Recent Progress on Eye-Tracking and Gaze Estimation for AR/VR Applications: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Classification of Gaze Estimation
2.1. Gaze Target Estimation
2.2. Gaze Point Estimation
3. Evaluation Metrics and Datasets
3.1. Performance Metrics and Error Sources
3.1.1. Head Posture
3.1.2. Blinking, Occlusion, and Illumination
3.1.3. Inter-Subject Variability
3.2. Dataset Limitations and Domain Generalization
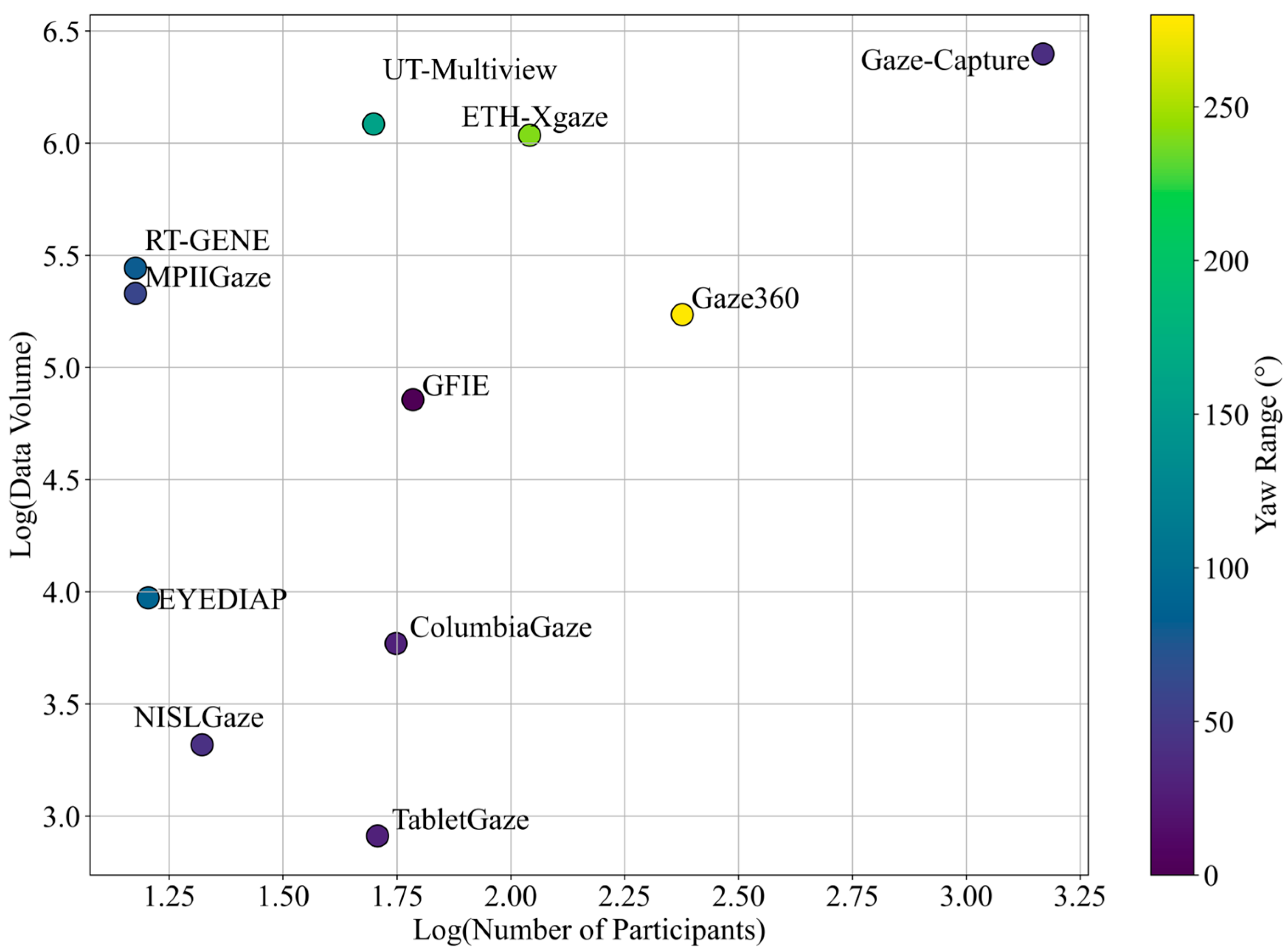
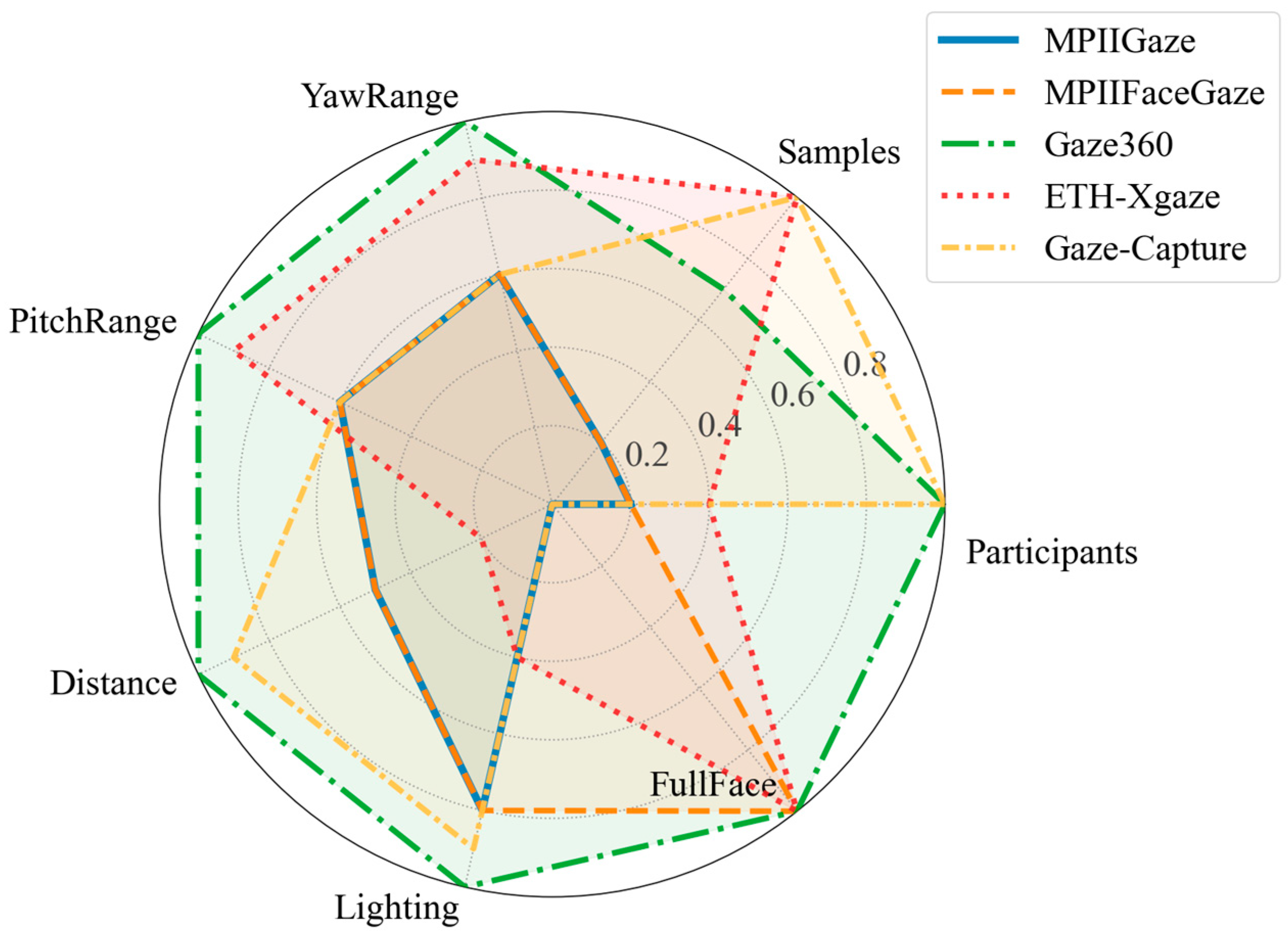
3.3. Public Gaze Datasets
| Dataset | RGB/RGB-D | Participants | Full Face | Amount of Data | Distance | Illumination Conditions |
| MPIIGaze [57] | RGB | 15 | No | 213,659 images | 40~60 cm | Daily life |
| MPIIFaceGaze [63] | RGB | 15 | Yes | 213,659 images | 40~60 cm | Daily life |
| UnityEyes [58] | RGB | - | No | user defined | user defined | User defined |
| ColumbiaGaze [64] | RGB | 56 | Yes | 5880 images | 200 cm | Lab |
| Gaze360 [65] | RGB | 238 | Yes | ~172 K images | ~200 cm | Daily life |
| ETH-XGaze [66] | RGB | 110 | Yes | 1,083,492 images | 100 cm | Lab |
| UT-Multiview [67] | RGB | 50 | No | 1,216,000 images | 60 cm | Lab |
| EYEDIAP [68] | RGB-D | 16 | Yes | 94 videos | 80~120 cm | Lab |
| RT-GENE [69] | RGB-D | 15 | Yes | 277,286 images | ~182 cm | - |
| NISLGaze [71] | RGB | 21 | Yes | 2079 videos | 90 cm | - |
| Gaze-Capture [29] | RGB | 1474 | Yes | >2.5 M images | Close | Daily life |
| TabletGaze [70] | RGB | 51 | Yes | 816 videos | 30~50 cm | Lab |
| GAFA [45] | RGB | - | Yes | 882,000 videos | 50 cm~7 m | Daily life |
| GFIE [56] | RGB-D | 61 | Yes | 71,799 videos | 1.04 m ~ 6.48 m | Daily life |
| Dataset | Gaze Pitch | Gaze Yaw | Head Pose Annot. | Gaze Pose Annot. | Head Pose Orient. | |
| MPIIGaze [57] | −5°~20° | −40°~20° | Yes | Yes | Frontal | |
| MPIIFaceGaze [63] | −5°~20° | −40°~20° | Yes | Yes | Frontal | |
| UnityEyes [58] | user defined | user defined | Yes | Yes | All | |
| ColumbiaGaze [64] | −10°~10° | −15°~15° | 5 orient | Yes | Frontal | |
| Gaze360 [65] | −50°~50° | −140°~140° | Yes | Yes | All | |
| ETH-XGaze [66] | −70°~70° | −120°~120° | Yes | Yes | All | |
| UT-Multiview [67] | −55°~65° | −80°~80° | Yes | Yes | All | |
| EYEDIAP [68] | −45°~45° | −45°~45° | Yes | Yes | Frontal | |
| RT-GENE [69] | −30°~30° | −40°~40° | Yes | Yes | All | |
| NISLGaze [71] | −21.48°~20.76° | −21.25°~21.04° | Yes | Yes | All | |
| Gaze-Capture [29] | −20°~20° | −20°~20° | - | Yes | Frontal | |
| TabletGaze [70] | −15°~0° | −20°~10° | - | Yes | Frontal | |
| GAFA [45] | −75°~75° | −150°~150° | Yes | Yes | All | |
| GFIE [56] | - | - | Yes | Yes | All | |
4. Algorithms
4.1. Model-Driven Methods
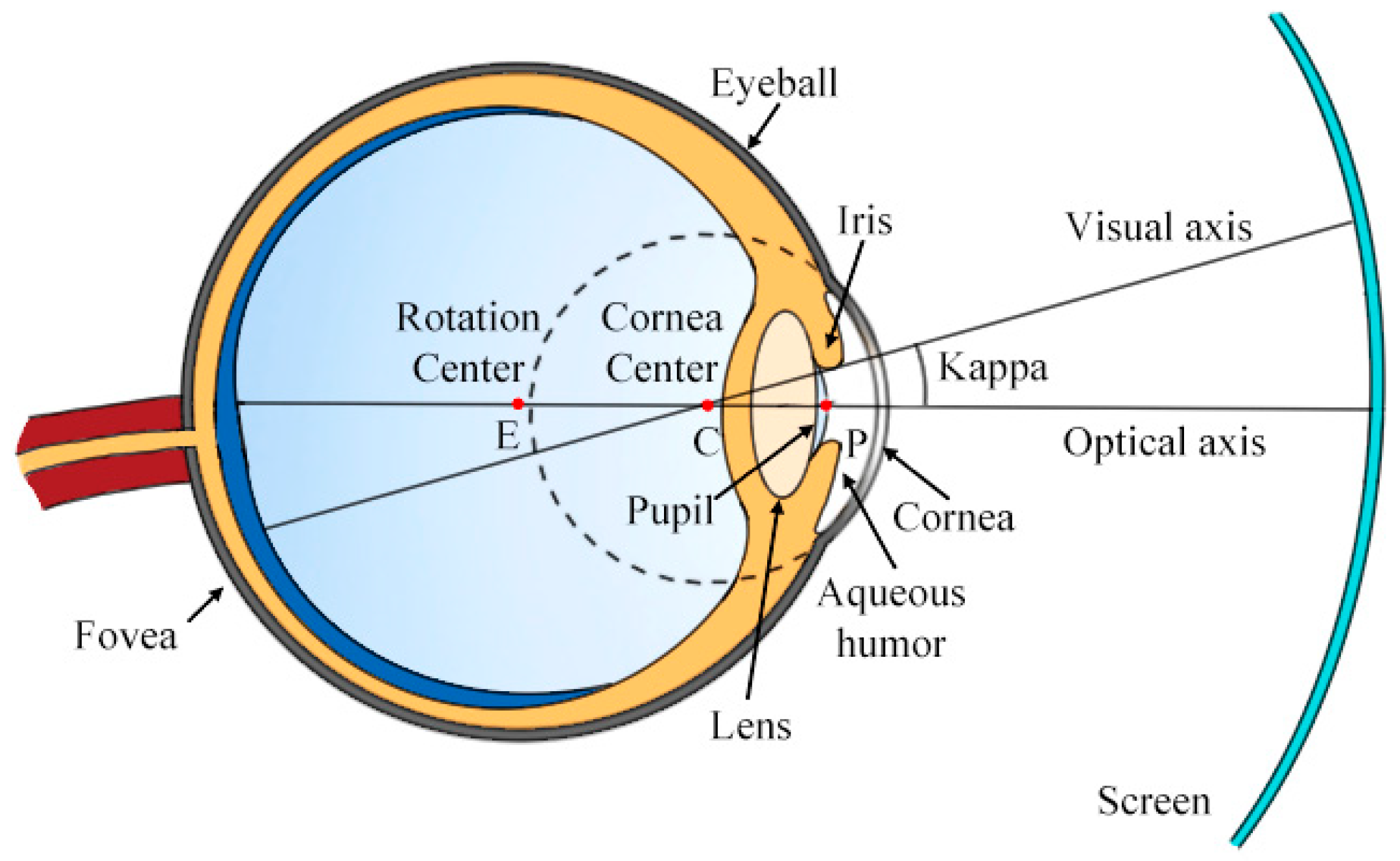
4.1.1. Monocular Geometry
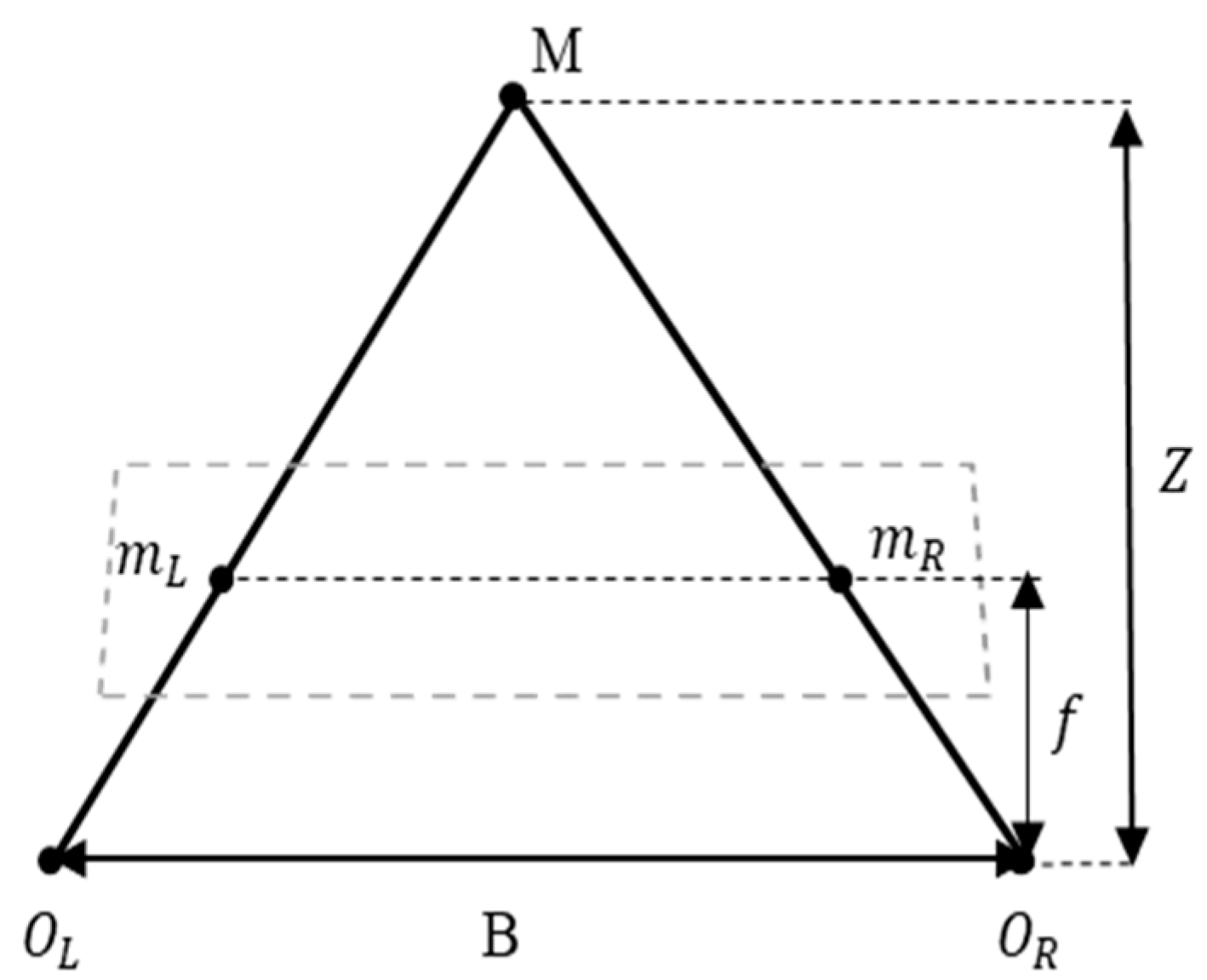
4.1.2. Stereo Triangulation and Gaze Depth Estimation
4.1.3. Calibration and Parameter Estimation
4.2. Data-Driven Methods
5. Challenges and Future Directions
5.1. Existing Challenges and Issues
5.2. Prospects
| Application Area | Task | Algorithms | Datasets |
|---|---|---|---|
| HCI | Contactless Interaction | CNN-based gaze regression [29] | GazeCapture [29] MPIIGaze [57] |
| Remote Gaze Synchronization | Gaze-following CNN [17] | GazeFollow [16] | |
| Wearable Eye-based Interaction | Multi-Stage CNN + SVM [111] | TabletGaze [70] | |
| AR/VR | Foveated Rendering | Real-time pupil tracking + foveated rendering [112] | GazeCapture [29] UnityEyes [58] |
| Visual Attention Analysis | LSTM-based sequence modeling [69] | ColumbiaGaze [64] Gaze360 [65] | |
| Gaze-based Interaction Control | Multi-task CNN (appearance + geometry) [66] | MPIIGaze [57] UnityEyes [58] | |
| Medical Diagnosis | Parkinson’s Screening | Saccadic movement analysis (RF, SVM) [113] | Clinical datasets [113] |
| Autism Spectrum Identification | Spatio-temporal gaze patterns (CNN + LSTM) [114] | ASD Eye-tracking datasets [115] | |
| Reading and Language Assessment | Scanpath analysis (HMM, RF) [116] | ZuCo [117] | |
| Automotive | Driver Attention Monitoring | Gaze zone classification (CNN, 3D CNN) [118] | DR(eye)VE [119] |
| Hazard Prediction | Temporal gaze prediction (LSTM) [120] | EyeTrackUAV2 [121] DR(eye)VE [119] |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Portugal, A.M.; Viktorsson, C.; Taylor, M.J.; Mason, L.; Tammimies, K.; Ronald, A.; Falck-Ytter, T. Infants’ looking preferences for social versus non-social objects reflect genetic variation. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2024, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.T.; Yang, H.; Xu, S.Q.; Ma, Y.Y.; Zhu, S.G.; Mao, Z.Y.; Chen, W.W.; Hu, Z.Z.; Pan, R.R.; Xu, Y.R.; et al. Frequency-encoded eye tracking smart contact lens for human-machine interaction. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poli, F.; Li, Y.L.; Naidu, P.; Mars, R.B.; Hunnius, S.; Ruggeri, A. Toddlers strategically adapt their information search. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde-Domingo, J.; Spitzer, B. Geometry of visuospatial working memory information in miniature gaze patterns. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2024, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, H.-J.; Jeong, H.-Y. A study on eye-tracking-based interface for VR/AR education platform. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 16719–16730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harezlak, K.; Kasprowski, P. Application of eye tracking in medicine: A survey, research issues and challenges. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2018, 65, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaduk, T.; Goeke, C.; Finger, H.; König, P. Webcam eye tracking close to laboratory standards: Comparing a new webcam-based system and the eyeLink 1000. Behav. Res. Methods 2024, 56, 5002–5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, G.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Bai, L.; Zhou, Y. Swift-Eye: Towards anti-blink pupil tracking for precise and robust high-frequency near-Eye movement analysis with event cameras. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2024, 30, 2077–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Guo, P. Eye-UNet: A UNet-based network with attention mechanism for low-quality human eye image segmentation. Signal Image Video Process. 2023, 17, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggert, T. Eye movement recordings: Methods. Dev. Ophthalmol. 2007, 40, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yang, P.; Lei, R.; Liu, Z.; Dong, X.; Tao, X.; Chu, X.; Wang, Z.L.; Chen, X. Eye tracking and eye expression decoding based on transparent, flexible and ultra-persistent electrostatic interface. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Gao, Y.; Tang, L.; Hou, J.; Hu, B. Wearable eye-tracking system for synchronized multimodal data acquisition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 5146–5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmi, R.; Rahmany, I.; Khlifa, N. Gaze estimation using convolutional neural networks. Signal Lmage Video Process. 2023, 18, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Lye, S.W.; Zakaria, Z.B. An integrated framework for eye tracking-assisted task capability recognition of air traffic controllers with machine learning. Adv. Eng. Inf. 2024, 62, 102784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohr, D.; Aziz, S.; Friedman, L.; Komogortsev, O.V. GazeBaseVR, a large-scale, longitudinal, binocular eye-tracking dataset collected in virtual reality. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recasens, A.; Khosla, A.; Vondrick, C.; Torralba, A. Where are they looking? In Proceedings of the 29th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 12 December 2015; pp. 199–207. [Google Scholar]
- Recasens, A.; Vondrick, C.; Khosla, A.; Torralba, A. Following gaze in video. In Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1444–1452. [Google Scholar]
- Backhaus, D.; Engbert, R. How body postures affect gaze control in scene viewing under specific task conditions. Exp. Brain Res. 2024, 242, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Gao, Q.; Gao, J.; Zhang, W. MDNN: Predicting student engagement via gaze direction and facial expression in collaborative learning. CMES-Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2023, 136, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Huang, S.; Wang, S.; Muhammad, K.; Bellavista, P.; Del Ser, J. Visual tracking in complex scenes: A location fusion mechanism based on the combination of multiple visual cognition flows. Inf. Fusion. 2023, 96, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deane, O.; Toth, E.; Yeo, S.-H. Deep-SAGA: A deep-learning-based system for automatic gaze annotation from eye-tracking data. Behav. Res. Methods 2023, 55, 1372–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonini, F.; Dall’Asen, N.; Beyan, C.; Ricci, E. Object-aware gaze target detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 21860–21869. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, D.Y.; Min, X.K.; Duan, H.Y.; Guo, G.D.; Zhai, G.T.; Shen, W. End-to-end human-gaze-target detection with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 2192–2200. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; He, Y.; Mou, Z.; Cao, Y. High-speed eye tracking based on a synchronized imaging mechanism by a dual-ring infrared lighting source. Appl. Opt. 2024, 63, 4293–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severitt, B.R.; Kübler, T.C.; Kasneci, E. Testing different function fitting methods for mobile eye-tracker calibration. J. Eye Mov. Res. 2023, 16, 10-16910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcio, C.A.; Sloan, K.R.; Kalina, R.E.; Hendrickson, A.E. Human photoreceptor topography. J. Comp. Neurol. 1990, 292, 497–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falch, L.; Lohan, K.S. Webcam-based gaze estimation for computer screen interaction. Front. Rob. AI 2024, 11, 1369566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, G.; Shi, F.; Guo, X.; Wan, P.; Wang, M. EM-Gaze: Eye context correlation and metric learning for gaze estimation. Vis. Comput. Ind. Biomed. Art. 2023, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krafka, K.; Khosla, A.; Kellnhofer, P.; Kannan, H.; Bhandarkar, S.; Matusik, W.; Torralba, A. Eye tracking for everyone. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2176–2184. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.F.; Pham, K.; Valliappan, N.; Xu, P.M.; Roberts, C.; Lagun, D.; Navalpakkam, V. On-device few-shot personalization for real-time gaze estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1149–1158. [Google Scholar]
- Algassir, A.O.M.; Manickam, S.; Anbar, M.; Nseaf, A.K. Acf-Gsvm: Cascade aggregate channel feature with gabor filters and support vector machine for enhanced face detection. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2023, 101, 7317–7327. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Li, S.; Lu, S. How frontal is a face? Quantitative estimation of face pose based on CNN and geometric projection. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 3035–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Deng, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.F. Orientation cues-aware facial relationship representation for head pose estimation via transformer. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 6289–6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzzi, A.; Shi, X.W.; Wang, X.; Li, G.Y.; De Mello, S.; Chang, H.J.; Zhang, X.C.; Hilliges, O. GazeNeRF: 3D-aware gaze redirection with neural radiance fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 9676–9685. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, A.; Jin, Z.; Guo, S.; Wu, D.; Chen, L. Unconstrained human gaze estimation approach for medium-distance scene based on monocular vision. Vis. Comput. 2023, 40, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisogni, C.; Cascone, L.; Nappi, M.; Pero, C. IoT-enabled biometric security: Enhancing smart car safety with depth-based head pose estimation. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2024, 20, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, M.; Mo, S.T.; Lin, Y.Z. EVA-GCN: Head pose estimation based on graph convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Virtual Conference, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 1462–1471. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Cong, L.; Qin, H. Mixed-pose positioning in smartphone-based pedestrian dead reckoning using hierarchical clustering. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 9514312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.F.; Xia, Y.L.; Luo, Y.; Wang, L. Multi-feature fusion gaze estimation based on attention mechanism. In Proceedings of the Conference on Optoelectronic Imaging and Multimedia Technology VIII, Nantong, China, 10–12 October 2021; pp. 172–182. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Fang, F.; Hou, G.; Li, Z.; Niu, R. Appearance-based gaze estimation with feature fusion of multi-level information elements. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2023, 10, 1080–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.D.; Ding, Z.M.; Fu, Y. Pose-dependent low-rank embedding for head pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 30th Association-for-the-Advancement-of-Artificial-Intelligence (AAAI) Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 12–17 February 2016; pp. 1422–1428. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, H.; Fang, W.; Guo, B.; Wang, J. Real-time wide-view eye tracking based on resolving the spatial depth. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 78, 14633–14655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Yang, H. Monocular free-head gaze tracking method for driving electric sickbed. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2023, 34, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, J. CI-Net: Appearance-based gaze estimation via cooperative network. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 78739–78746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, S.; Nobuhara, S.; Nishino, K. Dynamic 3D gaze from afar: Deep gaze estimation from temporal eye-head-body coordination. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 2182–2191. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Bao, Y.W.; Lu, F. PureGaze: Purifying gaze feature for generalizable gaze estimation. In Proceedings of the 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence/34th Conference on Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence/12th Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence, Virtual (Online), 22 February–1 March 2022; pp. 436–443. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Yu, Y.; Mora, K.A.F.; Odobez, J.M. A differential approach for gaze estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Liu, B.; Yu, J. An individual-difference-aware model for cross-person gaze estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process 2022, 31, 3322–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Chang, M.; Raychowdhury, A. E-Gaze: Gaze estimation with event camera. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 4796–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Liu, S.; Cheng, H.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Siebert, F.W. GaVe: A webcam-based gaze vending interface using one-point calibration. J. Eye Mov. Res. 2023, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, S.; Chen, W.; Gao, Z.; Wan, Z. Self-calibrating gaze estimation with optical axes projection for head-mounted eye tracking. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2024, 20, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortacero, K.; Fischer, T.; Demiris, Y. RT-BENE: A dataset and baselines for real-time blink estimation in natural environments. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1159–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, L.; Terwilliger, J.; Parab, A.; Wang, M.; Fridman, L.; Mehler, B.; Reimer, B. CLERA: A unified model for joint cognitive load and eye region analysis in the wild. ACM Trans. Comput.-Hum. Interact. 2023, 30, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guestrin, E.D.; Eizenman, M. General theory of remote gaze estimation using the pupil center and corneal reflections. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 53, 1124–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, D.W.; Pece, A.E.C. Eye tracking in the wild. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2005, 98, 155–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.X.; Yang, Y.X.; Zhai, X.L.; Yang, D.Y.; Zhou, B.H.; Liu, J.T. GFIE: A dataset and baseline for gaze-following from 2D to 3D in indoor environments. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 8907–8916. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Sugano, Y.; Fritz, M.; Bulling, A. MPIIGaze: Real-world dataset and deep appearance-based gaze estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 41, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, E.; Baltrusaitis, T.; Morency, L.P.; Robinson, P.; Bulling, A. Learning an appearance-based gaze estimator from one million synthesised images. In Proceedings of the 9th Biennial ACM Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications (ETRA), Charleston, SC, USA, 14–17 March 2016; pp. 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Prasse, P.; Reich, D.R.; Makowski, S.; Ahn, S.; Scheffer, T.; Jäger, L.A. SP-EyeGAN: Generating synthetic eye movement data with generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the 2023 Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications, Tubingen, Germany, 30 May–2 June 2023; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Wang, D.; Darrell, T.; Ebrahimi, S. Contrastive test-time adaptation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 295–305. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Y.W.; Liu, Y.F.; Wang, H.F.; Lu, F. Generalizing gaze estimation with rotation consistency. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 4197–4206. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; Zeng, J.B.; Shan, S.G.; Chen, X.L. Source-free adaptive gaze estimation by uncertainty reduction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 22035–22045. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Sugano, Y.; Fritz, M.; Bulling, A. It’s written all over your face: Full-face appearance-based gaze estimation. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2299–2308. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, B.A.; Yin, Q.; Feiner, S.K.; Nayar, S.K. Gaze locking. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, St. Andrews, UK; 2013; pp. 271–280. [Google Scholar]
- Kellnhofer, P.; Recasens, A.; Stent, S.; Matusik, W.; Torralba, A. Gaze360: Physically unconstrained gaze estimation in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6911–6920. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Park, S.; Beeler, T.; Bradley, D.; Tang, S.; Hilliges, O. ETH-XGaze: A large scale dataset for gaze estimation under extreme head pose and gaze variation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part V. pp. 365–381. [Google Scholar]
- Sugano, Y.; Matsushita, Y.; Sato, Y. Learning-by-synthesis for appearance-based 3D gaze estimation. In Proceedings of the 27th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1821–1828. [Google Scholar]
- Funes Mora, K.A.; Monay, F.; Odobez, J.M. Eyediap: A database for the development and evaluation of gaze estimation algorithms from RGB and RGB-D cameras. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications, Safety Harbor, FL, USA, 26–28 March 2014; pp. 255–258. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, T.; Chang, H.J.; Demiris, Y. RT-GENE: Real-time eye gaze estimation in natural environments. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 339–357. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Veeraraghavan, A.; Sabharwal, A. TabletGaze: Dataset and analysis for unconstrained appearance-based gaze estimation in mobile tablets. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2017, 28, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Shi, B.E. Towards high performance low complexity calibration in appearance based gaze estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 1174–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamatsu, T.; Hiroe, M.; Rigoll, G. Corneal-reflection-based wide range gaze tracking for a car. In Proceedings of the Human Interface and the Management of Information. Information in Intelligent Systems, Cham, Switzerland, 26–31 July 2019; pp. 385–400. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Ji, Q. Novel eye gaze tracking techniques under natural head movement. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 2246–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tian, W.; Wang, P.; Wang, F.; Xiong, L.; Li, H. EPro-PnP: Generalized end-to-end probabilistic perspective-n-points for monocular object pose estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Xiong, C.; Chen, W.; Zhang, H.; Wu, S. Pupil-contour-based gaze estimation with real pupil axes for head-mounted eye tracking. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 3640–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swirski, L.; Dodgson, N.A. A fully-automatic, temporal approach to single camera, glint-free 3D eye model fitting. In Proceedings of the Pervasive Eye Tracking Mobile Eye-Based Interact, Lund, Sweden, 13 August 2013; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Xu, B.; Cossairt, O.; Willomitzer, F. Accurate eye tracking from dense 3D surface reconstructions using single-shot deflectometry. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchowski, A.T.; Pelfrey, B.; House, D.H.; Wang, R. Measuring gaze depth with an eye tracker during stereoscopic display. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Applied Perception in Graphics and Visualization, Toulouse, France, 27–28 August 2011; pp. 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.I.; Pelfrey, B.; Duchowski, A.T.; House, D.H. Online 3D gaze localization on stereoscopic displays. ACM Trans. Appl. Percept. 2014, 11, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Li, M.; Hou, J.; Xiao, J. Single image-based head pose estimation with spherical parametrization and 3D morphing. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 103, 107316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.; Gering, S.; Kasneci, E. Static laser feedback interferometry-based gaze estimation for wearable glasses. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 7558–7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, T.; Sun, J.; Pun, S.; Liu, Y. Monocular 3D gaze estimation using feature discretization and attention mechanism. Optoelectron. Lett. 2023, 19, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, N.; Lin, C.Z.; Wetzstein, G.; Sun, Q. GazeFusion: Saliency-guided image generation. ACM Trans. Appl. Percept. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Cai, Y.; Li, Q.; Su, K.; Lv, C. Context-aware driver attention estimation using multi-hierarchy saliency fusion with gaze tracking. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 8602–8614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, H. 3D gaze estimation for head-mounted eye tracking system with auto-calibration method. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 104207–104215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Huang, K. Semi-supervised multitask learning using gaze focus for gaze estimation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 7935–7946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Hayat, M.; Dhall, A.; Knibbe, J. MTGLS: Multi-task gaze estimation with limited supervision. In Proceedings of the 22nd IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 4–8 January 2022; pp. 1161–1172. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Huang, J.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Hasegawa, Y. Natural grasp intention recognition based on gaze in human–robot interaction. IEEE J. Biomed. Health. Inf. 2023, 27, 2059–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.; Al-Dhahir, N.; Busso, C. Driver visual attention estimation using head pose and eye appearance information. IEEE Open J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 4, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Xu, J. Gaze-based human intention prediction in the hybrid foraging search task. Neurocomputing 2024, 587, 127648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Niu, H.; Wei, W.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S.; Ai, M. Eye-gaze-based intention recognition for selection task by using SVM-RF. In Proceedings of the Human-Computer Interaction, Washington, WA, USA, 29 June–4 July 2024; pp. 157–168. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Zhao, R.; Su, H.; Ji, Q. Generalizing eye tracking with bayesian adversarial learning. In Proceedings of the 32nd IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 11899–11908. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Zhao, R.; Ji, Q. A hierarchical generative model for eye image synthesis and eye gaze estimation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 440–448. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Zhang, X.; Bulling, A.; Hilliges, O. Learning to find eye region landmarks for remote gaze estimation in unconstrained settings. In Proceedings of the 2018 ACM Symposium on Eye Tracking Research & Applications, Warsaw, Poland, 14–17 June 2018; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Lu, F. Gaze estimation using transformer. In Proceedings of the 2022 26th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Montreal, QC, Canada, 21–25 August 2022; pp. 3341–3347. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W. Gaze Estimation based on convolutional structure and sliding window-based attention mechanism. Sensors 2023, 23, 6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Wang, Y.; Luo, S.; Shou, S.; Tang, P. Gaze-swin: Enhancing gaze estimation with a hybrid CNN-transformer network and dropkey mechanism. Electronics 2024, 13, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Wang, C. Attention mechanism based full-face gaze estimation for human-computer interaction. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Computer Network, Electronic and Automation (ICCNEA), Xi’an, China, 23–25 September 2022; pp. 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Shi, J.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; Du, Y.; Zhen, X.; Liu, H. Gaze estimation by attention-induced hierarchical variational auto-encoder. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2024, 54, 2592–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Rehg, J.M. In the eye of the beholder: Gaze and actions in first person video. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 6731–6747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Ren, W.; Noack, B.R.; Liu, H. Improving the reliability of gaze estimation through cross-dataset multi-task learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on High Performance Big Data and Intelligent Systems (HDIS), Tianjin, China, 10–11 December 2022; pp. 202–206. [Google Scholar]
- González-Díaz, I.; Molina-Moreno, M.; Benois-Pineau, J.; de Rugy, A. Asymmetric multi-task learning for interpretable gaze-driven grasping action forecasting. IEEE J. Biomed. Health. Inf. 2024, 28, 7517–7530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.F.; Xu, F. Towards eyeglasses refraction in appearance-based gaze estimation. In Proceedings of the 22nd IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR), Sydney, Australia, 16–20 October 2023; pp. 693–702. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.F.; Liu, Y.F.; Lu, F. GazeOnce: Real-time multi-person gaze estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 4187–4196. [Google Scholar]
- David-John, B.; Butler, K.; Jain, E. Privacy-preserving datasets of eye-tracking samples with applications in XR. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2023, 29, 2774–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkir, E.; Günlü, O.; Fuhl, W.; Schaefer, R.F.; Kasneci, E. Differential privacy for eye tracking with temporal correlations. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Lin, Z.; Lai, W.; Jiang, H.; Cai, J.; Chen, H.; Hao, W.; Ye, Y.; Xu, S.; Yan, Q.; et al. Micro-LED retinal projection for augmented reality near-eye displays. Laser Photonics Rev. 2025, 19, 2402083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Sun, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Jin, H.; Huo, Y.; Tseng, M.C.; Yeung, F.; Kwok, H.S.; Chen, E. Pupil-adaptive retina projection augment reality displays with switchable ultra-dense viewpoints. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2416961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Suh, K.H.; Lee, E.C. Multi-modal user interface combining eye tracking and hand gesture recognition. J. Multimodal User Interfaces 2017, 11, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinyelu, A.A.; Blignaut, P. Convolutional neural network-based technique for gaze estimation on mobile devices. Front. Artif. Intell. 2022, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patney, A.; Salvi, M.; Kim, J.; Kaplanyan, A.; Wyman, C.; Benty, N.; Luebke, D.; Lefohn, A. Towards foveated rendering for gaze-tracked virtual reality. ACM Trans. Graph. 2016, 35, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretegiani, E.; Optican, L.M. Eye movements in parkinson’s disease and inherited parkinsonian syndromes. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asmetha Jeyarani, R.; Senthilkumar, R. Eye tracking biomarkers for autism spectrum disorder detection using machine learning and deep learning techniques: Review. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2023, 108, 102228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilia, F.; Carette, R.; Elbattah, M.; Guérin, J.L.; Dequen, G. Eye-tracking dataset to support the research on autism spectrum disorder. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Scarce Data in Artificial Intelligence for Healthcare, Vienna, Austria, 23 July 2022; pp. 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Prabha, A.J.; Bhargavi, R. Predictive model for dyslexia from fixations and saccadic eye movement events. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 195, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollenstein, N.; Rotsztejn, J.; Troendle, M.; Pedroni, A.; Zhang, C.; Langer, N. ZuCo, a simultaneous EEG and eye-tracking resource for natural sentence reading. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.W.; Wang, Y.; Wei, R.; Guan, J.P.; Huang, X.H.; Cai, W.; Jiang, Z. An efficient multi-task learning CNN for driver attention monitoring. J. Syst. Architect. 2024, 148, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alletto, S.; Palazzi, A.; Solera, F.; Calderara, S.; Cucchiara, R. DR(eye)VE: A dataset for attention-based tasks with applications to autonomous and assisted driving. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Costela, F.M.; Castro-Torres, J.J. Risk prediction model using eye movements during simulated driving with logistic regressions and neural networks. Transp. Res. Pt. F-Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2020, 74, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, A.-F.; Krassanakis, V.; Zhang, L.; Ricordel, V.; Perreira Da Silva, M.; Le Meur, O. EyeTrackUAV2: A large-scale binocular eye-tracking dataset for UAV videos. Drones 2020, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Method | References | Input | Dataset | Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eye | Face | |||||
| Head posture | Appearance-based approach | [33] | √ | BiWi | 4.66° | |
| [32] | √ | AFLW | 5.77° | |||
| [41] | √ | CMU-PIE | 7.36° | |||
| √ | MIT-CBCL | 1.31° | ||||
| √ | YaleB | 7.584° | ||||
| Geometry-based method | [42] | √ | unknown | 2.63° | ||
| √ | unknown | 3.26° | ||||
| [43] | √ | MPIIGaze | 4.8° | |||
| [35] | √ | unknown | 7.65° | |||
| [34] | √ | ColumbiaGaze | 9.464° | |||
| √ | MPIIFaceGaze | 14.933° | ||||
| √ | GazeCapture | 10.463° | ||||
| Clustering-based method | [36] | √ | Biwi | 4.9° | ||
| [38] | √ | unknown | 1.57° | |||
| [37] | √ | AFLW2000 | 3.48° | |||
| √ | 300 W-LP | 3.92° | ||||
| √ | BIWI | 2.24° | ||||
| References | Input | Dataset | Accuracy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eye | Face | Other | ||||
| Blinking | [52] | √ | RT-BENE | AP:0.757 | ||
| Eyeblink8 | AP:0.997 | |||||
| [53] | √ | RT-BENE | AP:0.653 | |||
| Occlusion | [45] | Head position | GAFA | 20.4° (3D) | ||
| Body image | MoDiPro | 25.6° (2D) | ||||
| [44] | √ | √ | MPIIGaze | 3.8° | ||
| EYEDIAP | 5.4° | |||||
| RT-Gene | 7.9° | |||||
| Illumination | [46] | √ | MPIIGaze | 5.20° | ||
| EYEDIAP | 7.36° | |||||
| [47] | √ | MPIIGaze | 4.67° | |||
| EYEDIAP | 3.36° | |||||
| UT-Multiview | 4.33° | |||||
| Individual Differences | [48] | √ | EVE | 1.89° | ||
| MPIIGaze | 4.14°/3.02° | |||||
| Xgaze | 2.88° | |||||
| [54] | √ | - | 0.9° | |||
| [55] | √ | - | 4° | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, L.; Wu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Guo, W. Recent Progress on Eye-Tracking and Gaze Estimation for AR/VR Applications: A Review. Electronics 2025, 14, 3352. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173352
Lin L, Wu Z, Lu Y, Chen Z, Guo W. Recent Progress on Eye-Tracking and Gaze Estimation for AR/VR Applications: A Review. Electronics. 2025; 14(17):3352. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173352
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Liwan, Zongyu Wu, Yijun Lu, Zhong Chen, and Weijie Guo. 2025. "Recent Progress on Eye-Tracking and Gaze Estimation for AR/VR Applications: A Review" Electronics 14, no. 17: 3352. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173352
APA StyleLin, L., Wu, Z., Lu, Y., Chen, Z., & Guo, W. (2025). Recent Progress on Eye-Tracking and Gaze Estimation for AR/VR Applications: A Review. Electronics, 14(17), 3352. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173352








