All’s Well That FID’s Well? Result Quality and Metric Scores in GAN Models for Lip-Synchronization Tasks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Wasserstein GAN
L1WGAN-GP
4. Datasets and Metrics
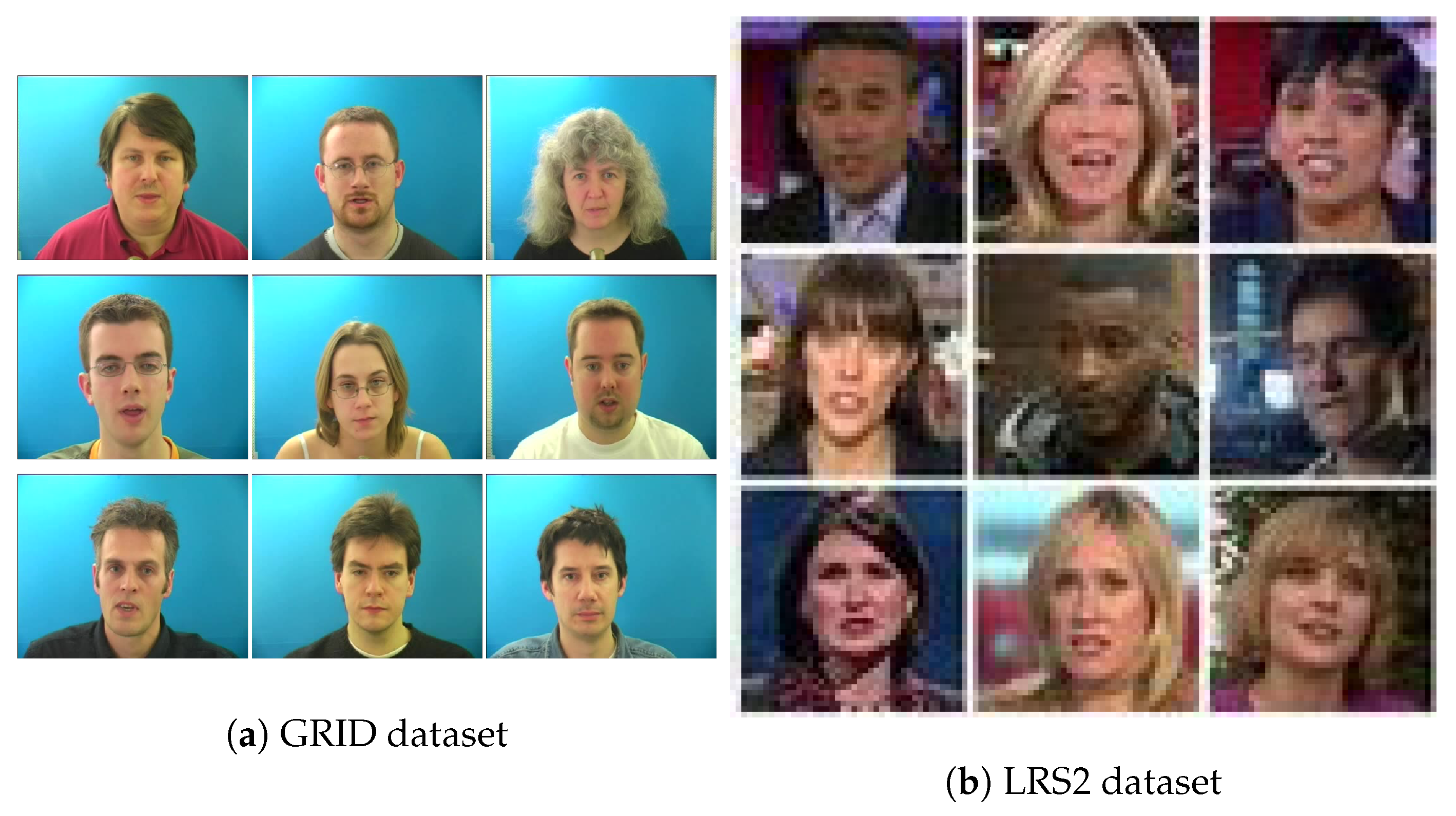
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Metrics
5. Experiment Overview
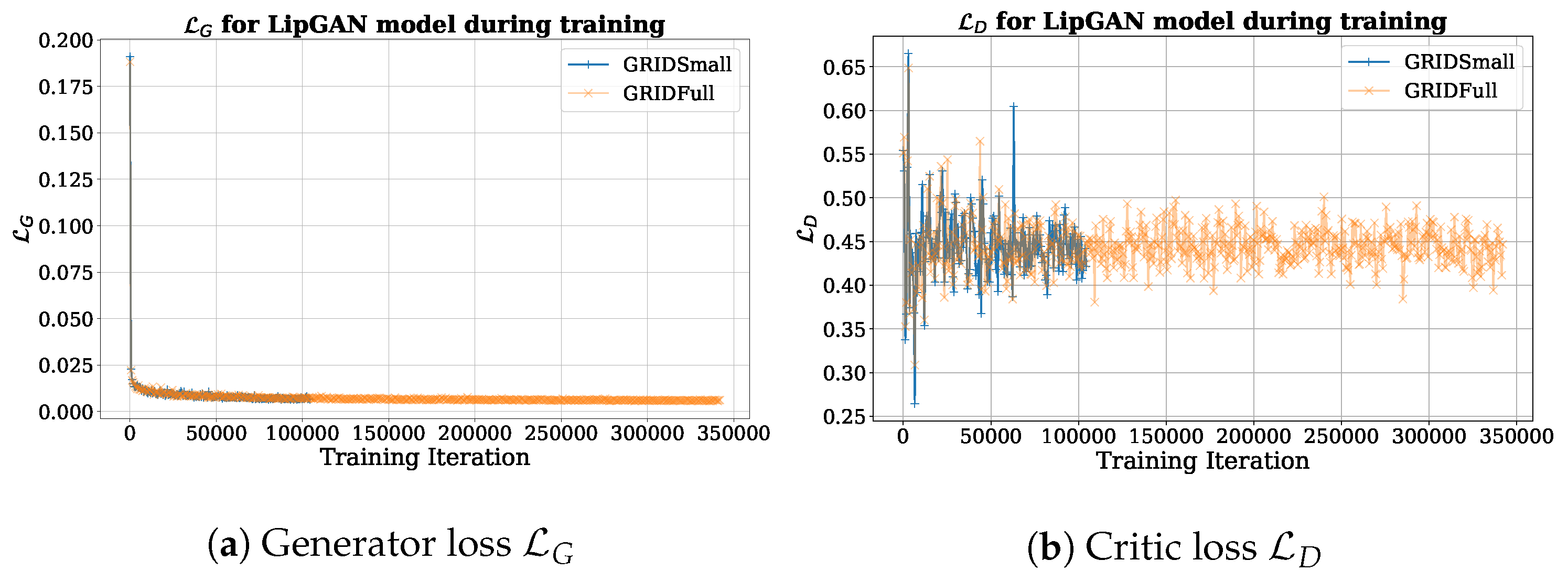
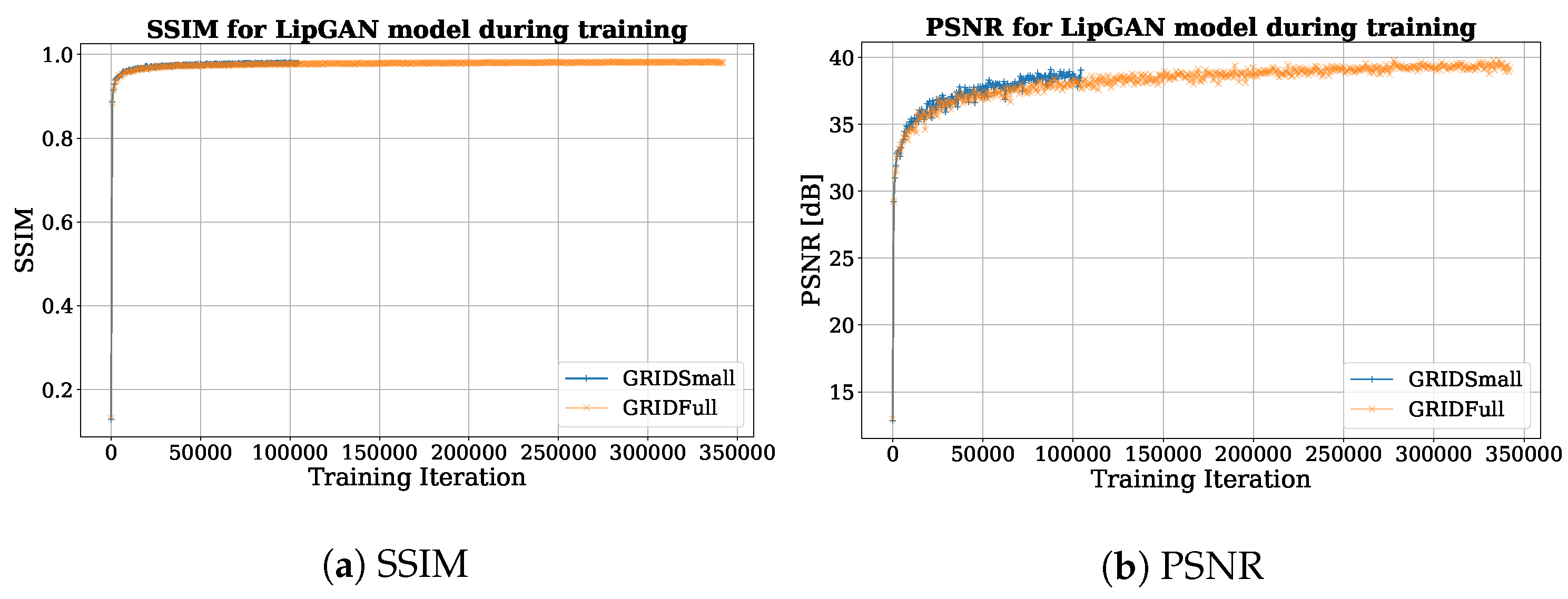
5.1. LipGAN
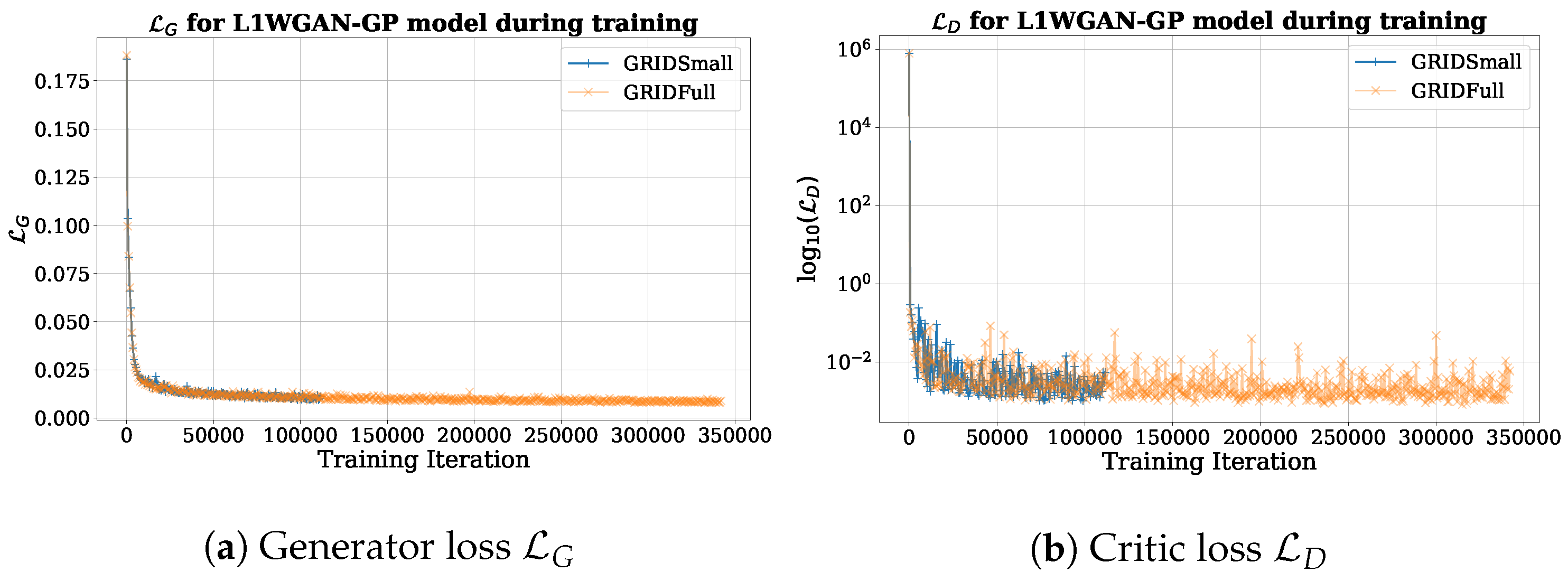
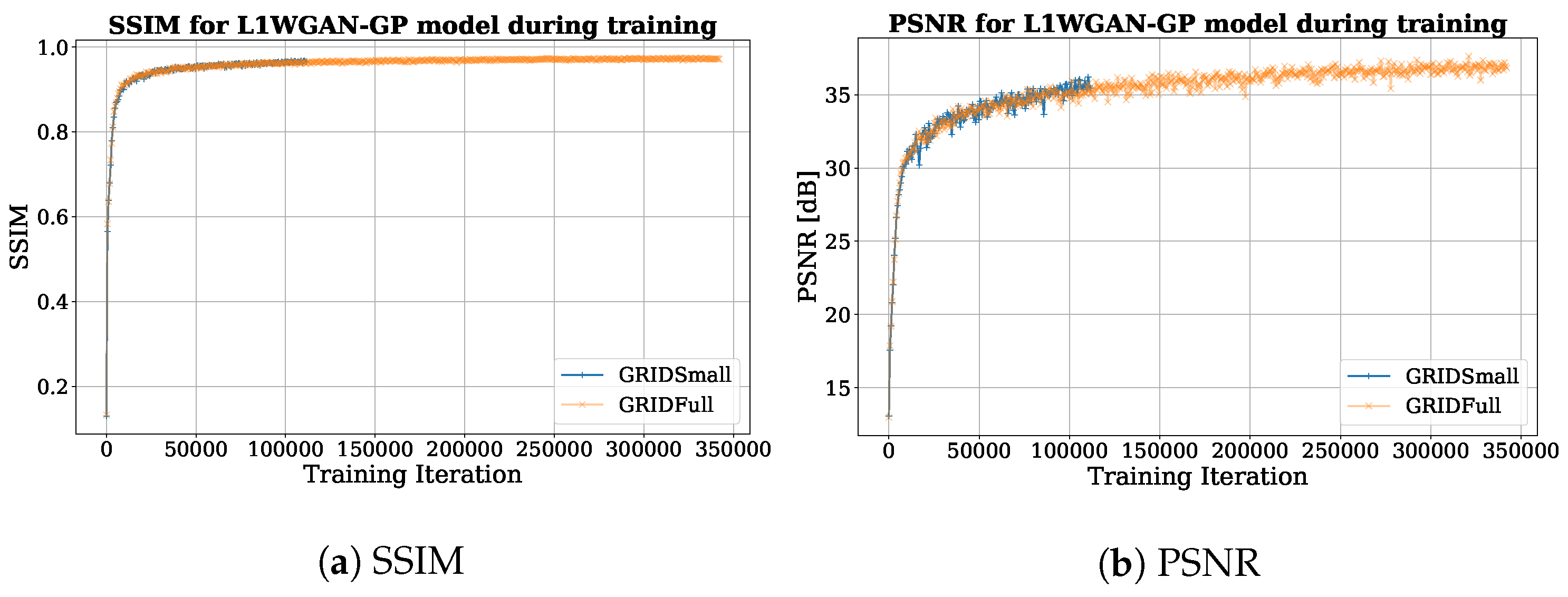
5.2. Experiments with L1WGAN-GP
6. Results
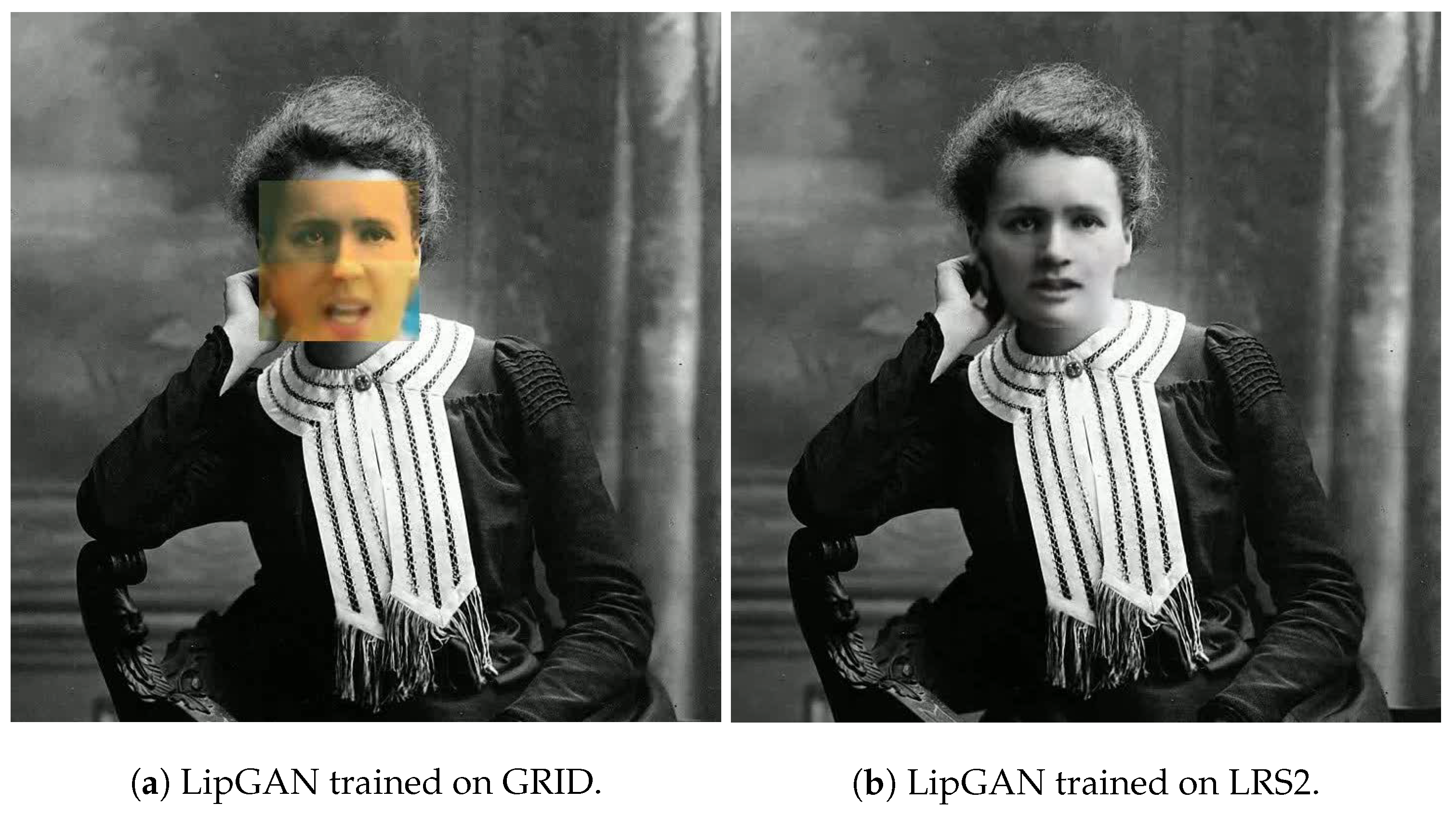
6.1. Dataset Impact on LipGAN
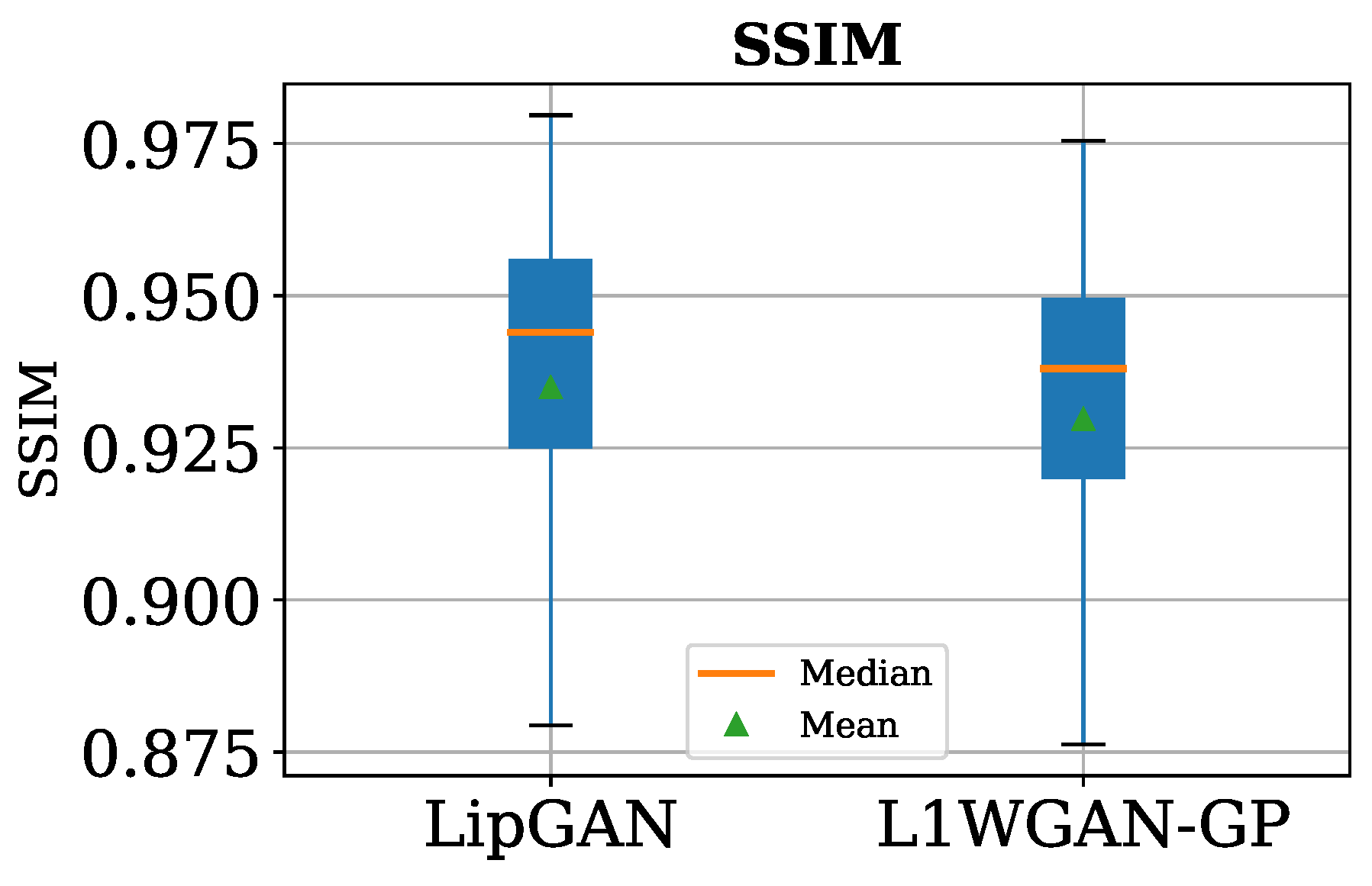
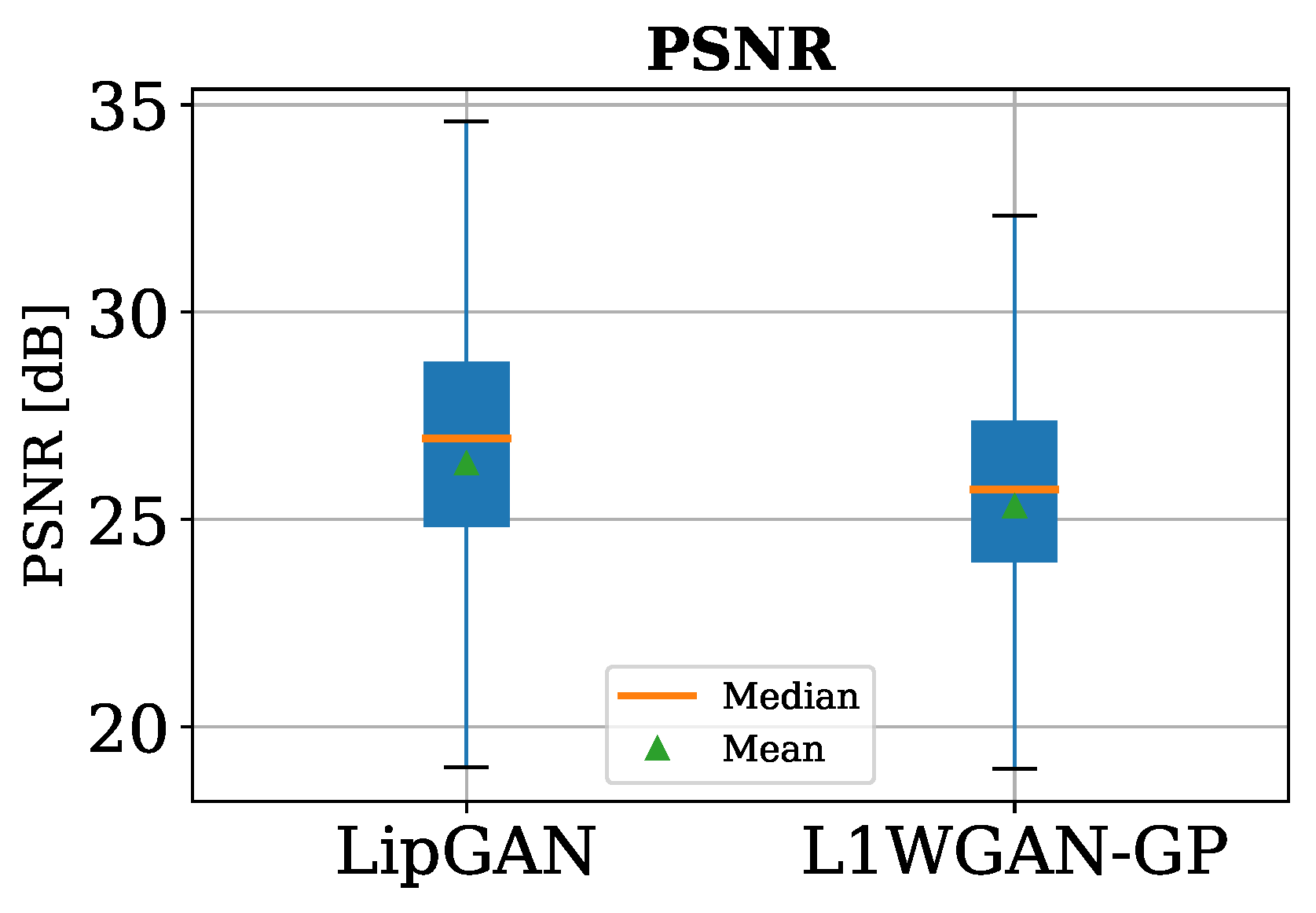
6.2. FID, SSIM, and PSNR Scores
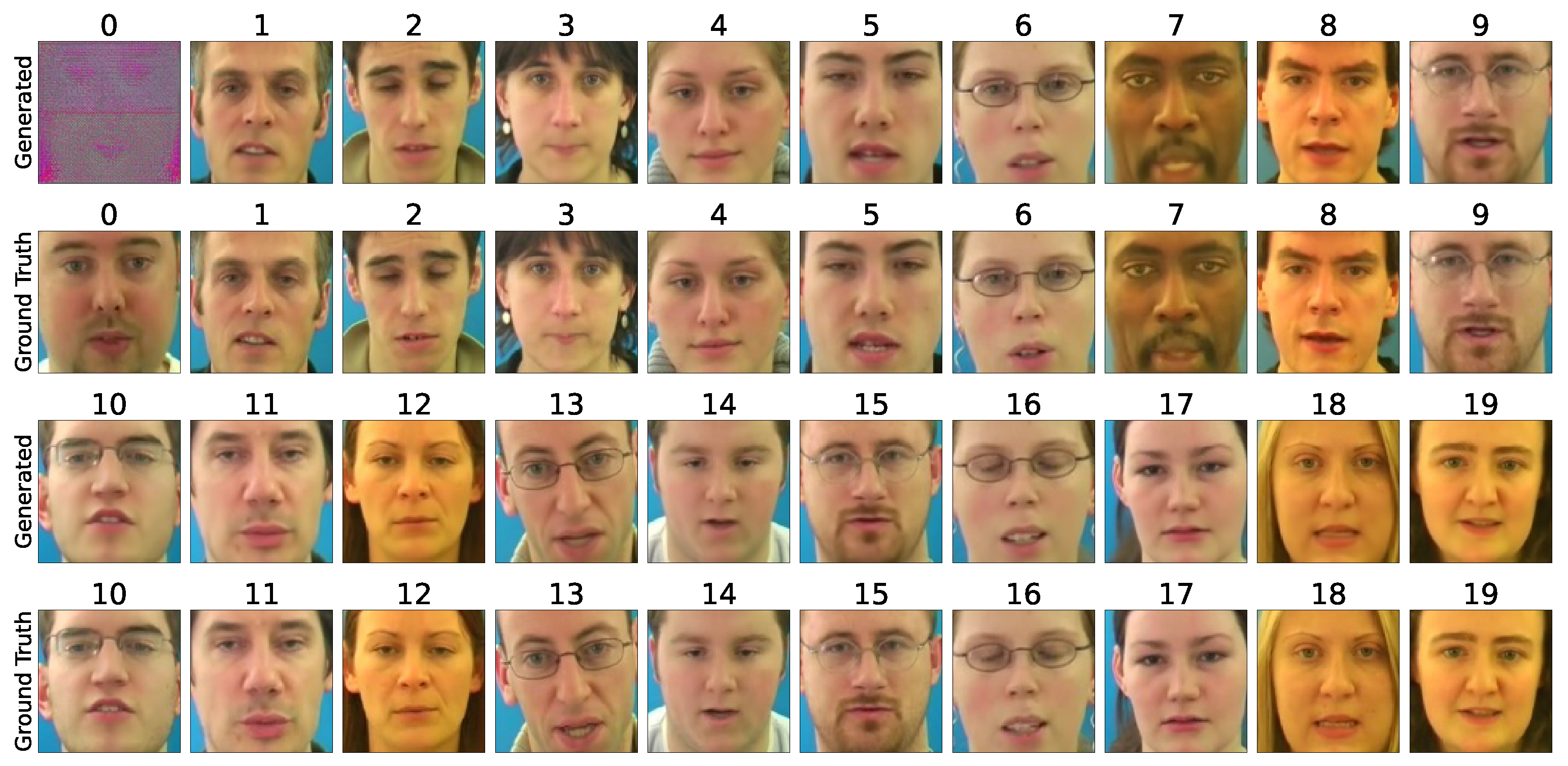
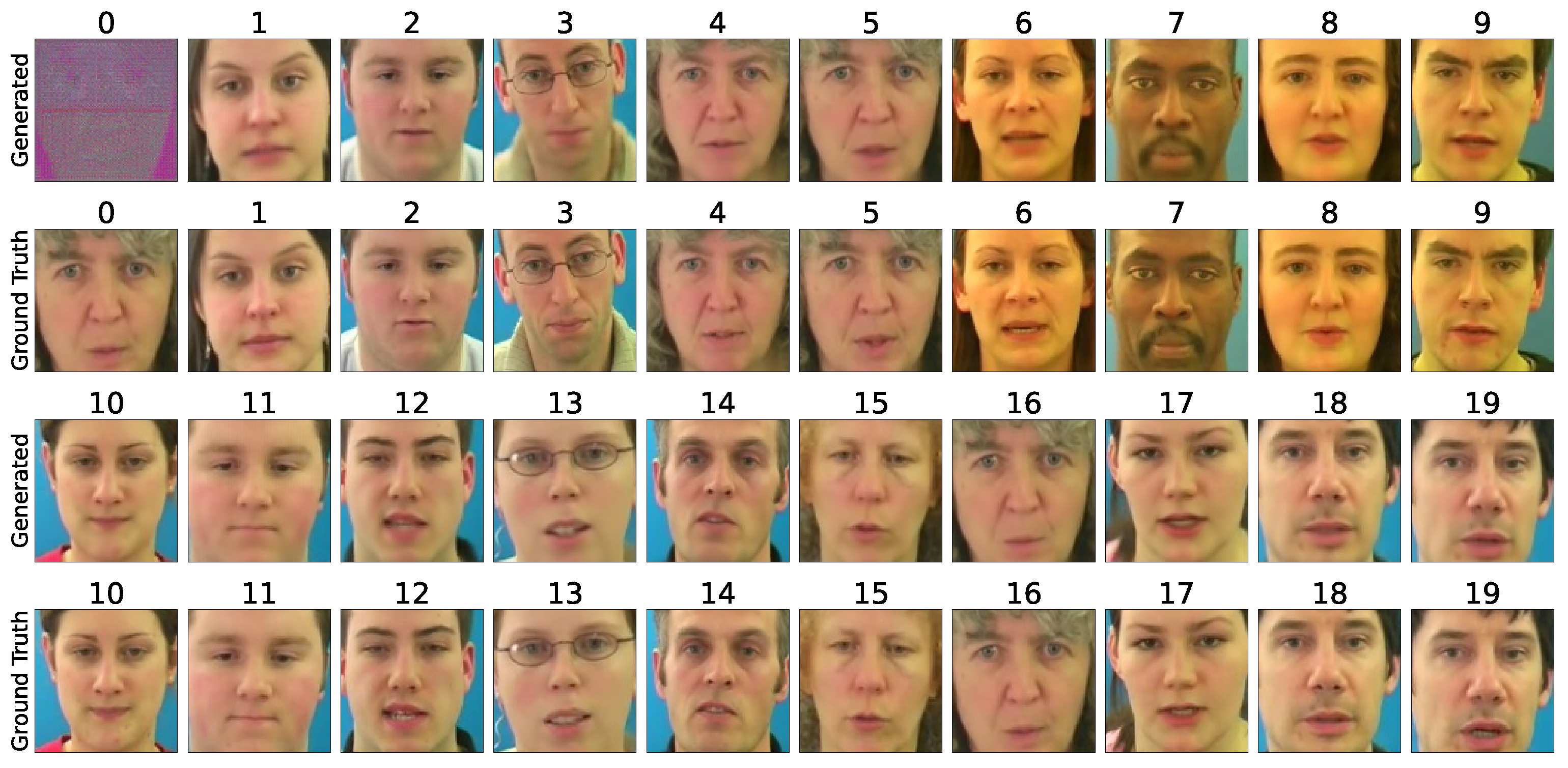
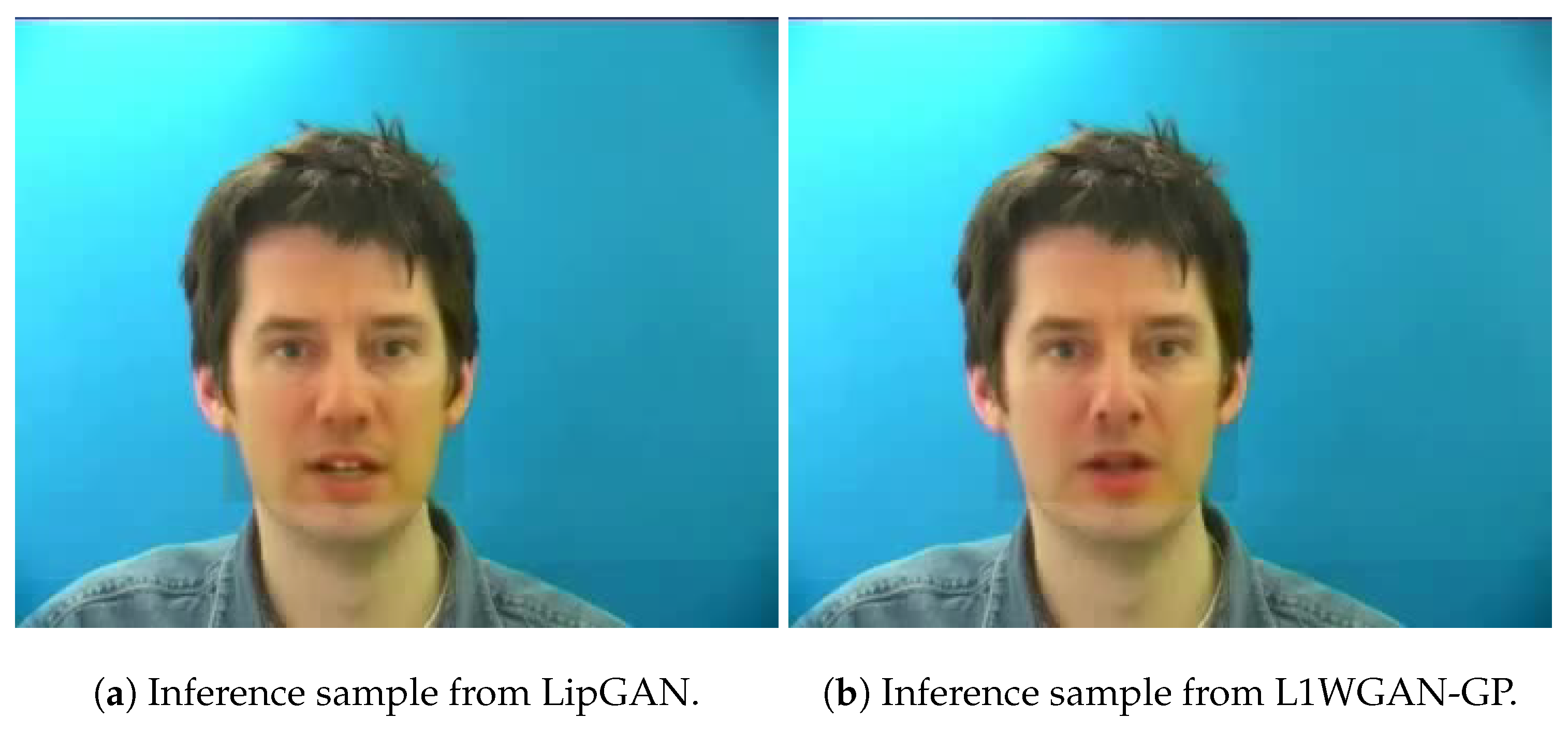
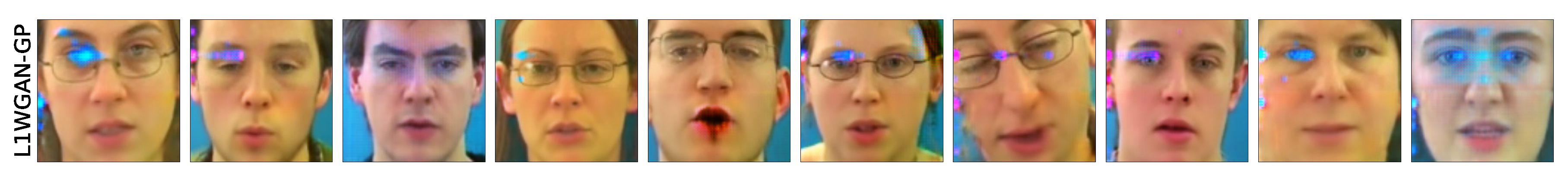
6.3. Qualitative Comparison
7. Conclusions and Outlook
8. Responsible AI Considerations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simons, A.; Cox, S. Generation of Mouthshape for a Synthetic Talking Head. In Proceedings of the Institute of Acoustics, 1990. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/243634521 (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Tan, S.; Ji, B.; Bi, M.; Pan, Y. Edtalk: Efficient disentanglement for emotional talking head synthesis. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 398–416. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Xu, W.; Lin, J.; Xie, J.; Feng, W.; Peng, B.; Chen, C.; Xing, W. LatentSync: Taming Audio-Conditioned Latent Diffusion Models for Lip Sync with SyncNet Supervision. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.09262. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.; Ji, C.; Xu, S.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, B.; Bo, L. Chatanyone: Stylized real-time portrait video generation with hierarchical motion diffusion model. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.21144. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Hu, J.; Liang, J.; Lin, G.; Chen, J.; Li, K.; Meng, Y. Sayanything: Audio-driven lip synchronization with conditional video diffusion. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.11515. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Liu, M.; Chen, Z.; Wu, B.; Zeng, Y.; Zhan, C.; He, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhou, W. MuseTalk: Real-Time High-Fidelity Video Dubbing via Spatio-Temporal Sampling. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.10122. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, G.; Ma, Z.; Li, Y.; Jing, J.; Yang, J.; Miao, Q. FaceEditTalker: Interactive Talking Head Generation with Facial Attribute Editing. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.22141. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Cho, J.; Park, J.; Hwang, S.; Kim, D.E.; Kim, G.; Yu, Y. DEEPTalk: Dynamic Emotion Embedding for Probabilistic Speech-Driven 3D Face Animation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 25 February–4 March 2025; Volume 39, pp. 4275–4283. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Ahn, J.; Kwak, D.; Yang, H.S.; Ju, Y.C.; Kim, I.H.; Kim, B.Y.; Chung, J.S. Faces that speak: Jointly synthesising talking face and speech from text. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 8818–8828. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Suri, S.; Gadde, R.T.; Shrivastava, A. Diff2lip: Audio conditioned diffusion models for lip-synchronization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024; pp. 5292–5302. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W. Enhancing Video Conferencing Experience through Speech Activity Detection and Lip Synchronization with Deep Learning Models. J. Comput. Technol. Appl. Math. 2025, 2, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Tang, S.; Wan, P.; Zhang, D.; Liu, H.; He, J. Omnisync: Towards universal lip synchronization via diffusion transformers. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.21448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Li, Z. VividWav2Lip: High-fidelity facial animation generation based on speech-driven lip synchronization. Electronics 2024, 13, 3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Alwan, A.; Keating, P.A.; Auer, E.T., Jr.; Bernstein, L.E. On the relationship between face movements, tongue movements, and speech acoustics. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2002, 2002, 506945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, C.L.; Park, H.; Hauswald, A.; Weisz, N. Neural speech tracking highlights the importance of visual speech in multi-speaker situations. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2024, 36, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thies, J.; Zollhofer, M.; Stamminger, M.; Theobalt, C.; Nießner, M. Face2face: Real-time face capture and reenactment of rgb videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2387–2395. [Google Scholar]
- Alshahrani, M.H.; Maashi, M.S. A Systematic Literature Review: Facial Expression and Lip Movement Synchronization of an Audio Track. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 75220–75237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, A.; Rane, S.; Mishra, A.K.; Sahu, S.K.; Singh, S.; Pathak, S.K. A Survey of Audio Synthesis and Lip-syncing for Synthetic Video Generation. EAI Endorsed Trans. Creat. Technol. 2021, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Liu, Z.Q. Realistic mouth-synching for speech-driven talking face using articulatory modelling. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2007, 9, 500–510. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Qian, X.; Han, W.; Soong, F.K. Synthesizing photo-real talking head via trajectory-guided sample selection. In Proceedings of the Eleventh Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Chiba, Japan, 26–30 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Llorach, G.; Evans, A.; Blat, J.; Grimm, G.; Hohmann, V. Web-based live speech-driven lip-sync. In Proceedings of the 2016 8th International Conference on Games and Virtual Worlds for Serious Applications (VS-GAMES), Barcelona, Spain, 7–9 September 2016; IEEE: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, B.; Wang, L.; Soong, F.K.; Xie, L. Photo-real talking head with deep bidirectional LSTM. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), South Brisbane, Australia, 19–24 April 2015; IEEE: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 4884–4888. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Yeh, R.A.; Tang, X.; Liu, Y.; Agarwala, A. Video frame synthesis using deep voxel flow. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4463–4471. [Google Scholar]
- Wiles, O.; Koepke, A.; Zisserman, A. X2face: A network for controlling face generation using images, audio, and pose codes. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 670–686. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, F.T.; Zhang, L.; Shen, L.; Xu, D. Depth-aware generative adversarial network for talking head video generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 3397–3406. [Google Scholar]
- Bounareli, S.; Tzelepis, C.; Argyriou, V.; Patras, I.; Tzimiropoulos, G. One-shot neural face reenactment via finding directions in gan’s latent space. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2024, 132, 3324–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Liu, K.; Chen, L.; Yao, J.; Liu, Q.; Lv, D. Audio-driven high-resolution seamless talking head video editing via stylegan. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 15–19 July 2024; IEEE: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zia, R.; Rehman, M.; Hussain, A.; Nazeer, S.; Anjum, M. Improving synthetic media generation and detection using generative adversarial networks. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2024, 10, e2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthel, F.; Morgenstern, W.; Hinzer, P.; Hilsmann, A.; Eisert, P. CGS-GAN: 3D Consistent Gaussian Splatting GANs for High Resolution Human Head Synthesis. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.17590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doukas, M.C.; Zafeiriou, S.; Sharmanska, V. Headgan: One-shot neural head synthesis and editing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 14398–14407. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, F.; Xie, Y.; Li, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, H.; Liu, Z.; Yao, W.; Ren, F.; Yu, F.R.; et al. A review of human emotion synthesis based on generative technology. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2025; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwajanakorn, S.; Seitz, S.M.; Kemelmacher-Shlizerman, I. Synthesizing Obama: Learning lip sync from audio. ACM Trans. Graph. (ToG) 2017, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Sotelo, J.; Kumar, K.; de Brebisson, A.; Bengio, Y. ObamaNet: Photo-realistic lip-sync from text. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1801.01442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaludin, A.; Chung, J.S.; Zisserman, A. You said that?: Synthesising talking faces from audio. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2019, 127, 1767–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajwal, K.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Namboodiri, V.P.; Jawahar, C. A lip sync expert is all you need for speech to lip generation in the wild. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 484–492. [Google Scholar]
- Afouras, T.; Chung, J.S.; Senior, A.; Vinyals, O.; Zisserman, A. Deep Audio-visual Speech Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 4, 8717–8727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prajwal, K.R.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Jerin, P.; Abhishek, J.; Namboodiri, V.; Jawahar, C.V. Towards Automatic Face-to-Face Translation. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019; MM ’19. pp. 1428–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, M.; Hong, J.; Choi, J.; Ro, Y.M. Synctalkface: Talking face generation with precise lip-syncing via audio-lip memory. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual, 22 February–1 March 2022; Volume 36, pp. 2062–2070. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Liu, Y.; Xing, J.; Wang, W.; Sun, M.; Dan, J.; Huang, T.; Li, S.; Cheng, Z.Q.; Tai, Y.; et al. Facechain-imagineid: Freely crafting high-fidelity diverse talking faces from disentangled audio. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 1292–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.; Cun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, M.; Yin, F.; Zhu, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, N. Videoretalking: Audio-based lip synchronization for talking head video editing in the wild. In Proceedings of the SIGGRAPH Asia 2022 Conference Papers, Daegu, Republic of Korea, 6–9 December 2022; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S.; Ji, B.; Pan, Y. Flowvqtalker: High-quality emotional talking face generation through normalizing flow and quantization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 26317–26327. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Hu, P.; Wu, Y.; Lyu, X.; Cao, Y.P.; Shan, Y.; Yang, W.; Sun, Z.; Qi, X. Speech2lip: High-fidelity speech to lip generation by learning from a short video. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 22168–22177. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, J. Lipformer: High-fidelity and generalizable talking face generation with a pre-learned facial codebook. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 13844–13853. [Google Scholar]
- Aneja, S.; Thies, J.; Dai, A.; Nießner, M. Facetalk: Audio-driven motion diffusion for neural parametric head models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 21263–21273. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Li, L.; Ding, Y.; Fan, C.; Yu, X. Audio2head: Audio-driven one-shot talking-head generation with natural head motion. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.09293. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, X.; Fried, O.; Fatahalian, K.; Agrawala, M. Iterative text-based editing of talking-heads using neural retargeting. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2021, 40, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Luo, P.; Wang, X. Talking face generation by adversarially disentangled audio-visual representation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 9299–9306. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.S.; Jamaludin, A.; Zisserman, A. You said that? arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.02966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Li, Z.; Maddox, R.K.; Duan, Z.; Xu, C. Lip movements generation at a glance. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 520–535. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Stypułkowski, M.; Vougioukas, K.; He, S.; Zięba, M.; Petridis, S.; Pantic, M. Diffused heads: Diffusion models beat gans on talking-face generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024; pp. 5091–5100. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Fan, X.; Gao, H.; Chen, Z.; Chang, P.; Han, M.; Hasegawa-Johnson, M. SyncDiff: Diffusion-Based Talking Head Synthesis with Bottlenecked Temporal Visual Prior for Improved Synchronization. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Tucson, AZ, USA, 26 February–6 March 2025; IEEE: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 4554–4563. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Li, T.; Zheng, R.; Yang, M.; Chen, J.; Yang, M. Ditto: Motion-space diffusion for controllable realtime talking head synthesis. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.19509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Lin, L.; Liu, C.; Xia, P.; Hu, P.; Ma, J.; Du, J.; Pan, J. DAWN: Dynamic Frame Avatar with Non-autoregressive Diffusion Framework for Talking Head Video Generation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.13726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, A.; Alonso, E.; Mondragón, E. DiT-Head: High Resolution Talkin Head Synthesis using Diffusion Transformers. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence, Rome, Italy, 24–26 February 2024; Volume 3, pp. 159–169. [Google Scholar]
- Chopin, B.; Dhamija, T.; Balaji, P.; Wang, Y.; Dantcheva, A. Dimitra: Audio-driven Diffusion model for Expressive Talking Head Generation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.17198. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Zhu, X.; Qi, G.; Qian, C.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, Z. Diffspeaker: Speech-driven 3d facial animation with diffusion transformer. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.05712. [Google Scholar]
- Rakesh, V.K.; Mazumdar, S.; Maity, R.P.; Pal, S.; Das, A.; Samanta, T. Advancing Talking Head Generation: A Comprehensive Survey of Multi-Modal Methodologies, Datasets, Evaluation Metrics, and Loss Functions. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.02900. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, H.; Luo, X.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, X.; Dai, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Yang, J.; et al. Human motion video generation: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2025; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Han, X.; Shechtman, E.; Echevarria, J.; Kalogerakis, E.; Li, D. Makelttalk: Speaker-aware talking-head animation. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2020, 39, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Sun, Y.; Wu, W.; Loy, C.C.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z. Pose-controllable talking face generation by implicitly modularized audio-visual representation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 4176–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Cun, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, X.; Guo, Y.; Shan, Y.; Wang, F. Sadtalker: Learning realistic 3d motion coefficients for stylized audio-driven single image talking face animation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and PATTERN Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 8652–8661. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, F.; Zhang, Y.; Cun, X.; Cao, M.; Fan, Y.; Wang, X.; Bai, Q.; Wu, B.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y. Styleheat: One-shot high-resolution editable talking face generation via pre-trained stylegan. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 85–101. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Huang, G.; Yuan, Y.; Guo, C.; Sun, Y.; Wu, F.; Weinberger, K. An empirical study on evaluation metrics of generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.07755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjovsky, M.; Chintala, S.; Bottou, L. Wasserstein generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 214–223. [Google Scholar]
- Villani, C. Optimal Transport: Old and New; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 338. [Google Scholar]
- Gulrajani, I.; Ahmed, F.; Arjovsky, M.; Dumoulin, V.; Courville, A.C. Improved training of wasserstein gans. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pinetz, T.; Soukup, D.; Pock, T. On the estimation of the Wasserstein distance in generative models. In Proceedings of the German Conference on Pattern Recognition, Konstanz, Germany, 27–30 September 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 156–170. [Google Scholar]
- Miyato, T.; Kataoka, T.; Koyama, M.; Yoshida, Y. Spectral normalization for generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.05957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimans, T.; Goodfellow, I.; Zaremba, W.; Cheung, V.; Radford, A.; Chen, X. Improved techniques for training gans. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cooke, M.; Barker, J.; Cunningham, S.; Shao, X. An audio-visual corpus for speech perception and automatic speech recognition. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 120, 2421–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurach, K.; Lucic, M.; Zhai, X.; Michalski, M.; Gelly, S. A Large-Scale Study on Regularization and Normalization in GANs. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1807.04720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, M.J.; Forsyth, D. Effectively unbiased fid and inception score and where to find them. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 6070–6079. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, C.; Gao, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhai, G.; Yang, X. A comparative study of perceptual quality metrics for audio-driven talking head videos. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 27–30 October 2024; IEEE: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1218–1224. [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen, J.; You, J. Peak signal-to-noise ratio revisited: Is simple beautiful? In Proceedings of the 2012 Fourth International Workshop on Quality of Multimedia Experience, Melbourne, Australia, 5–7 July 2012; IEEE: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 37–38. [Google Scholar]
- Hore, A.; Ziou, D. Image quality metrics: PSNR vs. SSIM. In Proceedings of the 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Istanbul, Turkey, 23–26 August 2010; IEEE: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 2366–2369. [Google Scholar]
- Avcıbaş, I.s.; Sankur, B.l.; Sayood, K. Statistical evaluation of image quality measures. J. Electron. Imaging 2002, 11, 206–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusel, M.; Ramsauer, H.; Unterthiner, T.; Nessler, B.; Hochreiter, S. Gans trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local nash equilibrium. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vougioukas, K.; Petridis, S.; Pantic, M. Realistic speech-driven facial animation with gans. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 128, 1398–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, M.; Viswanathan, M. Measuring speech quality for text-to-speech systems: Development and assessment of a modified mean opinion score (MOS) scale. Comput. Speech Lang. 2005, 19, 55–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streijl, R.C.; Winkler, S.; Hands, D.S. Mean opinion score (MOS) revisited: Methods and applications, limitations and alternatives. Multimed. Syst. 2016, 22, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piferi, F. CHATCARE: An Emotional-Aware Conversational Agent for Assisted Therapy; POLITesi—Politecnico di Milano: Milan, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mensio, M.; Rizzo, G.; Morisio, M. The rise of emotion-aware conversational agents: Threats in digital emotions. In Proceedings of the Companion Proceedings of the The Web Conference 2018, Lyon, France, 23–27 April 2018; pp. 1541–1544. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Lin, J.; Yang, Z.; Qing, C.; Lin, L. Learning adaptive spatial coherent correlations for speech-preserving facial expression manipulation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 7267–7276. [Google Scholar]
- Mirsky, Y.; Lee, W. The creation and detection of deepfakes: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2021, 54, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kietzmann, J.; Lee, L. Deepfakes: Trick or treat? Bus. Horizons 2020, 63, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Dang-Nguyen, D.T. Clipping the deception: Adapting vision-language models for universal deepfake detection. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, Phuket, Thailand, 10–14 June 2024; pp. 1006–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Yao, T.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, X.; Zhu, J.; Luo, D.; Wang, C.; Ding, S.; Wu, Y.; et al. Df40: Toward next-generation deepfake detection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 29387–29434. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, C.; Chen, B.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Rocha, A.; Kwong, S. Detect and locate: Exposing face manipulation by semantic-and noise-level telltales. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2022, 17, 1741–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Chen, G.; Guo, Y.X.; Yang, J.; Li, C.; Zang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, X.; Guo, B. Vasa-1: Lifelike audio-driven talking faces generated in real time. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 660–684. [Google Scholar]
- Rössler, A.; Cozzolino, D.; Verdoliva, L.; Riess, C.; Thies, J.; Nießner, M. FaceForensics++: Learning to detect manipulated facial images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Tolosana, R.; Vera-Rodriguez, R.; Fierrez, J.; Morales, A.; Ortega-Garcia, J. Deepfakes and beyond: A survey of face manipulation and fake detection. Inf. Fusion 2020, 64, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floridi, L.; Chiriatti, A. GPT-3: Its nature, scope, limits, and consequences. Minds Mach. 2020, 30, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.; Kraetzer, C.; Seidlitz, S.; Dittmann, J. Media Forensic Considerations of the Usage of Artificial Intelligence Using the Example of DeepFake Detection. J. Imaging 2024, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Data Attributes | |
|---|---|
| Input image horizontal/vertical dimension H | 96 |
| Frameshift time step | |
| Mel-frequency channels M | 80 |
| Mel-spectrogram time window T | 27 |
| Name | Type | Individual Samples | Videos per Speaker |
|---|---|---|---|
| GRIDSmall | Train | 670,758 | 300 |
| GRIDFull | Train | 2,190,517 | 980 |
| GRIDTest | Test | 44,589 | 20 |
| Model | FID Score ↓ |
|---|---|
| LipGAN | 15.11 |
| L1WGAN-GP | 14.49 |
| Model | Mean ↑ | Median ↑ | Max ↑ | Min ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LipGAN | 0.9348 | 0.9439 | 0.9796 | 0.7542 |
| L1WGAN-GP | 0.9296 | 0.9380 | 0.9754 | 0.7052 |
| Model | Mean [dB] ↑ | Median [dB] ↑ | Max [dB] ↑ | Min [dB] ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LipGAN | 26.34 | 26.96 | 35.35 | 13.67 |
| L1WGAN-GP | 25.32 | 25.72 | 34.84 | 12.81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geldhauser, C.; Liljegren, J.; Nordqvist, P. All’s Well That FID’s Well? Result Quality and Metric Scores in GAN Models for Lip-Synchronization Tasks. Electronics 2025, 14, 3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173487
Geldhauser C, Liljegren J, Nordqvist P. All’s Well That FID’s Well? Result Quality and Metric Scores in GAN Models for Lip-Synchronization Tasks. Electronics. 2025; 14(17):3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173487
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeldhauser, Carina, Johan Liljegren, and Pontus Nordqvist. 2025. "All’s Well That FID’s Well? Result Quality and Metric Scores in GAN Models for Lip-Synchronization Tasks" Electronics 14, no. 17: 3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173487
APA StyleGeldhauser, C., Liljegren, J., & Nordqvist, P. (2025). All’s Well That FID’s Well? Result Quality and Metric Scores in GAN Models for Lip-Synchronization Tasks. Electronics, 14(17), 3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173487






