Temporal Interest Dynamics and Virality Factors for High-Precision Ranking in Big Data Recommendation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A multimodal virality-aware module is designed by fusing text, image, audio, and user comment streams to enhance content-level virality assessment.
- Propagation potential factors are jointly introduced with click-sequence features to optimize the ranking mechanism, enabling accurate recommendations driven by both “interest” and “popularity”.
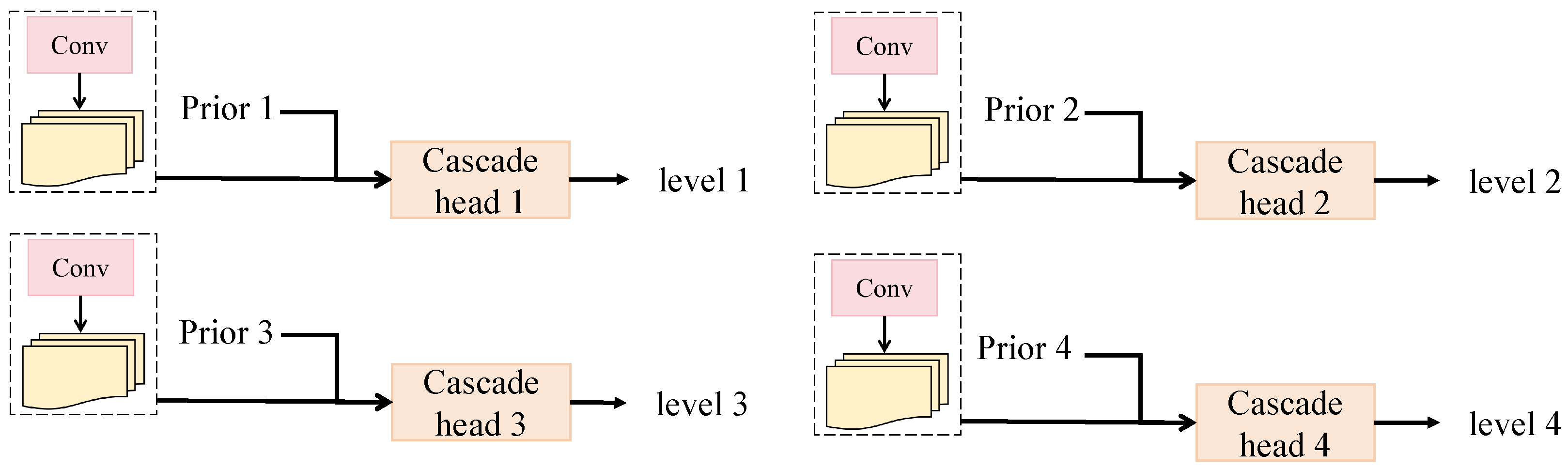
- Hierarchy classification heads are constructed to generate the final ranking outputs.
2. Related Work
2.1. CTR Prediction and Sequential Modeling Methods
2.2. Multimodal Content Understanding and Propagation Modeling
2.3. Content Popularity and Virality Modeling in Recommendation Systems
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Collection
3.2. Data Augmentation
3.3. Proposed Method
3.3.1. Overall
3.3.2. Multimodal Virality Encoder
3.3.3. Hierarchy Classification Heads
3.3.4. Joint Pruning Optimization Module
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Hyperparameter Settings
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Baseline
4.4. Overall Performance Comparison with Baseline Models
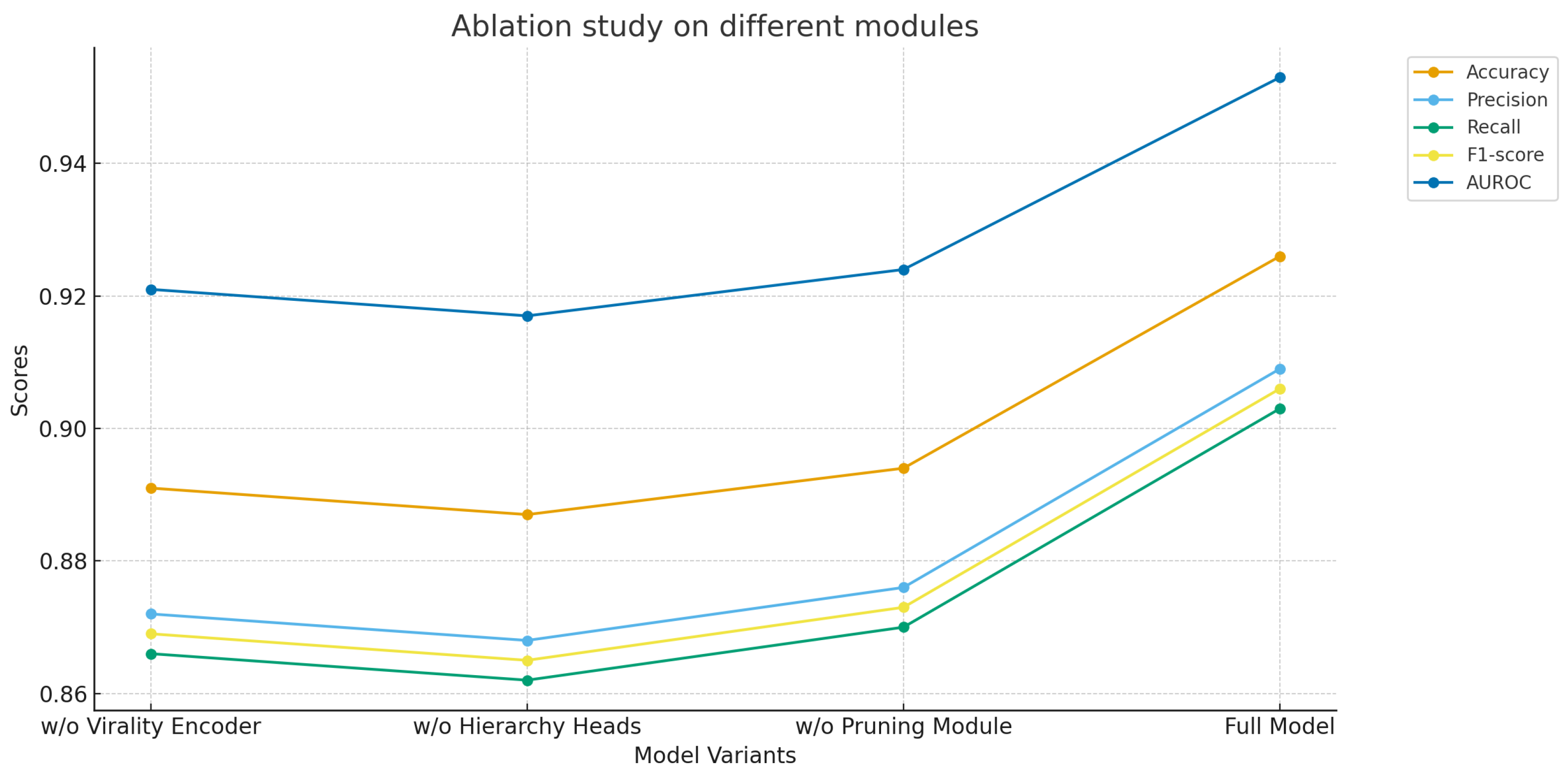
4.5. Ablation Study on Different Modules of the Proposed Model
4.6. Robustness Analysis Under Noisy and Imbalanced Data Conditions
4.7. Discussion
4.8. Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.; Liu, F.; Zhao, X.; Tan, Q. A CTR prediction model based on session interest. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0273048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Bai, J.; Song, J.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, X.; Gao, J. Atrank: An attention-based user behavior modeling framework for recommendation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Li, Z.; Su, Y.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L. GraphFM: Graph factorization machines for feature interaction modeling. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.11866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Geng, X.; Deng, J.; Xia, Z.; Jiang, H.; Yan, G.; Liang, J. A comprehensive survey on advertising click-through rate prediction algorithm. Knowl. Eng. Rev. 2025, 40, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, S.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, J.; Fan, D.; Lin, J.; Wang, Q. Atrous Pyramid GAN Segmentation Network for Fish Images with High Performance. Electronics 2022, 11, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Han, Y.; Yi, B.; Zhang, Z. Click-through rate prediction model integrating user interest and multi-head attention mechanism. J. Big Data 2023, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, D.; Jameel, S.; Yu, P.; Xu, G. Click-through rate prediction with multi-modal hypergraphs. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, Queensland, Australia, 1–5 November 2021; pp. 690–699. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Shen, D.; Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Yang, F.; Zhou, G.; Meng, G. ContentCTR: Frame-level live streaming click-through rate prediction with multimodal transformer. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.14392. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, K.; Woodland, P.C. Multi-head Temporal Latent Attention. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.13544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhu, X.; Song, C.; Fan, Y.; Zhu, H.; Ma, X.; Yan, Y.; Jin, J.; Li, H.; Gai, K. Deep interest network for click-through rate prediction. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, UK, 19–23 August 2018; pp. 1059–1068. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T. Video saliency prediction via single feature enhancement and temporal recurrence. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 160, 111840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Mou, N.; Fan, Y.; Pi, Q.; Bian, W.; Zhou, C.; Zhu, X.; Gai, K. Deep interest evolution network for click-through rate prediction. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 5941–5948. [Google Scholar]
- Dontu, S.; Addula, S.R.; Pareek, P.K.; Vallabhaneni, R.; Adnan, M.M. Attack detection from Internet of Things using TPE based self-attention based bidirectional long-short term memory. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Intelligent Algorithms for Computational Intelligence Systems (IACIS), Hassan, India, 23–24 August 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xiu, Z. Financial Transaction Anomaly Detection Based on Transformer Model. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2025, 262, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meenakshi, B.; Karunkuzhali, D. Enhancing cyber security in WSN using optimized self-attention-based provisional variational auto-encoder generative adversarial network. Comput. Stand. Interfaces 2024, 88, 103802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Pereira Moreira, G.; Rabhi, S.; Lee, J.M.; Ak, R.; Oldridge, E. Transformers4rec: Bridging the gap between nlp and sequential/session-based recommendation. In Proceedings of the 15th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 143–153. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, F.; Xing, S.; Zhao, X.; Li, T. Research on CTR prediction based on deep learning. IEEE Access 2018, 7, 12779–12789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Kong, Q.; Zhang, Y. Advances in Temporal Point Processes: Bayesian, Deep, and LLM Approaches. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.14291. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Yao, L. Modeling temporal positive and negative excitation for sequential recommendation. In Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2023, Austin, TX, USA, 30 April–4 May 2023; pp. 1252–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J. Temporal user interest modeling for online advertising using Bi-LSTM network improved by an updated version of Parrot Optimizer. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 18858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, Q.; Caron, G.M.; Aloise, D. A practical survey on faster and lighter transformers. Acm Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, M.A. Logarithmic memory networks (lmns): Efficient long-range sequence modeling for resource-constrained environments. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.07905. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, X.; Nie, L.; He, X.; Hong, R.; Chua, T.S. MMGCN: Multi-modal graph convolution network for personalized recommendation of micro-video. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019; pp. 1437–1445. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Yang, X.; Ke, Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J. Alleviating the inconsistency of multimodal data in cross-modal retrieval. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 40th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), Utrecht, The Netherlands, 13–16 May 2024; pp. 4643–4656. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, X. A new strategy for tuning ReLUs: Self-adaptive linear units (SALUs). In Proceedings of the ICMLCA 2021; 2nd International Conference on Machine Learning and Computer Application, Shenyang, China, 17–19 December 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, W.; Son, B.; Kim, I. Vilt: Vision-and-language transformer without convolution or region supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 5583–5594. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, Z.; Li, L.; Li, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Gao, J. Vision-language pre-training: Basics, recent advances, and future trends. Found. Trends® Comput. Graph. Vis. 2022, 14, 163–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Hu, R.; Goswami, V.; Couairon, G.; Galuba, W.; Rohrbach, M.; Kiela, D. Flava: A foundational language and vision alignment model. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 15638–15650. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Myers, A.; Vondrick, C.; Murphy, K.; Schmid, C. Videobert: A joint model for video and language representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 7464–7473. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Xu, R.; Wang, S.; Zhou, L.; Lin, X.; Zhu, C.; Zeng, M.; Ji, H.; Chang, S.F. Clip-event: Connecting text and images with event structures. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 16420–16429. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, J.; Chen, H. Epidemic model for information diffusion in web forums: Experiments in marketing exchange and political dialog. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Qian, M. Predicting popularity of viral content in social media through a temporal-spatial cascade convolutional learning framework. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.T.; Huynh, V.D.B.; Vo, K.D.; Phan, P.T.; Le, D.N. Deep Learning based Optimal Multimodal Fusion Framework for Intrusion Detection Systems for Healthcare Data. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 66, 2555–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, S.; Dong, E.; Jagadeesan, M.; Leqi, L. Recommender systems as dynamical systems: Interactions with viewers and creators. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Recommendation Ecosystems: Modeling, Optimization and Incentive Design, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–27 February 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Hu, C.; Fu, S.; Fang, M.; Xu, W. Predicting key events in the popularity evolution of online information. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial networks. Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; He, C.; Liu, Y.; Kim, K.C. Super-resolution reconstruction of turbulent velocity fields using a generative adversarial network-based artificial intelligence framework. Phys. Fluids 2019, 31, 125111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.; Vinyals, O.; Dean, J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1503.02531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Kornblith, S.; Norouzi, M.; Hinton, G. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 13–18 July 2020; pp. 1597–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.Y.; Kusoemo, D.; Gosno, R.A. Text mining-based construction site accident classification using hybrid supervised machine learning. Autom. Constr. 2020, 118, 103265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hládek, D.; Staš, J.; Pleva, M. Survey of automatic spelling correction. Electronics 2020, 9, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Dong, L.; Piao, S.; Wei, F. Beit: Bert pre-training of image transformers. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.08254. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Shi, N.; Hauer, B.; Wu, Z.; Kondrak, G.; Abdul-Mageed, M.; Lakshmanan, L.V. Cross-modal consistency in multimodal large language models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.09273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y.; Shi, L.; Wei, L. Detecting fake news by exploring the consistency of multimodal data. Inf. Process. Manag. 2021, 58, 102610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, R.; Chen, J. Progressive semantic aggregation and structured cognitive enhancement for image–text matching. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 274, 126943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshubaily, I. TextCNN with attention for text classification. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.01921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroteev, M.V. BERT: A review of applications in natural language processing and understanding. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.11943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voloshina, E.; Ilinykh, N.; Dobnik, S. Are language-and-vision transformers sensitive to discourse? A case study of ViLBERT. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Multimodal, Multilingual Natural Language Generation and Multilingual WebNLG Challenge (MM-NLG 2023), Prague, Czech Republic, 12 September 2023; pp. 28–38. [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay, D.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Ekbal, A. Seeing through VisualBERT: A causal adventure on memetic landscapes. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.13488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafner, M.; Katsantoni, M.; Köster, T.; Marks, J.; Mukherjee, J.; Staiger, D.; Ule, J.; Zavolan, M. CLIP and complementary methods. Nat. Rev. Methods Prim. 2021, 1, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visweswaran, M.; Mohan, J.; Kumar, S.S.; Soman, K. Synergistic detection of multimodal fake news leveraging TextGCN and Vision Transformer. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 235, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis, A.K.; Agamy, M. Homogeneous Versus Heterogeneous Graph Representation for Graph Neural Network Tasks on Electric Circuits. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2025, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dataset | Collection Period | Number of Items | User Behavior Logs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Short Video (Douyin/Bilibili) | 2023.01–2024.12 | 120,000 videos | 3,500,000 logs |
| News (MIND) | 2022.01–2023.12 | 65,000 articles | 1,200,000 logs |
| News (Self-built) | 2022.01–2023.12 | 40,000 articles | 850,000 logs |
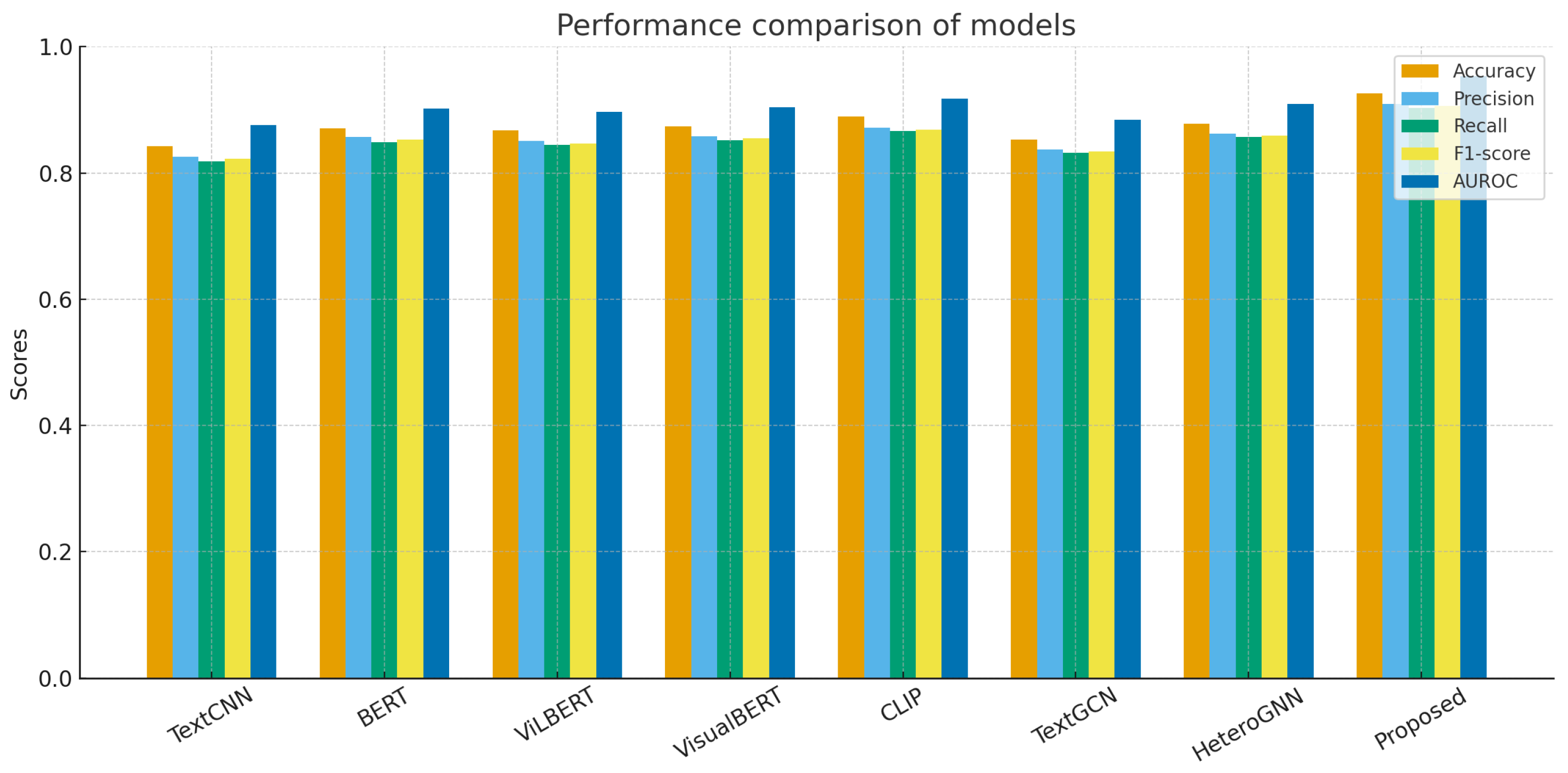
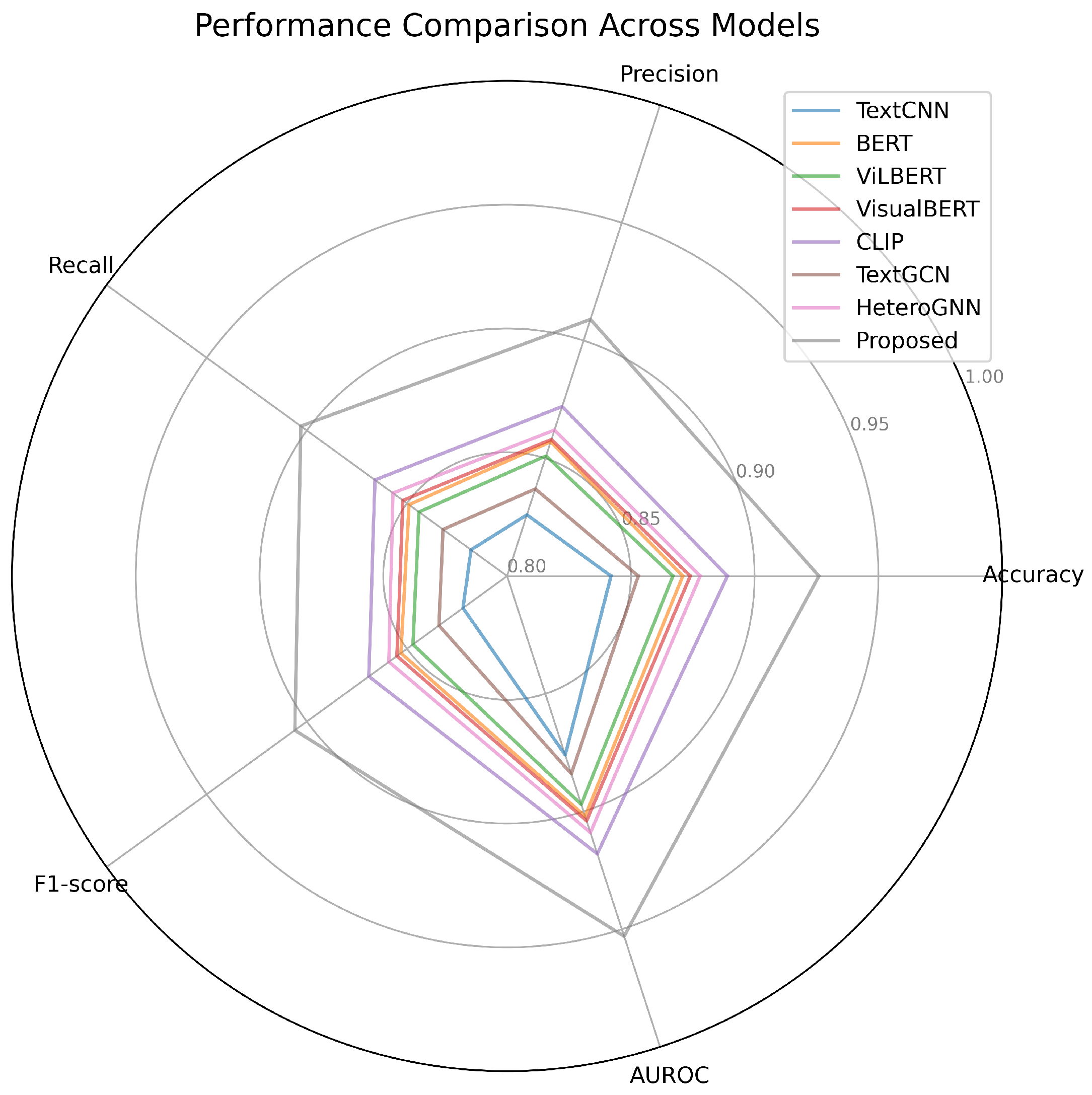
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | AUROC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TextCNN | 0.842 | 0.826 | 0.818 | 0.822 | 0.876 |
| BERT | 0.871 | 0.857 | 0.849 | 0.853 | 0.902 |
| ViLBERT | 0.867 | 0.851 | 0.844 | 0.847 | 0.897 |
| VisualBERT | 0.874 | 0.858 | 0.852 | 0.855 | 0.904 |
| CLIP | 0.889 | 0.872 | 0.866 | 0.869 | 0.918 |
| TextGCN | 0.853 | 0.837 | 0.832 | 0.834 | 0.884 |
| HeteroGNN | 0.878 | 0.862 | 0.857 | 0.859 | 0.909 |
| Proposed | 0.926 | 0.909 | 0.903 | 0.906 | 0.953 |
| Model Variant | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | AUROC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w/o Multimodal Virality Encoder | 0.891 | 0.872 | 0.866 | 0.869 | 0.921 |
| w/o Hierarchy Classification Heads | 0.887 | 0.868 | 0.862 | 0.865 | 0.917 |
| w/o Joint Pruning Optimization Module | 0.894 | 0.876 | 0.870 | 0.873 | 0.924 |
| Full Model | 0.926 | 0.909 | 0.903 | 0.906 | 0.953 |
| Condition | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | AUROC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20% Noisy Labels | 0.884 | 0.866 | 0.861 | 0.863 | 0.918 |
| 30% Data Imbalance | 0.893 | 0.875 | 0.870 | 0.872 | 0.927 |
| 50% Noisy + Imbalanced | 0.861 | 0.842 | 0.838 | 0.840 | 0.903 |
| Clean Data (Full Model) | 0.926 | 0.909 | 0.903 | 0.906 | 0.953 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, Z.; Yang, J.; Meng, F.; Li, M.; Zhan, Y. Integrating Temporal Interest Dynamics and Virality Factors for High-Precision Ranking in Big Data Recommendation. Electronics 2025, 14, 3687. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183687
Ye Z, Yang J, Meng F, Li M, Zhan Y. Integrating Temporal Interest Dynamics and Virality Factors for High-Precision Ranking in Big Data Recommendation. Electronics. 2025; 14(18):3687. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183687
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Zhaoyang, Jingyi Yang, Fanyu Meng, Manzhou Li, and Yan Zhan. 2025. "Integrating Temporal Interest Dynamics and Virality Factors for High-Precision Ranking in Big Data Recommendation" Electronics 14, no. 18: 3687. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183687
APA StyleYe, Z., Yang, J., Meng, F., Li, M., & Zhan, Y. (2025). Integrating Temporal Interest Dynamics and Virality Factors for High-Precision Ranking in Big Data Recommendation. Electronics, 14(18), 3687. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183687





