The Role of Modulation Techniques on Power Device Thermal Performance in Two-Level VSI Converters
Abstract
1. Introduction
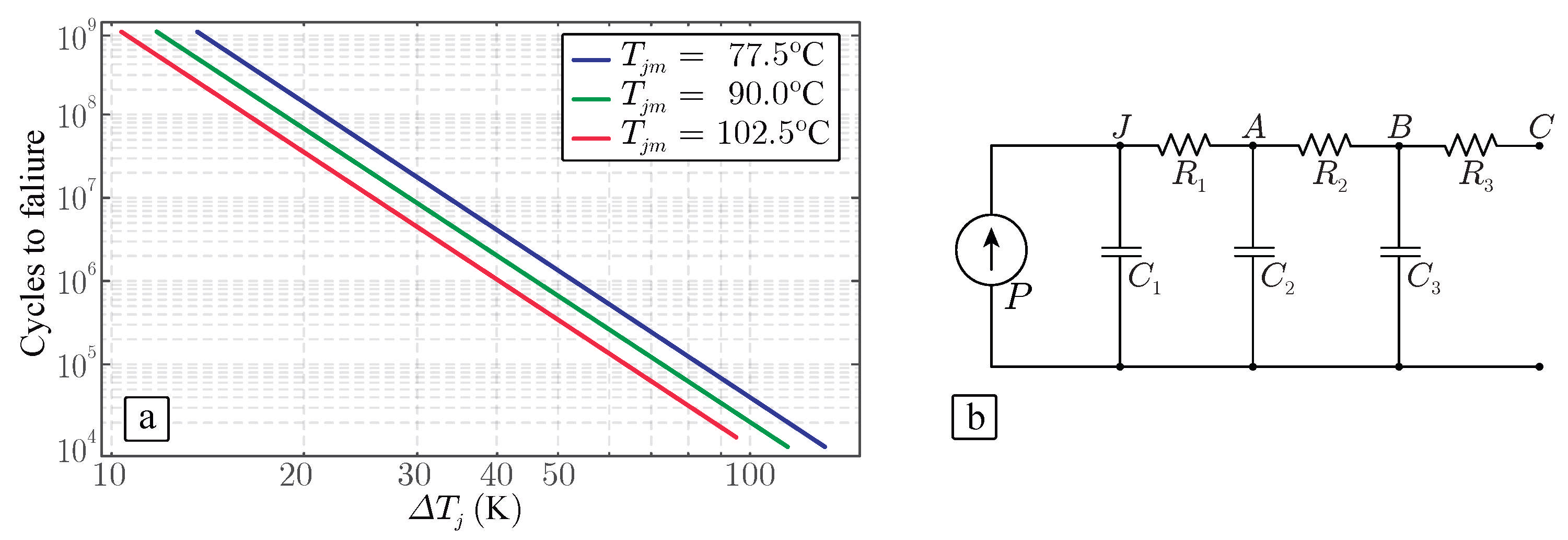
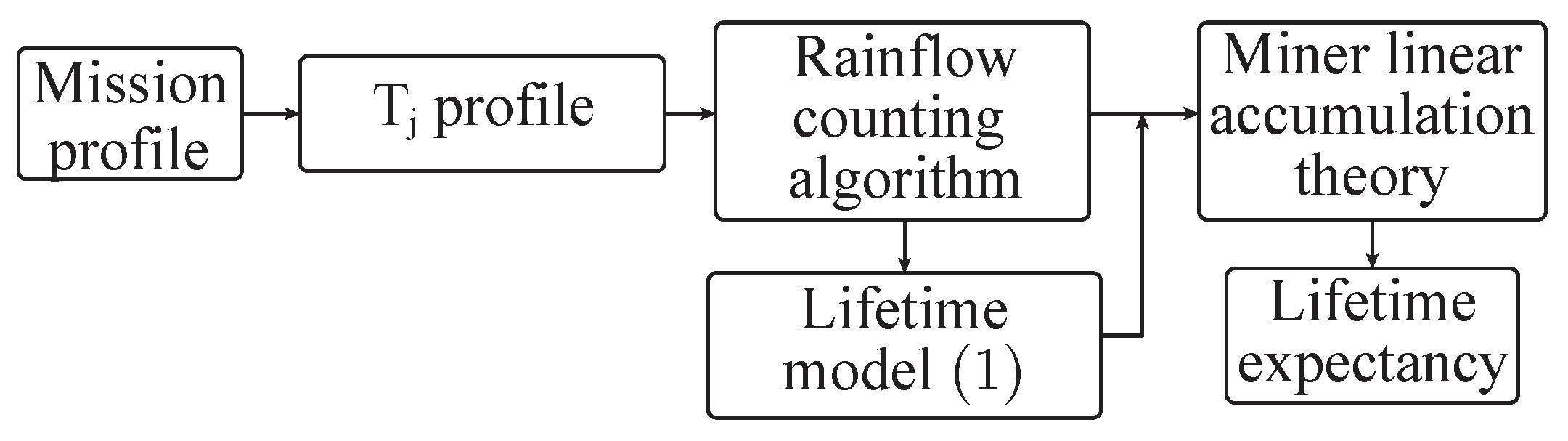
2. Power Devices Aging
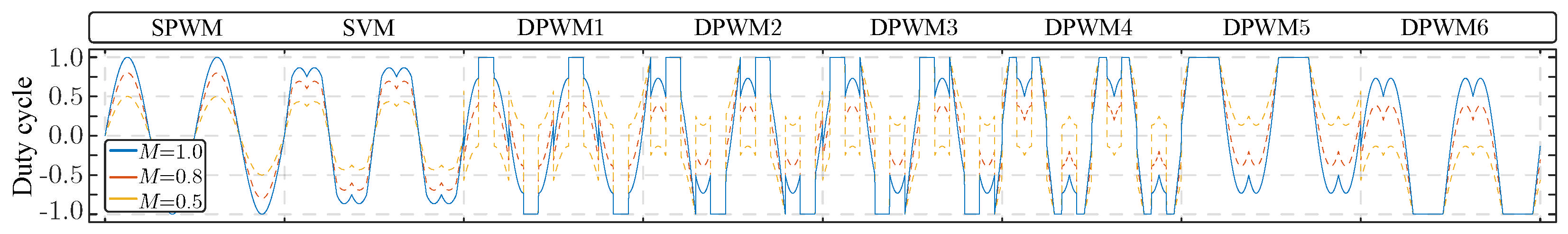
3. Carrier-Based Modulation Techniques Under Evaluation
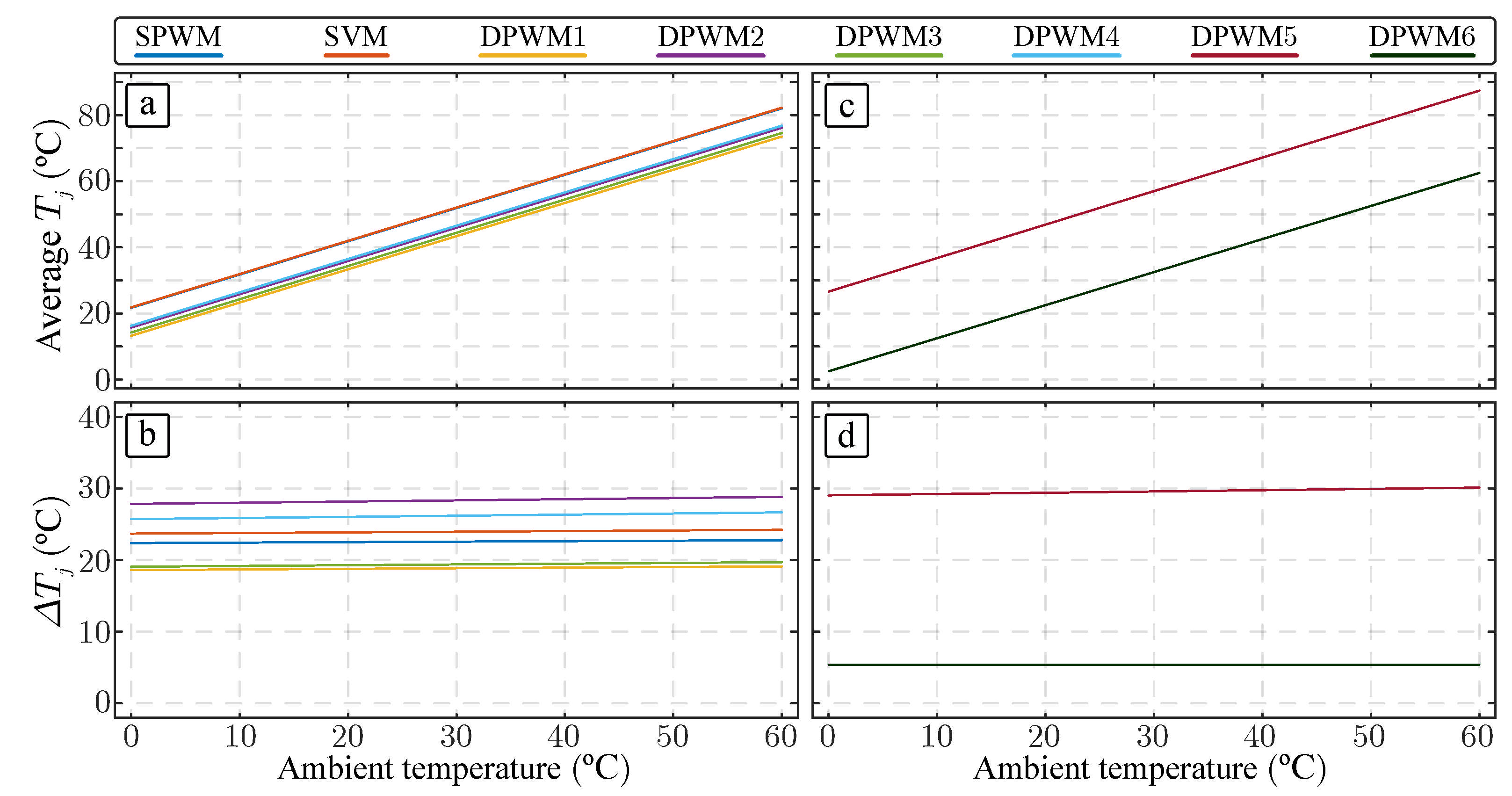
4. Impact of the Modulation Technique on the Junction Temperature of the Power Devices
- The set of modulation techniques present symmetrical behavior with respect to upper and lower devices in each power converter’s leg. In this sense, and for better readability of the obtained results, only the upper device behavior is shown in the following subsections. The lower device presents an identical operational behavior but shifted in each fundamental period.
- The modulation comparison was performed under the same conventional dq-frame linear controller scheme when needed, andthe control parameters were tuned for achieve the same operational behavior in terms of bandwidth, settle time. and overshoot characteristics.
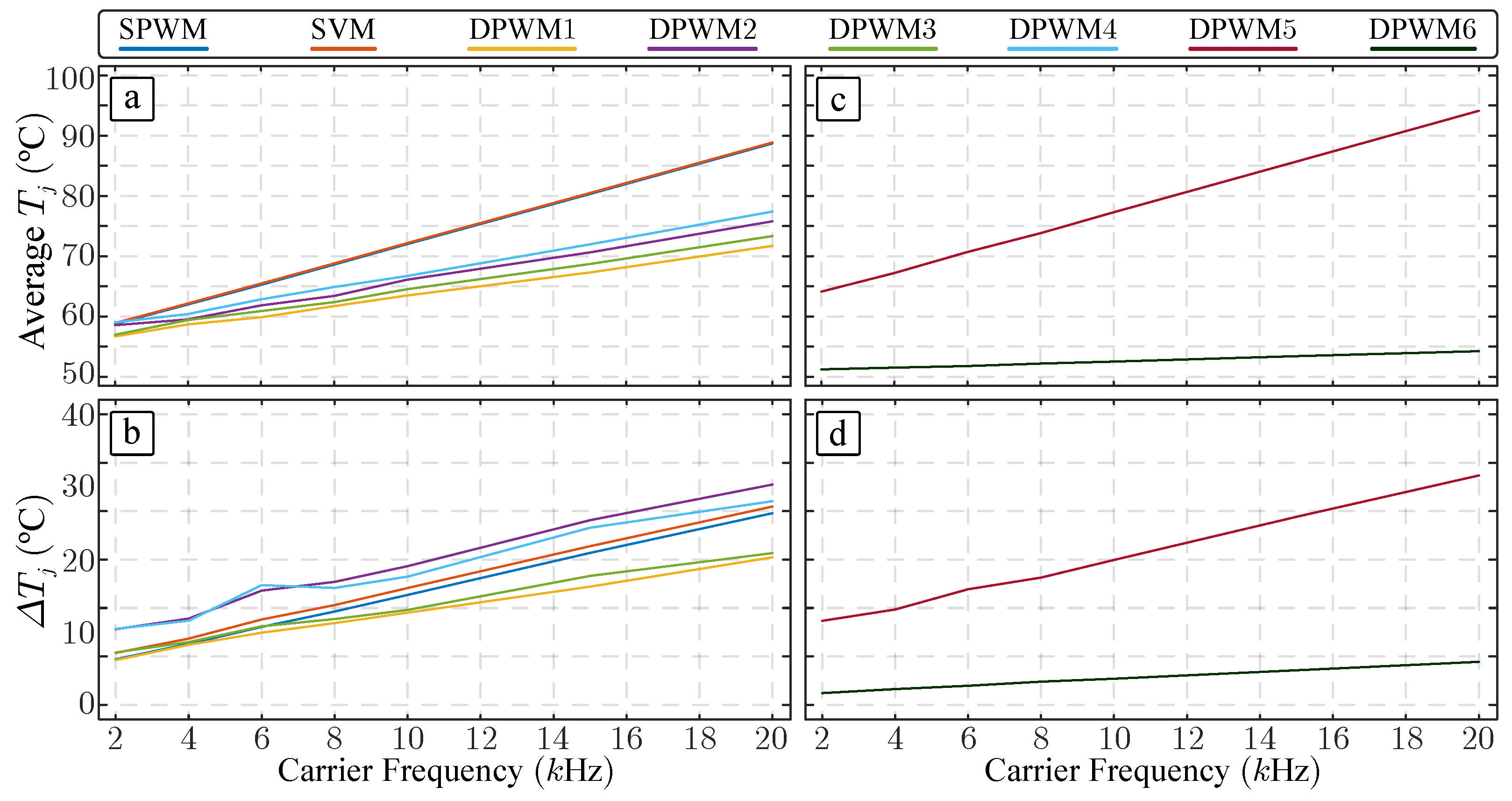
- As shown in Figure 5, modulation techniques DPWM5 and DPWM6 clamp the output voltage to the positive (negative) bar during part of the fundamental period. This obviously creates highly unbalanced operation and thermal stress on the power devices in each phase of the power converter. Furthermore, the stress suffered by the upper device in DPWM5 is analogously reproduced in the lower device considering DPWM6 and vice versa. These techniques are only valid under fault-tolerant operations when the damage provoked in the power device is very high and, during maintenance operations, the operator continues operating the power converter. For that reason, although these techniques are shown in the obtained results, techniques DPWM5 and DPWM6 are out of analysis and therefore out the scope of this work.
4.1. Analysis Considering Different Carrier Frequencies
4.2. Analysis Considering Different Fundamental Operation Frequencies
4.3. Analysis Considering Different Ambient Temperatures
4.4. Analysis Considering Different Power Loads
4.5. Analysis Considering Different Power Factors
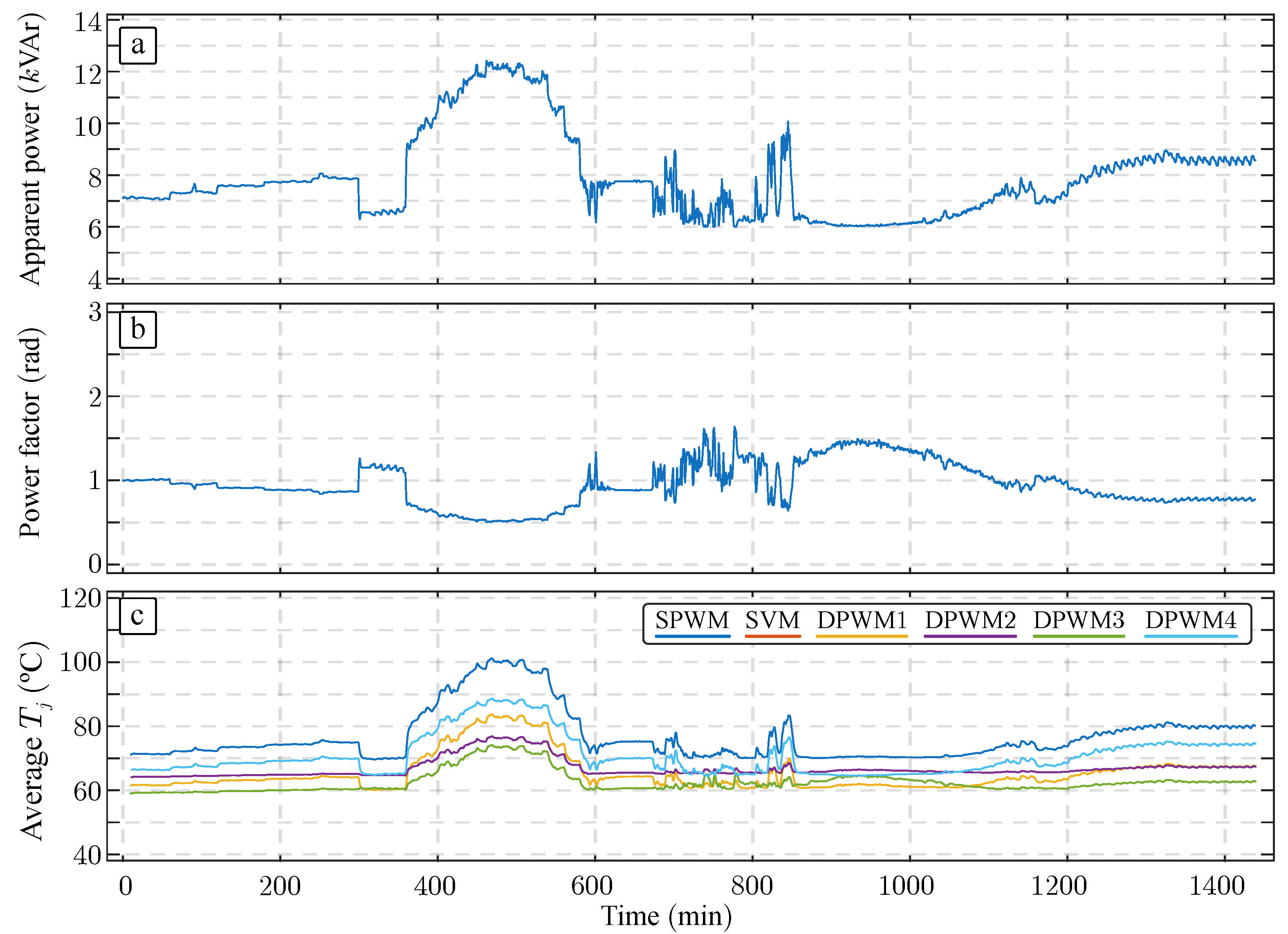
4.6. Evaluation of Case Study Example
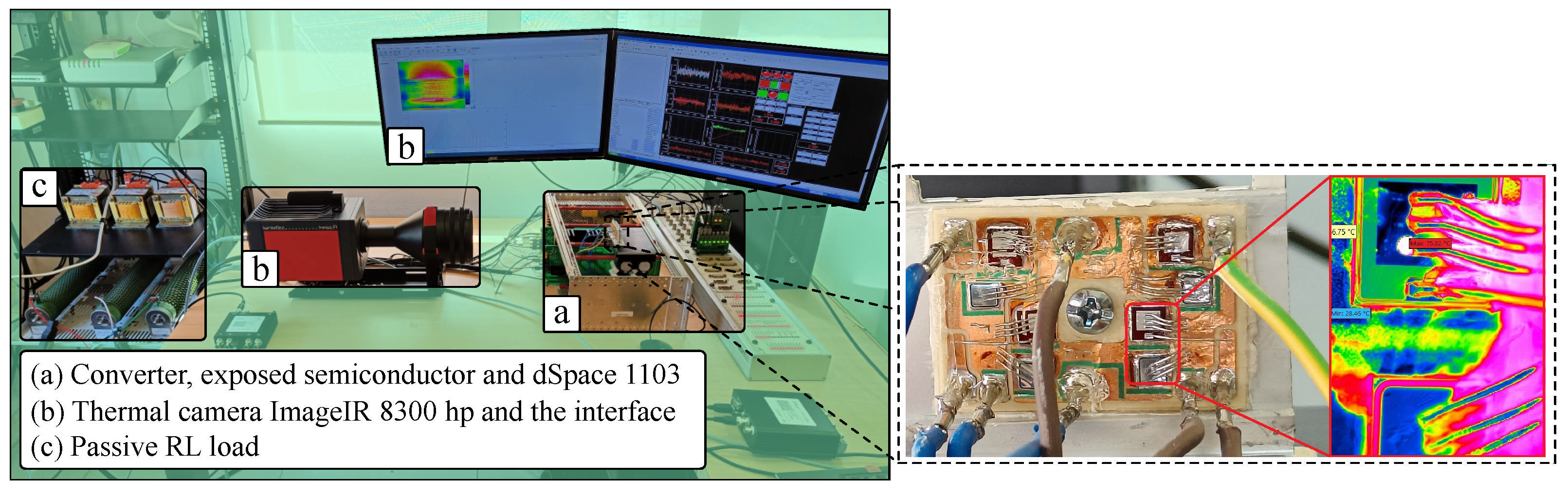
5. Experimental Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chung, H.; Wang, H.; Blaabjerg, F.; Pecht, M. Reliability of Power Electronic Converter Systems; Energy Engineering, Institution of Engineering and Technology: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Peyghami, S.; Wang, Z.; Blaabjerg, F. A Guideline for Reliability Prediction in Power Electronic Converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 10958–10968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Blaabjerg, F. Power Electronics Reliability: State of the Art and Outlook. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 9, 6476–6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyghami, S.; Blaabjerg, F.; Palensky, P. Incorporating Power Electronic Converters Reliability Into Modern Power System Reliability Analysis. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 9, 1668–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liserre, M.; Blaabjerg, F. Toward Reliable Power Electronics: Challenges, Design Tools, and Opportunities. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2013, 7, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Cai, J.; Du, X.; Zhou, L. Review of power semiconductor device reliability for power converters. CPSS Trans. Power Electron. Appl. 2017, 2, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liserre, M.; Buticchi, G.; Leon, J.I.; Marquez Alcaide, A.; Raveendran, V.; Ko, Y.; Andresen, M.; Monopoli, V.G.; Franquelo, L. Power Routing: A New Paradigm for Maintenance Scheduling. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2020, 14, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monopoli, V.G.; Marquez, A.; Leon, J.I.; Liserre, M.; Buticchi, G.; Franquelo, L.G.; Vazquez, S. Applications and Modulation Methods for Modular Converters Enabling Unequal Cell Power Sharing: Carrier Variable-Angle Phase-Displacement Modulation Methods. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2022, 16, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.W. The Evolutions of Multilevel Converter Topology: A Roadmap of Topological Invention. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2022, 16, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, J.I.; Kouro, S.; Franquelo, L.G.; Rodriguez, J.; Wu, B. The Essential Role and the Continuous Evolution of Modulation Techniques for Voltage-Source Inverters in the Past, Present, and Future Power Electronics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 2688–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaide, A.M.; Buticchi, G.; Chub, A.; Dalessandro, L. Design and Control for High-Reliability Power Electronics: State-of-the-Art and Future Trends. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Ind. Electron. 2024, 5, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Salem, M.; Kamarol, M.; Delgado, M.T.; Desa, M.K.M. Review of Active Thermal Control for Power Electronics: Potentials, Limitations, and Future Trends. IEEE Open J. Power Electron. 2024, 5, 414–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Lyu, X.; Yadav, O.P.; Singh, B.N.; Zheng, S.; Cao, D. Overview of Real-Time Lifetime Prediction and Extension for SiC Power Converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 7765–7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusmez, S.; Ali, S.H.; Heydarzadeh, M.; Kamath, A.S.; Duran, H.; Akin, B. Aging Precursor Identification and Lifetime Estimation for Thermally Aged Discrete Package Silicon Power Switches. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.C.; Kim, S.S.; Ha, M.W.; Kim, Y.S. Accelerated Degradation of IGBTs Due to High Gate Voltage at Various Temperature Environments. IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 2020, 20, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugur, E.; Dusmez, S.; Akin, B. An Investigation on Diagnosis-Based Power Switch Lifetime Extension Strategies for Three-Phase Inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 2064–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Luo, H.; Dong, Y.; Li, W.; He, X.; Chen, G.; Yang, E.; Dong, Z. Online junction temperature extraction with turn-off delay time for high power IGBTs. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 14–18 September 2014; pp. 4016–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falck, J.; Felgemacher, C.; Rojko, A.; Liserre, M.; Zacharias, P. Reliability of Power Electronic Systems: An Industry Perspective. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2018, 12, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciappa, M. Selected failure mechanisms of modern power modules. Microelectron. Reliab. 2002, 42, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornic, N.; Ibrahim, A.; Khatir, Z.; Degrenne, N.; Mollov, S.; Ingrosso, D. Analysis of the aging mechanism occurring at the bond-wire contact of IGBT power devices during power cycling. Microelectron. Reliab. 2020, 114, 113873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Kong, J.; Wang, N.; Zhang, K.; Blaabjerg, F.; Zhou, D. A Review on Junction Temperature and ON-state Voltage Condition Monitoring of Power Semiconductor Devices. Chin. J. Electr. Eng. 2025, 11, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, I.F.; Drofenik, U.; Kolar, J.W. New physical model for lifetime estimation of power modules. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Power Electronics Conference-ECCE ASIA-, Sapporo, Japan, 21–24 June 2010; pp. 2106–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, J.; Schlangenotto, H.; Scheuermann, U.; De Doncker, R. Semiconductor Power Devices: Physics, Characteristics, Reliability; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Liu, B.; Tan, H.; Xu, P.; Chen, J.; Tang, T.; Song, W. A Converter-Level Junction Temperature Monitoring Method for IGBT Based on the Turn-off Gate Electric Quantities. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wintrich, A.; Nicolai, U.; Tursky, W.; Reimann, T. Semikron Application Manual Power Semiconductors; ISLE: Ilmenau, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Mawby, P.A. A Lifetime Estimation Technique for Voltage Source Inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 4113–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Wang, H.; Blaabjerg, F. Mission Profile Based System-Level Reliability Analysis of DC/DC Converters for a Backup Power Application. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 8030–8039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, K.C.; Landzberg, A.H. Reliability of Controlled Collapse Interconnections. IBM J. Res. Dev. 1969, 13, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayerer, R.; Herrmann, T.; Licht, T.; Lutz, J.; Feller, M. Model for Power Cycling lifetime of IGBT Modules-various factors influencing lifetime. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Integrated Power Electronics Systems, Nuremberg, Germany, 11–13 March 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Xiang, D.; Bryant, A.; Mawby, P.; Ran, L.; Tavner, P. Condition Monitoring for Device Reliability in Power Electronic Converters: A Review. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 2734–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busca, C.; Teodorescu, R.; Blaabjerg, F.; Munk-Nielsen, S.; Helle, L.; Abeyasekera, T.; Rodriguez, P. An overview of the reliability prediction related aspects of high power IGBTs in wind power applications. Microelectron. Reliab. 2011, 51, 1903–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstenmaier, Y.C.; Wachutka, G. The minimal set of parameters for exact dynamic thermal models. In Proceedings of the 2008 14th International Workshop on Thermal Inveatigation of ICs and Systems, Rome, Italy, 24–26 September 2008; pp. 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.G.; Rojas, C.A.; Wilson-Veas, A.H.; Bugueño, R.A.; Peralta, A.; Salinas, S.; Marín, J.; Young, H.; Callegaro, L. On the Experimental Verification of Electrothermal Modeling of GaN-HEMT-Based DC–DC Converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 40, 5518–5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hava, A.; Kerkman, R.; Lipo, T. A high-performance generalized discontinuous PWM algorithm. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1998, 34, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, D.; Lipo, T. Pulse Width Modulation for Power Converters: Principles and Practice; IEEE Press Series on Power Engineering; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wintrich, A.; Nicolai, U.; Tursky, W.; Tobias, R. Application Manual Power Semiconductors; SEMIKRON International GmbH: Nurnberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]







| Cases of Study | Modulation Type | Acronym |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous modulation methods | Sinusoidal PWM | SPWM |
| Space vector modulation | SVM | |
| Discontinuous modulation methods | DPWM | DPWM1 |
| DPWM | DPWM2 | |
| phase-shift DPWM | DPWM3 | |
| phase-shift DPWM | DPWM4 | |
| DPWM with positive clamping | DPWM5 | |
| DPWM with negative clamping | DPWM6 |
| Parameter | Symbol | Value | Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DC voltage | 800 | Nominal power | S | 10 kVA | |
| Load inductance | L | 5 | Line frequency | 50 | |
| Carrier frequency | 10 | Ambient temperature | 50 °C | ||
| Power factor | 0 rad |
| Acronym | Absolute Damage | Relative Damage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| SPWM | 100 | |
| DPWM1 | ||
| DPWM2 | ||
| DPWM3 | ||
| DPWM4 |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| DC voltage | 250 | Load inductance | 15 |
| Load resistor | 10 | Output frequency | 1 |
| Ambient temperature | 25 °C | Switching frequency | 10 |
| IR camera frequency | 200 | dSPACE frequency | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alcaide, A.M.; Leon, J.I.; Rojas, C.A.; Berger, J.G.; Stowhas-Villa, A.; Wilson-Veas, A.H.; Buticchi, G.; Kouro, S. The Role of Modulation Techniques on Power Device Thermal Performance in Two-Level VSI Converters. Electronics 2025, 14, 2934. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14152934
Alcaide AM, Leon JI, Rojas CA, Berger JG, Stowhas-Villa A, Wilson-Veas AH, Buticchi G, Kouro S. The Role of Modulation Techniques on Power Device Thermal Performance in Two-Level VSI Converters. Electronics. 2025; 14(15):2934. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14152934
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlcaide, Abraham M., Jose I. Leon, Christian A. Rojas, Jhonattan G. Berger, Alejandro Stowhas-Villa, Alan H. Wilson-Veas, Giampaolo Buticchi, and Samir Kouro. 2025. "The Role of Modulation Techniques on Power Device Thermal Performance in Two-Level VSI Converters" Electronics 14, no. 15: 2934. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14152934
APA StyleAlcaide, A. M., Leon, J. I., Rojas, C. A., Berger, J. G., Stowhas-Villa, A., Wilson-Veas, A. H., Buticchi, G., & Kouro, S. (2025). The Role of Modulation Techniques on Power Device Thermal Performance in Two-Level VSI Converters. Electronics, 14(15), 2934. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14152934













