Hardware Accelerator Design by Using RT-Level Power Optimization Techniques on FPGA for Future AI Mobile Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Platform-Based RTL Design Flow and Low-Power Optimization Techniques for Tiny YOLOv4 on FPGA-SoC
2.1. Background
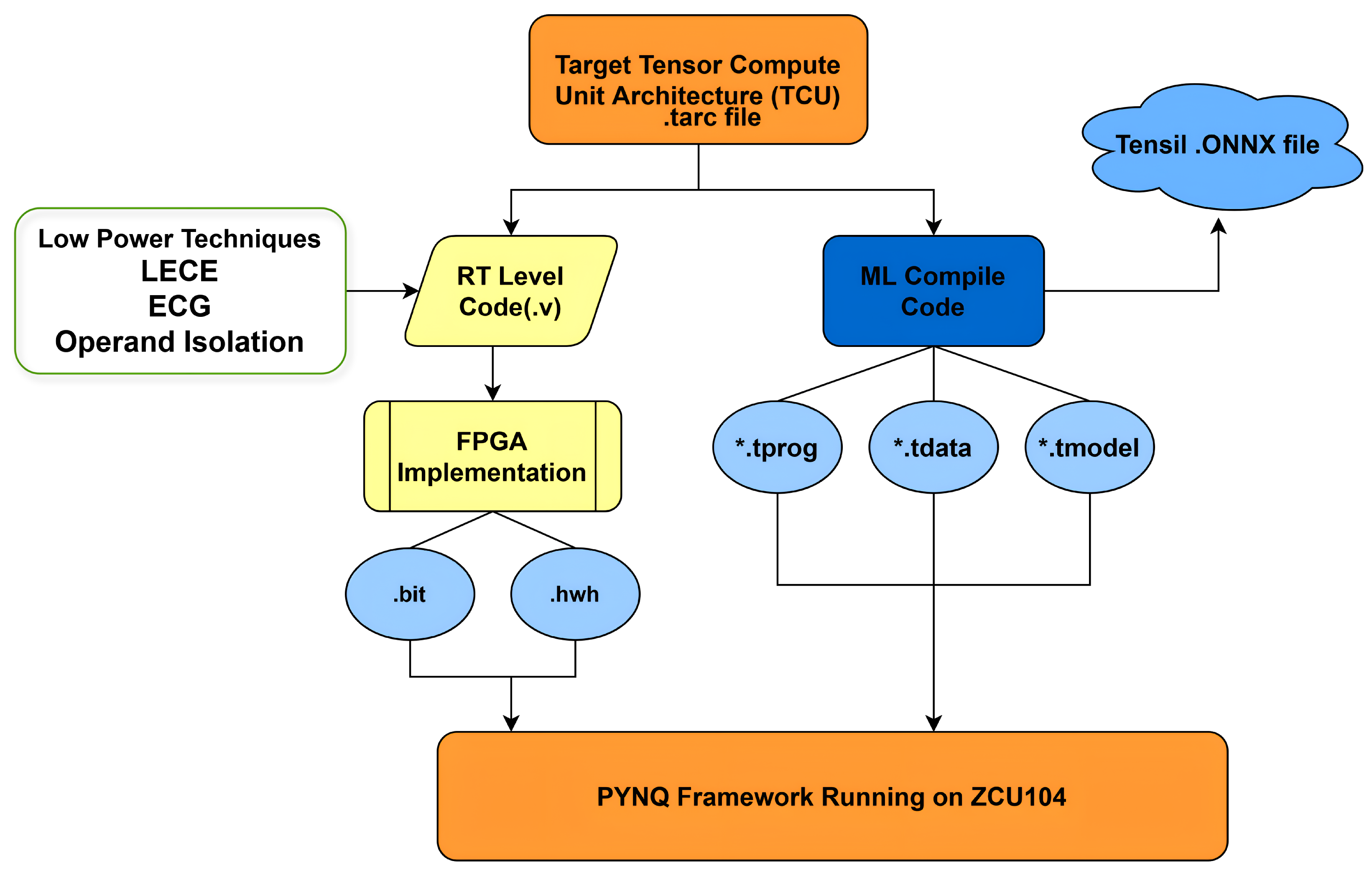
2.2. Platform-Based RTL Design Flow for CNN Accelerators
2.3. Baseline RTL Accelerator Generation Using Tensil
2.4. Low-Power RTL Techniques for Tiny YOLOv4 Deployment
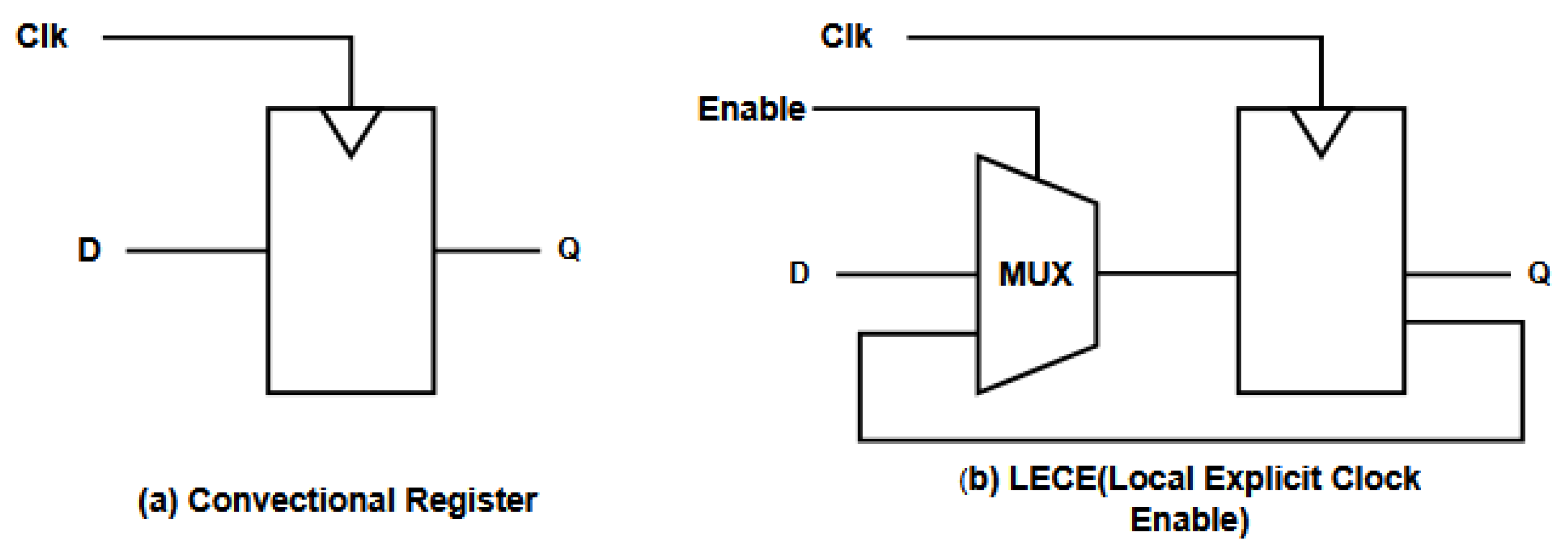
- Local Explicit Clock Enable (LECE)LECE is a clock-gating technique that uses a local ENABLE signal to selectively update the output of flip-flops or pipeline registers only when valid computation is required. As illustrated in Figure 2, LECE allows finer control over bit-level register updates, significantly reducing dynamic power in pipelines where many cycles involve idle data [17].
- Operand IsolationOperand isolation prevents unnecessary signal transitions in combination logic by decoupling inactive data paths. When a computation is not needed, isolating inputs to functional units such as multipliers and adders ensures that the internal switching activity is minimized. This is implemented using control gates such as AND or MUX units placed before input operands, allowing downstream MAC units to remain inactive during idle cycles. This method proves especially effective in reducing power during memory fetches, activation layers, and sparsely populated feature map computations in Tiny YOLOv4.
- Enhanced Clock Gating (ECG)Enhanced Clock Gating (ECG) uses XOR-based gating logic to minimize unnecessary signal propagation across wide datapaths and deep pipelines. As illustrated in Figure 3, ECG applies gating at multiple stages of the processing pipeline, utilizing XOR gates for lower switching power compared to traditional AND/OR logic [18]. This makes ECG particularly suitable for MAC units and activation blocks in Tiny YOLOv4, where high bit-width operations dominate.
3. Proposed Design and Optimization
3.1. Implementation of the Original Design
3.2. Tensil Clone and Module Integration
3.3. Low-Power Techniques on Original Design
3.3.1. Enhanced Clock Gating (ECG)
gclk = latch_q & clock & clk_enable;
| Algorithm 1 Low-Power CNN Computation with ECG and Operand Isolation |
|
3.3.2. Operand Isolation
if (data_active) begin output <= compute_result(input_a, input_b); end
4. Experiment and Results
4.1. ZCU104 Board Setup
4.2. Power Results
4.3. Combined Impact
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| ECG | Enhanced Clock Gating |
| OI | Operand Ioslation |
| LECG | Local Explicit Clock Gating |
| IP | Intellectual Property Blocks |
| BRAM | Block Random Access Memory |
| CONV | Convolution Layer |
| MAC | Multiply and Accumulate |
| RTL | Register Transfer Level |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| FPGA | Field-Programmable Gate Array |
| HLS | High-Level Synthesis |
| Soc | System-on-Chip |
| ONNX | Open Neural Network Exchange |
References
- Jameil, A.K.; Al-Raweshidy, H. Efficient CNN Architecture on FPGA Using High-evel Module for Healthcare Devices. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 60486–60495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Mahmud, M.A.P.; Kouzani, A.Z. FitNN: A Low-Resource FPGA-Based CNN Accelerator for Drones. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 21357–21369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gong, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Baker, T.; Zhou, J.; Lu, T. ABM-SpConv-SIMD: Accelerating Convolutional Neural Network Inference for Industrial IoT Applications on Edge Devices. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2023, 10, 3071–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikouei, S.Y.; Chen, Y.; Song, S.; Xu, R.; Choi, B.Y.; Faughnan, T.R. Smart Surveillance as an Edge Network Service: From Harr-Cascade, SVM to a Lightweight CNN. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.00331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamimi, S.; Ebrahimi, Z.; Khaleghi, B.; Asadi, H. An Efficient SRAM-Based Reconfigurable Architecture for Embedded Processors. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2019, 38, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, Z. A Flexible and Efficient FPGA Accelerator for Various Large-Scale and Lightweight CNNs. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2022, 69, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irmak, H.; Ziener, D.; Alachiotis, N. Increasing Flexibility of FPGA-based CNN Accelerators with Dynamic Partial Reconfiguration. In Proceedings of the 2021 31st International Conference on Field-Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL), Dresden, Germany, 30 August–3 September 2021; pp. 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Arora, A.; Li, R.; John, L. HLSDataset: Open-Source Dataset for ML-Assisted FPGA Design using High Level Synthesis. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 34th International Conference on Application-specific Systems, Architectures and Processors (ASAP), Porto, Portugal, 19–21 July 2023; pp. 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi Makrani, H.; Farahmand, F.; Sayadi, H.; Bondi, S.; Pudukotai Dinakarrao, S.M.; Homayoun, H.; Rafatirad, S. Pyramid: Machine Learning Framework to Estimate the Optimal Timing and Resource Usage of a High-Level Synthesis Design. In Proceedings of the 2019 29th International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL), Barcelona, Spain, 8–12 September 2019; pp. 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Rehman, S.; Shafique, M.; Kumar, A. High-Performance Accurate and Approximate Multipliers for FPGA-Based Hardware Accelerators. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2022, 41, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Luo, Y.; Sun, K.; Yadav, N.; Choi, K.K. A Novel FPGA Accelerator Design for Real-Time and Ultra-Low Power Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Compared with Titan X GPU. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 105455–105471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Geng, L. A Reconfigurable CNN Accelerator using Tile-by-Tile Computing and Dynamic Adaptive Data Truncation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Integrated Circuits, Technologies and Applications (ICTA), Chengdu, China, 13–15 November 2019; pp. 73–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Xiong, J.; Hwu, W.M.W.; Kindratenko, V.; Chen, D. Exploring HW/SW Co-Design for Video Analysis on CPU-FPGA Heterogeneous Systems. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2022, 41, 1606–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tensil. Learn Tensil with ResNet and PYNQ Z1. Available online: https://k155la3.blog/2022/04/04/tensil-tutorial-for-yolo-v4-tiny-on-ultra96-v2/ (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Kim, Y.; Tong, Q.; Choi, K.; Lee, E.; Jang, S.J.; Choi, B.H. System Level Power Reduction for YOLO2 Sub-modules for Object Detection of Future Autonomous Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2018 International SoC Design Conference (ISOCC), Daegu, Republic of Korea, 12–15 November 2018; pp. 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, H.; Yadav, N.; Li, S.; Choi, K.K. Low-Power RTL Code Generation for Advanced CNN Algorithms toward Object Detection in Autonomous Vehicles. Electronics 2020, 9, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Choi, K. Low Power FPGA-SoC Design Techniques for CNN-based Object Detection Accelerator. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 10th Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON), New York, NY, USA, 10–12 October 2019; pp. 1130–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, V.H.; Choi, K.K. A Reconfigurable CNN-Based Accelerator Design for Fast and Energy-Efficient Object Detection System on Mobile FPGA. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 59438–59445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tong, Q.; Li, L.; Wang, W.; Choi, K.; Jang, J.; Jung, H.; Ahn, S.Y. Automatic Register Transfer level CAD tool design for advanced clock gating and low power schemes. In Proceedings of the 2012 International SoC Design Conference (ISOCC), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 4–7 November 2012; pp. 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. AMD ZCU104. Available online: https://www.amd.com/en/products/adaptive-socs-and-fpgas/evaluation-boards/zcu104.html (accessed on 19 June 2024).
- Nguyen, D.-D.; Nguyen, D.-T.; Le, M.-T.; Nguyen, Q.-C. FPGA-SoC implementation of YOLOv4 for flying-object detection. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2024, 21, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadanzoj, Z.; Daryanavard, H.; Harifi, A. High-speed YOLOv4-tiny hardware accelerator for self-driving automotive. J. Supercomput. 2024, 80, 6699–6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, B.; Xu, F.; Gao, Y.; Xu, M.; et al. An FPGA-based online reconfigurable CNN edge computing device for object detection. Microelectron. J. 2023, 137, 105805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, D.; Rizk, M.; Douguet, R.; Baghdadi, A.; Diguet, J.-P. Marine objects detection using deep learning on embedded edge devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Rapid System Prototyping (RSP), Shanghai, China, 13 October 2022; pp. 1–7. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10039025 (accessed on 17 August 2025).
- Montgomerie-Corcoran, A.; Toupas, P.; Yu, Z.; Bouganis, C.-S. SATAY: A streaming architecture toolflow for accelerating YOLO models on FPGA devices. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Field Programmable Technology (ICFPT), Yokohama, Japan, 11–14 December 2023; pp. 179–187. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10416135 (accessed on 17 August 2025).
- Amin, R.A.; Hasan, M.; Wiese, V.; Obermaisser, R. FPGA-Based Real-Time Object Detection and Classification System Using YOLO for Edge Computing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 5–8 January 2024; pp. 1–6. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10537163/references#references (accessed on 17 August 2025).


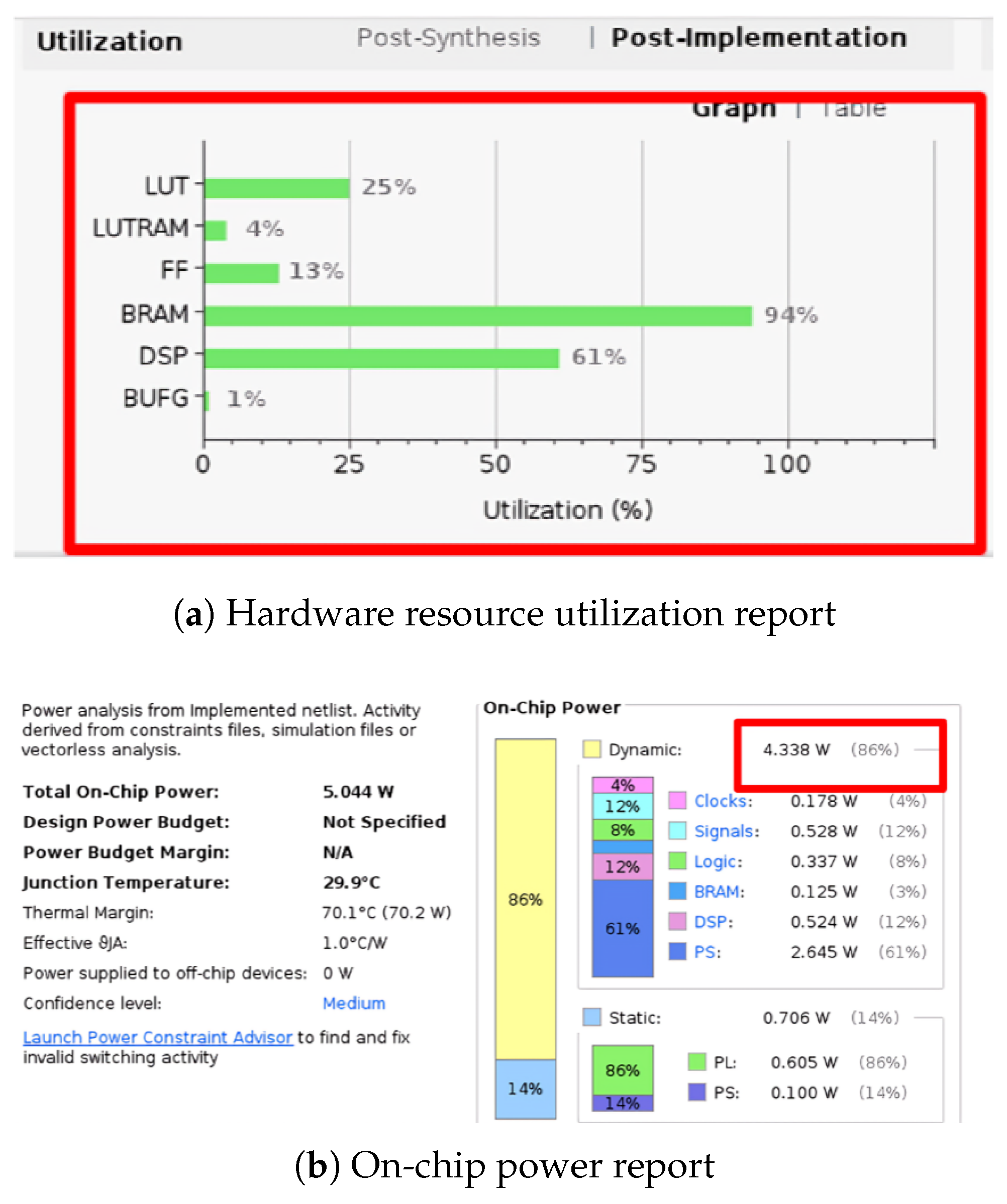

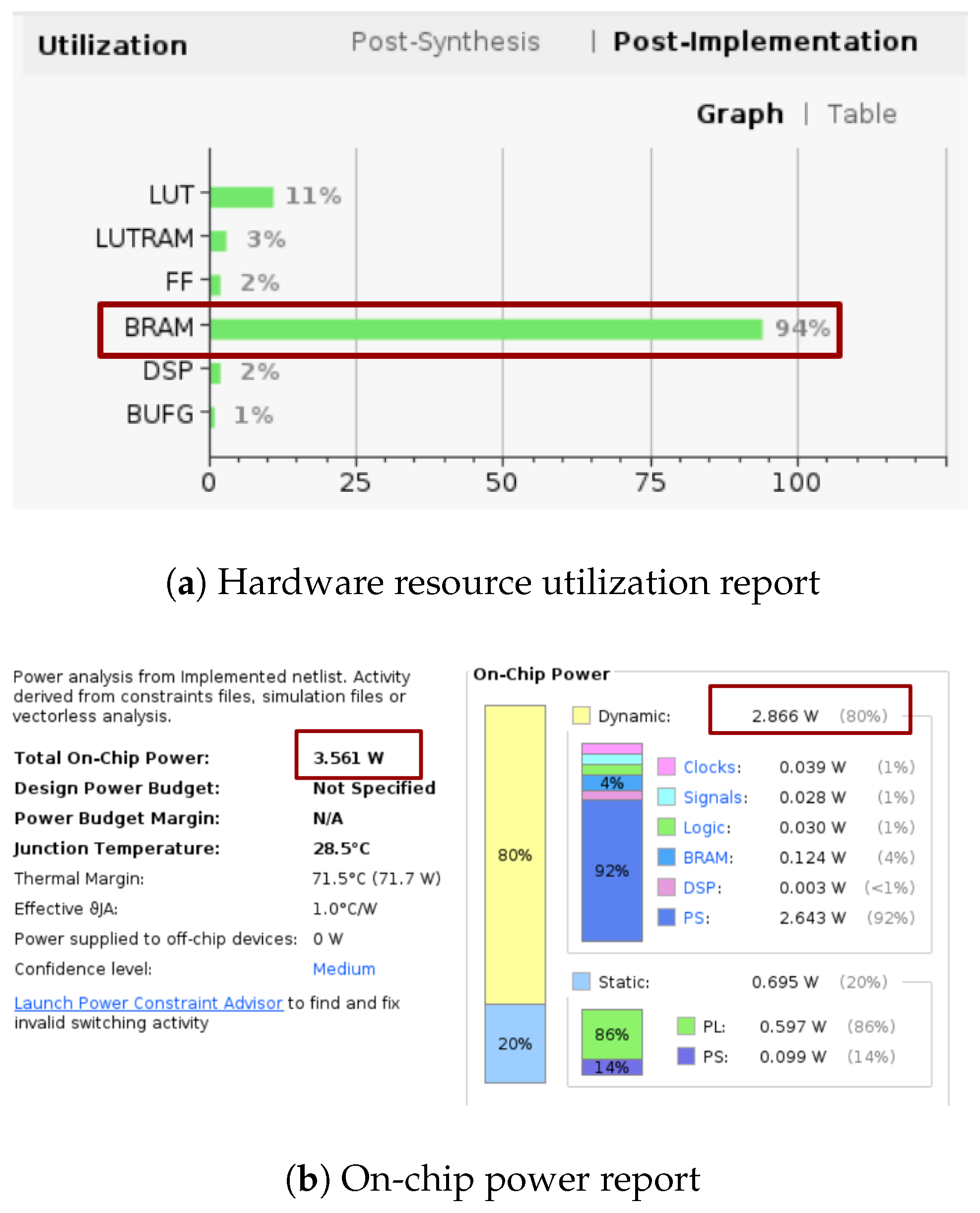
| Metric | ZCU104 Capacity [20] | Original Design [14] | Proposed Design |
|---|---|---|---|
| CLB LUTs | 274,080 | 57,345 (20.9%) | 24,744 (9.0%) |
| CLB Registers | 548,160 | 59,252 (10.8%) | 7718 (1.4%) |
| DSPs | 2520 | 1057 (41.9%) | 33 (1.3%) |
| Block RAM Tiles | 912 | 293.5 (32.2%) | 293.5 (32.2%) |
| LUT as Memory | 144,000 | 4220 (2.93%) | 3150 (2.19%) |
| Dynamic Power (W) | — | 4.338 | 2.866 |
| Author/Criteria | Year | NN Model | FPGA | Test Image Size | Accuracy (%) | Throughput (FPS) | Power (W) | Efficiency (FPS/W) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang et al. [23] | 2023 | CNN | Spartan-6 | 32×32 | 96 | 16 | 0.79 | 20.25 |
| Heller et al. [24] | 2022 | YOLO V4 Tiny | Kria KV 260 | HD | 75 | 15 | 8 | 1.87 |
| Corcoran et al. [25] | 2023 | YOLO V3 Tiny | VCU110 | 416×416 | - | 69 | 15.4 | 4.5 |
| Nguyen et al. [21] | 2024 | YOLO V4 Tiny | ZCU104 | HD | 78 | 125 | 26.4 | 4.7 |
| Valadanzoj et al. [22] | 2024 | YOLO V4 Tiny | ZC706 | 416×416 | 79 | 55 | 13.6 | 4.0 |
| R.A.Amin et al. [26] | 2024 | YOLO V3 Tiny | Kria KV260 | HD | 99 | 15 | 3.5 | 4.2 |
| This Work | 2025 | YOLO V4 Tiny | ZCU104 | HD | - | 9.87 | 2.866 | 3.44 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gundrapally, A.; Shah, Y.A.; Vemuri, S.M.; Choi, K. Hardware Accelerator Design by Using RT-Level Power Optimization Techniques on FPGA for Future AI Mobile Applications. Electronics 2025, 14, 3317. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14163317
Gundrapally A, Shah YA, Vemuri SM, Choi K. Hardware Accelerator Design by Using RT-Level Power Optimization Techniques on FPGA for Future AI Mobile Applications. Electronics. 2025; 14(16):3317. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14163317
Chicago/Turabian StyleGundrapally, Achyuth, Yatrik Ashish Shah, Sai Manohar Vemuri, and Kyuwon (Ken) Choi. 2025. "Hardware Accelerator Design by Using RT-Level Power Optimization Techniques on FPGA for Future AI Mobile Applications" Electronics 14, no. 16: 3317. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14163317
APA StyleGundrapally, A., Shah, Y. A., Vemuri, S. M., & Choi, K. (2025). Hardware Accelerator Design by Using RT-Level Power Optimization Techniques on FPGA for Future AI Mobile Applications. Electronics, 14(16), 3317. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14163317








