Abstract
Aiming at the problems of SiamFC, such as shallow network architecture, a fixed template, a lack of semantic understanding, and temporal modeling, this paper proposes a robust target-tracking algorithm that incorporates both channel and spatial attention mechanisms. The backbone network of our algorithm adopts depthwise, separable convolution to improve computational efficiency, adjusts the output stride and convolution kernel size to improve the network feature extraction capability, and optimizes the network structure through neural architecture search, enabling the extraction of deeper, richer features with stronger semantic information. In addition, we add channel attention to the target template branch after feature extraction to make it adaptively adjust the weights of different feature channels. In the search region branch, a sequential combination of channel and spatial attention is introduced to model spatial dependencies among pixels and suppress background and distractor information. Finally, we evaluate the proposed algorithm on the OTB2015, VOT2018, and VOT2016 datasets. The results show that our method achieves a tracking precision of 0.631 and a success rate of 0.468, improving upon the original SiamFC by 3.4% and 1.2%, respectively. The algorithm ensures robust tracking in complex scenarios, maintains real-time performance, and further reduces both parameter counts and overall computational complexity.
1. Introduction
Target tracking is a hot topic in the field of computer vision and is widely used in UAV-based monitoring [1] and video surveillance systems [2]. The goal of visual tracking is to predict and calibrate the target state (i.e., position and size) of the tracked target in the video, given only the bounding box information of the first frame without prior knowledge [3]. The methods of target state estimation can be divided into two categories: one is based on Siamese networks [4,5]. Some classical methods [6,7,8,9,10] employ Siamese networks trained offline to directly learn the similarity mapping between target templates and search regions, achieving end-to-end state estimation without requiring online model updates. The other approach is based on correlation filters (CFs) [11,12,13], which train a discriminative model online and locate the target by efficiently computing the response map between the target and background in the frequency domain. Although CF offers a significant speed advantage, there exists an inherent trade-off between the use of deep features and maintaining real-time performance [14]. In contrast, Siamese network-based tracking algorithms are more favored by most researchers, with the classic SiamFC still serving as the foundation for many state-of-the-art algorithms.
SiamFC [5] is the first algorithm that combines a Siamese network with kernel correlation filtering. The core of SiamFC is to use a symmetric Siamese network to extract features of the template image and the search image and then use a cross-correlation operation to measure the similarity and output a response score map. The position corresponding to the maximum value is the target position. Li et al. proposed SiamRPN [15] based on SiamFC. By adding a region proposal network (RPN) [16] branch to the Siamese network, one part of the network is used to classify the target and background, and the other part is used for bounding box regression, enabling SiamRPN to learn how to predict bounding boxes. SiamFC++ [17] preserves the efficient architecture of the original SiamFC while enhancing boundary localization accuracy through an anchor-free framework. Moreover, it incorporates a bounding box regression module that dynamically predicts target size and adapts to target deformations.
However, despite their effectiveness, these methods often fail in challenging scenarios involving shape deformation, illumination changes, background clutter with similar objects, or the partial and full occlusion of the target [18]. Recently, with the continuous development of deep learning technology, tracking algorithms based on Siamese networks have also been combined with architectures such as transformers [19], recurrent neural networks [20], and generative adversarial networks [21]. As the core computing unit of transformers, the attention mechanism dynamically adjusts feature weights to enable the model to focus on key information and suppress interference, thereby effectively coping with complex scenarios in target tracking [22]. Therefore, inspired by [23,24], we integrate channel attention and a spatial attention mechanism based on SiamFC. Channel attention enhances the model’s attention to key semantic features and suppresses background and useless feature channels; spatial attention improves the model’s spatial position perception ability, enabling it to more accurately predict the center position of the target [25]. However, spatial attention may blur position-sensitive features, interfering with the peak response in the SiamFC correlation map. To address this, we introduced IoU loss [26] to correct the boundary deviation caused by the attention mechanism. By compensating for the lack of position sensitivity of the attention mechanism, our algorithm has improved the accuracy and success rate by 3.4% and 1.2% respectively, and the robustness has improved by 0.2%.
The main innovations are as follows:
- We improved the AlexNetV2 backbone network by reducing the output stride to increase feature map resolution while employing depthwise separable convolutions to significantly reduce the total number of parameters.
- We added a channel and spatial attention mechanism to enhance the network’s focus on key semantic features and suppress background noise, thereby improving target perception and localization accuracy in complex scenes.
- We incorporated IoU loss into the overall loss function to more effectively optimize both the position and size of the predicted bounding boxes, thereby enhancing localization accuracy.
2. Algorithm Framework
Since target tracking tasks require both high real-time performance and robustness, self-attention and transformer-based mechanisms, though powerful, involve considerable computational overhead. Compared to them, channel and spatial attention mechanisms are more intuitive and efficient when dealing with small targets or local features [27]. In convolutional feature maps, different channels usually represent different semantic information. The channel attention mechanism effectively suppresses redundant channels by assigning importance weights to each channel, while spatial attention guides the network to focus on key target regions by assigning weights to each spatial position. Therefore, our algorithm combines both channel and spatial attention in sequence to highlight semantic features while strengthening attention to the target area.
The overall framework of the target-tracking algorithm based on the dual attention mechanism is shown in Figure 1. The input of the network includes a target patch and a search patch, and the output is a two-dimensional score map, which represents the similarity distribution of the template image at each position in the search image. The network consists of two sub-networks with a similar structure and shared weights. After receiving two relevant samples, the improved AlexNetv2 backbone network extracts multi-level features of the image, where shallow features contain detailed information such as edges, colors, and textures, and deep features contain high-level semantic information such as target categories [28]. Sub-networks integrate the channel attention mechanism and the spatial attention mechanism, generate channel weights through global average pooling and maximum pooling, and generate spatial weights through the pooling and convolution of the spatial dimension. Finally, the multi-level feature maps of the two sub-networks are used to calculate the cross-correlation response map between the template and the search area.
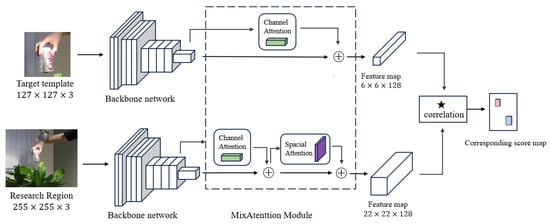
Figure 1.
The overall framework of the proposed algorithm.
2.1. Lightweight Backbone Network Design for Feature Extraction
In order to make the algorithm better distinguish the target and background features and improve the computational efficiency and speed, this paper uses the improved AlexNetv2 to replace the traditional backbone network. Compared with the traditional AlexNet [29], the improved network reduces the output step size to 4, which increases the feature map resolution. The stride of the second convolutional layer is also reduced to 1 to avoid early feature downsampling, enhancing the model’s suitability for fast-moving target scenarios. AlexNetV2 adopts depthwise separable convolution [30], where a small kernel is applied to each input channel independently, without inter-channel fusion. Point-by-point convolution uses a convolution kernel to perform linear combinations on all channels to fuse information between channels. Therefore, the number of parameters and the amount of computation are greatly reduced. The network structure and parameters of each layer are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Backbone network structure and parameters of each layer.
2.2. Attention Module
The attention module of this algorithm uses the serial structure of channel attention and spatial attention to enhance the representation ability of convolutional features. Channel attention can automatically learn the difference in the contribution of different feature channels, amplify the activation value of channels with strong discriminativeness, and reduce the response of noisy channels or redundant channels [31]. The spatial attention mechanism [32] mainly realizes the localization of key regions, that is, identifying the spatial position in the feature map that is most relevant to the task. It establishes spatial dependencies between pixels and captures long-range interactions, effectively addressing the limitation of conventional convolutions in modeling distant relationships. The channel attention mechanism of this paper is shown in Equation (1):
The channel attention structure is shown in Figure 2, where F is the input feature map, and are the results after average pooling and maximum pooling, W is a two-layer fully connected layer network, and is a sigmoid function used to normalize the weight. The channel attention first performs global average pooling and global maximum pooling on the input feature map, and then it sends the two pooling results to a shared multi-layer perceptron (MLP) for learning. The MLP outputs are merged through an element-wise sum and then processed via a sigmoid activation function to finally generate a channel attention weight matrix.
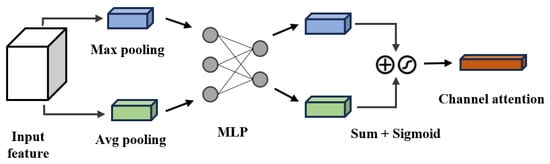
Figure 2.
Channel attention structure.
The spatial attention mechanism is shown in Equation (2):
The spatial attention structure is shown in Figure 3. It pools the feature map along the channel dimension to obtain two single-channel features, and . These features are then channel-wise concatenated and fused using a convolutional layer, where the large kernel size is specifically designed to capture wide-range spatial dependencies and effectively integrate the distinct characteristics of both pooling operations. Finally, the fused features are normalized through a sigmoid activation to produce spatial attention weights in the range of [0, 1].
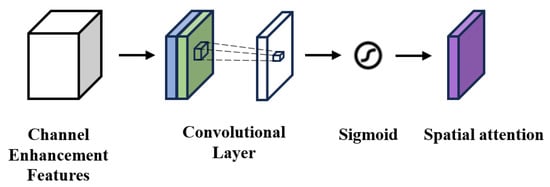
Figure 3.
Spatial attention structure.
Since the target template branch in the Siamese network holds richer information about the tracked object, a channel attention module is added to enhance sensitivity to key features. Conversely, the search branch contains more background and interference; therefore, the algorithm employs a channel attention module to reweight each channel and a spatial attention module to suppress background and interference by reducing gradient contributions from non-target regions.
2.3. Loss Function
The improved loss function in this paper consists of two parts: classification loss and IoU Loss. The classification loss uses balanced loss [33]. By adjusting the contribution of each class of samples to the total loss, each class is treated equally during the optimization process in training, which can effectively alleviate the problem of sample class imbalance. The classification loss is shown in Equation (3):
where is the label, p is the model output probability, and is used to balance the importance of positive and negative samples. IoU loss [34] is used to optimize the overlapping area between the predicted box and the true box to improve the localization accuracy of the detection. Its expression is shown in Equation (4):
are the predicted box and the true box, N is the total number of samples, and IoU is the intersection-over-union ratio of two rectangular boxes. The final loss function expression is shown in Equation (5):
is the weight coefficient for balancing the classification loss and localization loss.
3. The Tracking Process
The model first crops the target template from the target image and crops a larger search region from the current frame with the target position in the previous frame as the center. The cropped area not only contains the target but also retains certain context information to enhance robustness. The operation is as shown in Equation (6):
where is the size compensation of the context area and s is the side length of the square to be cropped. Then, this square area with a side length of s is used as a template image and a search image, and simultaneously input into a fully convolutional network, , with shared parameters, and its features, and are extracted, respectively. Then, the two feature maps are cross-correlated, as shown in Equation (7):
where * represents the cross-correlation, the position of the maximum value in the response map is the new position of the target in the current frame, and the position of the maximum response value in the response map is shown in Equation (8):
The algorithm is optimized using stochastic gradient descent, and the loss function gradually stabilizes after 10 rounds of training.
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
In this section, we first introduce the evaluation metrics used in our experiments. Secondly, to verify the effectiveness of the IoU loss function and the attention mechanism, we conducted an ablation experiment in OTB2015 [35]. Then, we compared the performance of six algorithms in VOT2018 [36] and VOT2016 [37] to further prove that our algorithm is the best in terms of robustness and the average overlap rate among them. The proposed algorithm uses the single target short-term tracking dataset GOT-10k [38] for offline training. This dataset includes more than 30 targets and more than 4000 video clips. The experimental setup uses a batch size of 8, the number of iterations is 50, the initial learning rate is 1 × 10−2, the final learning rate is 1 × 10−5, and the scaling factor of the network output response is 0.001 to prevent the value from being too large and causing unstable training.
4.1. Evaluation Metrics
The performance evaluation metrics of the target-tracking algorithm mainly include three aspects: the tracking accuracy, the tracking success rate, and the tracking speed. Specifically, the tracking accuracy can be measured using the center error or precision rate. The tracking success rate is measured using the area overlap or success rate curve, and FPS measures the tracking speed. The OTB evaluation system mainly includes two core metrics: precision and success rate. The precision refers to the proportion of frames in which the Euclidean distance between the center point of the tracking frame and the center point of the true frame is less than a given threshold, , as shown in Equation (9):
where N is the total number of frames in the video sequence, and are the center coordinates of the predicted box and the real box of the frame, respectively, and is the distance threshold, which is 20 pixels in the OTB metric. The success rate refers to the proportion of frames in which the IoU between the tracking box and the real box is greater than the given threshold. As shown in Equation (10),
where is the predicted box and the real box of the t-th frame, is the given IoU threshold, and by traversing different , the success rate curve can be drawn. The VOT challenges mainly calculate robustness and the expected average overlap (EAO). The robustness represents the number of times the tracker loses the target in the entire sequence, which is calculated using Equation (11):
where S is a constant that is taken as 30 in this paper, is the number of frames where tracking fails, and is the total number of frames. The fewer tracking failures an algorithm has, the better; therefore, a lower robustness score indicates better performance. EAO is a unique comprehensive metric of VOT, combining accuracy and robustness and reflecting the expected performance in the actual tracking process in a sequence of random length, as shown in Equation (12):
where l is the subsequence length, EAO is the core metric of VOT ranking, and the higher it is, the better the performance.
4.2. Ablation Experiments
In order to investigate the effects of the attention mechanism and IoU loss function, we organized some ablation experiments. Group 1 serves as the baseline, employing AlexNetV2 as the backbone network and balanced loss as the loss function. Groups 2 and 3 introduce two additional components: an attention mechanism and IoU Loss, respectively. Table 2 shows the results of the ablation experiment. When only the attention mechanism is added (Group 2), both accuracy and the success rate decrease compared to the baseline. This may be because SiamFC performs local template matching through a cross-correlation operation, which inherently emphasizes precise spatial alignment. But the spatial attention module blurs position-sensitive features, and especially large convolution kernels may destroy the target boundary information, resulting in a decrease in accuracy and the success rate. When only the IoU loss is added (Group 3), the accuracy increases slightly, but the success rate hardly changes. This may be because the success rate measures the comprehensive performance of the IoU between the predicted box and the true box under all thresholds. Since the backbone has not changed, the overall performance and success rate of the algorithm have not changed. The IoU loss reduces the drift of the center point by optimizing the bounding box coordinates, which increases the accuracy of Group 3 by 0.3%. Group 4 adds both the attention mechanism and the IoU loss, which is our proposed method. The attention mechanism directs focus to salient regions, while the IoU loss promotes global geometric alignment and corrects the attention weight distribution. This compensates for the positional insensitivity of the attention mechanism, resulting in a better balance between the accuracy and the success rate. As shown in Figure 4, Group 4 achieves the highest performance in both metrics, highlighting the importance of integrating both components.

Table 2.
Ablation Experiments results on OTB2015 test set.
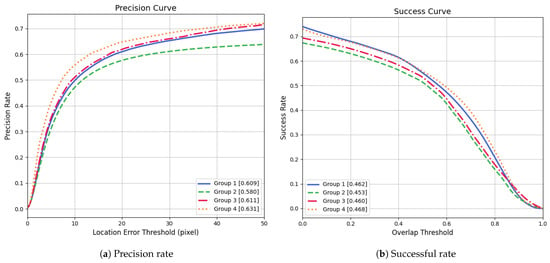
Figure 4.
Ablation Experiments results in OTB2015 dataset.
4.3. Experiments on OTB2015
In this section, we evaluate the proposed algorithm on the OTB2015 dataset, which consists of 100 video sequences spanning 11 challenging attributes. Tracking performance is assessed in terms of precision and the success rate. To comprehensively assess our method, we compare it with the original SiamFC using three different backbone networks and two loss functions. Additionally, we include the classical correlation filter-based tracker KCF for reference. Table 3 shows the structure and performance of the six groups of algorithms. The results of Group A to Group C show that AlexNetV2 achieves the best balance between accuracy and complexity. This is because, compared with AlexNetV1, AlexNetV2 has more channels in the convolutional layer, which enhances the ability of the algorithm to capture details. AlexNetV3 further increases the number of channels compared to V2, theoretically enabling richer feature extraction. However, this also significantly increases the number of parameters and inference latency. The results of Group C and Group D show that it is more appropriate to use BalancedLoss as the loss function because the focal loss [39] easily amplifies the gradient of difficult samples, while the capacity of lightweight backbone networks such as AlexNet is insufficient, and shallow features conflict with the gradient update direction of the focal loss, resulting in optimization oscillation. Group E is our proposed algorithm, which adds spatial and channel attention mechanisms and IoU loss to AlexNetV2. It can be seen that our proposed algorithm performed the best, with the precision and success rate increased by 4.9% and 0.8%, respectively, compared with Group B. In addition, we also compared KCF, which is far ahead in real-time performance. Because KCF only learns linear filters during training, uses circulant matrices to model image blocks, and converts filtering into frequency domain calculations through Fourier transformation, it greatly reduces the amount of calculation and memory consumption. Therefore, our proposed algorithm still reflects a gap with KCF in terms of parameter volume and latency. In terms of the number of parameters, the algorithm we proposed is twice as large as that of Group B, and the delay is also increased by 0.85 ms. However, our FPS reaches 346.42 frame/s, satisfying real-time processing requirements.

Table 3.
Comparison of other performance of algorithms.
Figure 5 presents the precision and success plots for the six algorithm groups. The precision curve reflects the percentage of frames where the center location error is below a specified threshold across all test frames. Typically, the precision at a 20-pixel threshold is used as the final performance metric (i.e., the precision value reported in Table 3). The success curve represents the percentage of frames where the intersection over union (IoU) exceeds varying thresholds (ranging from 0 to 1) across all test frames, with the area under the curve used as the final evaluation metric (i.e., the success score reported in Table 3). As shown, the proposed algorithm achieves the highest accuracy across all location error thresholds.
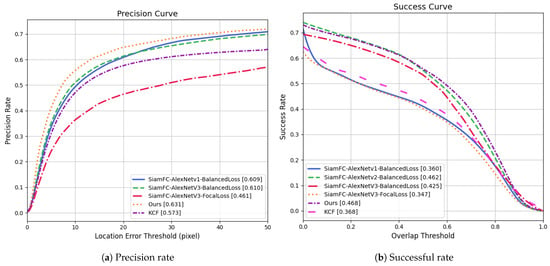
Figure 5.
Comparison of the precision and success rate of different algorithms in OTB2015 dataset.
OTB2015 contains a variety of challenging tracking scenarios, including illumination changes, occlusion, fast movement, complex background, scale changes, motion blur, etc. Based on the above challenges, this paper selects six representative video sequences and scenarios to demonstrate the tracking effect of our proposed algorithm, as shown in Figure 6. In the coke sequence, KCF (the green box) loses the target after the object is occluded. In motorrolling, our algorithm (red box) is more adaptable to the challenges of object shape changes and rotation than others. In the skating1 sequence, our algorithm achieves more outstanding bounding box localization accuracy at the 387th frame. In the soccer sequence, our algorithm can effectively cope with the challenges of a complex background. In the singer1 sequence, illumination changes impact the localization accuracy of the bounding box. KCF fails to adapt to these variations, leading to tracking drift at the 242th frame. In contrast, our algorithm maintains stable tracking. In the carscale sequence, SiamFC (the blue box) struggles to adapt to scale variations of the target, whereas our algorithm successfully handles the change and maintains accurate tracking.

Figure 6.
Visual comparison results of different algorithms on 4 selected sequences.
4.4. Experiments on VOT2018
We also use the VOT2018 dataset to compare the accuracy, robustness, and EAO of six tracking algorithms, with the results presented in Figure 7 and Table 4. Although our algorithm shows slightly lower accuracy compared to those using AlexNetv1 and AlexNetv2, it achieves the best robustness among all methods. Since robustness measures the number of tracking failures, a lower value indicates better performance. Our algorithm achieves a robustness score of 0.287. This may be because spatial attention enhances the response of the target region while neglecting edge details. For instance, when the target is rapidly rotating, an excessive focus on the central area can lead to incomplete coverage of the bounding box, slightly reducing accuracy. However, channel attention helps reduce mismatches with similar backgrounds. Furthermore, when the target briefly disappears, the attention weights can retain key feature memories, enhancing the algorithm’s re-detection capability. Therefore, the robustness of the proposed algorithm has been improved. Additionally, our algorithm achieved the highest EAO score of 0.532, indicating that it can consistently track the target while maintaining a high degree of overlap between the predicted and ground truth bounding boxes. This also proves that background and interference information can be effectively suppressed by adding the space and channel attention modules.
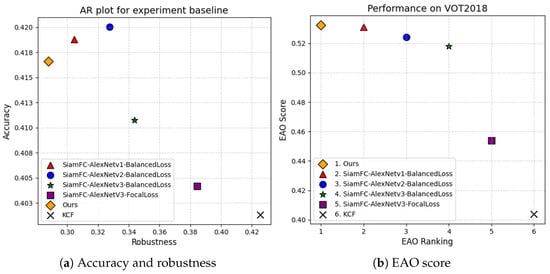
Figure 7.
Accuracy, robustness, and expected average overlap score on VOT2018.

Table 4.
Performance comparison of algorithms in VOT2018 dataset.
4.5. Experiments on VOT2016
We further conducted comprehensive experiments on the VOT2016 dataset [37], which consists of 60 challenging video sequences and also employs accuracy, robustness, and EAO as evaluation metrics. The results presented in Table 5 and Figure 8. Among all tested algorithms, the SiamFC-AlexNetv2-BlancedLoss achieves the highest accuracy, reflecting its strong localization capability. However, our proposed method demonstrates the best robustness score of 0.258. This is because the attention mechanism can establish long-range dependencies between features, helping the model understand positional variation patterns of the target across frames and thereby enabling a more robust tracking of moving objects. In addition, our method achieves the highest EAO score of 0.585, effectively balancing tracking accuracy and robustness and making it a strong comprehensive indicator of real-world performance. In terms of tracking speed, our method runs at 48.8 FPS, ranking second among the compared trackers. This speed is well above the real-time threshold (typically 25–30 FPS), ensuring its practical applicability in real-time tracking scenarios such as video surveillance, autonomous driving, or human–robot interaction. The above experiments clearly demonstrate that our proposed tracker achieves a strong trade-off between accuracy, robustness, and speed, outperforming several state-of-the-art methods and showing strong competitive performance on the VOT2016 benchmark.

Table 5.
Performance comparison of algorithms on VOT2016 dataset.
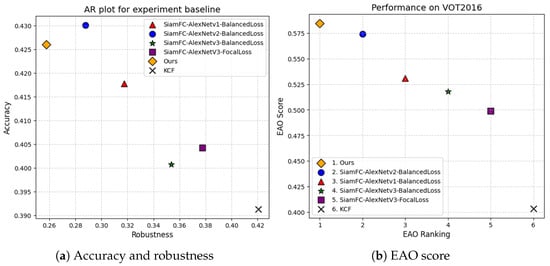
Figure 8.
Accuracy, robustness, and expected average overlap score on VOT2016.
5. Conclusions
This paper has proposed an improved target-tracking algorithm based on SiamFC. By introducing channel attention and spatial attention mechanisms, the feature discrimination ability and spatial perception ability were enhanced. In view of the problem that spatial attention may interfere with position-sensitive matching, the IoU loss was further introduced to correct boundary deviation. The experimental results show that the algorithm is not only superior to the original SiamFC in terms of the tracking accuracy and success rate but also superior to the method that only introduces the attention mechanism or the IoU loss. When facing challenges such as illumination changes, occlusion, and complex backgrounds, this algorithm shows more stable tracking performance. In future work, we plan to incorporate spatiotemporal information from historical frames to help the model better understand target continuity, dynamic behavior, and inter-frame correlations, thereby further improving long-term tracking accuracy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.C. and S.F.; methodology, X.C. and S.F.; software, X.C.; validation, V.M. and S.Y.; formal analysis, B.Z., W.J., J.Y., Y.F. and C.W.; writing—original draft preparation, X.C. and S.F.; writing—review and editing, S.F. and V.M.; supervision, S.F.; project administration, S.F.; funding acquisition, S.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Science Foundation of China under Grant No.62303100, the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. LTY22F020003, the Hebei Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. F2024501001, the General Projects of Zhejiang Provincial Department of Education under Grant No. Y202455235, the Educational Department of Liaoning Province of China under Grant No. LJKMZ20221793, the Doctoral Start-up Project of the Department of Science and Technology of Liaoning Province of China under Grant No. 2023-BS-208, and the Ministry of Education Theme Case Project in 2023 under Grant No. ZT-231034902.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Keawboontan, T.; Thammawichai, M. Toward real-time uav multi-target tracking using joint detection and tracking. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 65238–65254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhu, X.; Bao, W.; Fei, B.; Wu, J. SMART: Vision-based method of cooperative surveillance and tracking by multiple UAVs in the urban environment. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 24941–24956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Wang, D.; Bai, Y.; Chen, P.; Liu, F. Deep learning in visual tracking: A review. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 34, 5497–5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; He, K. Exploring simple siamese representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bertinetto, L.; Valmadre, J.; Henriques, J.F.; Vedaldi, A.; Torr, P.H. Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016 Workshops, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–10 and 15–16 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Peng, H. Deeper and wider siamese networks for real-time visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4591–4600. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Li, B.; Wu, W.; Yan, J.; Hu, W. Distractor-aware siamese networks for visual object tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 101–117. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Shen, J. Triplet loss in siamese network for object tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 459–474. [Google Scholar]
- Voigtlaender, P.; Luiten, J.; Torr, P.H.; Leibe, B. Siam r-cnn: Visual tracking by re-detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 6578–6588. [Google Scholar]
- He, A.; Luo, C.; Tian, X.; Zeng, W. A twofold siamese network for real-time object tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4834–4843. [Google Scholar]
- Bolme, D.S.; Beveridge, J.R.; Draper, B.A.; Lui, Y.M. Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Henriques, J.F.; Caseiro, R.; Martins, P.; Batista, J. High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 37, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriques, J.F.; Caseiro, R.; Martins, P.; Batista, J. Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2012: 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 7–13 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Danelljan, M.; Bhat, G.; Shahbaz Khan, F.; Felsberg, M. Eco: Efficient convolution operators for tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Yan, J.; Wu, W.; Zhu, Z.; Hu, X. High performance visual tracking with siamese region proposal network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Q.; Zhuo, W.; Tang, C.-K.; Tai, Y.-W. Few-shot object detection with attention-RPN and multi-relation detector. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, G. SiamFC++: Towards robust and accurate visual tracking with target estimation guidelines. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, Y.; Hu, W. Review of visual object tracking algorithms of adaptive direction and scale. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2020, 56, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2017/file/3f5ee243547dee91fbd053c1c4a845aa-Paper.pdf (accessed on 17 May 2025).
- Zaremba, W.; Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O. Recurrent neural network regularization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.2329. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial networks. Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, X.; Yang, J. Spatial group-wise enhance: Improving semantic feature learning in convolutional networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.09646. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Borji, A.; Itti, L. State-of-the-art in visual attention modeling. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 35, 185–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Ye, R.; Ren, D. Distance-IoU loss: Faster and better learning for bounding box regression. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 12993–13000. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Fan, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Ling, H. Swintrack: A simple and strong baseline for transformer tracking. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 16743–16754. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail Fawaz, H.; Lucas, B.; Forestier, G.; Pelletier, C.; Schmidt, D.F.; Weber, J.; Webb, G.I.; Idoumghar, L.; Muller, P.-A. Inceptiontime: Finding alexnet for time series classification. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2020, 34, 1936–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.Y.; Niu, Z. CNN with depthwise separable convolutions and combined kernels for rating prediction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 170, 114528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V.; Heess, N.; Graves, A.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Recurrent models of visual attention. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 27. Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2014/file/3e456b31302cf8210edd4029292a40ad-Paper.pdf (accessed on 17 May 2025).
- Jaderberg, M.; Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Spatial transformer networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28. Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2015/file/33ceb07bf4eeb3da587e268d663aba1a-Paper.pdf (accessed on 17 May 2025).
- Ren, J.; Zhang, M.; Yu, C.; Liu, Z. Balanced mse for imbalanced visual regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 7926–7935. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Shang, R.; Ju, Z.; Feng, J.; Xu, S.; Zhang, W. Ellipse IoU Loss: Better Learning for Rotated Bounding Box Regression. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lim, J.; Yang, M.-H. Online object tracking: A benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 2411–2418. [Google Scholar]
- Kristan, M.; Leonardis, A.; Matas, J.; Felsberg, M.; Pflugfelder, R. The sixth visual object tracking vot2018 challenge results. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Workshops, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Roffo, G.; Melzi, S. The visual object tracking VOT2016 challenge results. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2016 Workshops: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–10 and 15–16 October 2016, Proceedings, Part II; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 777–823. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Zhao, X.; Huang, K. Got-10k: A large high-diversity benchmark for generic object tracking in the wild. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 43, 1562–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, T.Y.; Dollár, G. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).