Abstract
Mental workload is an important predisposing factor for mental illnesses such as depression and is closely related to individual mental health. However, the suboptimal accuracy of utilizing photoplethysmography (PPG) exclusively for mental workload classification has constrained its application within pertinent professional domains. To this end, this paper proposes a signal processing method that combines continuous wavelet transform (CWT) and cardiopulmonary coupling mapping (CPC) to classify mental load via a convolutional neural network (ResAttNet). The method reflects changes in mental workload, as assessed by changes in the association between heart rate variability and respiration. In this paper, the strengths and weaknesses of this method are compared with other traditional psychological workload monitoring methods, such as heart rate variability (HRV), and its validation is performed on the publicly available dataset MAUS. The experiments show that the method is significantly better than previous machine learning methods based on heart rate variability correlation. Meanwhile, the accuracy of the method proposed in this paper reaches 80.5%, which is 6.2% higher than in previous studies. It is comparable to the result of 82.4% for the ECG-based mental workload monitoring system. Therefore, the method of combining CWT and CPC has considerable potential and provides new ideas for mental workload classification.
1. Introduction
Mental workload is the psychological burden that people experience when dealing with cognitive tasks, thinking [1], and decision-making. It is usually associated with factors such as attention, working memory, thinking ability, and mental stress. Prolonged exposure to high levels of mental load can affect personal lives and relationships, diminish job performance, and even negatively impact physical and mental health. Individuals may experience physical symptoms such as fatigue, insomnia, headaches, muscle tension, and digestive problems. In addition, high-stress states can lead to mood problems, depression, and emotional fatigue. Therefore, understanding mental load is essential for individuals and organizations [2]. It can help us rationally allocate cognitive resources and improve work efficiency, as well as prevent and manage stress and fatigue and promote physical and mental health.
Early monitoring of mental workload often employs electroencephalographic (EEG) signals, which constitute a method of obtaining information about mental activity by detecting voltage changes induced by neurons on the surface of the scalp cortex [3]. The signals generated by this electrical activity can be categorized into different frequency bands, such as α, β, θ, and δ waves. The different frequency bands and their relative intensities can reflect the cognitive state and mental load of the brain. Typically, beta waves are associated with alertness, cognitive activity, attention, and decision-making [4].
Iwanaga et al. found a correlation between mental load and physiological information such as blood pressure (BP) and heart rate (HR). This finding suggests that physiological parameters other than EEG signals can also be used to assess and monitor mental load [5]. Salahuddin et al. focused on the activity of the autonomic nervous system and determined the role of the autonomic nervous system in the regulation of mental load by analyzing heart rate variability (HRV) and other autonomic indicators [6]. Tamantini et al. extracted cardiorespiratory information and compared it as features in different machine learning models. The results show that machine learning algorithms are quite effective in risk monitoring [7].
At the present stage of research on the classification of mental workload using photoplethysmography (PPG), the signal is most popular due to its acquisition process, which does not depend on targeted implantation of sensors or transducers. PPG signals have the advantage of being non-invasive and easy to acquire in real time [8]. Compared to other physiological signals, such as ECG and EEG, PPG signals are more advantageous in the smart wearable space, where users can simply wear the device on their wrist or in other areas for real-time monitoring. In contrast, ECG and EEG devices typically require more electrodes and leads, as well as more specialized knowledge and skill to place and operate them correctly, making prolonged wear less practical. Therefore, although PPG signals may have motion artefacts that require manipulation, such as filtering and reconstruction [9], the use of PPG signals for the identification of cognitive load is still essential for studies that require long-term real-time monitoring (e.g., brain workload monitoring). At the same time, photoplethysmography technology allows for the acquisition of a wide range of physiological parameters, such as heart rate, HRV, and pulse waveform. These parameters provide a wealth of information about the activity of the cardiovascular system and cardiac function, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of the effects of mental workload.
In many past research studies, some researchers tended to use HRV feature sequences, NNI sequences, or 1D PPG signals as inputs in the problem of mental load recognition because these methods have been proven to be relevant to mental workload and do not require much pre-processing. Other researchers have taken into account the properties of convolutional neural networks and transformed 1D signals into 2D maps to facilitate network learning. Among them, methods such as Poincaré plots and continuous wavelet variation (CWT) have been used quite extensively [10].
Cinaz et al. used a wearable device to monitor mental load levels in everyday office-work scenarios. Their study demonstrated the feasibility of using physiological characteristics (e.g., HRV) to assess mental workload in real-life situations [11]. Liang et al. investigated the relationship between handcrafted features and mental workload, generating feature sets across multiple timescales from the perspectives of handcrafting and a deep learning (DL) analysis [12]. Xiao Z et al. investigated the influence of PPG morphology changes on mental workload, and this study concluded that PPG morphology characteristics can respond to mental load changes [13]. Some of the researchers used upscaling to process the signals; the study of Muhammad et al. employed the continuous wavelet transform method to process the signals and used the migration learning method to solve the problem of too-few samples [14]. The study by Zubair and Yoon extracted beat-by-beat interval sequences from PPG signals and used them to extract Poincaré diagrams as input to capture temporal information [15]. Some other researchers have compared both PPG and ECG signals, and Beh et al. proposed an outlier removal mechanism, an ECG-assisted labeling method, and developed an uncertainty estimation model to reduce the detrimental effect of the invalid inter-beat interval (IBI) in PPG signals. The experimental results show that the PPG signal can achieve the accuracy of the ECG signal in mental burden monitoring [16].
Cardiopulmonary coupling mapping (CPC) was first proposed in the field of sleep medicine as a quantitative measure of the interaction between heart rate and respiration. Thomas et al. investigated the relationship between CPC and the autonomic nervous system [17]. They developed a spectral method using ECG signals to dynamically track changes in CPC during sleep. From their findings, it is clear that CPC is highly correlated with changes in the autonomic nervous system. However, mental loads often lead to disturbances in the autonomic nervous system, including changes in heart rate and altered breathing patterns. By analyzing the interrelationship between cardiac activity and respiratory activity in cardiopulmonary coupling mapping, the response of the autonomic nervous system of an individual in the face of stress can be indirectly reflected, and the degree and impact of mental stress can then be inferred. Although early CPC algorithms were computed based on ECG signals and by synthesizing the relationship between cardiac and respiratory signals to reveal how cardiac activity is affected by respiratory patterns, any physiological signals that can be extracted from both cardiac and respiratory signals can be computed by CPC algorithms.
These results suggest that PPG signaling has excellent potential in the field of mental load monitoring. However, despite the multitude of related studies, the differences in mental load induction trials lead to too large of a gap in the performance of different methods studied in different datasets for direct comparison. For this reason, this study designed three sets of trials to objectively compare the performance of different treatments on the same dataset. This study aims to demonstrate that two-dimensional images extracted from raw PPGs using CPC combined with deep learning methods are superior to methods using features extracted from the IBI of the PPGs or time series for mental load classification.
Specifically, our contributions are listed below:
- In this paper, we propose a new interpretable pre-processing feature transformation method for mental load classification.
- This paper compares multiple feature extraction methods commonly used in the past on the same dataset to obtain a relatively objective conclusion.
- The method proposed in this paper achieves a performance that approximates the performance of using ECG signals when only PPG signals are used.
The remaining part of this paper is organized as follows: In Section 2, we first introduce the signal processing methodology proposed in this study and the models involved in the experiments. After that, we report all the results and data of this study in Section 3. Next, we analyze and discuss the results in detail in Section 4. Finally, we summarize our work in Section 5.
2. Materials and Methods
In this study, three commonly used machine learning methods were considered to classify mental burdens in PPG single. Three sets of trials were designed to evaluate the performance and effectiveness of these methods. The purpose of these trials was to investigate the ability of the selected machine learning algorithms to accurately classify mental burdens based on PPG data.
The research process is illustrated in Figure 1. On the left side of the flowchart is the content of Trial II, which includes the feature extraction of heart rate variability (HRV) and the training process of machine learning models. On the right side of the flowchart are sections related to Trial I and Trial III. Specifically, in Trial I, derived sequences are extracted through methods such as amplitude recognition and Empirical Mode Decomposition, and a one-dimensional convolutional neural network is utilized for training. In Trial III, the derived sequences from Trial I are further processed to generate 2D spectrograms and a neural network is trained to classify mental workload. The detailed descriptions of the trials are as follows.
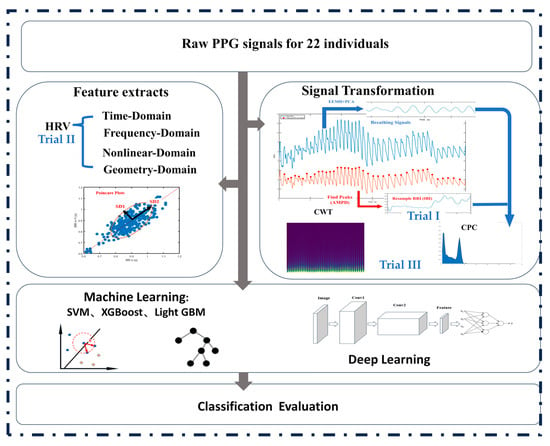
Figure 1.
The flowchart of this study. Note: PPG refers to photoplethysmography; EEMD, PCA, and AMPD refer to Ensemble Empirical Modal Decomposition, Principal Component Analysis, and automatic multiscale-based peak detection, respectively; CWT and CPC denote continuous wavelet transform and cardiopulmonary coupling map.
Trial I: In this trial, the use of one-dimensional sequences as input dimensions for mental workload classification was considered. The original PPG signal and its derived heart rate variability sequence, NNI, were extracted as inputs for this trial, while the classical 1DCNN+LSTM model was chosen.
Trial II: This trial considered the use of handcrafted features for mental workload classification. Thirty-one HRV features were extracted as inputs for this experiment, and their details are presented later. Meanwhile, the classical machine learning models, such as XGBoost, were chosen.
Trial III: In this trial, the sequences in Trial I were considered to be upscaled and transformed into 2-dimensional images as the model inputs for mental load classification. The methods of CPC and CWT were chosen for this purpose. The classical ResNet model was modified and used as the model for this part, with detailed model parameters described later.
2.1. Database
This study focuses on the assessment of mental workload level by which PPG signals are categorized from the MAUS dataset [18], a dataset that focuses on the relationship between wearable sensing signals and brain workload. It is a publicly available dataset that uses the N-back classical experimental paradigm as a source of mental workload. The N-back experimental paradigm is a commonly used psychological experiment. In an N-back task, participants are required to judge, based on a series of presented stimuli (e.g., numbers, letters, or graphs), whether the currently presented stimulus is the same as one of the previously presented stimuli. The value of N can vary depending on the experimental design, and it is usually 1-back, 2-back, or 3-back, among others. The N-back task allows researchers to assess participants’ working memory capacity, attentional control, and mental load on the brain. Typically, subjects participating in tasks with more than 2 backs are considered to be under high mental workloads.
The dataset contains numerous physiological signals, such as the Galvanic Skin Response (GSR), ECG, PPG, and other signals from 22 healthy individuals without cardiovascular disease. Each individual was provided with 35 min of signaling, consisting of 5 min of baseline signaling and 6 phases of 5 min of signaling under load in each phase.
This study focuses on the relationship between fingertip PPG signals and mental workload.
2.2. Signal Pre-Processing
- (1)
- Signal filtering
In this study, different signal processing methods were used for different feature extractions. Specifically, for Trial I and Trial III, 30-second-long PPG signals were taken as input, and a 5 s sliding window was used for data enhancement. A total of 7260 data segments were obtained. A data length of 30 s proved to be sufficient to reflect the cardiac variability information [19]. For Trial II, the recommendations of Castaldo et al. were adopted, and we used a 2-minute window per session, overlapping for 30 s to extract HRV features [20]. Subsequently, labels were added for the mental workload level based on the experimental difficulty of N-back. Specifically, data segments under 2-back and 3-back experiments were given the label of high mental workload. However, due to the long duration of mental load data and acquisition, most subjects will have various noises in the acquired signals due to wearing each experimental device for a long period of time, as well as high workload. In this study, a Butterworth second-order 8Hz zero-phase low-pass filter was used to preserve the low-frequency signal characteristics, especially the respiration-related characteristics.
- (2)
- Derived sequence extraction
For Trial I, two common physiological signals, namely the heart rate sequence and respiration sequence, were extracted from the PPG signal. The difference in the peak sequence of the PPG can be an excellent response to the time between two heartbeats. This means that we can obtain the instantaneous heart rate sequence from it. At the same time, the low-frequency component of the PPG and the envelope transformation of the waveform are affected by the respiratory rise and fall. In this study, the VPG signal was obtained via the first-order differentiation of the PPG signal because the peaks of the VPG have a higher detection contrast than the PPG. The AMPD [21] algorithm was used to detect peaks, as it is an adaptive frame-based peak-finding algorithm for periodic signals. As suggested by previous studies, data with peak-to-peak intervals greater than 1200 ms or less than 600 ms were excluded. The excluded data were populated with 3-fold spline interpolation and normalized in the frequency domain by resampling to 4 Hz, which is much greater than the maximum frequency of 2-fold instantaneous heart rate variability and therefore does not suffer from spectral aliasing [22]. The specific process is shown in Figure 2. The extraction of respiratory signals was conducted based on the trial conducted by Motin and colleagues, wherein the Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition (EEMD) and Principal Component Analysis (PCA) algorithms were utilized to extract respiratory waveforms by performing a PCA analysis on the Intrinsic Mode Functions (IMFs) that contained the respiratory frequency [17]. Figure 3 illustrates the specific extraction process of the respiratory signal.
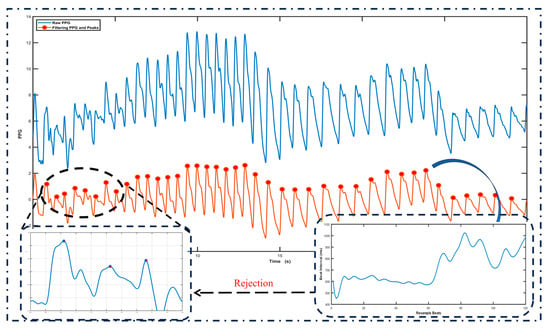
Figure 2.
AMPD peak recognition algorithm. Note: Raw PPG denotes the original pulse wave signal; Filtering PPG and Peaks denote the filtered PPG signal, with red dots marking the peaks; and IBI is the sequence of peak intervals of a 30-second pulse wave resampled to 4 Hz.
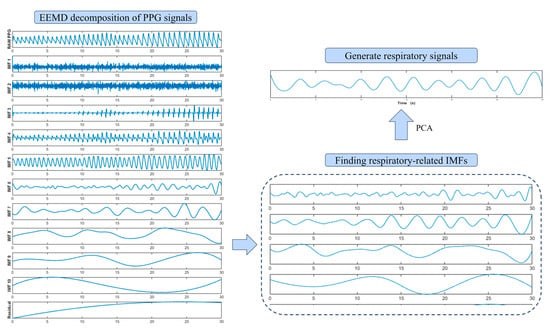
Figure 3.
The breathing wave extraction flowchart; Note: EEMD and PCA represent the integrated set empirical modal decomposition and Principal Component Analysis, respectively; IMF is the eigenmode function after modal decomposition, and the main frequency range of the selected IMF is between 0.2 and 0.4 Hz.
- (3)
- PPG feature extraction
For Trial II, numerous features based on the IBI were extracted that have been shown to be associated with mental workload, such as HRV features. HRV was shown to tend to diminish when individuals are in a high mental load environment [23]. The extracted features are shown in Table 1, whose detailed feature descriptions are listed in Appendix A.

Table 1.
Extracted features.
- (4)
- Signal Transformation
The sympathetic nervous system is usually activated when mental load occurs, such as when an individual experiences emotional excitement, tension, anxiety, and stress [24]. On the one hand, this change triggers a physiological response in the sympathetic nervous system, releasing epinephrine and norepinephrine. Epinephrine and norepinephrine are neurotransmitters of the sympathetic nervous system, and they have an important effect on the excitability of the heart [25]. This results in an increased heart rate and an increased cardiac pumping force to meet the body’s need for oxygen and energy under mental load. On the other hand, breathing usually becomes faster and deeper when the mental load increases [26]. This is the body’s instinctive response to provide an adequate supply of oxygen and to expel excess carbon dioxide. Activation of the sympathetic nervous system can also affect the respiratory center, resulting in faster and deeper breathing. The use of respiration and heart rate variability for monitoring mental workload was attempted as early as 2019 [27], but there have yet to be studies assessing mental load in terms of coupled heart rate and respiration variability.
In this paper, the PPG signal is used as the input signal to extract the NNI sequence containing cardiac information and the respiratory wave containing respiratory information through peak identification and EEMD combined with PCA, respectively. Figure 4 shows the overall flow and principle of the CPC algorithm.
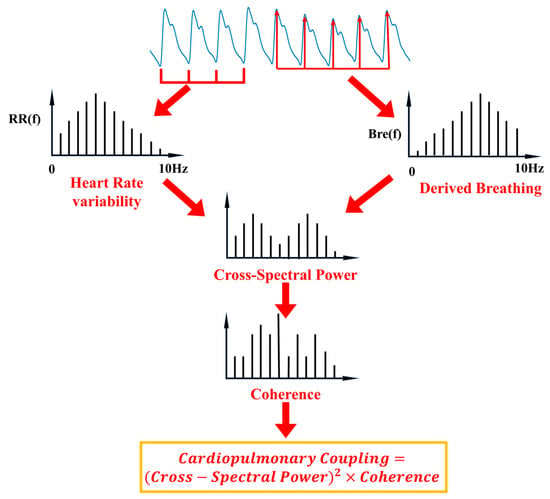
Figure 4.
Sequential steps for deriving cardiopulmonary coupling measurements. See section on math and technology for technical details.
Cardiopulmonary coupling algorithms: math and technology
Extraction of 2 physiologic time series from PPG signal: (1) the generation of heartbeat interval sequence based on PPG peak recognition is denoted as , and (2) the derived respiratory wave signals extracted based on EEMD and PCA are denoted as . There are two key factors to consider when assessing the strength of the coupling between these two signals: At a given frequency, if both signals oscillate with relatively large amplitudes, then they are likely to be coupled to each other [28]. This effect can be measured by calculating the cross-spectral power, which is the product of the power of the two signals at a given frequency. Further, if two oscillations of a given frequency are synchronized (i.e., they maintain a constant phase relationship), then this effect can be measured by calculating the coherence of these signals. The detailed calculation process is as follows.
Fourier transform: First, the heartbeat interval sequence, , and the derived respiratory wave signal, , are Fourier-transformed separately to obtain their spectra:
where and denote the representation of the heartbeat interval, , and the derived respiratory wave signal, , in the frequency domain, respectively.
Cross-spectral power: The cross-spectral power of two signals at a given frequency, f, can be calculated by multiplying their spectra:
where denotes the cross-spectral power at frequency, ; denotes the spectrum of the heartbeat interval, ; denotes the spectrum of the respiratory wave signal, ; and * denotes complex conjugation.
Coherence: The coherence of two signals at a given frequency, , can be calculated by the following equation:
where denotes coherence at frequency, ; is the cross-spectrum power; and and are the power spectra of heartbeat intervals, , and respiratory wave signals, , respectively.
Cardiopulmonary coupling index: the cardiopulmonary coupling index is the product of coherence and cross-spectral power squared and can be defined as follows:
This CPC value indicates the degree of cardiopulmonary coupling, and multiple CPC values can be calculated at different frequencies to reflect coupling in different frequency ranges. Figure 5 shows the actual calculation process.
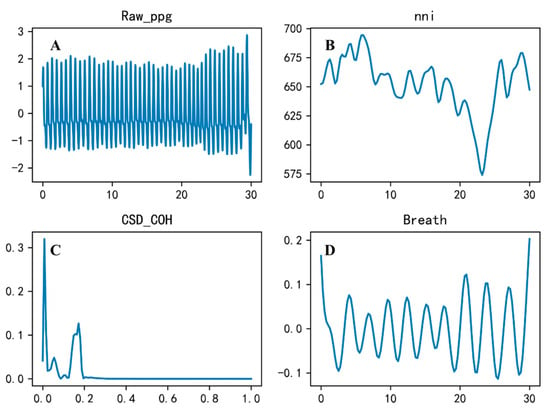
Figure 5.
Diagram of the cardiopulmonary coupling calculation process. Note: (A) Raw_ppg is the raw pulse wave sequence. (B) nni is the peak pulse wave interval sequence, resampled to 4 Hz. (C) CSD_COH is the sequence of cardiorespiratory coupling value calculations. (D) Breath is the derived respiratory signal, resampled to 4 Hz; the lengths of nni and breath are both 30 s, and the CSD_COH is the range of the frequency domain sequence (0 to 1 Hz).
In this study, CWT is a mathematical tool used to analyze the local features of a signal, especially the frequency features in the signal. It is based on a set of wavelet functions that can be translated and scaled to fit different parts of the signal. The CWT’s advantage regarding the PPG signal is that it can extract multi-scale features of the signal [29]. The continuous wavelet transform is able to decompose the signal in different frequency ranges, capturing the time–frequency characteristics of the pulse signal. The schematic spectrum of the signal transformation is shown in Figure 6.
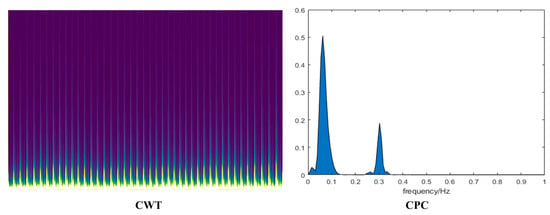
Figure 6.
Two maps for converting 1D signals to 2D images. CWT represents continuous wavelet transform, and CPC represents cardiopulmonary coupling map.
2.3. Machine and Deep Learning Model
As early as the 1950s, machine learning took shape. The early machine learning methods are mainly based on statistics and pattern recognition theory [30]. In this study, different machine learning classifiers were used based on different trials. Meanwhile, considering the rigor of the experiment, this study divided the dataset by subjects, with data from 17 subjects as the training set and data from 5 subjects as the test set. To be precise, in the machine learning part, this study used 714 segments of 2-min PPG signals to extract heart rate variability features for training and 210 segments of data for testing. In the deep learning part, we extracted 5558 30-s PPG signal segments to form the training set and 1596 segments to form the test set. The actual number of data segments is slightly less than the theoretical number of segments (7260 segments) because some signal segments were discarded due to poor quality.
CNN-LSTM: In Trial I, the classical one-dimensional 1DCNN+LSTM model was adopted, based on the methodology proposed by Mumtaz et al. This model configuration was utilized for the analysis and processing of the data in our study [21], which combines a one-dimensional convolutional neural network (CNN) with a bidirectional long-short-term memory (LSTM) network. The specific model architecture is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Detailed architecture of the CNN-LSTM network model.
Machine learning model: In Trial II, the extracted feature sequences were classified using machine learning techniques. Three commonly used machine learning algorithms, namely Support Vector Machine (SVM), XGBoost, and LightGBM, were compared to assess the influence of different classifiers. These algorithms were employed to evaluate the performance and effectiveness of the classification process. Among them, Support Vector Machine (SVM) is a binary classification algorithm based on the principle of maximum spacing, and XGBoost is an integrated algorithm for gradient boosting decision trees. LightGBM is a framework for the efficient implementation of gradient-boosting decision trees; it has a fast training speed and low memory consumption. These 3 algorithms have made a big splash on the Kaggle competition platform in recent years and have been used quite extensively in PPG signaling [31].
In machine learning, the performance of a model is often strongly influenced by the choice of hyperparameters, and in this study, Bayesian optimization was used to tune the hyperparameters of these models to help improve their performance and generalization. Bayesian optimization is a probabilistic model-based optimization method that finds the optimal solution in a finite number of iterations by modeling a proxy for the objective function (usually a Gaussian process) in the parameter space and using Bayesian inference to select the next most promising combination of parameters. Bayesian optimization can intelligently explore the hyperparameter space, avoiding the inefficiency and waste of computational resources found in traditional grid search or stochastic search methods. Table 3 and Table 4 show the main parameters of the models used in this paper.

Table 3.
SVM parameters.

Table 4.
XGBoost and LightGBM search space.
ResAttNet: In Trial III, a simple adaptation of the classical ResNet was made to realize ResAttNet with improved robustness in the field of mental load classification. ResAttNet, as a whole, consists of 2 modules. That is a 6-layer ResNet module and an attention mechanism module. The model first performs feature extraction on the input image through an initial convolutional layer and processes the data through batch normalization and activation functions. The model then passes the feature map to six ResNet blocks. Each ResNet block consists of two convolutional layers, batch normalization, and ReLU activation functions, and it directly sums the inputs to the outputs via jump-joins in order to preserve more low-level features.
Next, the model reduces the feature map to a vector by global average pooling. The feature vector is then processed through a densely connected layer to further extract and re-represent important feature information. To better focus on key features, the model introduces a channel attention mechanism. This mechanism generates a weight vector through a global average pooling operation and two fully connected layers and then multiplies the weight vector with the feature map, allowing the model to focus more on features that are more informative for the classification task. Finally, the model reduces the feature graph to a vector through a global average pooling layer and maps the feature vector to a softmax layer containing two output nodes through a fully connected layer. In this way, the model can perform image classification based on the extracted features. The model is characterized by the use of ResNet blocks to solve the gradient dispersion problem in deep networks and by jump connections to improve the training of the model. In addition, the model introduces an attention mechanism, which enables the model to focus more on important features and improves the classification accuracy. The structure of the ResAttNet network is shown in Figure 7.
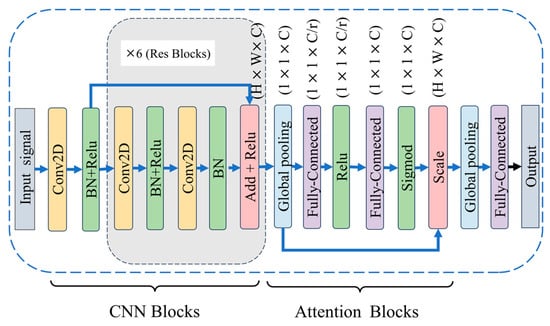
Figure 7.
Network structure of the ResAtt model. Note: CNN stands for convolutional neural network, and attention denotes channel attention mechanism.
2.4. Performance Evaluation
In this paper, six classical classification evaluation indexes are used in our study to assess the performance of the classification model, namely (accuracy), (precision), (sensitivity), (specificity), , and value (area under the ROC curve), to carry out a comprehensive evaluation of our novel signal pre-processing method. The following is the formula and description of each evaluation index:
In this trial, the network model is trained on a deep learning workstation with the following hardware facility details: the CPU is a 14-core Intel Xeon CPU E5-2690 v4 @ 2.60 GHz, the GPU graphics card with a quad Nvidia Titan Xp of 12G display memory, and the RAM with 192 GB.
3. Results
Feature extraction and signal transformation are commonly employed techniques for one-dimensional signal processing in the context of machine learning, unlike images or text sequences, which do not have direct visibility or textual meaning. Often, it is difficult for researchers to gain direct insight into an individual’s physiology based on the physiological signals themselves. With the intensive research on PPG measures of mental load, a variety of pre-processing methods have emerged. In this paper, these methods are stratified according to the difference in input dimensions in three trials, and for each trial, one or several classical models that have been proven to be useful are selected. Table 5 and Figure 8 below show a comparison of the operations and results for each trial.

Table 5.
Comparison of results of different PPG signal processing methods.
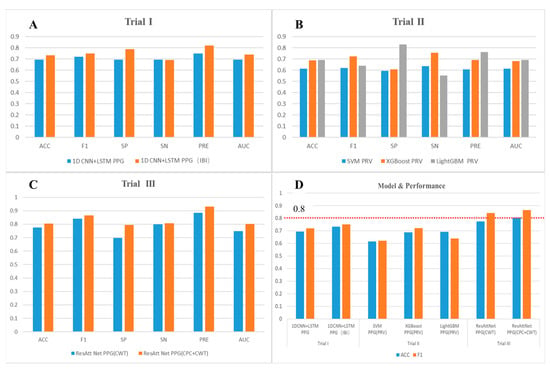
Figure 8.
Comparative graphs of experimental results. Note: (A) Histogram of results for Trial I. (B) Histogram of results for Trial II. (C) Histogram of results for Trial III. (D) Comparison of results across models.
ECG signals are often used as a standard for PPG signals because they are highly correlated, as they are both signals generated by the heartbeat, and, typically, ECG signals contain a more stable waveform, with less noise, than PPG [32]. In this study, ECG signals were also compared. The processing of ECG signals is basically the same as that of PPG, and we only changed the signal filtering operation in the pre-processing because ECG signals have a larger frequency band. For ECG signals, a Butterworth second-order low-pass filter at 40 Hz was chosen in this paper. The reason for choosing a low-pass filter was the same as for the PPG; the cutoff frequency was set to 40 Hz, which effectively removes the IF interferences and has little effect on the main features of interest in this study (heart rate variability and respiration). The experimental setup for ECG was identical to that of PPG. Table 6 and Figure 9 below show a comparison of the operation and results of each trial.

Table 6.
Comparison of results of different ECG signal processing methods.
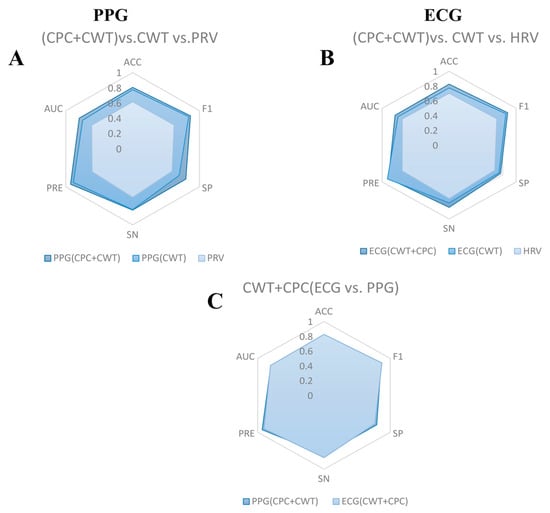
Figure 9.
Model performance for different treatments. (A) PPG: (CPC+CWT) vs. CWT vs. PRV. (B) ECG: (CPC+CWT) vs. CWT vs. PRV. (C) CWT+CPC (ECG vs. PPG). Notes: CPC, CWT, and HRV denote cardiopulmonary coupling, continuous wavelet transform, and heart rate variability, respectively. ACC denotes accuracy, PRE denotes precision, AUC denotes area under the curve, SP denotes specificity, and SN denotes sensitivity.
The method proposed in this study is compared with the results of other related studies, and Table 7 shows the details of the comparison. Higher accuracy results are indicated in bold. The results show that the accuracy of this study exceeds most of the similar studies. Only Gurel’s study and ours reached more than 80% accuracy; unlike their multi-signal fusion, the present technique only used the PPG signal, which is much easier to access. It demonstrates the strong potential of cardiopulmonary coupling algorithms for mental load recognition.

Table 7.
Performance comparison between the proposed system and related work.
4. Discussion
In past studies, HRV has been widely used for mental load monitoring because of its excellent interpretability. However, HRV measurements have certain requirements for sequence length. Usually, researchers need 2 min of data for more accurate calculations. In this paper, a method of feature fusion of continuous wavelet transform with CPC mapping for mental load monitoring is proposed and validated on the publicly available dataset MAUS, as well as the newly collected dataset in this study. In order to examine the reliability of the research method proposed in this paper compared to past research methods, the various research methods were compared on the same dataset to eliminate the effects arising from dataset differences. The study shows that the signal processing method of CPC and CWT proposed in this paper has a superior performance for mental load monitoring.
Signal processing is a crucial procedure for one-dimensional signals when employing machine learning methodologies. On the one hand, physiological signals are not directly interpretable and require a lot of feature extraction to respond to physiological changes; on the other hand, the physiological system is a tightly knitted whole, and physiological signals contain a large amount of information, but for a specific application, we usually focus on only a part of this information or these features. Signal processing can help us to enhance these features of interest from the raw signal. As shown in Table 4, three trials were designed to compare several processing methods commonly used in the past, and these methods were classified using models that had been proven effective. The results show that deep learning has an advantage over machine learning methods. On the one hand, deep learning requires shorter data segments than machine learning, which makes the same dataset have more signal segments for training using deep learning’s signal processing methods. On the other hand, the feature extraction required for machine learning has higher requirements on signal quality, and in the case of HRV features, for example, the extent to which misidentified peak intervals are a percentage of the overall IBI sequence has been shown to have a significant impact on the HRV values and even machine learning results [36].
In this study, the performance of different signal transformation methods in mental load classification was also compared against deep learning methods. For the network with one-dimensional inputs, the widely used IBI sequences, as well as the filtered sequences of the original signals, were extracted as inputs in this study. The results show that the IBI sequence classifies better than the original filtered sequence for both ECG and PPG signals. This may be due to the fact that the IBI sequence amplifies the heart rate variability features compared to the original filtered signal, making it easier for the same network to learn information related to mental load. However, for networks using two-dimensional inputs, this paper uses CWT mapping, which is a type of mapping in which the signal is time–frequency analyzed and plotted in the form of a heat map. In contrast to Trial I, this use of a two-dimensional atlas as an input typically achieves superior performance than the use of a one-dimensional sequence as an input. This is related to the characteristics of convolutional computation.
In Trial III, this paper tries a signal processing method based on the fusion of CPC and CWT features as the input to the neural network for mental workload classification. As shown in Table 5, the method proposed in this study performs well. Without any special processing and screening, the classification effect using only PPG reaches the performance of ECG. More importantly, CPC mapping has a well-established theoretical basis compared to CWT, which makes the interpretability of the method using cardiopulmonary coupled mapping much higher. On the one hand, the use of CWT and CPC fusion as the network input can preserve all the previous PPG information in order to avoid the loss of some useful information after manual feature screening. On the other hand, CPC mapping can reinforce features that have been proven to be effective, such as heart rate and respiration.
The novelty of this study is to propose a signal processing method based on cardiopulmonary coupling and CWT feature fusion. The cardiopulmonary coupling method is introduced to mental burden monitoring for the first time in this study. Furthermore, an interpretable signal transformation method is provided for deep learning to recognize mental burdens. Compared to previous studies, our method is more targeted. The use of this mental workload estimation method can help monitor the mental workload level of individuals in different tasks or environments. The application potential of this method is wide-ranging and includes, but is not limited to, areas such as employee mental health monitoring in work scenarios, fatigue monitoring for drivers, and cognitive load assessment during student learning. Monitoring and assessing mental workload levels in real time can help improve work efficiency, safety, and personal health.
However, the limitations of the method need to be clearly pointed out. First, the high computational complexity may limit its efficiency in real-time applications. Second, the accuracy of the method may be affected by individual physiological changes, environmental factors, etc., which require further validation and optimization. In addition, different model structural adjustments may also affect the results differently. Therefore, how to effectively reduce the computational complexity and improve the computational efficiency, and how to effectively improve the model structure to improve the recognition accuracy may be the top priority for future research.
5. Conclusions
This paper discusses the use of PPG signals only for mental workload classification and details a method called cardiopulmonary coupling for mental load classification. Also, the researchers propose a CPC and CWT signal processing method. In this study, CWT mapping was used to provide all time–frequency domain information of PPG, while CPC mapping was used to amplify the information of heart rate and respiration related to mental load. The two maps were fed into the neural network by stacking, and the information of the maps was learned by a convolution kernel. The fully connected attention mechanism can effectively weight the extracted feature information, thus focusing more on the information that is effective for mental load classification. Compared to past studies on this dataset, this study achieved a result of 80.47% slightly higher than previous studies. This study also compares multiple signal processing methods commonly used in the past for mental load classification, and through the analysis of the results, the method of transforming into a map using deep learning significantly outperforms the method using traditional HRV features plus machine learning classifiers. The limitation of this study is that it does not consider and compare the effects of different models of the same signal processing method on mental load classification too much; some positive model structure improvements usually have a positive impact on the experimental results, which will be the main direction of our subsequent research. Overall, this study is the first to use the idea of interpretable cardiopulmonary coupling for mental load classification. It is expected that this idea will provide new insights into the field of mental workload monitoring.
Author Contributions
H.Z. and Z.W. performed the experimental research and drafted the manuscript. H.Z. and Y.Z. performed some signal processing and data mining work. S.Y. and Z.C. analyzed and discussed the experimental results. Y.L. designed the study and led this investigation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62101148 and 62361013), Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi (2021GXNSFBA220051), and Guangxi Key Laboratory of Automatic Detecting Technology and Instruments (YQ19114).
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. These data can be found here: https://dx.doi.org/10.21227/q4td-yd35.
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful for the help and computational resources provided by the National Supercomputing Center in Xi’an, Guangxi Human Physiological Information Non-invasive Detection Engineering Technology Research Center, and Guangxi Colleges and Universities Key Laboratory of Biomedical Sensors and Intelligent Instruments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Appendix A. HRV Metrics Covered in This Article and Detailed Description
| Feature Type | Features | Detailed Description of the Features |
| Time domain | mean_nni | Mean of the normal-to-normal intervals (NNIs) |
| sdnn | Standard deviation of the NNIs, indicating overall HRV | |
| sdsd | Standard deviation of successive NNI differences | |
| nni_50 | Number of pairs of successive NNIs that differ by more than 50 ms | |
| pnni_50 | Percentage of NNI pairs differing by more than 50 ms | |
| nni_20 | Number of pairs of successive NNIs that differ by more than 20 ms | |
| pnni_20 | Percentage of NNI pairs differing by more than 20 ms | |
| rmssd | Root mean square of successive NNI differences | |
| median_nni | Median of NNIs indicating the central tendency of HRV values | |
| std_hr | Standard deviation of heart rate values | |
| range_nni | Difference between the maximum and minimum NNIs | |
| cssd | Corrected sum of squares of successive NNI differences | |
| cvnni | Coefficient of variation for NNIs | |
| mean_hr | Mean of heart rate values representing average heart rate | |
| max_hr | Maximum heart rate value observed during the recording period | |
| min_hr | Minimum heart rate value observed during the recording period | |
| Frequency domain | lf | Low-frequency power, representing the contribution of sympathetic and parasympathetic activities |
| hf | High-frequency power, indicating the parasympathetic activity | |
| lf_hf_ratio | Ratio of low-frequency power to high-frequency power | |
| lfnu | Normalized low-frequency power | |
| hfnu | Normalized high-frequency power | |
| total_power | Total power in the HRV signal | |
| vlf | Very low-frequency power reflecting long-term regulatory mechanisms | |
| Nonlinear domain | sd1 | Standard deviation of the points perpendicular to the line of identity in the Poincaré plot |
| sd2 | Standard deviation of the points along the line of identity in the Poincaré plot | |
| ratio_sd2_sd1 | Ratio of sd2 to sd1 | |
| sampen | Sample entropy, measuring the complexity or irregularity of the HRV signal | |
| csi | Cardiac Sympathetic Index | |
| cvi | Cardiac Vagal Index | |
| Modified_csi | Modified Cardiac Sympathetic Index | |
| Geometric domain | triangular_index | Quantifying the distribution of RR intervals |
References
- Dehais, F.; Lafont, A.; Roy, R.; Fairclough, S. A Neuroergonomics Approach to Mental Workload, Engagement and Human Performance. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Li, M.; Bai, B.; Wang, N.; Li, Y. The impact of AI-enabled service attributes on service hospitableness: The role of employee physical and psychological workload. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2022, 34, 1374–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Fan, C.; Fu, H.; Huang, J.; Chen, H.; Luo, X. Measuring and computing cognitive statuses of construction workers based on electroencephalogram: A critical review. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2022, 9, 1644–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevins, A.; Smith, M.E.; Leong, H.; McEvoy, L.; Whitfield, S.; Du, R.; Rush, G. Monitoring Working Memory Load during Computer-Based Tasks with EEG Pattern Recognition Methods. Hum. Factors J. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. 1998, 40, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, K.; Saito, S.; Shimomura, Y.; Harada, H.; Katsuura, T. The Effect of Mental Loads on Muscle Tension, Blood Pressure and Blink Rate. J. Physiol. Anthropol. Appl. Hum. Sci. 2000, 19, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahuddin, L.; Cho, J.; Jeong, M.G.; Kim, D. Ultra Short Term Analysis of Heart Rate Variability for Monitoring Mental Stress in Mobile Settings. In Proceedings of the 2007 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Lyon, France, 22–26 August 2007; pp. 4656–4659. [Google Scholar]
- Tamantini, C.; Rondoni, C.; Cordella, F.; Guglielmelli, E.; Zollo, L. A Classification Method for Workers’ Physical Risk. Sensors 2023, 23, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Q.; Wu, J.; Shen, J.; Ji, X.; Lyu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Assessing cognitive load in adolescent and adult students using photoplethysmogram morphometrics. Cogn. Neurodynamics 2020, 14, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Samper, J.M.; Tamantini, C.; Ávila-Navarro, E.; De La Casa-Lillo, M.; Zollo, L.; Sabater-Navarro, J.M.; Cordella, F. An ML-Based Approach to Reconstruct Heart Rate from PPG in Presence of Motion Artifacts. Biosensors 2023, 13, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-H.; Wu, Y.-C. A Novel Rapid Assessment of Mental Stress by Using PPG Signals Based on Deep Learning. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 21232–21239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinaz, B.; Arnrich, B.; La Marca, R.; Tröster, G. Monitoring of mental workload levels during an everyday life office-work scenario. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2013, 17, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Niu, X.; Wang, L.; Niu, J.; Zhu, X.; Dai, Z. Stress Detection via Multimodal Multitemporal-Scale Fusion: A Hybrid of Deep Learning and Handcrafted Feature Approach. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 27817–27827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lyu, Y.; Hu, X.; Hu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Yin, H. Evaluating Photoplethysmogram as a Real-Time Cognitive Load Assessment during Game Playing. Int. J. Hum.–Comput. Interact. 2018, 34, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Ullah, K.; Asif, M.; Waheed, A.; Haq, S.U.; Zareei, M.; Biswal, R.R. ECG-Based Driver’s Stress Detection Using Deep Transfer Learning and Fuzzy Logic Approaches. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 29788–29809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Yoon, C. Multilevel mental stress detection using ultra-short pulse rate variability series. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 57, 101736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beh, W.-K.; Wu, Y.-H.; Wu, A.-Y. Robust PPG-Based Mental Workload Assessment System Using Wearable Devices. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2023, 27, 2323–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, R.J.; Mietus, J.E.; Peng, C.-K.; Goldberger, A.L. An Electrocardiogram-Based Technique to Assess Cardiopulmonary Coupling During Sleep. Sleep 2005, 28, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beh, W.-K.; Wu, Y.-H.; Wu, A.-Y. MAUS: A Dataset for Mental Workload Assessment on N-Back Task Using Wearable Sensor. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.025612021. [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer, A.; Vagedes, J. How accurate is pulse rate variability as an estimate of heart rate variability? Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 166, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldo, R.; Montesinos, L.; Melillo, P.; James, C.; Pecchia, L. Ultra-short term HRV features as surrogates of short term HRV: A case study on mental stress detection in real life. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2019, 19, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholkmann, F.; Boss, J.; Wolf, M. An Efficient Algorithm for Automatic Peak Detection in Noisy Periodic and Quasi-Periodic Signals. Algorithms 2012, 5, 588–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlot, K.; Cornolo, J.; Brugniaux, J.V.; Richalet, J.P.; Pichon, A. Interchangeability between heart rate and photoplethysmography variabilities during sympathetic stimulations. Physiol. Meas. 2009, 30, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taelman, J.; Vandeput, S.; Spaepen, A.; Van Huffel, S. Influence of Mental Stress on Heart Rate and Heart Rate Variability. In Proceedings of the 4th European Conference of the International Federation for Medical and Biological Engineering, Antwerp, Belgium, 23–27 November 2008; Vander Sloten, J., Verdonck, P., Nyssen, M., Haueisen, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1366–1369. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-García, J.; González-Ponce, I.; Ponce-Bordón, J.C.; López-Gajardo, M.Á.; Ramírez-Bravo, I.; Rubio-Morales, A.; García-Calvo, T. Mental Load and Fatigue Assessment Instruments: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 19, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniela, M.; Catalina, L.; Ilie, O.; Paula, M.; Daniel-Andrei, I.; Ioana, B. Effects of Exercise Training on the Autonomic Nervous System with a Focus on Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidants Effects. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiľo, P.; Janoušek, O. The relation between physical and mental load, and the course of physiological functions and cognitive performance. Theor. Issues Ergon. Sci. 2022, 23, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, D.; Chowdhury, A.; Banerjee, T.; Chatterjee, D. Effect of Mental Workload on Breathing Pattern and Heart Rate for a Working Memory Task: A Pilot Study. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 2202–2206. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Peng, C.-K.; Wu, H.-L.; Mietus, J.E.; Liu, Y.; Sun, R.-S.; Thomas, R.J. ECG-derived cardiopulmonary analysis of pediatric sleep-disordered breathing. Sleep Med. 2011, 12, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, P.; Chen, Z.; Li, Q.; Gong, Q.; Zhu, J.; Liang, Y. Atrial Fibrillation Identification with PPG Signals Using a Combination of Time-Frequency Analysis and Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 172692–172706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handelman, G.S.; Kok, H.K.; Chandra, R.V.; Razavi, A.H.; Lee, M.J.; Asadi, H. eDoctor: Machine learning and the future of medicine. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 284, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Yin, S.; Zhang, X.; Menon, C.; Fang, C.; Chen, Z.; Elgendi, M.; Liang, Y. Blood pressure stratification using photoplethysmography and light gradient boosting machine. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1072273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esgalhado, F.; Batista, A.; Vassilenko, V.; Russo, S.; Ortigueira, M. Peak Detection and HRV Feature Evaluation on ECG and PPG Signals. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaule, F.; Johanssen, J.O.; Bruegge, B.; Loftness, V. Employing Consumer Wearables to Detect Office Workers’ Cognitive Load for Interruption Management. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2018, 2, 32:1–32:20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurel, N.Z.; Jung, H.; Hersek, S.; Inan, O.T. Fusing Near-Infrared Spectroscopy with Wearable Hemodynamic Measurements Improves Classification of Mental Stress. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 8522–8531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, N.; Chen, L.; Dautta, M.; Jimenez, A.; Tseng, P.; Al Faruque, M.A. Feature Augmented Hybrid CNN for Stress Recognition Using Wrist-based Photoplethysmography Sensor. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.03166. [Google Scholar]
- Morelli, D.; Rossi, A.; Cairo, M.; Clifton, D.A. Analysis of the Impact of Interpolation Methods of Missing RR-intervals Caused by Motion Artifacts on HRV Features Estimations. Sensors 2019, 19, 3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).