Abstract
This study explores fine-tuning methods and dataset structures for multilingual neural machine translation using the No Language Left Behind model, with a case study on Kazakh, English, and Russian. We compare single-stage and two-stage fine-tuning approaches, as well as triplet versus non-triplet dataset configurations, to improve translation quality. A high-quality, 50,000-triplet dataset in information technology domain, manually translated and expert-validated, serves as the in-domain benchmark, complemented by out-of-domain corpora like KazParC. Evaluations using BLEU, chrF, METEOR, and TER metrics reveal that single-stage fine-tuning excels for low-resource pairs (e.g., 0.48 BLEU, 0.77 chrF for Kazakh → Russian), while two-stage fine-tuning benefits high-resource pairs (Russian → English). Triplet datasets improve cross-linguistic consistency compared with non-triplet structures. Our reproducible framework offers practical guidance for adapting neural machine translation to technical domains and low-resource languages.
1. Introduction
Multilingual neural machine translation (NMT) has made significant progress in solving translation challenges, especially for languages with limited resources. The No Language Left Behind model (NLLB) [1] supports over 200 languages; however, it requires optimal fine-tuning and dataset strategies to adapt it to specific domains and languages. This study investigates single-stage and two-stage fine-tuning, as well as triplet versus non-triplet dataset structures, using a Kazakh–English–Russian case study to further the adoption of multilingual NMT applications.
Fine-tuning is necessary to adapt pre-trained NMT models to specific languages and domains, balancing specialization and generalization [2]. One-stage fine-tuning directly optimizes task-specific data, which can lead to overfitting and catastrophic loss of general domain knowledge [3,4]. Two-stage fine-tuning, including an intermediate phase of domain adaptation, aims to preserve generalization while achieving specialization [5]. Similarly, dataset structures affect translation performance. Triplet datasets, where sentences are aligned across three languages (e.g., Kazakh, English, and Russian), provide cross-linguistic consistency [6], while non-triplet datasets (e.g., individual language pairs) provide flexibility but may lack consistency. The combination of fine-tuning strategies and dataset structures that influence adaptation performance and ensure linguistic consistency of dataset alignment is essential for improving NMT, especially for resource-constrained languages [2,3].
We evaluate these approaches using a high-quality dataset of 50,000 manually translated and expert-verified Kazakh–English–Russian triplets from information technology (IT). The IT-domain dataset serves as a domain-specific adaptation model, while KazParC provides a domain-wide benchmark. In our experiments, we assess translation quality both within and across domains, with a particular focus on resource-constrained Kazakh and technical IT contexts. The main contributions of this work include the following:
- -
- Fine-tuning analysis: a thorough comparison of one-stage and two-stage fine-tuning strategies to balance domain specialization and generalization in multilingual NMT.
- -
- Dataset structure assessment: an analysis of the triplet and non-triplet structures of the dataset, demonstrating their impact on cross-linguistic consistency and translation accuracy.
- -
- High-quality dataset: A case study using an IT dataset of 50,000 manually translated and expert-validated Kazakh–English–Russian triplets to demonstrate domain-specific adaptation.
- -
- Generalizable framework: A reproducible framework for NMT optimization with suggestions for new methodologies and broader applicability to resource-constrained languages.
This paper is structured as follows: Section 2 reviews previous work on NMT, focusing on fine-tuning and dataset strategies. Section 3 describes the dataset in detail, including the IT-domain triplet dataset and out-of-domain corpora. It also describes the experimental framework, training methodologies, and evaluation metrics. Section 4 describes the experimental setup. Section 5 presents the results, analyzing model performance across fine-tuning strategies and dataset types. Section 6 explains these results and discusses their implications and limitations. Finally, Section 7 concludes the study by summarizing the main ideas and suggesting future research directions.
2. Literature Review
This section discusses previous work on NMT with a focus on domain adaptation, low-resource language challenges, and Kazakh-specific efforts.
Domain adaptation in machine translation (MT) has been extensively studied to improve the performance of general-purpose models on specialized tasks. Data-oriented strategies have been used to adapt the domain and address resource constraints. Subword regularization using pair byte encoding, which improves vocabulary flexibility for rare words, is introduced in [7]. Resource-limited Hindi to English translation considers synthetic data for multimodal NMT, which improves performance with image features depending on data quality [8]. Domain-and task-adaptive pre-learning in a large dataset improves domain-specific classification, which suggests early domain relevance at the cost of substantial data [9].
Architectural achievements and the frameworks of transfer learning underlie the adaptation of modern NMT. The Transformer model described in [10] is highly effective when using self-attention but is limited to single-stage training. Architectural flexibility is discussed in [11], demonstrating the effectiveness of using self-attention in the encoder while relying on recurrent neural networks (RNNs) or convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for the decoder, which improve adaptation through minimal adjustment. Sequential transfer learning is discussed in [12], broadly covering pre-training and adaptation.
Methods based on parameter optimization and robustness-enhancing techniques have been investigated for the adaptation of NMT. Adapters for effective adaptation, which retain the main weight when working with new domains, are proposed in [13]. A low-rank adaptation [14] is proposed that reduces computational costs by updating weights but is not domain-specific. Furthermore, [15] describes multi-task learning to train general and domain-specific features together, which requires complex architectures. For domain invariant features, adversarial training [16] improves robustness despite instability. Contrastive learning is used to improve the noise resistance of NMT but is limited to specific models [17]. Elastic weight consolidation was used to maintain performance in the overall domain when fine-tuning within the domain [18].
To balance generalization and specialization, multi-stage and gradual adaptation strategies have been developed. One study [19] describes an incremental fine-tuning for dialogue and event tasks, which reduces redundancy at the expense of increased complexity. Another work [5] provides a low-cost two-stage fine-tuning system for NMT that adapts the parent model to the child source data and then refines them with distillation. Curriculum learning is utilized in [20], organizing data by domain similarity to improve the use of TED Talks and patents. Catastrophic forgetting in NMT, associating it with verbal coverage and offering minimal mixed tuning, is analyzed in [21]. Multi-objective fine-tuning with knowledge distillation is recommended to balance in- and out-of-domain performance [22].
Challenges in NMT, which show a decrease in performance during resource constraints and when working outside the domain settings due to data scarcity and domain shifts, are described in [23]. Adaptation to conversational domains is shown in [3], which improves the BLEU score to 5.2 for the English–German language pair and shows competitive results for the English–Vietnamese language pair with limited resources. Using a “mixed fine tuning”, which combines out-of-domain pre-training with tagged mixed-corpus fine-tuning, was recommended in order to reduce overfitting [4]. Fast domain adaptation by ensembling is proposed in [24], which improves in-domain performance with minimal out-of-domain loss. Regularization techniques such as dropout and MAP-L2 [25] are used to maintain general competence during fine-tuning [25].
Several works have been undertaken to create the MT for the Kazakh language, taking into account its low resource status and morphological complexity. A publicly available parallel corpus of 371,902 human-translated sentences in Kazakh, English, Russian, and Turkish, KazParC is proposed to address the resource limitations of machine translation in Kazakh [6]. A Kazakh–English NMT using RNN, BRNN, and Transformer architecture with a synthetic corpus was studied in [26], achieving competitive BLEU scores. Morphological segmentation and synthetic data were applied to the English–Kazakh NMT, improving agglutinative structure processing [27]. Data-driven and hybrid approaches for Russian–Kazakh MT were compared in [28], with factored SMT being favored for morphology but NMT’s potential with more data being notable. A multi-source Transformer for Kazakh–Russian–English NMT that uses Russian as an auxiliary source to improve translation from Kazakh to English was developed in [29]. While this does provide benefits, it increases the complexity. Structural transfer rules for the Kazakh–English MT in Apertium were developed in [30], which, although not scalable, offer accuracy for small datasets. Synthetic corpora were developed for the Kazakh–English and Kazakh–Russian NMT, using suffix-based methods that improve quality but require preprocessing [31].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Dataset
This section describes a dataset developed to improve multilingual machine translation across Kazakh (KK), English (EN), and Russian (RU). Two main datasets were used: an in-domain dataset focused on information technology (IT-domain) to solve specialized translation tasks, and an out-domain dataset for broader linguistic coverage. The in-domain dataset contains parallel triplets (KK ↔ EN ↔ RU), while the out-domain dataset contains both triplets and a language-pair dataset consisting of separate KK ↔ RU, KK ↔ EN, and EN ↔ RU pairs to support various (non-triplet) training scenarios.
3.1.1. IT-Domain Dataset (KK ↔ EN ↔ RU)
The IT domain dataset for the KK ↔ EN ↔ RU triplet was created to support specialized translation tasks in the IT sector. To ensure high quality and relevance, we used content from the open access repository arXiv (arxiv.org), selected for its broad coverage of preprints on computer science and IT-related topics. Articles published between January 2023 and September 2024 were retrieved using the arXiv API. A total of 3093 articles from 39 computer science subcategories (e.g., artificial intelligence, robotics) were processed to obtain descriptive text.
Article processing began with cleaning the HTML content to isolate textual data. Non-text elements such as <head>, <nav>, <table>, <figure>, and <img> tags, as well as acknowledgement sections that mentioned grants or non-author contributors, were removed. Mathematical formulas, quotes, and parentheses were also removed to focus on the narrative text. Using structured HTML markup, the script extracted text content accurately, while extraneous elements were omitted, preserving the integrity of IT-related information. Subsequently, each article was converted into sentences using the sentence tokenizer from the Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK) library [32]. To maintain quality and consistency, sentences shorter than three words (e.g., trivial fragments) or longer than forty words (e.g., overly complex structures) were filtered out, allowing for a balance between brevity and informativeness.
Further refinement included a noise removal process to improve the quality of the dataset. The script performed several preprocessing steps: (1) removing mixed alphanumeric characters (e.g., “AI2024”), non-English words, and unnecessary characters (e.g., #, ^, *); (2) identifying the language to retain only English sentences; and (3) syntactic parsing using the Stanford Dependency Analyzer to check for grammatical coherence. The cleaned, syntactically correct sentences were saved to a separate file, resulting in a corpus of 125,763 English sentences suitable for translation and analysis.
From this corpus, a subset of 50,000 English sentences was selected to be translated into Kazakh and Russian to form parallel triplets KK ↔ EN ↔ RU. These were manually translated by a team of bilingual experts who were fluent in Kazakh, English, and Russian and had experience in IT. Table 1 provides basic statistics for each language pair, including the number of parallel sentence pairs (“# lines”), distinct sentences (“# sent”), total tokens (“# tokens”), and unique tokens (“# types”) obtained using the Moses tokenizer [33]. The final IT dataset was divided into training, validation, and test sets (Table 2).

Table 1.
Statistics of IT-domain dataset.

Table 2.
Splits of IT-domain dataset.
3.1.2. Out-of-Domain Dataset
KazParc dataset (KK ↔ EN ↔ RU). In this work, we used only the KK ↔ EN ↔ RU triplet from the KazParC dataset provided in [6]. It is designed to improve machine translation into Kazakh, English, Russian, and Turkish. This publicly available dataset consists of 371,902 carefully sorted sentence pairs. The data came from a variety of fields such as mass media, legal documents, general texts, education and science, and fiction, and showed high lexical and contextual diversity. To expand the scope of application, a synthetic corpus (KazParC_SynC) consisting of 1,797,066 sentences was created using web scraping and machine translation using Google Translate, enriching the core of human translation. Detailed information about the datasets is provided in Table 3 and Table 4, respectively. The KazParC and KazParC_SynC datasets were combined because work [6] showed that combining human-translated and synthetic data yields the best translation performance. Throughout this study, the term “KazParC dataset” refers to this combined corpus, which includes both the original and synthetic data, along with their corresponding training and validation sets.

Table 3.
Statistics of KazParC dataset.

Table 4.
Statistics of KazParC_SynC dataset.
LangPair Corpus (KK ↔ RU, KK ↔ EN, EN ↔ RU). Since there is no dataset that covers all three language pairs (KK ↔ RU, KK ↔ EN, and EN ↔ RU), we have created a combined resource for this study, which we will call the LangPair corpus for ease of use. The LangPair corpus consists of three non-triplet datasets: (1) NLA dataset (KK ↔ RU), (2) KazNU dataset (KK ↔ EN), and (3) ParaCrawl Corpus (EN ↔ RU). These corpora, summarized in Table 5, were selected to support targeted training of individual language pairs.

Table 5.
Statistics of LangPair corpus.
The NLA dataset [28] prepared in our laboratory contains 450,000 parallel KK ↔ RU sentence pairs from online news articles on 15 Kazakhstani websites related to government agencies, national companies, or quasi-governmental institutions. These sources follow a bilingualism policy that ensures consistent content in Kazakh and Russian. The dataset, which initially consisted of 890,000 sentence pairs, was subsampled to 400,000 pairs to optimize processing while maintaining representativeness. Preprocessing included normalization, removal of special characters, and filtering out misaligned sentences, resulting in a high-quality corpus for translation in the news domain.
The KazNU dataset [26] contains 450,000 parallel KK ↔ EN sentence pairs designed to solve NMT tasks in formal domains (e.g., social, political, scientific texts). It combines sentence pairs extracted from bilingual Kazakh–Kazakh government websites through web scraping and synthetic pairs created by translating monolingual Kazakh research articles into English using the forward translation method. Pre-processing included normalization, removal of extraneous characters, and removal of low-quality translation to achieve consistency and fluency.
The ParaCrawl corpus [34], part of the ParaCrawl project to build large-scale translation resources, contains 450,000 EN ↔ RU sentence pairs extracted from bilingual websites. This subset was selected from a larger dataset of 12,061,155 pairs (version 1.0) due to computational efficiency and quality. Pre-processing included removing duplicates, removing non-textual elements (e.g., HTML tags), and language detection to ensure correct sentence pairs.
3.2. Methods
This subsection describes an experimental framework for evaluating multilingual machine translation models in KK, EN, and RU. The focus is on the No Language Left Behind model, fine-tuning strategies, and evaluation metrics. The framework evaluates translation performance in IT-specific and general domains by comparing triplet and non-triplet dataset structures.
3.2.1. No Language Left Behind Method
The No Language Left Behind project [1] represents a breakthrough in the field of neural machine translation by delivering translations in 200 languages. In this study, the NLLB-200 model serves as a pre-trained model for our experimental setup. The distilled version (NLLB-200-distilled-1.3B), optimized for 1.3 billion parameters, addresses the data shortage using advanced data processing and modeling techniques. Its encoder–decoder architecture is optimized for multilingual translation and includes 12 layers. Each encoding layer includes a multi-head self-attention (16 heads) and feed-forward networks (FFNs) with GELU activations that scale from 1024 hidden dimensions to 4096 dimensions. Positional encodings extend input embeddings by supporting a vocabulary of 256,000 tokens to account for linguistic diversity.
The 12-layer decoder also uses masked multi-head self-attention for autoregressive generation and cross-attention to align source and target sequences. The main innovation is the Sparsely Gated Mixture of Experts (MoE) framework within FFN layers, which distributes language-specific tasks across subsets of 128 experts. This approach to conditional estimation improves scalability and efficiency, allowing for reliable performance across thousands of translation directions, especially for low-resource languages. The output layer projects the decoder representations into a dictionary, with softmax pre-defining the target tokens. Post-attention and post-FFN dropout, along with layer normalization, ensures training stability.
3.2.2. Domain-Specific Analysis
The NLLB model was fine-tuned on the high-quality IT domain dataset and out-of-domain dataset to evaluate translation performance in domain-specific and generic contexts. Cross-domain experiments evaluated generalization by testing the fine-tuned IT model on the KazParC test set and the fine-tuned KazParC model on the IT test set. Performance was assessed by analyzing quantitative metrics that identified terminology errors and qualitative errors (e.g., mismatches in technical meanings). This analysis provides a basis for domain adaptation strategies to balance specialization and generality in multilingual NMT.
3.2.3. Dataset Type Comparison
Two dataset structures were compared for multilingual NMT using the NLLB model: triplet datasets (KK ↔ EN ↔ RU, e.g., KazParC, IT-domain dataset) and the LangPair Corpus (separate KK ↔ RU, KK ↔ EN, EN ↔ RU pairs). Triplet datasets allow training in all three languages simultaneously, potentially enhancing cross-lingual coherence. The LangPair Corpus focuses on individual pairs. Experiments evaluated their impact on translation accuracy and efficiency.
3.2.4. Fine-Tuning Setup
Fine-tuning is necessary to adapt pre-trained machine translation models to specific tasks, but there is a risk of catastrophic forgetting when knowledge is lost in the general topic. This problem is especially relevant in multilingual NMT, which requires balanced performance in different languages and subject areas.
Single-stage fine-tuning, which is implemented on the basis of data relevant to the specific task, is effective but often leads to overfitting and reduced generalization. Two-stage fine-tuning allows for the mitigation of this, first adapting the model on a broader out-of-domain dataset before focusing on the target domain. Although this is reliable, it requires careful adjustment of the training approaches and data selection. Choosing the right fine-tuning strategy is essential for maintaining the quality of translation in both specialized domains and general areas.
Within the framework of a single-stage approach, a pre-trained multilingual NLLB model is directly trained on a mixed-domain dataset, which includes both in-domain (IT) triplets and general-domain parallel texts. This update is caused by the main limitations of the data in the subject area, which can lead to overwriting the general-domain linguistic capabilities, especially in low-resource scenarios [2,3].
To mitigate forgetting and improve the adaptation to a specific topic, a two-stage fine-grained parameterization was used. This differs from the single-stage method by introducing an intermediate stage of adaptation. Stage 1 leverages a large out-of-domain corpus, rich in linguistic variation across Kazakh, English, and Russian. The goal is to enhance the model’s general multilingual proficiency. Stage 2 fine-tunes the model on a smaller, highly specialized IT-domain dataset of 50,000 triplets. The objective here is to capture domain-specific terminology and stylistic nuances.
In this study, out-of-domain texts (such as KazParC) were included alongside in-domain IT texts for two main reasons. First, in the two-stage fine-tuning setup, the out-of-domain data is used in the initial stage to strengthen the model’s general linguistic capacity before domain-specific adaptation. This helps preserve broader language knowledge and mitigates catastrophic forgetting when the model is later fine-tuned on IT-specific texts. Second, in the single-stage experiments, we explore the effect of mixing out-of-domain and in-domain texts in a unified training phase. While these general texts are not topically aligned with IT content, they contribute linguistic variety and help stabilize training, particularly for low-resource language directions such as Kazakh ↔ English or Kazakh ↔ Russian. This approach allows us to evaluate the trade-offs between domain-specific specialization and general language robustness.
3.2.5. Evaluation Metrics
The quality of the translation was assessed using four metrics: BLEU [35], chrF [36], METEOR [37], and TER [38]. BLEU measures n-gram precision (n = 4), ranging from 0 to 1, with higher scores indicating better correspondence to the reference translations. METEOR evaluates unigram precision and recall with synonym and paraphrase matching, ranging from 0 to 1, with higher scores indicating improved semantic alignment. TER calculates the minimum edit rate (insertions, deletions, substitutions) needed to align translations with references, ranging from 0 to 1, where lower scores reflect better quality.
3.2.6. Statistical Significance Testing
To ensure the reliability of performance comparisons between models, we employed a paired bootstrap resampling test [39] to assess the statistical significance of BLEU score differences. This method is well-suited for machine translation evaluation, as it accounts for variability in test set translations by resampling with replacement. For each comparison (e.g., single-stage vs. two-stage fine-tuning, triplet vs. non-triplet datasets), we performed 10,000 bootstrap iterations to estimate the distribution of BLEU score differences. A p-value less than 0.05 indicates that the observed difference is statistically significant, suggesting that performance improvement is unlikely due to random variation. Additionally, we calculated 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for BLEU scores to quantify the uncertainty of the estimates, providing a range within which the true BLEU score is likely to lie with 95% confidence. These tests were applied to key comparisons on the IT-domain test set.
4. Experimental Setup
This section describes the experimental framework for evaluating the NLLB-200-distilled-1.3B model for multilingual NMT across Kazakh, English, and Russian. Experiments assess in-domain and out-of-domain training, single-stage and two-stage fine-tuning, triplet and non-triplet dataset structures, addressing fine-tuning setup, dataset comparison, and domain-specific performance. Table 6 summarizes the experimental setup.

Table 6.
Summary of experimental setup.
Table 7 summarizes the fine-tuning experiments for the NLLB-200-distilled-1.3B model, with common settings across all experiments: Adafactor optimizer, 2 × 10−5 learning rate, FP16 precision, 32 evaluation accumulation steps, and 256-token generation length, conducted on the DGX server with 8 V100 GPUs. As shown in Table 7, the number of Epochs and Evaluation Steps varies across models. This is due to differences in dataset sizes and training configurations. To ensure optimal performance and avoid overfitting, each model was trained with hyperparameters specifically tailored to the requirements of its respective task and dataset.

Table 7.
Configurations and duration of fine-tuning experiments.
The experiments were designed to address five key research questions:
- -
- Single vs. Two-Stage Fine-Tuning: S-Exp-1 vs. D-Exp-1, S-Exp-2 vs. D-Exp-2, S-Exp-3 vs. D-Exp-3 to assess whether sequential training mitigates catastrophic forgetting, enhancing IT-domain accuracy without sacrificing generalization.
- -
- In-Domain vs. Out-of-Domain: Exp-1 vs. Exp-2, Exp-3 to evaluate whether IT-specific training outperforms general-domain training on technical texts.
- -
- Triplet vs. non-triplet: Exp-1, Exp-2 vs. Exp-4 to compare whether simultaneous three-language training improves cross-lingual coherence over individual pair training.
- -
- LangPair Corpus Impact: S-Exp-1 vs. S-Exp-3, S-Exp-2 vs. Exp-4 to test non-triplet data’s contribution.
- -
- Benchmarking against Google and Yandex APIs.
5. Results
This section presents the performance of the NLLB-200-distilled-1.3B model for multilingual NMT across six translation directions (KK → EN, EN → KK, KK → RU, RU → KK, EN → RU, RU → EN). Table 8 and Table 9 summarize performance on IT-domain and KazParC test sets, respectively.

Table 8.
Experimental performance (BLEU↑|chrF↑|METEOR↑|TER↓) for IT-domain test set.

Table 9.
Experimental performance (BLEU↑|chrF↑|METEOR↑|TER↓) for KazParC test set.
Figure 1 illustrates the average values of BLEU, chrF, METEOR, and TER scores, highlighting trends across experiments. The bar charts illustrate Exp-1’s strong performance on the IT-domain dataset and Exp-3’s advantage on KazParC, with triplet-based models consistently outperforming the non-triplet base-line (Exp-4). Bar charts highlight METEOR’s alignment with BLEU/chrF trends and TER’s inverse correlation, reinforcing triplet dataset benefits.
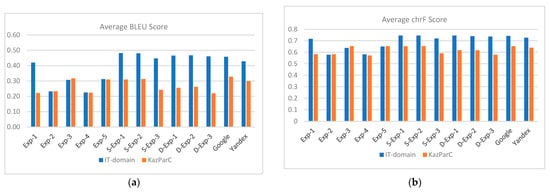
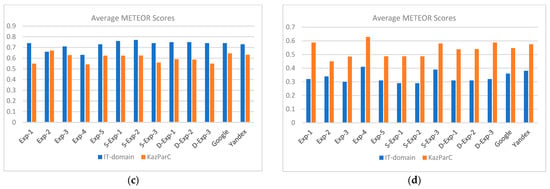
Figure 1.
Comparative analysis of translation performance metrics across test sets: average BLEU scores (a), average chrF scores (b), average METEOR scores (c), and average TER scores (d). The bar charts illustrate Exp-1’s strong performance on the IT-domain dataset and Exp-3’s advantage on KazParC, with triplet-based models consistently outperforming the non-triplet baseline (Exp-4).
Single-Stage vs. Two-Stage Fine-Tuning: The single-stage experiments (S-Exp-1, S-Exp-2, and S-Exp-3) showed good performance in the test set of the IT domain, in particular in directions with fewer resources EN → KK and KK → RU. For example, S-Exp-1 showed better results in EN → KK, which shows that direct training on domain-related data effectively captures specialized IT terminology and style.
In contrast, the two-stage setups (D-Exp-1 to D-Exp-3) showed good generalizations in high-resource directions such as RU → EN. The intermediate adaptation to the general domain dataset in stage 1 helped preserve broader language patterns, which is especially useful when translating from morphologically rich languages.
These results show that single-stage fine-tuning is more suitable for specialized tasks with fewer resources, while two-stage fine-tuning better supports generalization with higher resources.
In-Domain vs. Out-of-Domain Training: On the IT-domain test set, in-domain training (Exp-1) outperforms out-of-domain setups (Exp-2, Exp-3, Exp-4, Exp-5) in almost all directions. EN → KK and KK → RU have shown particularly great advances in demonstrating how domain matching in learning data increases terminological accuracy and fluency.
However, on the KazParC test set, out-of-domain setups such as the Exp-3 outperformed the Exp-1, confirming that performance was closely related to domain matching between training and test data. Cross-domain testing (e.g., the IT-trained model tested at KazParC) showed reduced scores, emphasizing the difficulty of generalization in domain-adapted NMTS.
Triplet vs. Non-triplet: Triplet-based training (Exp-1-Exp-3) has consistently surpassed non-triplet training (Exp-4, LangPair) in areas including the Kazakh language, such as KK → RU and EN → KK. These successes are due to the extended representative compatibility that facilitates inter-language identification when the three languages are taught together.
In contrast, Exp-4 showed weak performance, especially in areas of the IT domain, due to reduced compliance and increased lexical ambiguity. Even when paired with stronger samples (for example, in the S-Exp-2), non-triplet data input has slightly reduced performance, indicating that ternary alignment remains a strong advantage, especially for low-resource language combinations.
Impact of LangPair Data: The S-Exp-3 and Exp-4 experiments, which combined the LangPair dataset, showed a correspondence between extended learning coverage and domain specificity. Although LangPair has helped increase fluency in general domain areas (e.g., EN → RU, RU → EN), it has often reduced accuracy in IT domain tasks by introducing stylistic and terminological noise.
The most noticeable degradation occurred in EN → KK and KK → RU, where the model trained with LangPair Data (S-Exp-3) performed only lower compared with its triple counterpart (S-Exp-1). This emphasizes the importance of careful handling of additional cases so as not to weaken the accuracy of the domain.
Comparison with Commercial APIs: Compared with Google and Yandex Translate, the fine-tuned models (especially S-Exp-1 and D-Exp-1) surpassed both services in IT domain translations for low-resource pairs such as KK → EN and EN → KK. These successes were evident in nuanced, technical translations, where commercial systems struggled with precise terminology.
However, commercial APIs remained competitive for high resource general domain tasks such as RU → EN in KazParC. This shows that even though custom fine-tuning offers obvious advantages in specialized or less resource settings, pre-prepared commercial systems still work well in general contexts with good resources.
Statistical Significance Analysis. We conducted paired bootstrap resampling tests to assess the statistical significance of BLEU score differences only between key model comparisons—those central to our research questions—single-stage vs. two-stage fine-tuning (S-Exp-1 vs. D-Exp-1, S-Exp-2 vs. D-Exp-2) and triplet vs. non-triplet datasets (Exp-1 vs. Exp-4). This targeted approach avoids unnecessary multiple testing and focuses on meaningful performance differences. The results for selected comparisons on the IT-domain test set are presented in Table 10.

Table 10.
Statistical comparison of BLEU scores across experimental settings and translation directions.
For EN → KK and KK → RU, S-Exp-1 significantly outperforms D-Exp-1 (p = 0.021 and p = 0.048, respectively), confirming that single-stage fine-tuning is effective for low-resource pairs. The BLEU differences of 0.03 for EN → KK and 0.02 for KK → RU are statistically significant, indicating that these improvements are unlikely due to noise. For RU → EN, the difference between S-Exp-2 and D-Exp-2 (0.02 BLEU) is not significant (p = 0.067), suggesting that two-stage fine-tuning’s advantage for high-resource pairs may be less pronounced. Comparing triplet (Exp-1) and non-triplet (Exp-4) datasets, Exp-1 significantly outperforms Exp-4 for EN → KK (p = 0.008) and KK → RU (p = 0.012), with BLEU differences of 0.05 and 0.04, respectively. The 95% CIs indicate tighter ranges for S-Exp-1, reflecting stable performance for low-resource directions.
6. Discussion
6.1. Quantitative Analysis of Translation Outputs
The evaluation of the NLLB-200-distilled-1.3B for the Kazakh–English–Russian NMT presents our idea of optimizing fine parameters and the structure of the dataset depending on the resources and thematic area. Single-stage fine-tuning performs particularly well for low-resource language pairs such as EN → KK, achieving a BLEU score of 0.48 (95% CI: [0.45, 0.51]) and a chrF score of 0.73. This represents a statistically significant improvement over the two-stage approach (p = 0.021). The paired bootstrap test confirms that the 0.03 BLEU increase for EN → KK is unlikely to be due to chance, emphasizing the effectiveness of directly tuning on domain-specific data in better capturing IT-related terminology under low-resource conditions. Likewise, for KK → RU, a 0.02 BLEU gain (p = 0.048) further supports the benefits of single-stage fine-tuning. Additionally, the narrower confidence interval for S-Exp-1 ([0.46, 0.50] compared to [0.44, 0.48] for D-Exp-1) suggests more consistent performance.
Conversely, two-stage fine-tuning proves more beneficial for high-resource language pairs such as RU → EN, achieving a BLEU score of 0.52 (95% CI: [0.51, 0.55]), where general-domain pre-training contributes to greater robustness. However, the 0.02 BLEU improvement between S-Exp-2 and D-Exp-2 is not statistically significant (p = 0.067), indicating that the advantage of two-stage fine-tuning may be limited in high-resource scenarios. This lack of significance could be attributed to the minimal influence of general-domain pre-training when the evaluation set is closely aligned with the training domain, as reflected in the overlapping confidence intervals ([0.49, 0.53] for S-Exp-2 and [0.51, 0.55] for D-Exp-2). These findings emphasize the need to select fine-tuning strategies based on the resource level and domain alignment of the target language pair.
Triplet datasets outperform non-triplet structures in domain-aligned settings, particularly for KK → RU (p = 0.012) and EN → KK (p = 0.008), with BLEU differences of 0.04 and 0.05, respectively. The statistical significance of these differences confirms that triplet-based training reduces lexical ambiguity and enhances cross-linguistic consistency for low-resource languages. The tighter CIs for Exp-1 (e.g., [0.45, 0.51] for EN → KK) compared with Exp-4 ([0.40, 0.46]) reflect the robustness of triplet datasets in maintaining consistent terminology across Kazakh, English, and Russian. However, incorporating LangPair data in S-Exp-3 and Exp-4 introduces general-domain noise, reducing IT-domain accuracy, especially for EN → KK and KK → RU. This degradation is evident in the wider CIs and lower BLEU scores for Exp-4, underscoring the importance of domain-specific data alignment.
Our fine-tuned models (e.g., S-Exp-1) outperform Google and Yandex APIs in IT-domain translation tasks for low-resource language pairs, providing a cost-efficient alternative for domain-specific applications. Statistical significance tests reinforce the reliability of these findings, especially for EN → KK and KK → RU, where p-values below 0.05 confirm the advantage of our models over commercial systems. In contrast, for high-resource pairs such as RU → EN, commercial APIs still perform competitively—likely due to their access to vast training data. Nevertheless, the absence of statistically significant differences in some comparisons (e.g., S-Exp-2 vs. D-Exp-2) indicates that carefully fine-tuned models can deliver comparable results with more focused optimization.
We analyzed the performance and provided translation examples in Table 11, showing where the best and worst models succeed or encounter difficulties, as well as discussing the implications and limitations. Single-stage fine-tuning (S-Exp-1) excels for low-resource pairs (particularly EN → KK), making it the best model for this direction on the IT-domain test set (Table 8). The direct optimization of S-Exp-1 effectively captures its terminology. S-Exp-1 also outperforms two-stage fine-tuning (D-Exp-1) for KK → RU and RU → EN directions. Two-stage fine-tuning benefits high-resource pairs like RU → EN, since general-domain pre-training is used to increase reliability. The worst-performing model, Exp-4 (non-triplet LangPair), has problems with general-domain noise, and, therefore, struggles across all directions (Table 8).

Table 11.
Sample Translations by S-Exp-1 and Exp-4.
6.2. Qualitative Analysis of Translation Outputs
While quantitative metrics such as BLEU, chrF, METEOR, and TER provide valuable insights into model performance, they do not fully capture linguistic nuances, especially in domain-specific and low-resource settings. To address this, we conducted a qualitative analysis of translation outputs from the best-performing model (S-Exp-1, single-stage fine-tuning on IT-domain triplet dataset) and the worst-performing model (Exp-4, non-triplet LangPair dataset) across three translation directions: EN → KK, KK → RU, and RU → EN. This analysis focuses on three critical aspects: (1) terminology accuracy in the IT domain, (2) morphological handling in Kazakh, and (3) cross-linguistic consistency in triplet datasets. We present representative examples, followed by a discussion of error patterns and their implications.
The IT domain requires precise translation of technical terms, such as “blockchain,” “deep learning,” and “data processing.” S-Exp-1, trained on the IT-domain triplet dataset, consistently produces accurate translations for such terms, as seen in Table 11 (e.g., “тepeң oқытy aлгopитмдepi“ for “deep learning algorithms”). This success is attributed to the model’s direct optimization on domain-specific data, which captures IT terminology effectively.
The most problematic aspects of Exp-4 were technical terminology and contextual nuances. For EN → KK, it failed to capture IT-specific terms like “deep learning,” mistranslating it as “deep knowledge. In KK → RU, Exp-4 omitted “software” specificity, producing vague outputs (Table 11). These errors stem from the non-triplet LangPair dataset’s lack of domain-specific alignment, introducing general-domain noise that dilutes IT terminology precision.
Kazakh’s agglutinative nature, characterized by complex suffixes for case, number, and possession, poses unique challenges for NMT. Table 11’s EN → KK example shows S-Exp-1 correctly handling suffixes like “-ды” (past tense) in “Tepeң oқытy aлгopитмдepi нeйpoндық жeлiлepдi oңтaйлaндыpaды.” Exp-4, however, misapplies suffixes and uses incorrect terms, as seen in “Tepeң бiлiм aлгopитмдepi жeлiлepдi жaқcapтaды”. Further examples highlight this issue. In translating “Deep learning algorithms require high computational power,” S-Exp-1 applies the accusative “-ты” in “eceптey қyaтын тaлaп eтeдi,” while Exp-4’s “көп қyaтты қaжeт eтeдi” omits specificity and uses incorrect morphology. These errors align with Table 11’s findings, where Exp-4’s general-domain training fails to capture Kazakh’s morphological complexity. Triplet datasets, by providing cross-linguistic alignment with English and Russian, enable S-Exp-1 to better learn suffix patterns, as the consistent context across languages reinforces correct morphological structures.
Triplet datasets (KK ↔ EN ↔ RU) enable simultaneous training across three languages, promoting consistency in terminology and meaning. For example, S-Exp-1 maintains consistent translations of “artificial intelligence” across directions: “жacaнды интeллeкт” (KK), “иcкyccтвeнный интeллeкт” (RU), and “AI” or “artificial intelligence” (EN). This consistency is critical in technical domains, where terms must be unambiguous. Exp-4, trained on non-triplet LangPair data, introduces inconsistencies, such as translating “иcкyccтвeнный интeллeкт” as “artificial mind” (RU → EN) or “жacaнды paзyм” (KK → RU). These errors reflect the absence of cross-linguistic alignment in non-triplet datasets, which leads to lexical ambiguity. Triplet datasets thus provide a significant advantage for low-resource languages like Kazakh, where cross-lingual cues from English and Russian enhance translation quality.
6.3. Limitations and Future Work
The IT-domain dataset, comprising 50,000 triplets from recent arXiv papers, limits lexical diversity and may introduce topical bias due to its focus on cutting-edge areas like artificial intelligence. This restricts generalizability to broader IT domains, such as software engineering or cybersecurity. Additionally, reliance on BLEU, chrF, METEOR, and TER metrics may not fully capture semantic accuracy or fluency, which advanced metrics like COMET could better assess. The emphasis on Kazakh, English, and Russian excludes other low-resource languages, limiting broader applicability.
Future work will address these by expanding the dataset with diverse IT sources, such as technical documentation and blogs, to enhance lexical coverage and reduce bias. Incorporating Named Entity Recognition (NER) and morphological analyzers will enable detailed qualitative analysis of terminology and suffix accuracy, particularly for Kazakh’s agglutinative structure. Testing hybrid fine-tuning strategies and COMET metrics will refine performance. While statistical significance was assessed for BLEU scores due to their widespread use in NMT evaluation, future work will extend this analysis to chrF and METEOR for a broader assessment. Evaluating additional low-resource languages, like Kyrgyz and Uzbek, and exploring architectures such as adapter-based fine-tuning or multilingual large language models will improve scalability. Cross-lingual transfer learning could further leverage triplet dataset advantages for wider NMT applications.
7. Conclusions
This study contributes to the development of multilingual neural machine translation by optimizing fine-tuning strategies and the structure of datasets using the example of a Kazakh–English–Russian case study using the NLLB-200-distilled-1.3B model. Single-stage fine-tuning is effective for low-resource languages such as Kazakh, while two-stage fine-tuning is useful for high-resource pairs. Triplet datasets improve cross-linguistic consistency compared to non-triplet structures. A 50,000-triplet IT-domain dataset demonstrates in-domain adaptation, with out-of-domain corpora like KazParC providing general-domain benchmarks. Fine-tuned models outperform commercial APIs for low-resource languages, offering a robust framework for multilingual NMT. The results highlight the importance of using data relevant to a specific subject area and improving translations tailored to limited resources, especially in technical areas and other specialized fields.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, software, writing—review and editing, Z.K. and Z.Y.; formal analysis, writing—original draft and funding acquisition, Z.K.; data curation, Z.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Science Committee of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Republic of Kazakhstan (Grant No. AP23489529).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The IT-domain dataset developed and analyzed in this study is publicly available and can be accessed at the following repository: https://huggingface.co/datasets/zhanibekkm/IT-domain-NMT-dataset (accessed on 26 June 2025).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Costa-Jussà, M.R.; Cross, J.; Çelebi, O.; Elbayad, M.; Heafield, K.; Heffernan, K.; Kalbassi, E.; Lam, J.; Licht, D.; Maillard, J.; et al. No language left behind: Scaling human-centered machine translation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.04672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, D. Domain adaptation and multi-domain adaptation for neural machine translation: A survey. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2022, 75, 351–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, M.T.; Manning, C.D. Stanford neural machine translation systems for spoken language domains. In Proceedings of the 12th International Workshop on Spoken Language Translation: Evaluation Campaign, Da Nang, Vietnam, 3–4 December 2015; pp. 76–79. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, C.; Dabre, R.; Kurohashi, S. An empirical comparison of domain adaptation methods for neural machine translation. In Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 July–4 August 2017; pp. 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hou, F.; Wang, R. A Novel Two-step Fine-tuning Framework for Transfer Learning in Low-Resource Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the North American Association for Computational Linguistics (NAACL), Mexico City, Mexico, 16–21 June 2024; pp. 3214–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeshpanov, R.; Polonskaya, A.; Varol, H.A. KazParC: Kazakh Parallel Corpus for Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 2024 Joint International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC-COLING 2024), Torino, Italy, 20–25 May 2024; pp. 9633–9644. [Google Scholar]
- Sennrich, R.; Haddow, B.; Birch, A. Neural Machine Translation of Rare Words with Subword Units. In Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Berlin, Germany, 7–12 August 2016; pp. 1715–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, K.D.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Liu, Q. Multimodal Neural Machine Translation for Low-resource Language Pairs using Synthetic Data. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Deep Learning Approaches for Low-Resource NLP, Melbourne, Australia, 19 July 2018; pp. 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gururangan, S.; Marasović, A.; Swayamdipta, S.; Lo, K.; Beltagy, I.; Downey, D.; Smith, N.A. Don’t Stop Pretraining: Adapt Language Models to Domains and Tasks. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 6–10 July 2020; pp. 8342–8360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Domhan, T. How much attention do you need? A granular analysis of neural machine translation architectures. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Melbourne, Australia, 15–20 July 2018; pp. 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruder, S.; Peters, M.E.; Swayamdipta, S.; Wolf, T. Transfer learning in natural language processing. In Proceedings of the 2019 conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Tutorials, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bapna, A.; Firat, O. Simple, Scalable Adaptation for Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), Hong Kong, China, 3–7 November 2019; pp. 1538–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, E.J.; Shen, Y.; Wallis, P.; Allen-Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, W. Lora: Low-rank adaptation of large language models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Online, 25–29 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, M.Q.; Crego, J.M.; Yvon, F. Multi-Domain Adaptation in Neural Machine Translation with Dynamic Sampling Strategies. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual Conference of the European Association for Machine Translation, Ghent, Belgium, 1–3 June 2022; pp. 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhai, C.; Awadalla, H.H. Multi-task Learning for Multilingual Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Online, 8–12 November 2020; pp. 1022–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Sun, S.; Peng, S.; Xu, J.; Jia, X.; Li, W. Contrastive Preference Learning for Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the North American Association for Computational Linguistics (NAACL), Mexico City, Mexico, 16–21 June 2024; pp. 2724–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, B.; Gwinnup, J.; Khayrallah, H.; Duh, K.; Koehn, P. Overcoming catastrophic forgetting during domain adaptation of neural machine translation. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 2062–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ebner, S.; Yarmohammadi, M.; White, A.S.; Van Durme, B.; Murray, K. Gradual Fine-Tuning for Low-Resource Domain Adaptation. In Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Domain Adaptation for NLP, Kyiv, Ukraine, 19–20 April 2021; pp. 214–221. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Shapiro, P.; Kumar, G.; McNamee, P.; Carpuat, M.; Duh, K. Curriculum Learning for Domain Adaptation in Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 1903–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, D.; DeNeefe, S. Domain adapted machine translation: What does catastrophic forgetting forget and why? In Proceedings of the 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Miami, FL, USA, 12–16 November 2024; pp. 12660–12671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakwale, P.; Monz, C. Fine-tuning for neural machine translation with limited degradation across in-and out-of-domain data. In Proceedings of the Machine Translation Summit XVI: Research Track, Nagoya, Japan, 18–22 September 2017; pp. 156–169. [Google Scholar]
- Koehn, P.; Knowles, R. Six Challenges for Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Neural Machine Translation, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3–4 July 2017; pp. 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitag, M.; Al-Onaizan, Y. Fast domain adaptation for neural machine translation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1612.06897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miceli-Barone, A.V.; Haddow, B.; Germann, U.; Sennrich, R. Regularization techniques for fine-tuning in neural machine translation. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Copenhagen, Denmark, 7–11 September 2017; pp. 1489–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karyukin, V.; Rakhimova, D.; Karibayeva, A.; Turganbayeva, A.; Turarbek, A. The neural machine translation models for the low-resource Kazakh–English language pair. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2023, 9, e1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, A.T.; Edman, L.; Spenader, J.; Yeshmagambetova, G. Neural machine translation for English–Kazakh with morphological segmentation and synthetic data. In Proceedings of the Fourth Conference on Machine Translation, Florence, Italy, 1–2 August 2019; pp. 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makazhanov, A.; Myrzakhmetov, B.; Kozhirbayev, Z. On various approaches to machine translation from Russian to Kazakh. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Turkic Languages Processing (TurkLang 2017), Kazan, Russia, 18–21 October 2017; pp. 195–209. [Google Scholar]
- Littell, P.; Lo, C.-k.; Larkin, S.; Stewart, D. Multi-source transformer for Kazakh-Russian-English neural machine translation. In Proceedings of the Fourth Conference on Machine Translation, Florence, Italy, 1–2 August 2019; pp. 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundetova, A.; Forcada, M.; Tyers, F. A free/open-source machine translation system from English to Kazakh. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Turkic Languages Processing (TurkLang 2015), Kazan, Russia, 17–19 September 2015; pp. 78–90. [Google Scholar]
- Rakhimova, D.; Karibayeva, A. Aligning and extending technologies of parallel corpora for the Kazakh language. East.-Eur. J. Enterp. Technol. 2022, 4, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hu, F. The application of nltk library for python natural language processing in corpus research. Theory Pract. Lang. Stud. 2021, 11, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehn, P.; Hoang, H.; Birch, A.; Callison-Burch, C.; Federico, M.; Bertoldi, N.; Cowan, B.; Shen, W.; Moran, C.; Zens, R.; et al. Moses: Open source toolkit for statistical machine translation. In Proceedings of the 45th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics Companion Volume Proceedings of the Demo and Poster Sessions, Prague, Czech Republic, 23–30 June 2007; pp. 177–180. [Google Scholar]
- Bañón, M.; Chen, P.; Haddow, B.; Heafield, K.; Hoang, H.; Esplà-Gomis, M.; Forcada, M.; Kamran, A.; Kirefu, F.; Koehn, P.; et al. ParaCrawl: Web-scale acquisition of parallel corpora. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 5–10 July 2020; pp. 4555–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papineni, K.; Roukos, S.; Ward, T.; Zhu, W.J. Bleu: A method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 7–12 July 2002; pp. 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popović, M. chrF: Character n-gram F-score for automatic MT evaluation. In Proceedings of the Tenth Workshop on Statistical Machine Translation, Lisbon, Portugal, 17–18 September 2015; pp. 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snover, M.; Madnani, N.; Dorr, B.; Schwartz, R. Fluency, adequacy, or HTER? Exploring different human judgments with a tunable MT metric. In Proceedings of the Fourth Workshop on Statistical Machine Translation, Athens, Greece, 30–31 March 2009; pp. 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Lavie, A. METEOR: An automatic metric for MT evaluation with improved correlation with human judgments. In Proceedings of the ACL Workshop on Intrinsic and Extrinsic Evaluation Measures for Machine Translation and/or Summarization, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, June 2005; pp. 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Koehn, P. Statistical Significance Tests for Machine Translation Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2004 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Barcelona, Spain, 25–26 July 2004; pp. 388–395. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).