Comparing Metaheuristic Search Techniques in Addressing the Effectiveness of Clustering-Based DDoS Attack Detection Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
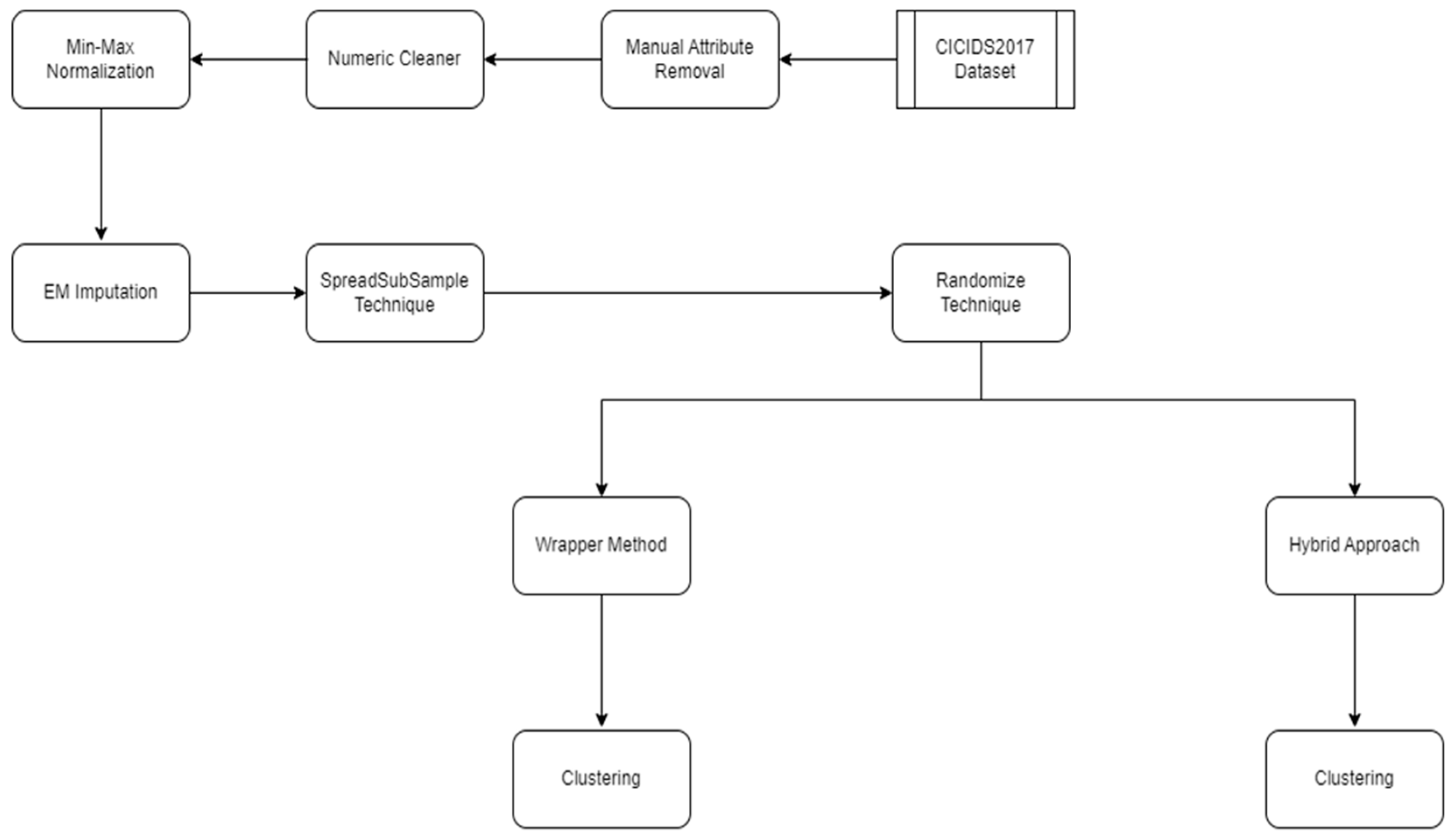
2. Materials and Methods
3. Literature Review
3.1. DDoS Attacks and the Consideration of Metaheuristic Search Methods
3.2. Application of the CRISP-DM to Applied IT Problem
4. Experiments and Evaluation
4.1. Statistical Analysis Using One-Way ANOVA
4.2. Comparison of the Wrapper Method in the First Experimentation
4.3. Comparison of the Hybrid Approach in the Second Experimentation
5. Discussion
6. Limitations and Implications
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Independent Variables Table
| Independent Variables | Procedures |
|---|---|
| Wrapper Method | (SimpleKMeans and CuckooSearch) (SimpleKMeans and FireFlySearch) (SimpleKMeans and FlowerSearch) (NaïveBayes and CuckooSearch) (NaïveBayes and FireFlySearch) (NaïveBayes and FlowerSearch) (SimpleKMeans and BestFirst) (NaïveBayes and BestFirst) |
| Hybrid Approach | (InfoGainAttributeEval) + (SimpleKMeans and CuckooSearch) (InfoGainAttributeEval) + (SimpleKMeans and FireFlySearch) (InfoGainAttributeEval) + (SimpleKMeans and FlowerSearch) (ChiSquaredAttributeEval) + (SimpleKMeans and CuckooSearch) (ChiSquaredAttributeEval) + (SimpleKMeans and FireFlySearch) (ChiSquaredAttributeEval) + (SimpleKMeans and FlowerSearch) (InfoGainAttributeEval) + (NaïveBayes and CuckooSearch) (InfoGainAttributeEval) + (NaïveBayes and FireFlySearch) (InfoGainAttributeEval) + (NaïveBayes and FlowerSearch) (ChiSquaredAttributeEval) + (NaïveBayes and CuckooSearch) (ChiSquaredAttributeEval) + (NaïveBayes and FireFlySearch) (ChiSquaredAttributeEval) + (NaïveBayes and FlowerSearch) (InfoGainAttributeEval) + (SimpleKMeans and BestFirst) (ChiSquaredAttributeEval) + (SimpleKMeans and BestFirst) (InfoGainAttributeEval) + (NaïveBayes and BestFirst) (ChiSquaredAttributeEval) + (NaïveBayes and BestFirst) |
Appendix B. Experimental Results
| DDoS Attacks Detection Methods Applied Procedures | False Positive Rates in DDoS Attack Identification |
|---|---|
| Cuckoo_0.25 → EM | 0.152 |
| Cuckoo_0.50 → EM | 0.129 |
| Cuckoo_0.75 → EM | 0.059 |
| FireFly_0.25 → EM | 0.071 |
| FireFly_0.50 → EM | 0.117 |
| FireFly_0.75 → EM | 0.108 |
| Flower_0.25 → EM | 0.054 |
| Flower_0.50 → EM | 0.129 |
| Flower_0.75 → EM | 0.129 |
| ChiSquared_Cuckoo_0.25 → EM | 0.045 |
| InfoGain_Cuckoo_0.25 → EM | 0.079 |
| ChiSquared_Cuckoo_0.50 → EM | 0.021 |
| InfoGain_Cuckoo_0.50 → EM | 0.016 |
| ChiSquared_Cuckoo_0.75 → EM | 0.407 |
| InfoGain_Cuckoo_0.75 → EM | 0.088 |
| ChiSquared_FireFly_0.25 → EM | 0.118 |
| InfoGain_FireFly_0.25 → EM | 0.142 |
| ChiSquared_FireFly_0.50 → EM | 0.053 |
| InfoGain_FireFly_0.50 → EM | 0.163 |
| ChiSquared_FireFly_0.75 → EM | 0.226 |
| InfoGain_FireFly_0.75 → EM | 0.010 |
| ChiSquared_Flower_0.25 → EM | 0.105 |
| InfoGain_Flower_0.25 → EM | 0.144 |
| ChiSquared_Flower_0.50 → EM | 0.284 |
| InfoGain_Flower_0.50 → EM | 0.161 |
| ChiSquared_Flower_0.75 → EM | 0.284 |
| InfoGain_Flower_0.75 → EM | 0.161 |
| Cuckoo_0.25 → SimpleKMeans | 0.146 |
| Cuckoo_0.50 → SimpleKmeans | 0.094 |
| Cuckoo_0.75 → SimpleKMeans | 0.156 |
| FireFly_0.25 → SimpleKMeans | 0.112 |
| FireFly_0.50 → SimpleKMeans | 0.107 |
| FireFly_0.75 → SimpleKMeans | 0.112 |
| Flower_0.25 → SimpleKMeans | 0.093 |
| Flower_0.50 → SimpleKMeans | 0.088 |
| Flower_0.75 → SimpleKMeans | 0.088 |
| ChiSquared_Cuckoo_0.25 → SimpleKMeans | 0.092 |
| InfoGain_Cuckoo_0.25 → SimpleKMeans | 0.006 |
| ChiSquared_Cuckoo_0.50 → SimpleKMeans | 0.176 |
| InfoGain_Cuckoo_0.50 → SimpleKMeans | 0.007 |
| ChiSquared_Cuckoo_0.75 → SimpleKMeans | 0.091 |
| InfoGain_Cuckoo_0.75 → SimpleKMeans | 0.009 |
| ChiSquared_FireFly_0.25 → SimpleKMeans | 0.098 |
| InfoGain_FireFly_0.25 → SimpleKMeans | 0.006 |
| ChiSquared_FireFly_0.50 → SimpleKMeans | 0.005 |
| InfoGain_FireFly_0.50 → SimpleKMeans | 0.006 |
| ChiSquared_FireFly_0.75 → SimpleKMeans | 0.008 |
| InfoGain_FireFly_0.75 → SimpleKMeans | 0.094 |
| ChiSquared_Flower_0.25 → SimpleKMeans | 0.086 |
| InfoGain_Flower_0.25 → SimpleKMeans | 0.007 |
| ChiSquared_Flower_0.50 → SimpleKMeans | 0.027 |
| InfoGain_Flower_0.50 → SimpleKMeans | 0.008 |
| ChiSquared_Flower_0.75 → SimpleKMeans | 0.027 |
| InfoGain_Flower_0.75 → SimpleKMeans | 0.008 |
| DDoS Attacks Detection Methods Applied Procedures | False Positive Rates in DDoS Attack Identification |
|---|---|
| Cuckoo_0.25 → EM | 0.229 |
| Cuckoo_0.50 → EM | 0.288 |
| Cuckoo_0.75 → EM | 0.184 |
| FireFly_0.25 → EM | 0.329 |
| FireFly_0.50 → EM | 0.282 |
| FireFly_0.75 → EM | 0.244 |
| Flower_0.25 → EM | 0.294 |
| Flower_0.50 → EM | 0.252 |
| Flower_0.75 → EM | 0.252 |
| ChiSquared_Cuckoo_0.25 → EM | 0.329 |
| InfoGain_Cuckoo_0.25 → EM | 0.154 |
| ChiSquared_Cuckoo_0.50 → EM | 0.272 |
| InfoGain_Cuckoo_0.50 → EM | 0.162 |
| ChiSquared_Cuckoo_0.75 → EM | 0.216 |
| InfoGain_Cuckoo_0.75 → EM | 0.109 |
| ChiSquared_FireFly_0.25 → EM | 0.349 |
| InfoGain_FireFly_0.25 → EM | 0.160 |
| ChiSquared_FireFly_0.50 → EM | 0.318 |
| InfoGain_FireFly_0.50 → EM | 0.154 |
| ChiSquared_FireFly_0.75 → EM | 0.292 |
| InfoGain_FireFly_0.75 → EM | 0.162 |
| ChiSquared_Flower_0.25 → EM | 0.269 |
| InfoGain_Flower_0.25 → EM | 0.160 |
| ChiSquared_Flower_0.50 → EM | 0.208 |
| InfoGain_Flower_0.50 → EM | 0.157 |
| ChiSquared_Flower_0.75 → EM | 0.208 |
| InfoGain_Flower_0.75 → EM | 0.157 |
| Cuckoo_0.25 → SimpleKMeans | 0.302 |
| Cuckoo_0.50 → SimpleKmeans | 0.127 |
| Cuckoo_0.75 → SimpleKMeans | 0.218 |
| FireFly_0.25 → SimpleKMeans | 0.248 |
| FireFly_0.50 → SimpleKMeans | 0.187 |
| FireFly_0.75 → SimpleKMeans | 0.293 |
| Flower_0.25 → SimpleKMeans | 0.229 |
| Flower_0.50 → SimpleKMeans | 0.268 |
| Flower_0.75 → SimpleKMeans | 0.268 |
| ChiSquared_Cuckoo_0.25 → SimpleKMeans | 0.155 |
| InfoGain_Cuckoo_0.25 → SimpleKMeans | 0.010 |
| ChiSquared_Cuckoo_0.50 → SimpleKMeans | 0.247 |
| InfoGain_Cuckoo_0.50 → SimpleKMeans | 0.060 |
| ChiSquared_Cuckoo_0.75 → SimpleKMeans | 0.282 |
| InfoGain_Cuckoo_0.75 → SimpleKMeans | 0.014 |
| ChiSquared_FireFly_0.25 → SimpleKMeans | 0.298 |
| InfoGain_FireFly_0.25 → SimpleKMeans | 0.014 |
| ChiSquared_FireFly_0.50 → SimpleKMeans | 0.224 |
| InfoGain_FireFly_0.50 → SimpleKMeans | 0.042 |
| ChiSquared_FireFly_0.75 → SimpleKMeans | 0.192 |
| InfoGain_FireFly_0.75 → SimpleKMeans | 0.043 |
| ChiSquared_Flower_0.25 → SimpleKMeans | 0.213 |
| InfoGain_Flower_0.25 → SimpleKMeans | 0.010 |
| ChiSquared_Flower_0.50 → SimpleKMeans | 0.275 |
| InfoGain_Flower_0.50 → SimpleKMeans | 0.025 |
| ChiSquared_Flower_0.75 → SimpleKMeans | 0.275 |
| InfoGain_Flower_0.75 → SimpleKMeans | 0.025 |
| DDoS Attacks Detection Methods Applied Procedures | False Positive Rates in DDoS Attack Identification |
|---|---|
| SimpleKMeans_BestFirst → EM | 0.086 |
| SimpleKMeans_BestFirst → SimpleKMeans | 0.005 |
| ChiSquared_ SimpleKMeans_BestFirst → EM | 0.006 |
| ChiSquared_ SimpleKMeans_BestFirst → SimpleKMeans | 0.102 |
| InfoGain_ SimpleKMeans_BestFirst → EM | 0.000 |
| InfoGain_ SimpleKMeans_BestFirst → SimpleKMeans | 0.006 |
| DDoS Attacks Detection Methods Applied Procedures | False Positive Rates in DDoS Attack Identification |
|---|---|
| NaïveBayes_BestFirst → EM | 0.330 |
| NaïveBayes_BestFirst → SimpleKMeans | 0.218 |
| ChiSquared_ NaïveBayes_BestFirst → EM | 0.330 |
| ChiSquared_ NaïveBayes_BestFirst → SimpleKMeans | 0.218 |
| InfoGain_ NaïveBayes_BestFirst → EM | 0.088 |
| InfoGain_ NaïveBayes_BestFirst → SimpleKMeans | 0.038 |
References
- Zhou, L.; Zhu, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Zong, T. A novel feature-based framework enabling multi-type DDoS attacks detection. World Wide Web 2023, 26, 163–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, X.; Wang, P.; Jin, X.; Yao, S. Multi-modal noise-robust DDoS attack detection architecture in large-scale networks based on tensor SVD. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2023, 10, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Chandra, S. VMFCVD: An optimized framework to combat volumetric DDoS attacks using machine learning. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 9965–9983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Gupta, N.; Gupta, B.B. Defensive mechanism against DDoS attack based on feature selection and multi-classifier algorithms. Telecommun. Syst. 2023, 82, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinalpour, A. Addressing High False Positive Rates of DDoS Attack Detection Methods. D.I.T. Thesis, Walden University, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Ghoreishi, S.M.; Issakhov, A. Improving the accuracy of network intrusion detection system in medical IoT systems through butterfly optimization algorithm. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2022, 126, 1999–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megantara, A.A.; Ahmad, T. A hybrid machine learning method for increasing the performance of network intrusion detection systems. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idhammad, M.; Afdel, K.; Belouch, M. Semi-supervised machine learning approach for DDoS detection. Appl. Intell. 2018, 48, 3193–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinalpour, A.; Ahmed, H.A. Addressing the effectiveness of DDoS-attack detection methods based on the clustering method using an ensemble method. Electronics 2022, 11, 2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saw, T.; Oo, W.M. Ranking-based feature selection with wrapper PSO search in high-dimensional data classification. Int. J. Comput. Sci. 2023, 50, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, K.; Kumar, G. Nature inspired techniques and applications in intrusion detection systems: Recent progress and updated perspective. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 2897–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniswamy, S.; Kandhasamy, P. Rough fuzzy cuckoo search for triclustering microarray gene expression data. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2019, 27, 4328–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanious, R.; Onghena, P. Randomized single-case experimental designs in healthcare research: What, why, and how. Healthcare 2019, 7, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cisco.com. Cisco Annual Internet Report (2018–2023) White Paper; Cisco: San Jose, CA, USA, 2020; Available online: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/executive-perspectives/annual-internet-report/white-paper-c11-741490.html (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Zayo. Protecting Your Business from Cyber Attacks: The State of DDoS Attacks DDoS Insights from Q1 & Q2, 2023. 2023. Available online: https://go.zayo.com/zayo-ddos-protection-ebook/ (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Chen, H.H.; Lee, C.H.; Huang, S.K. A Unified Ant Agent Framework for Solving DoS and QoS Problems. J. Inf. Sci. Eng. 2016, 32, 1397–1434. Available online: https://jise.iis.sinica.edu.tw (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Boveiri, H.R.; Khayami, R. On the performance of metaheuristics: A different perspective. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.08928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalfi, S.; Carafni, F.; Iacca, G. Metaheuristics in the balance: A survey on memory-saving approaches for platforms with seriously limited resources. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2023, 2023, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumathi, S.; Rajesh, R.; Lim, S. Recurrent and deep learning neural network models for DDoS attack detection. J. Sens. 2022, 2022, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arivudainambi, D.; Kumar, V.; Sibi Chakkaravarthy, S. LION IDS: A meta-heuristics approach to detect DDoS attacks against Software-Defined Networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, A.; Hussain, S.J.; Ali, M.U.; Lee, S.W. Metaheuristic optimization-based feature selection for imagery and arithmetic tasks: An fNIRS study. Sensors 2023, 23, 3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhosseini, M.; Nezamabadi-pour, H. Metaheuristic search algorithms in solving the n-similarity problem. Fundam. Informaticae 2017, 152, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, H.; Yurtay, N.; Yurtay, Y.; Zaimoğlu, E.A. Electrical search algorithm: A new metaheuristic algorithm for clustering problem. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 10153–10172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.E.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, H. Effective feature selection methods to detect IoT DDoS attack in 5g core network. Sensors 2022, 22, 3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, P.; Gupta, B.; Singh, A.K. Implementing attack detection system using filter-based feature selection methods for fog-enabled IoT networks. Telecommun. Syst. 2022, 81, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabas, N.; Ahlawat, P.; Sharma, P. An effective malware detection method using hybrid feature selection and machine learning algorithms. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 9749–9767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.A. An effective dimension reduction algorithm for clustering Arabic text. Egypt. Inform. J. 2019, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnykov, V.; Michael, S. Clustering large datasets by merging k-means solutions. J. Classif. 2019, 37, 97–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah, S.K.; Wirekoh, K.; Aidoo, E.N.; Oduro, S.D.; Arthur, Y.D. A model-based clustering of expectation–maximization and k-means algorithms in crime hotspot analysis. Res. Math. 2022, 9, 2073662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hao, L.; Zhao, X.; Lu, J.; Shi, Y.; Ma, C. Role of the EM clustering method in determining the geochemical background of As and Cr in soils: A case study in the north of Changchun, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 6675–6692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivk, A.; Vasilecas, O.; Kalibatiene, D.; Rupnik, R. On approach for the implementation of data mining to business process optimisation in commercial companies. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2013, 19, 237–256. [Google Scholar]
- Brzozowska, J.; Pizoń, J.; Baytikenova, G.; Gola, A.; Zakimova, A.; Piotrowska, K. Data engineering in CRISP-DM process production data—Case study. Appl. Comput. Sci. 2023, 19, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaggia, S.; Kelly, A.; Lertwachara, K.; Chen, L. Applying the CRISP-DM framework for teaching business analytics. Decis. Sci. J. Innov. Educ. 2020, 18, 612–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepański, M.; Pawlicki, M.; Kozik, R.; Choraś, M. The application of deep learning imputation and other advanced methods for handling missing values in network intrusion detection. Vietnam. J. Comput. Sci. 2023, 10, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzaoui, H.; Boukhamla, A.Z.E.; Arroyo, D.; Bensayah, A. Developing new deep-learning model to enhance network intrusion classification. Evol. Syst. 2022, 13, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddaiah, P.N.; Narayanan, P.P. An improved cuckoo search algorithm for optimization of artificial neural network training. Neural Process. Lett. 2023, 55, 12093–12120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgotra, R.; Mittal, N.; Mittal, V. A new parallel cuckoo flower search algorithm for training multi-layer perceptron. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicuaio, T.; Niyomubyeyi, O.; Shyndyapin, A.; Pilesjö, P.; Mansourian, A. Multi-objective optimization using evolutionary cuckoo search algorithm for evacuation planning. Geomatics 2022, 2, 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.S.; Karamanoglu, M.; Xingshi, H. Flower pollination algorithm: A novel approach for multiobjective optimization. Eng. Optim. 2013, 46, 1222–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emary, E.; Zawbaa, H.M.; Hassanien, A.E.; Parv, B. Multi-objective retinal vessel localization using flower pollination search algorithm with pattern search. Adv. Data Anal. Classif. 2017, 11, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.S. Firefly algorithms for multimodal optimization. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1003.1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, S. Firefly search algorithm based on leader strategy. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 123, 106328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomoush, W.; Omar, K.; Alrosan, A.; Alomari, Y.M.; Albashish, D.; Almomani, A. Firefly photinus search algorithm. J. King Saud Univ.–Comput. Inf. Sci. 2018, 32, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, A.; Saxena, A.; Ray, D. Comparative study of algorithms in artificial intelligence: Best first search, greedy best first search and iterative deepening. Int. J. Softw. Hardw. Res. Eng. 2018, 6, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Haviluddin; Puspitasari, N.; Burhandeny, A.E.; Nurulita, A.D.A.; Trahutomo, D. Naïve Bayes and K-nearest neighbor algorithms performance comparison in diabetes mellitus early diagnosis. Int. J. Online Biomed. Eng. 2022, 18, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, N.; Singh, A.; Al-Dabagh, M.Z.N.; Maitra, S.K. A Novel architecture for diabetes patients’ prediction using K-Means clustering and SVM. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khraisat, A.; Gondal, I.; Vamplew, P.; Kamruzzaman, J. Survey of intrusion detection systems: Techniques, datasets and challenges. Cybersecurity 2019, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.; Alesanco, Á.; Mehavilla, L.; Garcva, J. Evaluation of machine learning techniques for traffic flow-based intrusion detection. Sensors 2022, 22, 9326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.; Salleh, R.; Khan, M.K. SMARTbot: A behavioral analysis framework augmented with machine learning to identify mobile botnet applications. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskandar1, K.; Noprianto; Abbas, B.S.; Soewito, B.; Kosala, R. Two-way ANOVA with interaction approach to compare content creation speed performance in knowledge management system. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge, Information and Creativity Support Systems (KICSS), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 10–12 November 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.B.; Salkind, N.J. Using SPSS for Windows and Macintosh: Analyzing and Understanding the Data, 8th ed.; Pearson: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2017; p. 131. [Google Scholar]
- Panagiotou, P.; Mengidis, N.; Tsikrika, T.; Vrochidis, S.; Kompatsiaris, l. Host-based intrusion detection using signature-based and AI-driven anomaly detection methods. Inf. Secur. 2021, 50, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.K. Detection of anomaly intrusion utilizing self-adaptive grasshopper optimization algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 7541–7561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvari, S.; Sani, N.F.M.; Hanapi, Z.M.; Abdullah, M.T. An efficient anomaly intrusion detection method with feature selection and evolutionary neural network. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 70651–70663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaghthawi, Y.; Ahmed, I.; Alsaadi, F.E. Performance analysis of feature subset selection techniques for intrusion detection. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, T.J.; Levy, Y. Towards a guide for novice researchers on research methodology: Review and proposed methods. J. Issues Inf. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2009, 6, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cheng, G.; Jiang, S.; Dai, M. Building an efficient intrusion detection system based on feature selection and ensemble classifier. Comput. Netw. 2020, 174, 107247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Source | Type III Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | Partial Eta Squared |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrected Model | 0.001 a | 1 | 0.001 | 0.167 | 0.685 | 0.004 |
| Intercept | 0.413 | 1 | 0.413 | 52.508 | <0.001 | 0.580 |
| Method | 0.001 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.167 | 0.685 | 0.004 |
| Error | 0.299 | 38 | 0.008 | |||
| Total | 1.552 | 40 | ||||
| Corrected Total | 0.300 | 39 |
| Source | Type III Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | Partial Eta Squared |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrected Model | 0.008 a | 1 | 0.008 | 0.691 | 0.408 | 0.009 |
| Intercept | 0.383 | 1 | 0.383 | 32.638 | <0.001 | 0.295 |
| Method | 0.008 | 1 | 0.008 | 0.691 | 0.408 | 0.009 |
| Error | 0.915 | 78 | 0.012 | |||
| Total | 2.248 | 80 | ||||
| Corrected Total | 0.923 | 79 |
| Method | Mean | Std. Deviation | N |
|---|---|---|---|
| BestFirst-Wrapper | 0.15975 | 0.143486 | 4 |
| Metaheuristic-Wrapper | 0.17883 | 0.082272 | 36 |
| Total | 0.17693 | 0.087703 | 40 |
| Method | Mean | Std. Deviation | N |
|---|---|---|---|
| BestFirst-Hybrid | 0.09850 | 0.118605 | 8 |
| Metaheuristic-Hybrid | 0.13206 | 0.107217 | 72 |
| Total | 0.12870 | 0.108076 | 80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeinalpour, A.; McElroy, C.P. Comparing Metaheuristic Search Techniques in Addressing the Effectiveness of Clustering-Based DDoS Attack Detection Methods. Electronics 2024, 13, 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13050899
Zeinalpour A, McElroy CP. Comparing Metaheuristic Search Techniques in Addressing the Effectiveness of Clustering-Based DDoS Attack Detection Methods. Electronics. 2024; 13(5):899. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13050899
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeinalpour, Alireza, and Charles P. McElroy. 2024. "Comparing Metaheuristic Search Techniques in Addressing the Effectiveness of Clustering-Based DDoS Attack Detection Methods" Electronics 13, no. 5: 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13050899
APA StyleZeinalpour, A., & McElroy, C. P. (2024). Comparing Metaheuristic Search Techniques in Addressing the Effectiveness of Clustering-Based DDoS Attack Detection Methods. Electronics, 13(5), 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13050899





