DROPc-Dynamic Resource Optimization for Convolution Layer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Dynamic Resource Optimization Approach for Convolution
3.1. Design Methodology
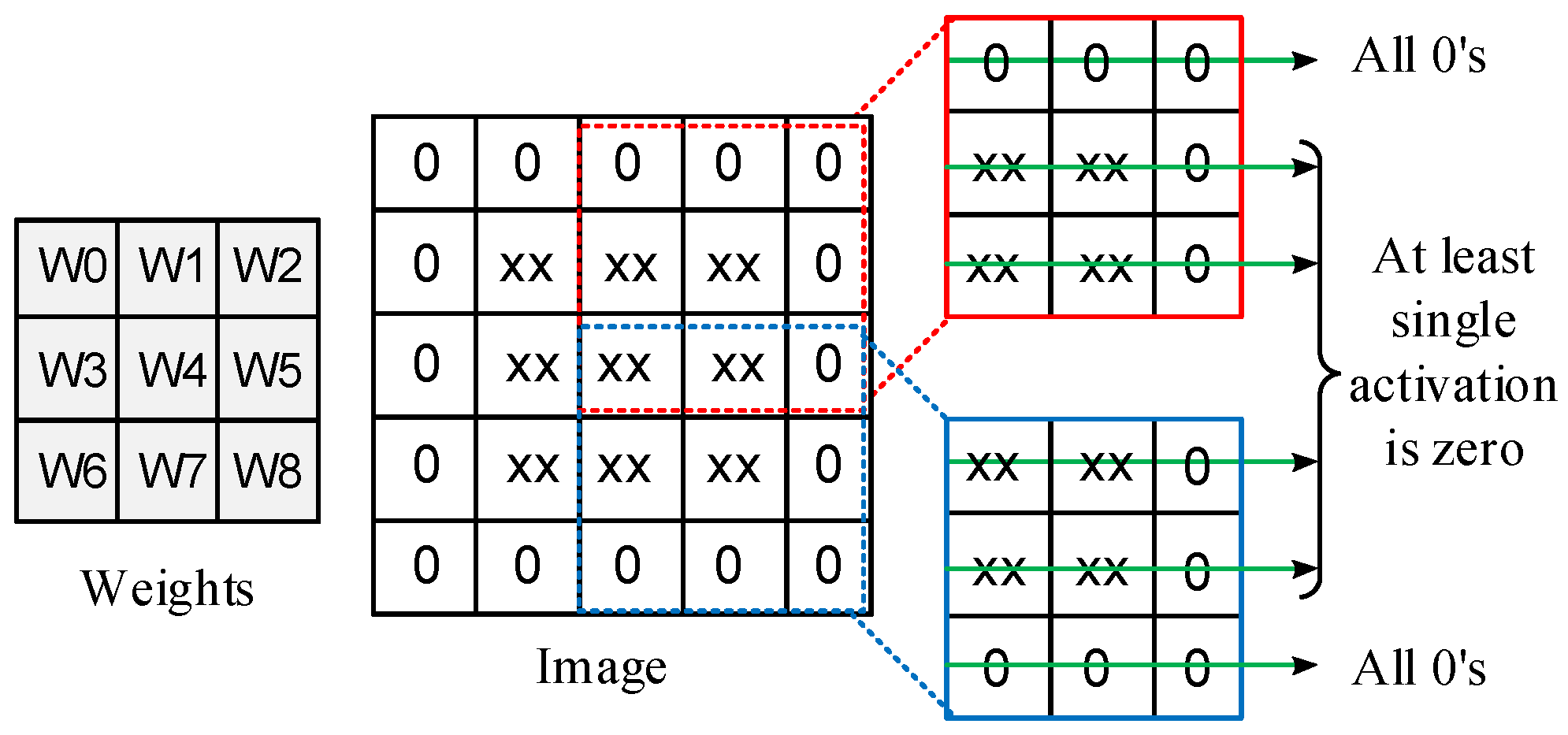
- Activation vector: Refers to the combination of activation bits from all lanes per cycle. For example, in the case of a 3 × 3 weight matrix, the activation bus consists of nine activation lanes, each having an 8-bit size, and for every cycle, we consider 1 bit from each lane. The single bits from all activation lanes are combined into an activation vector.
- Activation group or group of activation: Refers to a group of three activation lanes. For example, a 3 × 3 weight matrix will have three groups of activation.
- Interrupt: Indicates the presence of essential bits in the activation group at a given clock cycle. Each activation group has a dedicated interrupt signal.
3.2. Architectural Description
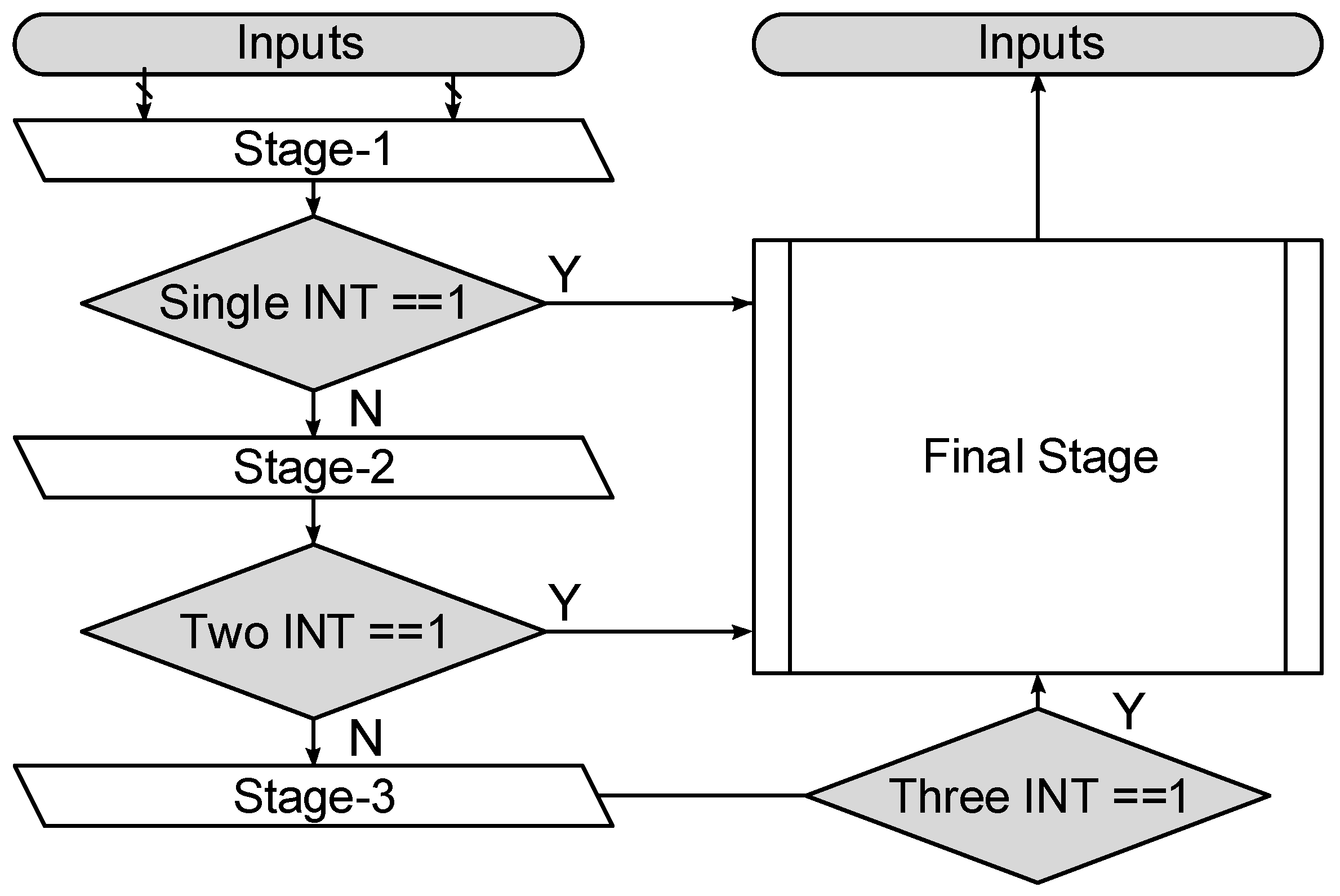
3.3. Operational Behavior
4. Results and Performance Comparison
4.1. Comparison with Conventional Approaches
4.2. Comparison with Zero-Skipping Approaches
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Zheng, T.; Lei, P.; Bai, X. Ground target classification in noisy SAR images using convolutional neural networks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 4180–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Xie, Y.; Wei, X.S.; Zhao, B.R.; Chen, Z.M.; Tan, X. Delving deep into spatial pooling for squeeze-and-excitation networks. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 121, 108159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Xun, G.; Jia, K.; Zhang, A. A multi-view deep learning framework for EEG seizure detection. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2019, 23, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cui, W.G.; Guo, Y.Z.; Huang, H.; Hu, Z.Y. Epileptic seizure detection in EEG signals using a unified temporal-spectral squeeze-and-excitation network. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 782–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaz, D.; Doss, M.M.; Collobert, R. Convolutional neural networks-based continuous speech recognition using raw speech signal. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), South Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 19–24 April 2015; pp. 4295–4299. [Google Scholar]
- Yalta, N.; Watanabe, S.; Hori, T.; Nakadai, K.; Ogata, T. CNN-based multichannel end-to-end speech recognition for everyday home environments. In Proceedings of the 27th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), A Coruna, Spain, 2–6 September 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, A.; Wang, D. A new framework for CNN-based speech enhancement in the time domain. IEEE/Acm Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2019, 27, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Teo, T.H.; Kok, C.L.; Koh, Y.Y. A Novel Single-Word Speech Recognition on Embedded Systems Using a Convolution Neuron Network with Improved Out-of-Distribution Detection. Electronics 2024, 13, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H. CNN-based single object detection and tracking in videos and its application to drone detection. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 34237–34248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashiq, F.; Asif, M.; Ahmad, M.B.; Zafar, S.; Masood, K.; Mahmood, T. CNN-based object recognition and tracking system to assist visually impaired people. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 14819–14834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H. Garbage recognition and classification system based on convolutional neural network vgg16. In Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE International Conference on Advanced Electronic Materials, Computers and Software Engineering (AEMCSE), Shenzhen, China, 24–26 April 2020; pp. 252–255. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, M.; Song, P.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Mandelis, A.; Qi, D. A novel deep convolutional neural network based on ResNet-18 and transfer learning for detection of wood knot defects. J. Sens. 2021, 2021, 428964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chansong, D.; Supratid, S. Impacts of Kernel size on different resized images in object recognition based on convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE International Electrical Engineering Congress (iEECON), Pattaya, Thailand, 10–12 March 2021; pp. 448–451. [Google Scholar]
- Zaniolo, L.; Marques, O. On the use of variable stride in convolutional neural networks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 13581–13598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Liang, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Yan, S. Evaluating fast algorithms for convolutional neural networks on FPGAs. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2019, 39, 857–870. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, J.; Pan, W.; Jiang, Z. A high-performance systolic array accelerator dedicated for CNN. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 19th International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT), Xi’an, China, 16–19 October 2019; pp. 1200–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Peltekis, C.; Filippas, D.; Nicopoulos, C.; Dimitrakopoulos, G. Fusedgcn: A systolic three-matrix multiplication architecture for graph convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 33rd International Conference on Application-specific Systems, Architectures and Processors (ASAP), Gothenburg, Sweden, 12–14 July 2022; pp. 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Arifeen, T.; Gorgin, S.; Gholamrezaei, M.H.; Ercegovac, M.D.; Lee, J.A. Low Latency and High Throughput Pipelined Online Adder for Streaming Inner product. J. Signal Process. Syst. 2017, 95, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albericio, J.; Delmás, A.; Judd, P.; Sharify, S.; O’Leary, G.; Genov, R. Bit-pragmatic Deep Neural Network Computing. In Proceedings of the 50th Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture, Boston, MA, USA, 14–17 October 2017; pp. 382–394. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Luo, T.; Liu, S.; Zhang, S.; He, L.; Wang, J. DaDianNao: A machine-learning supercomputer. In Proceedings of the 47th Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture, Cambridge, UK, 13–17 December 2014; pp. 609–622. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, T.; Liu, S.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, T.; Xu, Z.; Temam, O.; Chen, Y. DaDianNao: A neural network supercomputer. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2016, 66, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Ercegovac, M.D.; Lee, J.A. Low-Latency Online Multiplier with Reduced Activities and Minimized Interconnect for Inner Product Arrays. J. Signal Process. Syst. 2023, 95, 777–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, H.; Zheng, N. Lane Shared Bit-Pragmatic Deep Neural Network Computing Architecture and Circuit. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Express Briefs 2020, 68, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Ahn, J.; Yoo, S. Zena: Zero-aware neural network accelerator. IEEE Des. Test 2017, 35, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Krishna, T.; Emer, J.S.; Sze, V. Eyeriss: An energy-efficient reconfigurable accelerator for deep convolutional neural networks. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2016, 52, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Yang, T.J.; Emer, J.; Sze, V. Eyeriss v2: A flexible accelerator for emerging deep neural networks on mobile devices. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2019, 9, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parashar, A.; Rhu, M.; Mukkara, A.; Puglielli, A.; Venkatesan, R.; Khailany, B.; Emer, J.; Keckler, S.; Dally, W. SCNN: An accelerator for compressed-sparse convolutional neural networks. Acm Sigarch Comput. Archit. News 2017, 45, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondimalla, A.; Chesnut, N.; Thottethodi, M.; Vijaykumar, T.N. SparTen: A sparse tensor accelerator for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 52nd Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture, Columbus, OH, USA, 12–16 October 2019; pp. 151–165. [Google Scholar]
- Albericio, J.; Judd, P.; Hetherington, T.; Aamodt, T.; Jerger, N.E.; Moshovos, A. Cnvlutin: Ineffectual-neuron-free deep neural network computing. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM/IEEE 43rd Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 18–22 June 2016; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Liu, X.; Mao, H.; Pu, J.; Pedram, A.; Horowitz, M.A.; Dally, W.J. EIE: Efficient inference engine on compressed deep neural network. Acm Sigarch Comput. Archit. News 2016, 44, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Du, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lan, H.; Liu, S.; Li, L. Cambricon-X: An accelerator for sparse neural networks. In Proceedings of the 49th Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO), Taipei, Taiwan, 15–19 October 2016; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; He, Y.; Jiao, H. Efficient zero-activation-skipping for on-chip low-energy CNN acceleration. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence Circuits and Systems (AICAS), Washington, DC, USA, 6–9 June 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Zhou, C.; Qiu, S.; He, Y.; Jiao, H. CNN accelerator at the edge with adaptive zero skipping and sparsity-driven data flow. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 7084–7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.K.; Palisetty, R.; Ray, K.C. High-speed area efficient VLSI architecture of three-operand binary adder. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2020, 67, 3944–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.C.; Chiu, C.T.; Lin, K.T.; Chou, H.H.; Pu, Y.Y. Essa: An energy-aware bit-serial streaming deep convolutional neural network accelerator. J. Syst. Archit. 2020, 111, 101831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


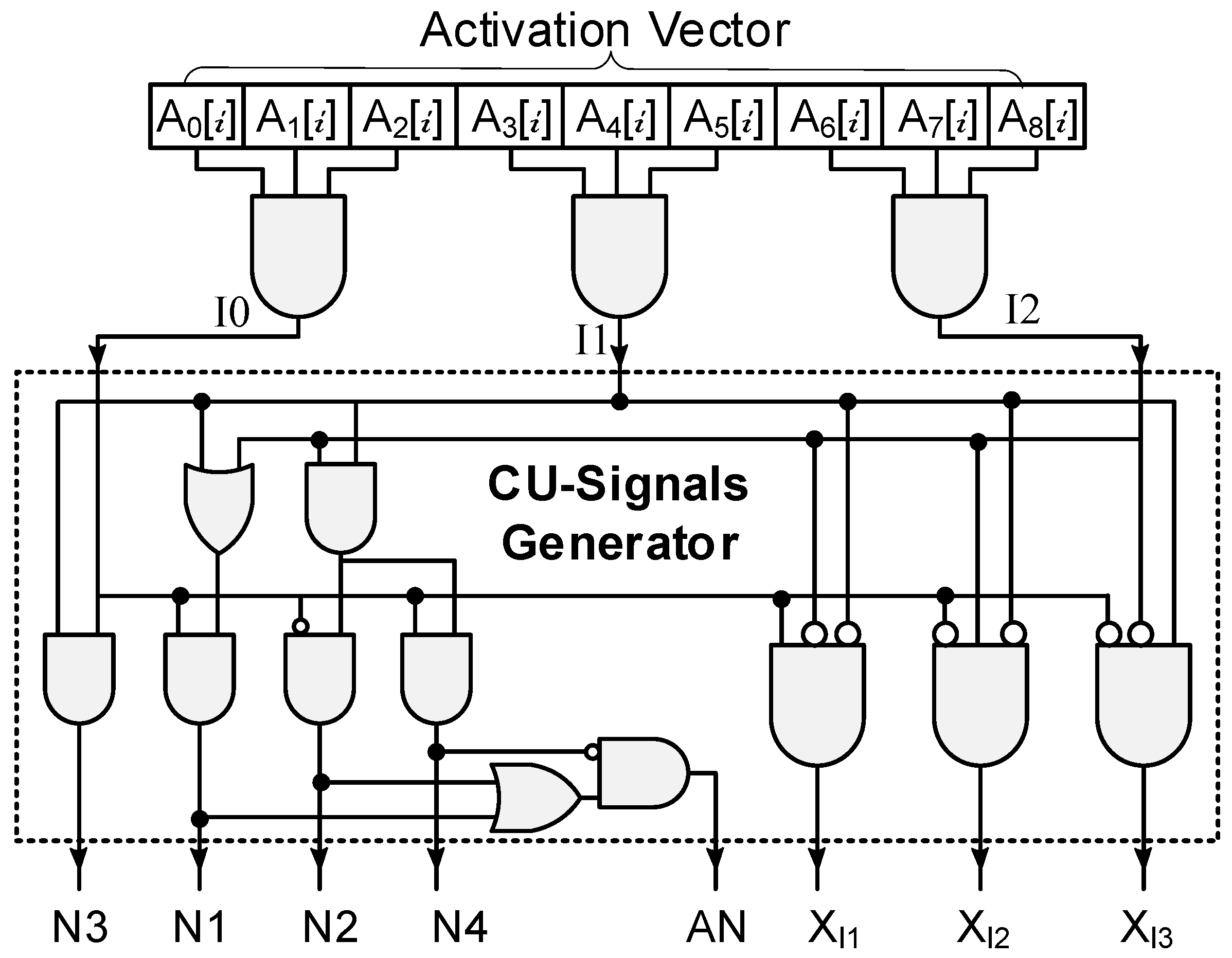


| Interrupts | Node Status | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I0 | I1 | I2 | N1 | N2 | N3 | N4 | AN |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Online Multiplier [23] | Online Adder [19] | Bit-Serial Multiplier [36] | Bit-Serial-Parallel (BSP) | Proposed | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case1 | Case2 | Case3 | |||||
| Technology | 45 nm | 45 nm | 90 nm | 180 nm | 180 nm | ||
| Area () | 3516.9 | 5338.4 | 70,277.5 | 14,747.3 | 17,021.5 | ||
| Power (mW) | 4.27 | 22.37 | 0.296 | 1.163 | 0.669 | 0.934 | 1.232 |
| Delay (ns) | 0.5 | 0.3 | N/A | 1.69 | 1.07 | 1.95 | 2.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akbar, M.A.; Wang, B.; Belhaouari, S.B.; Bermak, A. DROPc-Dynamic Resource Optimization for Convolution Layer. Electronics 2025, 14, 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14132658
Akbar MA, Wang B, Belhaouari SB, Bermak A. DROPc-Dynamic Resource Optimization for Convolution Layer. Electronics. 2025; 14(13):2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14132658
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkbar, Muhammad Ali, Bo Wang, Samir Brahim Belhaouari, and Amine Bermak. 2025. "DROPc-Dynamic Resource Optimization for Convolution Layer" Electronics 14, no. 13: 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14132658
APA StyleAkbar, M. A., Wang, B., Belhaouari, S. B., & Bermak, A. (2025). DROPc-Dynamic Resource Optimization for Convolution Layer. Electronics, 14(13), 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14132658








