Backpack Client Selection Keeping Swarm Learning in Industrial Digital Twins for Wireless Mapping
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- We designed a DT-driven industrial IoT SL architecture, in which DT technology realizes dynamic perception in complex industrial IoT environments, and SL enhances the interconnection between heterogeneous devices and production lines.
- (2)
- Based on DT-SL, we propose a novel KSL scheme based on the backpack model to construct the DT model. Moreover, we select clients with greater contributions to complete wireless mapping and Keeping SL twin modeling to optimize the wireless channel transmission rate.
- (3)
- Compared with the existing methods, the timeliness and convergence rate of the proposed method are improved.
2. Related Work
2.1. Digital Twins in Industrial IoT
2.2. Client Selection in Distributed Learning
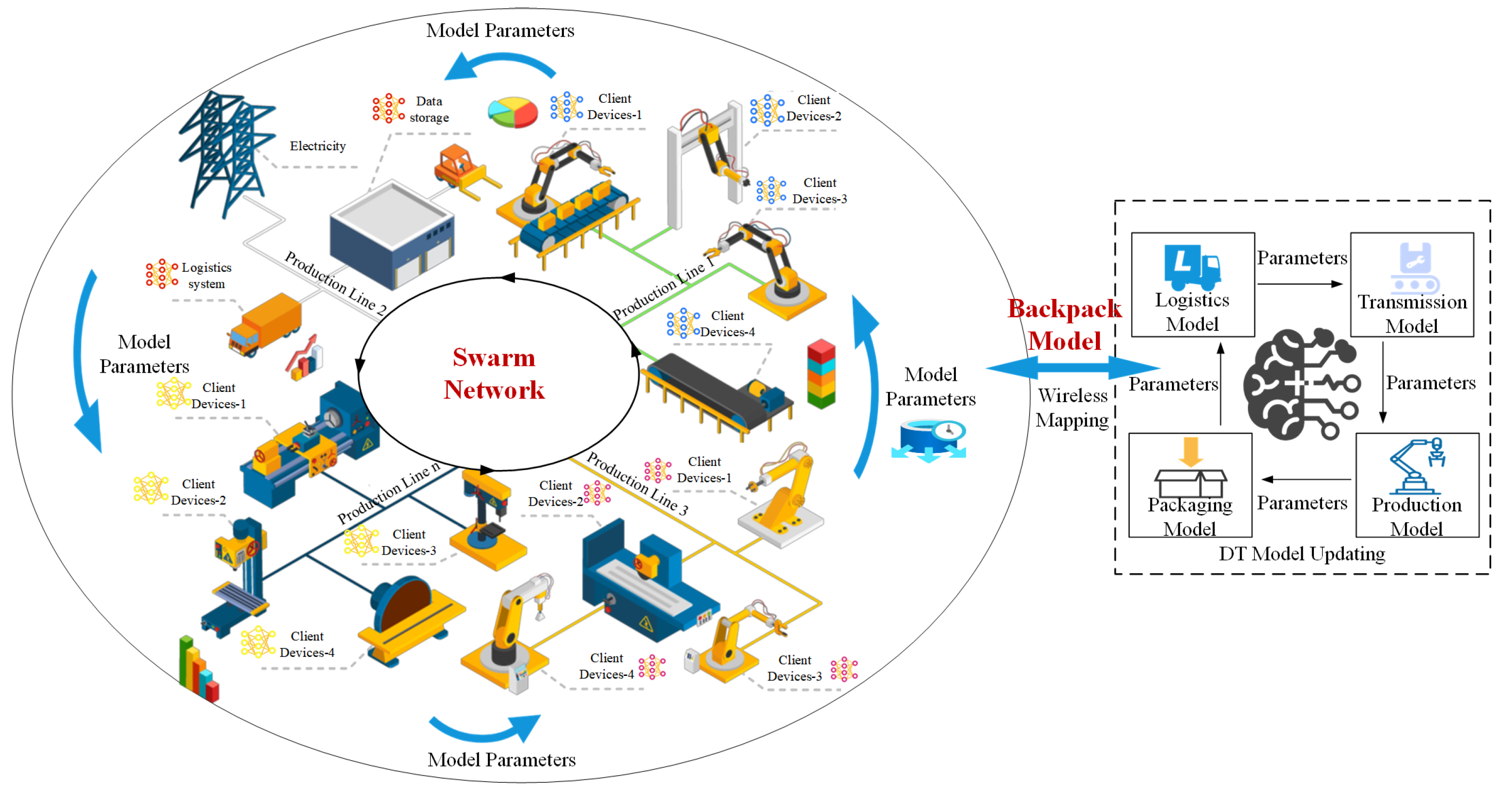
3. System Model
4. Client Selection and Backpack Model
4.1. Convergence Proof
4.2. Computational Complexity
| Algorithm 1: Backpack-Swarm Learning in DT |
| 1. Input: local dataset , number of local rounds , number of global rounds , local learning rate , initialization parameters . 2. for do 3. dataset from to client: 4. 5. for local training in do 6 if client is to satisfy: and 7. model update : 8. else select client training: 9. 10. end for 11. end for 12. Output: : updating each node of the swarm |
5. Numerical Results
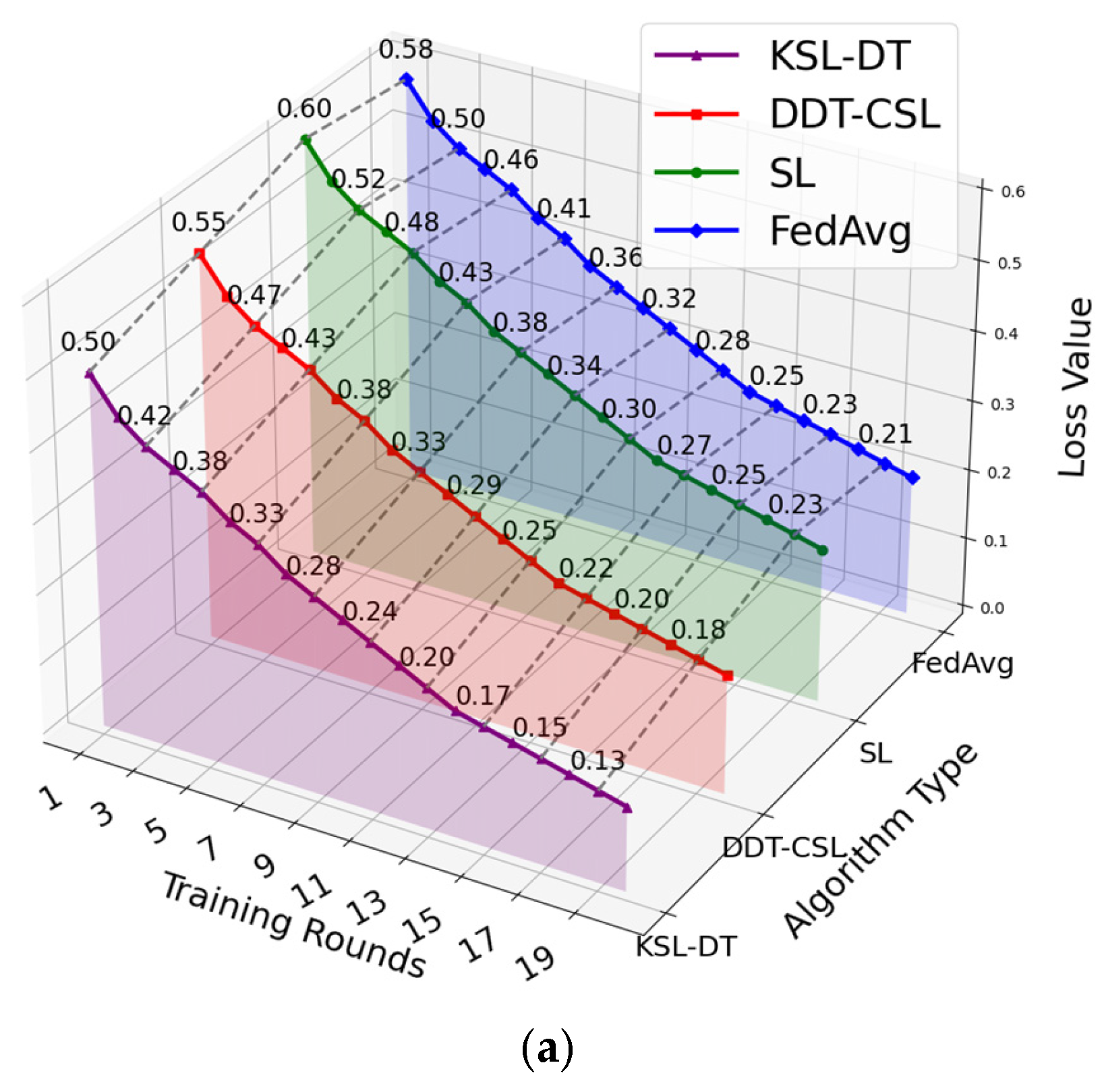
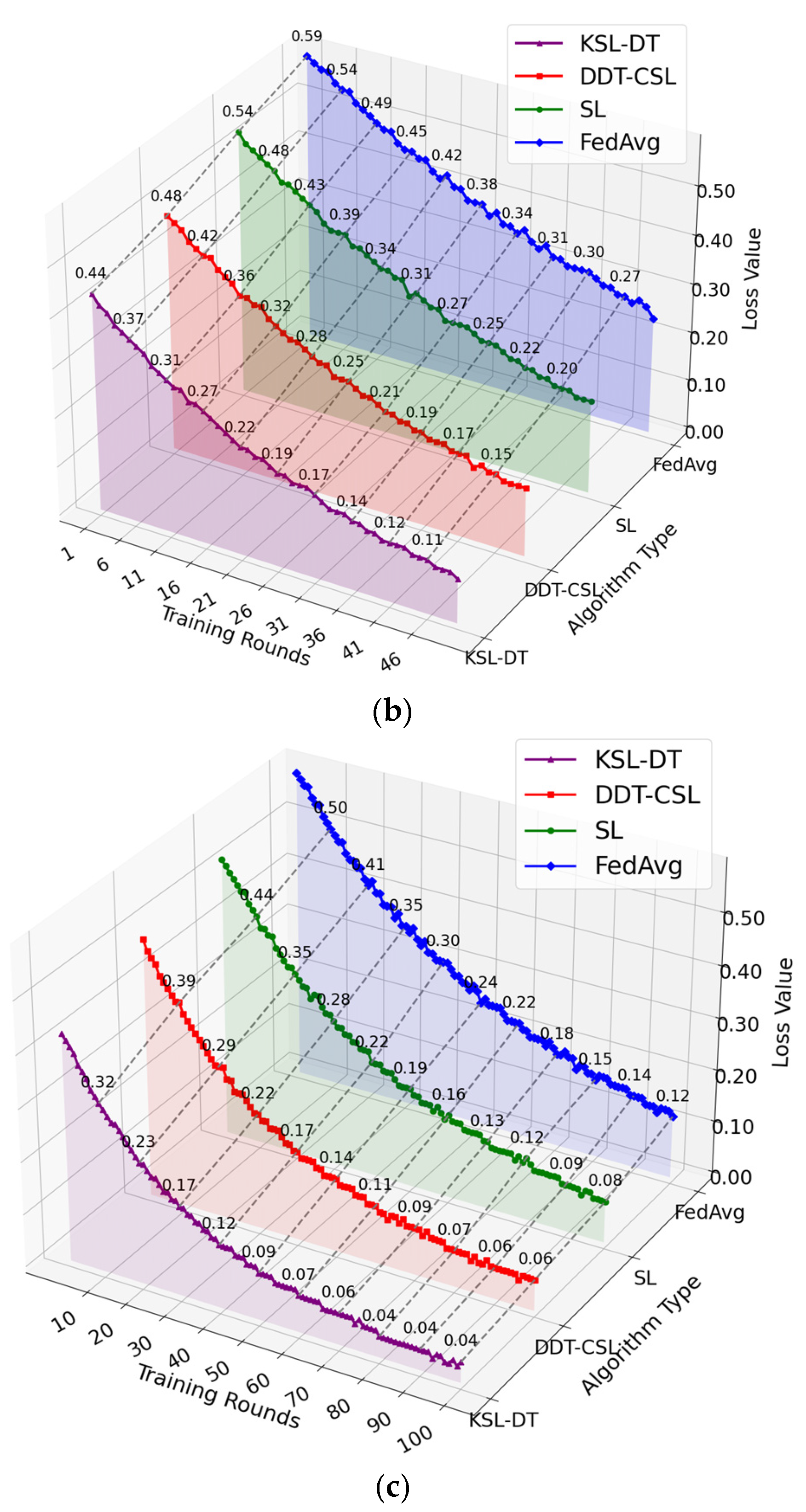
5.1. Convergence Rate of the Model
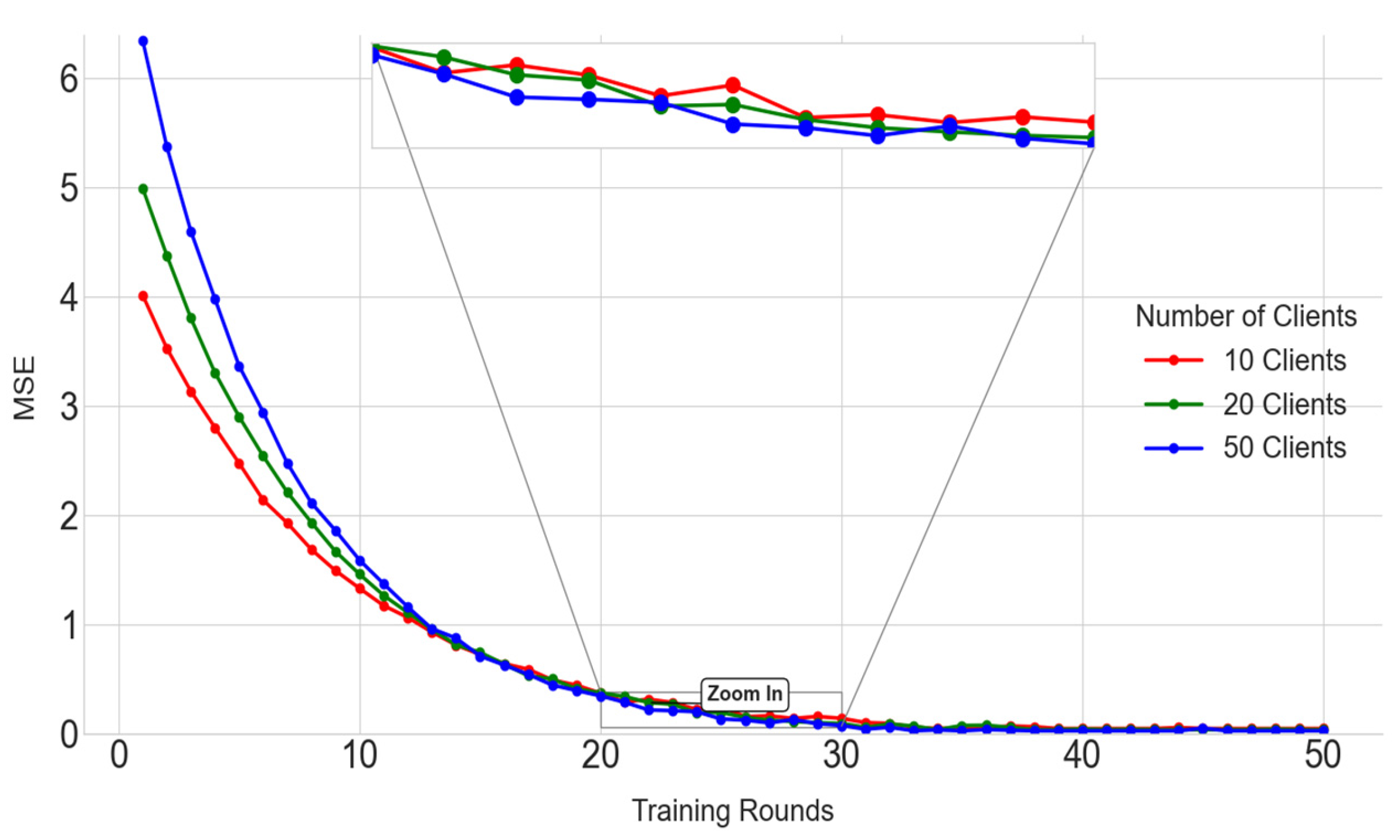
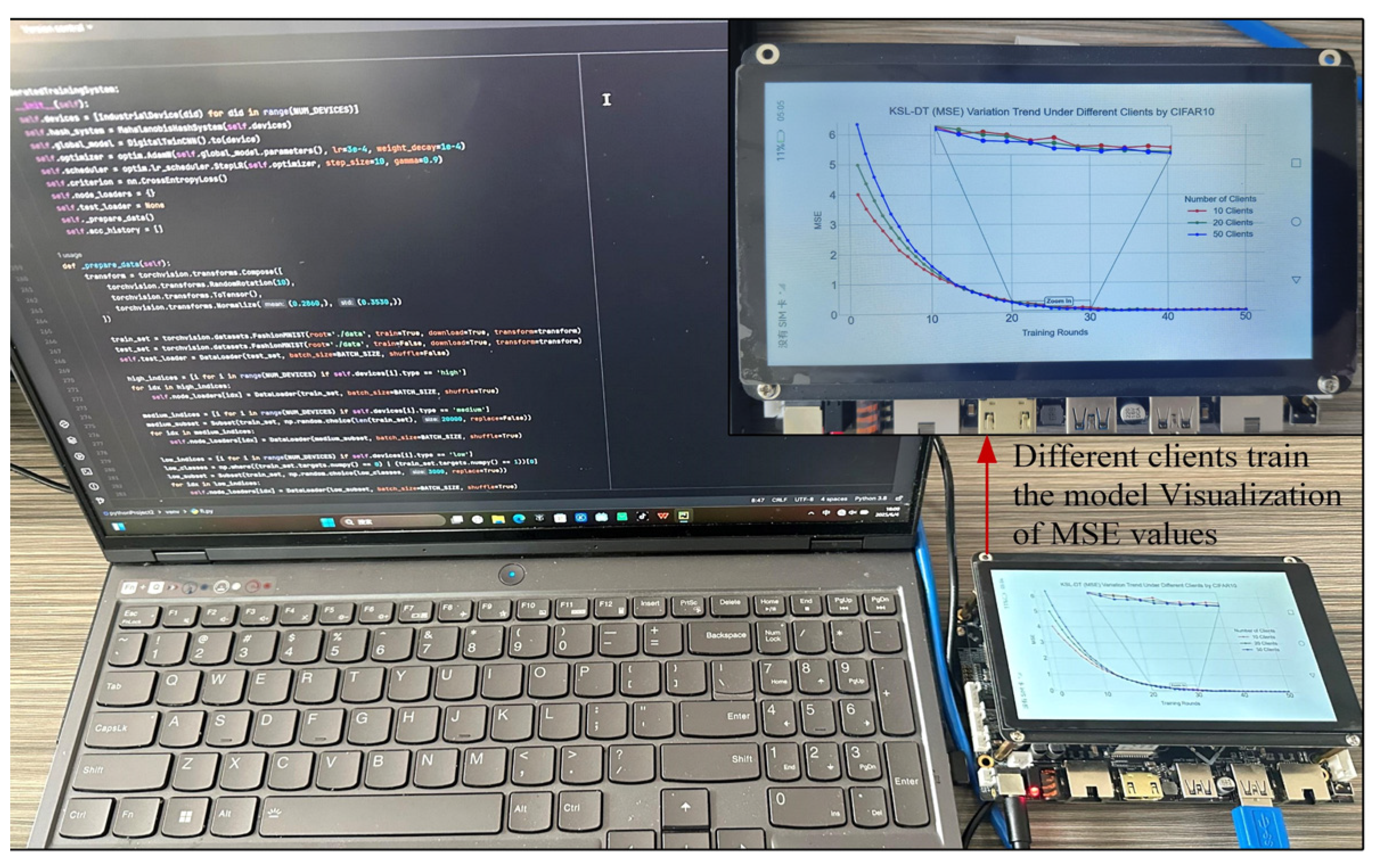
5.2. Model MSE Value Verification
5.3. Parameter Transmission Amount for the Model
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nguyen, D.C.; Pathirana, P.N.; Ding, M.; Seneviratne, A. Secure computation offloading in blockchain based IoT networks with deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2021, 8, 3192–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Cheng, Y.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, M. Theory and technology of cyber physical fusion in digital twin workshop. Comput. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2017, 23, 1603–1611. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, F.; Sui, F.; Liu, A.; Qi, Q.; Zhang, M.; Song, B.; Guo, Z.; Lu, S.C.-Y.; Nee, A.Y.C. Digital twin-driven product design framework. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 57, 3935–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrmann, C.; Gunnarsson, M. A digital twin-based industrial automation and control system security architecture. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 16, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wu, J.; Pan, Q.; Guan, X.; Guizani, M. A survey on digital twin for industrial internet of things: Applications, technologies and tools. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2023, 25, 2569–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Tao, F.; Hu, T.; Anwer, N.; Liu, A.; Wei, Y.; Wang, L.; Nee, A. Enabling technologies and tools for digital twin. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 58, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, D.; Wang, R.; Zhang, P.; Wu, Y. Efficient asynchronous federated learning research in the internet of vehicles. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 10, 7737–7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnat-Herresthal, S.; Schultze, H.; Shastry, K.L.; Manamohan, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Garg, V.; Sarveswara, R.; Händler, K.; Pickkers, P.; Aziz, N.A.; et al. Swarm learning for decentralized and confidential clinical machine learning. Nature 2021, 594, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldanha, O.L.; Quirke, P.; West, N.P.; James, J.A.; Loughrey, M.B.; Grabsch, H.I.; Salto-Tellez, M.; Alwers, E.; Cifci, D.; Laleh, N.G.; et al. Swarm learning for decentralized artificial intelligence in cancer histopathology. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, P.; Jin, J.; Yu, K. Digital twin empowered industrial IoT based on credibility-weighted swarm learning. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Zhao, P.; Gao, J.; Wu, H.; Ma, H. A survey of the social internet of vehicles: Secure data issues, solutions, and federated learning. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Mag. 2023, 15, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imteaj, A.; Thakker, U.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Amini, M.H. A survey on federated learning for resource constrained IoT devices. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, L.U.; Saad, W.; Han, Z.; Hossain, E.; Hong, C.S. Federated learning for internet of things: Recent advances, taxonomy, and open challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 1759–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.P.; Xiang, Y.; Lu, X.; Yearwood, J.; Gao, L. Federated learning via disentangled information bottleneck. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2022, 16, 1874–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lan, Y.; Cui, Z.; Cai, J.; Zhang, W. A survey on federated learning: Challenges and applications. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2023, 14, 513–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Ren, T.; Jiang, X.; Xu, M. Client selection and resource allocation for federated learning in digital-twin-enabled industrial internet of things. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Glasgow, UK, 26–29 March 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Yang, Y.; Xiang, W.; Yuan, L.; Yu, K.; Alonso, Á.H.; Ureña, J.U.; Pang, Z. Adaptive optimization federated learning enabled digital twins in industrial IoT. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2024, 38, 100521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Lin, K.-Y. Communication efficient federated learning for digital twin systems of industrial internet of things. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisinni, E.; Saifullah, A.; Han, S.; Jennehag, U.; Gidlund, M. Industrial internet of things: Challenges, opportunities, and directions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 4724–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, K.; Maharjan, S.; Zhang, Y. Communication-efficient federated learning for digital twin edge networks in industrial IoT. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 5709–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, T.; Yonetani, R. Client selection for federated learning with heterogeneous resources in mobile edge. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Shanghai, China, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulrahman, S.; Tout, H.; Mourad, A.; Talhi, C. FedMCCS: Multicriteria client selection model for optimal IoT federated learning. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 4723–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Z.; Ali, A.; Zawad, S.; Yan, E.; Yan, F.; Li, Y.; Zhou, T.; Rangwala, H. Tifl: A tier-based federated learning system. In Proceedings of the 29th International Symposium on High-Performance Parallel and Distributed Computing, Stockholm, Sweden, 23–26 June 2020; pp. 125–136. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lee, S.-J. Fedbalancer: Data and pace control for efficient federated learning on heterogeneous clients. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications and Services, Portland, OR, USA, 27 June–1 July 2022; pp. 436–449. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, F.; Zhu, X.; Madhyastha, H.V.; Chowdhury, M. Oort: Efficient federated learning via guided participant selection. In USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (OSDI); {USENIX} Association: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ribero, M.; Vikalo, H.; de Veciana, G. Federated learning under intermittent client availability and time-varying communication constraints. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2023, 17, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Guo, H.; Lau, V.K.N. Communication-efficient federated multitask learning over wireless networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.M.; Gunduz, D.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Poor, H.V. Convergence of update aware device scheduling for federated learning at the wireless edge. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 20, 3643–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.H.; Liu, Z.; Quek, T.Q.S.; Poor, H.V. Scheduling policies for federated learning in wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2020, 68, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, H. Client selection and bandwidth allocation in wireless federated learning networks: A long-term perspective. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 20, 1188–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Meaning | Source (Equations) |
|---|---|---|
| the loss function of device | (1), (3), (12)–(16) | |
| number of local dataset samples of device | (1), (2) | |
| model parameters of device at iteration | (3), (14)–(18), (22), (23) | |
| the gradient of loss function of device at the th iteration | (3)–(5) | |
| the communication volume (i.e., weight) of device | (11), (19)–(22) | |
| the system’s maximum communication overhead threshold | (7), (9), (10) | |
| strong convexity constant | (13), (15), (17), (18), (22), (23) | |
| variance of local data distribution | (21)–(23) |
| Data Name | MNIST | CIFAR-10 |
|---|---|---|
| Data Type | handwritten numbers | actual object image |
| Image Dimensions | 28 × 28, single channel (grayscale) | 32 × 32, 3 channels (RGB) |
| Number Of Categories | 10 (numbers 0 to 9) | 10 (airplane, bird, and so on) |
| Training Set Size | 70,000 | 60,000 |
| Data Source | Yann LeCun website | CIFAR website |
| Training Rounds | 10 Clients | 20 Clients | 50 Clients |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 4.02 | 4.99 | 6.35 |
| 3 | 2.50 | 3.05 | 3.84 |
| 5 | 2.01 | 2.37 | 2.96 |
| 10 | 1.56 | 1.78 | 1.89 |
| 20 | 0.79 | 0.95 | 0.99 |
| 50 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, X.; Su, N.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, P. Backpack Client Selection Keeping Swarm Learning in Industrial Digital Twins for Wireless Mapping. Electronics 2025, 14, 2323. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14122323
Wei X, Su N, Guo Y, Zhao P. Backpack Client Selection Keeping Swarm Learning in Industrial Digital Twins for Wireless Mapping. Electronics. 2025; 14(12):2323. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14122323
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Xingjia, Ning Su, Yikai Guo, and Pengcheng Zhao. 2025. "Backpack Client Selection Keeping Swarm Learning in Industrial Digital Twins for Wireless Mapping" Electronics 14, no. 12: 2323. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14122323
APA StyleWei, X., Su, N., Guo, Y., & Zhao, P. (2025). Backpack Client Selection Keeping Swarm Learning in Industrial Digital Twins for Wireless Mapping. Electronics, 14(12), 2323. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14122323







