Characteristics Improvement of Brushless Doubly-Fed Wind Turbine Generator with Minimized Asymmetric Phenomena
Abstract
1. Introduction
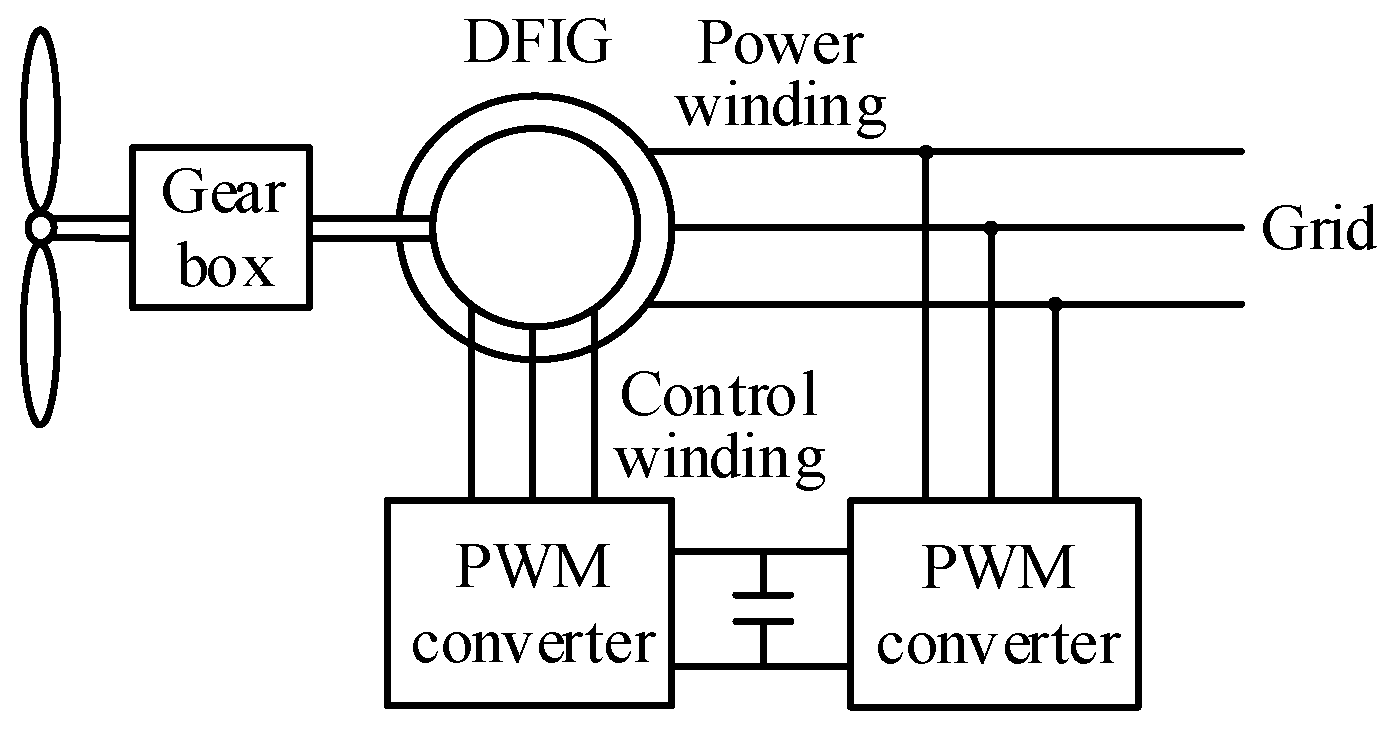
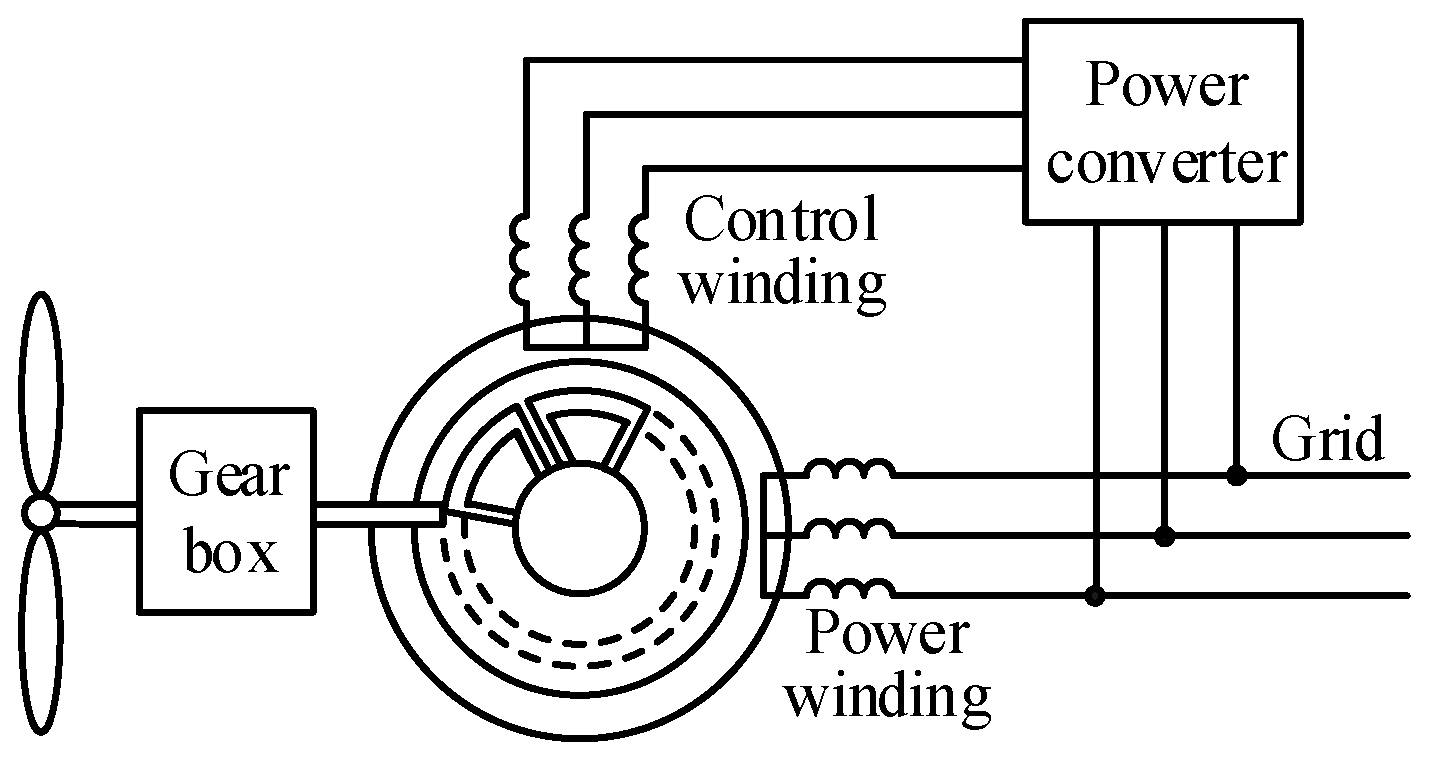
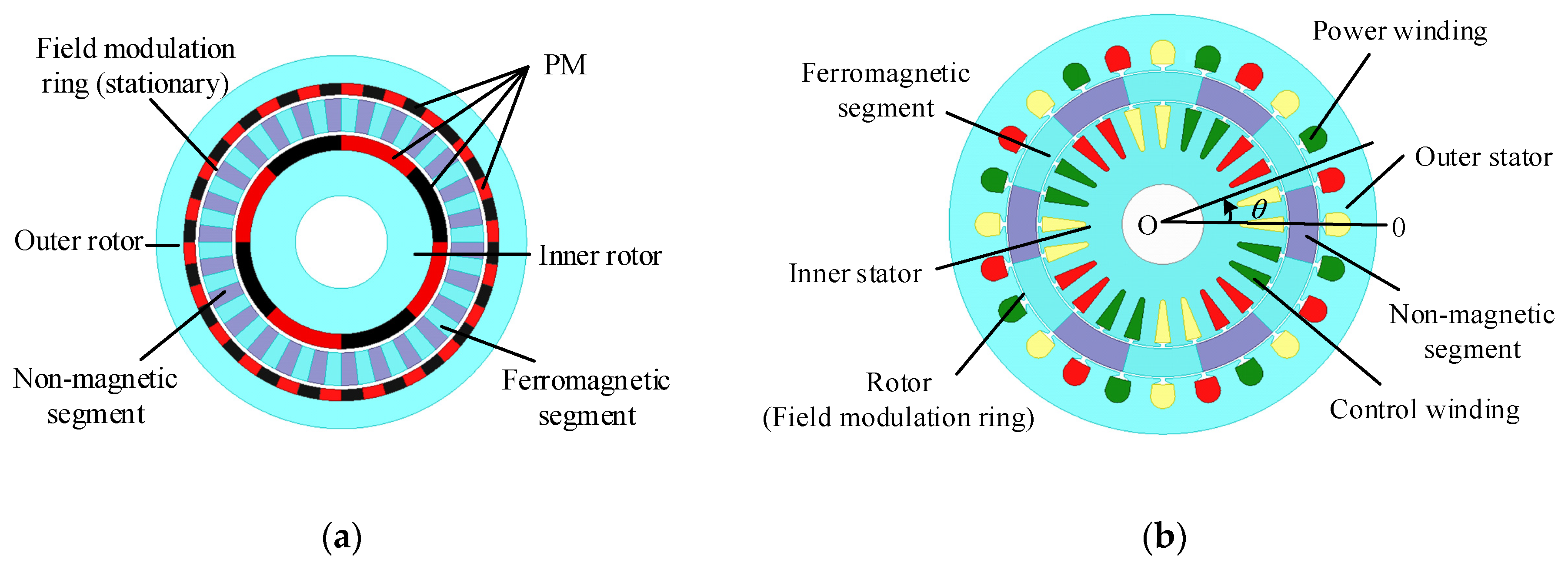
2. Topology and Operation Principle of Brushless Doubly-Fed Generator with Dual Stators
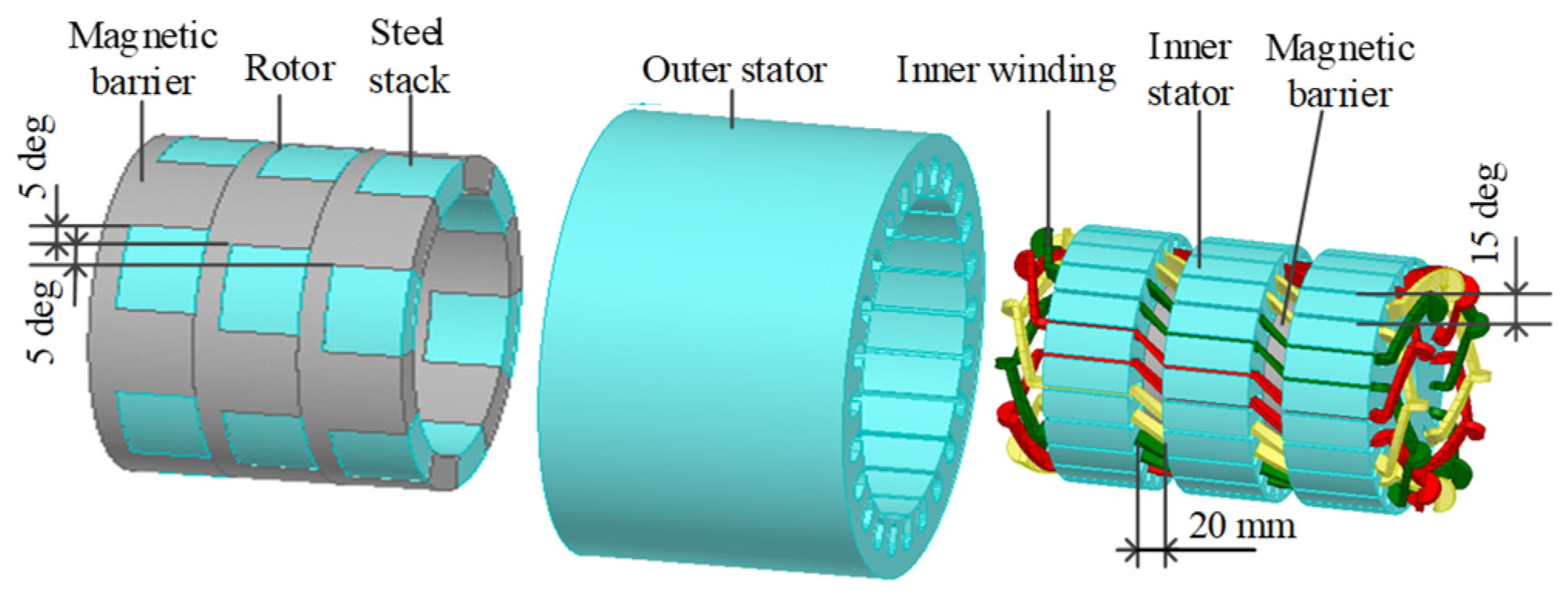
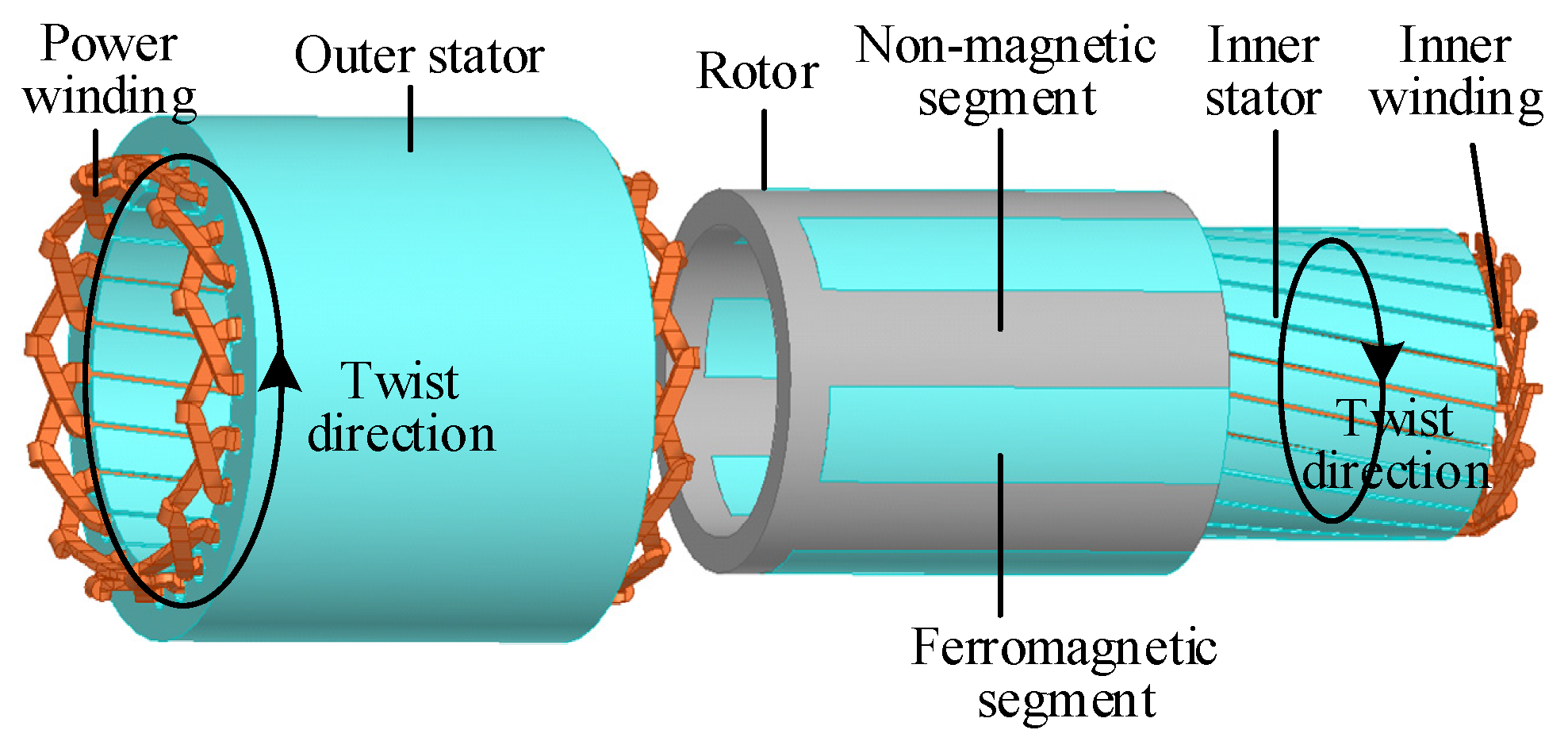
2.1. Topology of Brushless Doubly-Fed Generator with Dual Stators
2.2. Combination of Pole Pairs
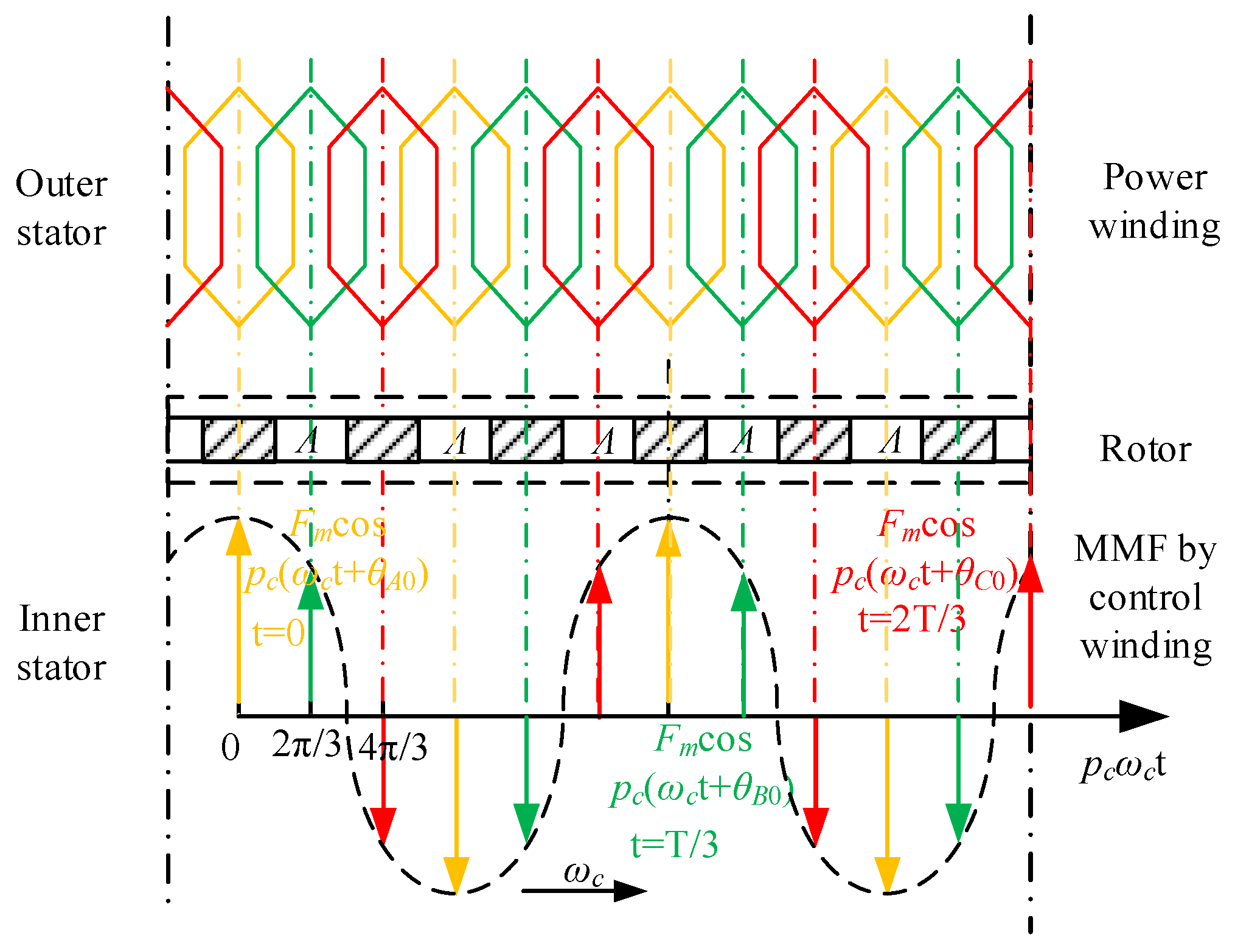
2.3. Operation Principle
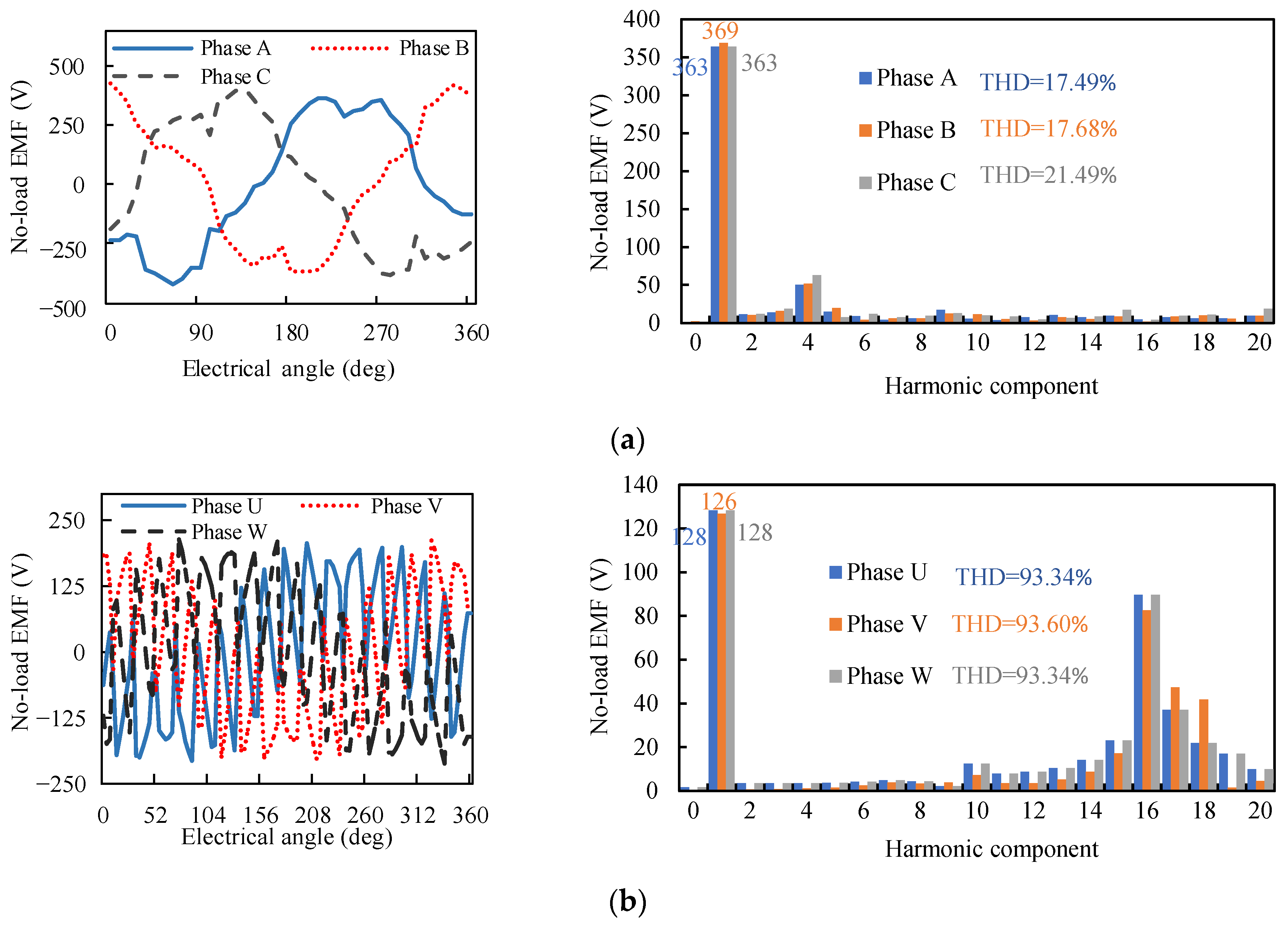
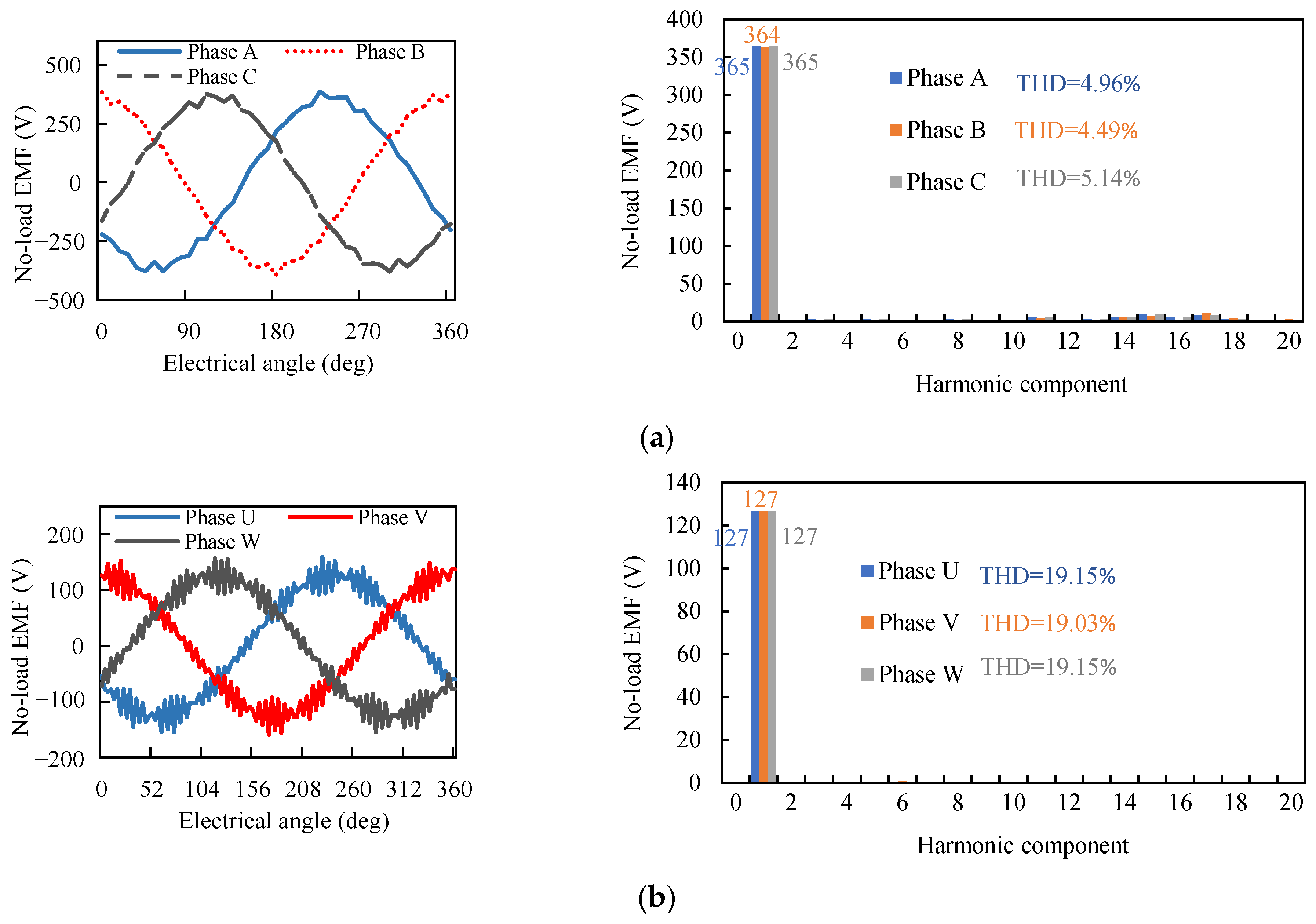
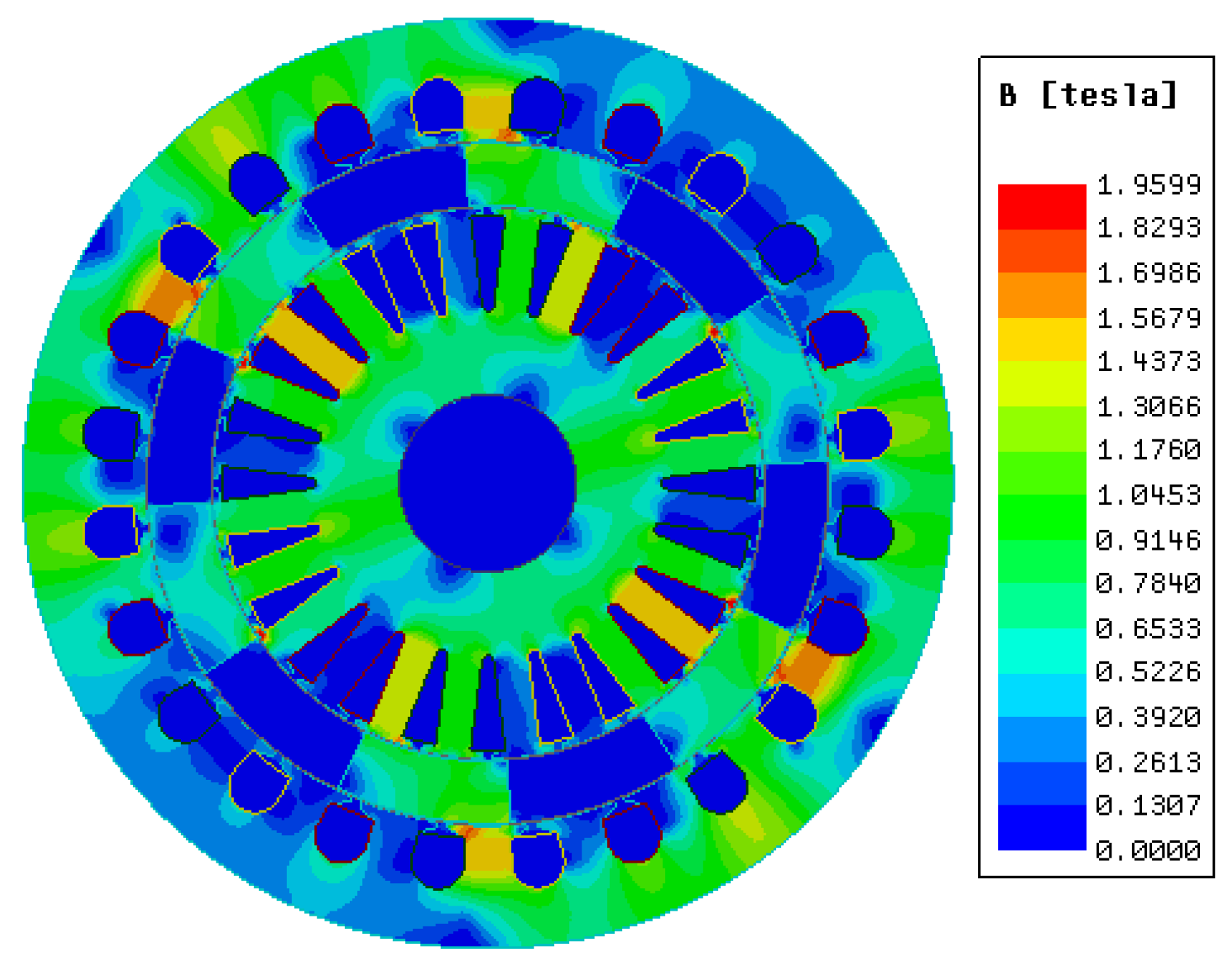
3. Asymmetric Phenomena
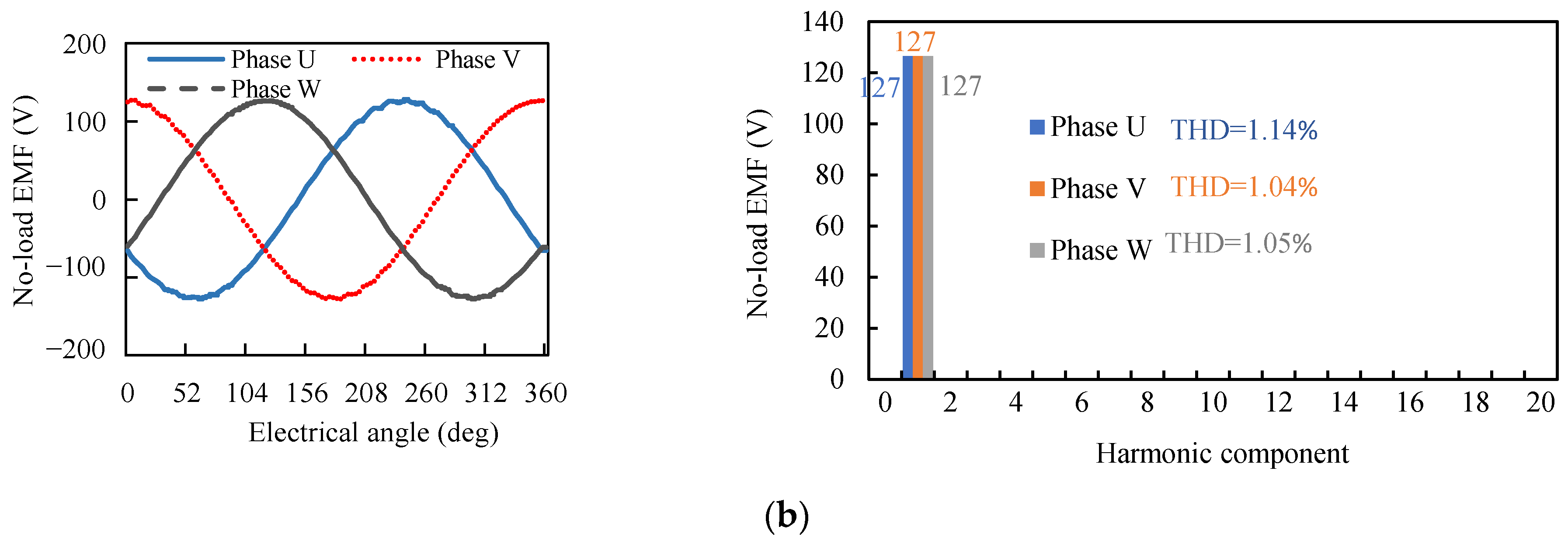
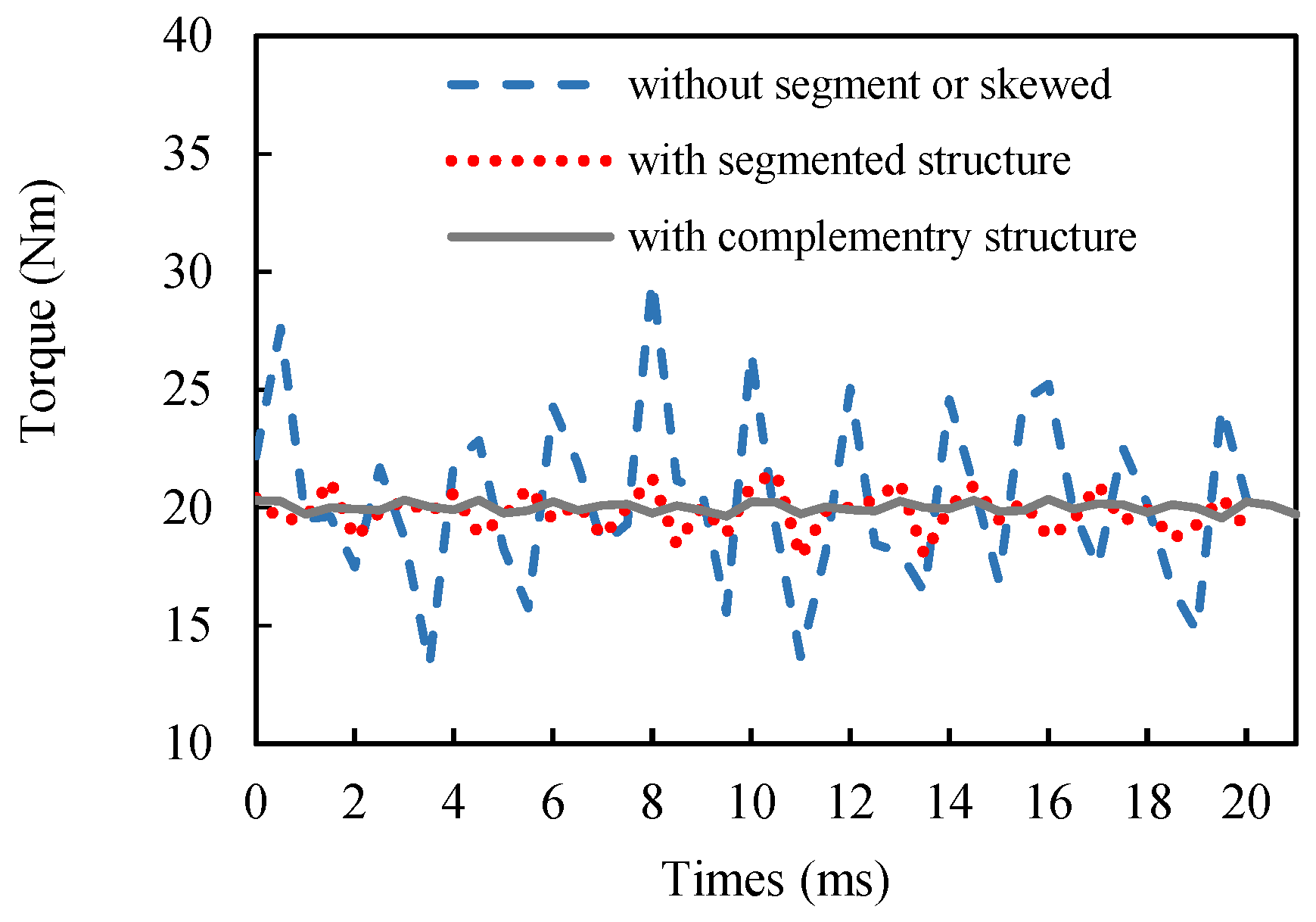
4. Improvements
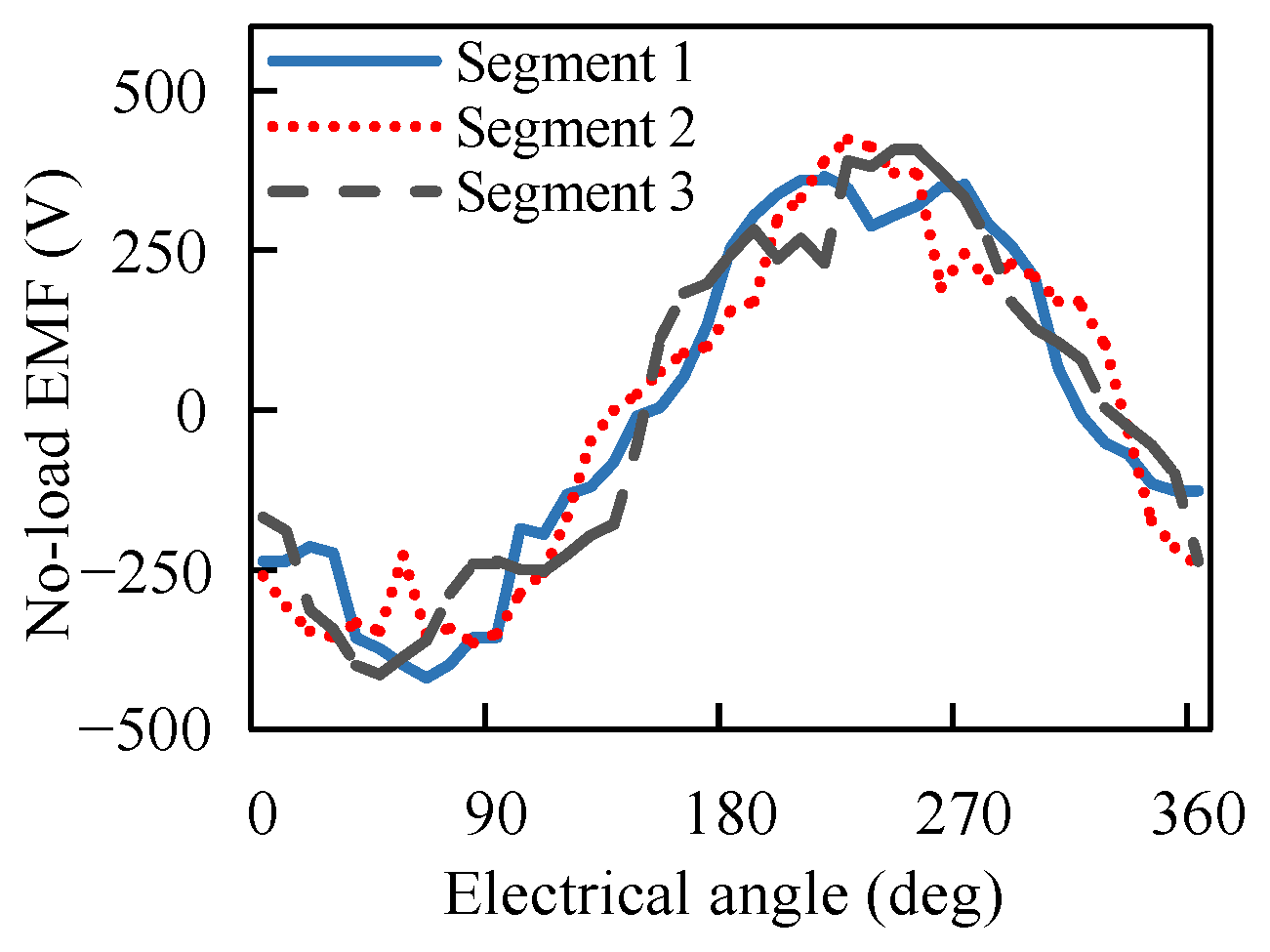
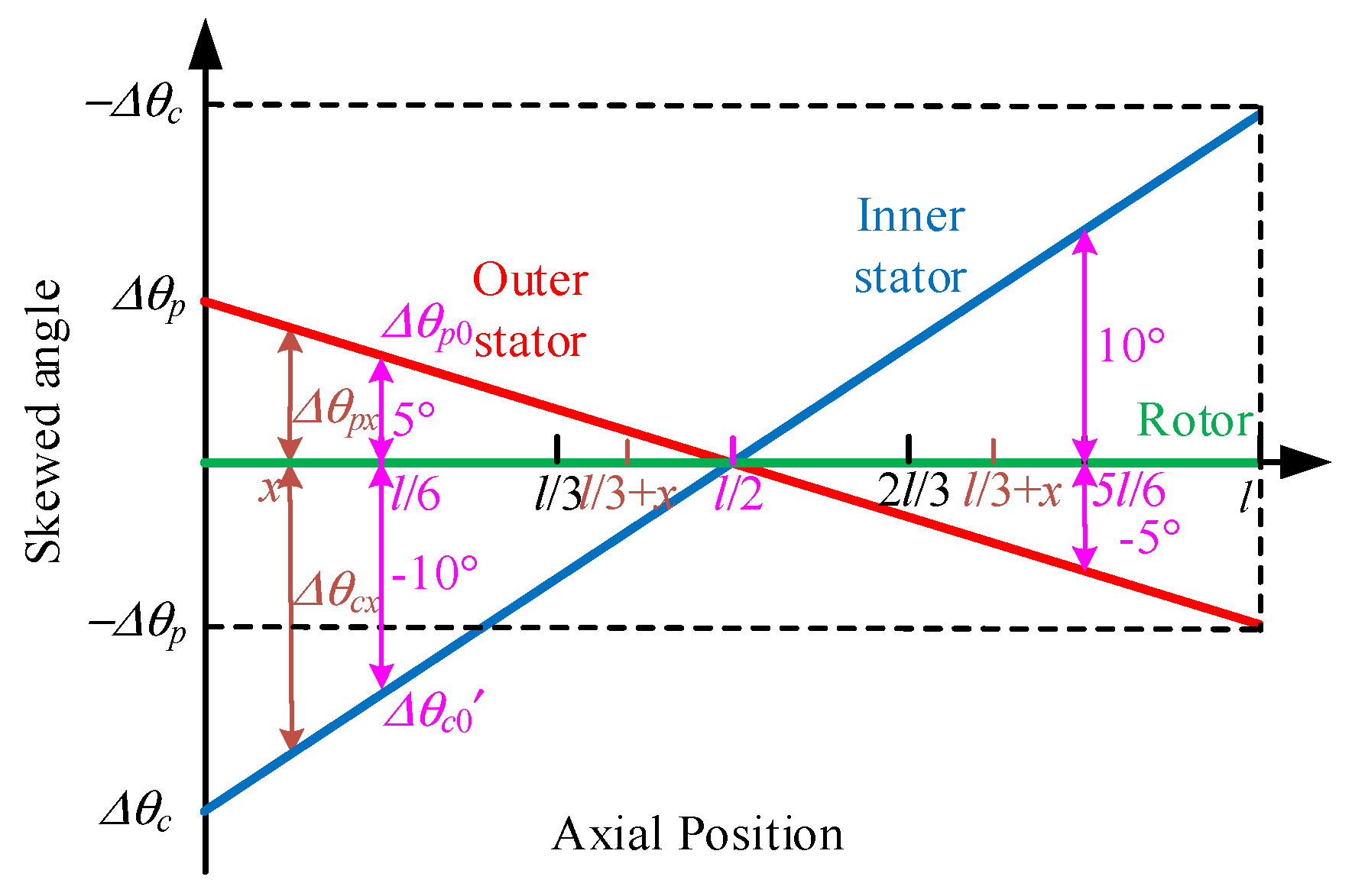
4.1. Axial Segmented Skewed Pole Structure
4.2. Complementary Skewed Stators
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, Y.; Zhu, D.; Hu, J.; Liu, R.; Zou, X.; Kang, Y. Optimized design of demagnetization control for dfig-based wind turbines to enhance transient stability during weak grid faults. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 40, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, X. An improved strategy of grid-forming dfig based on disturbance rejection stator flux control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 2498–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, L.; Su, M.; Zhou, F.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P. Fault current multi-stages calculation method for dfig-based wind farms with whole fault process attributes under asymmetrical grid fault conditions. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energ. 2024, 15, 2361–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, M.A.A.; Chakkarapani, M.; Nagamani, C.; Ilango, G.S. An Improved Angular Stator Flux Frequency Computation Method for Robust MPPT Operation of DFIG Under Unbalanced Grid Voltage. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 1162–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.H.; Jin, J.X. Unified power quality conditioner with advanced dual control for performance improvement of dfig-based wind farm. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energ. 2021, 12, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, C. Investigation of cascaded and modulated rotors for dual-stator brushless doubly-fed machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Conver. 2024, 39, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Liu, H.; Hu, S.; Sun, G.; Wang, E.; Tang, J. A proportional-integral-resonant current control strategy for a wind-driven brushless doubly fed generator during network unbalance. Electronics 2024, 13, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Pan, W.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y. Design of a brushless doubly fed generator with simplified three-phase wound rotor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 4427–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Shao, Y.; Shuai, Z.; Cheng, M. Performance analysis of a brushless doubly fed machine with asymmetrical composite flux barrier/magductance rotor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 6699–6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ma, J.; Yu, N.; Wang, S.; Lu, H. Research on control-winding-current orientation control for grid-connected brushless doubly fed induction generation system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 5919–5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Cheng, M. Backstepping-based direct power control for dual-cage rotor brushless doubly fed induction generator. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 2668–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Jin, S.; Zhang, H.; Nian, H. Design and performance analysis of dual-stator brushless doubly-fed machine with cage-barrier rotor. IEEE Trans. Energy Conver. 2019, 34, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Cheng, M.; Wei, X.; Xu, L. Dynamic modeling and performance analysis with iron saturation for dual-stator brushless doubly fed induction generator. IEEE Trans. Energy Conver. 2020, 35, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Cheng, M.; Wei, X.; Jiang, Y. Steady-state characteristics of the dual-stator brushless doubly-fed induction generator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, T. A segmented brushless doubly fed generator for wind power applications. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Q. Overview of novel magnetically geared machines with partitioned stators. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2018, 12, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, M.C.; Johnson, M.; Toliyat, H.A. Analysis of high gear ratio capabilities for single-stage, series multistage, and compound differential coaxial magnetic gears. IEEE Trans. Energy Conver. 2019, 34, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Im, S.Y.; Ryu, J.Y.; Lim, M.S. Optimum design process of coaxial magnetic gear using 3d performance prediction method considering axial flux leakage. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 3075–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praslicka, B.; Gardner, M.C.; Johnson, M.; Toliyat, H.A. Review and analysis of coaxial magnetic gear pole pair count selection effects. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Topics Power Electron. 2022, 10, 1813–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Tang, W.; Wang, T.; Ben, T.; Qu, R. Performance analysis of magnetically geared permanent magnet brushless motor for hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrific. 2022, 8, 2874–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Liu, J.; Zheng, P.; Tong, C. Design and analysis of a magnetic-field modulated brushless double-rotor machine—Part i: Pole pair combination of stator, pm rotor and magnetic blocks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 2540–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bai, J.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, P. Investigation of an integrated magnetic-field-modulated brushless double-rotor machine with an improved pm rotor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2021, 57, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, J.; Qian, F. Design and optimization of axial field flux-switching magnetic gear composite motor based on varying-network magnetic circuit. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 53749–53759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumashiro, A.; Chen, L.; Fujii, Y.; Chiba, A.; Gruber, W.; Amrhein, W.; Jungmayr, G. Novel reluctance-type magnetic-geared motor integrated with high-speed bearingless motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 3808–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathekga, M.E.; Ademi, S.; McMahon, R.A. Brushless doubly fed machine magnetic field distribution characteristics and their impact on the analysis and design. IEEE Trans. Energy Conver. 2019, 34, 2180–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Han, P.; Hua, W. General airgap field modulation theory for electrical machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 6063–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; EL-Refaie, A.M.; Zuo, Y.; Cai, S.; Tang, J.; Liu, Y. A permanent magnet brushless doubly fed electric machine for variable–speed constant–frequency wind turbines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 6663–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Wen, H.; Han, P.; Zhu, X. Analysis of airgap field modulation principle of simple salient poles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 2628–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, X.; Xu, S. A brushless doubly fed generator based on permanent magnet field modulation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 3505–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Outer diameter of outer stator | 210 mm |
| Inner diameter of outer stator | 154.4 mm |
| Outer air gap length | 0.5 mm |
| Thickness of rotor | 14 mm |
| Inner airgap length | 0.5 mm |
| Inner diameter of inner stator | 41 mm |
| Stack length | 150 mm |
| Polar arc coefficient of rotor (α) | 0.5 |
| Number of outer stator slot | 24 |
| Number of inner stator slot | 24 |
| Turns per slot of power winding | 120 |
| Turns per slot of control winding | 80 |
| Pole pairs of power winding (pp) | 4 |
| Pole pairs of control winding (pc) | 2 |
| Pole pairs of rotor (pr) | 6 |
| Iron material | DW360-50 |
| Rated speed (n0) | 500 rpm |
| Rated power of power winding | 1 kW |
| Rated power of control winding | 300 W |
| Situation | Pole Pair Numbers | Segmented Skewed Pole Angles |
|---|---|---|
| Situation 1 | ||
| Situation 2 | ||
| Situation 3 | The others |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Z. Characteristics Improvement of Brushless Doubly-Fed Wind Turbine Generator with Minimized Asymmetric Phenomena. Electronics 2025, 14, 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14081649
Jiang Y, Wang K, Zhou L, Zhang W, Hu Z. Characteristics Improvement of Brushless Doubly-Fed Wind Turbine Generator with Minimized Asymmetric Phenomena. Electronics. 2025; 14(8):1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14081649
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Yongjiang, Kejie Wang, Lingkang Zhou, Wenfeng Zhang, and Zhen Hu. 2025. "Characteristics Improvement of Brushless Doubly-Fed Wind Turbine Generator with Minimized Asymmetric Phenomena" Electronics 14, no. 8: 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14081649
APA StyleJiang, Y., Wang, K., Zhou, L., Zhang, W., & Hu, Z. (2025). Characteristics Improvement of Brushless Doubly-Fed Wind Turbine Generator with Minimized Asymmetric Phenomena. Electronics, 14(8), 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14081649







