A 57–64 GHz Receiver Front End in 40 nm CMOS
Abstract
1. Introduction
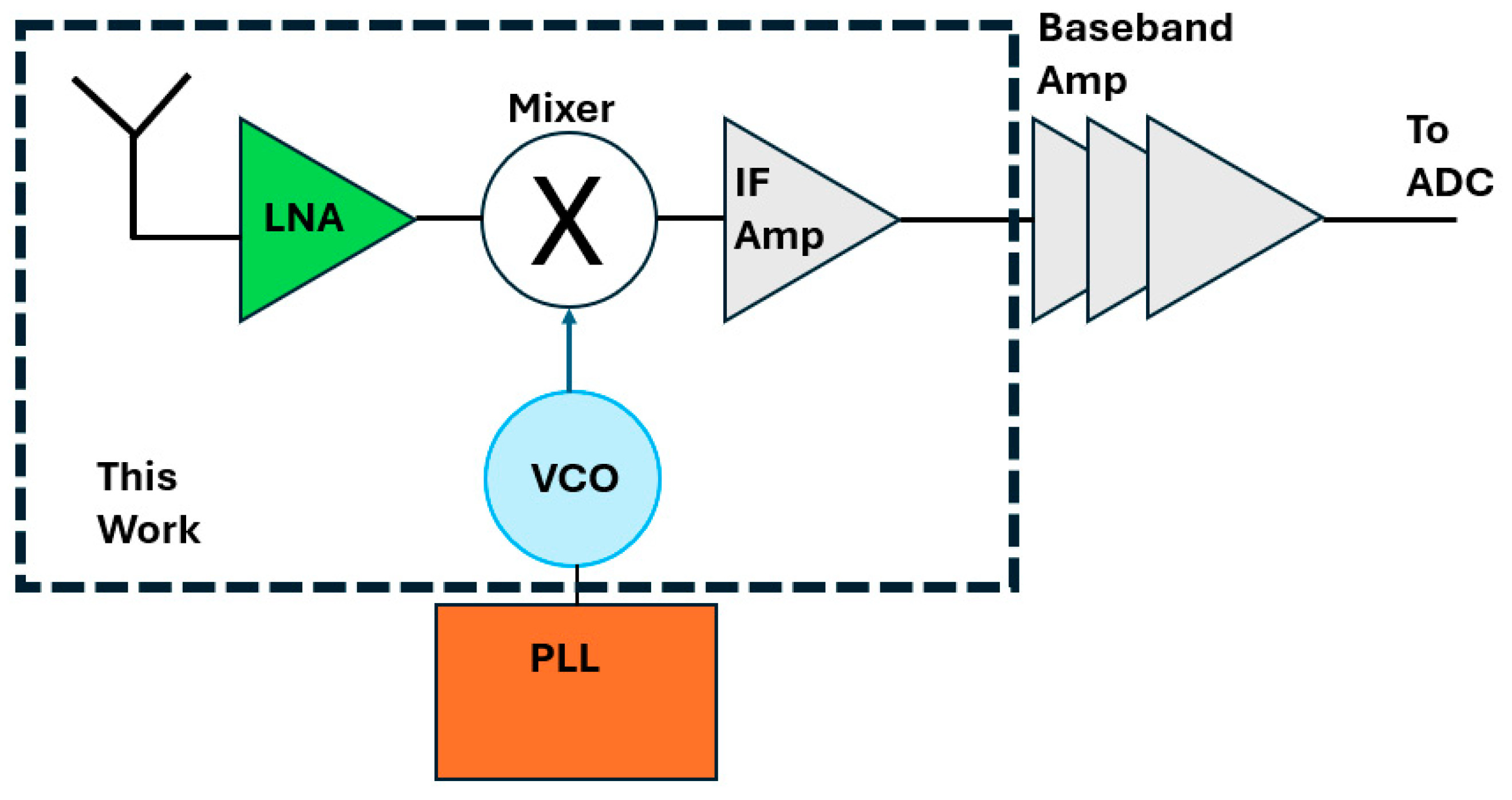
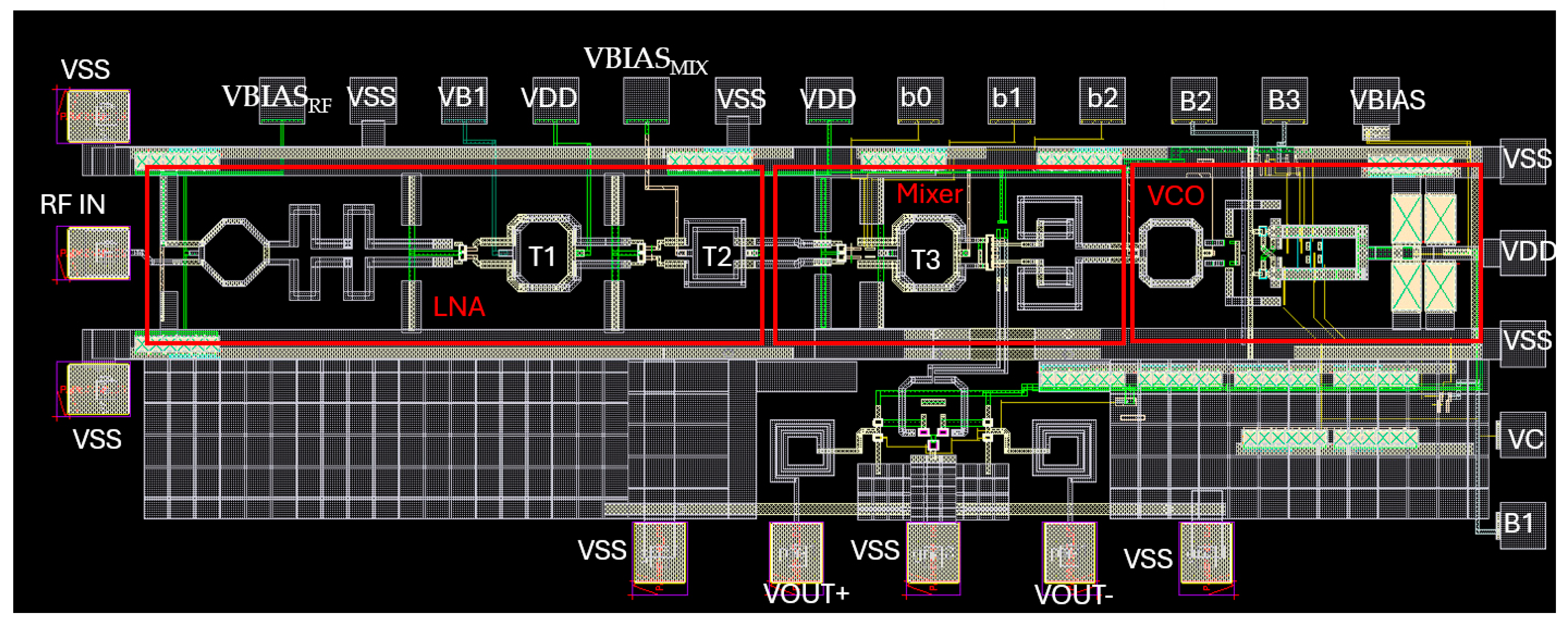
2. 60 GHz Receiver Components
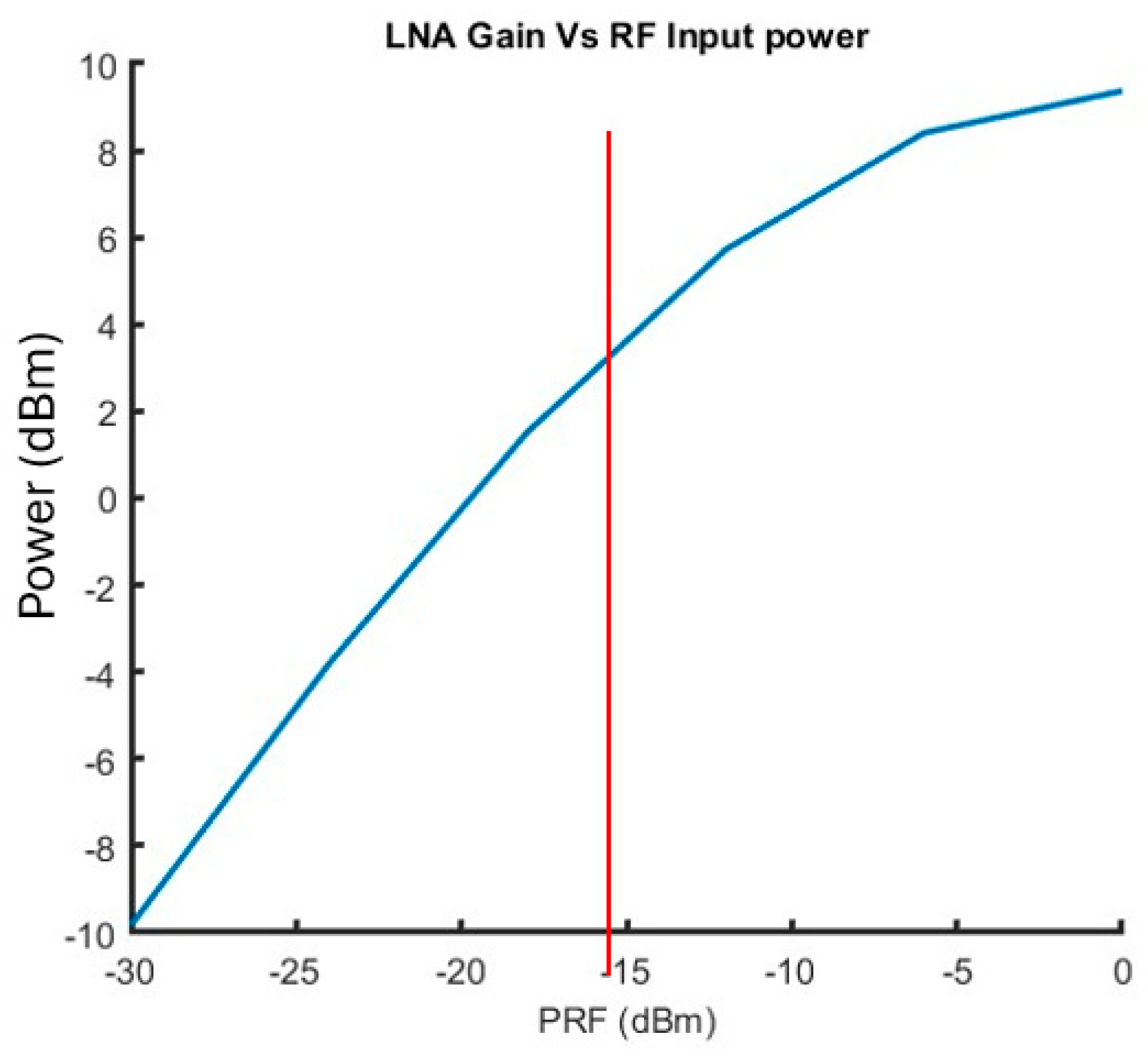
2.1. Low-Noise Amplifier (LNA)
LNA Post-Layout Simulation Results
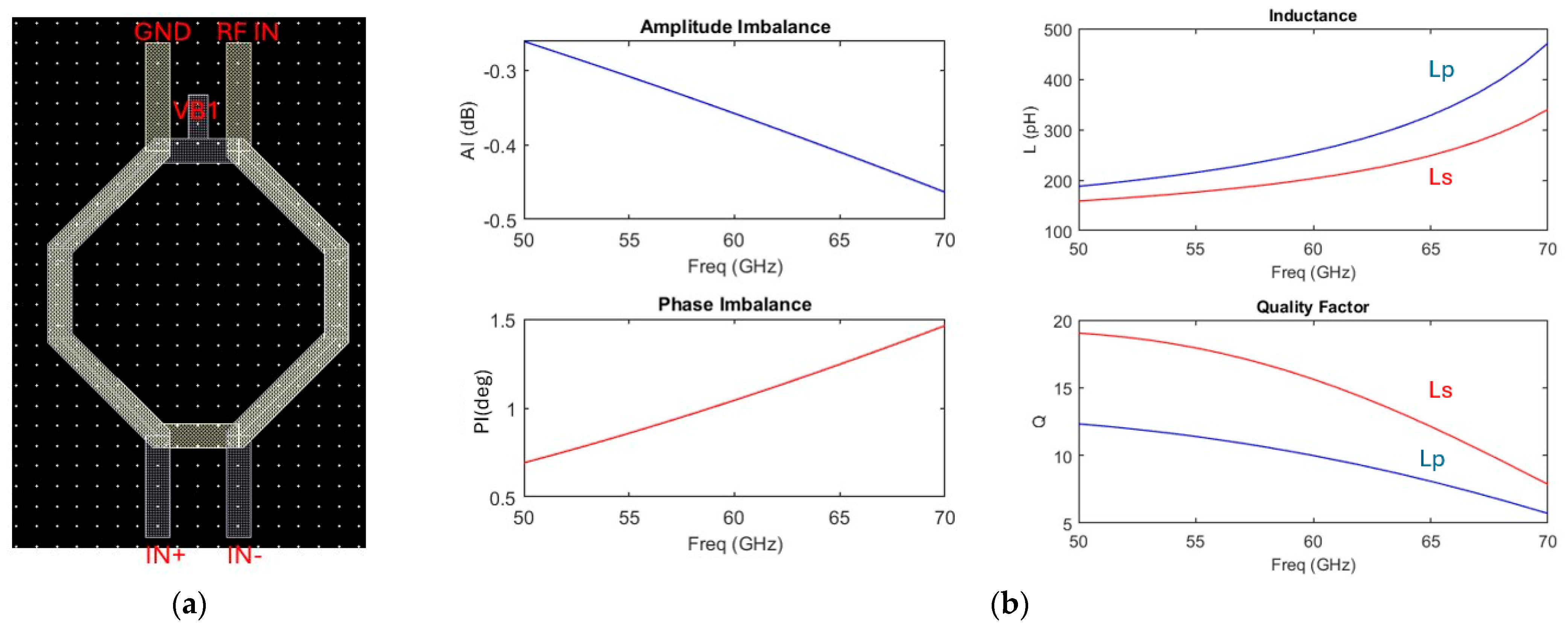
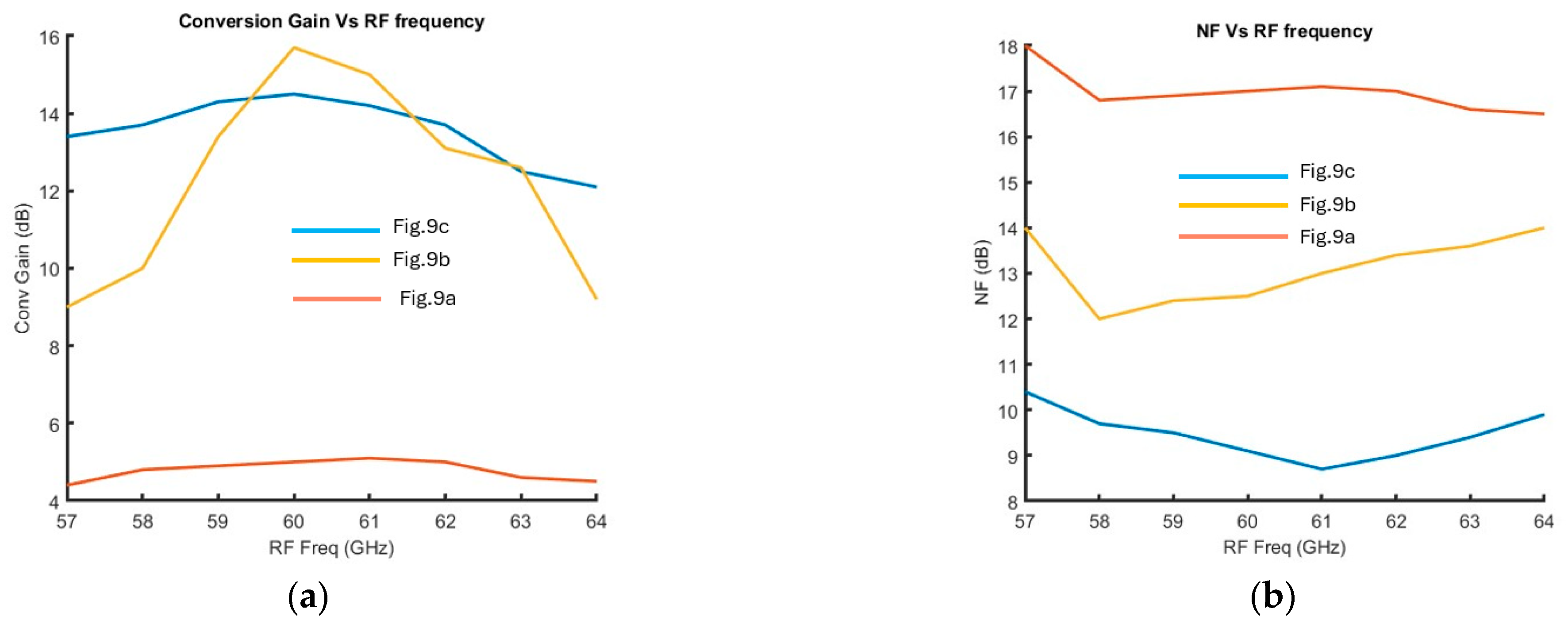
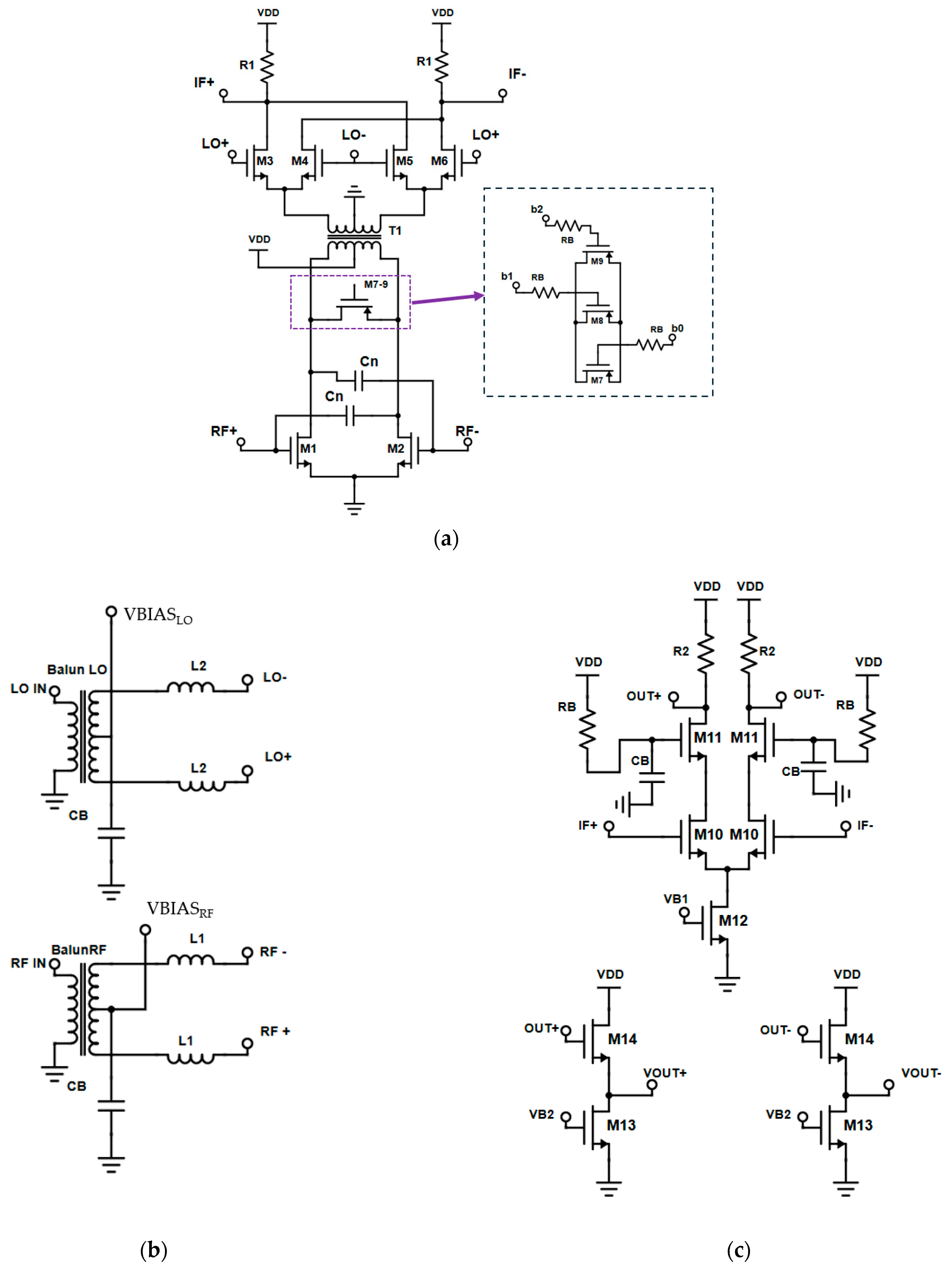
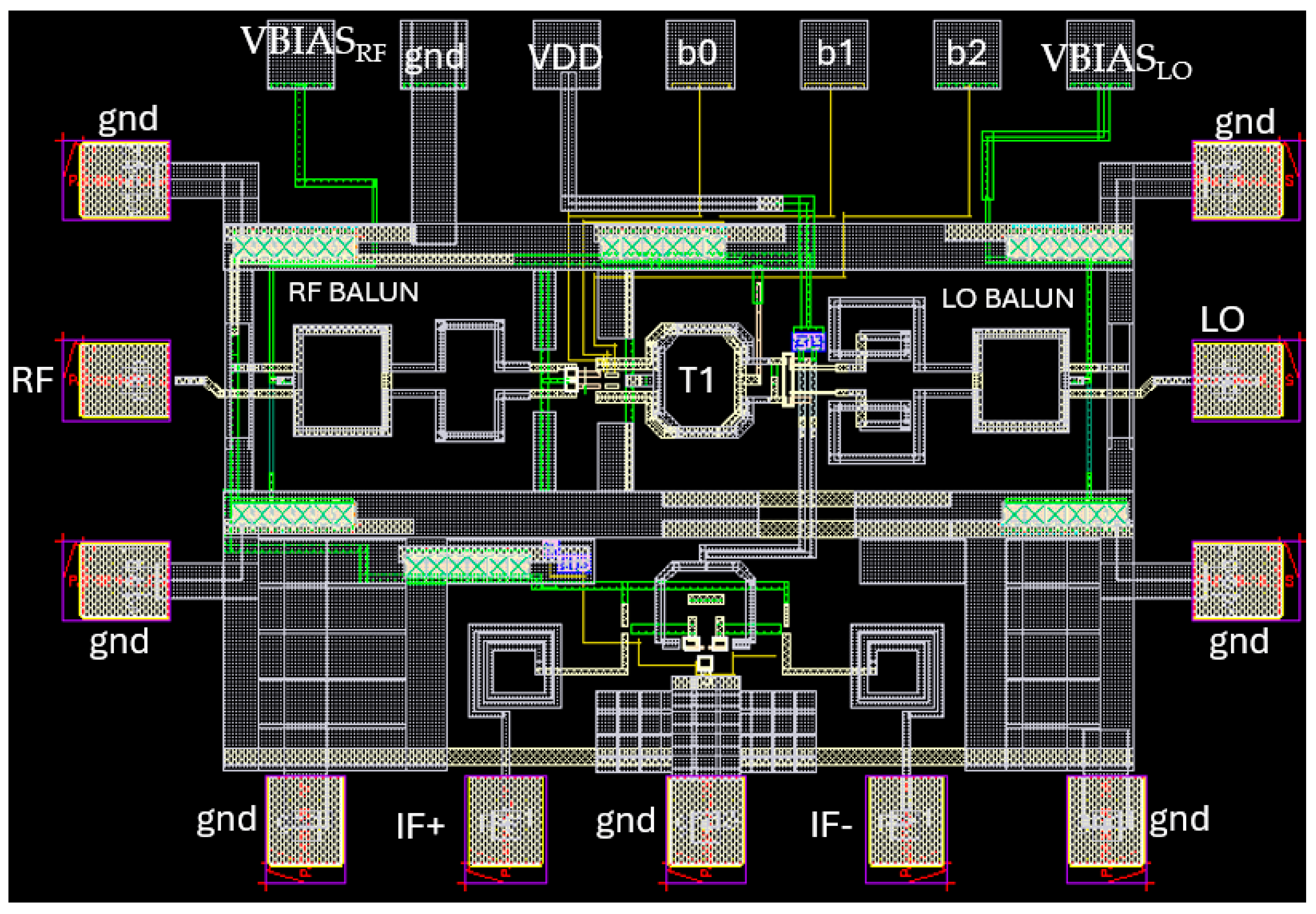
2.2. Down-Conversion 60 GHz Mixer
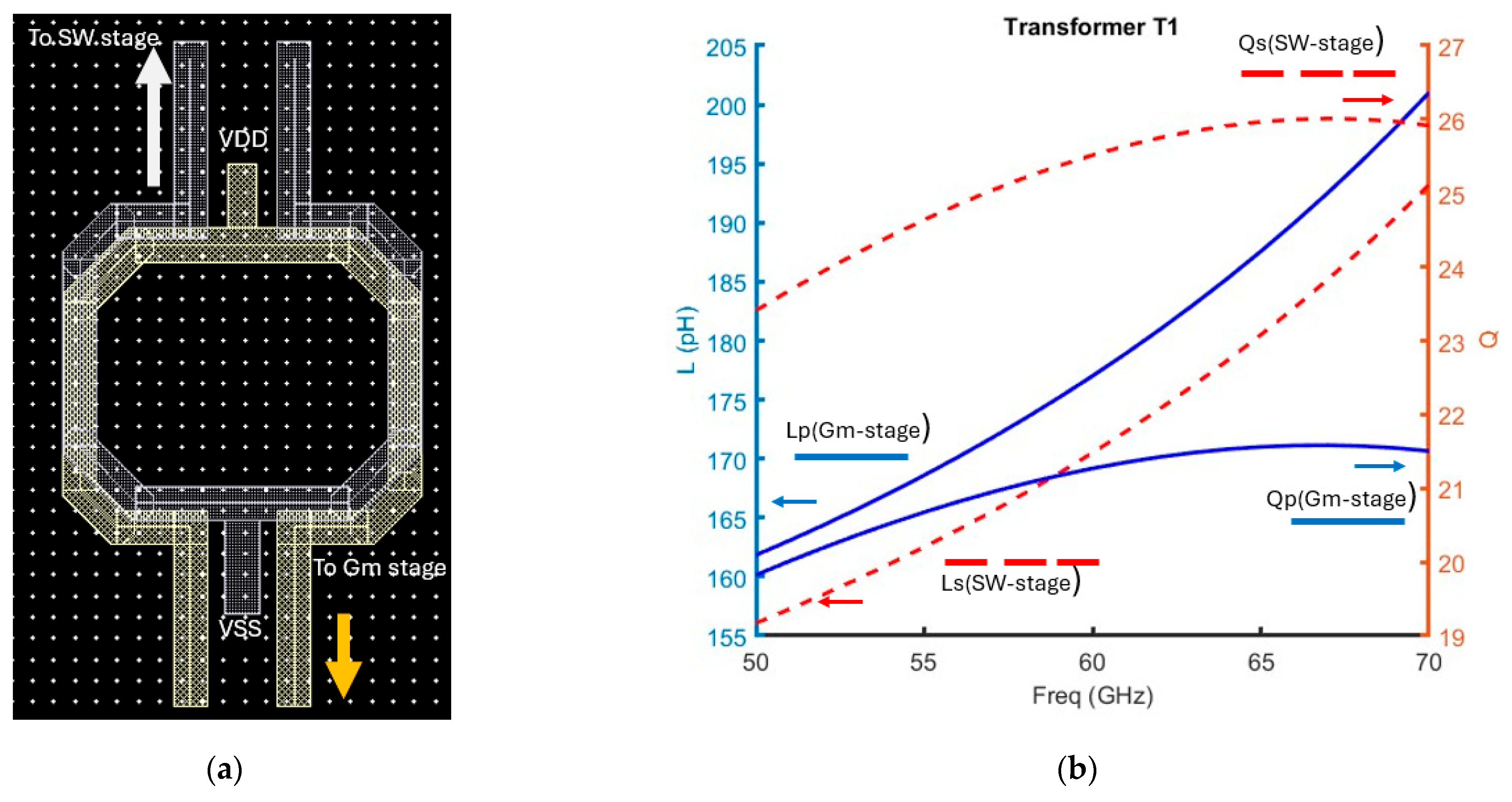
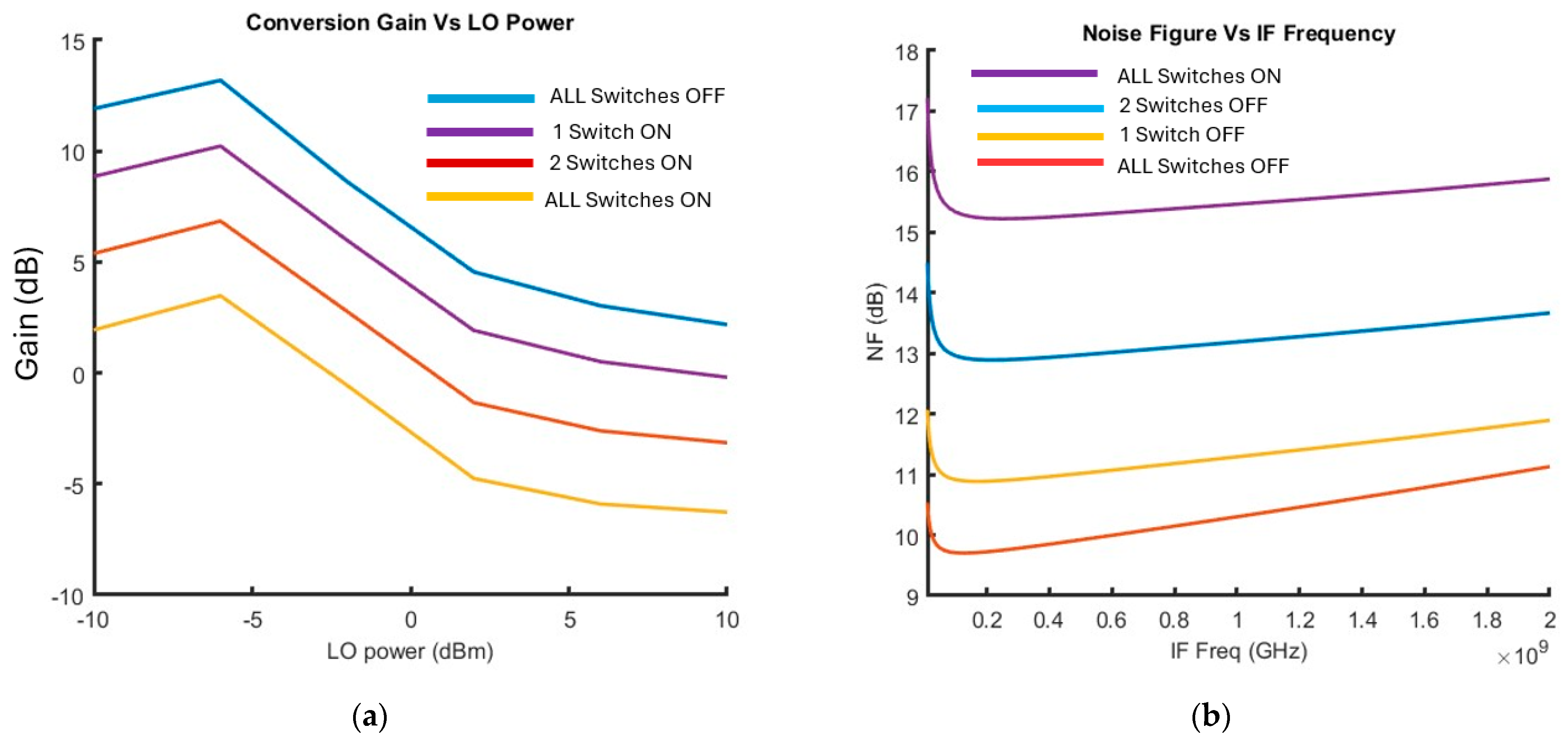
Mixer Post-Layout Simulation Results
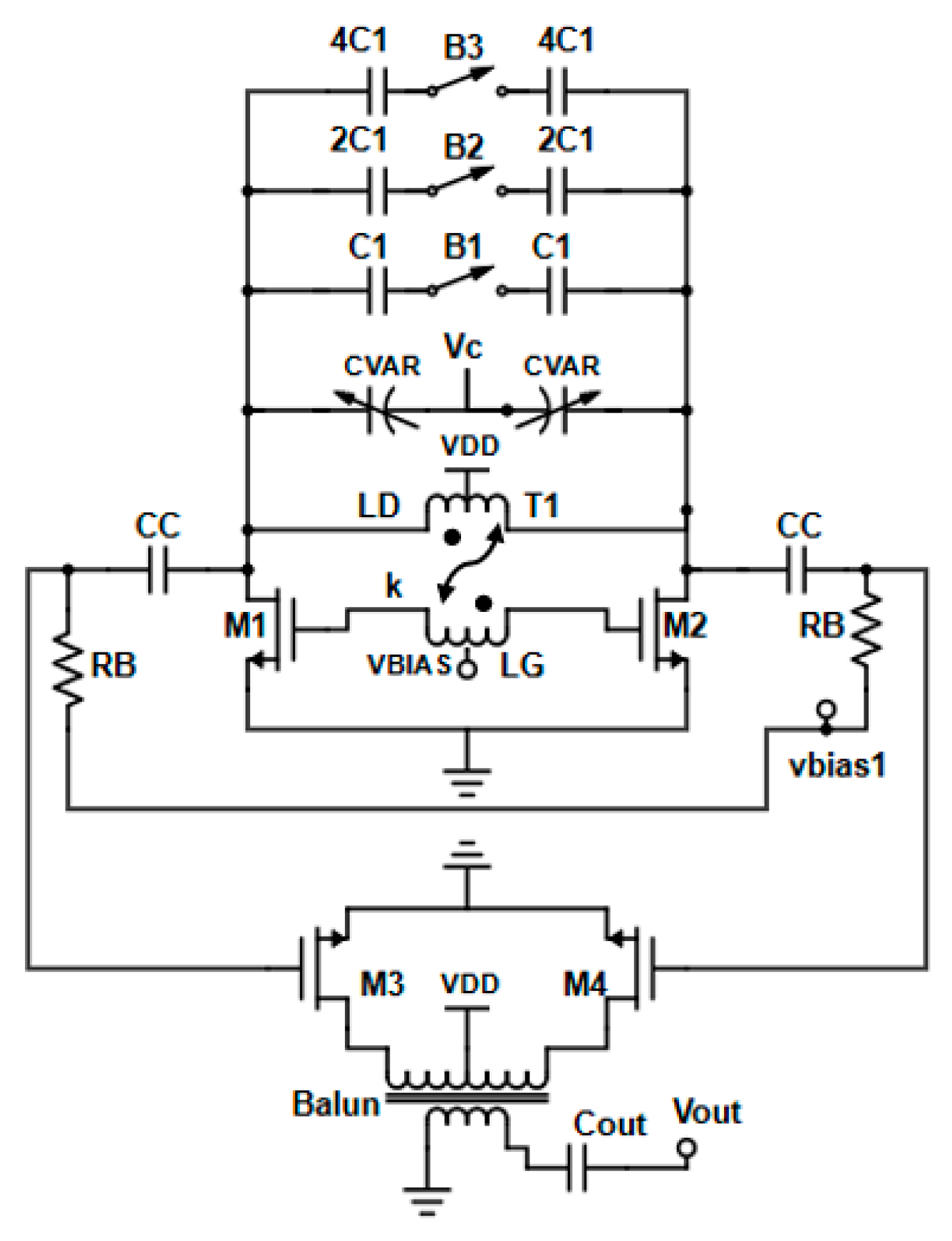
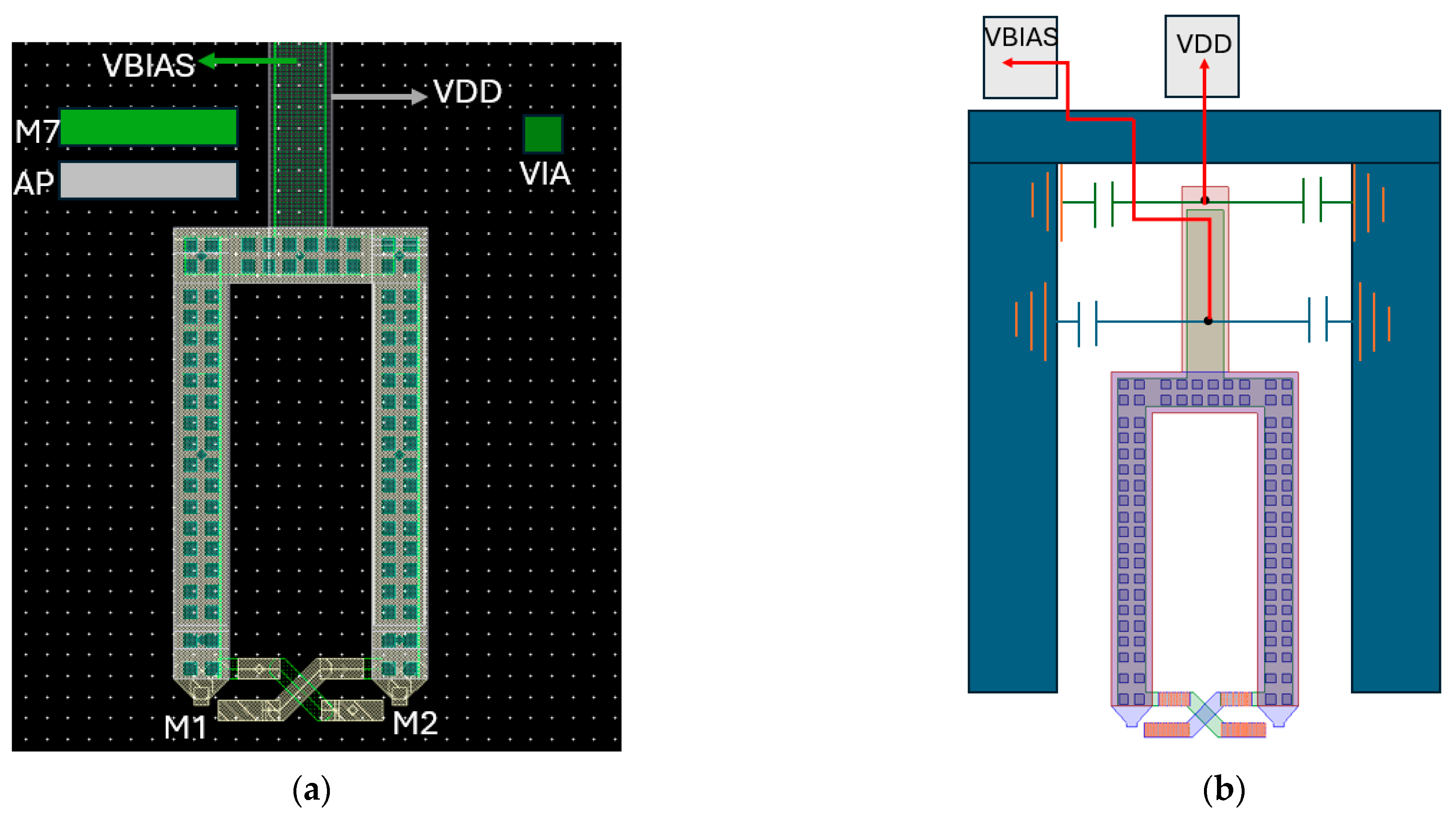
2.3. Voltage-Controlled Oscillator (VCO)
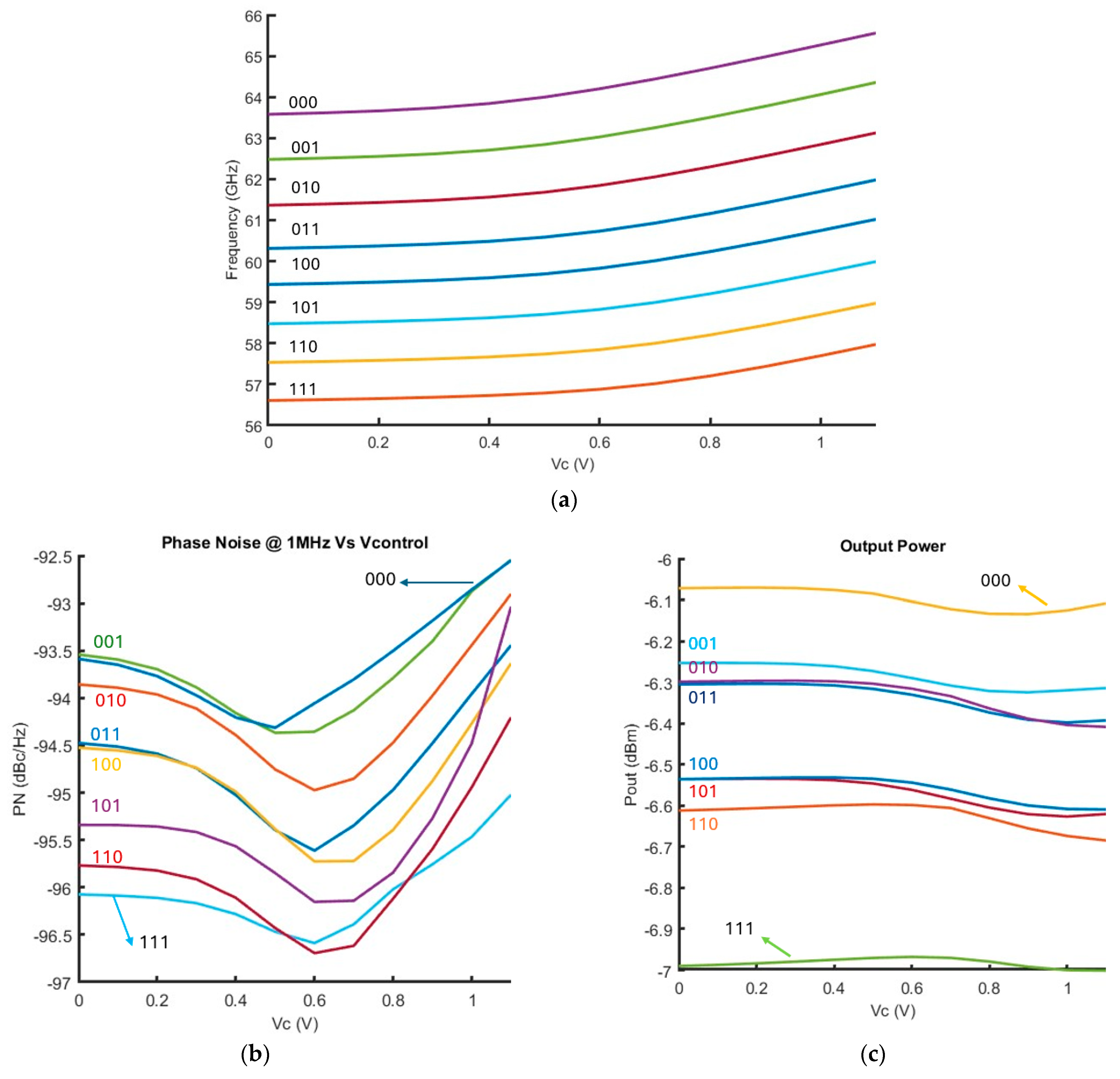
VCO Post-Layout Simulation Results
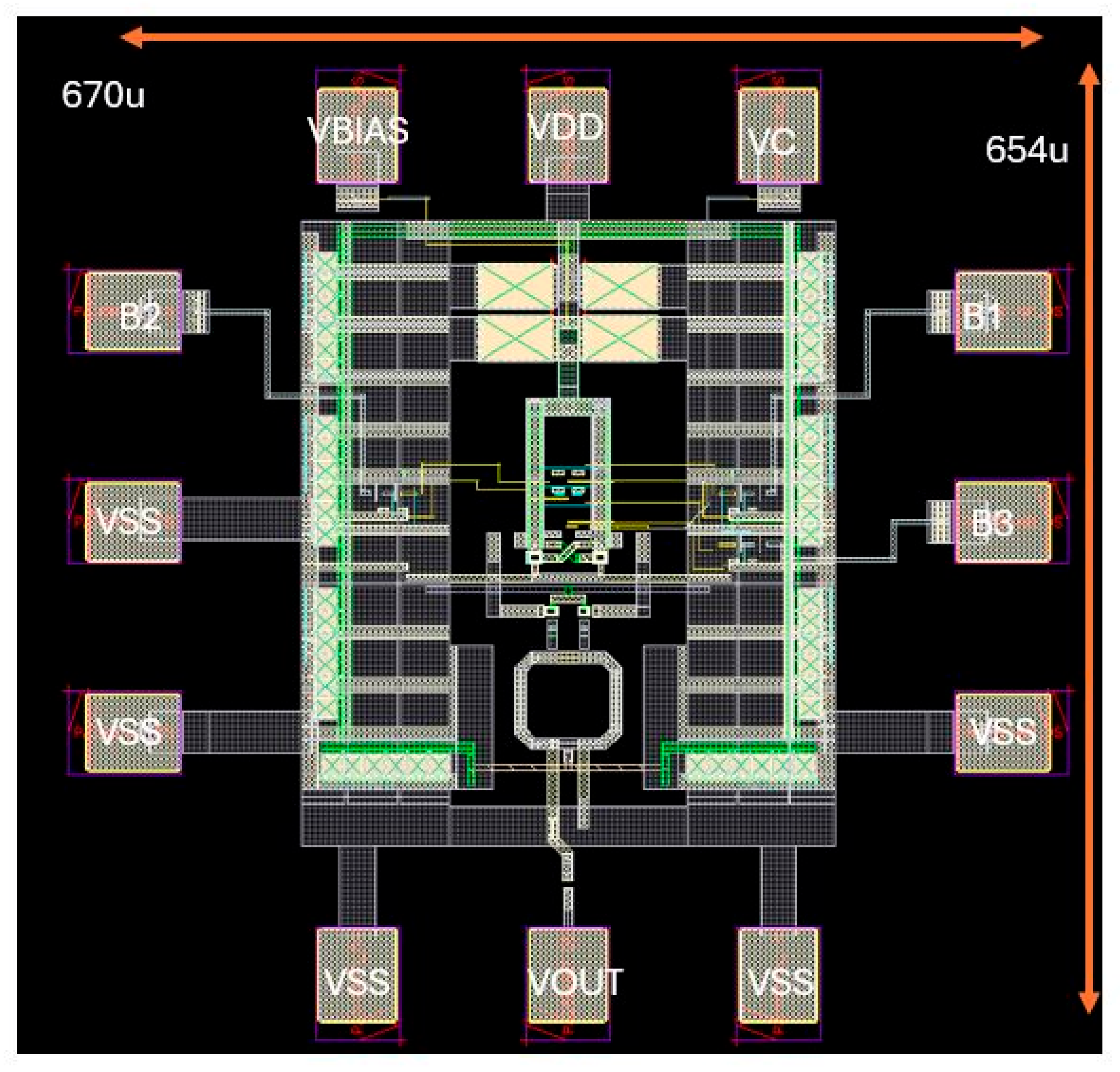
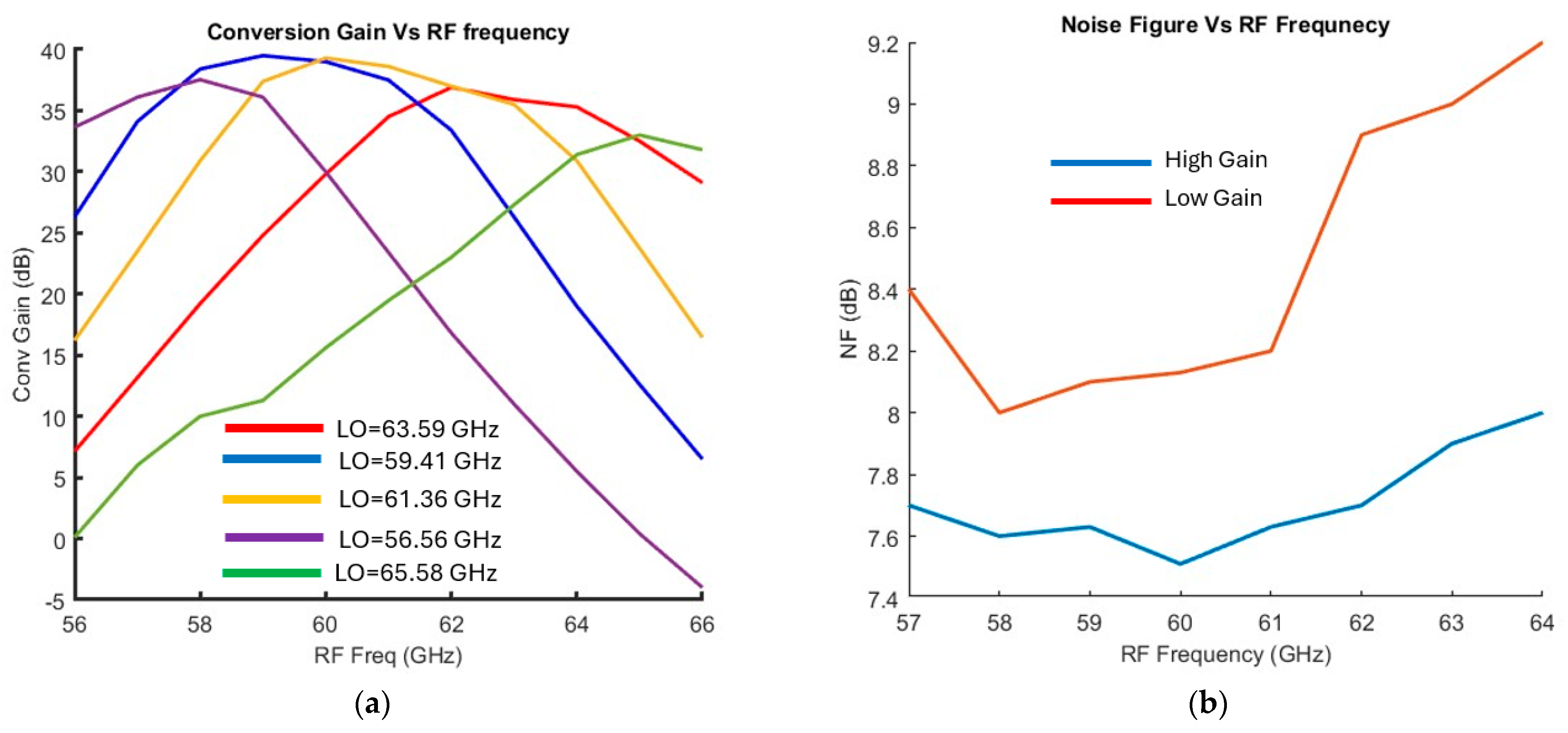
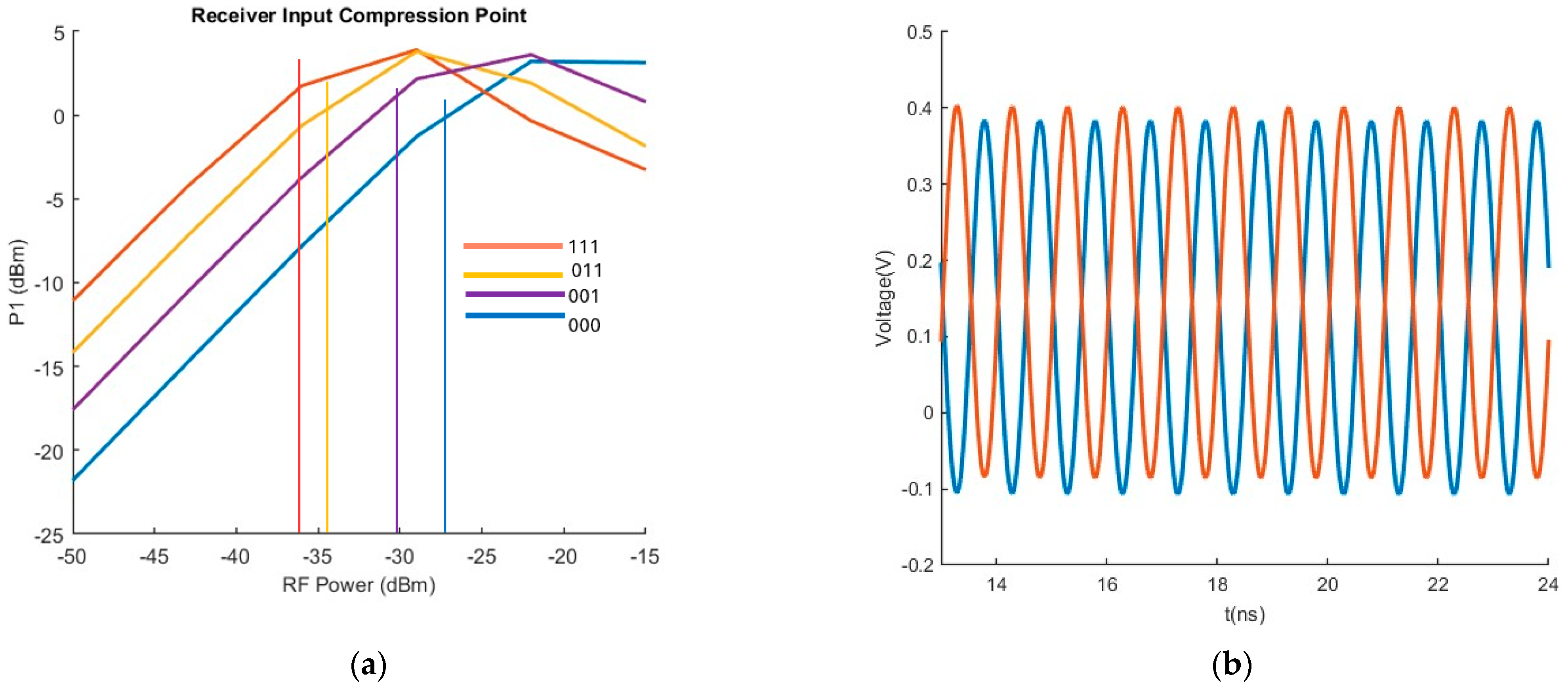
3. System Considerations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitomo, T.; Fujimoto, R.; Ono, N.; Tachibana, R.; Hoshino, H.; Yoshihara, Y. A 60-GHz CMOS Receiver Front-End with Frequency Synthesizer. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2008, 43, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinc, T.; Chakrabarti, A.; Krishnaswamy, H. A 60 GHz CMOS Full-Duplex Transceiver and Link with Polarization-Based Antenna and RF Cancellation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2016, 51, 1125–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomkins, A.; Poon, A.; Juntunen, E.; El-Gabaly, A.; Temkine, G.; To, Y.-L. A 60 GHz, 802.11ad/WiGig-Compliant Transceiver for Infrastructure and Mobile Applications in 130 nm SiGe BiCMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2015, 50, 2239–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocoveanu, R.; Issakov, V. Low-Power 60 GHz Receiver with an Integrated Analog Baseband for FMCW Radar Applications in 28 nm CMOS Technology. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 20th Topical Meeting on Silicon Monolithic Integrated Circuits in RF Systems (SiRF), San Diego, CA, USA, 17–20 January 2021; pp. 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shopov, S.; Girmat, M.G.; Hasch, J.; Voinigescu, S.P. An Ultra-Low-Power 4-Channel 60-GHz Radar Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS), Honolulu, HI, USA, 4–9 June 2017; pp. 1520–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.-I.; Ko, G.-H.; Kim, G.S.; Kim, J.-G.; Baek, D. A 54–64 GHz 4TXs-4RXs CMOS Transceiver with 10-GHz Bandwidth Single Chirp for FMCW Radar Applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2025, 73, 1532–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocoveanu, R.; Weigel, R.; Issakov, V. A Highly-Integrated 60 GHz Receiver for Radar Applications in 28 nm Bulk CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Microwaves, Antennas, Communications and Electronic Systems (COMCAS), Tel Aviv, Israel, 4–6 November 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmelspacher, J.; Ciocoveanu, R.; Steffan, G.; Bassi, M.; Issakov, V. Low Power Low Phase Noise 60 GHz Multichannel Transceiver in 28 nm CMOS for Radar Applications. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 21–23 June 2020; pp. 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, A.; Baek, D.; Kim, J.-G. A 60 GHz CMOS I/Q Receiver for High-Speed Wireless Communication System. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Shi, Y.; Huang, K.; Letaief, K.B. A Survey on Integrated Sensing and Communication. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2022, 40, 1728–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, B. RF Microelectronics, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall Communications Engineering and Emerging Technologies Series; Prentice Hall Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J. A 60 GHz Single-to-Differential LNA Using Slow-Wave CPW and Transformer Coupling in 28 nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 13th International Conference on ASIC (ASICON), Chongqing, China, 29 October–1 November 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Li, L.; Zhao, D.; Niu, X.; He, L.; Zheng, F. A 20-to-75 dB Gain 5-dB Noise Figure Broadband 60-GHz Receiver with Digital Calibration. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Radio-Frequency Integration Technology (RFIT), Taipei, Taiwan, 31 August–2 September 2016; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, H.; Matsushita, K.; Bunsen, K.; Okada, K.; Matsuzawa, A. A 60 GHz CMOS Power Amplifier Using Capacitive Cross-Coupling Neutralization with 16% PAE. In Proceedings of the 2011 6th European Microwave Integrated Circuit Conference, Manchester, UK, 10–11 October 2011; pp. 554–557. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Yan, X.; Guo, Y. A 60–64 GHz Power Amplifier for MM-Wave Radar Transceiver with 16.51-dBm Power and 23.34% PAE in 40-NM CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE MTT-S International Wireless Symposium (IWS), Qingdao, China, 10–13 May 2023; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, M.; Raschella, A.; Toma, O. Modelling and Analysis of Performance Characteristics in a 60 Ghz 802.11ad Wireless Mesh Backhaul Network for an Urban 5G Deployment. Future Internet 2022, 14, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, A.; Luo, X. A 60-GHz Current-Reused Cascode Noise-Canceling Low Noise Amplifier. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2024, 71, 4809–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wagner, J.; Carta, C.; Ellinger, F. A 60 GHz Broadband LNA With Joined Variable Gain Control and Switching in 22 nm FD-SOI. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 111627–111637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-T.; Lu, H.-C. A V-Band Low-Power Digital Variable-Gain Low-Noise Amplifier Using Current-Reused Technique with Stable Matching and Maintained OP1dB. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2019, 67, 4404–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Feng, G.; Wang, Y. A Compact 60 GHz LNA with 22.7-dB Gain and 4.4-dB NF in 40nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Integrated Circuits, Technologies and Applications (ICTA), Xi’an, China, 14–16 November 2022; pp. 152–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, C.; Hong, S. 60 GHz Variable Gain LNA with Small NF Variation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Radio-Frequency Integration Technology (RFIT), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 6–8 September 2017; pp. 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-S.; Lan, K.-S. Design and Analysis of a Low-Power 60–113 GHz CMOS Down-Conversion Mixer with High Conversion Gain. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium (RWS), San Antonio, TX, USA, 12–15 January 2020; pp. 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, R.; Zuo, Y.; Zhao, C.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y. A 60–90 GHz Mixer-First Receiver with Adaptive Temperature-Compensation Technique. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Technol. Lett. 2024, 34, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wagner, J.; Ellinger, F. A 60 GHz Down-Conversion Mixer featuring Energy-saving Standby-Mode in 22 nm FD-SOI. In Proceedings of the 2023 Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference (APMC), Taipei, Taiwan, 4–7 December 2023; pp. 122–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, P.; Rieß, V.; Carta, C.; Ellinger, F. An Inductorless 60 GHz Down-Conversion Mixer in 22nm FD-SOI CMOS Technology. In Proceedings of the 2019 14th European Microwave Integrated Circuits Conference (EuMIC), Paris, France, 29 September–1 October 2019; pp. 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, W.; Zhiqun, L.; Qin, L.; Yang, L.; Jia, C.; Zhigong, W. A 60 GHz Down-Conversion Mixer Using a Novel Topology in 65 nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2014 10th Conference on Ph.D. Research in Microelectronics and Electronics (PRIME), Grenoble, France, 29 June–3 July 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, M.; Ercoli, M.; Dragomirescu, D.; Plana, R. A Wideband Single-Balanced Down-Mixer for the 60 GHz Band in 65 nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2010 Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference, Yokohama, Japan, 12–15 December 2010; pp. 1849–1852. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.J.; Park, C.S. A D-Band Gain-Boosted Current Bleeding Down-Conversion Mixer in 65 nm CMOS for Chip-to-Chip Communication. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2016, 26, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Park, C.S. A 60-GHz Wideband Down-Conversion Mixer for Low-Power and High-Speed Wireless Communication. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Radio-Frequency Integration Technology (RFIT), Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 22–24 October 2018; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, H.; Lee, C.J.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.-K.; Lee, D.Y.; Na, I. A D-Band High-Linearity Down-Conversion Mixer for 6G Wireless Communications. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Technol. Lett. 2023, 33, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psycharis, I.-D.; Tsourtis, V.; Kalivas, G. A 60 GHz Low Phase Noise VCO with Second Harmonic Tail Extraction in 40-nm CMOS. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2024, 186, 154302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issakov, V. The State of the Art in CMOS VCOs: Mm-Wave VCOs in Advanced CMOS Technology Nodes. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2019, 20, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, V.-S.; Nam, H.; Song, J.-M.; Park, J.-D. A 78.8–84 GHz Phase Locked Loop Synthesizer for a W-Band Frequency-Hopping FMCW Radar Transceiver in 65 nm CMOS. Sensors 2022, 22, 3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, P. Millimeter-Wave Frequency Generation and Synthesis in Silicon. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC), San Diego, CA, USA, 8–11 April 2018; pp. 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, M.; Zekry, A.; Ali, M.K.; Shawkey, H. A Comparative Study between Class-C and Class-B Quadrature Voltage-Controlled Power Oscillator for Multi-Standard Applications. Microelectron. J. 2020, 98, 104731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripoli, D.; Maiellaro, G.; Pavone, S.C.; Ragonese, E. A Low-Phase-Noise and Area-Efficient Quad-Core VCO Based on Stacked Two-Port Inductors. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 87065–87076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psycharis, I.D.; Tsourtis, V.; Kalivas, G. A 60 GHz Class-C Wide Tuning-Range Two-Core VCO Utilizing a Gain-Boosting Frequency Doubling Technique and an Adaptive Bias Scheme for Robust Startup. Sensors 2025, 25, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zheng, W.; Xia, X.; Wang, Y. A 52.97–60.51-GHz Voltage-Controlled Oscillator with an 8-Shaped-Inductor-Based Triple-Coil Transformer. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Technol. Lett. 2023, 33, 1466–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, L.; Wang, D.; Fu, Y. 60 GHz CMOS VCO with Transformer Feedback Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE MTT-S International Wireless Symposium (IWS), Shanghai, China, 20–23 September 2020; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barajas, B.; Molavi, R.; Mirabbasi, S. A Wideband 65-nm 60-GHz Push-Push LC VCO Using a Nonlinear Varactor Array. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 67th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Springfield, MA, USA, 11–14 August 2024; pp. 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koop-Brinkmann, L.; Steffan, G.; Lasserre, V.; Padovan, F.; Bassi, M.; Issakov, V. A Low Phase Noise VCO for 60 GHz Radar Applications with a Direct Transformer-Based Fourth Harmonic Extraction in 28 nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2024 19th European Microwave Integrated Circuits Conference (EuMIC), Paris, France, 23–24 September 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer, M.; Dragomirescu, D.; Plana, R. Design of a Very Low-Power, Low-Cost 60 GHz Receiver Front-End Implemented in 65 nm CMOS Technology. Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 2011, 3, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, S.; Doan, C.H.; Niknejad, A.M.; Brodersen, R.W. A Highly Integrated 60 GHz CMOS Front-End Receiver. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference. Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–15 February 2007; pp. 190–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; Zuo, C.; Zhao, H.; Wu, Y. A 28-/60-GHz Dual-Band Receiver Front-End with Sideband-Selection Technique in 65-nm CMOS. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2024, 71, 4550–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchi, F.; Bozzola, S.; Pozzoni, M.; Guermandi, D.; Temporiti, E.; Repossi, M. A Wideband mm-Wave CMOS Receiver for Gb/s Communications Employing Interstage Coupled Resonators. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 7–11 February 2010; pp. 220–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| WM1–M2 | 1 × 30 μm |
| WM3–M4 | 2 × 18 μm |
| Cn | 8 fF |
| L | 40 nm |
| T1: Lp/Ls, Qp/Qs | 175/170 pH, 15/16.5 |
| CB | 5 pF |
| VB1 | 560 mV |
| VB2 | 600 mV |
| Reference | Hardware | FREQ (GHz) | Gain (dB) | PDC (mW) | NFMIN (dB) | IP1 (dBm) | Area (mm2) | Process |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [17] | measured | 50.6–67 | 16.8 | 33 | 4.4 | −13 | 0.1 1 | 40 nm CMOS |
| [18] | measured | 51.5–70 | 20 | 8.1 | 3.3 | −23.9 | 0.2 | 22 nm FD-SOI |
| [19] | measured | 55–65 | 19.8 | 18 | 6 | −29.5 | 0.2 | 40 nm CMOS |
| [20] | post-layout | 54–63 | 22.5 | 29.9 | 4.4 | −16.1 | 0.09 1 | 40 nm CMOS |
| [21] | measured | 56–61 | 20.2 | 28 | 5.16 2 | −25 | 0.43 | 65 nm CMOS |
| This work | post- layout | 57–64 | 20.1 | 19.8 | 4.2 | −15.6 | 0.28 | 40 nm CMOS |
| Mixer Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| WM1–M2 | 1 × 18 u |
| WM3–M6 | 1 × 22 u |
| LM1–M6 | 40 nm |
| WM7–M9 | 1 × 4, 1 × 7, 1 × 11 u |
| LM7–M9 | 40 nm |
| Cn | 11 fF |
| R1 | 700 |
| Lp, Ls | 176,165 pH |
| RB | 8 K |
| CB | 6 pF |
| VBIASRF | 550 mV |
| VBIASLO | 300 mV |
| WM10–M11,M12 | 4 × 10, 5 × 22 u |
| LM12,M13 | 120 n |
| WM13,M14 | 4 × 18, 5 × 25 u |
| VB1,VB2 | 550, 500 mV |
| R2 | 700 Ω |
| Ref | Hardware | RF (GHz) | CG (dB) | PDC (mW) | IF (GHz) | LO (dBm) | Area (mm2) | NF (dB) | P1 (dBm) | Process |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [24] | measured | 53–67 | 8 1 | 9 | 3–5 | −11 | 0.4 | 13 2 | −13 | 22 nm FD-SOI |
| [25] | measured | 56–66 | 6.5 | 18 | 0–1 | −4 | 0.05 3 | 13.5 4 | −18 | 22 nm FD-SOI |
| [26] | post- layout | 56–64 | 10.4 | 6 | 8–16 | 2 | 0.75 | 11.2 2 | −16 | 65 nm CMOS |
| [27] | measured | 54–65 | 9.1 | 16.8 | 0–2 | −5 | 0.26 | 12 4 | −15 | 65 nm CMOS |
| This work | post- layout | 57–64 | 13.5/4 | 22 | 0–1.8 | −6 | 0.45 | <11 4 | −13/−1 | 40 nm CMOS |
| VCO Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| WM1–M2 | 1 × 20 u |
| WM3–M4 | 1 × 9 u |
| LM1–M4 | 40 nm |
| WSwitch,B1–B3 | 2 × 6, 2 × 12, 2 × 24 u |
| LSwitch,B1–B3 | 40 nm |
| CC | 50 fF |
| VBIAS | 0.6 V |
| Vbias1 | 0.84 V |
| RB | 8 K |
| C1 | 25.4 fF |
| CVAR @ Vgs of 0–1.1 V | 24–32 fF |
| T1:LD,LG, QD,QG | 105 pH, 168 pH, 27, 16 |
| Balun: LP,LS, QP,QS | 140 pH, 125 pH, 15.1,13.4 |
| Cout | 24 fF |
| Reference | Hardware | Type | FREQ (GHz) | PN @ 1 MHz | PDC,VCO (mW) | FTR (%) | Pout (dBm) | Area (mm2) | FOM * | FOMT * | Process |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [38] | M 1 | Direct | 56.7 | −103.6 1 | 9 | 13.28 | −19 | 0.27 | −168.6 1 | −171.1 1 | 40 nm CMOS |
| [39] | M 1 | Direct | 61.3 | −94.9 | 8.4 | 9 | −10 | 0.09 2 | −183.4 | −180.5 | 65 nm CMOS |
| [40] | Post- Layout | 2nd Harmonic | 60 | −93.2 | 4.2 | 18.2 | −12 | 0.07 2 | −183 | −188 | 65 nm CMOS |
| [41] | M 1 | 4th Harmonic | 60.85 | −99.8 | 11.7 | 15.6 | - | 0.12 2 | −184.1 | −188 | 28 nm CMOS |
| This work | Post- Layout | Direct | 61 | −94.3 | 6.6 | 14 | −6.4 | 0.035 2 | −181.5 | −184.8 | 40 nm CMOS |
| Ref | Hardware | Components | RF (GHz) | CG (dB) | PDC (mW) | IF (GHz) | Area (mm2) | NF (dB) | P1 (dBm) | Process |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [42] | M 1 | LNA, mixer, VCO | 56–61.5 | 30 | 43 | 0–1.5 | 0.55 | 9.2 2 | −36 | 65 nm |
| [43] | M 1 | LNA, mixer, VCO, | 57–63 | 11.8 | 76.8 | 2 | 0.86 | 10.4 2 | −15.8 | 130 nm |
| [44] | M 1 | LNA, mixer, External LO | 55.6–60 | 26.3 | 53.5 | 0.3–1.9 | 1.29 | 7.5–10.1 3 | −31.5 | 65 nm |
| [7] | M 1 | LNA, mixer, External LO | 57–64 | 17.2–19.3 | 39.6 | 0.001 | 0.2 4 | 7.5–8.2 2,5 | >−13 | 28 nm |
| [45] 6 | M 1 | LNA, Mixers, VCO | 56–69 | 35.5 | 75 | 0–0.2 | 2.4 | 5.6–6.5 2 | −21 | 65 nm |
| This work | Post- Layout | LNA, Mixer, VCO | 57–64 | 39/29 | 56 | 0–1.8 | 0.88 | 7.5–9.2 3 | −37.1/−27.5 | 40 nm CMOS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Psycharis, I.-D.; Tsourtis, V.; Kalivas, G. A 57–64 GHz Receiver Front End in 40 nm CMOS. Electronics 2025, 14, 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102091
Psycharis I-D, Tsourtis V, Kalivas G. A 57–64 GHz Receiver Front End in 40 nm CMOS. Electronics. 2025; 14(10):2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102091
Chicago/Turabian StylePsycharis, Ioannis-Dimitrios, Vasileios Tsourtis, and Grigorios Kalivas. 2025. "A 57–64 GHz Receiver Front End in 40 nm CMOS" Electronics 14, no. 10: 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102091
APA StylePsycharis, I.-D., Tsourtis, V., & Kalivas, G. (2025). A 57–64 GHz Receiver Front End in 40 nm CMOS. Electronics, 14(10), 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102091







