Deepfake Voice Detection: An Approach Using End-to-End Transformer with Acoustic Feature Fusion by Cross-Attention
Abstract
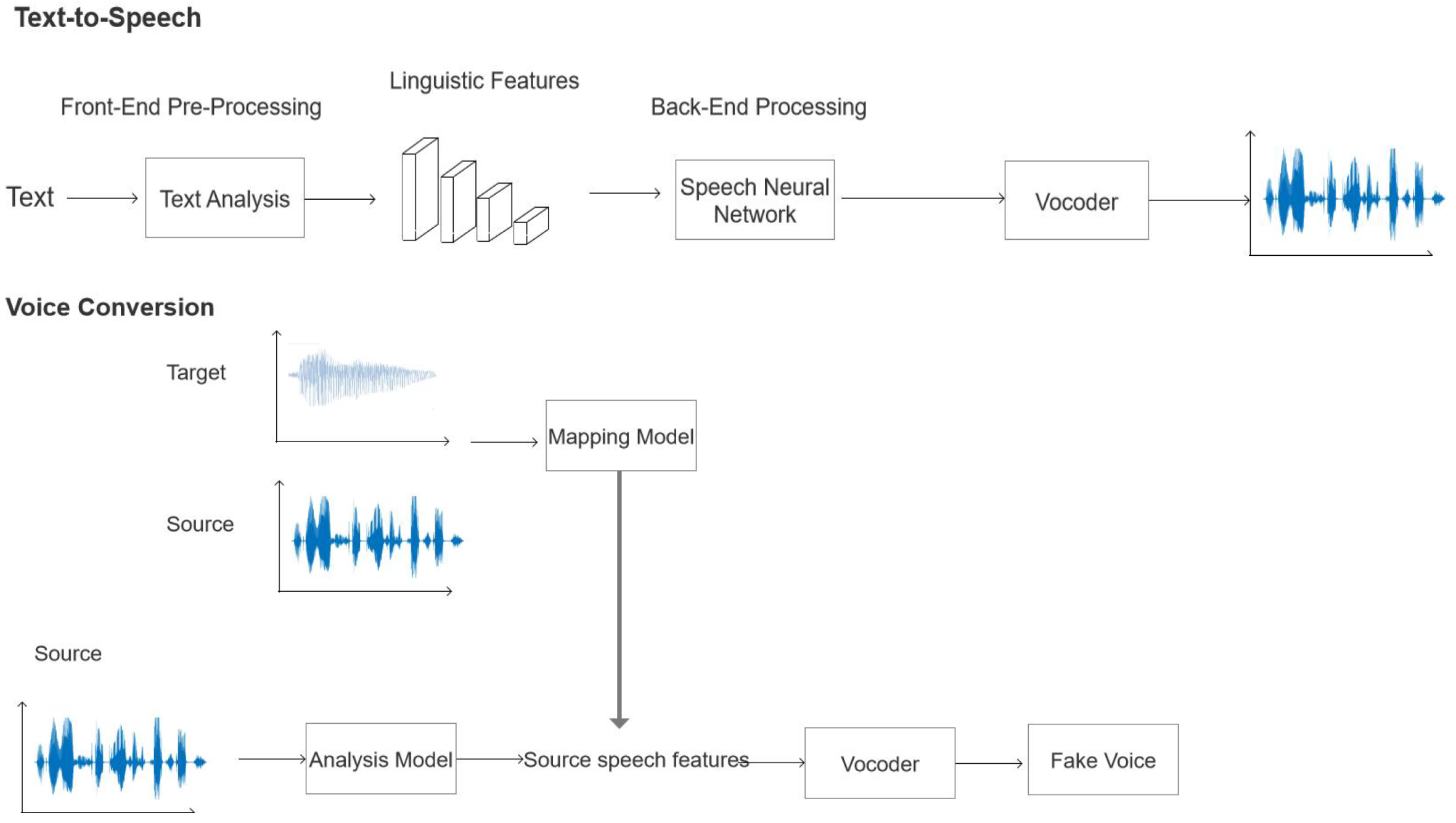
1. Introduction
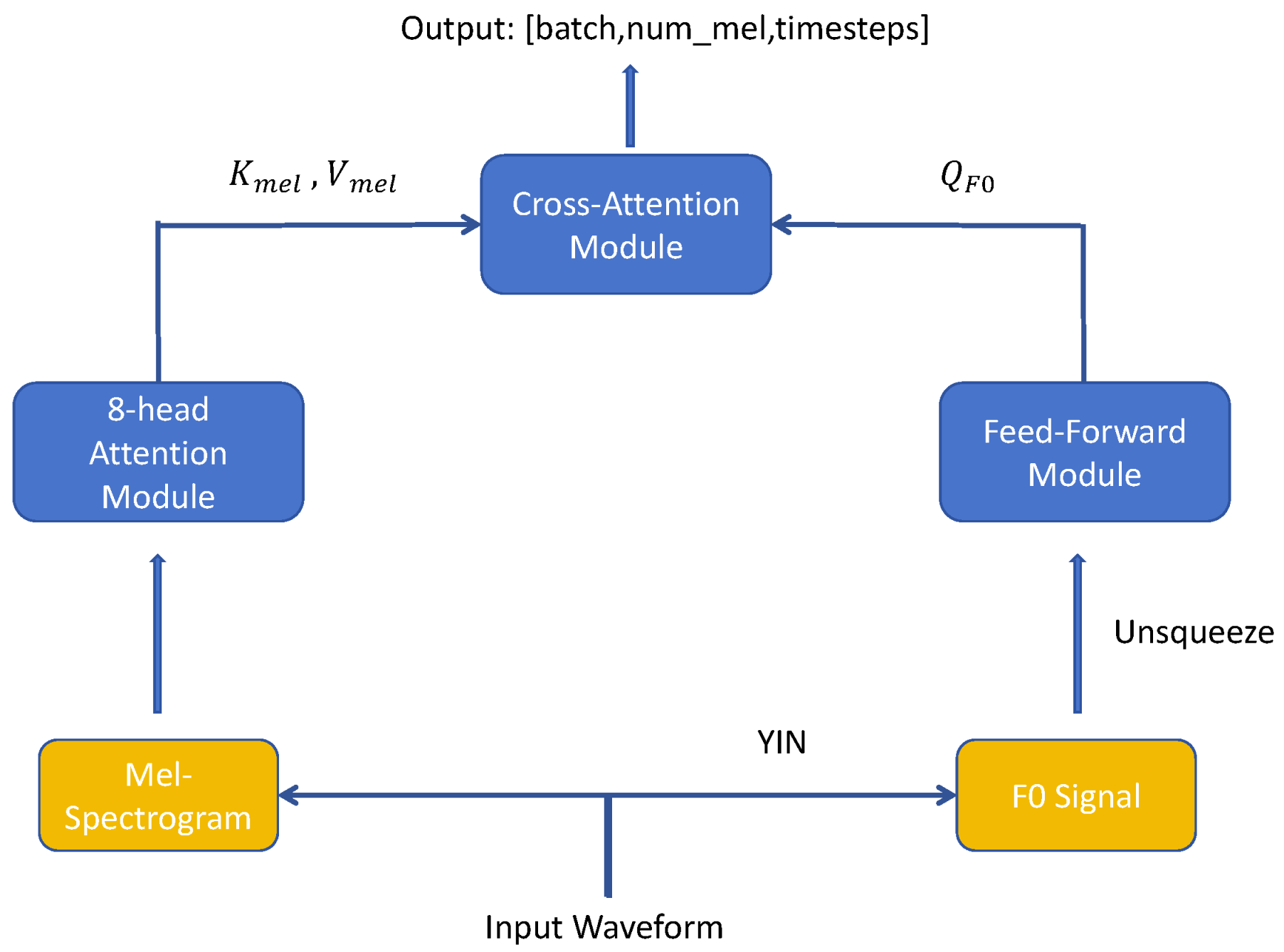
- To address the challenge of enriching the model’s input through the fusion of diverse acoustic features, we propose a PreNet architecture that incorporates an attention-based feature fusion method to adaptively combine the pitch representation and Mel-spectrogram features.
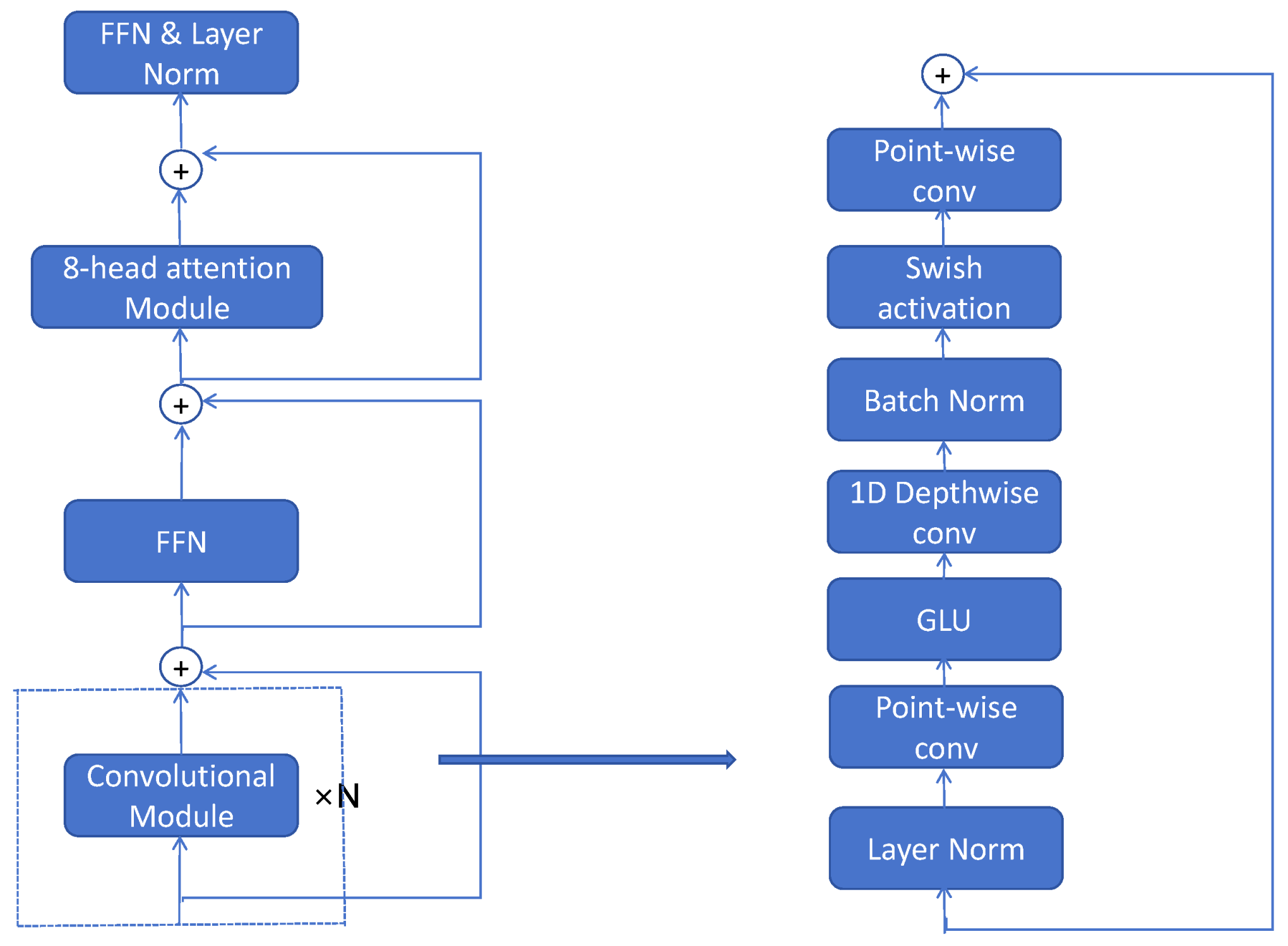
- To enhance acoustic feature extraction, the original Transformer integrates convolutional neural network (CNN) modules to separately capture local and global features. Unlike the Conformer architecture, we position the convolutional blocks at the beginning of the extractor workflow, followed by a feed-forward network (FFN) to adjust the input tensor’s dimensionality.
- We integrate the PreNet with the custom Transformer-based extractor as the front-end and connect it to a linear layer, forming an end-to-end Deepfake voice detector architecture. Subsequently, we adapted a portion of the pre-trained Conformer model’s weights and fine-tuned the system using the ASVspoof2019 dataset.
2. Related Work
2.1. Acoustic Features
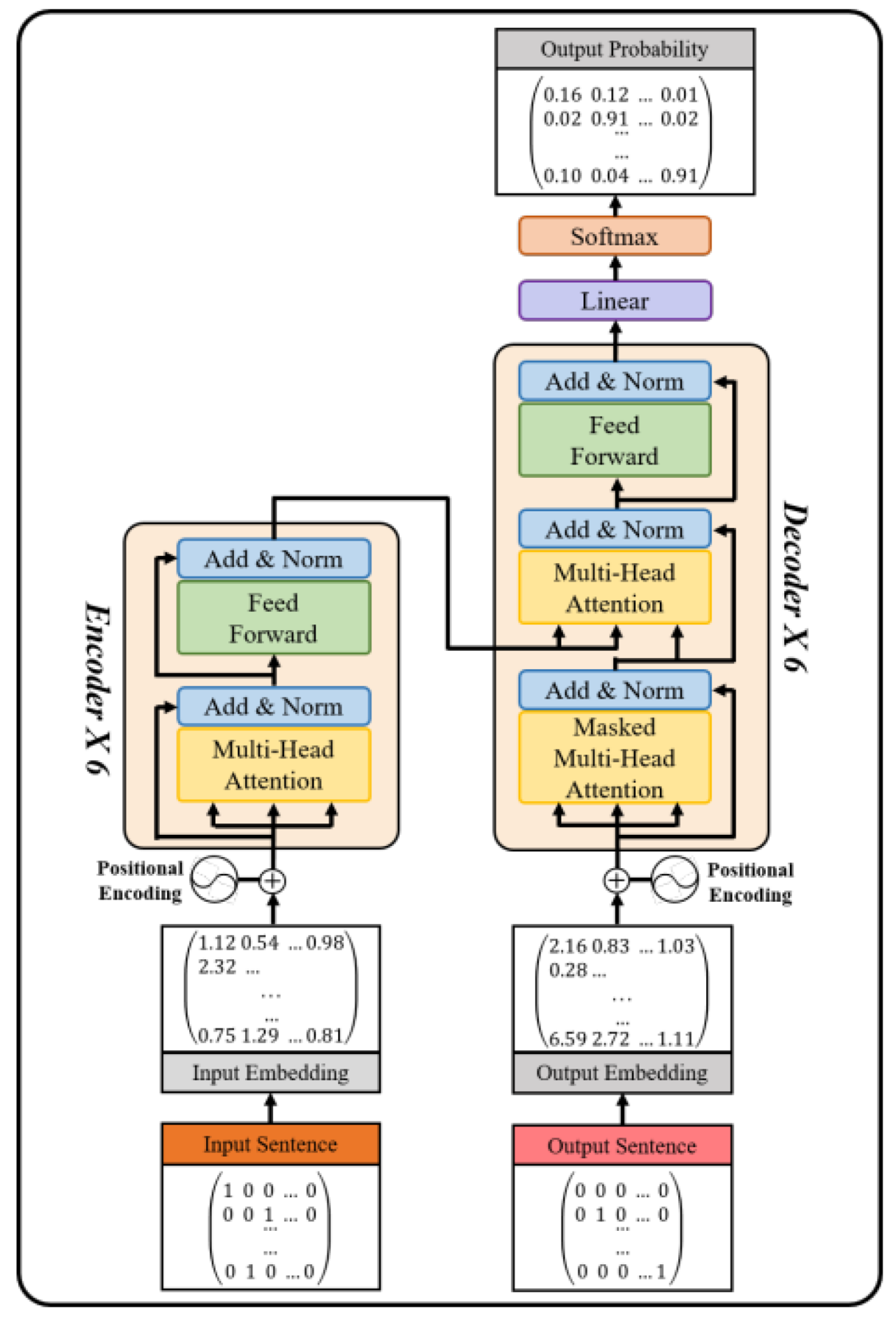
2.2. Transformer
2.3. Deepfake Voice Detection
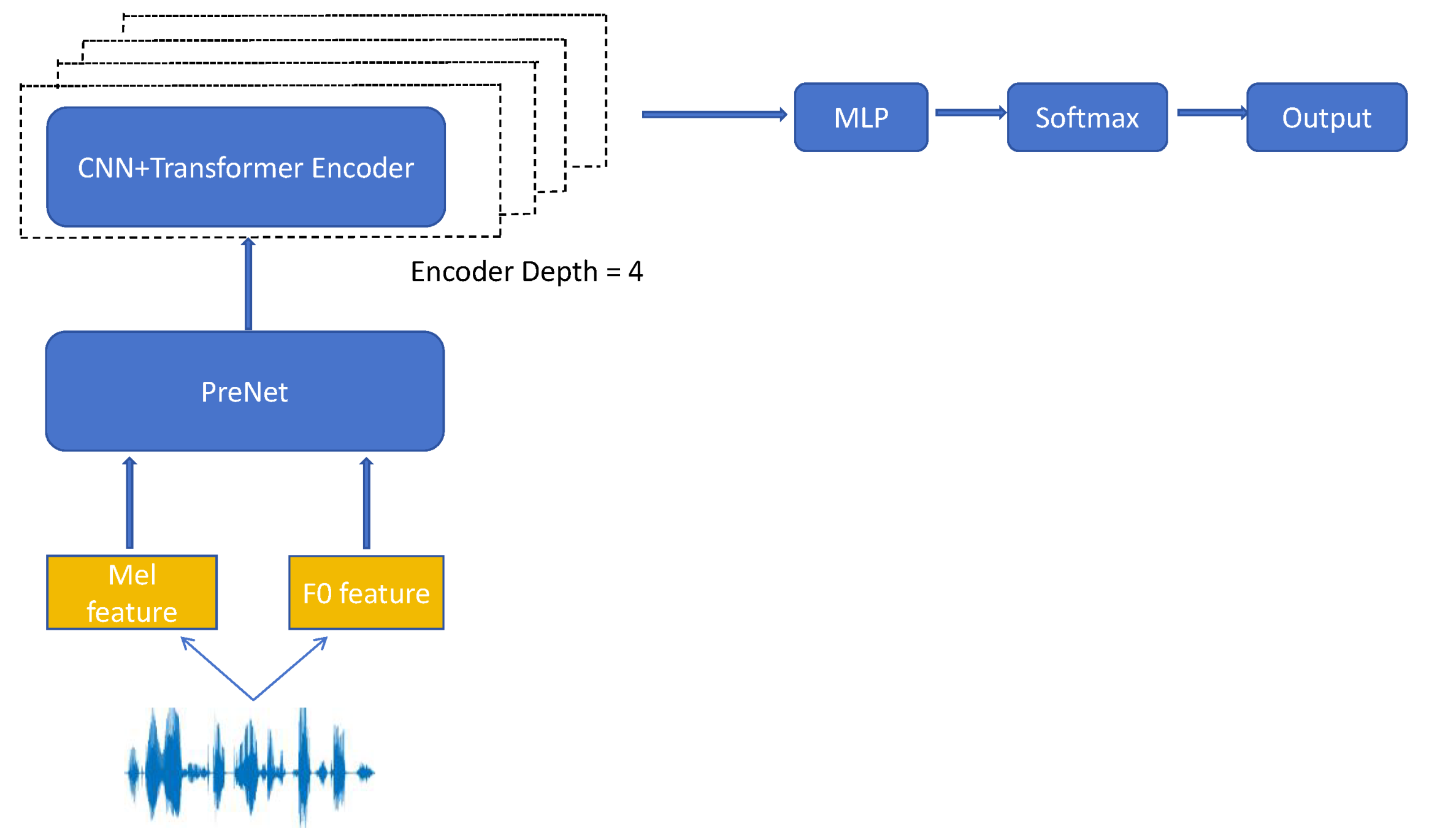
3. Proposed Method
3.1. PreNet
3.2. Transformer-Based Extractor
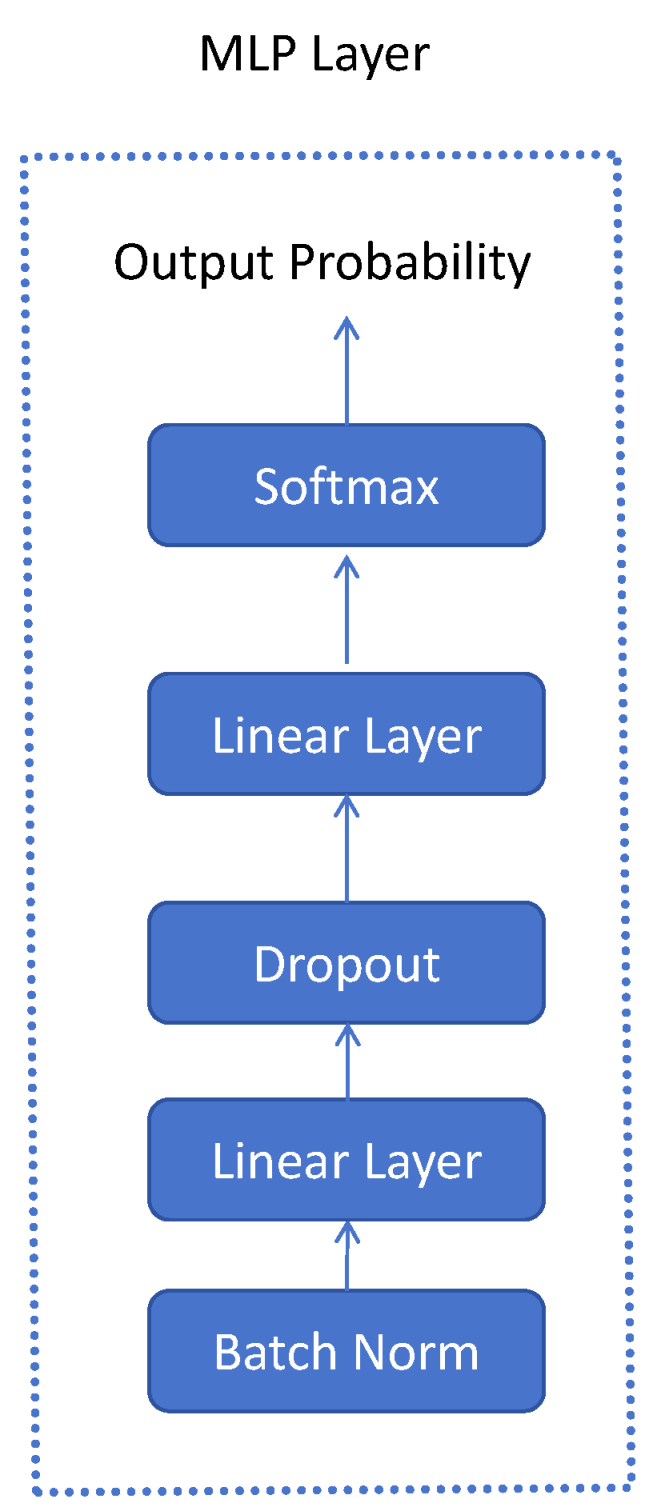
3.3. Back-End Model
4. Experimental Evaluation
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Experimental Setups
4.3. Evaluation Results
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hai, X.; Liu, X.; Tan, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, S.; Niu, W.; Zhou, R.; Zhou, X. What’s the Real: A Novel Design Philosophy for Robust AI-Synthesized Voice Detection. In Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, MM ’24, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 28 October–1 November 2024; pp. 6900–6909. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, L.Y.; Li, X.J.; Chong, P.H.J. Swin-Fake: A Consistency Learning Transformer-Based Deepfake Video Detector. Electronics 2024, 13, 3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.Y.; Li, X.J. A Contemporary Survey on Deepfake Detection: Datasets, Algorithms, and Challenges. Electronics 2024, 13, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Singh, R.; Raj, B. Voice Impersonation Using Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 2506–2510. [Google Scholar]
- Stylianou, Y.; Cappe, O.; Moulines, E. Continuous probabilistic transform for voice conversion. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 1998, 6, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morise, M.; Yokomori, F.; Ozawa, K. WORLD: A Vocoder-Based High-Quality Speech Synthesis System for Real-Time Applications. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 2016, 99-D, 1877–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yi, J.; Tao, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Fu, R.; Chen, X. TO-Rawnet: Improving RawNet with TCN and Orthogonal Regularization for Fake Audio Detection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.13701. [Google Scholar]
- Gulati, A.; Qin, J.; Chiu, C.C.; Parmar, N.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Han, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; et al. Conformer: Convolution-augmented transformer for speech recognition. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.08100. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yamagishi, J.; Todisco, M.; Delgado, H.; Nautsch, A.; Evans, N.; Sahidullah, M.; Vestman, V.; Kinnunen, T.; Lee, K.A.; et al. ASVspoof 2019: A large-scale public database of synthesized, converted and replayed speech. Comput. Speech Lang. 2020, 64, 101114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitela, A.D.; Monson, B.B.; Lotto, A.J. Phoneme categorization relying solely on high-frequency energy. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 137, EL65–EL70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, NIPS’17, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
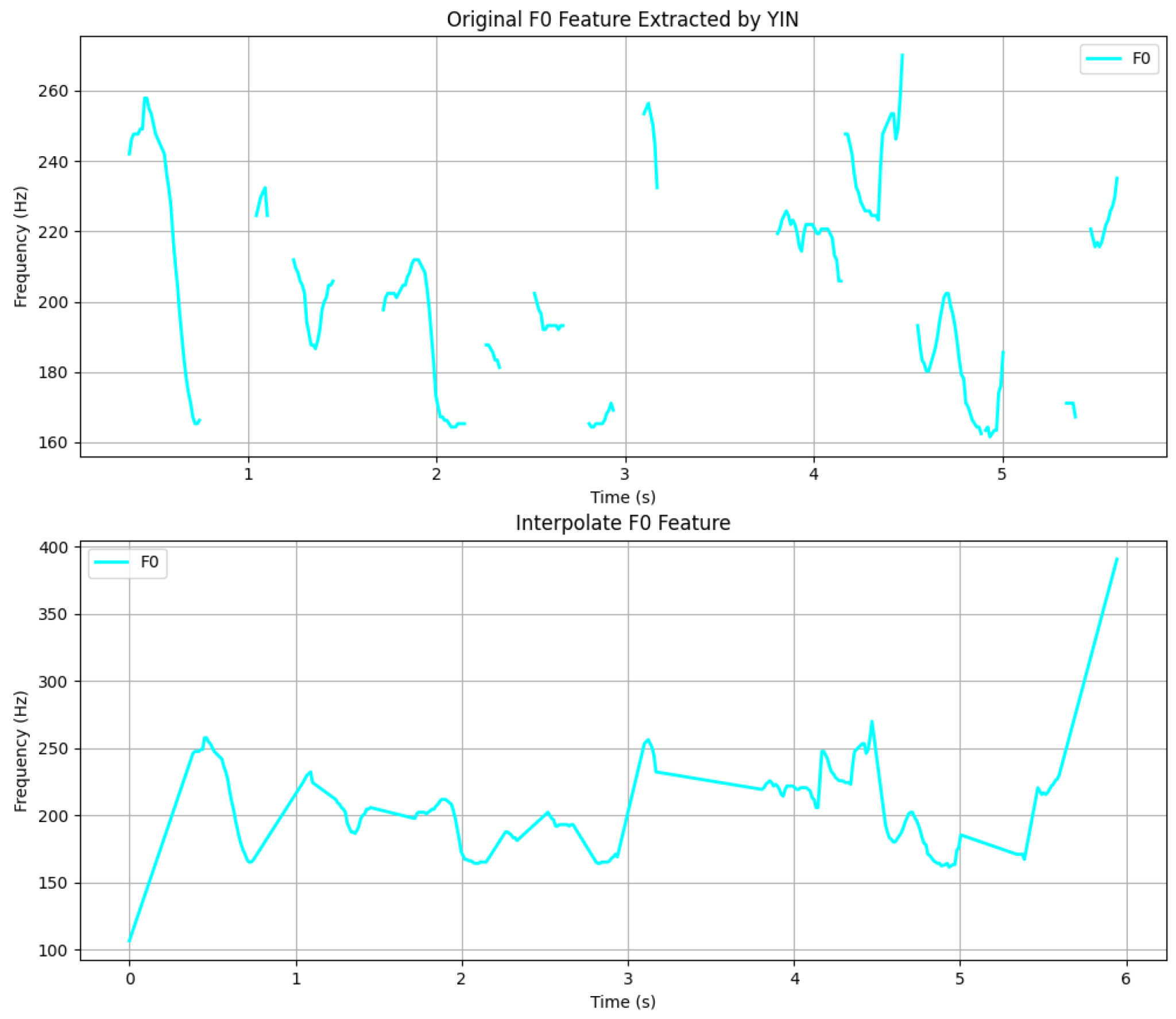
- Cheveigné, A.; Kawahara, H. YIN, A fundamental frequency estimator for speech and music. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002, 111, 1917–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaremba, W.; Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O. Recurrent Neural Network Regularization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.2329. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Pang, R.; Weiss, R.J.; Schuster, M.; Jaitly, N.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Skerrv-Ryan, R.; et al. Natural TTS Synthesis by Conditioning Wavenet on MEL Spectrogram Predictions. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 4779–4783. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Jung, H.Y.; Lee, M. Vocoder-free End-to-End Voice Conversion with Transformer Network. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Piscataway, NJ, USA, 19–24 July 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Su, Z. Detection of Voice Transformation Spoofing Based on Dense Convolutional Network. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019—2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 2587–2591. [Google Scholar]
- Ballesteros, D.M.; Rodriguez-Ortega, Y.; Renza, D.; Arce, G. Deep4SNet: Deep learning for fake speech classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 184, 115465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, H.; Patino, J.; Todisco, M.; Nautsch, A.; Evans, N.; Larcher, A. End-to-End anti-spoofing with RawNet2. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 6369–6373. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, A.; Yang, S.W.; Chi, P.H.; Hsu, P.c.; Lee, H.y. Mockingjay: Unsupervised Speech Repre- sentation Learning with Deep Bidirectional Transformer Encoders. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 6419–6423. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Yi, X.; Zhao, X. Fake Speech Detection Using Residual Network with Transformer Encoder. In Proceedings of the 2021 ACM Workshop on Information Hiding and Multimedia Security, IHMMSec ’21, Virtual, 22–25 June 2021; pp. 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1800–1807. [Google Scholar]
- ASVspoof 2021 Dataset Download Url. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/serjkalinovskiy/asvspoof2021-df (accessed on 7 June 2024).
- Jung, J.w.; Heo, H.S.; Tak, H.; Shim, H.j.; Chung, J.S.; Lee, B.J.; Yu, H.J.; Evans, N. AASIST: Audio Anti-Spoofing Using Integrated Spectro-Temporal Graph Attention Networks. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 6367–6371. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Q.; Teng, Z.; White, J.; Powell, M.; Schmidt, D.C. FastAudio: A Learnable Audio Front-End for Spoof Speech Detection. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tak, H.; Jung, J.W.; Patino, J.; Kamble, M.; Todisco, M.; Evans, N. End-to-end spectro-temporal graph attention networks for speaker verification anti-spoofing and speech deepfake detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.12710. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, Y.; Wang, S. Multi-Task Learning Improves Synthetic Speech Detection. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 6392–6396. [Google Scholar]
| Experimental Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Sample rate (SR) | 16,000 |
| Hop length | 256 |
| Mel-frequency channels | 80 |
| Multi-head attention number | 8 |
| Dropout rate | 0.2 |
| Model dimension | 1024 |
| Feed-forward network dimension | 2048 |
| Detectors | Dev EER | Eval EER |
|---|---|---|
| RawNet2 | 10.28% | 28.96% |
| AASIST | 14.40% | 30.96% |
| Fastaudio | 12.76% | 32.56% |
| MTLISSD | 27.31% | 37.56% |
| RawGAT-ST | 17.39% | 32.28% |
| Our model | 9.27% | 26.41% |
| Detectors | Eval EER |
|---|---|
| RawNet2 | 34.39% |
| AASIST | 32.15% |
| Fastaudio | 28.93% |
| MTLISSD | 43.75% |
| RawGAT-ST | 49.64% |
| Our model | 28.52% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, L.Y.; Li, X.J. Deepfake Voice Detection: An Approach Using End-to-End Transformer with Acoustic Feature Fusion by Cross-Attention. Electronics 2025, 14, 2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102040
Gong LY, Li XJ. Deepfake Voice Detection: An Approach Using End-to-End Transformer with Acoustic Feature Fusion by Cross-Attention. Electronics. 2025; 14(10):2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102040
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Liang Yu, and Xue Jun Li. 2025. "Deepfake Voice Detection: An Approach Using End-to-End Transformer with Acoustic Feature Fusion by Cross-Attention" Electronics 14, no. 10: 2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102040
APA StyleGong, L. Y., & Li, X. J. (2025). Deepfake Voice Detection: An Approach Using End-to-End Transformer with Acoustic Feature Fusion by Cross-Attention. Electronics, 14(10), 2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102040






