Electromagnetic Noise and Vibration Analyses in PMSMs: Considering Stator Tooth Modulation and Magnetic Force
Abstract
1. Introduction
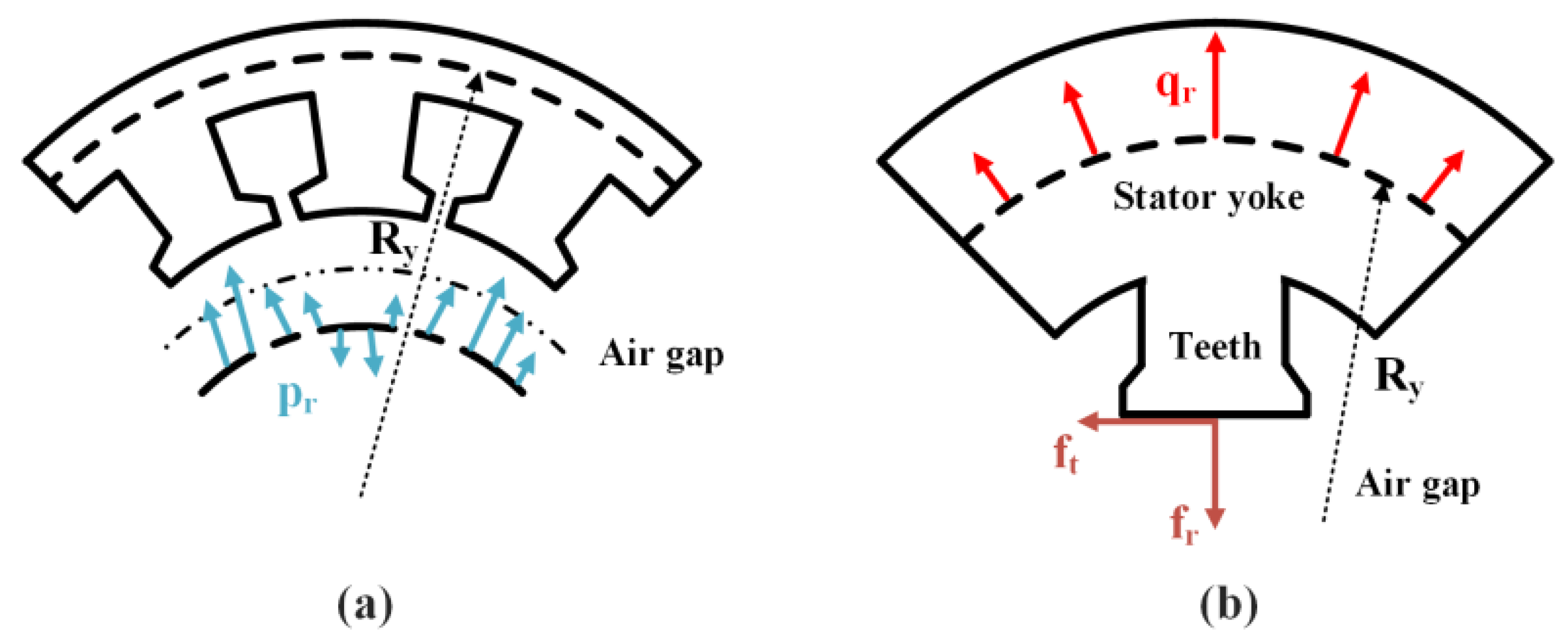
2. Electromagnetic Forces
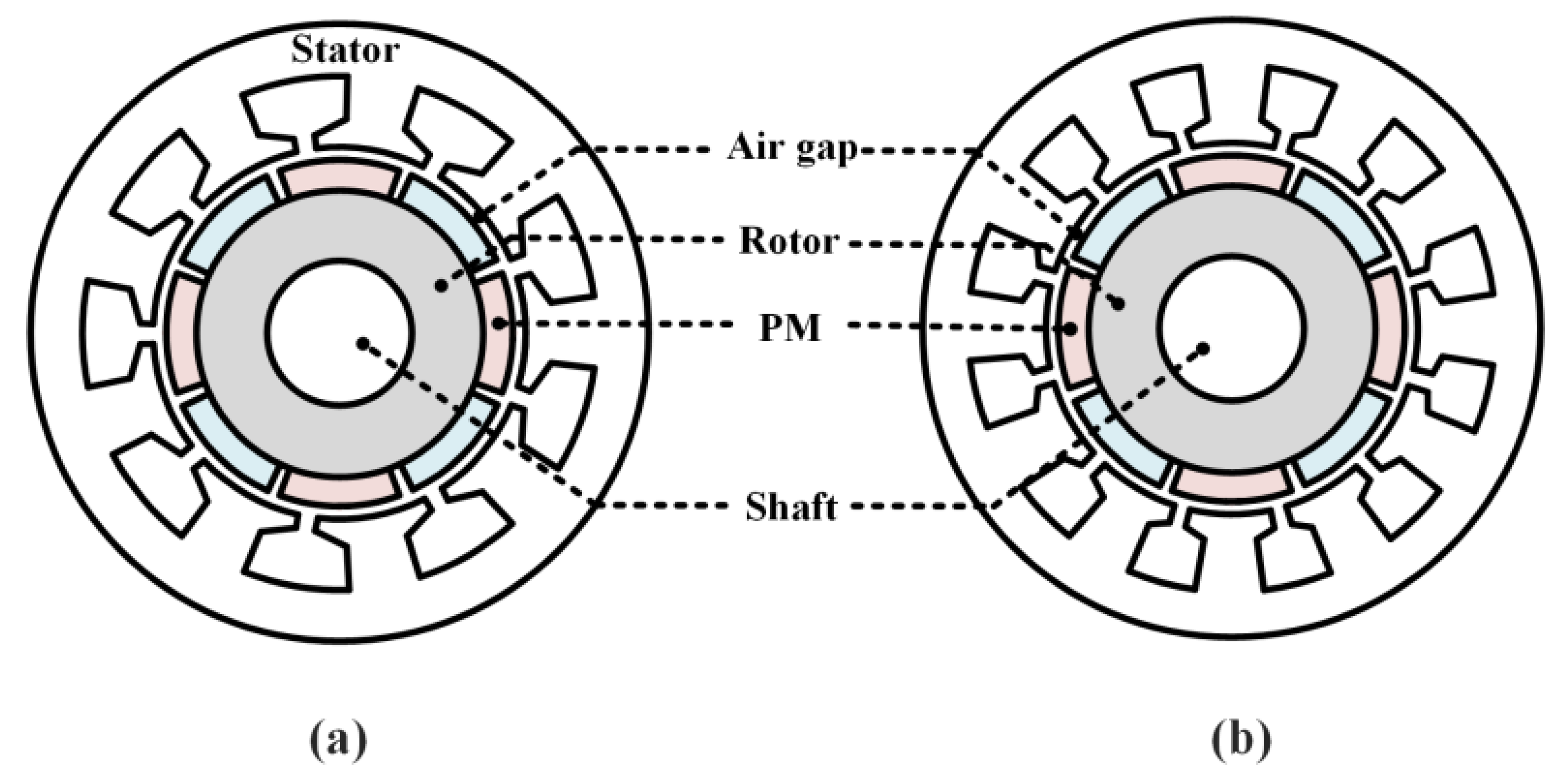
2.1. Analysis Model and Assumptions
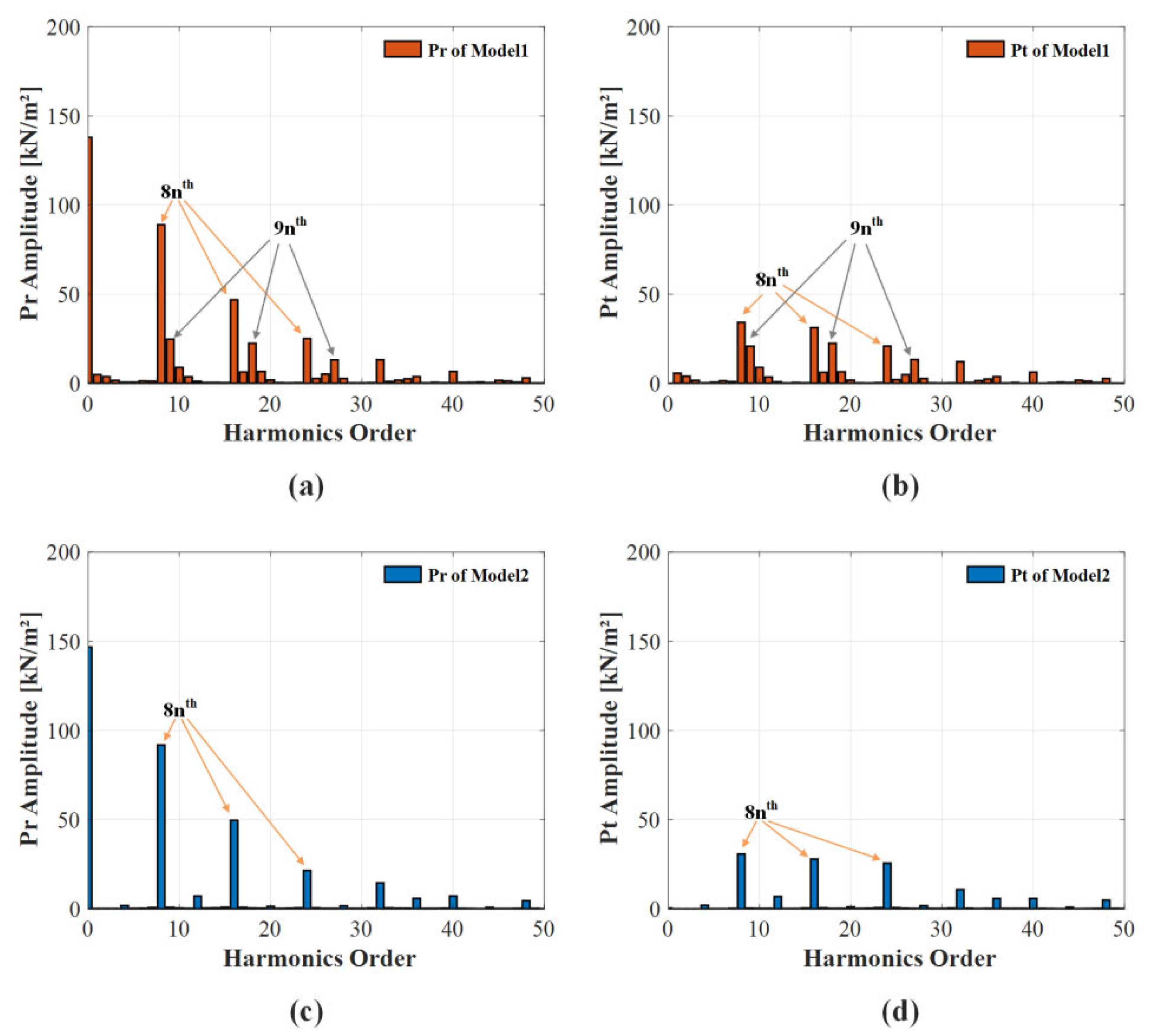
2.2. Tooth Modulation
3. Calculation of Stator Natural Frequencies
3.1. Mechanical Equivalent Parameters
3.2. Natural Frequencies
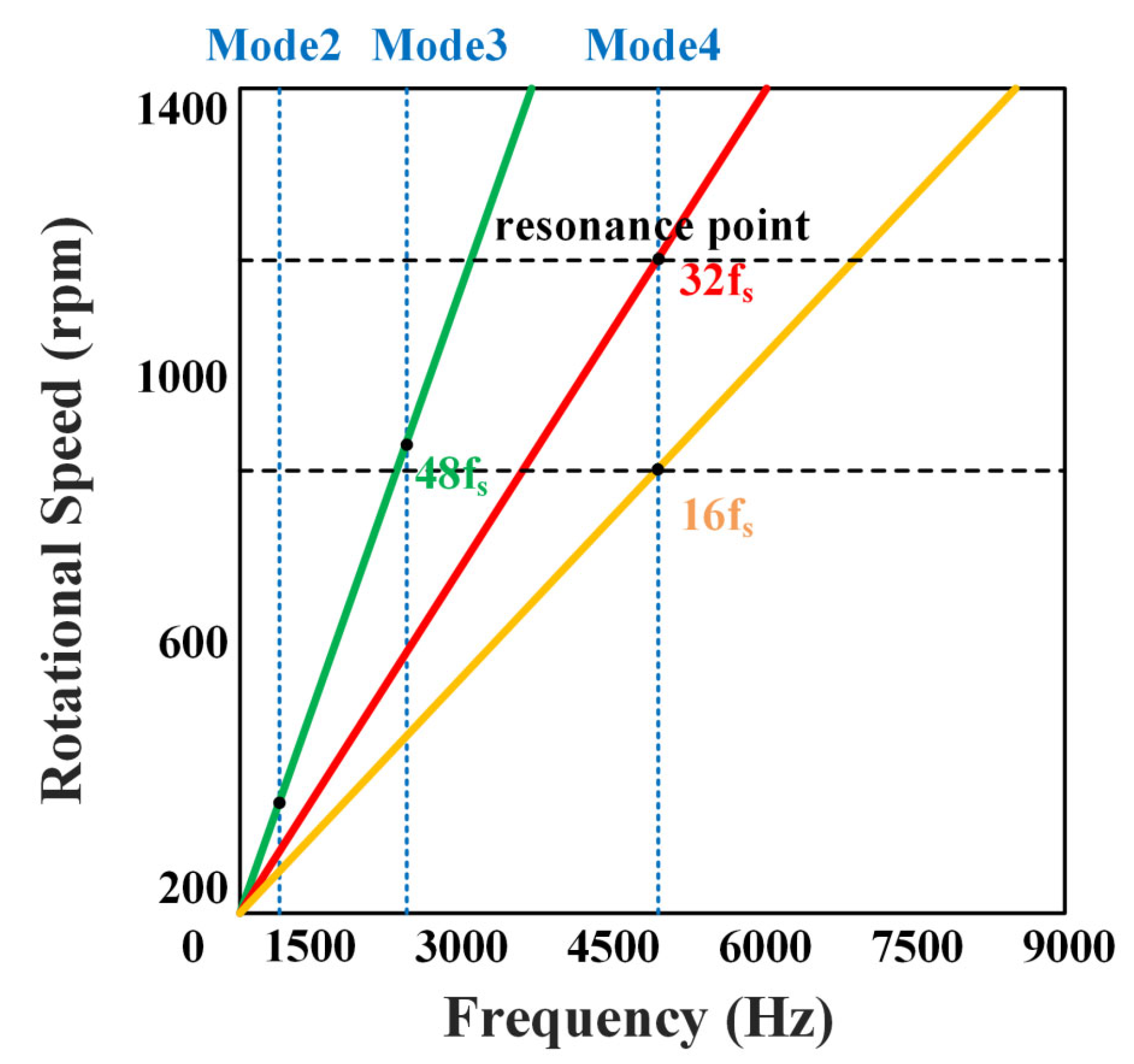
4. Vibroacoustic Analysis
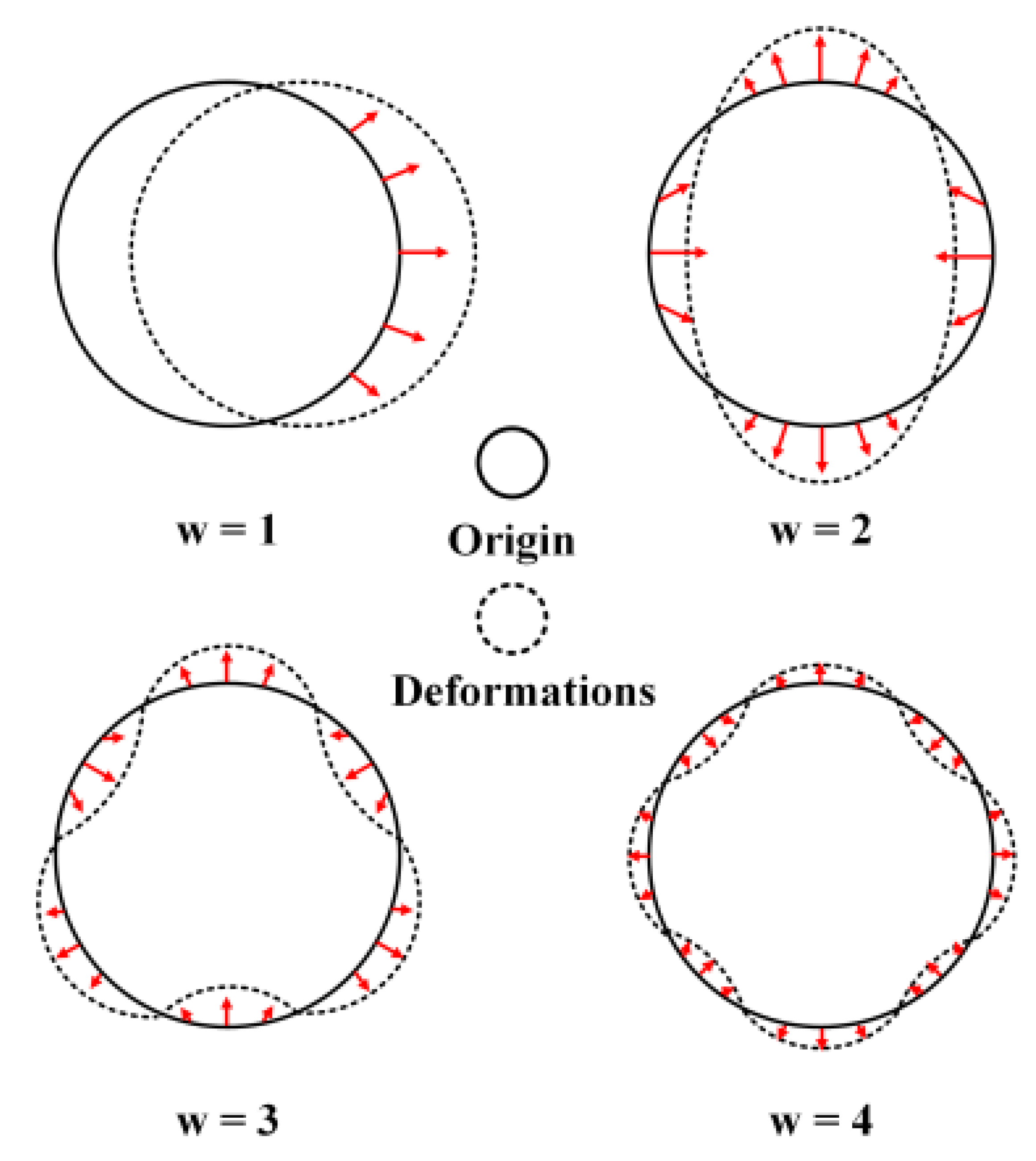
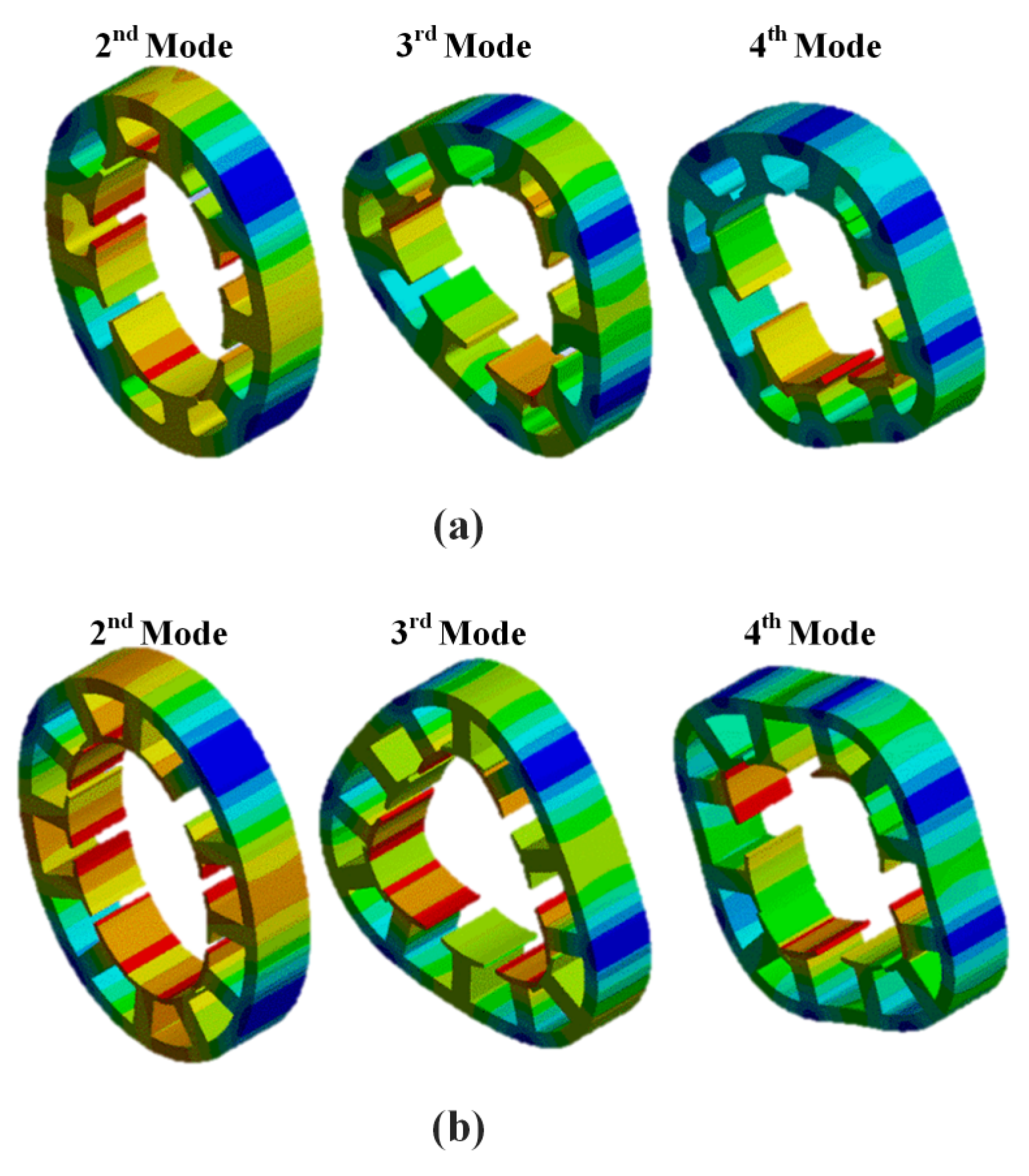
4.1. Structural Vibration Modes Analysis
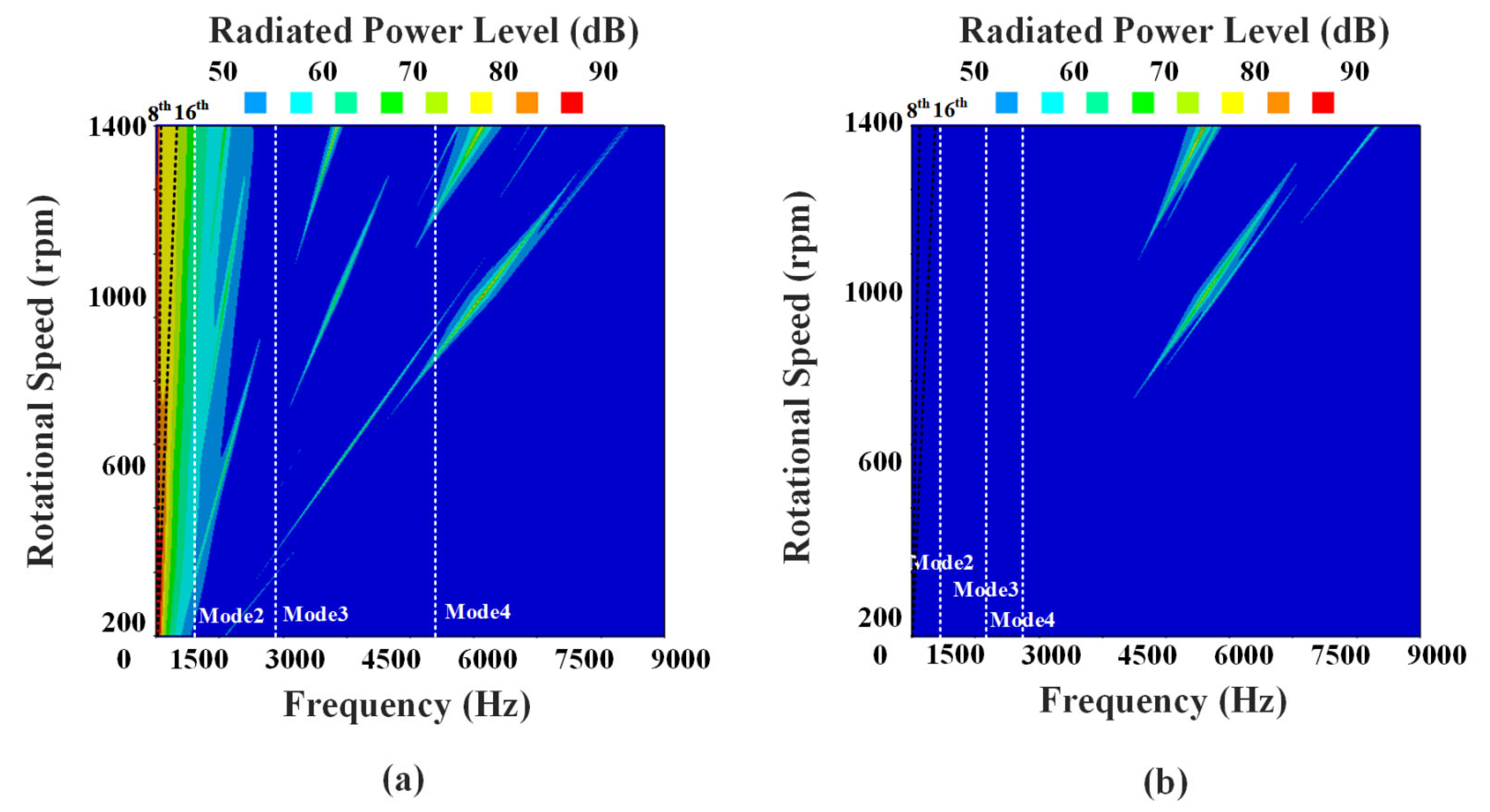
4.2. Acoustic Radiation Analysis
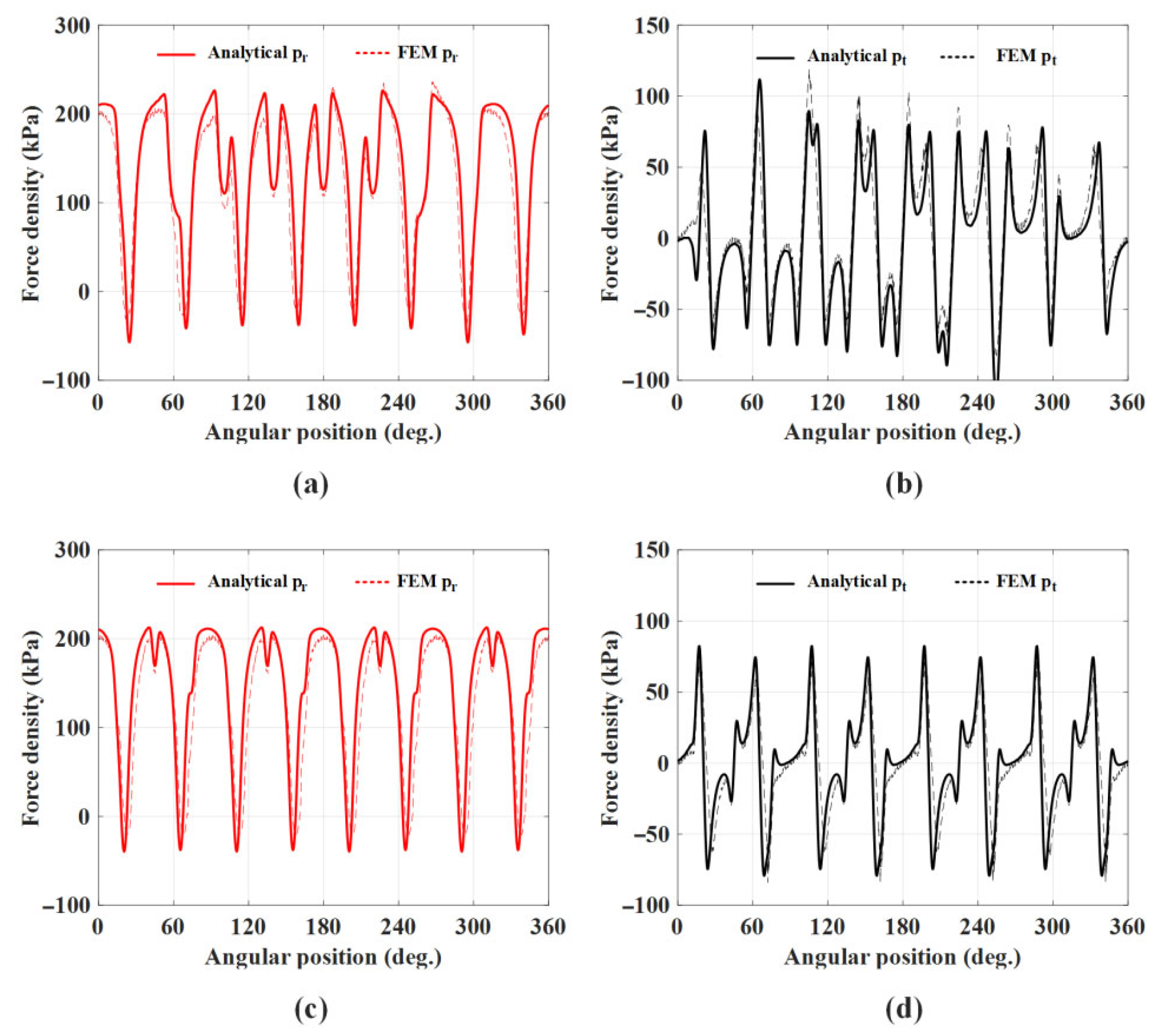
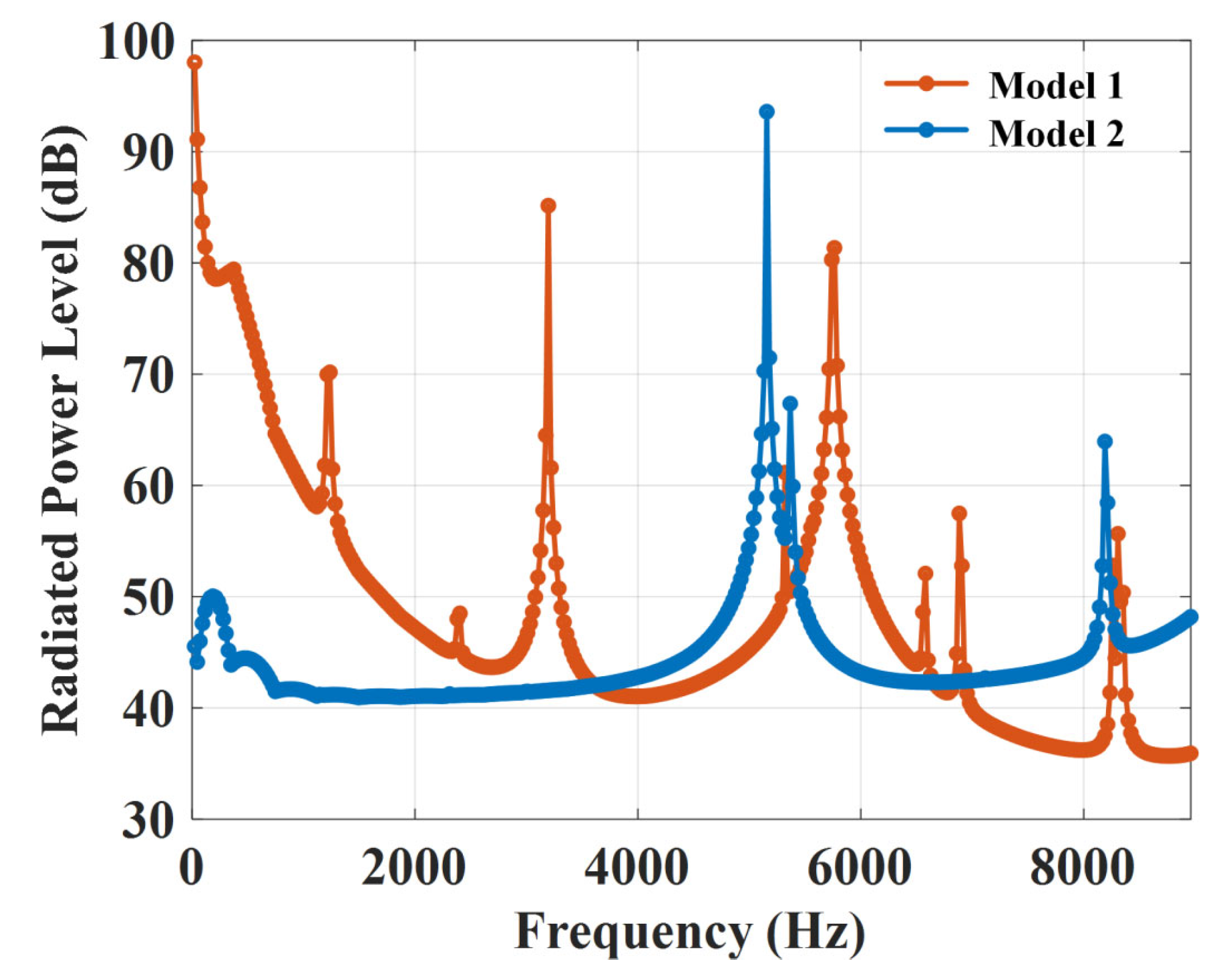
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Devillers, E. Electromagnetic Subdomain Modeling Technique for the Fast Prediction of Radial and Circumferential Stress Harmonics in Electrical Machines; Ecole Centrale de Lille: Villeneuve-d’Ascq, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.; Lan, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, B. Analysis of global and local force harmonics and their effects on vibration in permanent magnet synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2017, 32, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Zuo, S.; Deng, W.; Wu, S. Modeling and analysis of electromagnetic force, vibration, and noise in permanent-magnet synchronous motor considering current harmonics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 7455–7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, T. Vibroacoustic characterization of a permanent magnet synchronous motor powertrain for electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2017, 33, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Zuo, S.; Deng, W.; Wu, S. Noise prediction and sound quality analysis of variable-speed permanent magnet synchronous motor. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2017, 32, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weilharter, B.; Biro, O.; Lang, H.; Ofner, G.; Rainer, S. Validation of a comprehensive analytic noise computation method for induction machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 59, 2248–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, H. Electric Motor Silencer: Formation and Elimination of the Noises in the Electric Motors; Siemens-Schuckertwerke: Berlin, Germany, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Gieras, J.F.; Wang, C.; Lai, J.C. Noise of Polyphase Electric Motors; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Yang, J.-W.; Kim, Y.-J.; Shin, K.-H.; Choi, J.-Y. Analytical and Experimental Approaches to Predicting Magnetic Field Asymmetry and Electromagnetic Forces in Slotted Surface-Mounted Permanent Magnet Machines with Rotor Eccentricity. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliti, K.C. Modeling and Analysis of Magnetic Noise in Squirre-Cage Induction Motors; Institutionen för Elkraftteknik: Stockholm, Sweden, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Yuan, T.; Ma, L.; Wang, C. Electromagnetic noise analysis and optimization for permanent magnet synchronous motor used on electric vehicles. Eng. Comput. 2021, 38, 699–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devillers, E.; Hecquet, M.; Cimetiere, X.; Lecointe, J.-P.; Le Besnerais, J.; Lubin, T. Experimental benchmark for magnetic noise and vibrations analysis in electrical machines. In Proceedings of the 2018 XIII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Alexandroupoli, Greece, 3–6 September 2018; pp. 745–751. [Google Scholar]
- Pile, R.; Le Besnerais, J. Comparison of main magnetic force computation methods for noise and vibration assessment in electrical machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhao, W.; Sun, L.; Niu, N. Calculation method for natural frequencies of stator of permanent magnet synchronous motors based on three-dimensional elastic theory. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 36, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; Zou, J.; Xu, Y.; Liu, M. Effect of local tangential force on vibration performance in fractional-slot concentrated winding permanent magnet synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2018, 34, 1082–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Park, S.-H.; Ryu, J.-Y.; Lim, M.-S. Comparative study of vibration on 10-pole 12-slot and 14-pole 12-slot PMSM considering tooth modulation effect. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 70, 4007–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bösing, M. Acoustic Modeling of Electrical Drives: Noise and Vibration Synthesis Based on Force Response Superposition. Doctor Dissertation, Technische Hochschule Aachen, Aachen, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.; Bai, Y.; Yang, B.; Li, H. Analysis of nonlinear vibration in permanent magnet synchronous motors under unbalanced magnetic pull. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Besnerais, J. Reduction of Magnetic Noise in PWM-Supplied Induction Machines-Low-Noise Design Rules and Multi-Objective Optimization; Ecole Centrale de Lille: Villeneuve-d’Ascq, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, H.; Li, D.; Qu, R.; Yan, P. Modulation effect of slotted structure on vibration response in electrical machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 2998–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.-H.; Cho, H.-W.; Choi, J.-Y. Experimental verification and analytical calculation of unbalanced magnetic force in permanent magnet machines. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 056652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreou, P.; Hajjaj, A.Z.; Mohammadpour, M.; Theodossiades, S. Analytical Multiphysics Methodology to Predict Vibroacoustics in PMSMs Combining Tangential Electromagnetic Excitation and Tooth Modulation Effects. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 10, 5997–6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roivainen, J. Unit-Wave Response-Based Modeling of Electromechanical Noise and Vibration of Electrical Machines. Doctor Dissertation, Helsinki University of Technology, Espoo, Finland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ballo, F.; Gobbi, M.; Mastinu, G.; Palazzetti, R. Noise and vibration of permanent magnet synchronous electric motors: A simplified analytical model. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 9, 2486–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Symbol | Unit | Model 1 | Model 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pole number | P | - | 8 | - |
| Slot number | Q | - | 9 | 12 |
| Pole embrace | αp | - | 0.9 | - |
| Stack length | Lstk | mm | 30 | - |
| Rotor radius | Rr | mm | 38 | - |
| Radius at magnet surface | Rm | mm | 43 | - |
| Opening slot radius | Rs | mm | 47 | - |
| Slot outer radius | Rq | mm | 67 | 68 |
| Radius at center of yoke | Ry | mm | 73.5 | 74 |
| Radius at center of tooth | Rt | mm | 57 | 57.5 |
| Stator outer radius | Ro | mm | 80 | - |
| Stator tooth thickness | htooth | mm | 20 | 21 |
| Stator yoke thickness | hyoke | mm | 13 | 12 |
| Slot angle | δ | deg. | 20 | 15 |
| Opening slot angle | β | deg. | 5 | 4 |
| Vacuum permeability | μ0 | H/m | 4π·10−7 | - |
| Magnetic remanence | Br | T | 1.28 | - |
| Turns | - | - | 60 | - |
| Rated speed | - | rpm | 1400 | - |
| Parameters | Symbol | Unit | Model 1 | Model 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Young’s modulus of core | Ecore | GPa | 193 | - |
| Poisson’s ratio of core | - | - | 0.29 | - |
| Core mass density | ρcore | kg/m3 | 8000 | - |
| Mass of stator yoke | Wyoke | kg | 1.44 | 1.34 |
| Mass of stator tooth | Wtooth | kg | 0.86 | - |
| Stator yoke area | Ayoke | mm2 | 6000 | 5580 |
| Stator tooth area | Atooth | mm2 | 4000 | - |
| Parameter | 2nd Mode | 3rd Mode | 4th Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analytical | 996 Hz | 2657 Hz | 4983 Hz |
| FEM | 1036 Hz | 2716 Hz | 4575 Hz |
| Parameter | 2nd Mode | 3rd Mode | 4th Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analytical | 669 Hz | 1784 Hz | 3346 Hz |
| FEM | 615 Hz | 1615 Hz | 2803 Hz |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.-S.; Lee, H.-K.; Yang, J.-W.; Jung, W.-S.; Choi, Y.-T.; Jang, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Shin, K.-H.; Choi, J.-Y. Electromagnetic Noise and Vibration Analyses in PMSMs: Considering Stator Tooth Modulation and Magnetic Force. Electronics 2025, 14, 2882. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142882
Kim Y-S, Lee H-K, Yang J-W, Jung W-S, Choi Y-T, Jang J-H, Kim Y-J, Shin K-H, Choi J-Y. Electromagnetic Noise and Vibration Analyses in PMSMs: Considering Stator Tooth Modulation and Magnetic Force. Electronics. 2025; 14(14):2882. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142882
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yeon-Su, Hoon-Ki Lee, Jun-Won Yang, Woo-Sung Jung, Yeon-Tae Choi, Jun-Ho Jang, Yong-Joo Kim, Kyung-Hun Shin, and Jang-Young Choi. 2025. "Electromagnetic Noise and Vibration Analyses in PMSMs: Considering Stator Tooth Modulation and Magnetic Force" Electronics 14, no. 14: 2882. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142882
APA StyleKim, Y.-S., Lee, H.-K., Yang, J.-W., Jung, W.-S., Choi, Y.-T., Jang, J.-H., Kim, Y.-J., Shin, K.-H., & Choi, J.-Y. (2025). Electromagnetic Noise and Vibration Analyses in PMSMs: Considering Stator Tooth Modulation and Magnetic Force. Electronics, 14(14), 2882. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142882






