Speaker Recognition Based on the Combination of SincNet and Neuro-Fuzzy for Intelligent Home Service Robots
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. End-to-End Deep Learning Models for Speech Processing
2.2. Fuzzy Inference Systems for Signal Processing
2.3. Hybrid Models Combining Deep Learning Models and Fuzzy Inference Systems
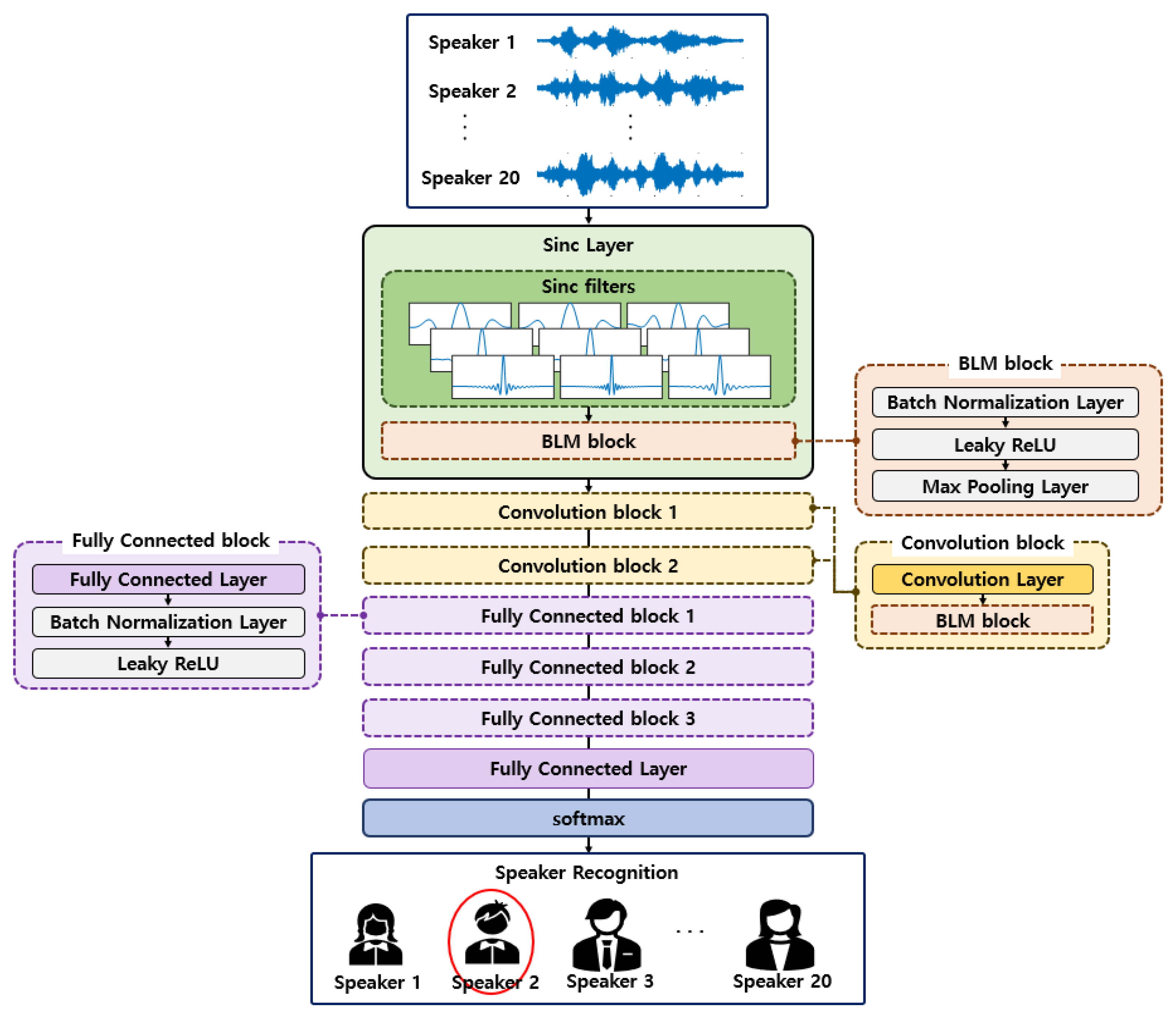
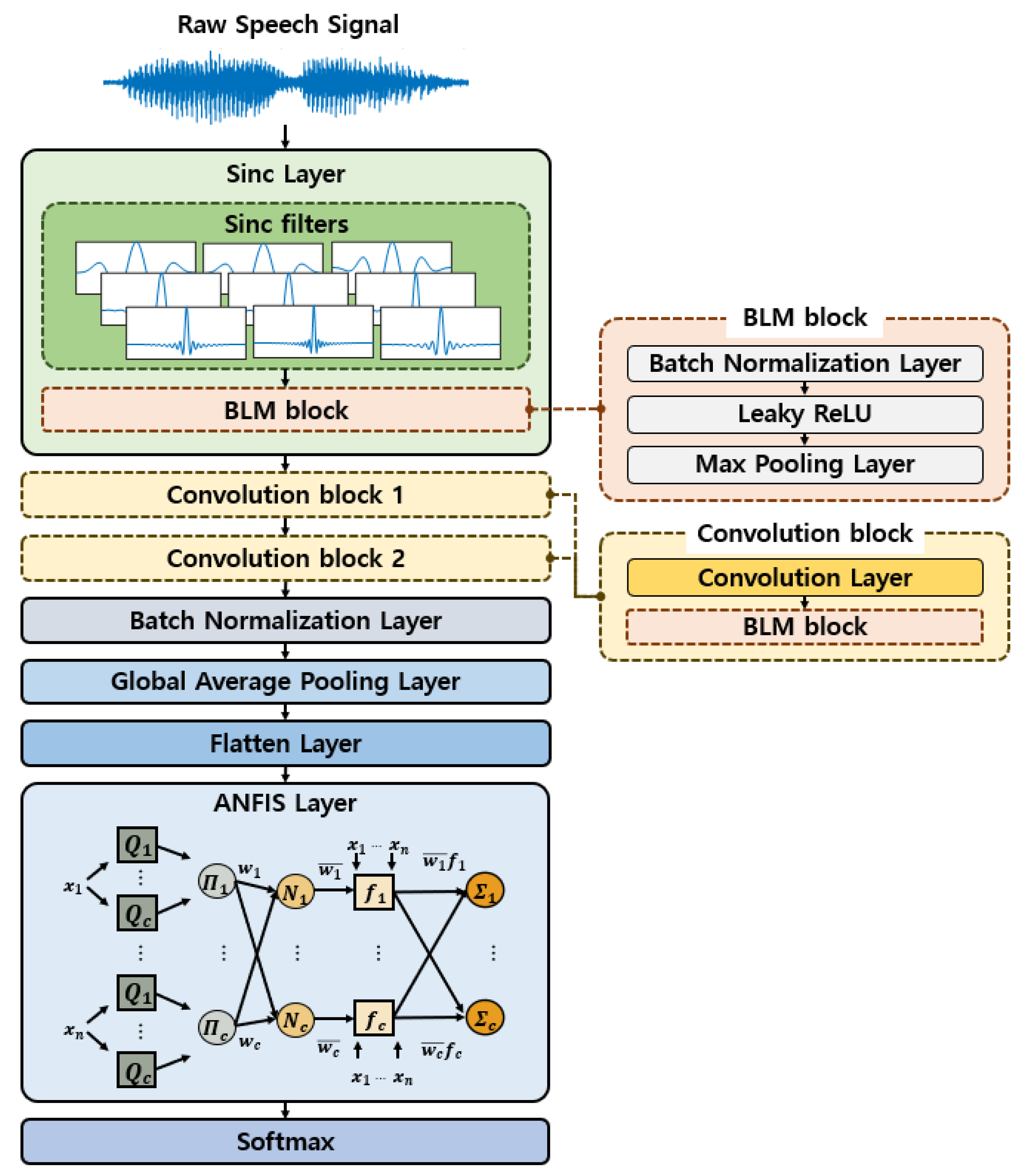
3. Speaker Recognition Model Based on SincNet-ANFIS
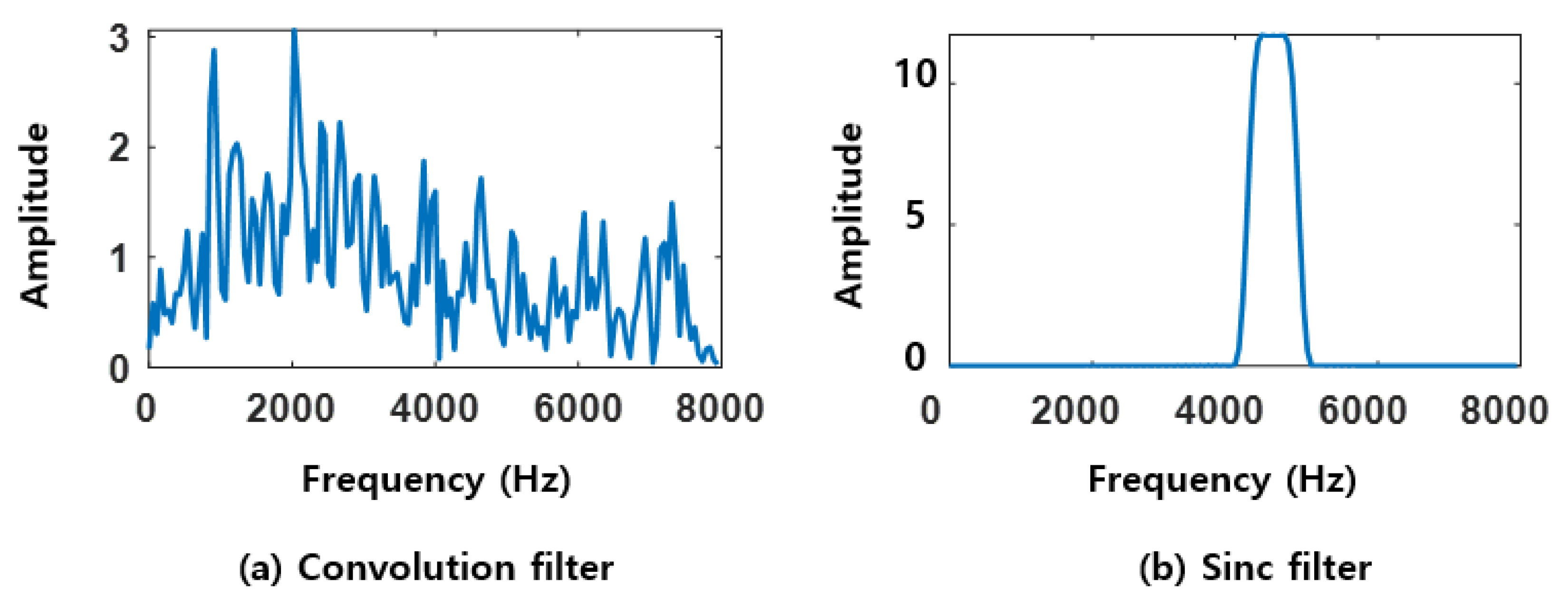
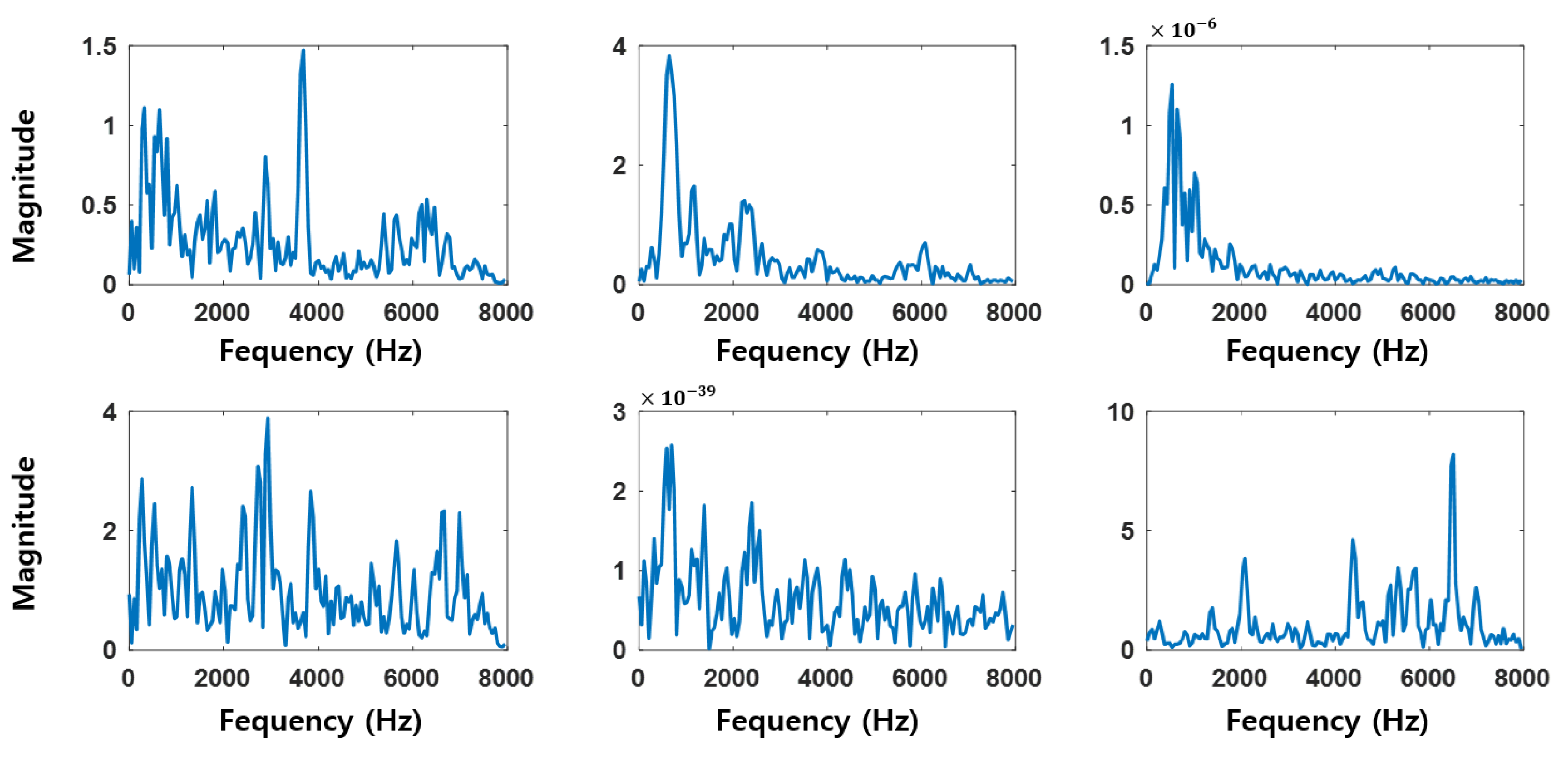
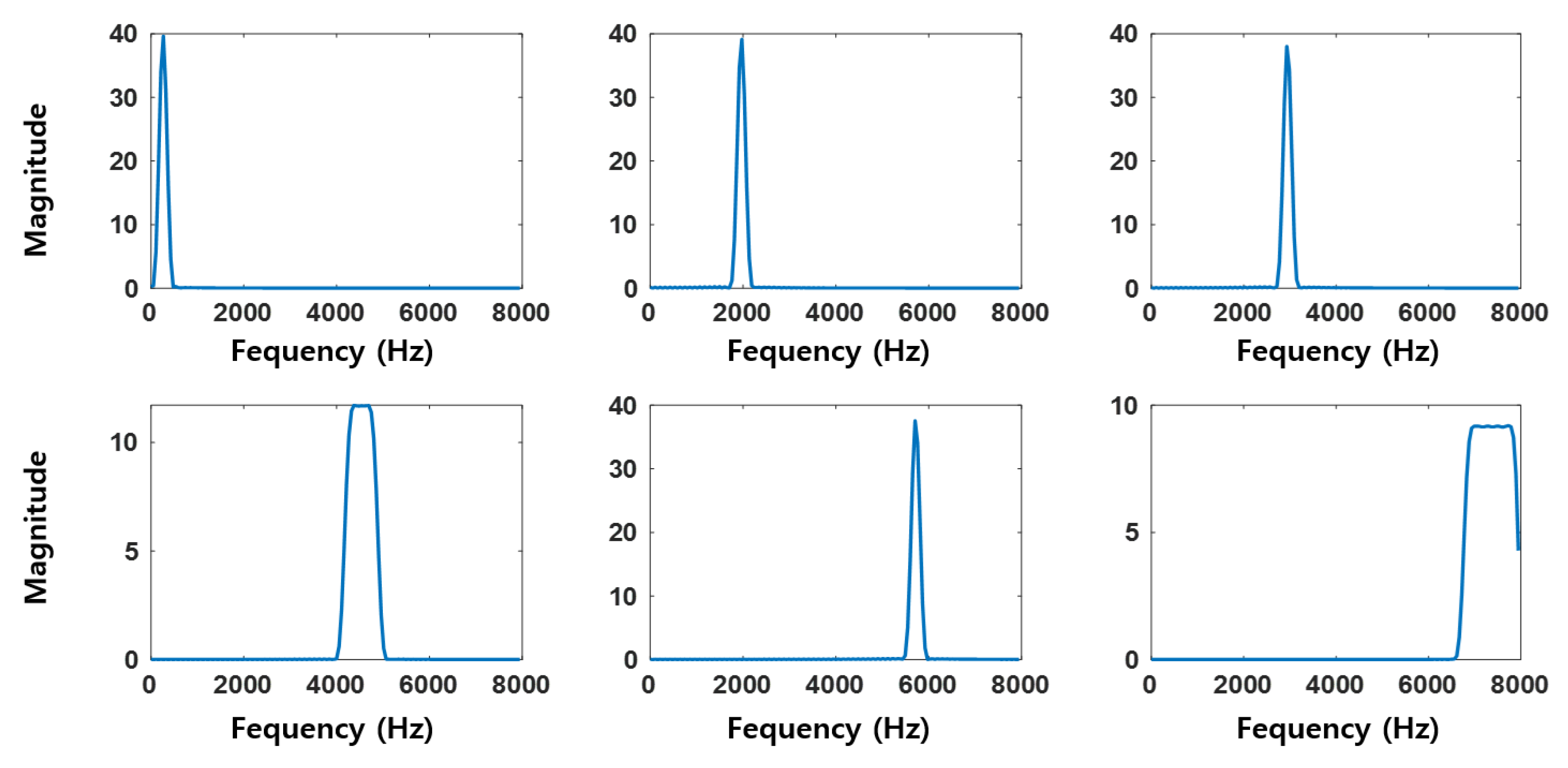
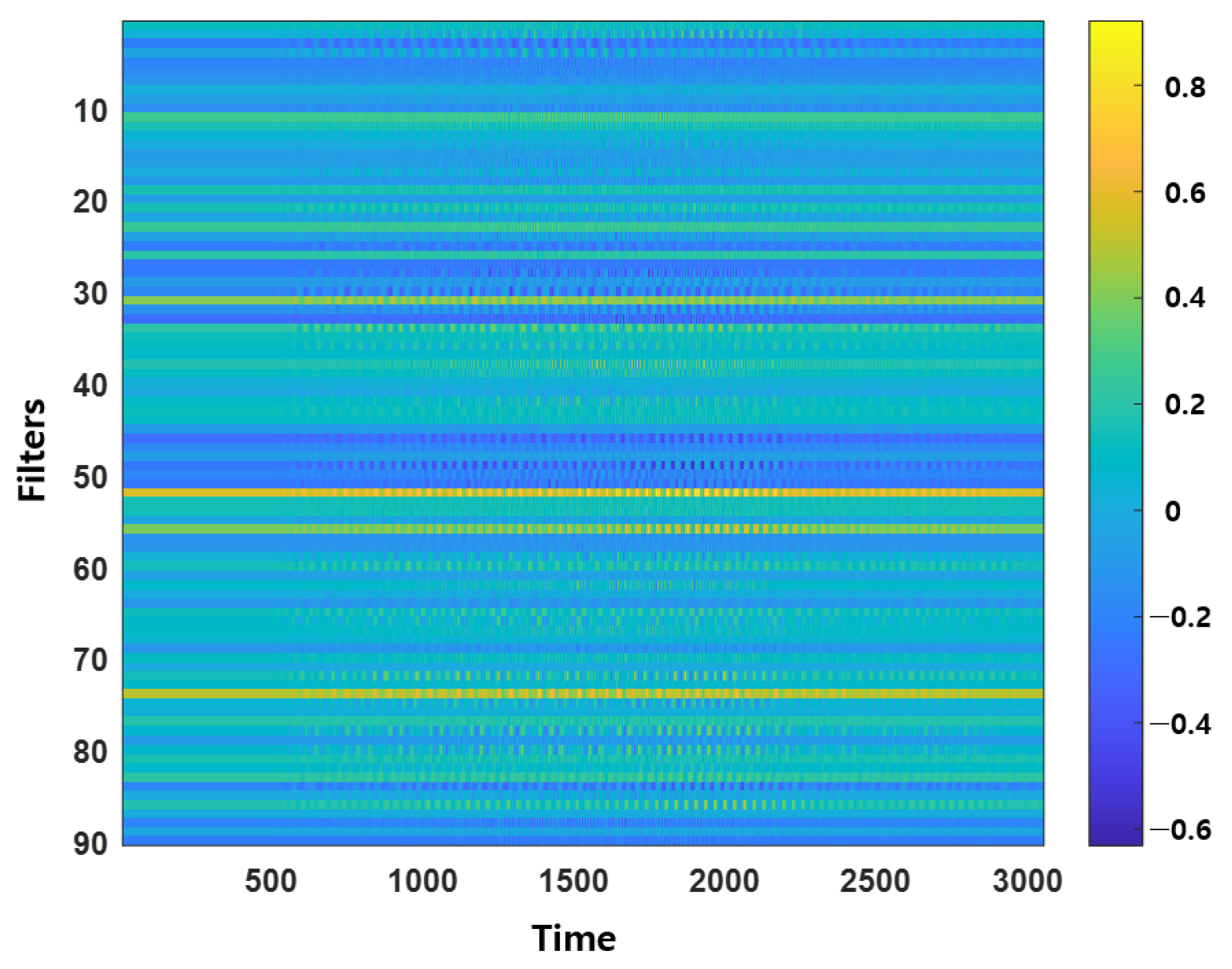
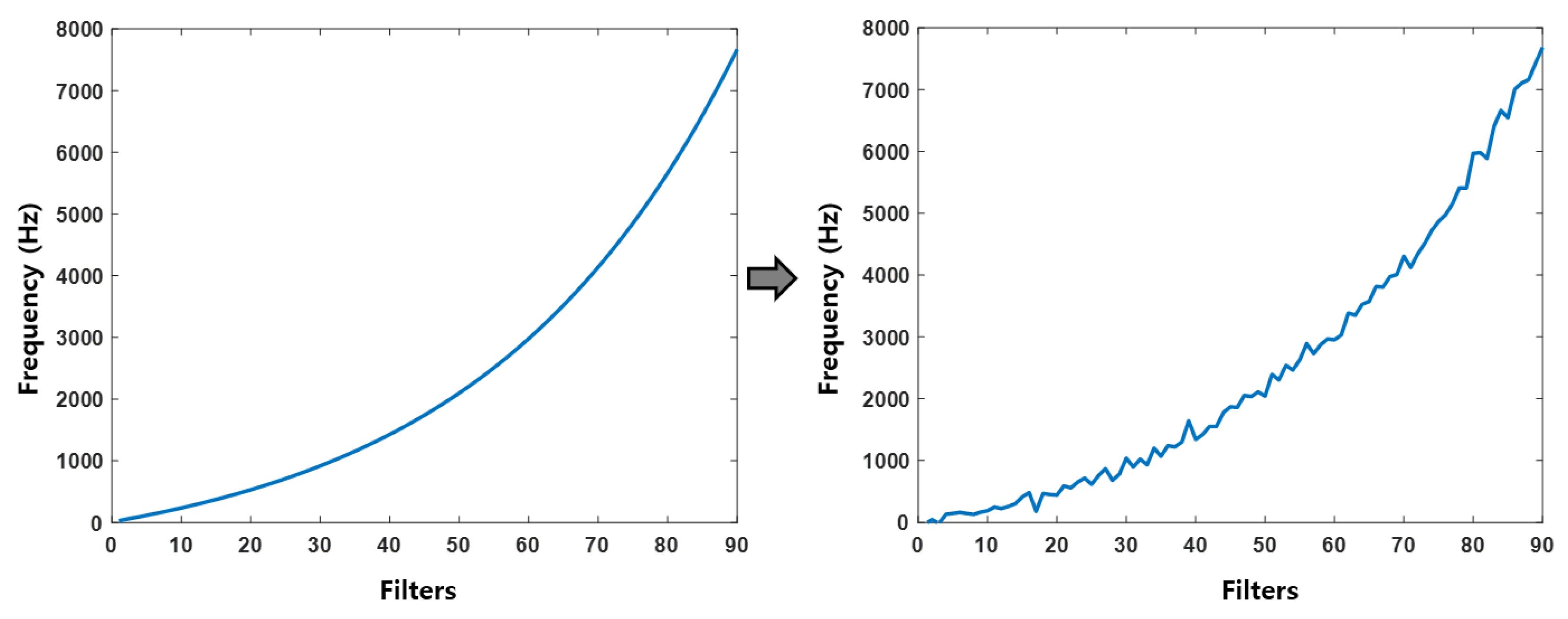
3.1. SincNet
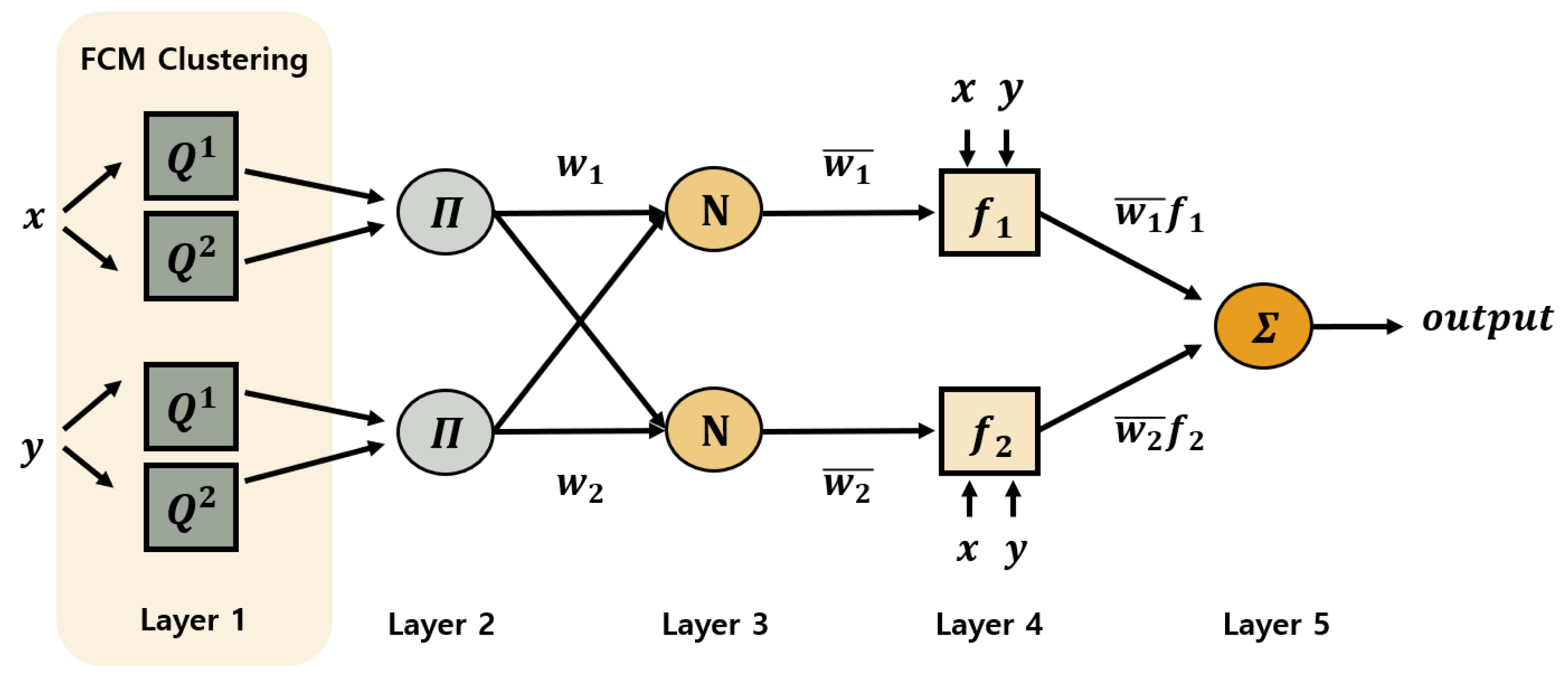
3.2. ANFIS
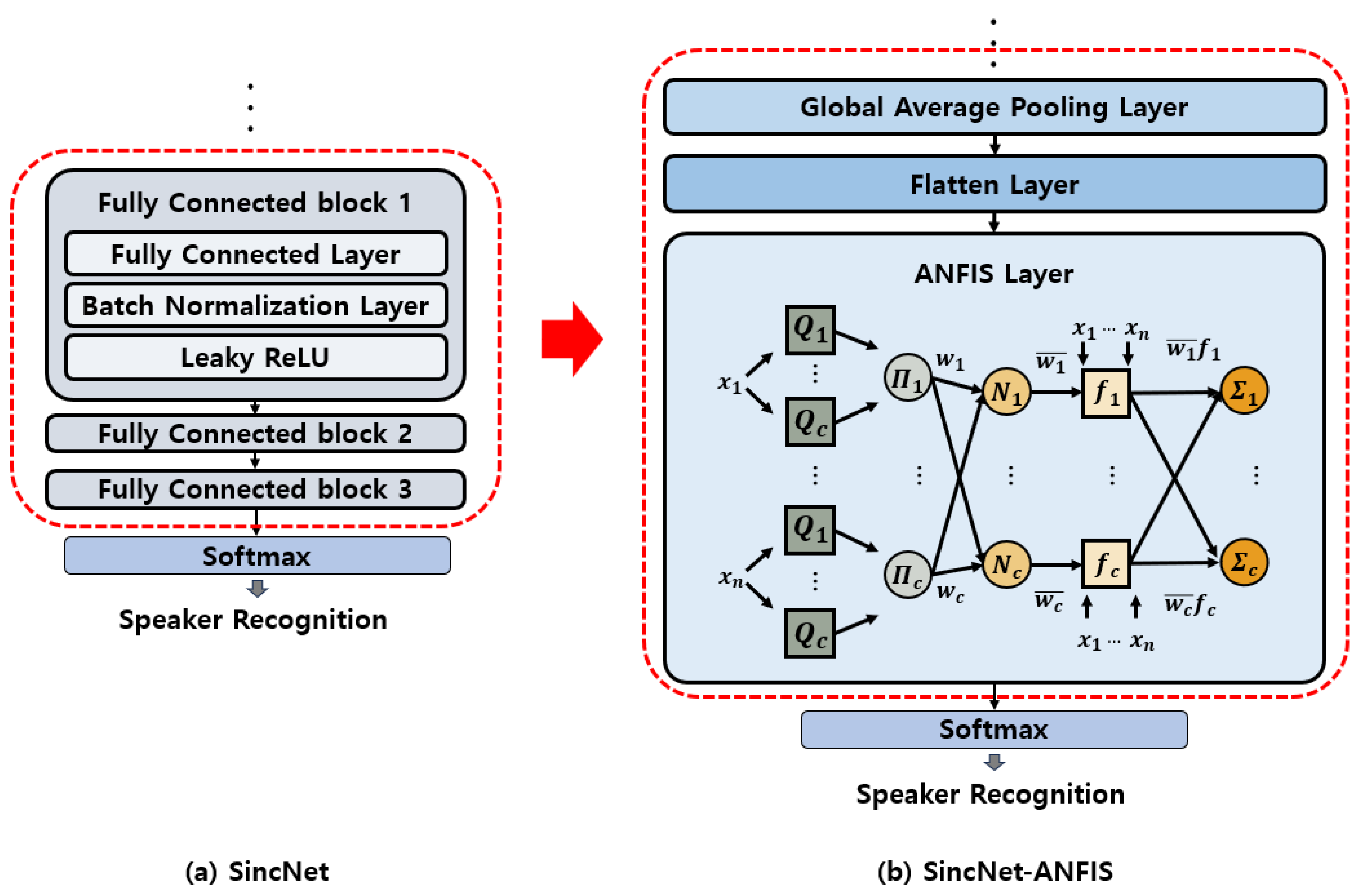
3.3. SincNet-ANFIS
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Database
4.2. Data Preprocessing
4.3. Experimental Setup
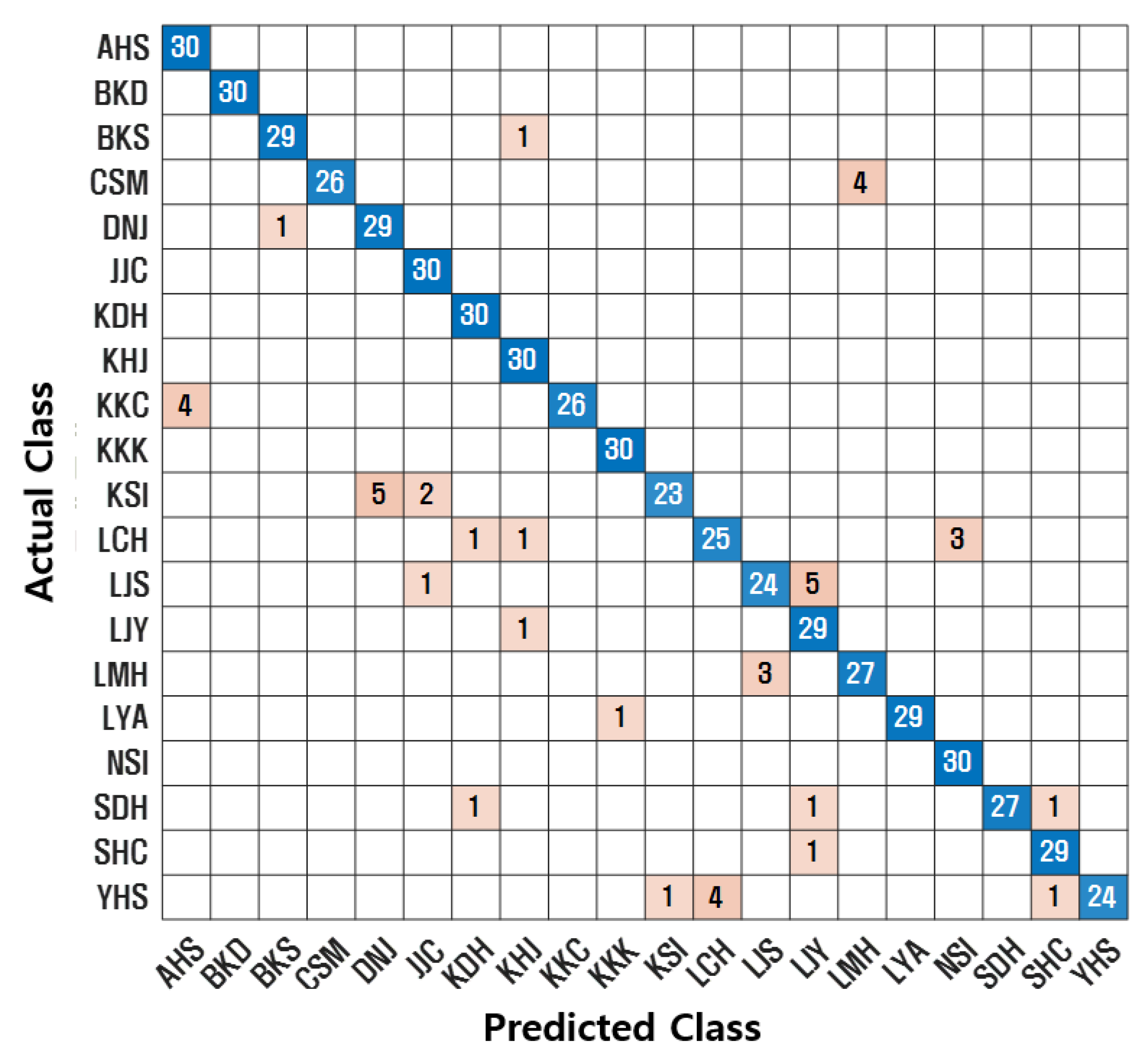
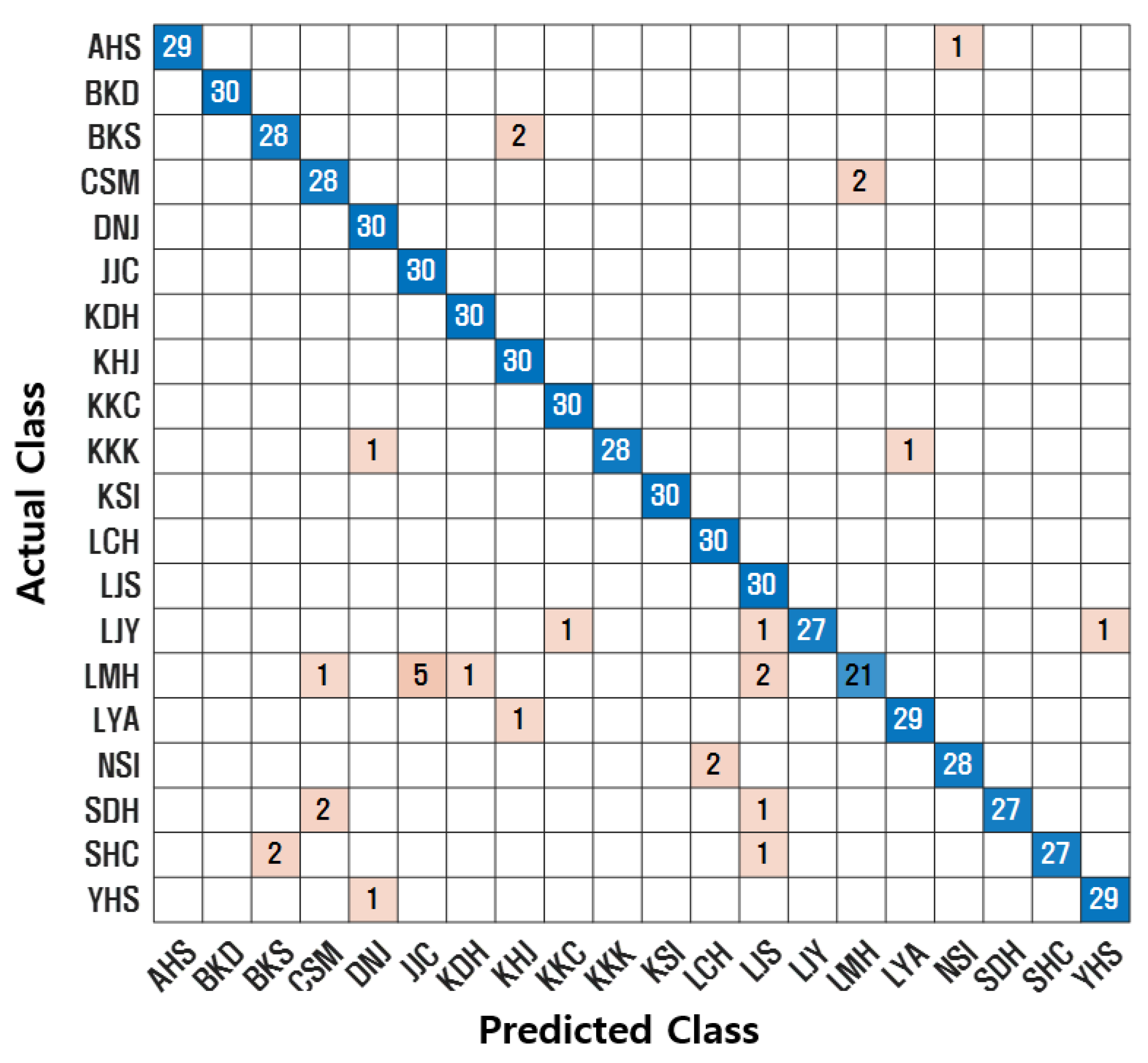
4.4. Experimental Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.-A.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Feng, H.-M.; Shen, P.-K.; Wu, Y.-C. Voice interaction recognition design in real-life scenario mobile robot applications. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artificial Intelligence Times. Personal Service Robots Armed with Artificial Intelligence. Global Market Expected to Reach 56 Trillion KRW by 2030. Available online: https://www.aitimes.kr/news/articleView.html?idxno=18582 (accessed on 6 December 2020).
- HouseHold Robot Market Outlook (2023 to 2033). (n.d.). Fact.MR. Available online: https://www.factmr.com/report/household-robot-market (accessed on 26 July 2025).
- Wang, W.; Seraj, F.; Meratnia, N.; Havinga, P.J. Speaker counting model based on transfer learning from SincNet bottleneck layer. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom), Austin, TX, USA, 23–27 March 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kozhirbayev, Z.; Erol, B.A.; Sharipbay, A.; Jamshidi, M. Speaker recognition for robotic control via an iot device. In Proceedings of the 2018 World Automation Congress (WAC), Stevenson, WA, USA, 3–6 June 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, I.-J.; Shi, J.-Y. Kinect microphone array-based speech and speaker recognition for the exhibition control of humanoid robots. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2017, 62, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuasikal, D.A.A.; Fakhrurroja, H.; Machbub, C. Voice activation using speaker recognition for controlling humanoid robot. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 8th International Conference on System Engineering and Technology (ICSET), Bandung, Indonesia, 15–16 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Saakshara, K.; Pranathi, K.; Gomathi, R.; Sivasangari, A.; Ajitha, P.; Anandhi, T. Speaker recognition system using Gaussian mixture model. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing (ICCSP), Chennai, India, 28–30 July 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Warohma, A.M.; Hindersah, H.; Lestari, D.P. Speaker Recognition Using MobileNetV3 for Voice-Based Robot Navigation. In Proceedings of the 2024 11th International Conference on Advanced Informatics: Concept, Theory and Application (ICAICTA), Singapore, 28–30 September 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kinnunen, T.; Li, H. An overview of text-independent speaker recognition: From features to supervectors. Speech Commun. 2010, 52, 12–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanelli, M.; Bengio, Y. Speaker recognition from raw waveform with sincnet. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT), Athens, Greece, 18–21 December 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-H.; Jo, A.-H.; Kwak, K.-C. SincNet-Based Speaker Identification for Robotic Environments with Varying Human–Robot Interaction Distance. Electronics 2024, 13, 4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, H.; Patino, J.; Todisco, M.; Nautsch, A.; Evans, N.; Larcher, A. End-to-end anti-spoofing with rawnet2. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.-W.; Heo, H.-S.; Kim, J.-H.; Shim, H.-J.; Yu, H.-J. Rawnet: Advanced end-to-end deep neural network using raw waveforms for text-independent speaker verification. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.08104. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.-W.; Kim, Y.; Heo, H.-S.; Lee, B.-J.; Kwon, Y.; Chung, J.S. Pushing the limits of raw waveform speaker recognition. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.08488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baevski, A.; Zhou, Y.; Mohamed, A.; Auli, M. wav2vec 2.0: A framework for self-supervised learning of speech representations. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 12449–12460. [Google Scholar]
- Ton-That, A.H.; Cao, N.T. Speech emotion recognition using a fuzzy approach. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 36, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar]
- Savchenko, A.V.; Savchenko, L.V. Savchenko. Towards the creation of reliable voice control system based on a fuzzy approach. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2015, 65, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnawazuddin, S.; Adiga, N.; Sai, B.T.; Ahmad, W.; Kathania, H.K. Developing speaker independent ASR system using limited data through prosody modification based on fuzzy classification of spectral bins. Digit. Signal Process. 2019, 93, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifi, F.; Hosseini, R.; Sharifi, A. Fuzzy deep learning for modeling uncertainty in character recognition using EEG signals. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 159, 111575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Ali, N.; Mishra, S.; Dandawate, A.; Tiwary, U.S. Deep fuzzy framework for emotion recognition using eeg signals and emotion representation in type-2 fuzzy vad space. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.07892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Su, W.; Wu, M.; Pedrycz, W.; Hirota, K. A fuzzy deep neural network with sparse autoencoder for emotional intention understanding in human–robot interaction. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 28, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadzadeh Nobari Azar, N.; Cavus, N.; Esmaili, P.; Sekeroglu, B.; Aşır, S. Detecting emotions through EEG signals based on modified convolutional fuzzy neural network. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baradaran, F.; Farzan, A.; Danishvar, S.; Sheykhivand, S. Automatic emotion recognition from EEG signals using a combination of type-2 fuzzy and deep convolutional networks. Electronics 2023, 12, 2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, C.F.; Quevedo, J.; Escandón, E.; Kiani, M.; Ding, W.; Andreu-Perez, J. Fuzzy temporal convolutional neural networks in P300-based Brain–computer interface for smart home interaction. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 117, 108359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, F.J. On the use of windows for harmonic analysis with the discrete Fourier transform. Proc. IEEE 2005, 66, 51–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbit, M. (Ed.) Digital Signal and Image Processing Using Matlab; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 666. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, J.-S.R. ANFIS: Adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1993, 23, 665–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezdek, J.C. Pattern Recognition with Fuzzy Objective Function Algorithms; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, K.C.; Kim, H.J.; Bae, K.S.; Yoon, H.S. Speaker identification and verification for intelligent service robots. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artifical Intelligence (ICAI), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25–28 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Desplanques, B.; Thienpondt, J.; Demuynck, K. Ecapa-tdnn: Emphasized channel attention, propagation and aggregation in tdnn based speaker verification. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.07143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaessen, N.; Van Leeuwen, D.A. Fine-tuning wav2vec2 for speaker recognition. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 23–27 May 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tanveer, M.; Sajid, M.; Akhtar, M.; Quadir, A.; Goel, T.; Aimen, A.; Mitra, S.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Lin, C.T.; Del Ser, J. Fuzzy deep learning for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: Approaches and challenges. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2024, 32, 5477–5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X. The fusion of deep learning and fuzzy systems: A state-of-the-art survey. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 30, 2783–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Training Data | Test Data | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Data | 1200 | 600 |
| Speech Duration | 40 m 34 s | 21 m 44 s |
| Training Data | Test Data | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Before Preprocessing | 1200 | 600 | |
| After Preprocessing | With Silence | 15,800 | 8464 |
| Without Silence | 11,984 | 6838 | |
| Experimental Setup | ||
|---|---|---|
| Hardware | GPU | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060 Ti |
| RAM | 64.0 GB | |
| CPU | 12th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-12700F 2.10 GHz | |
| Software | OS | Windows 11 Education |
| Programming Language | MATLAB R2024b | |
| Parameters | Optimizer | Mini-Batch Size | Learning Rate | Epochs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Values | Adam | 256 | 0.001 | 900 |
| Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|
| With Silence | Without Silence | |
| CNN | 92.00% | 91.00% |
| CNN-ANFIS | 90.83% | 95.17% |
| SincNet | 92.17% | 92.83% |
| SincNet-ANFIS | 94.50% | 96.00% |
| Number of Rules | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 93.17% | 93.33% | 94.67% | 94.50% | 96.00% | 93.17% | 95.33% |
| 1 m | 2 m | 3 m | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | 85.86% | 94.00% | 93.00% |
| CNN-ANFIS | 94.21% | 95.00% | 96.00% |
| SincNet [12] | 88.42% | 96.00% | 94.40% |
| SincNet-ANFIS | 91.90% | 98.50% | 97.50% |
| Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | 91.00% | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 |
| CNN-ANFIS | 95.17% | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 |
| SincNet [12] | 92.83% | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.93 |
| SincNet-ANFIS | 96.00% | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.-H.; Kim, T.-W.; Kwak, K.-C. Speaker Recognition Based on the Combination of SincNet and Neuro-Fuzzy for Intelligent Home Service Robots. Electronics 2025, 14, 3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183581
Kim S-H, Kim T-W, Kwak K-C. Speaker Recognition Based on the Combination of SincNet and Neuro-Fuzzy for Intelligent Home Service Robots. Electronics. 2025; 14(18):3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183581
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Seo-Hyun, Tae-Wan Kim, and Keun-Chang Kwak. 2025. "Speaker Recognition Based on the Combination of SincNet and Neuro-Fuzzy for Intelligent Home Service Robots" Electronics 14, no. 18: 3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183581
APA StyleKim, S.-H., Kim, T.-W., & Kwak, K.-C. (2025). Speaker Recognition Based on the Combination of SincNet and Neuro-Fuzzy for Intelligent Home Service Robots. Electronics, 14(18), 3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183581








