Adaptive Distributed Type-2 Fuzzy Dynamic Event-Triggered Formation Control for Switched Nonlinear Multi-Agent System with Actuator Faults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Problem Statement and Preliminaries
2.1. Graph Theory
2.2. Problem Formulation and Lemmas
- (1)
- , , actuators work properly.
- (2)
- , , actuators experience partial loss of effectiveness faults.
- (3)
- , , actuators have bias faults.
- (4)
- , , actuators have stuck faults.
2.3. Type-2 Fuzzy Logic Systems
3. Main Results
3.1. Adaptive Dynamic Event-Triggered Controller Design
3.2. Stability Analysis
3.3. The Exclusion of Zeno Phenomenon
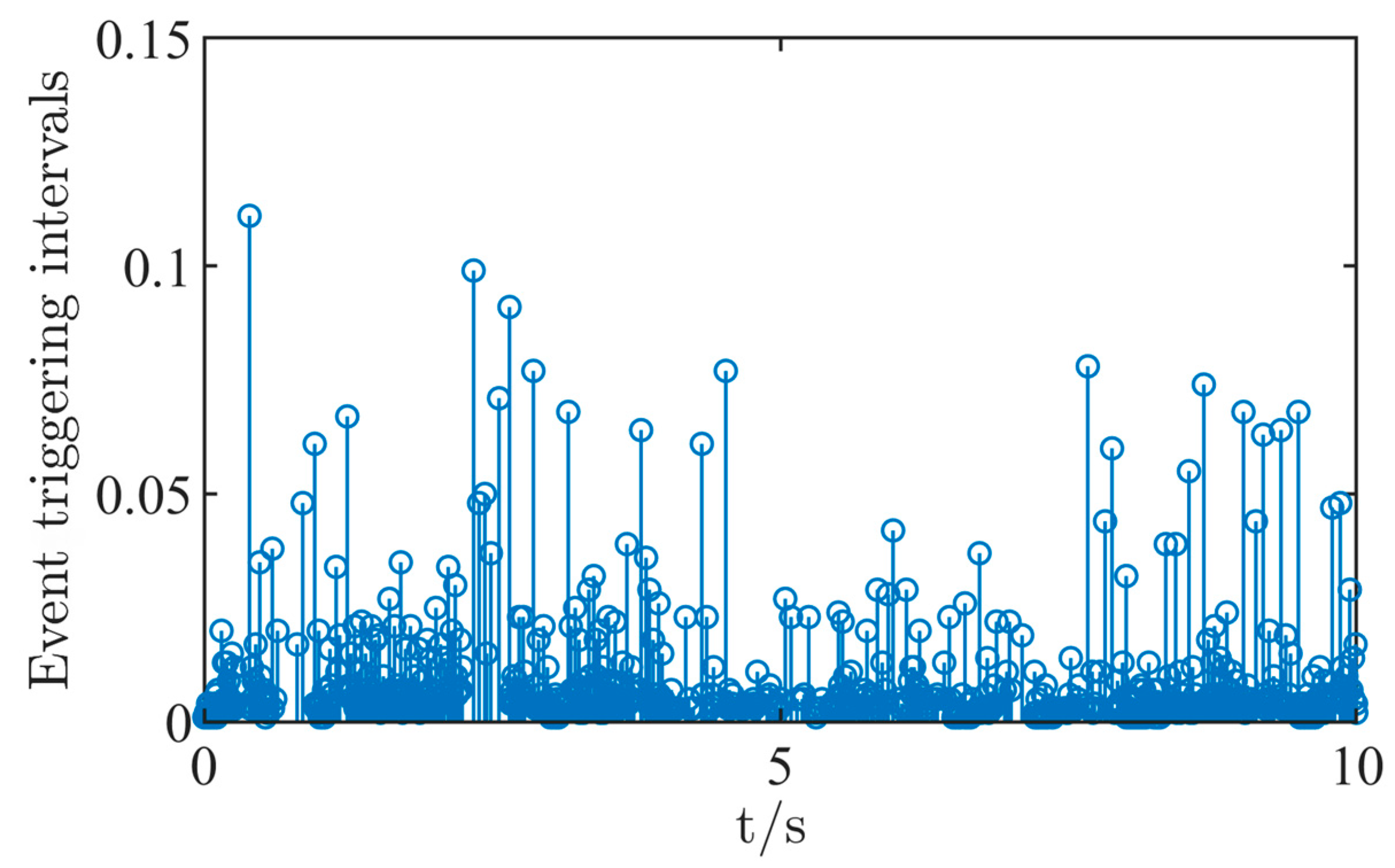
4. Simulation Example
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviations | |
| DET | dynamic event-triggered |
| SNMASs | switched nonlinear multi-agent systems |
| T2FLSs | type-2 fuzzy logic systems |
| UCRs | usage of communication resources |
| CLF | common Lyapunov function |
| MASs | multi-agent systems |
| NMASs | nonlinear multi-agent systems |
| T1FLSs | type-1 fuzzy logic systems |
| Parameter Annotations | |
| the number of agents | |
| the state vector | |
| the controller of agent | |
| the -th agent’s output | |
| the switching signal of agent | |
| the number of subsystems | |
| the unknown external disturbance | |
| the offset fault | |
| the actuator failure coefficient | |
| the relative position of agent | |
| the relative position of agent | |
| the virtual controller | |
| the positive design parameter | |
| the set of neighbors for the -th agent | |
| the positive constant | |
| the design parameters | |
| the design parameters | |
| the event-triggered error | |
| the design parameter | |
| the design parameter | |
| the design parameter | |
| the design parameter | |
| the design parameter | |
| the positive constant | |
| the memory span | |
| the positive parameter | |
| the initial state value | |
| the initial estimated value of adaptive parameter | |
References
- Guerrero-Bonilla, L.; Prorok, A.; Kumar, V. Formations for Resilient Robot Teams. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Sun, X.; Lv, M.; Liu, S. Distributed Coordinated Control for Fixed-Wing UAVs with Dynamic Event-triggered Communication. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 4665–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, W.; Jiao, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, P.; Xie, W.; Ru, L. Exact Consensus Control of Nonlinearly Parameterized Multi-Agent Systems with Unknown Control Directions. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 107276–107286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, Y.; Yin, G.; Xu, L.; Lu, Y.; Feng, J. A MAS-based hierarchical architecture for the cooperation control of connected and automated vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 72, 1559–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Govindarasu, M. Multi-Agent Based Attack-Resilient System Integrity Protection for Smart Grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 3447–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosayebi, M.; Khooban, M.H. A Robust Shipboard DC-DC Power Converter Control: Concept Analysis and Experimental Results. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2020, 67, 2612–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Liu, X.; Yu, W.; Zhu, L.; Tang, Q. Neural-Network Based Adaptive Self-Triggered Consensus of Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems With Sensor Saturation. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2021, 8, 1531–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Zhang, C.; Hu, P.; Cui, Y. Adaptive Neural Network Leader-Follower Formation Control for a Class of Second-Order Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems with Unknown Dynamics. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 148149–148156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fu, Y.; Fu, J. Adaptive Finite-Time Optimal Formation Control for Second-Order Nonlinear Multiagent Systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2023, 53, 6132–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, B. Adaptive Output Consensus of Heterogeneous Nonlinear Multi-Agent System Under Random Link Failures with Partially Unknown Transition Rates. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2024, 34, 7799–7820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, T.; Tong, S. Adaptive neural networks finite-time optimal control for a class of nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 31, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qu, F.; Tong, S. Observer-based fuzzy adaptive finite-time containment control of nonlinear multiagent systems with input delay. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 51, 4451–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Yu, W.; Cao, J.; Baldi, S. A Separation-Based Methodology to Consensus Tracking of Switched High-Order Non-linear Multiagent Systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 33, 5467–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Malik, M.; Sajid, M. Pinning Control Strategies for Bipartite Consensus in Nonlinear Hybrid Singular Switched Multi-Agent Systems. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 144420–144436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, X.; Zong, G.; Xu, N. Fully Distributed Consensus of Switched Heterogeneous Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems With Bouc-Wen Hysteresis Input. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 4198–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhan, X.; Han, T.; Yan, H. Distributed Adaptive Predefined-Time Bipartite Containment Algorithm for Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems with Actuator Faults. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2023, 70, 2141–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Li, Y.; Tong, S. Neural Network Output-Feedback Consensus Fault-Tolerant Control for Nonlinear Multiagent Systems With Intermittent Actuator Faults. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 34, 4728–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, W.X.; Kang, Y. Adaptive Sliding Mode Consensus Tracking for Second-Order Nonlinear Multiagent Systems with Actuator Faults. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 49, 1605–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Er, M.J.; Zhang, J. Distributed Adaptive Fuzzy Control for Output Consensus of Heterogeneous Stochastic Non-linear Multiagent Systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 26, 1138–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Liu, X.; Yu, W. Finite-Time Fuzzy Adaptive Consensus for Heterogeneous Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2020, 7, 3057–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Tong, S. Fixed-Time Adaptive Fuzzy Containment Dynamic Surface Control for Nonlinear Multiagent Systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 30, 5237–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, C. Switching-Event-Based Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Control for a Class of Uncertain Nonlinear Systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2024, 32, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Lam, H.K.; Xiao, B.; Wu, L. Tracking Control for Nonlinear Systems with Actuator Saturation via Interval Type-2 T-S Fuzzy Framework. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2023, 53, 7085–7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Long, J.; Wang, W. Event-Triggered Distributed Adaptive Leaderless Consensus of Uncertain Heterogenous Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2024, 71, 2694–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, R.; Wan, H.; Zhao, H. Adaptive Cluster Consensus Control of Nonlinear Multi-Agent System via the Dynamic Event-Triggered Strategy. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2024, 38, 1791–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Shi, P.; Lim, C. Robust Formation Control for Nonlinear Heterogeneous Multiagent Systems Based on Adaptive Event-Triggered Strategy. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2022, 19, 2788–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Niu, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, D. Adaptive Event-Triggered Consensus Tracking Control Schemes for Uncertain Constrained Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2024, 21, 7325–7335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hua, C.; Li, K.; Cui, H. Event-Triggered Control for High-Order Uncertain Nonlinear Multiagent Systems Subject to Denial-of-Service Attacks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2022, 52, 6129–6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ran, G.; Wu, Y.; Xue, L.; Sun, C. Dynamic Event-Triggered Practical Fixed-Time Consensus for Nonlinear Multiagent Systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 2156–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Huang, B.; Sun, J.; Xie, X.; Zhang, H.; Ren, J. Multi-Stage Dynamic Event-Triggered Containment Control of Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems with Input-Bounded Leaders and Time-Varying Delay. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2023, 33, 574–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; He, S.; Wu, Y. Distributed Dynamic Event-Triggered Leader-Following Consensus for Nonlinear Multiagent Systems Over Fading Channel. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2024, 54, 4593–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lu, G.; Li, K. Adaptive Fuzzy Secured Control for Multiagent Systems Under DoS Attacks and Intermittent Actuator Failures. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2024, 32, 2567–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, C.; Shen, X.; Yao, W.; Liu, J.; Wu, L. Adaptive Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Neural Network-Based Novel Fixed-Time Backstepping Control for Uncertain Euler-Lagrange Systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2024, 32, 2966–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Q.G.; Yu, J. Event-triggered adaptive neural network tracking control for uncertain systems with unknown input saturation based on command filters. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 35, 8702–8707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Q.G.; Yu, J. Convex optimization-based adaptive fuzzy control for uncertain nonlinear systems with input saturation using command filtered backstepping. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2023, 31, 2086–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Agent 1 | Agent 2 | Agent 3 | Agent 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1FLS-based fixed-threshold event triggering protocol | 4397 | 4787 | 3697 | 2239 |
| T2FLS-based DET protocol | 1819 | 1923 | 1836 | 1727 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ben, C.-Q.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Gu, J.-H. Adaptive Distributed Type-2 Fuzzy Dynamic Event-Triggered Formation Control for Switched Nonlinear Multi-Agent System with Actuator Faults. Electronics 2025, 14, 2907. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142907
Ben C-Q, Zhang X-Y, Gu J-H. Adaptive Distributed Type-2 Fuzzy Dynamic Event-Triggered Formation Control for Switched Nonlinear Multi-Agent System with Actuator Faults. Electronics. 2025; 14(14):2907. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142907
Chicago/Turabian StyleBen, Cheng-Qin, Xiao-Yu Zhang, and Ji-Hong Gu. 2025. "Adaptive Distributed Type-2 Fuzzy Dynamic Event-Triggered Formation Control for Switched Nonlinear Multi-Agent System with Actuator Faults" Electronics 14, no. 14: 2907. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142907
APA StyleBen, C.-Q., Zhang, X.-Y., & Gu, J.-H. (2025). Adaptive Distributed Type-2 Fuzzy Dynamic Event-Triggered Formation Control for Switched Nonlinear Multi-Agent System with Actuator Faults. Electronics, 14(14), 2907. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142907






