Torque Ripple Suppression Strategy Based on Online Identification of Flux Linkage Harmonics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Harmonic Model
2.1. Voltage Harmonic Equation
2.2. Torque Harmonic Equation
3. Method for Identifying Harmonic Parameters of Permanent Magnet Flux Linkage
3.1. Current Harmonic Extraction Based on Multiple Synchronous Rotating Reference Frames
3.2. Dead-Time Compensation Method
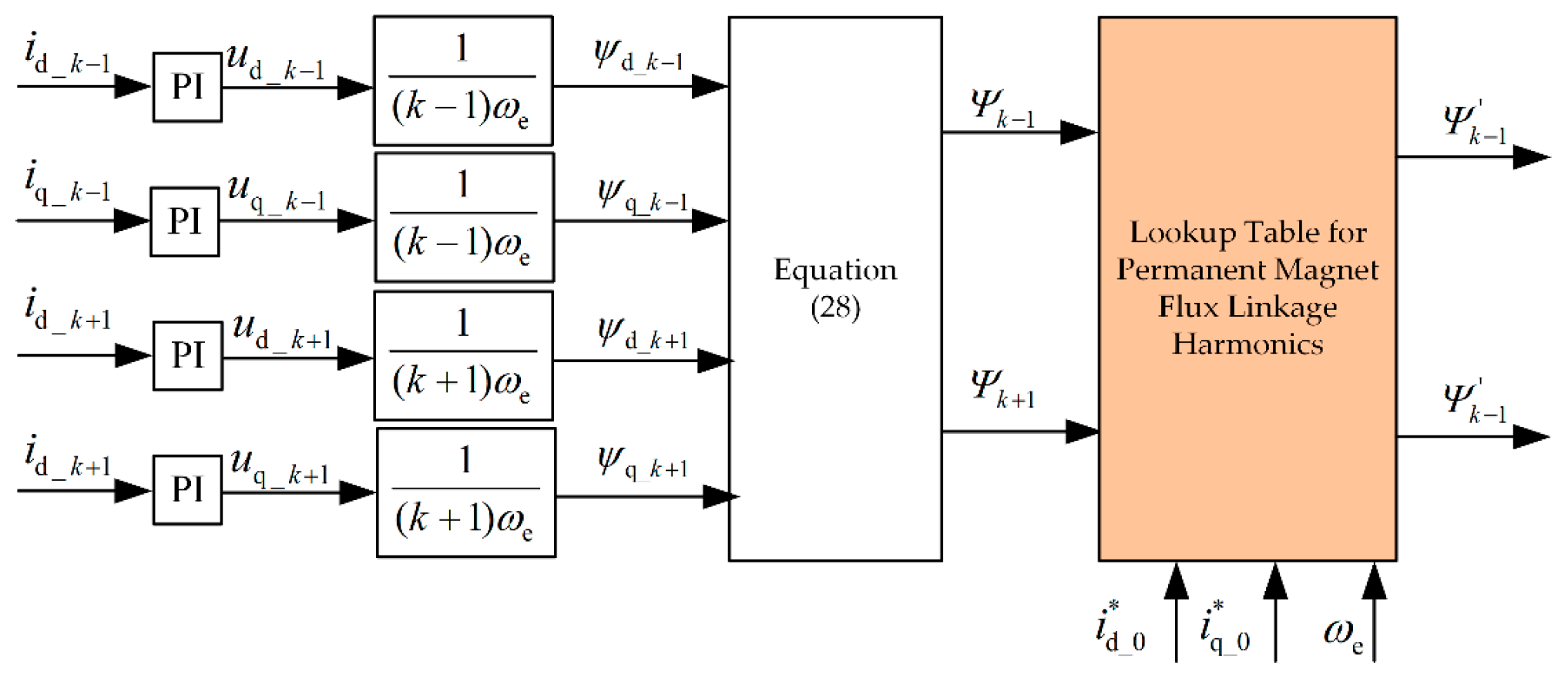
3.3. Online Identification Method for Permanent Magnet Flux Linkage Harmonics
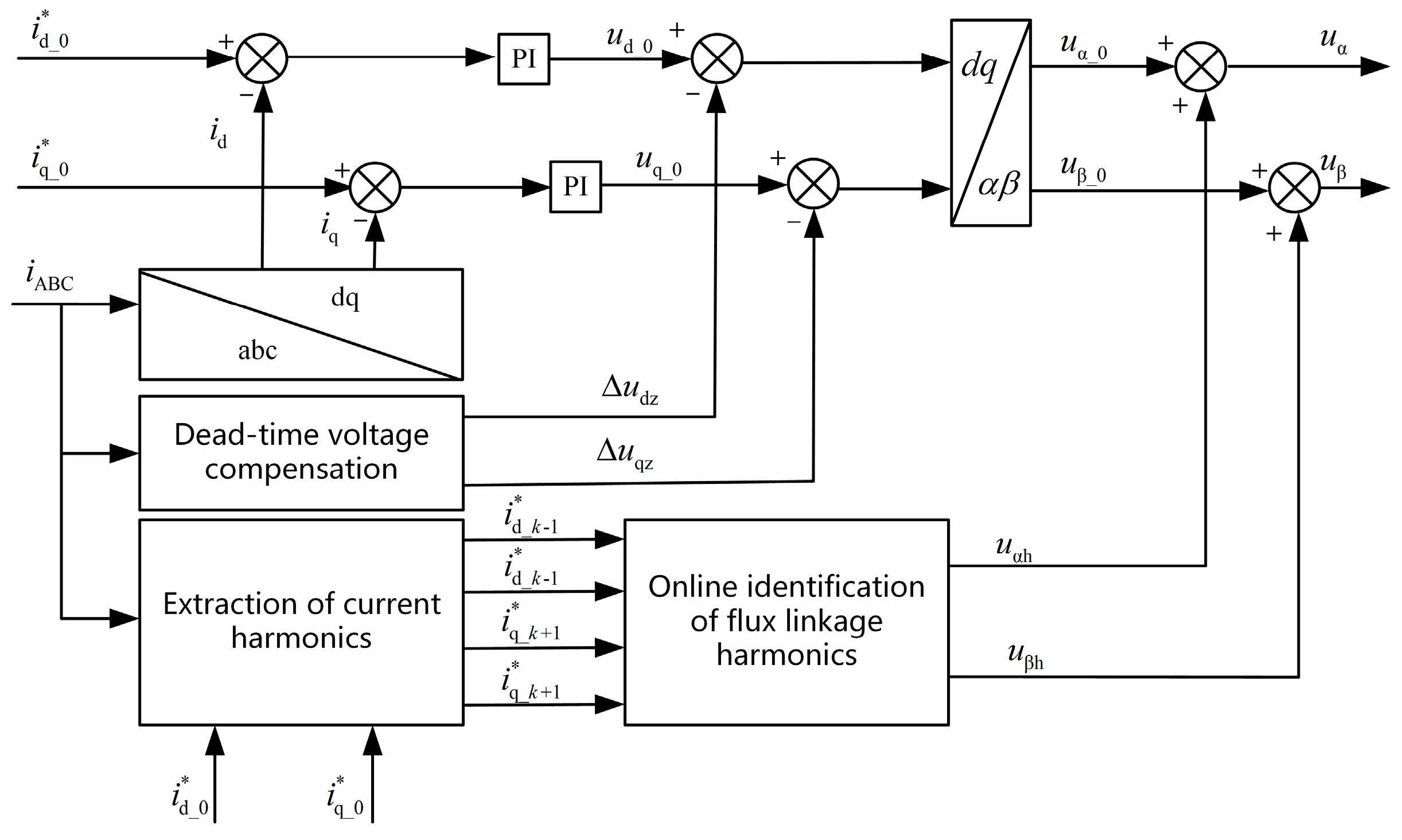
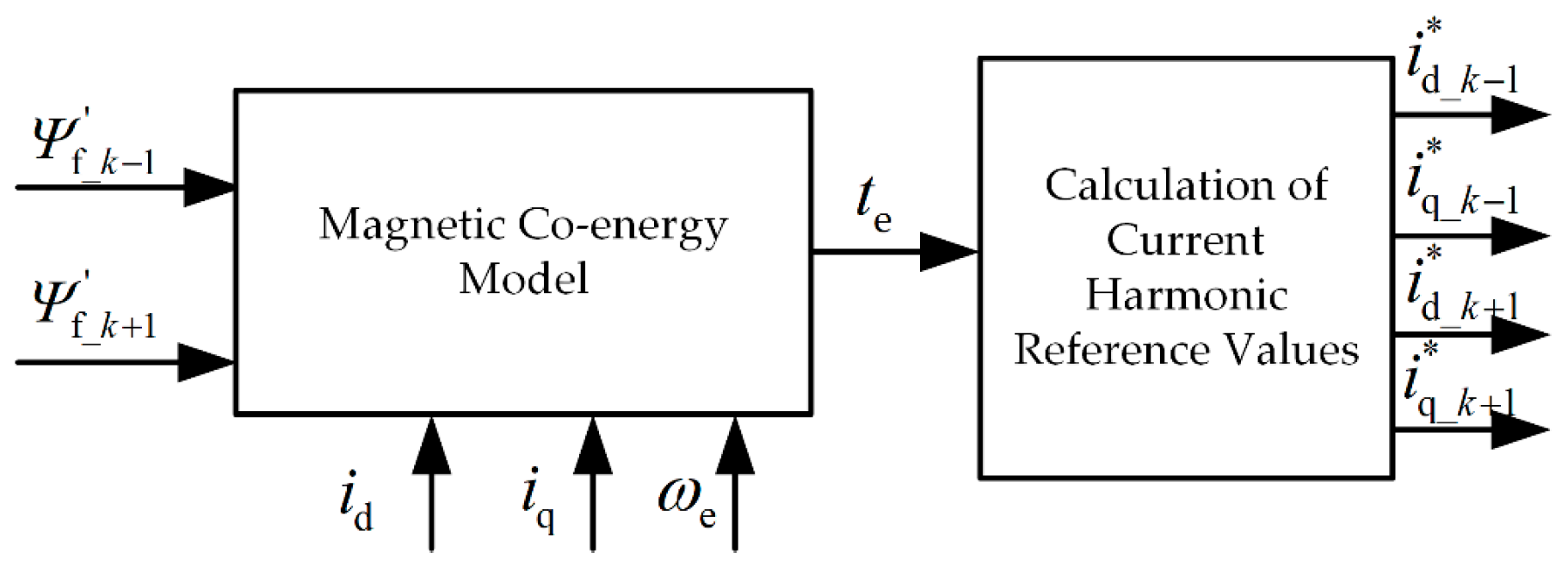
4. Torque Ripple Suppression Strategies
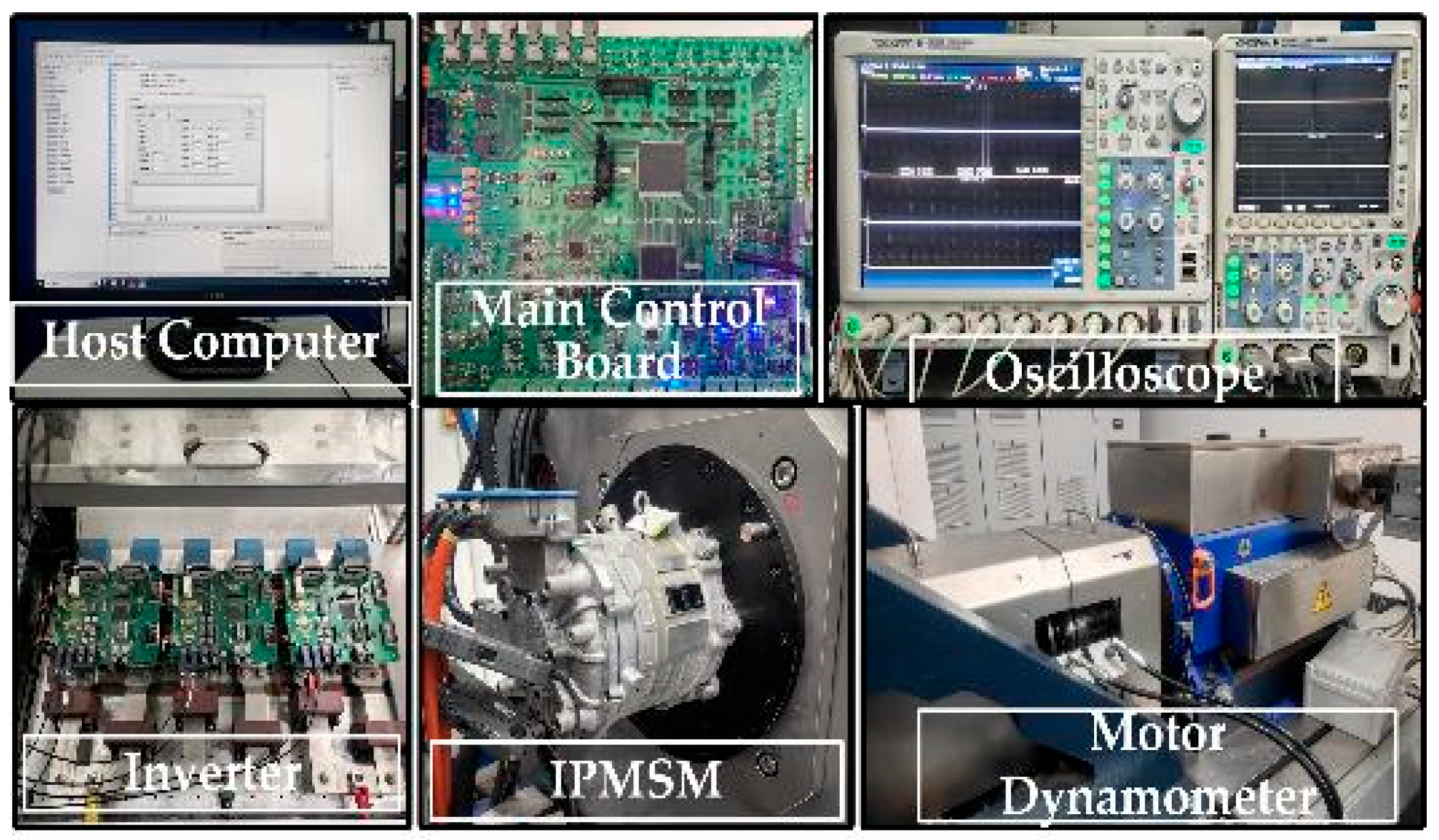
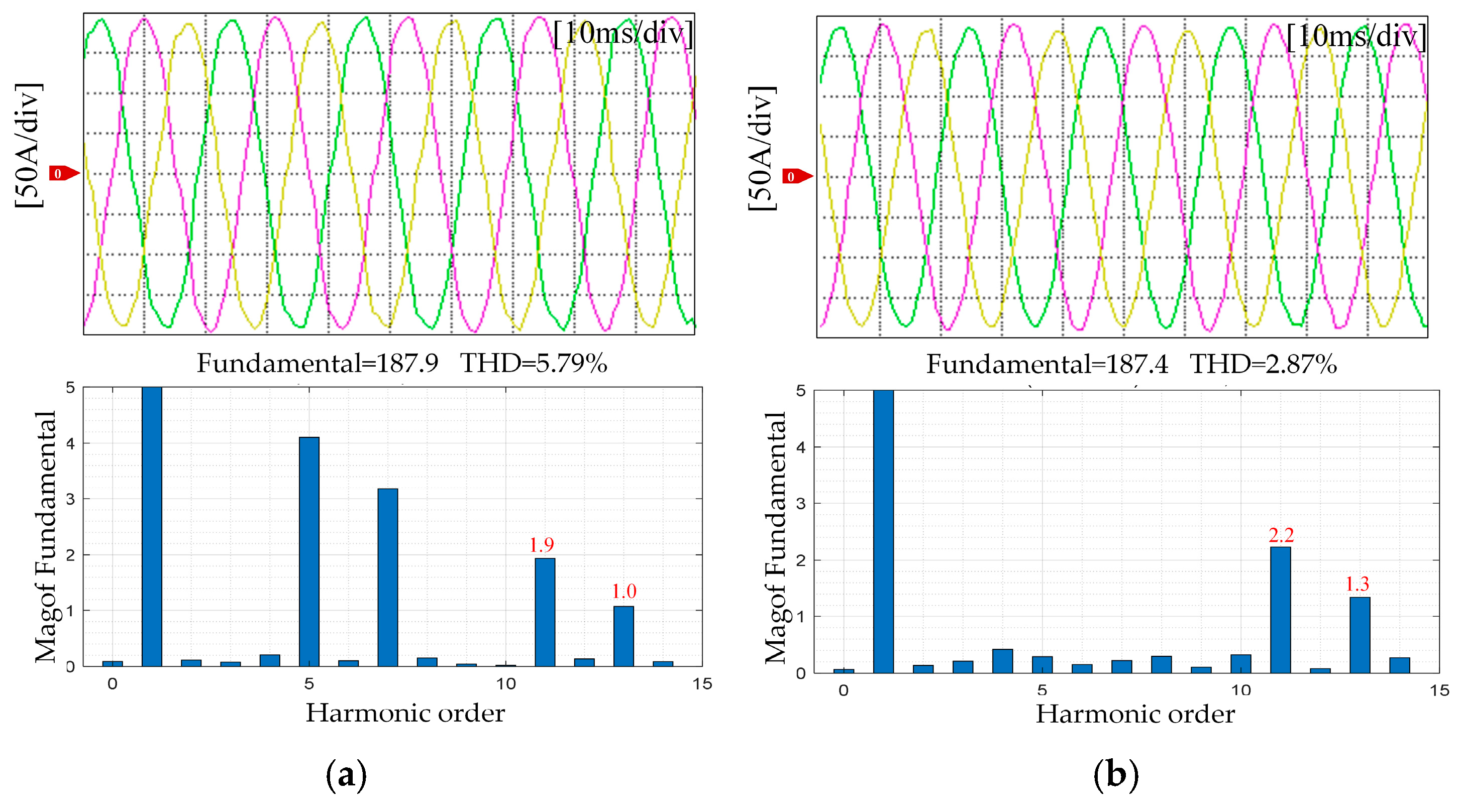
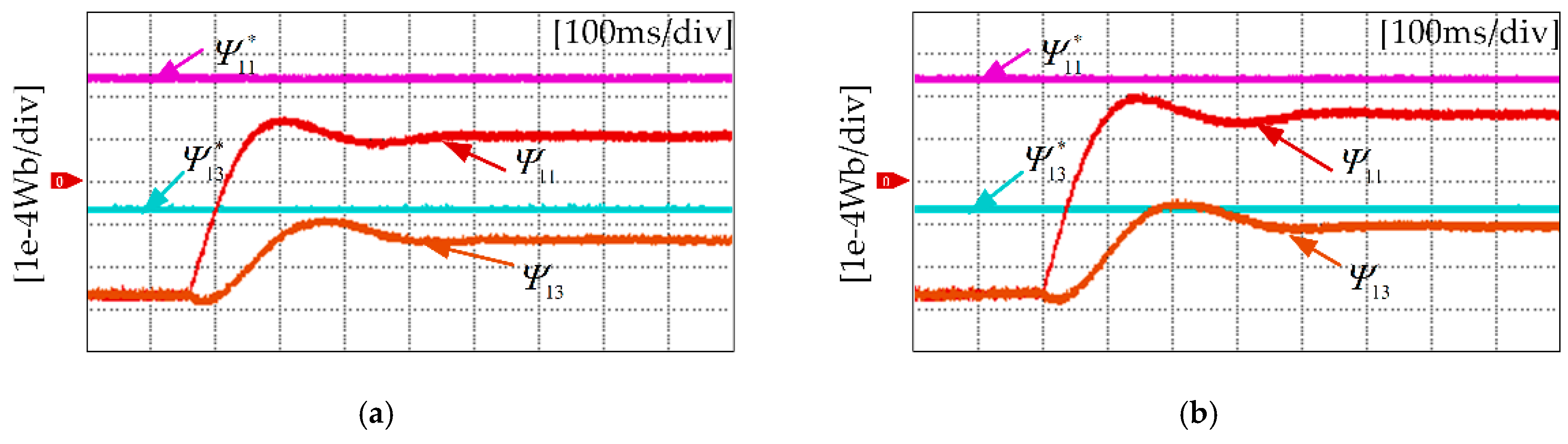
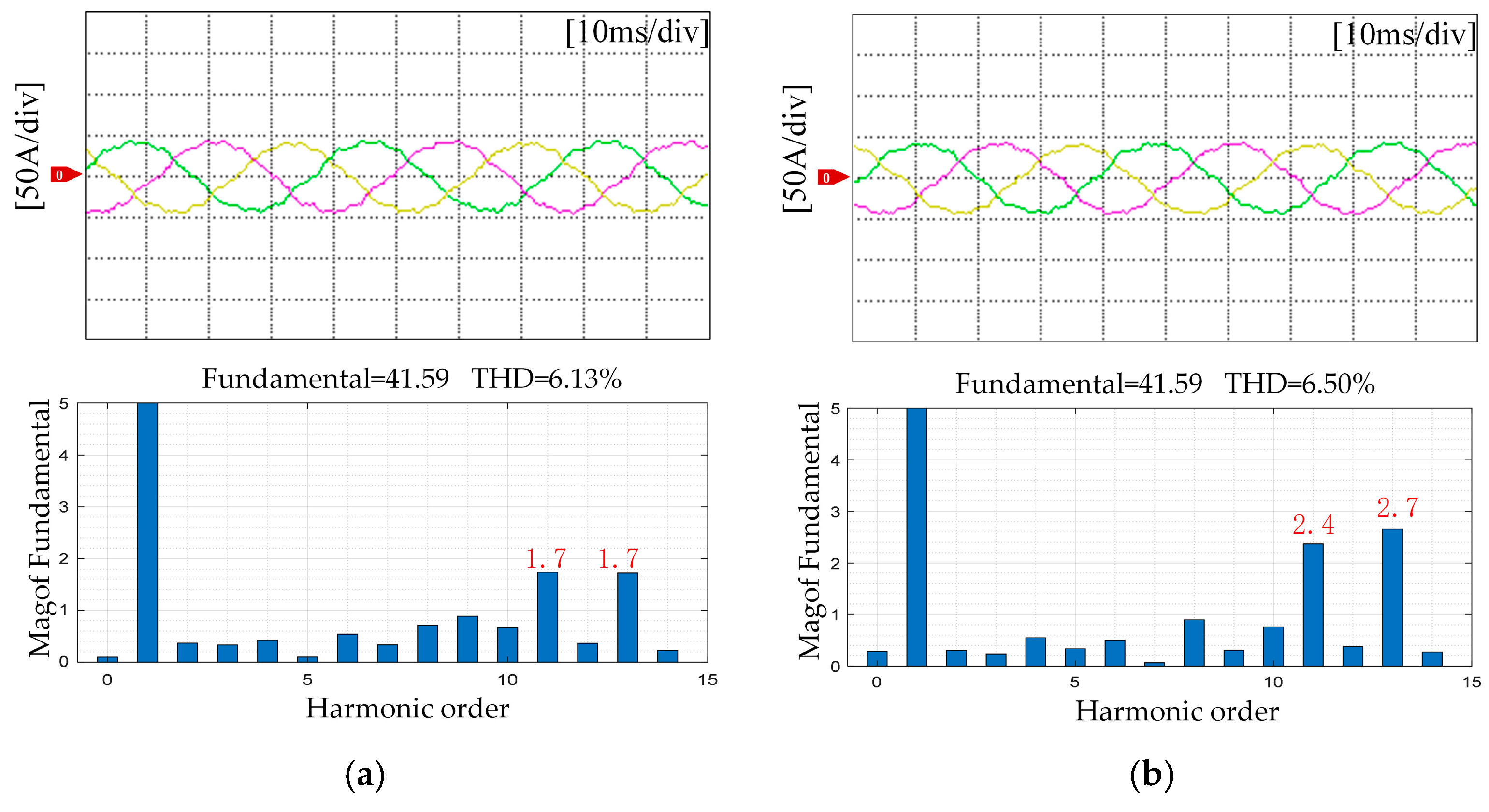
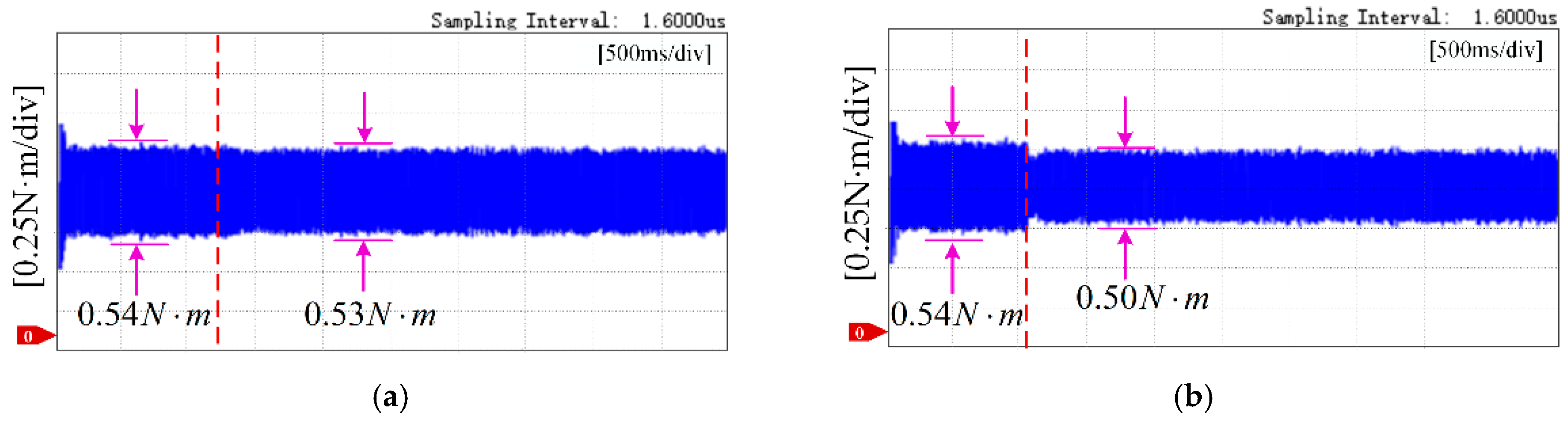
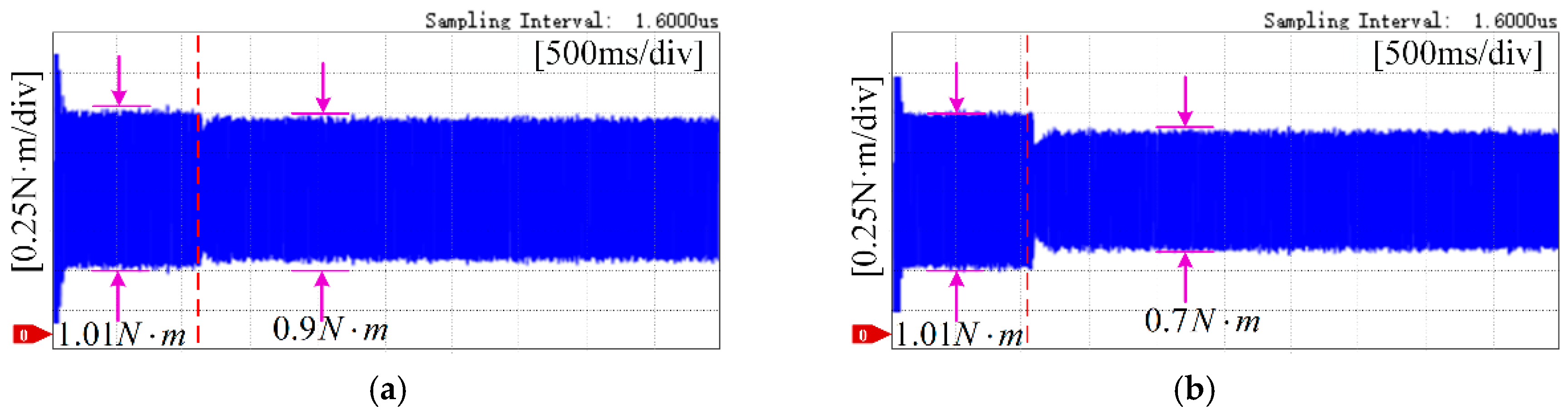
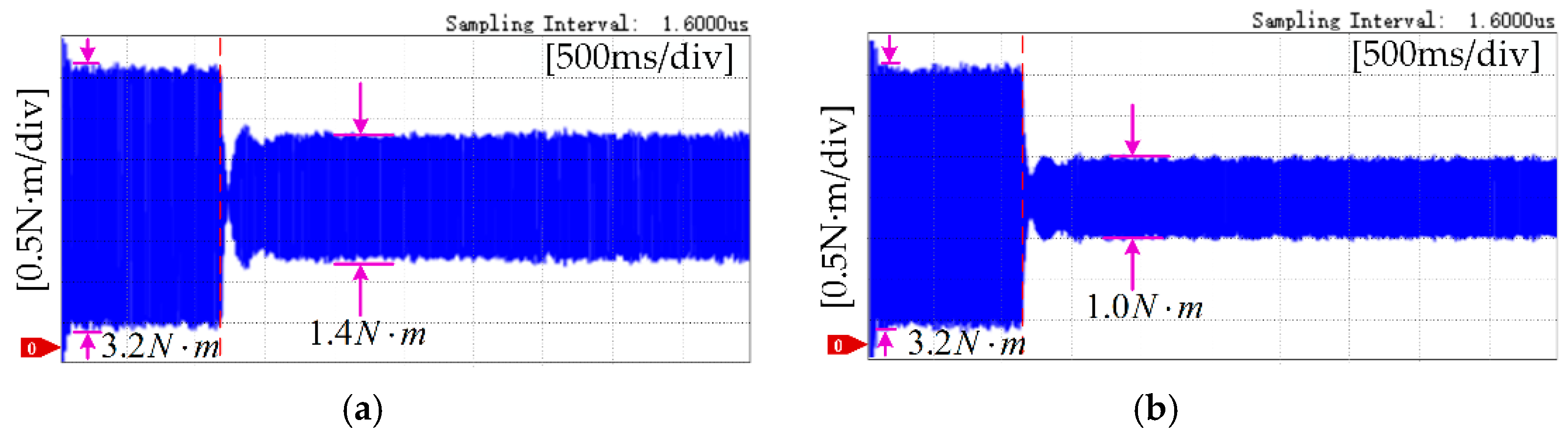
5. Experimental Results
5.1. Flux Linkage Harmonic Identification
5.2. Torque Ripple Suppression
6. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lan, Y.; Benomar, Y.; Deepak, K.; Aksoz, A.; Baghdadi, M.E.; Bostanci, E.; Hegazy, O. Switched Reluctance Motors and Drive Systems for Electric Vehicle Powertrains: State of the Art Analysis and Future Trends. Energies 2021, 14, 2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.; Zhang, R.; Dong, H.; Wan, S. Research on a Torque Ripple Suppression Method of Fuzzy Active Disturbance Rejection Control for a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. Electronics 2024, 13, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Guo, Y.; Xu, Q. PMSM Torque Ripple Suppression Method Based on SMA-Optimized ILC. Sensors 2023, 23, 9317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Su, H.; Li, W.; Yuan, H. A VSFPWM Strategy for High Frequency Torque Ripple Control of PMSM Based on Stator Flux Ripple Prediction. Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2024, 8, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Gao, F.; Zhang, P.; Dong, Y. Motor-Parameter-Free Solution of Optimal Harmonic Currents for Torque Ripple Reduction of PMSM Drives with Response Surface Method. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2024, 12, 2774–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Khalid, M.; Binojkumar, A.C. A Novel Sliding Hysteresis Band Based Direct Torque Control Scheme for PMSM Motors to Achieve Improved Current THD With Reduction in Torque and Flux Ripples Eliminating the Low-Speed Problems. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 67971–67985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuan, H.; Fazeli, S.M.; Wu, Z.; Burke, R. Mitigating the Torque Ripple in Electric Traction Using Proportional Integral Resonant Controller. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 10820–10831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.-H.; Son, Y.-D.; Kim, G.-T.; Hur, J. A Novel Cogging Torque Reduction Method for Interior-Type Permanent-Magnet Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2009, 45, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Liu, Y. Analysis of Air-Gap Field Modulation and Magnetic Gearing Effect in Fractional-Slot Concentrated-Winding Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 3688–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulez, K.; Adam, A.A.; Pastaci, H. Torque Ripple and EMI Noise Minimization in PMSM Using Active Filter Topology and Field-Oriented Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.; Feng, G.; Iyer, K.L.V.; Mukherjee, K.; Kar, N.C. Genetic Algorithm-Based Current Optimization for Torque Ripple Reduction of Interior PMSMs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 4493–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafaq, M.S.; Midgley, W.; Steffen, T. A Review of the State of the Art of Torque Ripple Minimization Techniques for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2024, 20, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieller, D.; Nguyen, N.K.; Wira, P.; Sturtzer, G.; Abdeslam, D.O.; Merckle, J. A Self-Learning Solution for Torque Ripple Reduction for Nonsinusoidal Permanent-Magnet Motor Drives Based on Artificial Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Z. Sliding-Mode Observer-Based Mechanical Parameter Estimation for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 5732–5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Panda, S.K.; Xu, J.-X. Torque Ripple Minimization in PM Synchronous Motors Using Iterative Learning Control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2004, 19, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Lai, C.; Kar, N.C. An Analytical Solution to Optimal Stator Current Design for PMSM Torque Ripple Minimization with Minimal Machine Losses. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 7655–7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-H.; Wei, H.-L.; Li, X.-H.; Liu, K.; Zhong, Q.-C. Global Identification of Electrical and Mechanical Parameters in PMSM Drive Based on Dynamic Self-Learning PSO. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 10858–10871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Morimoto, S.; Sanada, M. Performance Improvement of Sensorless IPMSM Drives in a Low-Speed Region Using Online Parameter Identification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhu, Z.Q. Mechanical Parameter Estimation of Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machines with Aiding from Estimation of Rotor PM Flux Linkage. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 3115–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedetti, N.; Calligaro, S.; Petrella, R. Stand-Still Self-Identification of Flux Characteristics for Synchronous Reluctance Machines Using Novel Saturation Approximating Function and Multiple Linear Regression. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 3083–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Han, Y.; Lee, K.; Bhattacharya, S. A Sinusoidal Current Control Strategy Based on Harmonic Voltage Injection for Harmonic Loss Reduction of PMSMs With Non-Sinusoidal Back-EMF. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 7032–7043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Shi, T.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Z.; Gu, X. Analysis and Control of Current Harmonic in IPMSM Field-Oriented Control System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 9571–9585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

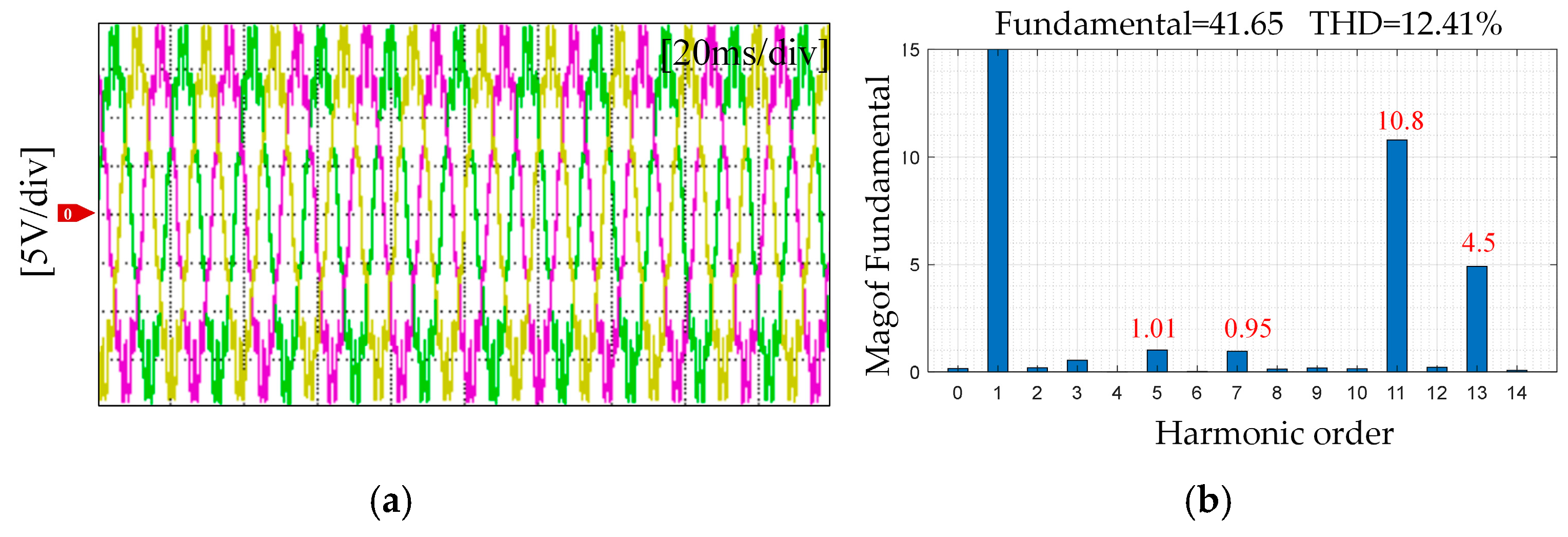
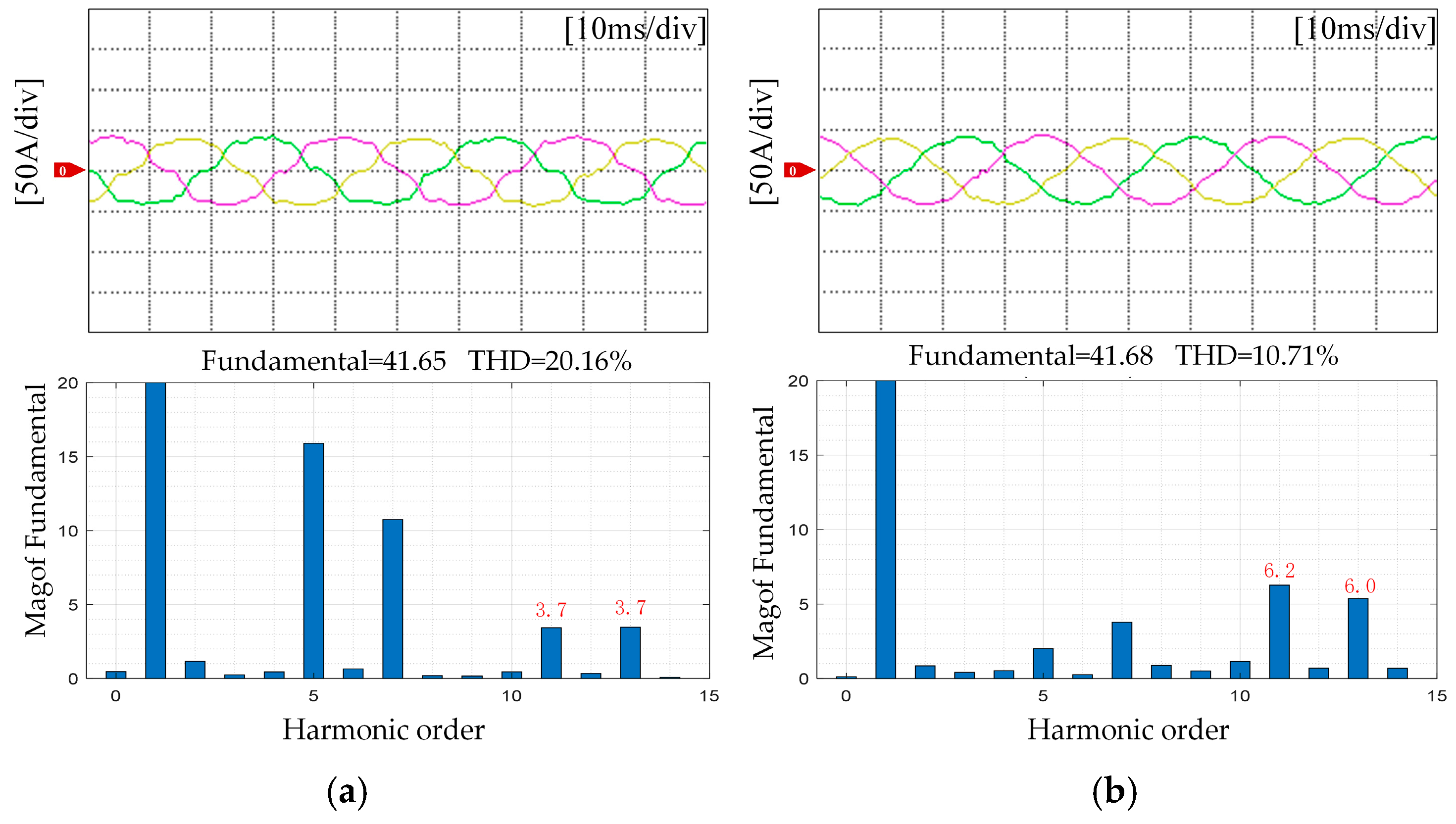
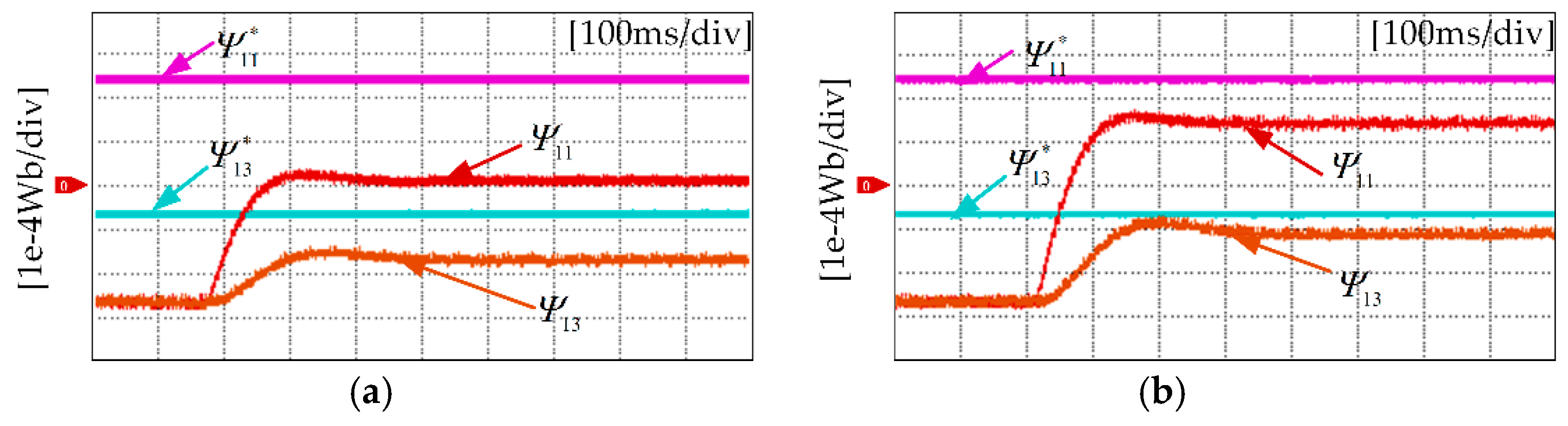
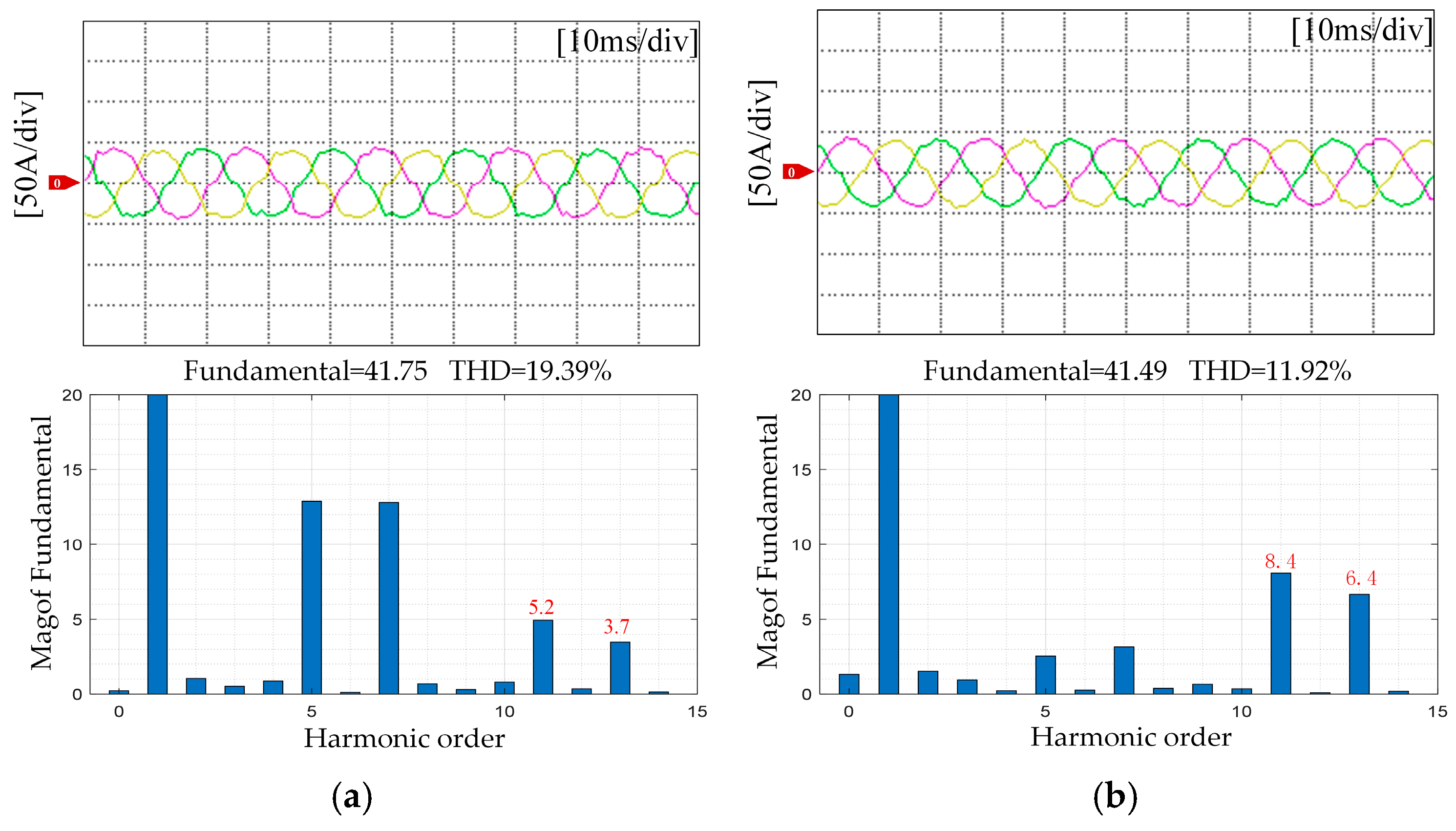




| Motor Parameter | Symbol | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rated voltage | UN | V | 346 |
| Rated current | iN | A | 180 |
| Number of pole pairs | p | -- | 4 |
| Stator resistance | R | Ω | 0.03 |
| d-axis inductance | Ld | H | 0.1049 |
| q-axis inductance | Lq | H | 0.3453 |
| Flux linkage | Ψ0 | Wb | 0.038749 |
| Ψ5* (Wb) | Ψ7* (Wb) | Ψ11* (Wb) | Ψ13* (Wb) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9.54 × 10−5 | 5.1054 × 10−5 | 3.8454 × 10−4 | 1.5254 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Jin, X.; Zhang, G.; Lin, Z. Torque Ripple Suppression Strategy Based on Online Identification of Flux Linkage Harmonics. Electronics 2025, 14, 2174. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14112174
Gu X, Zhang B, Wang Z, Jin X, Zhang G, Lin Z. Torque Ripple Suppression Strategy Based on Online Identification of Flux Linkage Harmonics. Electronics. 2025; 14(11):2174. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14112174
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Xin, Bingzhi Zhang, Zhiqiang Wang, Xuefeng Jin, Guozheng Zhang, and Zhichen Lin. 2025. "Torque Ripple Suppression Strategy Based on Online Identification of Flux Linkage Harmonics" Electronics 14, no. 11: 2174. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14112174
APA StyleGu, X., Zhang, B., Wang, Z., Jin, X., Zhang, G., & Lin, Z. (2025). Torque Ripple Suppression Strategy Based on Online Identification of Flux Linkage Harmonics. Electronics, 14(11), 2174. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14112174






